Vishay Intertechnology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Vishay Intertechnology Bundle
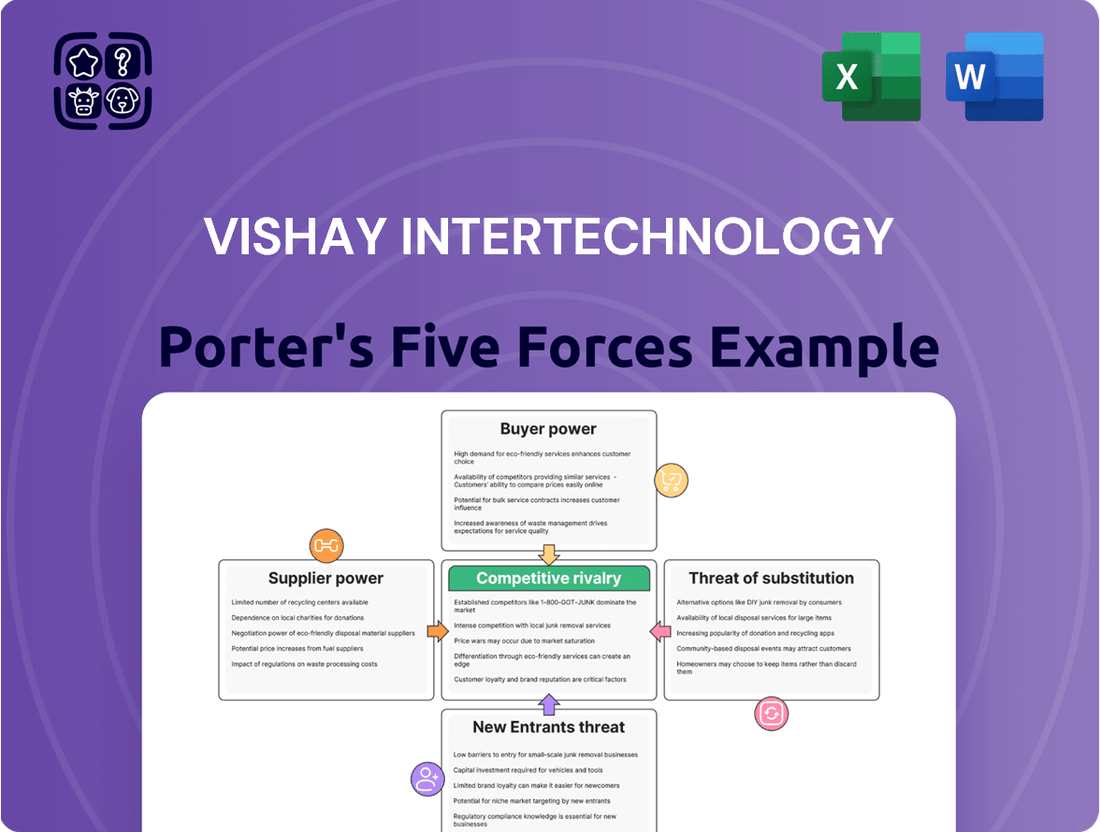
Vishay Intertechnology operates in a dynamic semiconductor market, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing players, the bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of substitute products is crucial for strategic positioning. The influence of suppliers and the potential for new entrants also shape Vishay's landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Vishay Intertechnology’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Vishay Intertechnology's reliance on concentrated raw material suppliers, such as those for silicon wafers, rare earth metals, and specialized chemicals, presents a significant bargaining power challenge. When a few key suppliers dominate the market for these essential inputs, they can dictate terms, potentially leading to increased costs for Vishay's discrete semiconductors and passive electronic components. For instance, the global shortage of semiconductor-grade silicon, exacerbated by increased demand in 2024, has demonstrated the leverage these concentrated suppliers hold.
Vishay Intertechnology relies heavily on suppliers of highly specialized manufacturing equipment and proprietary technologies for its advanced discrete semiconductors and passive components. These suppliers often operate in niche markets with few direct competitors, granting them significant leverage. Vishay's operational efficiency and capacity for innovation are directly tied to the availability and cost of these critical inputs, highlighting a key supplier bargaining power dynamic.
Vishay Intertechnology faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to high switching costs. For instance, the expense of retooling production lines, requalifying specialized raw materials, and retraining staff can be substantial when changing suppliers for critical components.
These elevated switching costs inherently diminish Vishay's negotiation leverage, strengthening the position of its current suppliers. This makes it challenging for Vishay to secure more favorable pricing or contract terms from these essential partners.
While Vishay's vertical integration strategy aids in managing certain internal production processes, the reliance on external, specialized inputs remains a key area where supplier power can be exerted. For example, sourcing advanced semiconductor materials often involves limited supplier options.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
When suppliers offer highly differentiated or proprietary materials and components, their bargaining power increases significantly. For Vishay Intertechnology, this is particularly relevant for specialized inputs critical to its high-performance product lines. These could include advanced semiconductor materials for emerging sectors like e-mobility or components vital for smart grid infrastructure, areas Vishay is actively targeting with its Vishay 3.0 strategy.
If these unique inputs are essential for Vishay to maintain its competitive edge and execute strategic initiatives, then the suppliers of these specialized products gain considerable leverage. This situation arises when Vishay has limited or no viable alternatives for these crucial components. For instance, a unique silicon carbide wafer technology or a proprietary passive component might be indispensable for a new product Vishay is developing to capture market share in rapidly growing segments. The reliance on such specialized suppliers can therefore exert upward pressure on costs and potentially impact supply chain stability.
- Supplier's Product Differentiation: Suppliers offering unique, proprietary components for Vishay's advanced product lines, such as those for e-mobility or smart grids, hold significant power.
- Strategic Importance: When these differentiated inputs are crucial for Vishay to maintain its competitive edge and support strategic initiatives like Vishay 3.0, supplier leverage is amplified.
- Limited Alternatives: The lack of readily available substitutes for these specialized components further strengthens the bargaining position of these suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a significant concern for Vishay Intertechnology. If a supplier of a critical component, such as specialized silicon wafers or advanced packaging materials, were to start manufacturing discrete semiconductors or passive components themselves, they would become a direct competitor. This would dramatically shift the power dynamic, allowing the supplier to dictate terms and potentially disrupt Vishay's operations.
Consider the semiconductor industry's capital-intensive nature; forward integration requires substantial investment in manufacturing facilities and R&D. For example, setting up a fabrication plant can cost billions of dollars. While no major supplier has publicly announced plans to integrate forward into Vishay's core discrete semiconductor or passive component markets, the potential remains, especially for those supplying highly specialized inputs.
- Potential for Competition: Suppliers could leverage their existing expertise and customer relationships to enter Vishay's market.
- Supply Chain Disruption: A supplier integrating forward could prioritize their own production, potentially limiting Vishay's access to critical materials.
- Increased Bargaining Power: If a supplier becomes a competitor, their ability to negotiate prices and terms with Vishay would increase substantially.
- Industry Dynamics: The highly technical and competitive nature of the semiconductor market means that strategic shifts, including forward integration, are always a theoretical possibility.
Vishay Intertechnology faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly those providing highly specialized raw materials and manufacturing equipment. The limited number of suppliers for critical inputs like silicon wafers and advanced chemicals, coupled with high switching costs for Vishay, amplifies supplier leverage. For example, the ongoing demand for advanced semiconductor materials in 2024, driven by sectors like automotive and industrial, has tightened supply chains and strengthened supplier pricing power.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Vishay | Example for Vishay |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base | Increased pricing power for suppliers | Few suppliers for high-purity silicon wafers |
| High Switching Costs | Reduced Vishay negotiation leverage | Retooling production lines for new materials |
| Supplier Differentiation | Stronger supplier position for unique inputs | Proprietary materials for e-mobility components |
| Potential for Forward Integration | Threat of direct competition | Supplier entering discrete semiconductor manufacturing |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Vishay Intertechnology's market, examining buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry to inform strategic positioning.
Vishay's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick, informed decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Vishay's broad OEM customer base, spanning automotive, industrial, computing, telecommunications, and consumer electronics, presents a nuanced picture regarding customer bargaining power. While this diversity helps mitigate risk, the sheer size and purchasing volume of major players in these sectors mean they can indeed exert significant pressure on pricing and terms. For instance, a single large automotive OEM could represent a substantial portion of Vishay's revenue, giving them considerable leverage.
For standardized passive components and discrete semiconductors, price is often the primary driver for customers. This leads to a highly competitive pricing environment for Vishay. Large buyers in sectors like consumer electronics can leverage their volume to negotiate significant price reductions.
This pressure forces Vishay to accept thinner profit margins to win or keep crucial contracts. In 2024, Vishay's gross profit margin saw a decline, reflecting this intense price sensitivity among its customer base and the resulting margin compression.
Customer switching costs for Vishay Intertechnology's components can significantly influence their bargaining power. For highly integrated or customized semiconductor solutions, the financial and operational burden of requalifying a new supplier, including engineering changes and testing, can be substantial. This complexity inherently limits a customer's ability to switch easily, thereby diminishing their bargaining leverage.
Conversely, for more commoditized or standard electronic components, the barriers to switching are considerably lower. In these segments, customers can readily compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, including competitors, and make a switch with minimal disruption. This price sensitivity for standard parts allows customers to exert greater pressure on Vishay for favorable terms.
Vishay's strategy to mitigate this by offering a broad product portfolio and a 'one-stop shop' approach is designed to foster customer loyalty and increase stickiness. By consolidating a significant portion of a customer's component needs, Vishay aims to raise the overall switching cost, even for individual standard parts, by making it less convenient to source those items elsewhere.
For instance, a customer relying on Vishay for a complex system-on-chip (SoC) might face requalification costs in the tens of thousands of dollars, making a switch unlikely. In contrast, a customer buying simple resistors might only need to compare unit prices, with switching costs near zero. This dynamic highlights the varied impact of switching costs across Vishay's diverse product offerings.
Customer Knowledge and Information Asymmetry
Large Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers wield considerable power due to their extensive market intelligence. They have a firm grasp on component pricing, readily identify alternative suppliers, and stay abreast of evolving technological trends. This deep well of information significantly erodes information asymmetry, equipping them to negotiate from a position of strength with Vishay. For instance, in 2024, major electronics manufacturers often leverage long-term supply agreements and bulk purchasing power to secure favorable pricing, a trend that continues to influence the semiconductor industry.
These sophisticated buyers thoroughly understand the intricacies of the supply chain. This allows them to effectively benchmark prices against industry standards and demand highly competitive terms from Vishay. Their ability to compare offerings and understand cost structures means they can push for lower prices and better service levels.
- Market Intelligence: OEMs possess detailed knowledge of component pricing, competitor offerings, and industry technological roadmaps.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Access to this information empowers customers to negotiate more effectively with suppliers like Vishay.
- Benchmarking Capabilities: Customers can compare Vishay's pricing and terms against a wide range of alternative suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: Deep supply chain understanding enables customers to demand competitive pricing and favorable contract terms.
Potential for Backward Integration by Customers
The potential for customers to engage in backward integration can significantly influence their bargaining power with Vishay Intertechnology. This is particularly relevant for larger customers possessing substantial in-house manufacturing expertise. While the highly specialized nature of many semiconductor components makes full backward integration challenging, the mere possibility can shift negotiation dynamics.
Consider a scenario where a major electronics manufacturer, a key Vishay customer, has the capacity to produce simpler, high-volume passive components internally. The credible threat of such a move empowers that customer to demand more favorable pricing or terms from Vishay. This is because Vishay would want to retain such business, especially if the customer’s internal production costs are competitive.
- Customer Capability: Large customers with advanced manufacturing facilities may possess the technical and operational capabilities to produce certain Vishay components in-house.
- Component Specialization: The threat is more pronounced for less complex, high-volume components where manufacturing know-how is more readily transferable.
- Negotiation Leverage: This potential for backward integration provides customers with a stronger position to negotiate pricing, delivery schedules, and other contractual terms.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, continued global supply chain reconfigurations could incentivize some large buyers to explore greater vertical integration for critical, albeit less specialized, electronic parts.
Vishay's diverse customer base offers a mixed bag regarding bargaining power. While large OEMs in automotive and consumer electronics can leverage their volume for price concessions, particularly on commoditized components, Vishay's integrated solutions and broad portfolio can raise switching costs for more complex needs. The company's 2024 financial performance, showing margin pressures, reflects the ongoing negotiation challenges with price-sensitive buyers.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Vishay | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Automotive OEMs | High Volume Purchasing | Significant price pressure on standard components | Continued demand for cost reductions impacting gross margins |
| Consumer Electronics Brands | Price Sensitivity & Switching | Leverage volume for discounts on commoditized parts | Increased competition in the mobile and computing sectors |
| Industrial & Telecom Customers | Customized Solutions & Integration | Higher switching costs due to requalification | Steady demand for specialized components, supporting margin stability in these segments |
| Overall Customer Base | Market Intelligence | Ability to benchmark pricing and identify alternatives | OEMs actively seeking supply chain diversification |
What You See Is What You Get
Vishay Intertechnology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version of the Vishay Intertechnology Porter's Five Forces Analysis—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive report details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the semiconductor industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making and identifying competitive advantages. The analysis presented here is ready for immediate application to your business planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Vishay operates in a market brimming with competition. The discrete semiconductor and passive electronic components sector is mature, hosting a vast array of global and regional manufacturers. This intense environment, populated by giants such as TDK, Murata, KEMET, NXP, Infineon, and STMicroelectronics, means companies constantly battle for market share across numerous applications and regions.
Vishay Intertechnology faces significant competitive rivalry, especially as its products, particularly passive components, can become commoditized. This trend naturally escalates price competition, a scenario intensified during economic downturns or periods of excess inventory. For instance, in Q1 2025, Vishay experienced compressed profit margins, a direct reflection of this industry-wide pressure.
The semiconductor and component manufacturing sector, where Vishay Intertechnology operates, is inherently capital-intensive. Significant investments in research and development, state-of-the-art fabrication plants, and sophisticated equipment are non-negotiable. These substantial upfront expenditures translate into high fixed costs for companies in this industry.
To offset these high fixed costs and achieve profitability, companies like Vishay must maintain high capacity utilization rates. This necessity intensifies competition, as firms are driven to secure orders to keep their production lines running efficiently and spread those fixed costs over a larger output. For instance, Vishay's ongoing Vishay 3.0 strategy includes substantial capital investments aimed at enhancing its manufacturing capabilities and efficiency.
Slow Industry Growth in Mature Segments
The discrete semiconductor and passive component market, particularly for established products, often experiences subdued growth. This maturity means that gains in market share are frequently achieved at the expense of competitors, rather than through an expanding overall market. For example, in 2023, the global semiconductor market saw a contraction, highlighting the competitive pressures in mature areas.
This slow industry growth intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies must fight harder for existing demand, leading to aggressive pricing strategies and increased marketing efforts. Vishay Intertechnology, operating in these mature segments, faces this dynamic directly.
- Mature Market Dynamics: Many segments Vishay serves, like general-purpose transistors and capacitors, exhibit single-digit or even flat growth rates.
- Zero-Sum Competition: In 2024, the battle for market share in these areas is fierce, with companies often competing on price and product availability.
- Impact on Profitability: Slow growth and intense competition can put pressure on profit margins, making operational efficiency crucial for Vishay.
Strategic Acquisitions and Consolidation
The semiconductor industry, including components like those Vishay Intertechnology produces, has experienced significant consolidation. This trend, often fueled by the pursuit of economies of scale and technological advancement, means fewer, larger players are emerging. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor M&A landscape saw notable activity, though deal values fluctuated with market conditions. This consolidation intensifies rivalry as these larger entities wield greater market power and financial resources, posing a challenge to companies like Vishay.
Vishay itself has actively participated in this consolidation, using strategic acquisitions to bolster its product portfolio and market presence. These moves are designed to enhance Vishay's competitive standing by integrating new technologies or expanding its geographical reach. The impact of these acquisitions is a more concentrated competitive landscape, where established players leverage their increased scale to compete aggressively.
Key aspects of this consolidation include:
- Drive for Scale: Mergers aim to reduce per-unit costs through increased production volume.
- Technology Acquisition: Companies buy others to gain access to critical patents or innovative designs.
- Market Expansion: Acquisitions can open doors to new customer segments or geographic regions.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Larger, consolidated firms often have more leverage with suppliers and customers.
Vishay Intertechnology operates in a highly competitive environment characterized by numerous global and regional players in the discrete semiconductor and passive electronic components market. The mature nature of many product segments, such as general-purpose transistors and capacitors, means growth is often achieved through taking market share from rivals, leading to intense price competition, especially during economic slowdowns. For instance, in the first quarter of 2025, Vishay's profit margins were compressed, reflecting industry-wide pressures from this intense rivalry.
The capital-intensive nature of semiconductor manufacturing, with substantial R&D and fabrication costs, necessitates high capacity utilization. This drives companies to aggressively pursue orders, intensifying competition. The industry has also seen significant consolidation, with larger entities gaining scale and market power, further challenging companies like Vishay. In 2024, the competition for market share in mature segments remained particularly fierce, emphasizing the need for operational efficiency.
| Key Competitors | Primary Product Focus | Market Presence |
|---|---|---|
| TDK Corporation | Passive components (capacitors, inductors), Sensors | Global |
| Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Ceramic capacitors, Filters, Wireless modules | Global |
| KEMET Corporation (now Yageo) | Capacitors (tantalum, ceramic), Inductors | Global |
| Infineon Technologies AG | Power semiconductors, Automotive chips | Global |
| STMicroelectronics N.V. | Microcontrollers, Sensors, Power devices | Global |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The integration of discrete components into sophisticated integrated circuits (ICs) presents a notable threat. As IC technology progresses, functions previously handled by individual diodes, resistors, and capacitors can now be embedded within a single chip. This advancement means that in certain applications, the demand for Vishay's standalone components might decrease as customers opt for these all-in-one solutions.
Innovations in material science and manufacturing processes present a significant threat of substitution for Vishay Intertechnology. New materials, such as advanced ceramics or advancements in nanotechnology, could offer improved performance characteristics or lower production costs for electronic components. For instance, the passive components market in 2024 continues to see significant investment in exploring novel materials that could potentially replace or outperform traditional silicon-based solutions. These emerging technologies might offer superior thermal management or higher energy density, directly challenging Vishay's established product lines by providing functionally equivalent or superior alternatives at a competitive price point.
The threat of substitutes for Vishay Intertechnology's products, particularly in the realm of software-defined functionality, is a growing concern. As electronic systems evolve, tasks once reliant on discrete hardware components are increasingly being handled by software. This shift can impact demand for certain physical components, especially at higher levels of system integration.
For instance, while fundamental components like resistors remain largely insulated, the rise of software-defined radios (SDRs) can reduce the need for specialized analog front-end hardware in communication systems. This trend means that if software can replicate or outperform the function of a specific hardware component, the demand for that component can diminish.
Miniaturization and Multi-functional Devices
The ongoing trend of miniaturization and the creation of multi-functional devices directly impacts the demand for discrete components. As electronics become more compact and integrated, fewer individual parts are needed for a single product. This shift presents a substitution threat as devices consolidate functionality, potentially reducing the overall volume of components like resistors, capacitors, and diodes that Vishay Intertechnology traditionally supplies.
For instance, the smartphone market, a key consumer of electronic components, continues to push for smaller and more integrated designs. A single advanced System-on-Chip (SoC) can now perform functions previously handled by multiple discrete components, directly reducing the need for Vishay's offerings in those areas. Vishay's own product development often focuses on achieving smaller footprints and higher integration, reflecting this market pressure.
- Miniaturization Threat: The drive for smaller electronic devices inherently reduces the total number of discrete components required per unit.
- Multi-functionality Impact: Integrated circuits that combine multiple functions decrease reliance on individual components, substituting them.
- Vishay's Response: Vishay's focus on smaller footprint products acknowledges and attempts to address this substitution trend.
- Market Example: The smartphone industry exemplifies how consolidation of functionality reduces the demand for discrete component suppliers.
Alternative Energy Storage and Power Management Technologies
Emerging alternative energy storage and power management technologies pose a significant threat of substitution for Vishay Intertechnology's traditional passive components like capacitors and inductors. For instance, advancements in battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries, offer higher energy density and faster charging times, potentially displacing components used in current battery management systems. Supercapacitors, while sometimes considered within the passive component realm, represent a distinct and growing alternative for rapid energy discharge and storage, impacting applications where traditional capacitors might have been the sole solution. In 2024, the global market for energy storage systems, encompassing batteries and supercapacitors, was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating a substantial and growing alternative market.
These technological shifts can directly influence demand for Vishay's core products. If alternative solutions provide superior efficiency, longer lifespan, or a more integrated approach to power management, they could erode the market share of discrete passive components in various sectors, including automotive and consumer electronics. For example, advancements in integrated power modules, which combine multiple functions, could reduce the need for individual capacitors and inductors. The automotive sector, a key market for Vishay, is rapidly adopting electric vehicle (EV) technology, where advanced battery and power management systems are paramount; the global EV market saw sales of over 14 million units in 2023.
The threat is amplified when these alternatives offer a compelling cost-benefit analysis. For applications where the stringent performance requirements of traditional passive components can be met by newer technologies at a lower overall system cost, substitution becomes more likely. This could particularly impact high-volume markets where cost sensitivity is a primary driver for design choices. The increasing integration and miniaturization trends in electronics further incentivize the adoption of consolidated power solutions over discrete components.
- Alternative Energy Storage: Solid-state batteries and next-generation lithium-ion chemistries offer higher energy density and faster charging compared to traditional solutions.
- Supercapacitors: These are increasingly used for rapid energy delivery and storage, posing an alternative to certain capacitor applications.
- Integrated Power Modules: These combine multiple power management functions, potentially reducing the need for discrete passive components.
- Market Growth: The global energy storage market was expected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant scale of alternative technologies.
- Automotive Sector Impact: With over 14 million EVs sold globally in 2023, the shift to EV powertrains drives demand for advanced, integrated power solutions.
The increasing sophistication of integrated circuits (ICs) presents a direct threat of substitution, as they can perform functions previously requiring multiple discrete components. This trend is evident as more complex operations are consolidated onto single chips, potentially reducing the demand for individual resistors, capacitors, and diodes.
New materials science advancements, such as novel ceramics or nanotechnology, could yield components with superior performance or lower costs, directly challenging Vishay's existing product lines. The passive components market in 2024 continues to see investment in these alternative materials, aiming for better thermal management or energy density.
Software-defined functionalities also pose a threat, where tasks once handled by hardware are increasingly managed by code, diminishing the need for specific physical components. For example, software-defined radios can lessen the requirement for specialized analog front-end hardware in communication systems.
| Threat Type | Description | Market Trend/Example |
| Integrated Circuits (ICs) | Consolidation of functions onto single chips. | System-on-Chip (SoC) in smartphones reducing discrete component count. |
| Advanced Materials | New materials offering improved performance or cost. | Research into advanced ceramics and nanotechnology for passive components (2024 focus). |
| Software-Defined Functionality | Software replacing hardware functions. | Software-Defined Radios (SDRs) reducing need for analog front-end hardware. |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor and electronic components industry, where Vishay Intertechnology operates, requires massive upfront capital for fabrication plants and cutting-edge equipment. These substantial investments, coupled with continuous research and development, create a formidable barrier to entry. Potential new competitors often find these costs prohibitive, effectively limiting the pool of viable entrants who can challenge established companies like Vishay.
For instance, Vishay’s commitment to innovation is evident in its substantial R&D spending, which was around $155 million in 2024. Furthermore, the company has outlined plans for significant capital investments totaling $2.6 billion, underscoring the high financial threshold required to maintain competitiveness in this sector.
Established players like Vishay Intertechnology enjoy substantial economies of scale across manufacturing, purchasing, and logistics. For instance, Vishay's extensive global manufacturing presence, with facilities in numerous countries, allows for optimized production runs and bulk material discounts that new entrants simply cannot match. This scale directly translates into lower per-unit costs, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
Furthermore, the experience curve effect plays a crucial role. Vishay has decades of accumulated knowledge in optimizing production processes, improving yields, and refining product design. This deep institutional learning creates a steep learning curve for any new entrant, requiring significant investment in time and resources to reach comparable levels of efficiency and quality, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors.
Vishay Intertechnology and its rivals hold substantial collections of patents and proprietary technologies covering component design, manufacturing methods, and material science. This intellectual property serves as a significant hurdle, deterring new companies from creating competitive offerings without risking patent infringement or undertaking extensive research and development. For instance, Vishay's commitment to innovation is evident in its continuous investment in R&D, which is crucial for maintaining its technological edge.
Established Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New entrants face a formidable barrier due to Vishay Intertechnology's deeply entrenched global distribution channels and strong, long-standing relationships with key Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). Developing access to these established networks and cultivating trust with major players in sectors like automotive and industrial requires substantial time and investment, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
Consider these points regarding established distribution channels and customer relationships:
- Access to Distribution: New entrants would need to invest heavily in building their own global distribution infrastructure or secure partnerships, a process Vishay has perfected over decades.
- Customer Loyalty: Convincing major OEMs, who often rely on Vishay for their proven track record and comprehensive product offerings, to switch suppliers presents a significant challenge.
- 'One-Stop Shop' Advantage: Vishay's ability to provide a wide range of components, from discrete semiconductors to passive electronic components, positions it as a convenient and reliable 'one-stop shop' for many customers, a difficult advantage for new entrants to replicate.
For instance, in the automotive sector, where component reliability is paramount, OEMs often have rigorous qualification processes that can take years to navigate, favoring established suppliers like Vishay.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The threat of new entrants for Vishay Intertechnology, particularly in sectors like automotive and medical electronics, is significantly dampened by substantial regulatory hurdles. Companies aiming to enter these markets must navigate a complex web of quality standards and certifications, such as the AEC-Q200 qualification essential for automotive components.
Meeting these stringent requirements demands considerable investment in time and resources, creating a high barrier to entry. For instance, the automotive industry's demand for reliability means new suppliers must prove their components can withstand extreme conditions and prolonged use, a process that can take years and significant capital outlay.
- Stringent Quality Standards: Automotive and medical sectors require components to meet rigorous quality and reliability benchmarks.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining necessary certifications like AEC-Q200 involves substantial financial investment and time.
- Navigating Complex Regulations: New entrants face the challenge of understanding and complying with diverse international and industry-specific regulations.
- Long Lead Times for Approval: The approval process for new components in regulated industries can extend for several years, delaying market entry.
The threat of new entrants for Vishay Intertechnology is generally low due to the industry's high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. Significant upfront investment in fabrication facilities and R&D, coupled with years of building distribution networks and OEM relationships, creates substantial barriers. Furthermore, intellectual property and stringent regulatory compliance in key sectors like automotive add further deterrents.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Intensity | High cost of fab plants and equipment. | Prohibitive for most newcomers. |
| Economies of Scale | Vishay's large-scale operations reduce per-unit costs. | New entrants struggle to compete on price. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents and proprietary technologies. | Requires significant R&D or risks infringement. |
| Distribution & Relationships | Established global channels and OEM trust. | Difficult and time-consuming to replicate. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Certifications like AEC-Q200 in automotive. | Demands significant time, investment, and expertise. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Vishay Intertechnology is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms like Gartner and IHS Markit. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics, supplier and buyer power, and potential threats.
