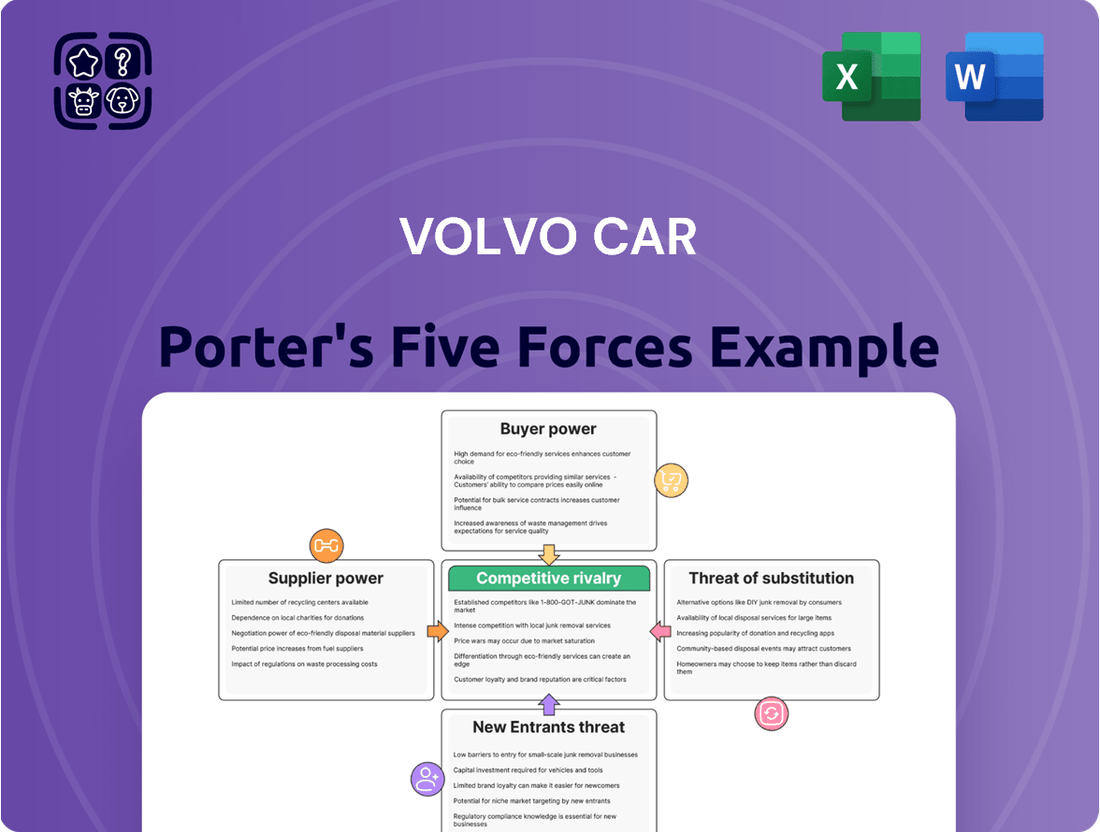
Volvo Car Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Volvo Car Bundle
Volvo Car navigates a complex automotive landscape, where intense rivalry and the threat of new entrants demand strategic agility. Understanding the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers is crucial for maintaining profitability and market share in this dynamic sector. Furthermore, the ever-present threat of substitute products requires continuous innovation and differentiation.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Volvo Car’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Volvo Car's dependence on critical component suppliers, especially for advanced semiconductors and electric vehicle batteries, creates a significant bargaining power for these suppliers. The limited number of qualified manufacturers for these high-tech parts means suppliers can dictate terms, impacting Volvo's production costs and efficiency. For instance, the global semiconductor shortage in 2021-2022 led to widespread production cuts across the automotive industry, demonstrating the direct impact of supplier dependency.
Suppliers who provide highly specialized technology, such as advanced safety features, sophisticated infotainment systems, or cutting-edge autonomous driving capabilities, wield significant bargaining power over automakers like Volvo. These suppliers often possess proprietary intellectual property that is not easily replicated, making it challenging for Volvo to switch to alternative providers without substantial cost and development delays. For instance, a company developing a unique lidar sensor for self-driving cars could dictate terms, impacting Volvo's product development timelines and cost structures.
Raw material cost fluctuations significantly influence the bargaining power of suppliers for automakers like Volvo. The prices of key components such as steel, aluminum, and essential rare earth minerals, critical for electric vehicle batteries, are inherently volatile due to global supply and demand dynamics. For instance, the price of lithium, a crucial element in EV batteries, saw substantial increases in 2023, impacting the cost structure for many automotive manufacturers.
When these commodity prices surge, suppliers are in a strong position to pass on these increased costs to Volvo. This directly escalates Volvo's production expenses. If Volvo cannot effectively absorb these higher raw material prices or pass them along to consumers through increased vehicle pricing, it can lead to a squeeze on profit margins, affecting overall profitability.
Labor Union Influence
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly concerning labor union influence, can significantly impact a company like Volvo. Strong labor unions within supplier factories can push for higher wages and better working conditions. This directly translates to increased production costs for those suppliers.
These elevated costs are then often passed on to automakers, including Volvo, as higher prices for components or manufactured parts. This dynamic can strain Volvo's procurement expenses and affect its overall profitability. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated that labor cost increases in key automotive manufacturing regions, influenced by union negotiations, contributed to a noticeable rise in component pricing for global car manufacturers.
- Labor Union Strength: Powerful unions can negotiate for higher wages and benefits, increasing supplier operating costs.
- Cost Pass-Through: Suppliers often pass these increased labor costs onto their customers, like Volvo.
- Impact on Volvo: This can lead to higher procurement expenses for Volvo, affecting their cost of goods sold.
- Regional Variations: The extent of this influence varies significantly by geographic region where suppliers are located.
Supply Chain Concentration
Supply chain concentration significantly impacts Volvo's bargaining power with its suppliers. If Volvo relies heavily on a limited number of suppliers for critical components, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This dependence makes it difficult and costly for Volvo to switch providers, especially in the rapidly evolving automotive sector where specialized components are common.
For instance, the semiconductor shortage in 2021-2022 highlighted this issue across the entire auto industry, including Volvo. Manufacturers struggled to secure chips, leading to production cuts and increased costs, demonstrating the immense power held by concentrated chip suppliers. Volvo itself had to temporarily halt production at some plants due to this scarcity.
- Component Dependency: Volvo's reliance on a few key suppliers for advanced battery technology or specialized electronic control units amplifies supplier bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with retooling, R&D, and qualifying new suppliers for complex automotive parts can lock Volvo into existing relationships, strengthening suppliers.
- Industry Trends: The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving necessitates new, often scarce, components, potentially concentrating supply and increasing supplier leverage.
Volvo Car's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly challenged by the concentration of critical component manufacturing. For example, the electric vehicle battery market is dominated by a few large players, giving them substantial leverage. In 2024, reports indicated that global EV battery production capacity was heavily concentrated, with Chinese manufacturers holding a significant share, impacting pricing and supply availability for automakers worldwide.
Suppliers who differentiate through unique technologies or intellectual property also command higher bargaining power. Companies developing proprietary advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or specialized electric powertrain components can dictate terms due to the high R&D investment and difficulty in replication. This allows them to command premium prices, impacting Volvo's cost structure.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Volvo's Bargaining Power | Example/Data (2024/2025 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Component Specialization | Reduces Volvo's ability to switch suppliers easily | Suppliers of lidar sensors for autonomous driving systems; limited number of qualified providers. |
| Raw Material Volatility | Increases supplier leverage during price surges | Lithium prices saw significant fluctuations in 2023-2024, affecting battery component costs. |
| Supply Chain Concentration | Empowers dominant suppliers due to limited alternatives | Dominance of a few key semiconductor manufacturers, leading to ongoing supply chain vulnerabilities. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive landscape for Volvo Cars, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive industry.
Visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, instantly highlighting Volvo's strategic vulnerabilities and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
The high price of luxury vehicles makes customers very attuned to price changes. For example, in 2024, the average transaction price for a new luxury vehicle in the US hovered around $65,000, a figure that significantly impacts household budgets. This sensitivity means buyers will actively seek out the best deals.
Because luxury cars are a substantial purchase, customers often conduct extensive research. They compare everything from fuel efficiency and advanced safety features to brand reputation and resale value. This diligence empowers them to negotiate for better prices and more favorable terms from manufacturers like Volvo.
Customers' willingness to switch brands if they perceive better value is a key factor. For instance, if Volvo's pricing or offerings become less competitive compared to rivals in the premium segment, buyers have numerous alternatives readily available. This threat of customer defection forces Volvo to maintain competitive pricing and a strong value proposition.
The automotive market is brimming with choices for luxury car buyers. With numerous global manufacturers like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and even newer entrants offering premium vehicles, customers have a vast selection. This abundance of alternatives significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
If Volvo doesn't meet a customer's expectations regarding price, features, or the quality of service, they can readily switch to a competitor. For instance, in 2024, the premium sedan segment alone saw over a dozen major brands vying for market share, each with multiple models. This easy switchability means Volvo must remain highly competitive to retain its customer base.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, thanks to the vast amount of information accessible online. Think about it: detailed vehicle reviews, side-by-side comparison tools, and readily available pricing data mean buyers know exactly what they're looking at. This transparency significantly shifts the power dynamic, allowing them to negotiate more effectively and expect higher quality and service.
For instance, a 2024 study found that over 80% of car buyers conduct extensive online research before visiting a dealership. This readily available data on specifications, reliability ratings, and pricing allows them to easily compare Volvo's offerings against competitors, putting pressure on the company to provide competitive pricing and superior features. If a customer can easily see that a rival offers similar features for less, their bargaining power increases substantially.
After-Sales Service and Warranty Expectations
Customers buying premium automobiles like Volvos anticipate robust after-sales care. This includes extended warranties, scheduled maintenance, and reliable repair services. In 2023, customer satisfaction scores for after-sales service were a key differentiator in the luxury segment, with brands offering proactive service alerts and personalized support seeing higher retention rates.
The quality and responsiveness of these services directly impact customer retention and brand advocacy. This gives buyers considerable leverage to negotiate for excellent service standards from Volvo and its authorized dealerships. For instance, a significant portion of luxury car buyers cite poor after-sales experiences as a primary reason for switching brands.
- Customer Expectations: Luxury car buyers prioritize comprehensive warranties and accessible, high-quality maintenance and repair.
- Brand Loyalty Impact: Positive after-sales experiences are crucial for fostering customer loyalty and encouraging positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Bargaining Power: High expectations for service quality grant customers leverage to demand better support from manufacturers and dealerships.
- Market Trends: In 2023, brands excelling in proactive service and personalized support experienced improved customer retention in the luxury automotive market.
Brand Loyalty vs. Switching Costs
Volvo benefits from a strong brand image associated with safety and pioneering technology, which fosters a degree of customer loyalty. However, this loyalty isn't absolute; customers may be swayed by competitors offering what they perceive as superior value or more appealing features. For instance, in 2024, advancements in electric vehicle technology from brands like Tesla and BYD have intensified competition, potentially drawing customers away from established players like Volvo if perceived benefits are significant enough.
While switching from a Volvo might involve a learning curve with new infotainment systems or driving dynamics, the substantial upfront cost of purchasing a new vehicle means customers are often willing to make that change to achieve better overall value or satisfaction. This willingness to switch, even with minor inconveniences, directly amplifies the bargaining power of customers. They understand that their significant investment gives them leverage to seek out the best options available in the market, pushing manufacturers to remain competitive on price and features.
- Brand Loyalty: Volvo's reputation for safety and innovation creates a loyal customer base.
- Competitive Landscape: In 2024, competitors like Tesla and BYD are challenging this loyalty with advanced EV tech.
- Switching Costs: While some learning is involved, the high initial purchase price makes customers willing to switch for better value.
- Customer Leverage: This willingness to switch increases customer bargaining power, forcing manufacturers to compete on price and features.
Customers in the premium automotive segment, including Volvo buyers, possess significant bargaining power. Their high sensitivity to price, driven by the substantial cost of luxury vehicles, encourages thorough research and comparison shopping. This informed approach, coupled with numerous competitive alternatives in the market, allows them to negotiate effectively for better deals and value.
The willingness of customers to switch brands if they perceive better value, even with minor inconveniences, amplifies their leverage. For instance, in 2024, the luxury SUV market alone featured over fifteen distinct brands, each offering multiple models, providing buyers with ample choice. This broad availability of substitutes means manufacturers like Volvo must continuously offer competitive pricing and compelling features to retain their customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Volvo | Supporting Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High. Customers closely monitor pricing due to significant purchase cost. | Average luxury vehicle transaction price in US ~$65,000. |
| Information Availability | Empowers customers with knowledge for negotiation. | Over 80% of car buyers conduct extensive online research pre-purchase. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Significant. Numerous premium brands offer competitive alternatives. | Luxury sedan segment offers over a dozen major brands with multiple models. |
| Switching Costs (Perceived) | Manageable. Customers willing to switch for perceived better value. | Advancements in EV tech from competitors potentially drawing customers. |
Same Document Delivered
Volvo Car Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Volvo Car Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for Volvo's strategic decision-making and long-term success. The insights provided will equip you with a thorough understanding of the external factors influencing Volvo's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Volvo Car operates within a fiercely competitive luxury automotive sector, facing off against established giants like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and Lexus. These rivals boast significant brand equity, diverse model ranges, and widespread global sales and service infrastructure, intensifying the struggle for market dominance.
In 2024, the luxury car market continued to see aggressive strategies from these players. For instance, BMW Group reported a strong performance, with its premium segment sales showing resilience. Similarly, Mercedes-Benz Group maintained its position, highlighting the sustained demand for high-end vehicles despite economic fluctuations.
This intense rivalry means Volvo must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings, from electrification to user experience, to capture and retain customers. The established brand loyalty and extensive resources of competitors present a significant barrier for Volvo to gain substantial market share increases.
The electric vehicle (EV) market is incredibly competitive, with established luxury brands and newer EV specialists like Tesla all fighting for market share. This rapid shift means Volvo must constantly push its boundaries in areas like battery efficiency, charging solutions, and overall electric performance to keep pace. For instance, in 2024, the global EV market is projected to see significant growth, with many legacy automakers releasing multiple new EV models, directly challenging Volvo's position.
Competitive rivalry in the global automotive market is intense, with established players like Volkswagen Group, Toyota, and Stellantis constantly vying for market share worldwide. These giants, much like Volvo, are actively pursuing expansion in high-growth emerging markets, such as Southeast Asia and India, while simultaneously fortifying their positions in mature markets like Europe and North America. For instance, in 2023, the global automotive market saw vehicle sales rebound, with major players reporting significant unit sales, highlighting the ongoing battle for consumer preference and operational reach.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Race
Competitive rivalry in the automotive sector, particularly for brands like Volvo, is intensely fueled by a relentless pursuit of product differentiation and innovation. This race is most evident in advancements in safety features, the burgeoning field of autonomous driving technology, enhanced vehicle connectivity, and the increasing demand for sustainable materials. Companies are locked in a constant battle to stand out, often by offering superior technology or unique features that capture consumer interest.
This dynamic forces significant investment in research and development (R&D) to maintain a competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the global automotive R&D spending was projected to exceed $200 billion, with a substantial portion dedicated to these very areas. Volvo itself has committed billions to electrification and autonomous driving, aiming to be a fully electric car maker by 2030.
- Safety Innovation: Volvo's historical strength, with ongoing development in areas like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and collision avoidance.
- Autonomous Driving: Significant investment in AI and sensor technology to develop and deploy self-driving capabilities, a key differentiator for many premium brands.
- Connectivity: Integration of sophisticated infotainment systems, over-the-air updates, and seamless smartphone integration, crucial for modern vehicle appeal.
- Sustainability: Focus on recycled materials, reduced carbon footprints, and electric powertrains as core elements of brand identity and product offering.
Aggressive Pricing and Marketing Strategies
Competitive rivalry in the automotive sector is intense, with players frequently employing aggressive pricing and marketing tactics. Competitors often resort to price wars, extensive promotional campaigns, and attractive financing deals to win over consumers. For instance, in 2024, many brands offered substantial discounts and low-interest loan options to stimulate demand amidst economic uncertainties.
This competitive landscape forces Volvo to tread a careful path. To maintain sales volumes and its market standing, Volvo must strategically manage its pricing structure, ensuring it remains competitive without sacrificing profitability. The company also needs to develop and execute impactful marketing campaigns that resonate with its target audience and highlight its unique value proposition, such as safety and Scandinavian design.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are highly sensitive to price, especially in the premium segment where Volvo operates.
- Promotional Activities: Competitors like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi frequently run aggressive sales promotions and offer significant discounts.
- Financing Options: Attractive financing packages, including low APR rates and leasing deals, are commonly used to lower the barrier to entry for new car purchases.
- Marketing Spend: Significant marketing budgets are allocated to brand building and product launches, creating a noisy market for consumer attention.
The automotive industry, especially the luxury segment where Volvo competes, is characterized by intense rivalry. Established players like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi possess strong brand loyalty and extensive resources, making it challenging for Volvo to significantly increase its market share.
In 2024, this rivalry is amplified by the rapid transition to electric vehicles (EVs), with numerous manufacturers, including traditional luxury brands and EV specialists, aggressively expanding their EV portfolios. This necessitates continuous innovation from Volvo in areas like battery technology and charging infrastructure to remain competitive.
Competitors frequently engage in aggressive pricing and marketing strategies, offering discounts and attractive financing to capture customers, which forces Volvo to carefully balance pricing and promotional activities to maintain sales and profitability.
The global automotive market saw significant sales figures in 2023, with major manufacturers reporting strong unit sales, underscoring the constant battle for consumer preference and market reach.
| Competitor | 2023 Global Sales (approx. units) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| BMW Group | ~2.5 million | Electrification, Digitalization, Premium Segment Dominance |
| Mercedes-Benz Group | ~2.0 million | Luxury Segment Leadership, EV Expansion, Software Development |
| Audi (VW Group) | ~1.9 million | Electric Mobility, Digital User Experience, SUV Portfolio |
| Lexus (Toyota) | ~0.8 million | Hybrid Technology, Luxury Craftsmanship, Customer Service |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many urban residents, robust public transportation networks present a significant threat of substitution to private car ownership. In 2023, cities like London and Tokyo reported consistent ridership numbers, with millions of daily commuters relying on trains, buses, and subways. This trend is amplified by growing environmental consciousness and governmental pushes for greener urban development.
The perceived cost-effectiveness and convenience of public transit, especially in congested urban areas, directly challenge the necessity of owning a car. For instance, the average monthly cost of public transport passes in major European cities often remains substantially lower than the combined expenses of car ownership, including fuel, insurance, and maintenance. This economic advantage, coupled with the time saved avoiding parking searches and traffic, makes public transport an increasingly attractive option.
Furthermore, advancements in public transit technology, such as integrated ticketing systems and real-time information apps, are enhancing the user experience. As cities continue to invest in expanding and modernizing their public transport infrastructure, the appeal of private vehicles as a primary mode of urban mobility is likely to further erode, impacting demand for new vehicles like those produced by Volvo.
The rise of ride-sharing and car-sharing services poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional car ownership, and by extension, for automakers like Volvo. Platforms such as Uber and Lyft offer readily available transportation, eliminating the need for personal vehicle purchase and maintenance. This convenience is particularly attractive to urban dwellers or those who don't require a car daily.
These services directly compete with the primary function of a car: providing mobility. For individuals who can access these alternatives reliably, the perceived value of owning a car diminishes. For instance, in 2024, ride-sharing services continued to expand their global reach, with millions of daily active users in major metropolitan areas, directly impacting personal transportation choices.
The economic argument for car-sharing and ride-sharing can be compelling, especially when considering the total cost of ownership for a new vehicle, which includes depreciation, insurance, fuel, and maintenance. As these services become more integrated into urban transit ecosystems, the barrier to entry for potential car buyers is effectively lowered, thereby constraining the market for new vehicle sales.
The used car market presents a significant threat of substitution for new car sales, particularly within the luxury segment. Consumers seeking premium features at a more accessible price point often turn to pre-owned vehicles. For instance, in 2024, the used car market continued to demonstrate resilience, with many well-maintained luxury models, including Volvos, offering a compelling alternative to buying new. The availability of these certified pre-owned options directly competes with new vehicle sales by providing a lower total cost of ownership.
Micromobility Solutions
The growing availability of micromobility options presents a significant threat of substitutes for automakers like Volvo, particularly in urban settings. Electric scooters, bikes, and mopeds offer convenient and often more affordable alternatives for short commutes. This is especially true for secondary car usage or as a primary mode of transport for certain demographics.
These alternatives directly compete with smaller, urban-focused car models. For instance, the global electric scooter market was valued at approximately $22.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This trend indicates a tangible shift in consumer preferences for short-distance travel, potentially reducing demand for traditional compact vehicles within city limits.
- Increased adoption of e-scooters and e-bikes for last-mile connectivity.
- Growing environmental consciousness driving preference for sustainable transport.
- Cost-effectiveness compared to car ownership and maintenance for short trips.
- Government initiatives promoting micromobility infrastructure and usage.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Models
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) presents a significant long-term threat to traditional automotive manufacturers like Volvo. These models, which offer bundled transportation services via subscription, could shift consumer preference away from personal vehicle ownership.
As of early 2024, the MaaS market is experiencing considerable growth, with companies like Uber and Lyft expanding their integrated offerings. For instance, Uber One members in select markets can access discounts on rides, Eats, and even rental cars, hinting at a more comprehensive service bundle.
- Growing MaaS Adoption: Projections suggest the global MaaS market could reach hundreds of billions of dollars by the end of the decade, indicating a substantial shift in transportation consumption.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Younger demographics, particularly in urban areas, are increasingly open to subscription-based mobility, valuing convenience and cost predictability over outright ownership.
- Integration of Services: MaaS platforms are integrating various modes of transport, including ride-sharing, public transit, and micro-mobility, creating a compelling alternative to owning a car.
If MaaS solutions become sufficiently cost-effective and convenient, they could erode demand for new vehicle sales, fundamentally challenging Volvo's established business model centered on car manufacturing and sales.
Alternative transportation methods are a substantial threat to Volvo. Public transit networks, especially in dense urban environments, offer a cost-effective and convenient alternative to private car ownership. For example, in 2024, major cities continued to see strong public transport usage, with millions of daily commuters relying on these systems, making personal vehicle purchase less appealing.
Entrants Threaten
The automotive manufacturing industry, especially the premium segment where Volvo operates, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Developing cutting-edge research and development, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and building a robust global supply chain necessitate billions of dollars in initial investment.
For instance, the average cost to launch a new vehicle model can easily exceed $1 billion, encompassing design, engineering, testing, and tooling. Furthermore, creating a competitive brand presence and a comprehensive marketing strategy requires substantial ongoing financial commitment, making it incredibly challenging for newcomers to challenge established players like Volvo.
Incumbent luxury automakers like Volvo have cultivated decades of strong brand loyalty and reputation, built on pillars of safety, quality, and performance. For instance, Volvo's commitment to safety, exemplified by its pioneering of the three-point seatbelt in 1959, continues to resonate with consumers, fostering deep trust. This established goodwill makes it exceptionally difficult for new entrants to attract and retain customers in a segment where brand perception is paramount.
The automotive sector is heavily regulated, with strict safety standards like those mandated by the NHTSA in the US and stringent environmental rules such as Euro 7 emissions standards in Europe. New companies entering this market must invest substantial capital and time to meet these complex requirements, including extensive testing and certification, creating a significant barrier to entry.
Established Supply Chains and Distribution Networks
Established players like Volvo leverage deeply entrenched supply chains and distribution networks, built over decades of operation. These existing relationships with a global base of suppliers and a widespread dealer and service infrastructure represent a significant barrier for newcomers. In 2024, the automotive industry continues to see substantial investment in optimizing these logistical arteries, with companies like Volvo investing billions in advanced manufacturing and digital supply chain solutions to enhance efficiency and responsiveness.
New entrants face the daunting task of replicating these extensive and efficient networks. The sheer scale and complexity of establishing reliable sourcing for hundreds of intricate automotive components, alongside building out a customer-facing distribution and after-sales service system, present substantial capital and time investment requirements. For example, establishing a comparable global supplier base for electric vehicle components, which often involves specialized materials and advanced battery technology, is particularly challenging and costly.
- Established Relationships: Volvo benefits from long-standing, trusted partnerships with global suppliers, ensuring consistent quality and volume of components.
- Global Reach: The company possesses an extensive network of dealerships and service centers worldwide, providing crucial market access and customer support.
- Economies of Scale: Existing players can achieve significant cost advantages through the sheer volume of their operations within these established networks.
- Replication Difficulty: New entrants would require massive capital outlays and considerable time to build comparable supply chain and distribution capabilities.
Emergence of Tech Companies and EV Startups
While established automakers face high capital requirements and complex supply chains, the automotive landscape is being reshaped by agile tech giants and burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) startups. These new entrants, unburdened by the costs of traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) infrastructure, are leveraging significant capital and software prowess. For instance, by mid-2024, major tech firms had announced multi-billion dollar investments in EV and autonomous driving research and development.
These disruptive forces are rapidly advancing battery technology, charging infrastructure, and in-car digital experiences, areas where traditional manufacturers may be slower to adapt. The success of companies like Tesla, which entered the market with a focus on premium EVs and direct-to-consumer sales, demonstrates the potential for new players to carve out significant market share. By early 2024, Tesla's market capitalization consistently placed it among the top automotive manufacturers globally, highlighting the valuation potential for innovative EV companies.
- Rapid Innovation: New EV startups and tech companies can develop and deploy new technologies, like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and over-the-air software updates, at a pace that challenges established players.
- Lower Legacy Costs: Unlike traditional automakers, many new entrants start with a clean slate, avoiding the significant costs associated with retooling factories for ICE vehicles and managing existing dealership networks.
- Software-Centric Approach: Companies like Rivian and Lucid, for example, have prioritized software integration and user experience from the ground up, attracting consumers who value digital connectivity and advanced infotainment.
- Access to Capital: Many tech companies entering the automotive space have access to vast financial resources, enabling them to fund extensive R&D and market penetration strategies without the immediate pressure of profitability that often faces legacy automakers.
The threat of new entrants in the premium automotive sector, where Volvo competes, remains moderate due to substantial barriers, yet is evolving. While immense capital is needed for R&D, manufacturing, and brand building, with new vehicle launches often exceeding $1 billion, established players like Volvo possess strong brand loyalty and regulatory compliance expertise, which are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
However, the rise of electric vehicle (EV) startups and tech companies poses a growing challenge. These new players, unburdened by legacy internal combustion engine infrastructure, are attracting significant investment, with tech giants announcing multi-billion dollar commitments to EV and autonomous driving by mid-2024. Their rapid innovation in battery technology and software integration, exemplified by Tesla's market success, demonstrates their potential to disrupt the market.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High Barrier | Average cost to launch a new vehicle model: >$1 billion |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | High Barrier | Volvo's safety legacy (e.g., three-point seatbelt, 1959) fosters deep customer trust. |
| Regulation & Compliance | High Barrier | Meeting NHTSA (US) safety and Euro 7 (EU) emissions standards requires substantial investment. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | High Barrier | Volvo's established global networks require massive capital and time to replicate. |
| EV & Tech Disruption | Moderate to High Threat | Tech firms invested billions in EV/autonomous R&D by mid-2024; Tesla's market cap highlights EV potential. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Volvo Cars is built upon a robust foundation of data, including annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit. We also incorporate publicly available information from regulatory bodies and automotive trade publications to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
