AAC Technologies Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AAC Technologies Holdings Bundle
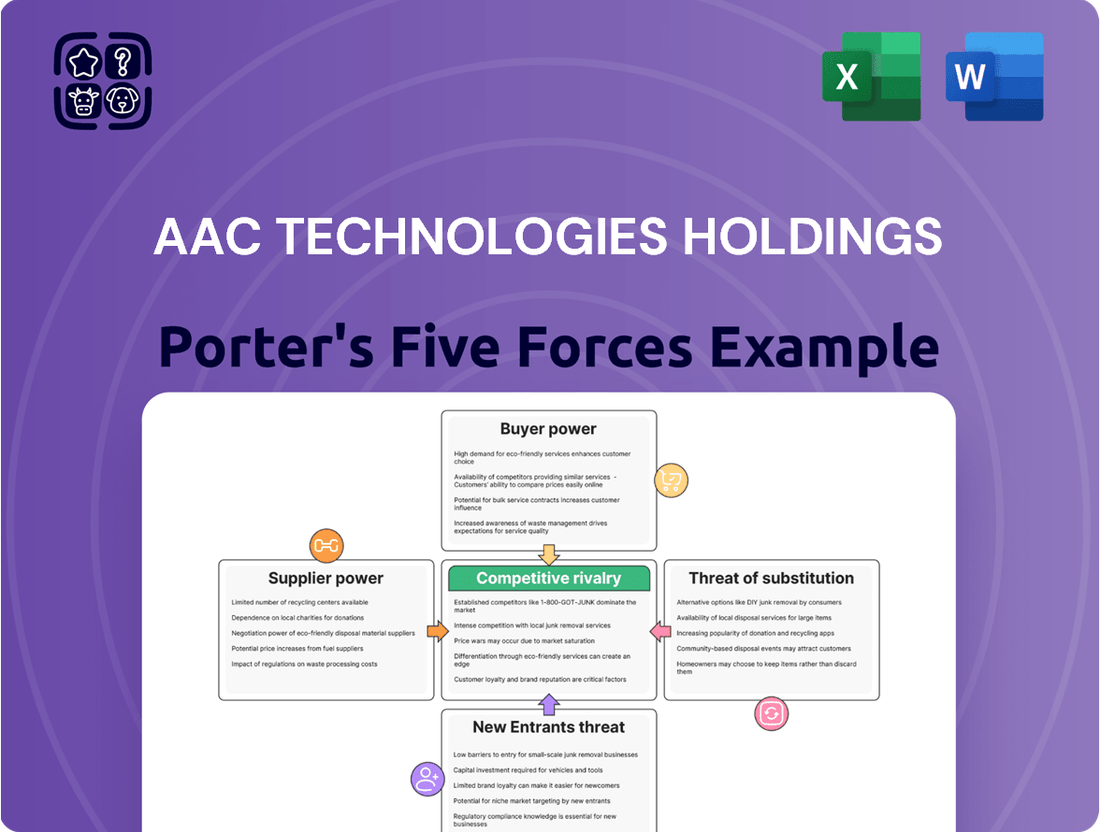
AAC Technologies Holdings operates within a dynamic market shaped by intense competition and evolving technological landscapes. Understanding the forces of rivalry, buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and substitutes is crucial for navigating its strategic path. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these critical market dynamics. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore AAC Technologies Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The market for high-quality, specialized precision components, crucial for companies like AAC Technologies, features a limited pool of highly capable manufacturers. This scarcity of specialized suppliers, particularly for advanced materials or unique electronic parts, grants them considerable bargaining power. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, the top ten suppliers held over 60% of the market share as of 2024, illustrating a pronounced concentration at the supplier level.
Switching suppliers for highly integrated or customized components can involve substantial costs for AAC Technologies. These costs can include significant re-engineering expenses, lengthy qualification processes, and the risk of production delays, all of which empower suppliers.
These high switching costs, often representing 20-30% of the annual purchasing budget for critical high-tech components, significantly strengthen the bargaining power of AAC's suppliers. It becomes financially challenging and operationally disruptive for AAC to change its sources without incurring considerable expenses.
Suppliers with proprietary technology, especially in areas like advanced acoustics or optical components, hold significant sway. AAC Technologies' reliance on these specialized inputs means suppliers can dictate terms if their innovations are critical to AAC's product differentiation and market competitiveness. For instance, a supplier of unique micro-speaker technology, crucial for AAC's miniaturized audio solutions, would possess strong bargaining power.
Supplier's Importance to AAC Technologies' Product Quality and Innovation
AAC Technologies' commitment to innovation and high-performance products means it relies heavily on suppliers capable of providing components that meet rigorous quality and performance specifications. When suppliers provide critical components that enable AAC to differentiate its offerings or achieve advancements like miniaturization, their bargaining power increases significantly.
The caliber and dependability of these sourced materials directly influence AAC's standing in the market and its competitive edge. For instance, in 2023, AAC Technologies reported that its research and development expenditure was approximately HKD 1.04 billion, underscoring the importance of cutting-edge components from its suppliers to fuel this innovation pipeline.
- Supplier Dependence: AAC's need for specialized, high-quality components for its acoustic, electro-mechanical, and radio frequency products grants power to suppliers who can consistently meet these demands.
- Innovation Contribution: Suppliers whose materials are integral to AAC's product differentiation and technological advancements, such as advanced acoustic transducer technology, possess enhanced bargaining leverage.
- Quality Impact: The reliability of supplier inputs directly impacts AAC's final product quality, its brand reputation, and its ability to maintain a competitive market position.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
While not a frequent occurrence, the possibility of suppliers integrating forward into their customers' value chains, such as component assembly or even final product manufacturing, can indeed bolster their bargaining power. This strategy, if pursued by large, technologically adept suppliers, presents a latent threat to buyers by potentially limiting their negotiation leverage.
This dynamic is closely tied to a supplier's strategic objectives and their inherent capabilities. For instance, a supplier holding critical intellectual property or possessing unique manufacturing expertise might find forward integration a more viable option.
Consider the semiconductor industry. Some advanced chip manufacturers have the technical prowess to move into designing and even producing more complex integrated modules, directly competing with companies that previously only purchased their raw chips. The high barriers to entry in advanced chip fabrication, with R&D costs often running into billions of dollars, exemplify the significant investment required for such integration.
- Potential for Forward Integration: Suppliers might integrate forward into assembly or end-product manufacturing.
- Impact on Buyer Leverage: This threat can diminish a buyer's negotiating power.
- Supplier-Specific Factors: The feasibility depends heavily on supplier strategy and technological capabilities.
- Industry Examples: Advanced manufacturing sectors often present a higher theoretical risk of supplier forward integration.
The bargaining power of suppliers for AAC Technologies is significantly influenced by the concentration of specialized component manufacturers. In 2024, the top suppliers in critical component sectors often held substantial market shares, sometimes exceeding 60%, indicating limited alternatives for AAC. This concentration, coupled with high switching costs for AAC Technologies, which can involve extensive re-engineering and qualification processes, strengthens supplier leverage.
Proprietary technology held by suppliers is another key factor. When suppliers provide unique or critical inputs, like advanced acoustic transducer technology essential for AAC's product differentiation, their ability to dictate terms increases. For instance, AAC's 2023 R&D expenditure of approximately HKD 1.04 billion highlights its reliance on suppliers providing cutting-edge components to fuel its innovation pipeline.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power for AAC Technologies | Supporting Data/Example (as of 2024 or recent) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Top 10 semiconductor suppliers held >60% market share in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | High | Can represent 20-30% of annual budget for critical components. |
| Proprietary Technology | High | Suppliers of unique micro-speaker tech crucial for miniaturization. |
| Supplier Dependence | High | AAC's need for specialized, high-quality acoustic components. |
What is included in the product
AAC Technologies Holdings' Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its acoustic and haptic component market.
Instantly grasp the competitive landscape and identify strategic vulnerabilities within the electronics manufacturing sector, simplifying complex market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
AAC Technologies' customer base is heavily concentrated among major global consumer electronics brands, including leading smartphone, wearable, and tablet manufacturers. These significant buyers, such as Apple and Samsung, wield substantial bargaining power due to their immense order volumes and advanced procurement processes. This concentration means that losing even a single key client can have a considerable impact on AAC's revenue. For instance, in 2023, the top five customers accounted for a significant portion of AAC's revenue, highlighting their influence on pricing negotiations and contract terms.
The consumer electronics market, particularly for smartphones, is intensely competitive. This fierce competition forces end-product manufacturers to aggressively pursue cost reductions throughout their supply chains. As a result, component suppliers like AAC Technologies face significant pressure to lower their prices, impacting AAC's bargaining power.
Even though AAC Technologies specializes in high-performance components, the broader market's emphasis on cost-effectiveness limits their ability to command premium pricing. This underlying trend directly affects their negotiation leverage with large, price-sensitive buyers.
In 2024, the average selling price of smartphones saw some fluctuations, with mid-range devices becoming increasingly popular, further amplifying the demand for cost-efficient components. This market dynamic underscores the significant bargaining power customers wield in securing favorable pricing from suppliers like AAC.
While AAC Technologies Holdings is known for its advanced acoustic and haptic solutions, the bargaining power of its customers is influenced by the availability of alternative component suppliers. For certain components, customers might find comparable offerings from competitors such as GoerTek or Luxshare, which can provide them with more leverage during negotiations.
The broader electronic components market features numerous suppliers capable of producing similar products, enabling customers to shop around and demand more favorable pricing. This competitive landscape directly impacts AAC's ability to dictate terms, as customers can more readily switch if price or performance expectations are not met, thereby dampening AAC's pricing power.
Customers' Ability to Integrate Backwards or Develop In-house Capabilities
The bargaining power of customers is a key consideration for AAC Technologies. Some of the largest players in the consumer electronics industry, like Apple or Samsung, have substantial financial resources and advanced technical capabilities. This allows them to explore developing certain components internally or even acquiring smaller, specialized manufacturers. While this level of backward integration is a significant undertaking and a high barrier, the mere possibility of it gives these major customers considerable leverage during price negotiations with suppliers like AAC.
This potential for backward integration pressures AAC Technologies to maintain competitive pricing and favorable contract terms. For instance, if a major client like Apple were to seriously consider developing its own acoustic components, it would significantly alter the negotiation dynamic. In 2023, the global consumer electronics market was valued at over $1 trillion, highlighting the immense purchasing power concentrated among a few key customers. This market size underscores why AAC must remain vigilant about its customers' potential to develop in-house capabilities.
- Potential for Backward Integration: Large consumer electronics firms can invest in developing their own components or acquiring existing manufacturers.
- Customer Leverage: The mere threat of a major customer bringing production in-house provides significant bargaining power.
- Pricing Pressure: This leverage compels AAC Technologies to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain business.
- Market Dynamics: The immense scale of the consumer electronics market amplifies the bargaining power of its largest participants.
Standardization of Certain Components
For standardized components, customers gain leverage because it's simpler to compare offerings and switch suppliers. If AAC Technologies Holdings produces parts that meet basic, widely accepted specifications, multiple vendors can fulfill these needs. This situation empowers customers to negotiate for lower prices or more favorable contract terms. For instance, in 2023, the consumer electronics market, a key sector for AAC, saw intense price competition, particularly for more commoditized acoustic components.
This increased bargaining power for customers arises when switching costs are low. When a customer can easily move to another supplier without significant expense or disruption, they have more influence. While AAC is known for its innovation in areas like advanced acoustic solutions and haptics, certain foundational components within its product lines might be more susceptible to this commoditization effect. The ability for customers to source similar, albeit less advanced, alternatives elsewhere directly impacts AAC's pricing flexibility.
However, AAC's strategic focus on developing high-end, differentiated, and proprietary technologies significantly counters this customer power. By investing heavily in research and development, AAC aims to offer unique value propositions that competitors cannot easily replicate. This focus on innovation, particularly in areas like miniaturization and advanced material science for acoustic modules, creates stickier customer relationships and reduces the impact of standardization on its overall market position. For example, AAC's advancements in micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) microphones offer performance advantages that are not readily available from all suppliers.
- Standardization Impact: Customers gain power when components are easily substitutable, leading to price pressures.
- Switching Costs: Low switching costs amplify customer bargaining power, enabling easier supplier changes.
- AAC's Mitigation: AAC's emphasis on innovation and differentiated products helps reduce customer leverage.
- Market Context: Price competition in the consumer electronics sector in 2023 highlighted the importance of such differentiation.
The bargaining power of AAC Technologies' customers is significant, primarily due to the concentration of its client base among major global consumer electronics brands. These large buyers, such as Apple and Samsung, possess substantial leverage through their immense order volumes and sophisticated procurement strategies. This concentration means that losing even one key client can materially impact AAC's revenue and pricing power.
The intense competition within the consumer electronics sector, particularly for smartphones, forces end-product manufacturers to relentlessly pursue cost reductions across their supply chains. Consequently, component suppliers like AAC Technologies face considerable pressure to lower prices, which directly diminishes AAC's negotiating leverage.
Customers also gain bargaining power when components become more standardized and easily substitutable. For such parts, customers can readily compare offerings and switch suppliers with minimal cost or disruption. This dynamic empowers them to negotiate for lower prices and more favorable terms, especially in a market like consumer electronics, which experienced notable price competition in 2023 for more commoditized acoustic components.
AAC's strategic focus on innovation and differentiated products, such as advanced acoustic solutions and proprietary haptic technologies, serves as a crucial countermeasure to this customer leverage. By investing in R&D, AAC aims to provide unique value propositions that are difficult for competitors to replicate, fostering customer loyalty and mitigating the impact of commoditization on its market position.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on AAC's Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration (e.g., Top 5 clients) | High Leverage | Top customers still represent a substantial revenue share, maintaining their influence. |
| Industry Price Sensitivity | Lowered Prices Demanded | Continued demand for cost-effective components in mid-range smartphones amplifies this. |
| Availability of Alternative Suppliers | Increased Customer Options | Competitors like GoerTek and Luxshare offer comparable solutions for certain components. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Significant Leverage | Major clients' financial strength allows for consideration of in-house development or acquisition. |
Same Document Delivered
AAC Technologies Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for AAC Technologies Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within its industry. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, which thoroughly examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This insightful analysis provides actionable intelligence for understanding AAC Technologies Holdings' competitive environment and formulating effective business strategies.
Rivalry Among Competitors
AAC Technologies navigates a landscape with a substantial number of competitors across its diverse business segments. While it holds a strong position in miniature acoustic components, other areas such as MEMS sensors and precision functional parts are characterized by significant market fragmentation and a high density of players.
The MEMS sensor market, for example, sees intense rivalry from established giants like Bosch, STMicroelectronics, and Analog Devices, as well as a multitude of smaller, specialized firms. This crowded competitive environment necessitates continuous innovation and cost efficiency for AAC Technologies to maintain its market share and profitability.
The presence of numerous competitors in segments like precision mechanics means that price competition can be a significant factor, putting pressure on margins. AAC Technologies must leverage its scale, technological expertise, and operational efficiency to differentiate itself and secure its competitive advantage.
The global smartphone market, a key revenue source for AAC Technologies Holdings, has seen a noticeable slowdown and increasing maturity. This maturity intensifies the competitive rivalry among component suppliers, as companies fight harder for a smaller slice of growth. In 2023, global smartphone shipments declined by 3.2% year-over-year, reaching 1.17 billion units, according to IDC data, highlighting this challenging environment.
AAC is actively exploring new avenues for growth, notably in automotive and augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR) solutions. However, these emerging sectors are also highly competitive. Established automotive suppliers and new tech entrants are all vying for market share in these dynamic fields. For instance, the automotive sensor market, where AAC has ambitions, is projected to grow, but it’s already populated by significant players with existing relationships and technology.
Competitive rivalry in the acoustic and consumer electronics components sector is largely driven by continuous technological innovation, miniaturization, and performance enhancement. Companies like AAC Technologies must consistently invest heavily in R&D to stay ahead, introducing new and improved components such as advanced camera modules and haptic devices. For instance, in 2023, AAC Technologies reported R&D expenditure of approximately HKD 3.07 billion, underscoring the significant investment required to maintain a competitive edge.
The imperative to differentiate through innovation means companies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, integrating features like AI into their offerings. Failure to innovate quickly leads to a loss of competitive advantage, as market demand shifts towards the latest advancements. This intense focus on R&D is a direct response to customer demands for more sophisticated and integrated functionalities in their devices.
Price Competition and Margin Pressure
The consumer electronics sector is notoriously competitive, and this translates to intense price pressure on component suppliers like AAC Technologies. Large customers, leveraging the sheer volume of their orders, often play suppliers against each other to secure the lowest possible prices. This dynamic directly impacts profitability.
AAC Technologies has felt this squeeze. For instance, in the first half of 2023, the company reported a gross profit margin of 16.3%, a noticeable decrease from earlier periods where margins were considerably higher. This decline is a direct consequence of the relentless price competition in the market.
- Intense Customer Pressure: Major electronics brands exert significant leverage, demanding lower prices for components.
- Margin Erosion: Fierce competition among suppliers leads to narrowed profit margins for companies like AAC Technologies.
- Supplier Showdowns: Customers often pit different component manufacturers against each other to drive down costs.
- 2023 Performance Impact: Gross margins in H1 2023 reflected this competitive reality, falling to 16.3%.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Companies within the acoustics and audio solutions sector actively pursue strategic acquisitions and partnerships. This strategy allows them to enhance their technological expertise, broaden their product offerings, and gain entry into new markets. AAC Technologies' acquisition of Premium Sound Solutions in 2024 is a prime example, designed to strengthen its position in the automotive sector and diversify its income sources. This ongoing consolidation and collaboration significantly escalate competitive rivalry.
These strategic moves directly impact the competitive intensity by consolidating market share and creating larger, more integrated players. For instance, the Premium Sound Solutions acquisition by AAC Technologies in 2024 was aimed at leveraging PSS's established presence and technology in automotive audio systems. Such actions can lead to increased pricing pressures and a greater need for innovation among remaining independent firms.
- Strategic Consolidation: Acquisitions and mergers are reshaping the competitive landscape, often creating larger entities with broader capabilities.
- Technology Access: Partnerships and buyouts are key routes for companies to acquire advanced technologies, such as those in advanced acoustic materials or digital signal processing.
- Market Expansion: Collaborations and acquisitions facilitate faster market penetration and access to new customer segments, particularly in high-growth areas like automotive electronics.
- Increased Rivalry: The trend towards consolidation and strategic alliances inherently intensifies competition as companies strive to maintain or improve their market standing.
AAC Technologies operates in highly competitive markets, particularly for consumer electronics components and MEMS sensors, facing pressure from both established giants and numerous smaller players.
The maturity of the smartphone market, which saw a 3.2% decline in global shipments in 2023, intensifies rivalry among suppliers fighting for market share.
Continuous innovation is crucial, with AAC's R&D expenditure of HKD 3.07 billion in 2023 highlighting the investment needed to combat price pressures and evolving customer demands for advanced features.
Strategic moves like AAC's 2024 acquisition of Premium Sound Solutions demonstrate an effort to bolster capabilities and expand into new sectors like automotive, a trend that further reshapes the competitive landscape.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Intensity Factor | 2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Components | Goertek, Luxshare Precision | Price competition, technological advancements | Global smartphone shipments declined 3.2% |
| MEMS Sensors | Bosch, STMicroelectronics, Analog Devices | High fragmentation, innovation race | Continued demand for miniaturization and performance |
| Precision Functional Parts | Various specialized manufacturers | Price sensitivity, volume leverage | Pressure on gross margins for component suppliers |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While AAC Technologies Holdings Inc. is firmly rooted in hardware, the burgeoning power of software presents a subtle but growing threat of substitutes. Advanced algorithms, especially those leveraging AI and machine learning, are increasingly capable of replicating or enhancing functionalities traditionally reliant on specialized hardware. For instance, sophisticated image processing software can significantly boost camera quality, potentially lessening the need for some of the most cutting-edge optical hardware components.
This trend is particularly relevant as AI continues to permeate mobile device capabilities. In 2024, the market saw a continued push towards AI-optimized features within smartphones, influencing consumer expectations for performance. While a complete hardware replacement is improbable given the fundamental nature of AAC's acoustic and sensor components, the software evolution means that incremental improvements in hardware might be less impactful if software can achieve comparable results, thereby influencing demand for specific component upgrades.
The increasing trend of integrating multiple functionalities into single System-on-Chips (SoCs) or advanced modules presents a significant threat of substitution for companies like AAC Technologies. This technological shift means that components previously supplied separately could be consolidated, diminishing demand for discrete acoustic or haptic modules.
For instance, in 2024, the smartphone market continues to see aggressive SoC advancements, with manufacturers aiming to embed more features, including sophisticated audio processing and haptic feedback engines, directly onto the main processor. This consolidation directly challenges the need for specialized, standalone components that AAC historically provides.
This integration not only simplifies product design and potentially lowers manufacturing costs for device makers but also often leads to improved performance and power efficiency. Consequently, the value proposition of discrete component suppliers like AAC is directly impacted as these integrated solutions become more compelling alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for AAC Technologies Holdings' acoustic components is influenced by emerging alternative materials and manufacturing processes. For instance, advancements in novel material science or additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing, could lead to the development of components that match or even surpass the performance of AAC's current offerings while potentially being more cost-effective. This could disrupt the market by providing manufacturers with viable, lower-cost alternatives to traditional acoustic solutions, impacting AAC's market share and pricing power.
Shifts in Consumer Preferences and Device Form Factors
Significant shifts in what consumers want and the rise of new device types, like augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) headsets or even entirely new gadget categories, could change the need for AAC's specific parts. While AAC is expanding into AR/VR, a very fast, game-changing shift could still be a risk if their current product offerings can't keep up.
For instance, if a new device form factor emerges that doesn't rely on the acoustic or haptic components AAC specializes in, demand for their products could plummet. The market for mobile devices, a key sector for AAC, saw global shipments decline by approximately 3.2% in 2023 compared to 2022, highlighting the volatility and potential for rapid shifts in consumer electronics demand.
- Shifting Demand: A major change in consumer preferences away from current smartphone designs towards, for example, wearable AR glasses could reduce the need for traditional smartphone speakers and haptic engines.
- AR/VR Adoption Rate: While AAC is investing in AR/VR components, the actual speed of consumer adoption for these technologies is a critical factor; slower adoption limits this diversification as a buffer against threats.
- Component Obsolescence: The rapid pace of technological innovation means that components AAC currently produces could become obsolete if new device designs don't require them.
- New Technology Integration: If substitute devices integrate entirely new sensory feedback mechanisms that bypass traditional acoustic or haptic technologies, AAC's core offerings would face a direct threat.
Lower-Cost, Lower-Performance Alternatives in Emerging Markets
In price-sensitive emerging markets, the threat of substitutes takes on a distinct character. Lower-cost, albeit potentially lower-performance, components can emerge as viable alternatives to AAC Technologies' premium acoustic and haptic solutions. This dynamic is particularly relevant in regions where cost is a primary driver for consumers and businesses. For instance, in 2024, many developing economies continued to see a strong demand for budget-friendly electronics, where even minor cost savings on components can significantly impact final product pricing and market competitiveness.
While AAC Technologies Holdings focuses on delivering high-performance acoustic and haptic feedback solutions, the presence of these cheaper alternatives can indeed constrain its market penetration. These substitutes might not match AAC's technological sophistication or build quality, but they can fulfill the basic functional requirements for a segment of the market. Consider the smartphone market in Southeast Asia or parts of Africa, where a significant portion of consumers prioritize affordability. In these contexts, a functional, albeit less refined, speaker module or vibration motor at a fraction of the cost can be a compelling substitute, directly impacting AAC's potential market share in those specific product tiers or geographic segments.
- Emerging Market Price Sensitivity: Emerging economies often exhibit higher price sensitivity, making lower-cost substitutes more attractive.
- Performance Trade-offs: While substitutes may offer lower performance, they can still meet the essential functional needs of price-conscious consumers.
- Market Segmentation Impact: The availability of cheaper alternatives can limit AAC's penetration into specific product segments or lower-tier device categories within these markets.
- Competitive Pressure: This threat necessitates that AAC continuously balances its premium offerings with value propositions that resonate even in cost-driven environments.
The threat of substitutes for AAC Technologies Holdings' core offerings is evolving, driven by both technological advancements and shifting market dynamics. While hardware remains crucial, sophisticated software is increasingly capable of mimicking or enhancing certain functionalities, potentially reducing the demand for specific hardware upgrades. Furthermore, the consolidation of components into integrated solutions like System-on-Chips (SoCs) poses a direct substitution risk by diminishing the need for discrete acoustic and haptic modules.
Emerging materials and manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, also present a threat by offering potentially more cost-effective alternatives that could match or exceed current performance levels. This is particularly relevant in price-sensitive emerging markets where lower-cost components, even with some performance trade-offs, can gain traction. For instance, the global smartphone market, a key sector for AAC, saw a slight decline in shipments in 2023, underscoring the volatility and the impact of cost-conscious consumer behavior on component demand.
| Threat of Substitutes Factor | Impact on AAC Technologies | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Software-driven functionality | Can reduce reliance on specialized hardware for enhanced features. | Increased AI integration in mobile devices, improving camera and audio processing via software. |
| Component Integration (SoCs) | Diminishes demand for discrete acoustic and haptic modules. | Continued advancements in SoC capabilities, embedding more audio and haptic functions. |
| New Materials & Manufacturing | Potential for cost-effective, high-performance alternatives. | Growth in additive manufacturing and material science research for electronics. |
| Emerging Market Price Sensitivity | Lower-cost, lower-performance components can capture market share. | Persistent demand for affordable electronics in developing economies. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the precision components market, particularly for advanced acoustic, optical, and MEMS devices, demands significant upfront capital. AAC Technologies Holdings operates in a sector where state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and cutting-edge research and development are non-negotiable. For instance, the development of next-generation micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) often involves multi-million dollar investments in specialized fabrication equipment and materials science expertise. This high level of initial investment acts as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential new entrants who may lack the necessary financial resources.
The need for specialized expertise and robust intellectual property presents a significant barrier for new entrants looking to compete with established players like AAC Technologies. Developing and manufacturing precision acoustic components requires deep engineering knowledge and years of accumulated technical know-how, which are not easily replicated.
AAC Technologies Holdings, for instance, has invested heavily in research and development over decades, building a substantial portfolio of patents and trade secrets. This accumulated intellectual property, crucial for their product innovation and manufacturing processes, makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to establish a comparable technological foundation and differentiate themselves in the market. In 2023, AAC Technologies continued to emphasize R&D, dedicating approximately 5.7% of its revenue to innovation, a testament to its commitment to maintaining a technological edge.
AAC Technologies Holdings benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched relationships with global tier-1 customers, a major deterrent for new entrants. These partnerships are not easily replicated, requiring substantial time and investment to establish. For instance, companies like Apple and Samsung, major AAC clients, have multi-year agreements and intricate supply chain integrations that new competitors would struggle to penetrate.
Securing design wins with these industry giants involves rigorous qualification processes and a proven track record of reliability and innovation. A new entrant would likely spend years and significant capital trying to achieve the same level of trust and integration that AAC already possesses. This barrier is amplified by the sheer scale of these clients' operations, demanding robust manufacturing capabilities and consistent quality that are hard-won.
In 2024, the smart device market continues to be dominated by a few key players, making access to their supply chains critical for any new component manufacturer. AAC's established presence means they are often involved in the early stages of product development, giving them a significant lead over potential new competitors. This early access ensures they can tailor their offerings to specific client needs, further solidifying their position and making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Effects
Existing manufacturers like AAC Technologies leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This means they can produce acoustic components and other micro-electronic parts at a considerably lower cost per unit than a new, smaller competitor could. For instance, in 2023, AAC Technologies reported substantial production volumes, enabling them to negotiate better raw material prices and optimize manufacturing processes, a feat difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
The experience curve further solidifies AAC Technologies' competitive position. As companies produce more over time, they become more efficient, reducing costs and improving quality. This accumulated knowledge and refined operational expertise create a substantial barrier. A new entrant would need to invest heavily and operate at a significant scale for years to catch up to the process efficiencies AAC Technologies has already achieved, making it a tough uphill battle.
- Economies of Scale: AAC Technologies benefits from lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes.
- Procurement Advantages: Large-scale purchasing allows for better pricing on raw materials.
- Experience Curve Benefits: Accumulated operational knowledge leads to greater efficiency and quality.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Start-ups face higher initial per-unit costs without comparable scale.
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles, Especially in Automotive and Healthcare
As AAC Technologies Holdings potentially expands into highly regulated sectors like automotive and healthcare, the threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory and certification hurdles. For instance, in the automotive industry, new component suppliers must navigate complex safety standards such as ISO 26262 for functional safety, a process that can take years and millions in development and testing. Similarly, the healthcare sector demands adherence to rigorous quality management systems like ISO 13485 for medical devices, alongside country-specific approvals from bodies like the FDA in the United States or the EMA in Europe. These extensive compliance requirements create a formidable barrier to entry, demanding significant capital investment and specialized expertise that established players like AAC have already cultivated.
Meeting these stringent safety, reliability, and quality benchmarks is not a trivial undertaking. New companies entering these markets would need to invest heavily in R&D, specialized manufacturing processes, and robust quality assurance systems. For example, the development cycle for a new automotive sensor might involve over 50,000 hours of testing alone. This extensive time and financial commitment acts as a powerful deterrent, making it challenging for newcomers to compete effectively with established firms that have already proven their capabilities and secured necessary certifications.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Companies entering automotive or healthcare must invest heavily in obtaining certifications, often costing millions of dollars.
- Safety and Quality Standards: Industries like automotive (ISO 26262) and healthcare (ISO 13485) demand exceptionally high, proven levels of safety and quality.
- Time to Market: The lengthy certification processes can extend product development timelines by several years, delaying revenue generation for new entrants.
- Established Expertise: Incumbent firms possess deep knowledge and experience in navigating these complex regulatory landscapes, a significant advantage over newcomers.
The threat of new entrants into the precision components market, where AAC Technologies operates, is considerably low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for advanced manufacturing facilities and cutting-edge R&D, often running into millions of dollars for specialized equipment. Furthermore, the need for deep engineering expertise and a robust intellectual property portfolio, built over years and protected by patents, presents a significant hurdle. For instance, AAC Technologies continued to invest approximately 5.7% of its revenue in R&D in 2023 to maintain its technological edge.
Established customer relationships with major global clients, like Apple and Samsung, are another key barrier. These tier-1 customers have intricate, often multi-year, supply chain integrations and rigorous qualification processes that take years and significant capital for newcomers to penetrate. In 2024, access to these dominant smart device manufacturers’ supply chains remains critical, and AAC's early involvement in product development solidifies its advantage.
Economies of scale and experience curve benefits further deter new entrants. AAC Technologies' high production volumes in 2023 enabled lower per-unit costs and better raw material procurement. New competitors face a cost disadvantage and must invest heavily to achieve comparable operational efficiencies and quality. Additionally, stringent regulatory and certification requirements in sectors like automotive (ISO 26262) and healthcare (ISO 13485) add years and millions in costs, demanding expertise that established players like AAC have already cultivated.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for AAC Technologies Holdings is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research and reports from reputable financial data providers.
We integrate insights from competitor analysis, trade publications, and macroeconomic indicators to thoroughly assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the acoustic components industry.
