Sysco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sysco Bundle
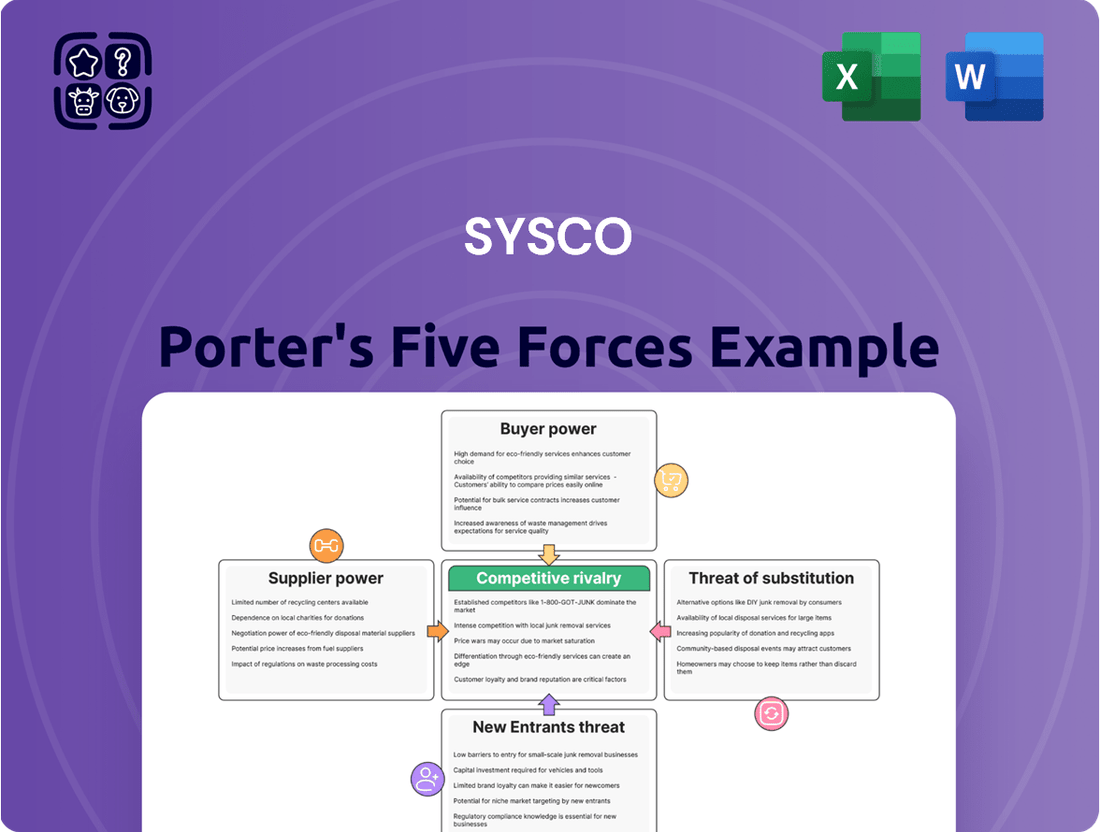
Sysco operates in a dynamic food service distribution landscape, facing significant pressure from powerful buyers like large restaurant chains and institutional clients. Understanding the nuances of buyer bargaining power is crucial for any stakeholder in this sector.
The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by Sysco's established infrastructure and economies of scale. However, agile, niche players can still disrupt specific market segments.
The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, including large national distributors and regional players, dictates pricing strategies and service levels. This competition significantly shapes Sysco's market position.
Suppliers, particularly those providing specialized or branded food products, can exert considerable influence, impacting Sysco's cost of goods sold and product availability.
The threat of substitutes, such as direct-to-consumer meal kits or in-house food preparation, presents an ongoing challenge to Sysco's traditional business model.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Sysco’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Sysco's immense purchasing volume, reaching $78.8 billion in fiscal year 2024 sales, provides substantial leverage over its suppliers. This scale allows Sysco to negotiate highly favorable terms and pricing, even when dealing with large food manufacturers.
The sheer quantity of products Sysco procures makes it an indispensable distribution channel for numerous food producers. This dependency strengthens Sysco's bargaining position, as suppliers recognize the significant revenue generated by their partnership.
Sysco strategically cultivates relationships with a vast and varied supplier network, sourcing over 90% of its products domestically. This extensive reach significantly dampens the bargaining power of any single supplier by reducing dependence and fostering competition among providers.
The company's global perspective on sourcing, even for items not produced locally, ensures stable pricing and availability. This broadens Sysco's negotiation leverage, making it less susceptible to price hikes from individual suppliers.
This diversified sourcing strategy is crucial in managing costs and ensuring a consistent supply chain, which is vital in the food service industry where reliability is paramount. For instance, in 2024, Sysco continued to emphasize robust supplier relationships, a key component of its operational resilience.
For many smaller and mid-sized food producers, Sysco's extensive distribution network and broad customer reach are critical for market access. This makes Sysco an indispensable partner, providing a gateway to hundreds of thousands of customer locations globally.
Sysco's ability to guarantee consistent demand for its suppliers’ products significantly enhances its bargaining power. This reliance means that a disruption in the relationship with Sysco could lead to a substantial drop in revenue for these suppliers.
In 2023, Sysco reported annual revenue of $72.8 billion, underscoring its immense scale within the food distribution industry. This massive revenue base highlights the significant volume of business suppliers stand to lose if they cannot meet Sysco's terms.
Product Differentiation of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers can be amplified when they offer highly differentiated or specialized food products, especially when Sysco has limited alternative sources. For instance, premium organic produce or unique imported specialty items might originate from a smaller pool of suppliers, granting them greater leverage. Sysco's vast purchasing volume and diverse product catalog, however, often allow it to negotiate favorable terms, mitigating some of this supplier power.
Sysco's strategic sourcing and extensive network of suppliers across various categories generally dilute individual supplier power. Nonetheless, for certain niche or high-demand ingredients, suppliers with unique capabilities or exclusive access can exert more influence. For example, a supplier of a specific, rare truffle or an artisanal cheese might command higher prices if Sysco's customer demand for that particular item is strong and alternatives are scarce.
- Sysco's Scale Advantage: With revenues often exceeding $70 billion annually, Sysco's sheer purchasing power can offset the differentiation of many suppliers by creating competition among them.
- Private Label Counterbalance: Sysco's development of its own private label brands, which account for a significant portion of its sales, allows it to gain more control over product specifications and sourcing, reducing reliance on branded, differentiated supplier products.
- Supplier Concentration: While Sysco works with thousands of suppliers, the market for certain highly specialized food products might be more concentrated, potentially increasing the bargaining power of those select few.
- Logistical Complexity: The complexity of Sysco's distribution network can also influence supplier relationships, as suppliers who can reliably meet Sysco's stringent delivery and quality requirements may have an advantage.
Integration Threats from Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, such as a food manufacturer establishing its own distribution network, is generally low for Sysco. This is primarily due to the substantial capital outlay and intricate logistical operations inherent in foodservice distribution. For instance, building and maintaining a network comparable to Sysco's, which operates 340 distribution facilities, demands immense financial resources and specialized expertise.
Sysco's extensive and highly automated supply chain infrastructure presents a formidable barrier to entry for any supplier considering forward integration. This established efficiency and scale make it economically unfeasible for most suppliers to replicate Sysco's distribution capabilities. In 2023, Sysco reported over $72 billion in revenue, underscoring the sheer scale of its operations and the difficulty suppliers would face in competing directly.
- High Capital Investment: Suppliers would need to invest heavily in trucks, warehouses, and technology to match Sysco's reach.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing a nationwide distribution network requires sophisticated planning and execution, a core competency for Sysco.
- Economies of Scale: Sysco's size allows for cost efficiencies that smaller, newly integrated operations would struggle to achieve.
- Established Customer Relationships: Sysco has long-standing relationships with a vast customer base that would be difficult for new entrants to displace.
Sysco's immense purchasing volume, often exceeding $70 billion in annual sales, significantly limits supplier bargaining power by fostering competition among a broad network. While suppliers of differentiated or niche products may hold some leverage, Sysco's scale and private label strategy often counterbalance this. The threat of supplier forward integration is minimal due to the substantial capital and logistical expertise required to rival Sysco's distribution capabilities.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Sysco's Position (FY2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Volume | Lowers supplier power | $78.8 billion in sales, enabling favorable terms |
| Supplier Diversity | Lowers supplier power | Sources over 90% domestically from a vast network |
| Private Labels | Lowers supplier power | Reduces reliance on branded, differentiated products |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low | High capital and logistical barriers to entry |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Sysco's position in the foodservice distribution industry.
Unlock strategic clarity by visualizing competitive pressures with a dynamic spider chart, transforming complex analysis into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Sysco's customer base is broad, encompassing everything from small diners to large hospitals. However, the real leverage lies with its major chain accounts. These large customers, by virtue of the sheer volume of products they purchase, hold considerable sway. For instance, a national restaurant chain can negotiate for significant price reductions or specialized delivery schedules because their business represents a substantial portion of Sysco's sales.
This concentration of purchasing power means these major clients can effectively dictate terms, pushing Sysco to offer better pricing and service. Sysco's SYGMA division, specifically designed to cater to these large chain operations, is a clear indicator of this customer dynamic. In 2023, Sysco reported that its top 10 customers accounted for approximately 17% of its total sales, highlighting the significant impact these large entities have on the company's performance.
Customer switching costs for Sysco are generally low. Many restaurants and foodservice businesses can easily switch to competitors like US Foods or Performance Food Group, as these distributors offer comparable product lines and service offerings.
This ease of switching means customers can readily compare pricing and service quality, creating significant pressure on Sysco to maintain competitive rates and deliver excellent customer experiences to retain their business.
For instance, in 2023, the foodservice distribution market remained highly competitive, with Sysco holding a substantial market share but facing consistent challenges from its major rivals, underscoring the importance of customer retention strategies.
The low barrier to switching compels Sysco to focus on cultivating robust customer loyalty through superior service and value, rather than relying on high switching costs to lock in clients.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Sysco. Independent restaurants, a key customer segment, often struggle with tight profit margins, making them acutely aware of every cost. This means they are constantly looking for the best deals and are quick to switch suppliers if prices rise.
Economic headwinds, like those experienced in early fiscal year 2025 with lingering inflation and consumer spending caution, exacerbate this. When consumers dine out less, restaurants see reduced revenue, amplifying their need to control food costs. This directly translates to increased pressure on Sysco to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate the overall value of its products and services.
For example, during periods of economic slowdown, the demand for premium products might dip as customers opt for more budget-friendly alternatives. Sysco must therefore maintain a delicate balance, offering a range of price points to cater to diverse customer needs while still ensuring profitability.
Information Availability to Customers
The digital transformation sweeping the food distribution industry significantly boosts information availability for customers. This means buyers can readily compare pricing and product specifications from various suppliers, directly impacting their negotiation leverage.
With easy access to online platforms and industry data, customers are better equipped to identify alternative sourcing options. For instance, by mid-2024, online marketplaces and procurement platforms have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for rapid supplier discovery and price benchmarking.
Sysco's own digital initiatives, while designed to improve customer experience and operational efficiency through tools like their online ordering portal, also contribute to this heightened transparency. This dual effect means customers are not only more informed but also more empowered to drive favorable terms.
- Increased Price Transparency: Customers can easily compare prices across multiple distributors, putting pressure on suppliers to remain competitive.
- Enhanced Product Information: Detailed product specifications and reviews are readily available, allowing customers to make informed choices and demand specific quality.
- Access to Alternatives: Digital platforms facilitate the discovery of new suppliers, reducing customer reliance on any single distributor.
- Negotiation Power: Armed with comprehensive data, customers are in a stronger position to negotiate pricing, terms, and service levels.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
While large restaurant chains, such as McDonald's or Starbucks, might explore direct purchasing from food manufacturers to gain cost advantages, the sheer scale of logistics and distribution needed to match Sysco's capabilities makes full backward integration economically unfeasible for most.
Sysco's established network, boasting over 330 distribution facilities as of its 2023 fiscal year, along with sophisticated supply chain management and a fleet of thousands of delivery vehicles, creates a formidable barrier. Replicating this complex infrastructure would demand enormous capital investment and operational expertise, which most individual or even large customer groups would find prohibitively expensive.
- High Capital Investment: Building and maintaining a nationwide distribution network comparable to Sysco's requires billions in capital expenditures.
- Operational Complexity: Managing a diverse product catalog, cold chain logistics, and timely deliveries across vast geographies is a significant operational challenge.
- Economies of Scale: Sysco leverages its immense purchasing power and distribution volume to achieve cost efficiencies that are difficult for individual customers to replicate.
- Focus on Core Competencies: For restaurant chains, focusing on food preparation and customer service is generally a more strategic use of resources than managing distribution.
The bargaining power of Sysco's customers is significant, particularly from large chain accounts that represent a substantial portion of sales. These major clients can leverage their volume to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, as demonstrated by Sysco's SYGMA division catering to such operations. While customer switching costs are generally low, with numerous competitors offering similar products, Sysco mitigates this by focusing on service and value to foster loyalty.
Customer price sensitivity is amplified by tight profit margins for many independent restaurants, driving them to seek the best deals. Economic downturns, like the inflationary pressures seen in early 2025, further intensify this, as restaurants focus on controlling food costs. Digital transformation has also empowered customers, increasing price transparency and access to alternative suppliers, thereby strengthening their negotiation position.
Despite the leverage customers hold, replicating Sysco's vast distribution network, comprising over 330 facilities as of fiscal year 2023 and thousands of delivery vehicles, is prohibitively expensive for most. This immense capital investment and operational complexity create a formidable barrier, limiting the feasibility of backward integration for the majority of Sysco's customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Sysco | Supporting Data (Fiscal Year 2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High bargaining power for major clients | Top 10 customers accounted for ~17% of total sales |
| Switching Costs | Low, increasing competitive pressure | Competitors offer comparable products and services |
| Price Sensitivity | High, especially for independent restaurants | Economic headwinds (e.g., inflation in early 2025) exacerbate cost control needs |
| Information Availability | Enhanced customer negotiation power | Sophistication of online marketplaces and procurement platforms (mid-2024) |
| Distribution Network Scale | Barrier to customer integration | Over 330 distribution facilities |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Sysco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for Sysco, offering a comprehensive look at the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted report you'll receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. It details each force, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the food service distribution industry. You're looking at the final, ready-to-use analysis, so you can confidently make your purchase knowing you'll get exactly what you preview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The foodservice distribution sector is a crowded arena, dominated by a few major players like Sysco, US Foods, and Performance Food Group. These giants, however, operate alongside a vast number of smaller, regional, and local distributors, ensuring a consistently competitive environment.
Sysco, a key player, commands a substantial market share in North America, estimated to be between 16.7% and 17%. This significant presence still doesn't shield it from intense rivalry with its large-scale competitors.
The collective market share held by the top three distributors highlights a landscape that is both consolidated and fiercely contested. This concentration means that strategic moves by any of these leading firms can have a considerable impact on the overall market dynamics.
The foodservice industry is poised for steady, albeit moderate, real growth. Projections for 2025 indicate a 1% to 2% real growth rate, which, when combined with an estimated 2%+ inflation, translates to a nominal growth of 3% to 4%. This environment, while positive, means companies must actively compete for customers, potentially increasing rivalry.
Sysco itself is targeting net sales growth between 4% and 6% for fiscal year 2025. This ambition suggests the company aims to capture market share beyond the industry's overall projected expansion, highlighting a proactive stance in a moderately growing but competitive landscape.
Competitive rivalry in the food service distribution industry extends well beyond mere price. Companies vie for market share through the breadth and quality of their product offerings, the efficiency and reliability of their delivery services, and the overall customer experience. Sysco, for instance, distinguishes itself with an expansive product catalog, encompassing everything from everyday staples to specialized gourmet items and kitchen equipment. This comprehensive range, coupled with a strong emphasis on supply chain optimization and dedicated customer support, forms a significant part of its competitive strategy.
However, this focus on differentiation through product and service is a common battleground. Sysco's rivals are also heavily invested in enhancing their own product selections and service capabilities. For example, US Foods has been actively expanding its portfolio of specialty and private-label products, aiming to offer unique value propositions to its customers. Performance Food Group (PFG) continues to invest in its distribution network and technology to improve delivery accuracy and speed. This shared commitment to innovation means that service and product differentiation are not static advantages but require ongoing investment and adaptation to maintain a competitive edge.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
The foodservice distribution sector is inherently capital-intensive, demanding significant outlays for warehouses, delivery fleets, and sophisticated technology. This substantial fixed cost base often fuels aggressive price competition. When demand falters, companies are compelled to push volume to cover their overheads, leading to price wars. For instance, in 2023, Sysco continued to invest in modernizing its distribution centers and fleet, with capital expenditures totaling $1.2 billion, reflecting the ongoing need to maintain and upgrade these essential assets.
These high fixed costs create a powerful incentive for established players like Sysco to maintain market share and achieve economies of scale. Companies with greater capacity utilization can spread their fixed costs over a larger revenue base, leading to lower per-unit costs and potentially higher profit margins. This dynamic intensifies rivalry as firms seek to maximize their operational efficiency and competitive pricing power.
- Industry Capital Intensity: Foodservice distribution requires substantial investment in physical infrastructure like warehouses and transportation fleets.
- Price Competition Driver: High fixed costs pressure companies to compete aggressively on price to ensure capacity utilization.
- Sysco's Investment Strategy: Sysco's ongoing investments in supply chain technology and automation are designed to enhance efficiency and manage these inherent costs.
- Impact on Rivalry: The need to cover fixed costs contributes directly to the intensity of competitive rivalry within the sector.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the foodservice distribution industry, including Sysco's sector, are notably high. These barriers are often tied to significant investments in specialized assets like extensive distribution centers and a large fleet of temperature-controlled trucks. For instance, in 2024, Sysco continued to operate a vast network of over 330 distribution facilities, a considerable capital commitment that makes exiting difficult.
These substantial fixed costs, combined with deeply entrenched customer relationships built over years, mean that companies are often compelled to stay and compete even when profitability is low. This persistence fuels ongoing competitive rivalry. Sysco's long-standing partnerships with restaurants and institutional clients, often secured through exclusive supply agreements and tailored service packages, represent a significant barrier for new entrants and a disincentive for existing players to leave.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized assets like distribution centers and refrigerated trucks represent substantial, often industry-specific, capital outlays, making divestment challenging.
- Customer Loyalty: Long-term relationships and customized service agreements create sticky customer bases, discouraging firms from exiting due to the loss of predictable revenue streams.
- Operational Scale: The economies of scale achieved through large operational footprints and supply chain efficiencies are difficult to replicate, further entrenching incumbents.
- Brand Reputation: Established brands in this sector carry significant weight, and exiting would mean abandoning years of reputation-building efforts.
Competitive rivalry is intense in the foodservice distribution sector, with Sysco, US Foods, and Performance Food Group holding significant market shares, estimated between 16.7% and 17% for Sysco alone in North America. This consolidation doesn't prevent fierce competition, as a multitude of smaller distributors also operate, ensuring a dynamic market. The industry's moderate projected real growth of 1% to 2% for 2025 means companies must actively fight for customers, often intensifying rivalry.
Companies compete not just on price but also on product breadth, service quality, and customer experience. Sysco offers an extensive product catalog and emphasizes supply chain optimization. Rivals like US Foods are expanding private-label offerings, and Performance Food Group invests in technology for better delivery. These ongoing efforts in differentiation mean that maintaining a competitive edge requires continuous investment and adaptation.
The capital-intensive nature of the industry, with substantial investments in warehouses and delivery fleets, drives aggressive price competition. High fixed costs, such as Sysco's $1.2 billion in capital expenditures in 2023 for fleet and distribution center modernization, pressure firms to maintain high capacity utilization. This often leads to price wars as companies strive to cover overheads and achieve economies of scale, further intensifying rivalry.
High exit barriers, including significant investments in specialized assets like over 330 distribution facilities operated by Sysco in 2024, and entrenched customer relationships, compel companies to remain and compete. These factors, coupled with the difficulty of replicating established economies of scale and brand reputation, contribute to persistent and fierce competition within the sector.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large restaurant chains and institutional buyers, particularly those with significant purchasing power, can opt to buy directly from food manufacturers. This bypasses intermediaries like Sysco, especially for high-volume, commoditized items. For instance, a major hotel group might negotiate directly with a national dairy producer for all its milk and cheese needs.
This direct sourcing acts as a significant substitute threat. It allows these large customers to potentially secure better pricing and more tailored product specifications, cutting out the distributor's margin. This can erode Sysco's market share within these powerful customer segments.
However, the practicalities of direct purchasing often present a barrier. The logistical complexities, including warehousing, transportation, and inventory management, can be prohibitive for smaller or less sophisticated operators. This is where distributors like Sysco continue to provide essential value.
In 2024, the trend of large foodservice operators exploring direct sourcing continued, driven by a desire for cost optimization. While specific data on the percentage of Sysco’s business directly threatened by this is proprietary, industry analysts observe that such initiatives are more prevalent among the top-tier customers who can absorb the operational overhead.
Cash-and-carry stores and wholesale clubs like Costco Business Center and Restaurant Depot present a significant threat. These alternatives allow customers, particularly smaller businesses or those with tight inventory control, to purchase food and supplies in bulk at often lower price points. This direct-to-consumer model bypasses traditional distribution, appealing to price-sensitive buyers.
Sysco is actively addressing this threat by developing its own cash-and-carry channel, known as 'Sysco To Go'. This strategic move aims to capture a segment of the market that prefers direct purchasing and immediate availability, mirroring the convenience offered by competitors. In 2023, Sysco reported a 7.4% increase in sales for its specialty businesses, which includes services that could align with this evolving customer preference.
The increasing popularity of local sourcing and specialty suppliers poses a significant threat of substitutes for Sysco. Independent restaurants and food service businesses are increasingly looking for unique ingredients directly from farmers' markets or through direct-to-farm purchasing models.
This shift allows these businesses to curate distinctive menus and potentially secure fresher, higher-quality products. For instance, the direct sales channel for U.S. farms reached an estimated $9.5 billion in 2022, a figure that continues to grow, indicating a substantial market for these alternative sourcing methods.
While Sysco offers a vast array of products, the appeal of hyper-local or niche specialty items sourced directly can bypass traditional distribution channels. This can directly impact Sysco's sales volumes for specific ingredients, especially for smaller, trend-conscious establishments.
In-house Food Preparation
A growing trend towards in-house food preparation by restaurants and foodservice establishments can act as a threat of substitutes, indirectly impacting Sysco. This shift means customers might opt for making more items from scratch rather than purchasing Sysco’s value-added or pre-prepared ingredients. For example, a restaurant deciding to make its own pasta or sauces instead of buying them from a distributor reduces demand for those specific product lines.
This move is often driven by a desire for cost control or greater ingredient transparency. In 2024, many operators faced rising food costs, leading some to re-evaluate their sourcing and preparation methods. A survey indicated that a significant percentage of independent restaurants were exploring ways to increase in-house production to manage margins better.
- Reduced demand for Sysco's value-added products
- Potential impact on sales volumes for specific ingredient categories
- Cost-saving motivations driving in-house preparation
- Desire for greater ingredient control by foodservice operators
Alternative Food Delivery Models
The threat of substitutes for Sysco is generally considered moderate. While alternatives to traditional foodservice exist, Sysco's business model primarily serves business-to-business clients, insulating it from some direct consumer-level substitutes.
The proliferation of meal kit services and direct-to-consumer food delivery platforms, while growing, primarily targets residential customers. These services could indirectly impact the away-from-home dining market, a sector Sysco serves. However, Sysco's core business is supplying restaurants, hotels, and healthcare facilities, making these consumer-focused alternatives a less potent direct threat.
- Meal Kit Services: Companies like HelloFresh and Blue Apron have seen significant growth, but their focus is home consumption, not foodservice operations.
- Ghost Kitchens: While ghost kitchens represent a shift in restaurant operations, they still require food supply, often from distributors like Sysco.
- Grocery Delivery: Increased grocery delivery adoption might reduce some restaurant visits, but it doesn't directly substitute the need for Sysco's products by its business clients.
- DIY Food Preparation: A return to more home cooking, potentially driven by economic factors, could marginally affect restaurant demand.
Large customers can bypass Sysco by sourcing directly from manufacturers, especially for high-volume, standardized goods, potentially securing better pricing. However, the logistical demands of direct purchasing often favor established distributors like Sysco, particularly for smaller or less experienced operators. In 2024, large foodservice operations continued exploring direct sourcing for cost savings, though the operational complexity remains a deterrent for many.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the massive foodservice distribution market, especially at a scale that could rival established players like Sysco, demands a colossal upfront investment. We're talking about significant capital needed for building and maintaining extensive warehousing facilities, sophisticated cold storage systems to preserve perishable goods, and a large, reliable fleet of trucks for efficient delivery. On top of that, cutting-edge logistics technology is essential for managing inventory, optimizing routes, and ensuring timely service.
This sheer financial hurdle acts as a powerful deterrent for most aspiring newcomers. Imagine the cost of acquiring or leasing vast warehouse spaces and equipping them with advanced temperature control systems. Then there's the expense of purchasing and maintaining a diverse fleet of refrigerated vehicles, all while investing in the software and hardware to run a complex, modern distribution network.
For context, Sysco itself reported capital expenditures of $1.5 billion in fiscal year 2023, a significant portion of which is directed towards enhancing its distribution infrastructure and technology. Furthermore, the company's ongoing efforts in distribution center automation, aiming for higher efficiency and lower operating costs, further elevate the entry barrier by requiring new entrants to match these advanced operational capabilities from day one.
Sysco, as a leading food service distributor, enjoys substantial economies of scale and scope. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger volume of business, leading to lower per-unit costs in purchasing, warehousing, and distribution. For instance, their massive purchasing power allows them to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, a significant advantage that new entrants would find incredibly difficult to replicate.
New companies entering the food service distribution market would face a steep uphill battle in matching Sysco's cost structure. Without achieving similar operational scale, it would be challenging to offer competitive pricing and simultaneously achieve profitability. This cost disadvantage acts as a strong barrier, deterring potential new players from entering the market.
Sysco's extensive network and high sales volume translate into superior route density, optimizing delivery efficiency and reducing transportation expenses. In 2023, Sysco reported revenue of $37.1 billion, a testament to its vast operational footprint and market penetration. This scale not only lowers their operating costs but also enhances their ability to serve a wide range of customers effectively, further solidifying their market position.
Sysco's extensive and well-established distribution network presents a significant barrier to new entrants. The company boasts 340 facilities globally, enabling it to reach roughly 730,000 customer locations efficiently.
Replicating this vast logistical infrastructure and the deep, long-standing relationships Sysco has cultivated with both suppliers and a diverse customer base of hundreds of thousands is an incredibly difficult undertaking for any new competitor.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The foodservice distribution industry faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous food safety regulations and traceability mandates. For instance, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) 204, implemented in 2023, imposes extensive record-keeping requirements for companies handling certain foods, demanding substantial investment in technology and processes for compliance. New companies entering the market must navigate these complex and evolving standards, which can be costly and time-consuming. This regulatory environment acts as a deterrent, particularly for smaller or less capitalized potential competitors.
Sysco, as a market leader, has established robust systems to meet and exceed these stringent requirements. Their investments in supply chain visibility and quality control, including advanced traceability solutions, position them favorably against potential new entrants who would need to make similar, significant capital outlays to achieve compliance. For example, Sysco’s continued focus on food safety programs and their ability to manage complex supply chains efficiently are critical differentiators.
- FSMA 204 Compliance: Requires enhanced record-keeping for food traceability, impacting new entrants’ operational setup costs.
- High Capital Investment: Meeting stringent food safety and quality standards necessitates significant upfront investment in infrastructure and technology.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating a web of federal, state, and local food safety laws adds a layer of difficulty and cost for new market participants.
- Sysco's Advantage: Existing investments in food safety and traceability systems provide a competitive edge, making it harder for new entrants to match their operational capabilities.
Brand Recognition and Reputation
Sysco's entrenched brand recognition acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. As a global leader in foodservice distribution with a long history, Sysco has cultivated a strong reputation and customer trust, which is difficult and expensive for newcomers to replicate. This established brand equity, built over decades, means new companies must invest heavily in marketing and outreach to even begin competing.
The challenge for potential entrants is not just about offering competitive pricing but also about overcoming Sysco's established name and the loyalty it commands. For instance, in 2023, Sysco reported net sales of $72.8 billion, underscoring its vast market presence and the scale of brand investment required to approach such figures. New players face the daunting task of convincing a wide array of customers, from small restaurants to large hotel chains, to switch from a trusted, well-known supplier.
- Brand Advantage: Sysco's established global leadership and reputation in foodservice distribution offer a substantial competitive advantage.
- Customer Trust: Building the necessary trust and recognition with a broad customer base requires significant time and marketing expenditure.
- Market Entry Hurdle: New entrants face considerable challenges in quickly establishing credibility and capturing market share against Sysco's brand strength.
The threat of new entrants for Sysco is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements and the established economies of scale. Building a distribution network comparable to Sysco's, with its extensive warehousing, refrigerated fleet, and advanced logistics technology, demands billions in upfront investment. For example, Sysco's 2023 capital expenditures were $1.5 billion, highlighting the scale of investment needed to maintain and grow such an operation, a figure that dwarfs what most new entrants could realistically muster.
Furthermore, the sheer complexity of navigating stringent food safety regulations, such as FSMA 204, adds substantial costs and operational hurdles for newcomers. Sysco, having already invested in robust traceability and quality control systems, possesses a significant advantage. This regulatory landscape, coupled with the need to match Sysco's operational efficiency and cost structure derived from its $72.8 billion in 2023 net sales, makes market entry exceptionally challenging.
Sysco's deeply entrenched brand recognition and extensive customer relationships, built over decades, present another formidable barrier. Potential entrants must overcome not only Sysco's scale and cost advantages but also its established reputation and the trust it commands across hundreds of thousands of customer locations served by its 340 global facilities.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Sysco's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Extremely High (Warehousing, Fleet, Tech) | Established infrastructure, ongoing investment (e.g., $1.5B CAPEX in FY23) |
| Economies of Scale | Difficult to Achieve; Higher per-unit costs | Significant cost advantages from massive purchasing power and operational volume |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly & Complex (e.g., FSMA 204 traceability) | Existing robust systems and expertise in food safety |
| Brand Recognition & Relationships | Requires significant time & marketing investment | Strong, established brand loyalty and deep customer ties |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Sysco Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of publicly available information, including Sysco's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial news outlets to capture competitive dynamics.
