Yamada Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Yamada Holdings Bundle
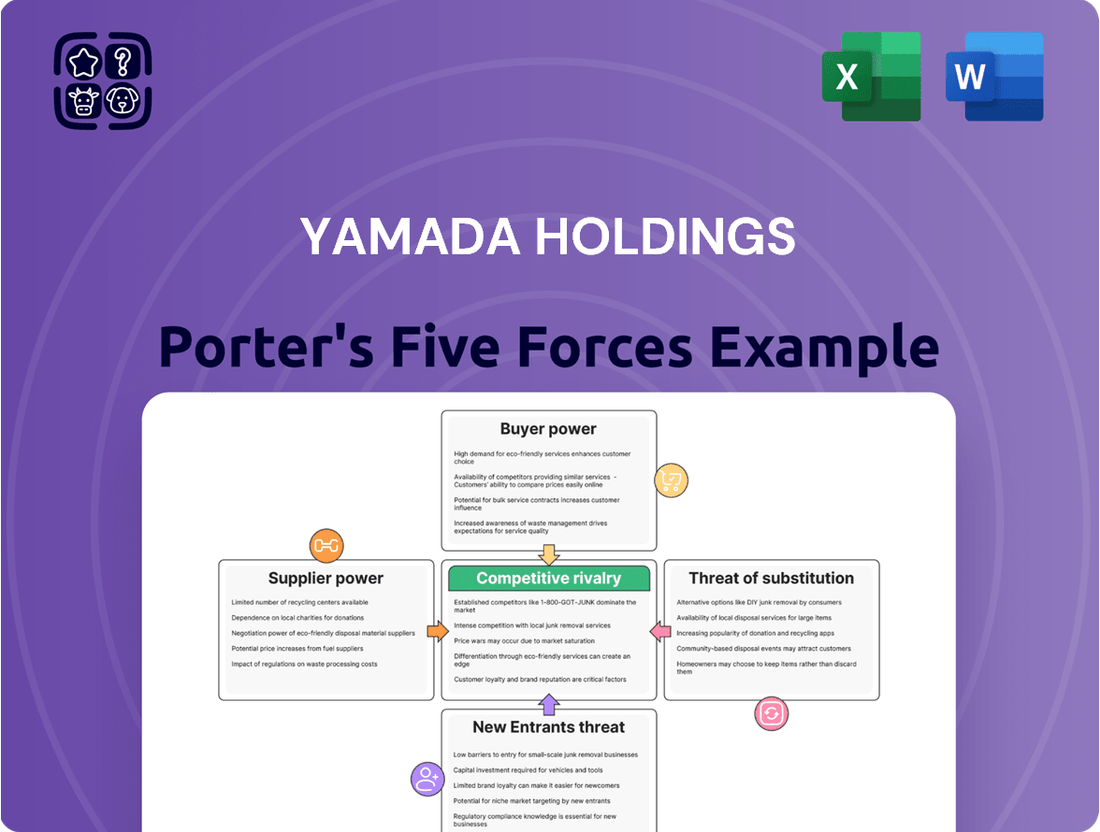
Yamada Holdings navigates a complex retail landscape, facing moderate threat from new entrants due to established brand loyalty and economies of scale in Japanese home electronics. Supplier power is a significant factor, with key component manufacturers holding considerable leverage. The intense rivalry among existing players, including Bic Camera and Yodobashi Camera, further shapes the competitive intensity.
Buyer bargaining power is substantial, driven by price sensitivity and the availability of numerous alternatives, impacting Yamada's pricing strategies. The threat of substitutes, though less pronounced in electronics, exists through online marketplaces and alternative product categories. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Yamada Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Yamada Holdings faces significant supplier power due to its reliance on a concentrated group of major global electronics brands. Companies like Sony, Panasonic, Apple, and Samsung represent a substantial portion of its inventory. This concentration means these established brands, with their strong brand recognition and proprietary technology, can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms, particularly for high-demand or exclusive products.
The bargaining power of these dominant suppliers can directly impact Yamada's profitability. For instance, if a key supplier like Apple decides to adjust its wholesale pricing for its popular iPhones, Yamada has limited options to negotiate a better deal, especially given the high consumer demand for these devices. This dynamic can constrain Yamada's ability to secure more favorable terms or pass on cost savings to consumers.
Yamada Holdings, as a major Japanese electronics retailer, procures goods in substantial quantities. This significant purchasing volume makes Yamada a vital sales avenue for many electronics manufacturers and component providers, establishing its importance to their distribution strategies.
The sheer scale of Yamada's orders grants it considerable bargaining power. Suppliers are motivated to cultivate strong ties with Yamada and offer favorable pricing to ensure they capture these large volume orders and maintain access to the Japanese market.
Yamada's considerable market presence and purchasing might enable it to negotiate more advantageous terms. This can include securing substantial bulk discounts, favorable payment schedules, and crucial marketing support from its electronics suppliers.
Switching core suppliers for major electronics categories like TVs, refrigerators, and smartphones presents substantial costs and complexities for Yamada Holdings. This includes the need to reconfigure inventory systems, adapt marketing campaigns, and retrain customer service staff. For instance, integrating a new major smartphone brand could require significant IT infrastructure upgrades and extensive sales associate training, impacting operational efficiency.
While the impact of switching costs is less pronounced for smaller, commoditized products, the investment in time, resources, and potential disruption associated with changing key brand partnerships generally bolsters supplier leverage. For Yamada, the effort involved in onboarding a new major appliance supplier, for example, can be a deterrent to frequent changes.
However, Yamada Holdings' extensive product range, spanning across various electronics and home services, helps to somewhat dilute the overall bargaining power of individual suppliers. This diversification allows Yamada to potentially shift focus or negotiate more favorably by leveraging relationships with other suppliers within its broad network.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a notable consideration for Yamada Holdings. Some electronics manufacturers are increasingly establishing their own direct-to-consumer sales channels, including online stores and brand-specific retail locations. This trend allows suppliers to bypass traditional retailers like Yamada, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
If a significant number of key suppliers were to successfully shift their sales strategy towards direct-to-consumer models, Yamada could face reduced sales volume and potentially be forced to accept less favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the direct-to-consumer e-commerce sales for electronics globally were projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, indicating a substantial market shift.
- Direct Sales Channels: Many electronics brands now operate their own online shops, offering products directly to consumers.
- Retail Outlet Expansion: Some manufacturers are also investing in their own physical retail stores to control the customer experience.
- Increased Supplier Power: A successful shift to direct sales by suppliers could diminish Yamada's role as an intermediary, strengthening supplier leverage.
- Market Trend: The growing e-commerce penetration in the electronics sector, with direct sales becoming more prevalent, highlights this evolving dynamic.
However, the comprehensive retail experience and extensive physical footprint that Yamada provides remain significant value propositions. This makes complete forward integration by many suppliers less likely in the immediate future, as they may still rely on retailers for broad market reach and customer engagement.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers for Other Segments
Yamada Holdings' strategic expansion beyond its core electronics business into areas like home renovation, housing construction, and furniture significantly alters the bargaining power of its suppliers. This diversification taps into a broader spectrum of suppliers, many of whom operate in less consolidated and more fragmented markets.
By engaging with a wider array of suppliers across these diverse segments, Yamada can leverage competition to its advantage. This allows for sourcing materials and products from a larger pool of smaller, localized, or specialized providers. The increased number of potential suppliers in these niche markets typically translates to diminished individual supplier power, as Yamada has more viable alternatives.
- Diversification into new sectors like home renovation and construction broadens Yamada's supplier base.
- Fragmented markets for housing materials and furniture reduce the leverage of individual suppliers.
- Greater choice in sourcing allows Yamada to negotiate more favorable terms.
- Access to numerous specialized or localized suppliers limits the impact of any single supplier's demands.
Yamada Holdings' supplier power is influenced by its substantial purchasing volume, which makes it a key channel for many electronics manufacturers. This scale allows Yamada to negotiate favorable terms, including bulk discounts and marketing support.
However, the bargaining power of major electronics brands like Apple and Samsung is significant due to high consumer demand and proprietary technology, limiting Yamada's negotiation flexibility for popular items.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into direct-to-consumer sales, a trend supported by the growing global e-commerce market (projected to exceed $1.5 trillion in electronics sales in 2024), could further shift power towards suppliers.
Yamada's diversification into sectors like home renovation and construction taps into more fragmented markets, thereby reducing the bargaining power of individual suppliers in these new areas.
| Factor | Impact on Yamada | Key Suppliers/Sectors | Example Data (2024 Projections) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for dominant brands | Apple, Samsung, Sony, Panasonic | Concentration of sales from top 5 suppliers could exceed 60% for certain electronics categories. |
| Purchasing Volume | Strong negotiation leverage for Yamada | All suppliers | Yamada's annual procurement likely in the billions of USD. |
| Switching Costs | Deters frequent supplier changes, bolstering supplier power | Major electronics brands | Integration of new major product lines can take 6-12 months and significant investment. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential to bypass retailers, increasing supplier power | Major electronics brands | Global D2C e-commerce for electronics projected over $1.5 trillion in 2024. |
| Diversification Impact | Reduces leverage of suppliers in new, fragmented markets | Home renovation, construction materials, furniture | Fragmented markets for building materials often have hundreds of smaller suppliers. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Yamada Holdings' retail and financial services sectors.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Yamada Holdings' five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Yamada Holdings in the Japanese electronics market. Intense competition from both online giants and brick-and-mortar rivals means consumers are keenly aware of pricing. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spending on electronics in Japan remained robust, but the demand for discounts and bundled offers was particularly high, indicating a strong preference for value over brand loyalty alone.
Yamada Holdings needs to maintain competitive pricing strategies and run frequent sales events to draw in and keep customers. This necessity directly curtails their power to dictate higher prices, inevitably affecting their profit margins. The widespread use of online price comparison websites in Japan in 2024 further amplifies this customer leverage, making it easier than ever for shoppers to find the best deals.
Customers today wield considerable power due to readily available information. Online platforms offer easy access to product details, customer reviews, and side-by-side price comparisons, making it simple for consumers to research and evaluate their options. This transparency directly impacts Yamada Holdings, compelling them to differentiate not solely on price but also on the quality of their service, the breadth of their product offerings, and the overall customer experience.
The ease with which customers can research and compare options means that if Yamada Holdings fails to meet expectations, consumers can swiftly identify and switch to competitors. For instance, in the competitive electronics retail space, customers can quickly find better deals or superior product availability from online giants or specialized retailers, directly challenging Yamada’s market position.
Yamada Holdings likely experiences low switching costs for many of its core offerings, such as consumer electronics and furniture. This means customers can easily shift to a competitor if they find a better price or a more appealing product. For instance, if a customer wants a new television, they can readily compare prices and features across multiple retailers without significant effort or expense.
This ease of switching directly empowers customers, as they have readily available alternatives. In 2024, the prevalence of online marketplaces and price comparison websites further reduces these costs, allowing consumers to quickly identify the best value. This accessibility means Yamada Holdings must remain competitive on both price and service to retain its customer base.
Customer Volume and Fragmentation
Yamada Holdings, despite its large customer base, experiences fragmented power among individual buyers. The low purchase volume per customer typically dilutes the bargaining clout of any single consumer. However, the collective demand, especially for high-demand items or during significant promotional periods, can exert pressure on Yamada's pricing strategies and stock management.
Yamada's strategic focus on becoming a comprehensive, one-stop solution is designed to cultivate higher customer lifetime value. This approach aims to shift the dynamic from individual transaction-based power to a more enduring customer relationship, thereby mitigating the bargaining power derived from single purchases.
- Low Individual Purchase Volume: Most customers buy single or few items, limiting their individual leverage.
- Fragmented Customer Base: With millions of customers, no single customer or small group can significantly dictate terms.
- Aggregate Demand Influence: However, surges in demand, like during the 2024 Golden Week sales, can temporarily increase collective customer influence on inventory and promotions.
- "One-Stop Solution" Strategy: Yamada aims to increase loyalty and reduce reliance on individual transaction power by offering a broad range of products and services.
Diversity of Customer Needs Across Segments
Yamada Holdings' strategic diversification into housing construction, renovation, and financial services directly addresses a spectrum of customer needs. This multi-faceted approach can dilute individual customer bargaining power by presenting a bundled value proposition. For instance, customers looking for an end-to-end solution, like purchasing a new home and immediately furnishing it, or seeking financing for a comprehensive renovation project, often value the convenience and integrated service over the lowest price for each separate element.
This integration creates a stickier customer relationship. In 2024, the trend towards seeking comprehensive home solutions has intensified, with consumers increasingly preferring a single point of contact for major life events like home buying and improvement. For Yamada Holdings, this means that while a customer might negotiate on the price of furniture, their willingness to switch providers for the entire package is reduced if the convenience and quality of the integrated service are perceived as superior.
- Integrated Offerings: Yamada's expansion into construction, renovation, and finance creates a one-stop-shop, reducing the incentive for customers to source components individually.
- Bundled Value: Customers prioritize convenience and comprehensive service in major life events like home buying and improvement, making price comparisons across disparate services less critical.
- Customer Loyalty: The complexity of coordinating multiple specialized providers for home projects fosters greater loyalty to companies offering integrated solutions.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: For customers seeking seamless execution, the overall value of the integrated package often outweighs minor price differences in individual services.
Yamada Holdings faces significant customer bargaining power due to high price sensitivity and low switching costs in the Japanese electronics market. Customers readily compare prices online, compelling Yamada to offer competitive pricing and frequent sales, which can impact profit margins. While individual customer purchase volume is low, the collective demand, especially during peak sales periods like Golden Week in 2024, can influence inventory and promotional strategies.
| Factor | Impact on Yamada Holdings | Evidence (2024 Data/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High; requires competitive pricing and promotions. | Robust consumer spending on electronics, but high demand for discounts. |
| Switching Costs | Low for core electronics; easy for customers to move to competitors. | Prevalence of online marketplaces and price comparison sites. |
| Information Availability | High; customers easily research products, reviews, and prices. | Online platforms provide transparent product details and price comparisons. |
| Customer Fragmentation | Low individual leverage, but collective demand can exert pressure. | Aggregate demand influence during 2024 sales events. |
| Diversification Strategy | Mitigates bargaining power by offering bundled value and convenience. | Increasing consumer preference for integrated home solutions. |
Same Document Delivered
Yamada Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Yamada Holdings you'll receive immediately after purchase. You are looking at the actual, professionally formatted document detailing the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within Yamada Holdings' industry. No surprises, no placeholders – this is the complete, ready-to-use analysis. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Yamada Holdings operates in a fiercely competitive Japanese electronics retail sector. The market is populated by numerous established brick-and-mortar giants like Bic Camera and Yodobashi Camera, alongside dominant online retailers such as Amazon Japan and Rakuten. This crowded environment fuels intense price competition and frequent promotional campaigns, creating significant pressure on Yamada Holdings to differentiate itself and capture market share.
The Japanese consumer electronics market, while showing some overall growth, faces intense rivalry in its core segments. Areas like computers and traditional home audio/video are projected to see stagnation or even a slight downturn in demand. This mature market dynamic means companies like Yamada Holdings must compete fiercely for a shrinking or slow-growing pool of customers, often resorting to price wars that pressure profit margins.
Yamada Holdings operates in an industry characterized by significant fixed costs, stemming from its extensive network of physical retail locations and the associated infrastructure for inventory storage and distribution. These substantial overheads, reported at ¥380 billion for property and equipment as of March 2024, necessitate robust sales volumes to ensure profitability, intensifying price-based competition.
The fast-paced nature of the electronics market demands highly efficient inventory management to mitigate the risk of product obsolescence. Yamada's inventory turnover ratio for fiscal year 2024 was 4.5 times, indicating the importance of rapid stock movement to avoid carrying outdated merchandise and incurring write-downs, which directly impacts its ability to compete on price and margin.
Diversification into New Segments
Yamada Holdings' strategic move into home renovation, housing construction, furniture, and financial services exposes it to a fresh wave of rivals. For instance, the housing construction sector in Japan is populated by established players, and in 2024, the market saw continued activity from companies like Sekisui House and Daiwa House, which have long-standing reputations and extensive supply chains. This diversification means Yamada must now compete effectively against these seasoned entities in addition to its existing battles in electronics.
The furniture market also presents a competitive landscape, with both domestic and international brands vying for consumer attention. Yamada's entry means it will face off against retailers like Nitori, a dominant force in Japan known for its affordable and stylish home furnishings, and IKEA, which commands a significant global presence. Successfully gaining market share requires Yamada to differentiate its offerings and build brand loyalty in these new arenas.
- Diversification creates new competitive arenas: Yamada's expansion into housing, furniture, and finance means confronting distinct sets of competitors in each sector.
- Established players pose challenges: In housing, companies like Sekisui House and Daiwa House represent formidable, long-established rivals.
- Retail giants are key competitors: The furniture segment includes strong players such as Nitori and IKEA, demanding significant differentiation.
- Financial services add complexity: Entering financial services requires Yamada to compete with established banks and fintech companies, each with unique strengths.
Online vs. Offline Competition
The competitive landscape for Yamada Holdings is significantly shaped by the ongoing shift from traditional brick-and-mortar retail to e-commerce. Online retailers often present a compelling value proposition through convenience and competitive pricing, directly challenging Yamada's established physical presence.
Yamada Holdings must therefore continuously refine its omni-channel strategy. This involves seamlessly integrating its extensive network of physical stores with sophisticated online platforms, a crucial step to not only compete but also to provide customers with a unified and satisfactory shopping journey. For instance, in 2024, the global e-commerce market is projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, highlighting the scale of this digital shift.
- E-commerce Growth: The global e-commerce market is expected to surpass $6.3 trillion in 2024, presenting a substantial challenge and opportunity for traditional retailers.
- Omni-channel Imperative: Retailers like Yamada Holdings need robust omni-channel strategies to bridge the gap between physical and digital customer experiences.
- Customer Expectations: Consumers increasingly demand convenience and competitive pricing, driving the preference for online shopping channels.
- Competitive Pressure: The ease of price comparison and accessibility offered by online platforms intensifies rivalry, forcing offline players to innovate.
Yamada Holdings faces intense competition from both established electronics retailers like Bic Camera and Yodobashi Camera, and online giants such as Amazon Japan and Rakuten. This rivalry is amplified by the mature nature of key electronics segments, leading to price wars that pressure Yamada's profit margins. The company's significant fixed costs, totaling ¥380 billion in property and equipment as of March 2024, further necessitate high sales volumes, intensifying this competitive pressure.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Impact on Yamada |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics Retail (Brick-and-Mortar) | Bic Camera, Yodobashi Camera | Intense price competition, need for differentiation |
| Electronics Retail (Online) | Amazon Japan, Rakuten | Convenience, competitive pricing pressure |
| Home Renovation/Construction | Sekisui House, Daiwa House | New competitive arenas, established reputations |
| Furniture Retail | Nitori, IKEA | Market share battles, need for unique offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of online direct-to-consumer (DTC) channels presents a significant threat of substitution for Yamada Holdings. Consumers now have the convenience of purchasing electronics directly from manufacturers' websites or through vast online marketplaces, effectively bypassing traditional brick-and-mortar retailers. This shift is fueled by competitive pricing and readily available product details, directly challenging Yamada's established sales model and market share.
The threat of substitutes for Yamada Holdings in the home solutions market is significant, especially from Do-It-Yourself (DIY) and self-service alternatives. Consumers can readily choose to undertake home renovation projects or assemble furniture themselves, bypassing Yamada's comprehensive services. This DIY trend is fueled by readily available online tutorials and affordable materials, empowering individuals to manage tasks that might otherwise require professional assistance.
Furthermore, the market is populated by numerous smaller, independent contractors and specialized shops offering niche services or products. These entities often compete on price and flexibility, presenting a compelling alternative for budget-conscious consumers who may not require Yamada's full-service offering. For instance, the growing popularity of online marketplaces connecting homeowners with local tradespeople in Japan provides a direct substitute for Yamada's more centralized approach.
The expanding recommerce market, especially for electronics and home goods in Japan, presents a significant threat of substitutes for Yamada Holdings. This growing sector, driven by both sustainability awareness and economic pragmatism, offers consumers more affordable alternatives to brand-new items.
In 2024, the global used goods market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, with Japan being a key contributor. This trend directly impacts Yamada's sales by providing a viable, lower-cost option for consumers who might otherwise purchase new appliances or electronics from their stores.
For instance, the increasing popularity of refurbished smartphones and home appliances means customers can acquire functional products at a fraction of the original price. This can lead to a substantial diversion of potential revenue away from Yamada's new product lines.
Consumer willingness to embrace second-hand or refurbished items is on the rise, fueled by environmental consciousness and a desire for value. This shift in consumer behavior directly challenges Yamada's traditional business model of selling new merchandise.
Technological Obsolescence and Delaying Purchases
Rapid technological advancements in consumer electronics present a significant threat of substitutes for retailers like Yamada Holdings. Consumers often delay purchases, waiting for the next generation of devices or for current models to become more affordable. This anticipation of future improvements or price drops effectively substitutes for buying a new product immediately.
This trend directly impacts Yamada's sales cycles and inventory management. For instance, in late 2023 and early 2024, many consumers held off on purchasing smartphones and laptops, anticipating major releases in the latter half of 2024. This cautious buying behavior means Yamada must manage inventory more carefully to avoid obsolescence itself.
- Consumer behavior: Buyers increasingly postpone upgrades due to the rapid pace of innovation.
- Market impact: This delay acts as a substitute for immediate sales, affecting revenue and inventory turnover for electronics retailers.
- Example: In 2024, the anticipation of new chipsets and display technologies for smartphones led many consumers to defer upgrades, impacting sales figures for existing models.
- Yamada's challenge: Retailers like Yamada must adapt to shorter product lifecycles and fluctuating consumer demand driven by technological obsolescence.
Alternative Leisure and Spending Options
Consumers have numerous ways to spend their discretionary income, and these choices can directly impact demand for Yamada Holdings' products. For instance, a significant portion of household budgets can be directed towards experiences like travel or entertainment, or towards other durable goods and luxury items. In 2024, global tourism spending is projected to reach trillions of dollars, demonstrating a strong alternative allocation of consumer funds.
This wide array of alternative leisure and spending options acts as a significant substitute threat to Yamada's core business. When consumers prioritize travel or other forms of entertainment over purchasing electronics or home improvement items, Yamada's sales volumes can be directly affected. This is particularly relevant during periods of economic uncertainty when consumers may opt for immediate gratification through experiences rather than longer-term investments in home goods.
Consider these specific substitute areas:
- Travel and Tourism: The World Travel & Tourism Council reported that travel and tourism contributed significantly to global GDP in recent years, a figure expected to grow.
- Entertainment: Spending on streaming services, gaming, and live events continues to rise, offering compelling alternatives to home-based spending.
- Other Retail Categories: Apparel, automotive, and personal care products also compete for the same consumer discretionary dollars.
The threat of substitutes for Yamada Holdings remains substantial, driven by evolving consumer preferences and market dynamics. Direct-to-consumer online channels, DIY alternatives, and the burgeoning recommerce market all offer compelling alternatives that chip away at Yamada's traditional sales. Furthermore, consumers increasingly divert discretionary spending towards experiences like travel and entertainment, presenting another layer of substitution risk.
In 2024, the global used goods market is a significant factor, with Japan being a key player. This trend directly impacts Yamada's sales by offering lower-cost options for electronics and home goods. For instance, refurbished electronics provide functional products at a fraction of the original price, diverting revenue from new product lines as consumer embrace for second-hand items grows due to environmental and value considerations.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Yamada Holdings | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Online DTC Channels | Bypasses traditional retail, competitive pricing | Continued growth in e-commerce penetration |
| DIY & Self-Service | Reduces demand for comprehensive services | Availability of online tutorials fuels self-sufficiency |
| Recommerce Market | Offers affordable alternatives to new goods | Global used goods market valued in hundreds of billions |
| Experiences (Travel/Entertainment) | Diverts discretionary spending | Global tourism spending projected in trillions |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a large physical retail presence, much like Yamada Holdings operates, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes securing prime real estate, stocking a wide variety of electronics, and building out the necessary operational infrastructure. For instance, acquiring and fitting out a single large-format electronics store can easily run into millions of dollars.
This substantial financial commitment acts as a significant deterrent, making it exceedingly difficult for new players to emerge and compete directly with Yamada's established network. The sheer scale of investment required discourages many potential entrants from even attempting to replicate the existing physical footprint, effectively limiting the threat of new competitors in this specific sector.
Yamada Holdings benefits from its deeply entrenched supply chain and distribution networks, built over years of operation. These long-standing relationships with key electronics manufacturers give them preferential access and terms, a significant hurdle for any newcomer. Establishing a comparable network across Japan would involve immense capital investment and time, making it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively on cost and availability.
Yamada Holdings has cultivated strong brand recognition and customer loyalty over many years as a leading electronics retailer in Japan. This deep-seated trust means new competitors face a significant hurdle in attracting customers away from established relationships. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Yamada Holdings reported net sales of ¥1,131.3 billion, demonstrating its substantial market presence and customer engagement.
Regulatory Hurdles and Licensing in Housing/Finance
Yamada Holdings' diversification into housing construction, renovation, and financial services means navigating a complex web of regulations. These include building codes, environmental standards for construction, and stringent licensing for financial activities, such as mortgage lending and insurance brokering. For instance, in Japan, obtaining the necessary licenses for financial services can be a lengthy and capital-intensive process, potentially taking over a year and requiring significant compliance investment.
These industry-specific regulations act as substantial barriers for potential new entrants wanting to replicate Yamada’s integrated model. New companies would need to secure multiple licenses and comply with diverse regulatory frameworks across construction and finance simultaneously. This complexity significantly raises the cost and time required to establish a competitive presence, thereby diminishing the threat of new entrants.
- Regulatory Complexity: Yamada’s multi-sector approach requires adherence to building codes, environmental regulations, and financial licensing, creating a high barrier.
- Licensing Requirements: Obtaining necessary financial service licenses in Japan, for example, can take over a year and involves substantial capital and compliance costs.
- Increased Barriers to Entry: The combined regulatory burden makes it difficult for new firms to offer a similar comprehensive ‘one-stop solution’.
- Reduced Threat: These significant hurdles effectively limit the number of new competitors capable of entering and challenging Yamada’s integrated business model.
Potential for Online-Only Disruptors
The threat of new entrants, particularly from online-only disruptors, remains a significant concern for retailers like Yamada Holdings. While traditional brick-and-mortar stores face substantial barriers to entry, the digital landscape allows agile players to emerge with considerably lower overheads. These online businesses can leverage streamlined operations and competitive pricing to challenge established retailers in segments like electronics and certain home goods, bypassing the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
In 2024, the e-commerce growth trajectory continued to be strong, with global retail e-commerce sales projected to reach approximately $6.4 trillion. This digital-first environment favors new entrants who can quickly adapt to market trends and consumer preferences without the legacy costs associated with physical store networks. Their ability to target specific niches and offer personalized customer experiences further amplifies their competitive edge.
- Lower Overhead Costs: Online-only retailers avoid expenses like rent, utilities, and staffing for physical locations, allowing for more aggressive pricing.
- Agile Operations: Digital businesses can pivot quickly to new technologies and market demands, offering a more responsive customer experience.
- Aggressive Pricing Strategies: Reduced operating costs enable online disruptors to undercut traditional retailers on price, attracting price-sensitive consumers.
- Targeted Market Penetration: Online entrants can focus on specific product categories or customer segments, building a loyal customer base without the broad market reach of established players.
The threat of new entrants for Yamada Holdings is moderated by significant capital requirements for physical retail, high distribution network setup costs, and established brand loyalty. However, online-only competitors pose a notable challenge due to their lower overheads and agility.
In 2024, global retail e-commerce sales were projected to reach approximately $6.4 trillion, highlighting the growing influence of digital channels. New entrants leveraging these platforms can offer competitive pricing and targeted experiences, bypassing traditional barriers.
Yamada Holdings' diversified operations in housing and finance introduce regulatory complexities, including building codes and financial licensing, which create substantial barriers for new entrants aiming to replicate its integrated model.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Yamada Holdings' Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (Physical Retail) | High barrier, millions of dollars for a single store. | Established network deterrent. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Requires immense capital and time to replicate. | Preferential access and terms with manufacturers. |
| Brand Recognition & Loyalty | Significant hurdle to attract customers. | Deep-seated trust, strong market presence (¥1,131.3 billion net sales FY2024). |
| Regulatory Complexity (Diversified Ops) | High cost and time for multiple licenses and compliance. | Navigates building codes, environmental standards, financial licensing. |
| Online Competition | Lower overheads, agile operations, aggressive pricing. | Needs to adapt to digital-first environment and evolving consumer preferences. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Yamada Holdings utilizes publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and competitor news releases to understand competitive dynamics.
