Shriram Transport Finance Co. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Shriram Transport Finance Co. Bundle
Shriram Transport Finance Co. operates in a segment with moderate bargaining power from suppliers, primarily banks and financial institutions providing capital. The threat of new entrants is somewhat limited due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. However, the intense competition among existing players and the availability of substitute financing options present significant challenges.
The bargaining power of buyers, largely individual vehicle owners and small fleet operators, is moderate, influenced by the essential nature of their financing needs. The threat of substitutes is notable, with alternative lending channels and the option of outright cash purchases for some. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic positioning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting Shriram Transport Finance Co., complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Shriram Finance Limited, as a prominent non-banking financial company (NBFC), depends significantly on capital from banks, institutional investors, and public deposits. The power these capital providers wield is shaped by market liquidity, interest rate movements, and the perceived creditworthiness of NBFCs, particularly in light of evolving Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulations.
In 2024, Shriram Finance's reliance on these sources meant that favorable borrowing costs were crucial for its profitability. For instance, if interest rates climbed generally, their cost of funds would increase, impacting their lending margins.
Furthermore, the bargaining power of capital providers can be amplified if there's a perception of increased risk within the NBFC sector, perhaps due to tighter regulatory oversight or economic downturns. This could lead to demands for higher interest rates or stricter lending covenants.
Technology and digital solution providers hold significant bargaining power in the financial sector, especially for companies like Shriram Transport Finance Co. (Shriram Finance) that are increasingly reliant on advanced IT infrastructure and digital platforms. Their power stems from the uniqueness and sophistication of their software, the necessity of tailored solutions for Shriram Finance's specific operational needs, and the considerable expense and complexity involved in migrating to different vendors. For instance, Shriram Finance's investment in its Shriram Super App underscores the critical nature of these technology partnerships.
Skilled professionals in finance, credit risk, sales, and technology are crucial suppliers for Shriram Transport Finance. The availability and demand for these specialized skills in India's financial sector directly impact employee bargaining power regarding salaries and benefits.
In 2023, the Indian financial services sector saw a notable increase in demand for tech-savvy professionals, with salaries for roles like data scientists and cybersecurity experts rising significantly, potentially increasing employee leverage.
Shriram Transport Finance's ability to retain experienced staff is paramount for maintaining its operational efficiency and competitive edge in the market.
High attrition rates among specialized roles can lead to increased recruitment costs and a temporary dip in service quality, thus amplifying the bargaining power of remaining skilled employees.
Credit Rating Agencies
Credit rating agencies like CRISIL and ICRA hold significant sway over Shriram Transport Finance Co. Their assessments directly influence Shriram Finance's access to capital and the interest rates it pays. A higher credit rating can unlock cheaper borrowing, crucial for a finance company.
Favorable ratings are not just about cost; they are vital for attracting a broader investor base. This includes tapping into both domestic and international debt markets, diversifying funding sources. Investor confidence, heavily reliant on these ratings, underpins Shriram Finance's stability and growth prospects.
- CRISIL's BBB+ rating for Shriram Transport Finance's long-term debt in early 2024 underscored its stable financial health.
- ICRA's reaffirmed rating of [Insert Latest ICRA Rating Here, e.g., AA-] for Shriram Finance's bank facilities highlights continued market trust.
- The cost of funds for NBFCs like Shriram Finance is directly correlated with their credit ratings, with a single notch difference potentially impacting borrowing costs by tens of basis points.
- A strong rating from these agencies is a prerequisite for Shriram Finance to issue commercial paper and NCDs, essential components of its funding strategy.
Regulatory Bodies (RBI)
While not traditional suppliers, regulatory bodies like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) exert significant influence over Shriram Finance. The RBI's directives on capital adequacy, lending practices, and governance directly shape the operational landscape for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs). For instance, the RBI’s classification of NBFCs into different layers and the associated prudential norms, effective from October 1, 2022, introduce compliance costs and strategic considerations for Shriram Finance.
These regulations, particularly those impacting group entities and risk management, can alter Shriram Finance's cost of doing business and its ability to offer certain financial products. The RBI's ongoing focus on financial stability and consumer protection means that Shriram Finance must continually adapt its strategies to align with evolving regulatory requirements, thereby demonstrating a high degree of bargaining power.
- RBI's Regulatory Framework: The RBI's oversight of NBFCs, including Shriram Finance, involves setting prudential norms, capital requirements, and operational guidelines.
- Impact on NBFCs: Regulations such as those for Upper Layer NBFCs and restrictions on bank-NBFC group entities directly influence Shriram Finance's operational structure and compliance expenses.
- Cost of Compliance: Adhering to new or revised regulations often necessitates investments in technology, reporting systems, and skilled personnel, increasing operational costs for Shriram Finance.
- Strategic Adaptations: Shriram Finance must proactively adjust its business model and risk management strategies to remain compliant with the RBI's directives, showcasing the regulator's substantial power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Shriram Finance is primarily concentrated among its capital providers, technology vendors, and key personnel. For instance, in 2024, the cost of borrowing from banks and institutional investors remained a critical factor, directly influencing Shriram Finance's profitability and lending rates.
Technology suppliers wield significant influence due to the specialized nature of their software and the cost of switching, as demonstrated by Shriram Finance's investment in its digital platforms. Similarly, skilled finance and tech professionals, in high demand in India's financial sector, can command better compensation, as evidenced by rising salaries for data scientists in 2023.
Credit rating agencies like CRISIL and ICRA possess substantial power, as their assessments directly impact Shriram Finance's capital access and borrowing costs, with a BBB+ rating from CRISIL in early 2024 highlighting its stable financial health.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Shriram Finance | 2024/2023 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Providers (Banks, Investors) | Market liquidity, interest rates, perceived creditworthiness, RBI regulations | Determines cost of funds, impacting lending margins and profitability | Favorable borrowing costs were crucial for profitability in 2024. |
| Technology & Digital Solution Providers | Uniqueness of solutions, switching costs, reliance on specialized platforms | Dictates IT infrastructure costs and operational efficiency | Shriram Finance's investment in its Shriram Super App highlights dependency. |
| Skilled Personnel (Finance, Tech) | Demand for specialized skills, attrition rates, availability in the market | Influences salary and benefit costs, impacts operational continuity | Salaries for tech-savvy roles rose significantly in 2023, increasing employee leverage. |
| Credit Rating Agencies (CRISIL, ICRA) | Credit ratings, market perception of financial health | Affects access to capital, borrowing costs, and investor confidence | CRISIL's BBB+ rating in early 2024 signaled stable financial health. |
What is included in the product
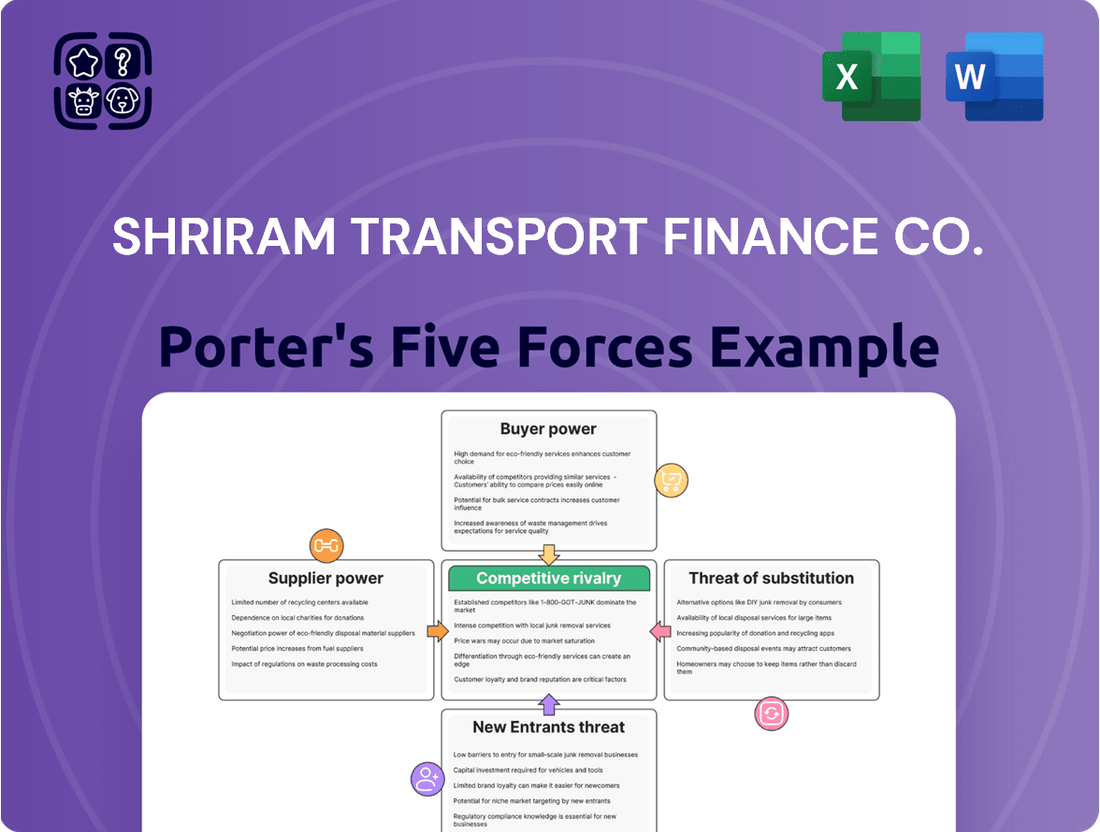
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to Shriram Transport Finance Co., evaluating the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the commercial vehicle financing sector.
Shriram Transport Finance Co.'s Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of competitive pressures, aiding in swift strategic adjustments by highlighting areas of vulnerability to new entrants or shifts in buyer power.
Customers Bargaining Power
Shriram Finance's customer base, predominantly small truck owners and individual fleet operators, is highly fragmented. This dispersal across rural and semi-urban geographies means no single customer holds substantial sway. Consequently, their collective bargaining power is significantly diminished, as their individual contributions to Shriram Finance's Assets Under Management (AUM) are typically small.
Customers today benefit from a significantly wider array of financing choices. Beyond traditional banks, options now include numerous Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), public sector banks, private sector banks, and a growing number of fintech lenders.
This competitive landscape, especially in areas like used commercial vehicle financing, directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers. They can more readily compare interest rates, loan terms, and repayment schedules across different providers.
For instance, in 2024, the vehicle finance market saw robust activity from various players. Shriram Transport Finance, a key player, operates in a segment where customer churn is a real consideration due to the availability of alternatives.
The ease with which customers can explore and switch lenders means they can negotiate more favorable terms, pushing down the profitability for any single financier if they cannot offer competitive advantages.
Small truck owners and fleet operators are acutely sensitive to the cost of financing, as interest rates and loan terms directly impact their bottom line. For instance, a slight increase in interest rates on vehicle loans can significantly reduce the profitability of a single truck operation. This sensitivity compels them to shop around for the best deals, putting pressure on lenders like Shriram Finance to offer competitive pricing and flexible repayment options to secure business.
Dependence on Financing for Livelihood
Shriram Transport Finance Co. (now Shriram Finance) serves a customer base where access to commercial vehicle financing is not just a convenience but a fundamental necessity for earning a livelihood. This reliance means many customers have limited alternatives and are therefore less empowered to dictate terms. For instance, a large segment of Shriram Finance's borrowers are small truck owners and operators whose income is directly tied to their ability to finance and operate their vehicles.
This dependence can temper customer bargaining power, as the immediate need for capital often outweighs the ability to negotiate aggressively on interest rates or loan conditions. Shriram Finance's deep understanding of this segment, cultivated over years of operation, allows them to manage this dynamic effectively. In the fiscal year 2024, Shriram Finance reported a robust Net Interest Margin (NIM) of 8.86%, indicating their ability to profitably manage lending to this customer base despite their inherent need.
- Critical Need: For many of Shriram Finance's customers, commercial vehicle finance is essential for their primary income generation.
- Reduced Bargaining Leverage: This dependence limits customers' ability to demand highly favorable loan terms.
- Shriram Finance's Market Position: The company's extensive reach in financing commercial vehicles for the unbanked and underbanked segments solidifies this customer dependency.
- Financial Performance Indicator: Shriram Finance's NIM of 8.86% in FY24 reflects its success in managing lending to this crucial, yet dependent, customer segment.
Customer Credit Profile and Switching Costs
Customer credit profiles are a significant determinant of their bargaining power with Shriram Transport Finance. Clients with robust credit histories and higher credit scores are better positioned to negotiate favorable loan terms, including interest rates and repayment schedules. This is because lenders perceive them as lower risk, making them more attractive to competitors as well. For instance, a customer with a credit score above 750 is likely to command more favorable terms than one with a score below 600.
While historically, switching financiers might have involved considerable hassle, the digital transformation in the financial sector has notably reduced these barriers. The proliferation of online application portals and the ease of comparing offers from various lenders mean that the effective switching costs for customers are diminishing. This increased ease of movement empowers customers to seek out and accept more competitive deals, thereby enhancing their overall bargaining leverage against Shriram Transport Finance.
- Customer Creditworthiness: Stronger credit profiles translate to greater negotiation power for loan terms.
- Digitalization Impact: Online platforms and easy comparison tools are lowering the costs and effort associated with switching financiers.
- Competitive Landscape: Increased ease of switching encourages customers to explore and accept better offers from rival institutions.
- Negotiation Leverage: Lower switching costs directly empower customers to demand more favorable conditions from Shriram Transport Finance.
Shriram Finance's customer base, largely comprising small truck owners and individual fleet operators, is highly fragmented, meaning no single customer wields significant individual power. This inherent dispersion, coupled with the critical need for vehicle financing for their livelihoods, limits their collective bargaining leverage. While the digital shift has lowered switching costs, making comparison easier, Shriram Finance's deep market penetration and understanding of this segment allow for effective management of customer relationships.
The company's success in maintaining a healthy Net Interest Margin of 8.86% in FY24 highlights its ability to profitably serve this customer base, despite their sensitivity to financing costs and the growing availability of alternative lenders. Customers with stronger credit profiles are better positioned to negotiate, but the core customer segment's reliance on vehicle financing for income generation remains a key factor tempering their overall bargaining power.
Full Version Awaits
Shriram Transport Finance Co. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Porter's Five Forces analysis of Shriram Transport Finance Co. you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the intense competition from other NBFCs and banks, the growing threat of new entrants leveraging digital platforms, and the significant bargaining power of customers due to readily available financing options. You'll also find insights into the moderate threat of substitute products like direct vehicle ownership or leasing arrangements and the constant pressure from suppliers, particularly those in the vehicle financing ecosystem, all presented in a professionally formatted and ready-to-use document.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian commercial vehicle financing landscape is intensely competitive, with major public and private sector banks holding a significant presence. These banks often leverage a lower cost of funds, giving them a competitive edge in pricing loans. For instance, in 2023, public sector banks collectively held a substantial portion of the overall banking sector assets, allowing them to offer more attractive interest rates.
Beyond traditional banks, a multitude of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) further intensify this rivalry. These NBFCs range from broadly diversified financial institutions to those with a specific focus on vehicle financing, all vying for market share. This crowded market means companies like Shriram Transport Finance Co. must constantly innovate and offer compelling value propositions to attract and retain customers.
The commercial vehicle loan market, a core area for Shriram Finance, is characterized by significant product commoditization. This means that the loans themselves are very similar across different lenders, making it difficult for companies to stand out based on the loan product alone. Consequently, competition often boils down to price, with interest rates and processing fees becoming key battlegrounds.
This intense pricing pressure directly impacts Shriram Finance's profitability. In 2023, the average interest rate for commercial vehicle loans in India hovered around 9-11%, a highly competitive landscape where even small differences in rates can sway customer decisions. The focus on speed of loan disbursal also adds to operational costs, further squeezing margins.
The Indian commercial vehicle market's growth fuels competition, pushing companies like Shriram Finance to adopt aggressive tactics for AUM expansion. Shriram Finance reported a significant AUM of ₹2.65 lakh crore as of March 31, 2024, demonstrating robust growth following its merger.
Sustaining this impressive AUM trajectory amidst intense rivalry necessitates ongoing innovation in product offerings and customer acquisition strategies. The company’s ability to attract and retain customers will be crucial in the face of numerous established and emerging players in the financing sector.
Regional and Niche Competition
Shriram Finance also contends with competition from regional and niche players. These entities, often smaller Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) or even informal lenders, can offer highly tailored services to specific customer segments or geographic areas, particularly in rural and semi-urban markets where Shriram Finance has a strong foothold. While Shriram Finance's broad network is a significant advantage, this localized competition can still impact market share.
These niche competitors might focus on particular vehicle types, lending to specific professions, or offering more flexible repayment schedules that appeal to a localized customer base. For instance, in certain agricultural belts, informal lenders might provide quick, albeit potentially higher-cost, credit that bypasses the more formal processes of larger NBFCs.
- Localized Competition: Smaller NBFCs and informal lenders target specific regions and customer needs.
- Tailored Services: Niche players offer customized products, potentially impacting Shriram Finance's market share in localized areas.
- Rural & Semi-Urban Focus: Shriram Finance's extensive presence in these areas helps, but localized competition remains a factor.
Regulatory Landscape and Consolidation
The regulatory environment, particularly the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) Scale Based Regulation for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), is significantly influencing competitive dynamics. This framework categorizes NBFCs based on size and risk, imposing varying capital and operational requirements that can favor larger, well-capitalized entities.
Market-driven consolidations, exemplified by the merger that created the current Shriram entity, are actively reshaping the competitive arena. While these mergers reduce the overall number of independent players, they simultaneously forge larger, more powerful competitors, thus intensifying rivalry among the leading NBFCs and established banks. For instance, the Indian NBFC sector saw a notable consolidation trend leading up to 2024, with the Shriram Group's merger being a prime example of this strategic realignment.
- Regulatory Impact: RBI's Scale Based Regulation aims to strengthen the NBFC sector, potentially leading to higher compliance costs for smaller players and creating an advantage for larger, more regulated entities.
- Consolidation Effects: Mergers and acquisitions, such as the Shriram transaction, create stronger, more diversified financial institutions, increasing competitive pressure on remaining independent NBFCs and banks.
- Intensified Rivalry: The emergence of larger, consolidated players means that competition for market share, customer acquisition, and talent will likely become more pronounced among the top-tier financial institutions.
- Market Dynamics: By 2024, the Indian financial services market continues to see a push towards consolidation, driven by both regulatory pressures and strategic business decisions to achieve scale and efficiency.
Shriram Finance faces intense competition from public sector banks, which often offer lower interest rates due to their lower cost of funds, and a vast number of NBFCs, including those specializing in vehicle financing. This crowded market forces Shriram Finance to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings to capture and retain customers.
The commoditized nature of commercial vehicle loans means competition frequently centers on pricing, with interest rates and processing fees being key battlegrounds, directly impacting Shriram Finance's profitability margins.
The company's substantial Assets Under Management (AUM) of ₹2.65 lakh crore as of March 31, 2024, underscores the need for aggressive strategies to expand further amidst this rivalry.
Furthermore, localized competition from niche NBFCs and informal lenders, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, presents a challenge, even with Shriram Finance's strong network.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Shriram Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Public Sector Banks | Lower cost of funds, competitive pricing | Pressure on interest rates, customer acquisition |
| Diversified NBFCs | Wide product range, aggressive market share pursuit | Intensified rivalry across segments |
| Niche/Regional NBFCs | Tailored services, localized focus | Potential market share erosion in specific geographies |
| Informal Lenders | Quick disbursal, flexible terms (often higher cost) | Competition in specific customer segments, especially rural |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Larger fleet operators and established businesses with robust cash flows might choose to self-finance vehicle purchases or rely on internal accruals. This directly substitutes the need for external financing from companies like Shriram Finance. For instance, a company with significant retained earnings could bypass loan applications entirely, reducing the pool of potential borrowers, especially for its more creditworthy clients.
Informal lending channels pose a significant threat for Shriram Transport Finance. For many small truck owners, especially in rural or less developed areas, informal lenders offer a quick alternative. These lenders often require less paperwork and can disburse funds faster than formal institutions, which is crucial for operators facing immediate cash flow needs.
While informal loans can carry higher interest rates, the speed and accessibility make them a viable substitute, particularly for those without extensive credit histories or collateral. This can limit Shriram Transport Finance's ability to attract and retain customers who prioritize immediate access over long-term cost efficiency.
The increasing popularity of commercial vehicle leasing and rental services offers a significant substitute for traditional vehicle ownership financed by loans. Companies like Zoomcar and Revv, expanding their fleet services, provide businesses with flexible alternatives. This shift can reduce the demand for Shriram Transport Finance's loan products as businesses opt for the agility and potentially lower initial capital outlay of leasing, especially when considering the tax advantages often associated with rental agreements. For instance, the Indian commercial vehicle leasing market is projected to grow substantially, with many businesses increasingly seeing leasing as a more capital-efficient strategy, directly impacting the need for financed purchases.
Diversified Financial Products
Customers seeking to finance vehicle acquisition have a range of alternatives beyond specialized commercial vehicle loans. They can obtain general business loans, personal loans, or even gold loans from traditional banks or other Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs). These funds can then be redirected towards purchasing commercial vehicles, acting as a substitute for Shriram Finance's core offerings.
Shriram Finance itself contributes to this by offering a broad spectrum of financial products. This diversification includes services like gold loans and financing for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). While these products cater to different needs, their availability means customers might find alternative funding solutions within Shriram Finance's own ecosystem, potentially reducing reliance on a dedicated commercial vehicle loan.
The availability of these diversified financial products from various institutions presents a tangible threat of substitutes for Shriram Transport Finance. For instance, if a customer can secure a personal loan with a competitive interest rate, they might opt for that over a specialized commercial vehicle finance product, especially if the terms are more flexible or perceived as less complex. This broadens the competitive landscape significantly.
- Alternative Funding Sources: Customers can access general business loans, personal loans, or gold loans from banks and other NBFCs for vehicle acquisition.
- Shriram Finance's Diversification: Shriram Finance offers its own gold loans and MSME financing, providing internal alternatives for customers.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous financial institutions offering a wide array of loan products intensifies the threat of substitutes.
- Customer Flexibility: Customers can leverage flexible terms or lower perceived complexity of general loans to substitute specialized commercial vehicle financing.
Alternative Transport and Logistics Solutions
The threat of substitutes for Shriram Transport Finance Co. (STFC) stems from evolving logistics and transportation models. Long-term shifts towards shared commercial vehicle platforms, enhanced public transportation, or more streamlined freight networks could diminish the demand for individual commercial vehicle ownership. This, in turn, would impact the need for new vehicle financing, a core business for STFC.
For instance, consider the rise of integrated logistics solutions. Companies are increasingly looking for end-to-end services rather than just vehicle financing. This could mean a move towards leasing models or full-service providers who manage fleets, maintenance, and even the financing aspect. In 2024, the logistics sector continues to see innovation aimed at efficiency and cost reduction, which could accelerate the adoption of these alternative models.
- Shared Mobility Platforms: The growth of platforms that allow for the sharing of commercial vehicles, reducing the need for individual ownership, poses a substitute threat.
- Integrated Logistics Providers: Companies offering comprehensive logistics services, including fleet management and financing, can bypass traditional financiers like STFC.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in autonomous trucking and advanced freight routing could lead to more efficient, consolidated freight movement, potentially lowering the overall volume of vehicles required.
- Public and Intermodal Transport: While primarily for passengers, advancements in public transport and more efficient intermodal freight solutions (combining different modes of transport) can indirectly reduce reliance on individual commercial vehicles for certain goods movement.
The threat of substitutes for Shriram Transport Finance (STF) is substantial, driven by various alternative funding and operational models in the commercial vehicle sector. Informal lending channels, while often carrying higher interest, provide a quick and accessible alternative for many small truck owners, particularly in less developed regions. This speed and reduced paperwork can be a decisive factor for operators facing immediate cash flow pressures, diverting business away from formal financiers like STF.
Furthermore, the growing trend of commercial vehicle leasing and rental services presents a direct substitute for traditional financed ownership. Companies are increasingly opting for the flexibility and potentially lower upfront capital requirements of leasing, especially when tax advantages are considered. For instance, the Indian commercial vehicle leasing market is expected to see significant expansion, indicating a strategic shift by businesses towards capital efficiency that bypasses the need for loans from STF.
Customers also have recourse to a broader range of financial products from both other institutions and even STF's own diversified offerings. General business loans, personal loans, or gold loans can be used to finance vehicle acquisition, offering alternative pathways for customers who might find specialized commercial vehicle finance less appealing due to terms or perceived complexity. STF’s own provision of services like gold loans and MSME financing means customers may find internal substitutes, thereby potentially reducing their dependence on dedicated commercial vehicle financing products.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on STF | Example/Data Point (2024/Pre-2025) |
| Informal Lending | Speed, less paperwork, accessibility | Loss of smaller, cash-strapped borrowers | Prevalence of informal credit in rural India for vehicle purchases. |
| Vehicle Leasing/Rental | Flexibility, lower upfront cost, tax benefits | Reduced demand for new vehicle financing | Projected growth in India's commercial vehicle leasing market. |
| General Loans (Banks/NBFCs) | Broader terms, potentially simpler application | Diversion of creditworthy customers | Availability of competitive personal and business loans from major banks. |
| STF's Internal Diversification | Gold loans, MSME financing | Potential for customers to self-substitute within STF's offerings | STF's existing product portfolio includes gold loans and MSME finance. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the commercial vehicle financing sector, particularly to compete with established players like Shriram Finance, demands immense capital. Building a substantial loan portfolio, ensuring sufficient liquidity, and adhering to stringent regulatory capital adequacy requirements necessitate significant upfront investment. For instance, in 2024, the Reserve Bank of India mandates a Net Owned Fund of ₹15 crore for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in the upper layer, with higher requirements for larger operations, acting as a strong deterrent for new entrants.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintains a rigorous regulatory environment for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), significantly deterring new entrants. Obtaining the necessary licenses, adhering to ongoing compliance mandates, and operating under the RBI's Scale Based Regulation (SBR) framework all represent substantial hurdles.
These stringent requirements mean that any aspiring NBFC must invest heavily in legal expertise and robust compliance infrastructure from day one. For instance, the SBR framework, implemented in stages, categorizes NBFCs based on their asset size and systemic importance, each with tailored prudential norms and supervisory intensity, demanding specialized knowledge and resources to navigate effectively.
Navigating this complex web of legal and compliance obligations is a significant barrier. New companies face considerable upfront costs and a lengthy approval process, making it difficult to establish a foothold in the market. This regulatory moat protects established players like Shriram Transport Finance Co. by limiting the influx of new competition.
Shriram Finance's formidable distribution network, with over 3,000 branches as of March 2024, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This extensive reach, particularly in rural and semi-urban markets, is vital for their customer acquisition and loan recovery processes.
Establishing a comparable network requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and manpower, making it a daunting task for potential competitors. The sheer scale and established presence of Shriram Finance’s distribution channels create a high hurdle to overcome, effectively deterring many new players from entering the market.
Credit Assessment and Collection Expertise
The threat of new entrants for Shriram Transport Finance Co. (STFC) in its core business of financing small truck owners and fleet operators is mitigated by the significant expertise required in credit assessment and collection. Success hinges on developing specialized underwriting models and risk assessment capabilities tailored to customers with modest credit profiles. STFC’s long-standing presence has allowed it to cultivate deep domain knowledge and build trust within this segment.
STFC’s established infrastructure and proven track record in managing collections are substantial barriers. For instance, in FY23, STFC reported a Gross Non-Performing Asset (GNPA) ratio of 5.03% and a Net Non-Performing Asset (NNPA) ratio of 2.58%, demonstrating effective management of credit risk and collections even within a challenging segment. New players would need to replicate this operational efficiency and risk mitigation strategy, which is a considerable undertaking.
- Deep Domain Expertise: STFC's ability to accurately assess the creditworthiness of small truck owners and fleet operators, often with limited formal credit history, is a key differentiator.
- Efficient Collection Mechanisms: The company has honed its collection processes over decades, crucial for maintaining profitability in a segment with potentially higher default risks.
- Established Trust and Relationships: Years of serving this niche market have allowed STFC to build strong relationships and a reputation for reliability, which new entrants would find difficult to match quickly.
- Regulatory Navigation: Understanding and complying with the regulatory landscape for vehicle financing and lending in India is complex and requires significant experience.
Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
Shriram Finance, with its long-standing presence, enjoys significant brand recognition. This established reputation makes it difficult for newcomers to attract customers who prioritize trust and reliability in financial services. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and customer service to even begin to compete with the loyalty Shriram Finance has cultivated over many years.
The threat of new entrants is significantly reduced by the strong brand reputation and customer loyalty enjoyed by established players like Shriram Finance. Building this level of trust takes considerable time and consistent performance. For instance, Shriram Finance's customer base is built on decades of service, making it a formidable barrier.
- Brand Recognition: Shriram Finance benefits from decades of brand building, creating a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customer relationships are difficult and costly for new companies to replicate.
- Trust Factor: In the financial sector, trust is paramount, and new players must earn it, a process that can take years.
The high capital requirements for establishing a significant loan portfolio and meeting regulatory capital adequacy, such as the ₹15 crore Net Owned Fund for NBFCs in the upper layer as mandated by the RBI in 2024, act as a major deterrent.
Furthermore, the complex regulatory environment, including licensing and ongoing compliance under the RBI's Scale Based Regulation framework, necessitates substantial investment in legal and compliance infrastructure, creating a significant barrier for new entrants.
Shriram Finance's extensive branch network, exceeding 3,000 locations by March 2024, coupled with deep domain expertise in credit assessment and efficient collection mechanisms evidenced by its FY23 GNPA of 5.03%, presents formidable operational hurdles for any new competitor.
The established brand reputation and customer loyalty, cultivated over decades of service, are critical intangible assets that new entrants find extremely difficult and costly to replicate, further solidifying the low threat of new entrants in this segment.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Shriram Transport Finance Co. leverages data from the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEBI filings. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific research reports and financial news outlets to capture market dynamics.
