Stepan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Stepan Bundle
Stepan's competitive landscape is meticulously mapped by Porter's Five Forces, revealing the intricate interplay of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the ever-present threats of substitutes and new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for comprehending Stepan's strategic positioning and the inherent pressures within its markets. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Stepan’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Stepan Company's reliance on petrochemicals and natural oils for its core surfactant and polymer products places it squarely in the sights of powerful suppliers. The prices of these essential inputs are notoriously volatile, influenced by global commodity markets, geopolitical tensions, and the ever-present threat of supply chain snags. For instance, crude oil prices, a significant driver for petrochemicals, experienced considerable fluctuations throughout 2024, impacting the cost base for Stepan.
For highly specialized chemical intermediates or unique formulations crucial to Stepan's specialty product lines, the pool of qualified suppliers is often quite limited. This scarcity of alternatives can significantly shift bargaining power towards these suppliers.
When only a few companies can produce a necessary input, they gain leverage to influence pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines. For instance, if a specific high-purity additive used in Stepan's surfactants is only produced by a handful of global manufacturers, those suppliers can command premium prices, potentially impacting Stepan's cost of goods sold and profit margins.
This supplier concentration increases Stepan's dependence on a narrow base of providers. If one of these key suppliers experiences production issues or decides to increase prices substantially, Stepan may have few immediate alternatives, forcing them to accept less favorable terms or face potential supply disruptions.
In 2023, the specialty chemicals sector, where Stepan operates, saw price increases for key raw materials driven by supply chain constraints and geopolitical factors, highlighting the real-world impact of supplier concentration on companies in this space.
Stepan faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers due to the substantial costs associated with switching chemical inputs. For instance, re-qualifying a new supplier's product can involve extensive testing and R&D, potentially costing millions of dollars and delaying production timelines. This inherent friction in changing suppliers limits Stepan's ability to negotiate favorable terms, as the expense and effort involved in finding and integrating an alternative are often prohibitive.
In 2024, the chemical industry continued to experience supply chain volatility, further amplifying supplier leverage. Companies like Stepan, reliant on specialized chemical inputs, found that sourcing alternatives often required significant capital investment in process modifications and product re-validation. This situation directly translates to suppliers holding greater sway in pricing and contract negotiations, as the cost and complexity of Stepan finding a new source are substantial barriers.
Proprietary Nature of Some Raw Materials
When Stepan Company needs raw materials that are unique or patented, the suppliers of these specific ingredients hold significant power. This is because there are often no other places to get these essential components, allowing the suppliers to dictate terms and prices. For instance, if a key ingredient for a new specialty chemical is only produced by one company, that supplier can charge a premium, impacting Stepan's cost structure and profitability.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers of proprietary raw materials can command higher prices due to the lack of substitutes.
- Cost Impact: Reliance on unique inputs can increase Stepan's cost of goods sold, potentially reducing profit margins.
- Limited Negotiation: Stepan's ability to negotiate favorable terms is diminished when alternatives are scarce or non-existent.
- Innovation Dependence: The company's ability to bring innovative products to market can be hindered if key proprietary materials become too expensive or unavailable.
Supplier's Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers forward integrating into Stepan's core business, while less prevalent in specialized chemical manufacturing, could significantly shift bargaining power. If a major raw material provider were to enter Stepan's market, it would create substantial competitive pressure.
This theoretical risk necessitates Stepan cultivating robust, cooperative relationships with its essential suppliers. Maintaining open communication and mutually beneficial partnerships can mitigate this potential challenge.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: While uncommon in Stepan's niche, a raw material supplier entering the chemical production market could increase their leverage.
- Relationship Management: Stepan's strategy should prioritize strong, collaborative ties with critical raw material providers to preempt this threat.
- Market Dynamics: The specialized nature of chemical production makes direct forward integration by suppliers a less frequent but potent concern.
Stepan Company's suppliers hold significant bargaining power, largely due to the concentrated nature of key petrochemical and natural oil inputs. Fluctuations in crude oil prices, a primary driver for petrochemicals, continued to impact raw material costs throughout 2024, directly affecting Stepan's cost of goods sold.
The limited number of suppliers for specialized chemical intermediates further amplifies this power. When few entities can produce a necessary input, they gain leverage to dictate pricing and terms, potentially squeezing Stepan's profit margins.
The substantial costs and time involved in switching chemical suppliers, often running into millions of dollars for re-qualification and process adjustments, create high switching costs. This friction severely limits Stepan's ability to negotiate, as finding and integrating alternatives is often prohibitively expensive and time-consuming, a reality underscored by continued supply chain volatility in 2024.
| Input Type | Supplier Concentration | Potential Impact on Stepan | 2024 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petrochemicals (e.g., Propylene Oxide) | Moderate to High | Price Volatility, Cost Increases | Crude oil price fluctuations impacted input costs. |
| Natural Oils (e.g., Palm Kernel Oil) | Moderate | Price Sensitivity, Supply Availability | Market demand and weather patterns influenced pricing. |
| Specialized Intermediates | Low to Moderate | High Switching Costs, Limited Negotiation Power | R&D and re-validation costs for new suppliers were significant barriers. |
What is included in the product
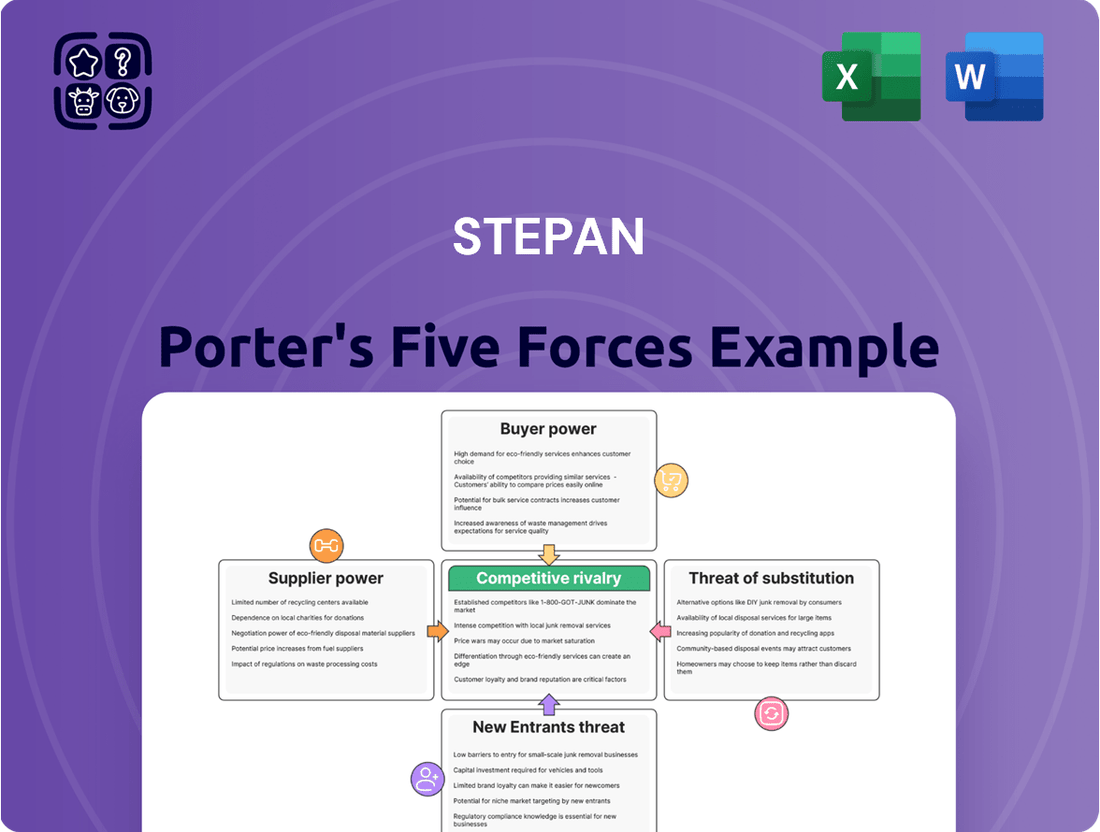
Stepan's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and prioritize competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, allowing for targeted strategy development and risk mitigation.
Customers Bargaining Power
Stepan Company's position in key end markets like consumer products, industrial cleaning, and agriculture means it often deals with large, multinational corporations. This customer concentration can significantly influence Stepan's bargaining power.
When a few major clients represent a substantial chunk of Stepan's sales, these customers gain leverage. They can use their purchasing volume to demand lower prices, customized product formulations, or specific service agreements, potentially squeezing Stepan's profit margins.
For instance, if a single large consumer goods manufacturer accounts for 15% of Stepan's revenue, that customer can exert considerable pressure during contract negotiations. This is a common dynamic in specialty chemical supply chains where buyer power is amplified by scale.
This concentration risk means Stepan must carefully manage relationships with its key accounts, balancing the need for volume with the imperative to maintain profitable pricing and terms. Any loss of a major customer due to competitive pressure or shifting market demands could have a notable impact.
The bargaining power of Stepan's customers is significantly influenced by varying switching costs, directly tied to the nature of the products purchased. For instance, customers relying on highly specialized chemical formulations developed in close collaboration with Stepan will face substantial costs and disruptions if they were to switch to a new supplier. This complexity, often involving unique manufacturing processes or product integration, inherently raises switching barriers, thereby diminishing customer leverage.
Conversely, customers procuring more standardized or commoditized chemicals from Stepan encounter considerably lower switching costs. In these scenarios, alternative suppliers are more readily available, and the integration of a new product into existing operations is generally less challenging. This ease of substitution empowers these customers, allowing them to exert greater pressure on Stepan regarding pricing and terms, as evidenced by the competitive landscape for basic chemical ingredients.
Stepan Company's capacity to differentiate its surfactants and polymers is a key lever in managing customer bargaining power. By focusing on innovation, such as developing more effective or environmentally friendly formulations, Stepan can create a value proposition that transcends mere price competition. This differentiation makes it more challenging for customers to simply switch to a competitor based on cost alone, thereby reducing their leverage.
Customer Price Sensitivity in Competitive Markets
Many of Stepan’s customers operate in highly competitive sectors like detergents and personal care. This means they are very focused on price, putting pressure on Stepan to keep its own prices competitive, especially for products that aren't particularly unique.
For instance, in the consumer staples segment, which heavily relies on Stepan's surfactants, price fluctuations can significantly impact a customer's profitability. In 2024, the global household cleaning market was valued at approximately $230 billion, with intense competition driving a strong emphasis on cost management for manufacturers.
- High Competition in End Markets: Stepan's customers in sectors like detergents and personal care face intense competition, leading to a strong focus on cost of goods sold.
- Price Sensitivity: This competitive environment makes Stepan's customers highly sensitive to the prices of raw materials and intermediate chemicals, directly impacting their purchasing decisions.
- Impact on Stepan's Pricing: The need to offer competitive pricing is a constant challenge for Stepan, particularly for its less differentiated product lines.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the personal care market alone was projected to reach over $600 billion globally, highlighting the scale and competitive nature of industries relying on Stepan's products.
Customer's Potential for Backward Integration
Large customers, particularly those with substantial chemical knowledge, might explore backward integration, meaning they could start producing some chemical ingredients in-house. This is a significant consideration for companies like Stepan, as it directly impacts their customer relationships and pricing power.
While building such production capabilities is very expensive, the mere *possibility* of backward integration gives customers considerable leverage. This leverage is often used in price negotiations, pushing suppliers to offer more competitive terms to retain business. For instance, a major consumer goods company might assess the cost and feasibility of producing a key surfactant Stepan supplies, even if they ultimately decide against it, the threat itself can lead to price concessions.
- Customer Expertise: The chemical expertise of a customer directly correlates to their ability to consider and execute backward integration.
- Capital Intensity: The significant capital investment required for backward integration acts as a barrier, but a determined customer can overcome it.
- Negotiating Leverage: The threat of a customer producing an ingredient themselves gives them substantial power in pricing discussions with suppliers like Stepan.
- Market Dynamics: In markets where ingredient costs are a substantial portion of a final product's cost, backward integration becomes a more attractive option for large buyers.
Stepan's customers, especially those in high-volume, competitive sectors, wield significant bargaining power. This power is amplified when switching costs are low, enabling customers to easily seek alternative suppliers. In 2024, the intense competition within the personal care and cleaning industries, valued at hundreds of billions globally, forces these customers to be highly price-sensitive, directly impacting Stepan's pricing strategies for less differentiated products.
| Factor | Impact on Stepan | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large buyers | Dominance of large multinational corporations in end markets |
| Switching Costs | Low for standardized products | Ease of finding alternative suppliers for basic chemicals |
| End-Market Competition | Pressure for competitive pricing | Global household cleaning market ~$230 billion; personal care market >$600 billion |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential loss of business | Customer expertise and capital investment can drive this consideration |
Full Version Awaits
Stepan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Stepan Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our detailed breakdown meticulously examines the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic positioning of Stepan within its industry. This professionally written document is fully formatted and ready to be integrated into your strategic planning efforts.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Stepan Company operates within a highly competitive specialty and intermediate chemicals market. This sector is characterized by a significant number of global and regional players, creating a fragmented landscape. Major diversified chemical conglomerates like BASF, Solvay, Eastman, Huntsman, and Celanese are key competitors, bringing substantial resources and broad product portfolios to the market.
Beyond these giants, a multitude of smaller, specialized chemical manufacturers also vie for market share. This diverse competitive environment means Stepan must continuously innovate and maintain cost-efficiency to hold its ground. The sheer volume of participants intensifies rivalry, putting pressure on pricing and market access for all involved.
In the specialty chemicals sector, competitive rivalry is intense, with innovation and robust Research and Development (R&D) forming the primary battlegrounds. Companies continuously pour resources into developing novel formulations and improving existing ones, aiming for superior performance and enhanced sustainability. For instance, Stepan Company's commitment to R&D is evident in its strategic focus on areas like bio-based surfactants and advanced polymer technologies, seeking to capture market share through differentiated offerings.
Overcapacity in several chemical sectors, especially in Asia, is a significant factor, driving companies to adopt aggressive pricing tactics to secure market share. This intense competition directly impacts overall industry profitability and creates a difficult pricing landscape for Stepan.
In 2024, the global chemical industry continued to grapple with oversupply in certain segments. For instance, the polyethylene market experienced significant capacity additions, particularly in Asia, leading to price erosion. This overcapacity can force established players like Stepan to lower their prices to remain competitive, squeezing margins.
This pressure is not theoretical; in the first half of 2024, several chemical producers reported lower average selling prices for key products due to this competitive dynamic. Stepan's performance is therefore closely tied to its ability to manage production costs and differentiate its offerings in a market where price is often a primary consideration.
Focus on Sustainable and Bio-based Solutions
The chemical industry is experiencing heightened competition as companies increasingly focus on sustainable and bio-based alternatives. This trend is driven by stricter environmental regulations and a growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. For instance, in 2024, the global bio-based chemicals market was projected to reach over $100 billion, showcasing a significant growth area where rivalry is particularly fierce.
Companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative, greener chemical solutions. This race to market greener products not only addresses regulatory pressures but also captures market share from competitors relying on traditional, less sustainable methods. The ability to effectively market and price these bio-based options is becoming a key differentiator.
- Innovation in Bio-based Feedstocks: Companies are competing to secure sustainable and cost-effective bio-based raw materials.
- Development of Biodegradable Products: The market is seeing a surge in demand for biodegradable polymers and chemicals, intensifying R&D efforts.
- Regulatory Compliance and Green Certifications: Achieving certifications for sustainability is becoming a competitive advantage.
- Consumer Preference for Eco-friendly Brands: Companies with strong sustainability credentials are gaining favor with environmentally conscious consumers, impacting market share.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The chemical industry, by its very nature, demands significant capital outlay. Stepan, like many in this sector, operates with substantial investments in manufacturing plants, research and development, and sophisticated production technologies. These aren't small, easily shed assets; they represent long-term commitments.
This capital intensity creates high fixed costs. Once these facilities are built and operational, companies are incentivized to run them at high capacity to spread those costs. This can lead to aggressive pricing and output decisions, even when market demand softens, as shutting down or reducing production can be prohibitively expensive.
Furthermore, exit barriers in the chemical industry are often considerable. These can include specialized equipment that's difficult to repurpose, environmental remediation obligations, and long-term contracts. For instance, in 2024, companies in sectors with similar characteristics often faced challenges divesting assets without incurring substantial losses, reinforcing the need to stay the course.
- High Capital Investment: The chemical industry requires massive upfront investment in plants and equipment, making it difficult for new entrants and costly for existing players to exit.
- Operational Scale Imperative: To achieve economies of scale and manage high fixed costs, companies like Stepan must maintain high production volumes, intensifying competition.
- Exit Barriers: Specialized assets and regulatory requirements create significant hurdles for companies looking to leave the market, trapping them in competitive environments.
- Impact on Pricing: The pressure to cover fixed costs can lead to price wars, especially during economic downturns or periods of oversupply.
Competitive rivalry within Stepan's markets is fierce, driven by numerous global and regional players, including giants like BASF and Solvay, alongside specialized firms. This fragmentation necessitates continuous innovation and cost efficiency. For example, in 2024, overcapacity in segments like polyethylene, particularly from Asian producers, led to price erosion, impacting average selling prices for key products across the industry.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing emphasis on sustainability is fueling the rise of bio-based and green chemical alternatives, directly challenging Stepan's traditional petroleum-derived offerings. These eco-friendly substitutes, sourced from renewable materials, are increasingly capturing market share, particularly in consumer-facing applications where environmental consciousness is high. For instance, the global bio-based chemicals market was valued at approximately $108 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $267 billion by 2030, indicating a significant shift away from conventional products.
The threat of substitutes for Stepan Company's chemical products is significantly influenced by the performance-cost trade-off of new materials emerging in the market. If alternative materials can deliver comparable or even better performance for applications like surfactants, polymers, or specialty chemicals, while being more cost-effective, they pose a direct challenge. For instance, advancements in bio-based surfactants or novel synthetic polymers could offer a more attractive value proposition to customers in sectors such as personal care, agriculture, or industrial cleaning.
Consider the personal care industry, a key market for Stepan. In 2024, there's a growing demand for ingredients that meet stringent sustainability and performance criteria. If new, readily available, and cost-competitive bio-based alternatives to Stepan's traditional surfactants emerge that offer comparable cleaning efficacy and mildness, they could capture market share. This is particularly true if these substitutes also align with evolving consumer preferences for eco-friendly products, potentially impacting Stepan's pricing power and market penetration in this segment.
The increasing regulatory pressure for safer chemicals presents a significant threat of substitutes for Stepan Company. Governments worldwide, including the EU and the US, are implementing evolving and stricter environmental and health regulations. For instance, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation continues to drive demand for less hazardous substances. This regulatory landscape can accelerate the adoption of alternative ingredients that more readily meet new compliance standards, potentially impacting Stepan's existing product lines.
Customer Adoption of New Technologies
The speed at which Stepan's customers adopt new materials, which could be substitutes, hinges on how easily these new materials can be incorporated into their current product recipes. If integration is straightforward, it lowers the barrier for switching. For instance, in 2024, many specialty chemical users are prioritizing formulations that require minimal changes to their manufacturing processes to avoid disruption.
Significant capital investment for new machinery or technology also plays a crucial role. Customers are more hesitant to adopt substitutes if it means substantial upfront costs for new equipment. This reluctance can slow down the perceived threat from substitutes, especially for smaller businesses that may have tighter budgets.
The perceived risks associated with a new substitute material, such as performance uncertainties or regulatory hurdles, can further influence adoption rates. Customers weigh these risks against potential benefits like cost savings or improved product features. In late 2024, many industries are still navigating evolving environmental regulations, making the adoption of unproven 'greener' substitutes a cautious decision.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when adoption barriers are low. Consider the coatings industry: if a new, cost-effective binder emerges that performs comparably to existing ones and requires no significant equipment changes, its adoption could be rapid, posing a direct threat to Stepan's market share in that segment. Data from late 2024 indicates that customers are actively seeking solutions that offer both performance and cost advantages with minimal operational disruption.
- Ease of Integration: Customers prefer substitutes that seamlessly fit into existing manufacturing processes, minimizing downtime and reformulation efforts.
- Capital Expenditure: High costs for new equipment or technology upgrades deter customers from adopting potentially disruptive substitute materials.
- Perceived Risk: Uncertainties regarding performance, reliability, or regulatory compliance of substitutes can significantly slow down customer adoption.
- Market Trends (2024): A growing emphasis on sustainability and cost-efficiency in 2024 pushes customers to evaluate substitutes, but only those with clear, low-risk advantages will see rapid uptake.
Innovation in Material Science and Biotechnology
The threat of substitutes for Stepan Company's chemical products is amplified by ongoing innovation in material science and biotechnology. Discoveries in nanotechnology and advanced material engineering could yield entirely new substances or production methods that replicate or surpass the performance of Stepan's current offerings. For instance, the development of bio-based surfactants or novel biodegradable polymers could directly challenge Stepan's established product lines in the cleaning and specialty chemicals sectors. This emergence of alternative materials, often developed with sustainability and cost-efficiency in mind, presents a significant challenge to market share and pricing power.
Consider the impact on Stepan's polyurethane business. Advances in bio-based polyols, derived from renewable resources, are gaining traction as substitutes for petroleum-based polyols, a core Stepan product. In 2024, the global bio-based chemicals market is projected to reach significant growth, indicating a clear trend towards these alternative materials. Furthermore, breakthroughs in material science might lead to the creation of entirely new functional materials that perform the same tasks as Stepan's specialty chemicals, but through different chemical pathways or physical properties.
- Advancements in bio-based polymers offer potential replacements for conventional polymers used in various Stepan applications.
- Nanotechnology could enable the creation of materials with enhanced properties, potentially reducing the need for certain chemical additives Stepan provides.
- Biotechnology may lead to the development of bio-surfactants and bio-solvents that compete with traditional chemical formulations.
- The **global specialty chemicals market**, valued at over $650 billion in 2023, is susceptible to disruption from these novel material substitutes, impacting Stepan's revenue streams.
The threat of substitutes for Stepan Company's products is a dynamic challenge, influenced by innovation and market demand for alternatives. Advancements in material science and biotechnology are continuously introducing new substances that can perform similar functions to Stepan's offerings, particularly in areas like surfactants and polymers. These emerging substitutes are often driven by a desire for enhanced sustainability and cost-effectiveness. For example, the global market for bio-based chemicals, a direct source of substitutes, was valued at around $108 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially, indicating a clear market shift.
Customers' willingness to adopt substitutes is heavily influenced by the ease of integration into their existing production processes and the capital expenditure required. In 2024, businesses are prioritizing solutions that minimize disruption and upfront costs. Perceived risks associated with new materials, such as performance uncertainties or regulatory compliance issues, also play a crucial role in slowing down adoption. However, market trends in 2024 show a clear push towards more sustainable and cost-efficient options, making substitutes attractive if they offer clear, low-risk advantages.
| Factor | Impact on Stepan's Substitutability | 2024 Market Insight |
| Innovation in Bio-based Materials | High potential to replace petroleum-based chemicals. | Global bio-based chemicals market expected to see significant growth. |
| Ease of Integration | Low integration barriers accelerate substitute adoption. | Customers prioritize minimal changes to existing manufacturing. |
| Cost-Performance Trade-off | Substitutes offering better value proposition gain traction. | Focus on competitive pricing and equivalent or superior performance. |
| Regulatory Environment | Stricter regulations favor compliant alternatives. | Evolving chemical regulations drive demand for safer substances. |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty and intermediate chemicals manufacturing sector demands substantial upfront capital. Stepan, for instance, operates complex, large-scale production facilities that require significant investment in R&D, advanced machinery, and stringent safety and environmental compliance. These high financial barriers effectively deter potential new competitors from entering the market.
For example, building a new, state-of-the-art chemical plant in 2024 can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This immense capital outlay, coupled with the ongoing need for technological upgrades and research, creates a formidable obstacle for any nascent player looking to challenge established companies like Stepan.
The chemical industry is heavily regulated, with new entrants facing substantial compliance costs. Navigating global environmental, health, and safety standards, including REACH in Europe and TSCA in the U.S., requires significant investment in legal counsel and compliance infrastructure. For example, the cost of registering a new chemical under REACH can run into hundreds of thousands of euros, posing a considerable barrier to smaller players.
Established players in the chemical industry, like Stepan, often leverage significant economies of scale. For instance, Stepan's substantial purchasing power allows them to secure raw materials at more favorable prices than a new entrant could. This cost advantage extends to their large-scale manufacturing operations, where fixed costs are spread over a much higher output volume, leading to lower per-unit production costs.
These cost efficiencies are a formidable barrier for newcomers. A new entrant would find it incredibly challenging to match Stepan's unit costs without a comparable level of production and procurement volume. This disparity in cost structure makes it difficult for new companies to compete on price, a critical factor in many chemical markets, thereby diminishing the threat of new entrants.
Challenges in Establishing Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Building robust global supply chains and securing access to established distribution networks is a time-consuming and complex endeavor for new entrants. Companies like Stepan, with decades of experience, have cultivated deep relationships and infrastructure that are difficult and expensive to replicate.
New entrants face significant challenges in creating effective channels to reach diverse customer bases. For instance, in the specialty chemicals sector, where Stepan operates, reaching niche markets often requires specialized logistics and sales forces, which are substantial upfront investments. In 2024, the global logistics market was valued at over $9 trillion, highlighting the scale of investment needed to establish competitive operations.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing warehousing, transportation fleets, and inventory management systems demands significant capital outlay, often exceeding the resources of a new player.
- Established Relationships: Existing players have long-standing contracts with suppliers and distributors, making it hard for newcomers to secure favorable terms or even access to critical partners.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating international trade regulations, import/export laws, and compliance standards for chemical distribution adds layers of complexity and cost for new entrants.
- Brand Trust and Reliability: Customers often prefer suppliers with proven track records for timely delivery and product integrity, which new companies must earn over time.
Proprietary Technology, Patents, and Expertise
Stepan Company and its established competitors benefit significantly from proprietary technology, patents, and deep-seated expertise. This intellectual property, encompassing patented chemical formulations and unique manufacturing processes, creates a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
For instance, Stepan's commitment to innovation is reflected in its ongoing R&D investments, which allow it to maintain a technological edge. In 2023, the company reported $120 million in R&D expenses, a 10% increase from 2022, demonstrating a clear strategy to reinforce its competitive advantages through technological advancement.
New entrants would need to either replicate this extensive R&D effort, a costly and time-consuming endeavor, or secure expensive licensing agreements for existing technologies. This high barrier effectively deters many potential market entrants, safeguarding the market share of incumbents like Stepan.
- Patented Formulations: Stepan holds numerous patents for its specialty chemical formulations, providing exclusive rights and market differentiation.
- Proprietary Manufacturing: The company employs unique manufacturing techniques developed over decades, leading to cost efficiencies and product quality advantages.
- Accumulated Expertise: Decades of experience in chemical synthesis and application development translate into invaluable technical knowledge that is difficult to replicate.
- R&D Investment: Stepan's consistent investment in research and development, totaling over $120 million in 2023, fuels continuous innovation and strengthens its intellectual property portfolio.
The threat of new entrants in the chemicals sector, specifically for companies like Stepan, is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for plant construction and technology, stringent regulatory compliance costs, and the advantage of economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents. Furthermore, established players benefit from proprietary technology, patents, and deep industry expertise, making market entry exceptionally challenging for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example (Stepan Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High cost of building and maintaining advanced chemical facilities. | Building a new chemical plant in 2024 can cost hundreds of millions to billions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting global environmental, health, and safety standards. | REACH registration costs can reach hundreds of thousands of euros per chemical. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale production and purchasing. | Stepan's purchasing power secures raw materials at lower prices than new entrants. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technology, patents, and accumulated expertise. | Stepan's 2023 R&D investment of $120 million protects its technological edge. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic data to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
