Volkswagen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Volkswagen Bundle
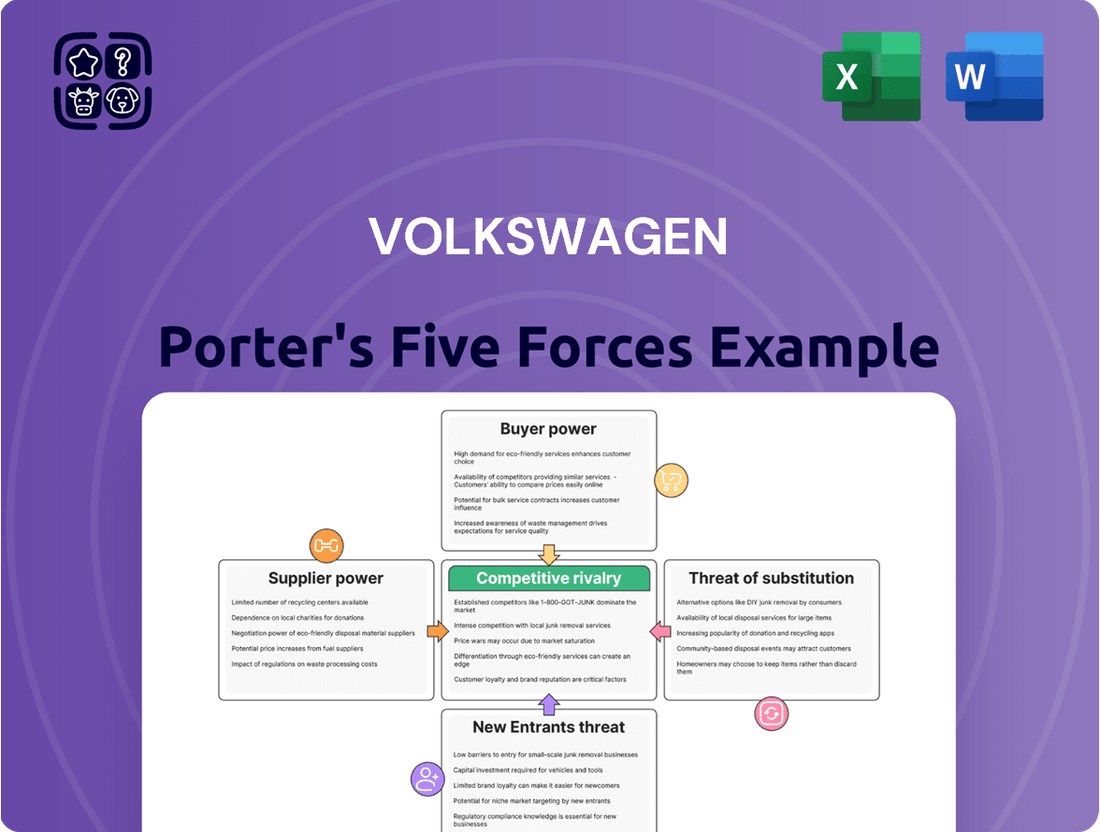
Volkswagen faces a dynamic automotive landscape, with intense rivalry among established players and the looming threat of new entrants, particularly from the electric vehicle sector. Buyer power is significant due to brand loyalty shifts and the availability of numerous alternatives. The bargaining power of suppliers, especially for critical components like batteries, can also impact profitability.
The threat of substitutes, ranging from public transportation to ride-sharing services, adds another layer of complexity to Volkswagen's market position. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry's challenges and capitalizing on opportunities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Volkswagen’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Volkswagen's reliance on a vast, global supply chain means that concentrated suppliers of specialized components, like advanced semiconductors and EV batteries, wield considerable power. For instance, the automotive industry's dependence on a few key semiconductor manufacturers, a situation exacerbated by global chip shortages in recent years, allows these suppliers to dictate terms and pricing. This concentration is amplified in emerging technologies, where a limited pool of experts in areas like battery chemistry and autonomous driving software means Volkswagen must negotiate from a less advantageous position.
Switching suppliers for Volkswagen is a significant undertaking due to the intricate nature of automotive manufacturing. The process often necessitates substantial investments in retooling production lines, a move that can cost millions. For instance, a single component redesign might require new molds and assembly jigs, impacting a substantial portion of the manufacturing setup.
Beyond physical retooling, extensive testing and certification are mandatory for any new supplier to ensure safety and quality standards are met. This rigorous process can take many months, sometimes even years, delaying product development and increasing costs. Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, demanding thorough validation of new materials and processes.
Integrating new parts with existing vehicle architectures and complex software systems presents further challenges. Compatibility issues can arise, requiring extensive software modifications and recalibrations. Volkswagen's reliance on highly specialized components, often developed in close collaboration with specific suppliers, further exacerbates these integration hurdles.
These high switching costs effectively reduce Volkswagen's negotiation leverage and strengthen the bargaining power of its established suppliers. Suppliers who have deeply integrated their products and processes into Volkswagen's manufacturing ecosystem are in a more favorable position, often commanding higher prices or more favorable terms due to the difficulty and expense of replacement.
The quality and reliability of components are absolutely crucial for Volkswagen's manufacturing process and its esteemed brand image. Any hiccup in the delivery of essential parts can directly impact production schedules and, consequently, financial performance.
Recent years have highlighted this vulnerability, particularly with the global semiconductor shortage. This disruption demonstrated how suppliers of critical, high-quality, or difficult-to-source inputs can wield significant influence over automakers like Volkswagen.
In 2023, the automotive industry continued to grapple with supply chain challenges, though some easing was observed. However, the strategic importance of securing consistent access to specialized components, such as advanced electronics and battery materials for electric vehicles, remains a key factor in supplier bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, particularly those in advanced sectors like battery technology and software, presents a notable aspect of supplier bargaining power for Volkswagen. Some large, technologically sophisticated suppliers have both the capacity and the strategic inclination to move into vehicle manufacturing themselves. While it is unlikely for these suppliers to become direct competitors in full-scale car production, their ability to provide essential components to various original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or to develop their own proprietary technology platforms can significantly enhance their negotiating leverage over Volkswagen.
For instance, in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, a battery supplier that controls a crucial aspect of battery chemistry or manufacturing could potentially dictate terms or even explore producing their own EV models. This would allow them to capture more of the value chain. Consider the significant investments companies like CATL, a leading EV battery supplier, are making in expanding their global production capacity. By 2024, CATL's planned capacity is projected to reach over 600 GWh globally, highlighting their substantial market influence and the potential for them to exert greater control over their automotive clients.
- Potential for Control: Suppliers with critical, proprietary technology, such as advanced battery management systems or autonomous driving software, can gain substantial leverage.
- Market Influence: Large suppliers like LG Energy Solution or Samsung SDI, with significant production scale in EV batteries, can influence pricing and supply terms due to their indispensability.
- Strategic Intent: While full integration into car manufacturing is rare, suppliers can integrate forward by offering more complete subsystems or even developing their own EV platforms, increasing their power.
- Industry Dynamics: The ongoing shift towards electric and connected vehicles empowers tech-focused suppliers, as their innovations become central to a vehicle’s performance and appeal, amplifying their bargaining position.
Supplier's Unique or Differentiated Products
Suppliers offering unique, patented technologies or highly differentiated components, particularly in areas like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, or advanced powertrains, wield significant bargaining power. Volkswagen's reliance on these innovative elements to maintain its competitive edge in the fast-paced automotive sector amplifies the influence of these specialized suppliers.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor shortage underscored the critical dependence on chip manufacturers for advanced automotive electronics. Companies like Infineon Technologies, a key supplier for Volkswagen, demonstrated this power due to the highly specialized nature of their products and limited alternative sources for certain high-performance chips.
- High Dependence on Specialized Components: Volkswagen's product development often necessitates proprietary or highly customized electronic components, increasing supplier leverage.
- Innovation as a Differentiator: Suppliers with patented ADAS features or unique battery management systems for electric vehicles (EVs) can command higher prices and favorable terms.
- Limited Substitutability: For cutting-edge technologies where few suppliers exist, Volkswagen faces greater pressure to accept supplier terms.
- Impact on Vehicle Performance: The quality and advancement of these differentiated components directly affect Volkswagen's vehicle performance and market appeal, further strengthening supplier negotiating positions.
Suppliers of critical, specialized components, especially those with proprietary technology, hold significant bargaining power over Volkswagen. This is particularly true for advanced semiconductors and EV batteries, where a concentrated supply base and high switching costs empower these suppliers to dictate terms and pricing. For example, the ongoing demand for advanced automotive electronics in 2024 means that key semiconductor manufacturers can continue to exert considerable influence.
The automotive industry's reliance on a few key semiconductor manufacturers, a situation exacerbated by global chip shortages in recent years, allows these suppliers to dictate terms and pricing. This concentration is amplified in emerging technologies, where a limited pool of experts in areas like battery chemistry and autonomous driving software means Volkswagen must negotiate from a less advantageous position.
| Key Component Area | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Volkswagen |
| Semiconductors | Concentrated supply, high specialization | Potential for price increases, production delays |
| EV Batteries | Limited number of large-scale producers, critical technology | Negotiation leverage on cost and supply volume |
| Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Proprietary technology, limited alternatives | Higher component costs, dependence on innovation |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Volkswagen's Porter's Five Forces examines the intense competition, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes within the automotive industry, providing strategic insights for Volkswagen's market position.
Effortlessly assess competitive pressures impacting the Volkswagen Porter, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Volkswagen, like other volume automakers, operates in a highly competitive automotive market where customers are very sensitive to price. This sensitivity means that even small changes in vehicle cost can significantly influence purchasing decisions. For instance, in 2024, the average transaction price for new vehicles in the US remained elevated, but consumers actively sought deals and incentives to offset these costs.
Economic conditions play a crucial role in amplifying customer price sensitivity. During periods of high inflation or rising interest rates, as seen in many global economies throughout 2023 and into 2024, consumers become more cautious with their spending. This heightened caution translates directly into increased demand for discounts, rebates, and favorable financing options from manufacturers like Volkswagen.
The pressure on pricing directly impacts Volkswagen's profitability. When customers demand more discounts, the company’s profit margins can shrink, especially in markets with aggressive price competition. This is particularly evident in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) segment, where intense price wars, notably in China during 2024, force manufacturers to offer substantial incentives, thereby squeezing margins.
Customers face a vast selection of automotive choices, with numerous global and regional manufacturers, including a surge of electric vehicle (EV) startups and competitive Chinese brands, readily available. This abundance of alternatives significantly empowers buyers.
The continuous introduction of new EV models, coupled with a discernible trend of increasing brand defection worldwide, means consumers can readily shift their allegiance to competing brands if Volkswagen's products fail to align with their expectations regarding price, features, or performance. For instance, the global EV market is projected to grow substantially, with sales expected to reach over 15 million units in 2024, presenting a clear alternative for consumers.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed. With the internet, comparison websites, and countless reviews, they can easily research vehicle features, compare prices, and check performance data for virtually any car brand. This means they know what's out there and what others are paying.
This abundance of information significantly boosts customer bargaining power. They can pinpoint the best deals and understand true market value, making it harder for Volkswagen to charge higher prices unless they offer truly unique features or superior quality. For instance, in 2024, the average new car price in the US hovered around $47,000, a figure consumers readily access and use in negotiations.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for car buyers are generally moderate. While purchasing a new vehicle requires time and research, the financial and practical hurdles to moving between brands are not insurmountable, especially with competitive financing and trade-in deals. For instance, in 2024, the average manufacturer incentive on new vehicles reached approximately $5,000, helping to offset potential switching costs.
Customers can easily transition between brands, particularly within similar vehicle segments, as they are not significantly locked into a specific manufacturer's ecosystem. This accessibility to alternatives means Volkswagen faces a degree of customer bargaining power.
- Moderate Switching Costs: Financial and practical switching costs for car buyers are generally in the mid-range.
- Competitive Incentives: In 2024, average manufacturer incentives on new vehicles were around $5,000, easing the financial burden of switching.
- Ease of Transition: Customers can readily move between brands, especially within similar vehicle categories.
- Limited Ecosystem Lock-in: Buyers are not heavily tied to specific brands, allowing for easy consideration of competitors.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers is minimal for Volkswagen, as individual or corporate buyers are highly unlikely to enter the complex and capital-intensive field of vehicle manufacturing.
However, significant volume purchasers like major fleet operators or large car rental agencies can wield considerable buyer power. This power is primarily exercised through negotiations on pricing, customized features, and delivery terms, effectively influencing Volkswagen's profitability on these substantial orders. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of vehicle sales for many automakers, including Volkswagen, comes from fleet deals, highlighting the importance of managing these relationships.
- Minimal Threat: Individual and most corporate customers lack the resources and expertise for backward integration into automotive production.
- Buyer Power of Fleet Customers: Large fleet buyers, due to high purchase volumes, can significantly influence pricing and contract terms.
- Impact on Volkswagen: This buyer power can pressure profit margins on fleet sales, which are a crucial segment for many automakers.
- 2024 Context: Fleet sales continue to represent a substantial percentage of the automotive market, underscoring the ongoing relevance of this buyer influence.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to a wide array of choices, including numerous global and emerging EV manufacturers, making brand switching easier. This is amplified by readily available information on pricing and features, allowing consumers to negotiate effectively. For instance, in 2024, the average transaction price for new cars in the US was around $47,000, a figure consumers actively used in their purchasing decisions.
Switching costs are generally moderate, with incentives around $5,000 offered by manufacturers in 2024 helping to reduce barriers. The threat of backward integration by customers is negligible. However, large fleet buyers can exert considerable influence on pricing and terms, impacting Volkswagen's profitability on these substantial orders, which remained a key market segment in 2024.
| Factor | Description | 2024 Relevance | Impact on VW |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous global and EV brands offer extensive choices. | High, with projected EV sales exceeding 15 million units. | Increases customer leverage. |
| Information Accessibility | Online research provides price, feature, and performance data. | Very high, enabling informed price comparisons. | Pressures profit margins. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate, aided by manufacturer incentives. | Average incentives around $5,000. | Facilitates brand loyalty challenges. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Minimal for individual or most corporate buyers. | Negligible in automotive manufacturing. | No significant threat. |
| Fleet Buyer Power | Large volume purchasers negotiate terms. | Fleet sales represent a substantial market share. | Can reduce margins on large orders. |
Full Version Awaits
Volkswagen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Volkswagen Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive and market forces impacting Volkswagen's commercial vehicle segment. You'll receive this exact, professionally written document immediately upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. It thoroughly covers the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the commercial vehicle industry. This is the final, ready-to-use analysis you'll download, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global automotive industry's growth is a complex picture. While electric vehicle (EV) sales are on the rise, with global EV sales projected to reach 20 million units in 2024, the pace of this growth has moderated in certain key markets, creating a more competitive environment. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle sales are facing stagnation or even decline in some developed economies, intensifying the battle for remaining market share.
Volkswagen faces formidable competitive rivalry due to the sheer number and diversity of players in the automotive sector. Global giants like Toyota, Stellantis, General Motors, and Hyundai-Kia maintain significant market share and established brand loyalty.
The landscape is further intensified by the swift ascent of Chinese original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) such as BYD, Nio, and Geely, which are increasingly capturing global attention and market share, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) segment. For instance, BYD’s sales of new energy vehicles (NEVs) surged by approximately 45% in 2023 compared to 2022, showcasing their aggressive growth trajectory.
Adding to this complexity are innovative EV-focused companies like Tesla and Rivian, which have disrupted traditional automotive models with their technology and direct-to-consumer approaches. Tesla, a pioneer in the EV market, reported record deliveries in 2023, demonstrating its continued influence and competitive pressure on established automakers.
This multifaceted competitive environment, characterized by varied business models, from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) manufacturers to cutting-edge EV startups, creates a dynamic and intensely competitive market. Volkswagen must navigate these diverse strategies and technological advancements to maintain its position.
Volkswagen faces intense competition as product differentiation becomes harder. Competitors are aggressively innovating in electric vehicle technology, advanced software integration, and autonomous driving systems. This rapid pace of innovation means Volkswagen must invest heavily in research and development to maintain its edge.
In 2024, the automotive industry saw significant R&D spending. For instance, Volkswagen Group reported substantial investments in future mobility, with electrification and digitalization being key focus areas. This commitment reflects the pressure to differentiate in a market where technological advancements are quickly becoming standard features.
High Exit Barriers
The automotive sector, including giants like Volkswagen, faces intense competitive rivalry, partly due to high exit barriers. These barriers are a direct consequence of the industry's enormous fixed costs. Think about the sheer scale of investment required for manufacturing facilities, research and development (R&D) for new models and technologies, and the intricate global supply chains that need to be maintained. These are not costs that can be easily recouped if a company decides to leave the market.
Because of these substantial sunk costs, companies are effectively locked into the industry. Even when market conditions become challenging, or profitability dips, exiting is often not a financially viable option. This situation forces players to remain and battle for market share, intensifying the competition. For example, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to grapple with the high capital expenditures needed for the transition to electric vehicles (EVs), further cementing these high exit barriers.
- Massive Fixed Costs: The automotive industry requires billions in investments for production, R&D, and supply chains.
- Sunk Costs: High initial investments make it difficult and costly to exit the market.
- Intensified Rivalry: Companies tend to stay and compete fiercely, even in weak markets, due to exit barriers.
- EV Transition Impact: Ongoing investments in electric vehicle technology in 2024 reinforce these high exit barriers.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness of Competitors
Competitive rivalry within the automotive sector is intensely high, with key players like Volkswagen, Toyota, General Motors, and Stellantis aggressively vying for market share. This competition is particularly fierce in rapidly expanding segments such as electric vehicles (EVs) and in strategically vital growth markets like China and the United States. For instance, in 2024, the global EV market continued its robust expansion, with sales projected to surpass 15 million units, a significant jump from previous years, putting pressure on all manufacturers to innovate and capture a larger piece of this pie.
These strategic stakes are driving aggressive actions across the industry. Manufacturers are undertaking substantial investments in new technologies, with R&D spending in areas like battery technology, autonomous driving, and advanced software systems reaching unprecedented levels. Volkswagen alone committed billions of euros to its electrification strategy, aiming to launch numerous new EV models by 2025 and beyond. This arms race for technological superiority, coupled with regional expansion efforts and an increasing propensity for price competition, particularly in the EV segment, significantly escalates the overall intensity of competitive rivalry.
- Intense EV Competition: Major automakers are heavily investing in electric vehicle development and production, aiming to capture market share in this rapidly growing segment.
- Growth Market Focus: Competition is particularly aggressive in key growth markets such as China, where domestic brands are also gaining significant traction.
- Strategic Investments: Companies are making substantial financial commitments to R&D, new manufacturing facilities, and talent acquisition to stay ahead technologically.
- Price Wars Emerge: In response to market pressures and increased competition, price adjustments and incentives are becoming more common, especially in the EV sector.
Volkswagen faces a highly competitive landscape, with global automotive giants like Toyota, Stellantis, and General Motors as formidable rivals. The rise of aggressive Chinese manufacturers, such as BYD, which saw its NEV sales climb by approximately 45% in 2023, and EV disruptors like Tesla, which reported record deliveries in 2023, further intensifies this rivalry.
The pressure to innovate is immense, forcing companies like Volkswagen to pour billions into R&D for electrification and autonomous driving, as seen in their significant investments in 2024. This technological race, combined with intense competition in growth markets and a growing trend towards price adjustments, particularly in the EV segment, elevates the overall rivalry.
| Competitor | Key Strength | 2023 Performance Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota | Hybrid leadership, global reach | Reported strong sales, maintaining market share |
| Stellantis | Diverse brand portfolio, regional strength | Navigating EV transition with multiple brand strategies |
| General Motors | EV investment, North American presence | Expanding Ultium platform for new EV models |
| BYD | EV dominance, vertical integration | ~45% NEV sales growth in 2023 |
| Tesla | EV innovation, direct sales model | Record deliveries in 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of public transportation and ride-sharing services presents a growing threat to Volkswagen. In 2023, global ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft facilitated billions of rides, offering convenient alternatives to car ownership, particularly in densely populated urban centers. This trend directly impacts Volkswagen's potential sales volume by reducing the perceived necessity of owning a personal vehicle.
For shorter urban trips, cycling and micro-mobility options like e-scooters are becoming a significant alternative to traditional cars. These solutions are often more convenient and cost-effective in congested city centers. The growing popularity of these alternatives means some consumers might opt out of car ownership or delay purchasing a new vehicle, impacting Volkswagen's traditional market.
In 2024, the adoption of e-scooters and e-bikes continued to rise globally, with many cities investing in dedicated infrastructure. For instance, cities like Paris have seen a substantial increase in micro-mobility usage for daily commutes, directly competing with short-distance car journeys. This trend indicates a genuine threat to car sales for certain use cases, particularly within urban environments.
Walking and active transportation present a significant threat to Volkswagen, particularly in urban settings. For short commutes, especially those under two miles, pedestrian travel is often the most convenient and cost-effective option, directly substituting for the need for a car. Cities are increasingly investing in pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, like expanded sidewalks and dedicated bike lanes, making active transport more appealing. For instance, a 2023 study indicated that over 40% of urban car trips in Europe are less than 5 kilometers, a distance easily covered by walking or cycling.
Telecommuting and Virtual Connectivity
The increasing prevalence of telecommuting and virtual connectivity presents a significant threat of substitutes for Volkswagen. As more professionals work remotely, the need for daily commutes diminishes, directly impacting vehicle demand. This shift means fewer miles driven annually, potentially leading to longer vehicle ownership periods and a reduced frequency of new car purchases.
In 2024, the trend of remote and hybrid work continued to be a dominant force. For instance, surveys indicated that a substantial percentage of the workforce maintained at least a hybrid schedule, meaning fewer days spent commuting. This behavioral change, while not a direct product substitute, effectively reduces the overall utility and perceived necessity of owning a personal vehicle for many, especially for urban dwellers who might otherwise rely on a car for daily transit.
The implications for Volkswagen are clear: slower sales growth and potentially extended replacement cycles for their existing customer base. This indirect substitution effect from changing work habits can dampen demand for new vehicles, particularly those traditionally purchased for commuting purposes.
- Telecommuting reduces daily travel needs, impacting vehicle mileage.
- Virtual connectivity offers alternatives to business travel.
- Longer vehicle lifespans can result from decreased usage.
- This trend may lead to delayed new vehicle replacement cycles.
Evolving Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Models
The long-term development of comprehensive Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms poses a significant threat to traditional vehicle ownership models. These platforms integrate various transportation modes, like ride-sharing, public transit, and micro-mobility, into a single, on-demand service. This integration could fundamentally shift consumer preferences away from private car ownership.
While still in its early stages, the potential for MaaS to offer a compelling and convenient alternative to owning a personal vehicle represents a future threat for automakers like Volkswagen. For instance, by 2024, many urban centers are seeing increased investment and adoption of integrated public transport and ride-sharing apps. Cities like Helsinki’s Whim service, a pioneer in MaaS, continue to refine their offerings, demonstrating the viability of this model.
- Growing MaaS Adoption: MaaS platforms are expanding their reach, integrating more services and user bases, which could reduce the perceived necessity of private car ownership.
- Cost-Effectiveness for Consumers: For many urban dwellers, a subscription-based MaaS model could become more cost-effective than car ownership, factoring in purchase price, insurance, maintenance, and parking.
- Environmental and Convenience Factors: MaaS can also appeal to consumers seeking more sustainable and convenient transportation options, bypassing the hassles of parking and vehicle upkeep.
- Regulatory Support: Governments in various regions are actively supporting MaaS initiatives to promote efficient urban mobility and reduce congestion, further bolstering the threat.
The threat of substitutes for Volkswagen is multifaceted, encompassing both direct transportation alternatives and shifts in consumer behavior. Public transportation, ride-sharing, and micro-mobility options like e-scooters and e-bikes offer convenient and often more cost-effective solutions, particularly in urban areas. Telecommuting and virtual connectivity also reduce the need for daily travel, potentially extending vehicle ownership periods. The burgeoning Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) sector presents a significant long-term challenge by integrating various transport modes into a single, subscription-based offering.
| Substitute Type | 2023/2024 Trend/Data Point | Impact on Volkswagen |
|---|---|---|
| Ride-Sharing (e.g., Uber, Lyft) | Billions of rides facilitated globally in 2023; continued growth in urban adoption. | Reduces perceived necessity of personal car ownership, impacting sales volume. |
| Micro-mobility (e.g., e-scooters, e-bikes) | Increased investment in urban infrastructure for micro-mobility in 2024; significant usage rise in cities like Paris for short commutes. | Competes with short-distance car journeys, potentially leading to delayed purchases or opting out of car ownership. |
| Telecommuting/Remote Work | Continued dominance of hybrid work models in 2024; substantial workforce maintaining hybrid schedules. | Diminishes daily commute needs, reducing vehicle demand and potentially lengthening replacement cycles. |
| Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) | Increased investment and adoption of integrated transport apps by 2024; services like Helsinki's Whim refining offerings. | Offers a compelling, integrated alternative to private car ownership, potentially shifting consumer preferences. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive sector, including players like Volkswagen, necessitates monumental capital outlays. This includes significant investment in research and development to innovate, building and equipping state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and establishing extensive global supply chains and distribution networks. For instance, developing a new vehicle platform can cost billions of dollars, a substantial hurdle for any aspiring entrant.
Volkswagen enjoys robust brand loyalty, cultivated over decades of consistent quality and marketing. This loyalty translates into a significant hurdle for newcomers aiming to capture market share. For example, in 2023, Volkswagen Group's global deliveries reached 9.24 million vehicles, demonstrating the sheer scale of its existing customer base and brand recognition.
The established and extensive distribution and after-sales service network represents another formidable barrier. New entrants must invest heavily to replicate Volkswagen's global footprint of dealerships and service centers, which are crucial for customer satisfaction and retention. Building this infrastructure from the ground up is both time-consuming and capital-intensive, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively on accessibility and support.
The automotive sector is a minefield of regulations, impacting everything from vehicle safety and emissions to environmental impact. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce its strict CO2 emission targets, requiring manufacturers to achieve an average of 95g CO2/km for new passenger cars, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
New entrants face the daunting task of understanding and adhering to these diverse and often evolving rules across global markets. This involves securing numerous certifications, from crash safety standards to specific pollutant limits, each demanding significant investment in research, development, and testing.
The sheer expense of compliance is a major deterrent. Beyond initial certifications, ongoing monitoring and adaptation to new regulations, such as those related to battery recycling or autonomous driving safety in 2024, add substantial operational costs. These compliance burdens effectively raise the barrier to entry, making it exceedingly difficult for smaller or less-capitalized companies to compete with established players like Volkswagen.
Access to Technology and Skilled Labor
Developing cutting-edge vehicles, particularly in the electric and autonomous driving sectors, demands significant technological expertise, protected intellectual property, and a specialized workforce. Newcomers face substantial hurdles in acquiring the necessary engineering, software development, and advanced manufacturing skills. Volkswagen, for instance, benefits from decades of R&D and a vast pool of experienced talent, making it difficult for new entrants to match this deep-seated capability.
The barriers to entry are amplified by the substantial capital investment required for research, development, and establishing production facilities. For example, the global automotive industry saw significant investment in EV technology throughout 2024, with major automakers committing billions. New entrants must not only compete with established technological advantages but also overcome the financial muscle of incumbents.
- Technological Sophistication: The complexity of modern vehicle technology, especially in areas like battery management systems and AI for autonomous driving, represents a high barrier.
- Intellectual Property: Established automakers hold numerous patents covering critical vehicle components and software, which new entrants must either license or develop around, incurring further costs and time.
- Skilled Workforce Acquisition: The demand for specialized engineers and software developers in the automotive sector is intense, making it challenging and expensive for new companies to recruit and retain top talent.
- Capital Intensive R&D: Significant ongoing investment is needed to stay abreast of rapid technological advancements, a burden that can be prohibitive for startups.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Volkswagen's immense economies of scale present a formidable barrier to new entrants in the automotive industry. The sheer volume of vehicles produced, estimated at over 8.3 million units globally in 2023, allows Volkswagen to spread its significant R&D, manufacturing, and procurement costs over a vast output. This translates to lower per-unit production costs, a significant advantage when competing on price. Newcomers simply cannot match this scale initially, leading to higher per-unit expenses and a competitive disadvantage.
The experience curve further solidifies Volkswagen's position. Years of refining production processes, optimizing supply chains, and developing manufacturing expertise mean Volkswagen can produce vehicles more efficiently and with fewer defects. New entrants must invest heavily to climb this learning curve, facing higher initial costs and potential quality issues as they establish their operations. For instance, achieving the same level of automation and supply chain integration as Volkswagen would require billions in upfront investment.
- Economies of Scale: Volkswagen's global production of over 8.3 million vehicles in 2023 allows for significant cost advantages in manufacturing, R&D, and procurement.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational refinement enable Volkswagen to produce vehicles more efficiently and cost-effectively than emerging competitors.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants face challenges in replicating Volkswagen's scale and accumulated manufacturing knowledge, resulting in higher initial costs and a steeper learning curve.
- Competitive Pricing: The cost efficiencies derived from scale and experience enable Volkswagen to offer competitive pricing, making it difficult for new players to enter the market profitably.
The threat of new entrants for Volkswagen is generally low, primarily due to the immense capital requirements, strong brand loyalty, and extensive established networks. The sheer cost of setting up R&D, manufacturing, and distribution in the automotive sector, especially for electric and autonomous technologies, acts as a significant deterrent. For example, developing a new electric vehicle platform can easily cost billions of dollars, a hurdle that most new players find insurmountable.
Established brands like Volkswagen benefit from decades of customer trust and recognition, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share. In 2023, Volkswagen Group delivered 9.24 million vehicles, illustrating the depth of its existing customer base. Furthermore, replicating Volkswagen's global network of dealerships and after-sales service centers demands massive investment and time, creating a substantial barrier for any aspiring competitor.
Regulatory compliance, particularly concerning emissions and safety standards, adds another layer of complexity and cost for new entrants. For instance, in 2024, stringent CO2 emission targets in regions like the EU require significant R&D and technological investment that established players are better equipped to handle. The need for specialized talent in areas like battery technology and AI further complicates entry, as acquiring and retaining such expertise is challenging and costly.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Massive investment for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Prohibitive cost for most new companies. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of established customer trust and recognition. | Difficult to capture market share from incumbents. |
| Distribution & Service Network | Extensive global presence of dealerships and service centers. | Requires substantial investment to replicate infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to strict safety, emissions, and environmental standards. | High cost and complexity for new players to navigate. |
| Technological Expertise | Need for advanced skills in EV, AI, and autonomous driving. | Challenges in talent acquisition and R&D investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Volkswagen Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Volkswagen's annual reports and investor relations disclosures, alongside industry-specific publications and market research reports from firms like IHS Markit and Statista.
