Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd Bundle
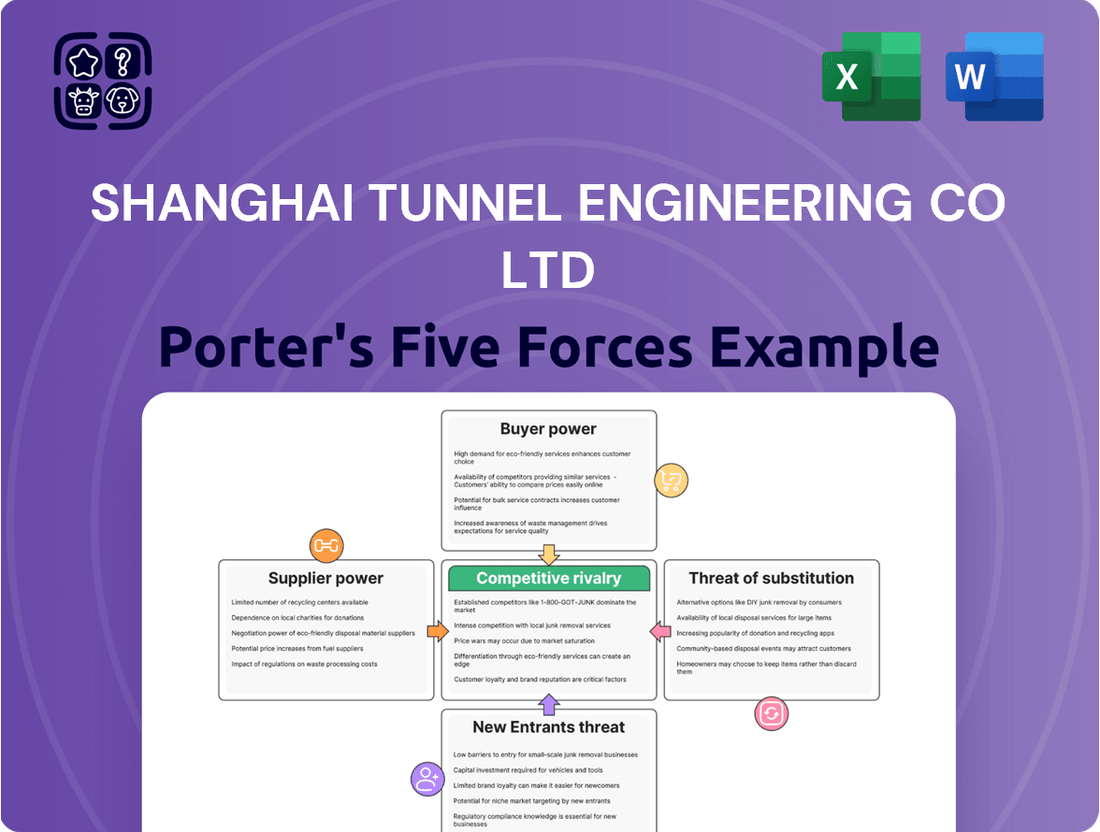
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, where the threat of new entrants is moderate due to high capital requirements. The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly for specialized machinery and materials, presents a notable challenge.
The threat of substitute products, while present in broader infrastructure development, is less direct for specialized tunneling projects, offering some stability. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized tunneling machinery and advanced engineering software wield considerable influence. Their power stems from the niche nature of their offerings, which are critical for STEC's complex underground projects.
A limited number of vendors can provide the cutting-edge technology STEC requires, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing. For instance, the global underground electric construction equipment market, a key segment for such suppliers, is expected to see substantial growth, reinforcing demand for advanced machinery.
The significant capital investment and lengthy procurement cycles for this sophisticated equipment further bolster supplier leverage. This creates a dependency for STEC, as acquiring these essential assets involves high costs and extended lead times, solidifying the suppliers' bargaining position.
Suppliers of essential raw materials for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), such as steel, concrete, and specialized chemicals, generally hold moderate bargaining power. These materials are largely standardized, but the sheer volume required for large infrastructure projects means STEC is sensitive to supply chain stability and price volatility. For example, the cost of construction materials experienced a notable increase in 2024, directly influencing supplier negotiations and STEC's project economics.
The availability of highly skilled engineers and specialized construction workers significantly bolsters supplier power for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. (STEC). Professionals with deep expertise in complex underground engineering are in high global demand, and their relative scarcity can translate into increased wage expectations and recruitment hurdles for STEC.
This dependency on a specialized workforce, including recruitment agencies and individual expert consultants, elevates the bargaining power of labor suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior tunneling engineer in major global infrastructure hubs often exceeded $150,000 annually, reflecting this demand.
Subcontractors for Niche Services
For highly specialized tasks within its tunnel engineering projects, Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) may depend on a select few subcontractors possessing unique expertise or certifications. These niche service providers can leverage their limited availability to dictate terms and pricing, as finding suitable replacements quickly is challenging.
The bargaining power of these subcontractors is amplified by the critical nature of their contributions to STEC's complex, integrated projects. Any disruption or compromise in quality from these specialized suppliers can lead to significant delays and cost overruns, impacting STEC's overall project execution and profitability. For instance, a delay in a specialized geological survey subcontractor could push back the entire tunneling schedule, incurring penalties for STEC.
- Limited Alternatives: STEC may face a scarcity of qualified subcontractors for specific, highly technical aspects of tunnel construction.
- Price Setting Ability: The unique skill sets of these subcontractors allow them to command higher prices due to the difficulty in sourcing comparable services.
- Project Interdependence: Delays or quality issues from niche subcontractors can have a cascading negative effect on STEC's project timelines and budgets.
- Impact on STEC's Operations: The inability to secure these specialized services on favorable terms can directly affect STEC's competitive bidding and project profitability.
Financial Institutions and Funding
Financial institutions are critical suppliers for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), providing essential capital through project financing, bonds, and credit lines. The substantial financial needs of large infrastructure projects mean these institutions hold considerable sway. Their bargaining power is amplified by the prevailing interest rate environment and the overall health of credit markets, directly impacting STEC's cost of capital. For instance, STEC's ability to secure favorable terms on its funding in 2024 and 2025 would be a direct reflection of these suppliers' influence and STEC's own credit standing.
- Capital as a Supplier: Banks and other financial entities act as suppliers of crucial funding for STEC's extensive projects.
- Influence of Market Conditions: Interest rates and credit availability significantly shape the bargaining power of these financial suppliers.
- STEC's Creditworthiness: The company's financial health directly affects the cost and accessibility of capital from these institutions.
- Impact on Project Viability: Favorable or unfavorable financing terms from these suppliers can make or break the economic feasibility of STEC's ventures.
Suppliers of specialized tunneling equipment and advanced engineering software possess significant bargaining power due to the niche nature of their products, critical for STEC's complex projects. The limited number of vendors capable of providing cutting-edge technology allows them to influence pricing and terms. For instance, the global underground construction equipment market is projected for robust growth, underscoring continued demand for these specialized suppliers.
The bargaining power of raw material suppliers, such as those providing steel and concrete, is generally moderate for STEC. While these materials are standardized, the substantial volumes required for infrastructure projects make STEC sensitive to price fluctuations and supply chain stability, especially given that construction material costs saw notable increases in 2024.
Labor suppliers, particularly those providing highly skilled tunneling engineers and specialized construction workers, wield considerable influence. The high global demand and relative scarcity of professionals with deep expertise in complex underground engineering can lead to increased wage expectations, impacting STEC's recruitment efforts. In 2024, senior tunneling engineers in major hubs earned upwards of $150,000 annually.
Niche subcontractors with unique expertise or certifications also hold significant bargaining power. Their limited availability for highly specialized tasks means they can dictate terms, as finding quick replacements is challenging. Any disruption from these critical suppliers can lead to project delays and cost overruns for STEC, highlighting their leverage.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power | Example Data/Trend (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Machinery & Software | High | Niche products, limited vendors, critical technology | Global underground construction equipment market growth |
| Raw Materials (Steel, Concrete) | Moderate | Standardized products, high volume sensitivity, price volatility | Construction material cost increases in 2024 |
| Skilled Labor (Tunneling Engineers) | High | High demand, scarcity of expertise, specialized skills | Senior tunneling engineer salaries exceeding $150,000 annually (2024) |
| Niche Subcontractors | High | Unique expertise, limited availability, critical project interdependence | Project delays due to subcontractor issues |
What is included in the product
Explores market dynamics that deter new entrants and protect incumbents like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd, detailing competitive rivalry, buyer/supplier power, and the threat of substitutes.
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd's Porter's Five Forces Analysis acts as a pain point reliever by providing a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Government and public sector clients, especially for large-scale infrastructure projects, possess substantial bargaining power over companies like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC). These entities often control the entire tender process, which typically involves multiple competing firms, allowing them to secure favorable pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, many government infrastructure tenders worldwide saw significant cost overruns in initial bids, leading to intense negotiation and downward pressure on final awarded prices.
Furthermore, government bodies wield considerable influence through their regulatory authority and control over project funding and approvals. This oversight means they can significantly impact project timelines and profitability, giving them leverage to negotiate more aggressively. The sheer scale of public projects means that securing these contracts is vital, making firms more amenable to client demands.
The global market for major underground infrastructure projects, while substantial in value, is characterized by a finite number of large-scale contracts. This limited pool of high-value opportunities means that potential clients, often government entities or large corporations, hold considerable bargaining power.
For Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), this concentration of demand translates into situations where a few key clients can exert significant influence. For instance, in 2024, major infrastructure developments like high-speed rail extensions or significant urban transit upgrades represent the primary targets for STEC, and these often involve a single dominant client.
Customers can effectively use this scarcity to their advantage, pushing for more competitive pricing, tighter delivery schedules, and expanded project specifications. This dynamic is particularly evident in bidding processes for flagship projects, where the limited number of qualified contractors amplifies the client's leverage.
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd.'s (STEC) customers, often large government bodies or consortiums, hold significant bargaining power due to the highly customized nature of infrastructure projects. Each project demands unique engineering solutions, giving clients considerable sway over design specifications and material choices. This bespoke approach means STEC must tailor its services precisely to client needs, limiting its ability to standardize offerings.
Reputation and Track Record
Customers, especially government entities, highly prioritize a contractor's history of successful project completion, safety statistics, and consistent on-time, on-budget delivery. This strong reputation, while beneficial for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), also creates an expectation of unwavering excellence.
Any slip in performance can empower clients to demand better terms or explore other contractors for subsequent projects. For instance, a single significant delay on a major infrastructure project, even if resolved, could embolden future clients to negotiate harder on pricing or payment schedules. STEC's 2024 performance metrics, particularly concerning project timelines and budget adherence, are crucial in managing this customer leverage.
- Reputation as a Key Lever: Public sector clients often prioritize reliability and a clean safety record, giving them significant bargaining power.
- Performance Expectations: STEC's established track record means clients expect perfection, making any deviation a potential point of negotiation.
- Impact of Lapses: Perceived failures in delivery can lead customers to seek concessions or alternative suppliers for future engagements.
- Data-Driven Defense: Maintaining strong 2024 performance data on project completion and safety is vital to counter customer bargaining power.
Price Sensitivity in Public Projects
Customers in public projects, including those undertaken by Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is driven by strict budget allocations and the need for public accountability, compelling them to seek the most cost-effective solutions available.
This heightened price sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. It necessitates that STEC and similar firms engage in highly competitive bidding processes, often leading to reduced profit margins.
The pressure to offer competitive pricing was particularly evident in 2024. Data indicates that infrastructure projects experienced average cost reductions, a direct consequence of intense competition among bidding companies.
- Price Sensitivity: Public project clients prioritize cost-effectiveness due to budget limitations and public scrutiny.
- Impact on Margins: Intense bidding and price sensitivity can compress profit margins for engineering firms like STEC.
- 2024 Trend: Infrastructure projects in 2024 saw average cost reductions driven by aggressive competition.
Customers, particularly government bodies managing large infrastructure projects, possess considerable bargaining power due to their ability to influence tender processes and control funding. This leverage is amplified by the finite number of high-value contracts available, forcing firms like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) into competitive bidding. For example, in 2024, many global infrastructure tenders saw intense price negotiations, leading to reduced final awarded prices, directly impacting STEC's potential margins.
| Factor | Description | Impact on STEC | 2024 Relevance |
| Client Concentration | Limited number of large-scale project clients. | Increased client leverage over pricing and terms. | Key infrastructure developments in 2024 concentrated demand. |
| Price Sensitivity | Government clients prioritize cost-effectiveness due to budgets and accountability. | Pressure for competitive pricing, potentially reducing profit margins. | Average cost reductions observed in infrastructure projects in 2024. |
| Reputation & Performance | Clients demand proven track records, safety, and timely delivery. | Any performance lapse can empower clients to negotiate harder. | STEC's 2024 performance metrics are crucial for managing this. |
What You See Is What You Get
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing actionable insights into the strategic positioning of STECL within the global infrastructure development sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) faces significant competitive rivalry in the Chinese construction market, largely due to the pervasive presence of large state-owned enterprises (SOEs). These SOEs, like China State Construction Engineering and China Railway Group, command substantial resources and enjoy strong government support, creating an intensely competitive landscape for major domestic projects. For instance, in 2023, China State Construction Engineering reported a revenue of over 1.8 trillion RMB, showcasing their immense scale and market dominance.
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) contends with formidable global construction conglomerates beyond its domestic state-owned enterprises. Companies like China Communications Construction Company (CCCC), Bechtel, and Vinci actively vie for the same high-value international infrastructure contracts that STEC targets. These global rivals often possess greater financial reserves and a broader spectrum of technological expertise, intensifying competition in global tenders.
The competitive landscape for large-scale tunnel and infrastructure projects is characterized by a handful of major international players who can mobilize significant capital and sophisticated engineering capabilities. For instance, in 2023, global infrastructure spending continued its upward trajectory, with major projects in North America and Asia attracting bids from multiple multinational firms. STEC's strategy must therefore focus on leveraging its specialized tunneling technology and cost efficiencies to secure a competitive edge against these well-resourced international competitors.
The heavy civil engineering sector, which Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. (STEC) operates within, is defined by substantial fixed costs. These include investments in specialized machinery, a highly trained workforce, and essential design expertise. For instance, major tunnel boring machines can cost tens of millions of dollars, representing a significant upfront capital outlay.
These high fixed costs create a powerful incentive for companies like STEC to constantly secure new projects. The continuous need to cover overheads drives aggressive bidding and intense competition among players in the market. This dynamic often leads to price wars as firms vie for contracts.
The inherently project-based nature of the industry means that STEC and its rivals are perpetually in pursuit of the next available contract. This constant competition for work intensifies rivalry, as securing a steady pipeline of projects is crucial for maintaining operational stability and profitability. In 2023, STEC reported revenue of approximately ¥102.5 billion (around $14.2 billion USD), underscoring the scale of operations and the need for consistent project acquisition.
Differentiation based on Expertise and Technology
Competitive rivalry in the underground engineering sector extends beyond mere pricing, focusing heavily on specialized technical know-how, novel construction techniques, and cutting-edge tunneling technology. Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) and its peers must consistently allocate resources to research and development alongside nurturing their workforce to stay ahead. For instance, in 2023, STEC reported significant investments in technological advancements, contributing to its ability to secure large-scale infrastructure projects globally.
The capacity to successfully execute intricate and technically demanding projects with high efficiency is a critical factor that sets leading companies apart. STEC's track record, including its involvement in landmark projects like the Gotthard Base Tunnel's expansion phases, showcases this technical prowess. This differentiation is crucial as clients increasingly prioritize reliability and innovative solutions over cost alone, especially for projects with long-term implications.
- Technical Expertise: The ability to handle complex geological conditions and design innovative solutions is paramount.
- Technological Adoption: Early and effective integration of advanced tunneling equipment and software provides a significant advantage.
- Project Execution: A proven history of delivering large, complex projects on time and within budget builds client trust and market reputation.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in research and development allows companies to offer more efficient and sustainable tunneling methods.
Government Infrastructure Spending and Policy
Government infrastructure spending is a major driver of competition for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd. China's commitment to infrastructure development, particularly in areas like smart cities and transportation networks, fuels demand. For instance, the nation's fixed-asset investment in infrastructure projects reached trillions of yuan in recent years, creating a large market. This robust spending environment generally softens rivalry by offering ample opportunities for many firms. However, fluctuations in government investment can directly impact competitive intensity; periods of reduced spending force companies to vie more aggressively for a smaller pool of projects.
The level of government investment in infrastructure development significantly impacts the intensity of competitive rivalry. China's infrastructure market is forecast to grow, with government initiatives and smart city technologies fueling demand. Periods of high spending can reduce rivalry by providing more opportunities, while slowdowns can intensify it as companies fight for fewer projects. For example, the Belt and Road Initiative, a significant infrastructure push, has historically opened new avenues for companies like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering. When such large-scale projects are announced, the competition to secure contracts can be fierce, but the sheer volume of work can also absorb multiple players.
- Government investment levels directly shape competitive intensity in China's infrastructure sector.
- Forecasts indicate continued growth in the infrastructure market, driven by smart city technologies and government initiatives.
- Periods of high government spending tend to dilute competitive rivalry by increasing available projects.
- Conversely, slowdowns in infrastructure investment heighten competition as companies scramble for limited opportunities.
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) operates in a fiercely competitive environment, characterized by numerous players, both domestic and international. The presence of large state-owned enterprises in China, such as China State Construction Engineering, with revenues exceeding 1.8 trillion RMB in 2023, creates a significant challenge due to their scale and government backing. Global giants like Bechtel and Vinci also vie for major infrastructure contracts, bringing substantial financial and technological advantages, intensifying rivalry for STEC.
High fixed costs, including the substantial investment in specialized machinery like tunnel boring machines costing tens of millions of dollars, incentivize aggressive bidding among firms. This drives a constant pursuit of new projects to cover overheads, often leading to price wars. The project-based nature of the industry further fuels this rivalry, as securing a consistent project pipeline is crucial for operational stability. In 2023, STEC's revenue of approximately ¥102.5 billion ($14.2 billion USD) highlights the scale of operations and the perpetual need for contract acquisition.
Competitive rivalry is also shaped by the need for specialized technical expertise and advanced tunneling technology, pushing companies like STEC to invest heavily in R&D. Differentiation through proven project execution and innovation is key, as clients increasingly prioritize reliability. STEC's involvement in projects like the Gotthard Base Tunnel expansion underscores its technical prowess in this high-stakes arena.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC), the threat of substitutes in urban transit is a significant consideration. While subways are a core business, alternatives like Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) systems and elevated rail networks pose a competitive threat. These options can sometimes be implemented more quickly and at a lower initial capital cost compared to extensive underground tunneling. For instance, many cities in 2024 are prioritizing phased infrastructure development, making BRT and light rail attractive for immediate capacity improvements.
The appeal of these alternatives stems from their potential for faster deployment and potentially lower upfront investment. Municipalities, especially those with budget constraints or urgent needs for improved transit, might favor BRT or surface-level rail over the complex and time-consuming process of subway construction. This can divert public funding and demand away from STEC's core tunneling services. The global trend in urban development in 2024 shows a continued focus on integrated transport solutions, where these alternatives play a crucial role.
Traditional above-ground construction presents a significant substitute for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd's (STEC) underground space utilization projects. For general urban space needs, such as parking or commercial facilities, building upwards is often a more familiar and sometimes more cost-effective approach. In 2024, the global construction market saw continued investment in high-rise buildings, indicating a strong preference for vertical expansion where feasible.
While STEC's underground solutions offer advantages like minimal surface disruption and efficient land use, especially in densely populated areas like Shanghai, above-ground alternatives can be more appealing. Factors such as established construction methods, potentially lower initial capital outlay for certain project types, and direct street-level accessibility can steer developers towards conventional building. For instance, the cost per square foot for a new office building above ground can be significantly lower than developing a comparable underground space, making it a competitive alternative for many commercial ventures.
The renovation and upgrade of existing infrastructure present a significant threat of substitutes for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC). Instead of investing in entirely new underground projects, clients might opt for extensive upgrades or expansions of current above-ground or older underground systems. This can be a more budget-friendly and less disruptive alternative to new construction. For instance, in 2024, many cities globally are re-evaluating their infrastructure spending, with a growing focus on rehabilitation projects over greenfield developments to optimize capital allocation.
STEC's core business in new tunnel construction and large-scale underground engineering can be partially substituted by firms specializing in infrastructure rehabilitation. These companies might focus on reinforcing aging tunnels, upgrading existing subway lines, or enhancing public transport networks through less invasive methods. The global infrastructure rehabilitation market is projected to see substantial growth, driven by the need to maintain and extend the lifespan of existing assets, potentially diverting investment from new STEC projects.
Technological Advancements in Surface Solutions
Technological advancements in surface transportation and urban planning pose a threat of substitution for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC). Innovations like advanced traffic management systems, which can optimize existing road networks, or compact modular building techniques that allow for denser surface development, could decrease the perceived need for extensive underground infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, many cities are investing heavily in smart city initiatives focused on surface-level efficiency, potentially diverting funds and attention from subterranean projects.
While these advancements do not directly replace tunneling’s function for specific transit needs, they can subtly shift urban development priorities. If surface solutions become significantly more efficient and cost-effective, the strategic advantage of underground construction might diminish. The long-term viability and scalability of these surface alternatives are key factors influencing demand for STEC's core services.
- Smart City Investments: Global smart city market projected to reach over $3.5 trillion by 2030, with significant portions allocated to traffic and mobility solutions.
- Modular Construction Growth: The global modular construction market is expected to grow, indicating increased feasibility of rapid surface-based development.
- Urban Planning Focus: Many metropolitan areas are prioritizing integrated urban planning that emphasizes surface-level connectivity and sustainability.
Shift in Urban Development Paradigms
A significant shift in how cities are planned and developed could present a threat of substitution for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC). For instance, a move towards more decentralized urban models or a reduced emphasis on massive public transportation systems might lessen the need for new underground infrastructure projects. While these alternative development styles are unlikely to completely eliminate the demand for tunnels, they could certainly influence investment priorities and potentially divert funding away from STEC's core competencies.
Consider the potential impact on infrastructure spending. For example, if urban planning trends in major global cities, like those observed in 2024, continue to favor smaller, distributed development hubs over the large, centralized transit networks traditionally requiring extensive tunneling, STEC could see a slowdown in certain types of project pipelines. This represents a more subtle, long-term substitution threat that requires ongoing monitoring of urban planning philosophies and technological advancements in alternative transportation solutions.
- Decentralization Trends: Cities exploring polycentric development models may reduce the need for massive, radial transit tunnels.
- Alternative Transportation: Advancements in surface-level autonomous vehicles or elevated transit could offer substitutes for underground systems.
- Reprioritization of Infrastructure: Governments might shift capital towards digital infrastructure or green energy projects instead of large-scale civil engineering.
- Reduced Urban Density: A widespread move towards lower-density living could decrease reliance on the high-capacity transit often facilitated by tunnels.
The threat of substitutes for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) is multifaceted, encompassing alternative transit systems and different urban development approaches. Options like Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) and elevated rail can be quicker to deploy and require less initial capital than subway projects, making them attractive in 2024 for cities needing immediate transit improvements. Furthermore, above-ground construction for space utilization, such as parking or commercial facilities, often represents a more conventional and sometimes less expensive alternative to underground development, especially with ongoing investment in high-rise buildings globally.
Infrastructure rehabilitation also serves as a substitute, as cities may opt to upgrade existing systems rather than invest in new tunnels. This trend, noted in 2024's infrastructure spending re-evaluations, prioritizes extending the life of current assets. Additionally, technological advancements in surface transportation and smart city initiatives can optimize existing networks, potentially reducing the perceived need for extensive underground infrastructure and diverting funds from subterranean projects.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on STEC | 2024 Trend Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Transit (BRT, Elevated Rail) | Faster deployment, lower initial capital cost | Diverts demand from subway projects | Cities prioritize phased development |
| Above-Ground Construction | Familiar methods, potentially lower upfront cost for certain uses | Competes for urban space development | Continued investment in high-rise buildings |
| Infrastructure Rehabilitation | Budget-friendly, less disruptive than new builds | Reduces investment in greenfield tunneling | Focus on maintaining existing assets |
| Surface Tech & Smart Cities | Optimizes existing networks, shifts priorities | Diminishes strategic advantage of underground construction | Heavy investment in surface-level efficiency |
Entrants Threaten
The heavy civil and underground engineering sector, where Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. operates, presents a formidable threat of new entrants primarily due to exceptionally high capital investment requirements. Aspiring competitors must secure substantial funding to acquire specialized tunneling boring machines (TBMs), which can cost tens of millions of dollars each, alongside advanced surveying equipment and robust safety systems.
For instance, a single large-diameter TBM can easily exceed $50 million, and a comprehensive suite of supporting machinery and technology for complex projects can push initial outlays into the hundreds of millions. This immense upfront financial barrier significantly deters potential new players from entering the market, effectively protecting existing firms like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering.
Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd operates in a sector where specialized expertise and technical know-how represent a significant barrier to new entrants. The intricate design, construction, and project management of complex tunnels and underground infrastructure demand a deep understanding of geotechnical engineering, advanced materials, and sophisticated construction techniques. This isn't knowledge easily replicated; it's built over years of hands-on experience and continuous learning.
Developing this level of technical acumen requires a substantial investment in human capital, including attracting and retaining highly skilled engineers and specialized labor. For instance, the successful completion of projects like the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge's undersea tunnel sections, a feat requiring immense engineering precision, underscores the specialized skills involved. New companies would need to navigate this steep learning curve, a process that typically takes many years, making it difficult to compete with established players like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd.
The infrastructure construction sector, where Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd (STEC) operates, is characterized by substantial regulatory hurdles. New entrants must navigate a complex web of permits, licenses, and rigorous compliance with safety and environmental standards. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain all necessary permits for a major infrastructure project in China could extend several months, representing a significant upfront investment and operational delay for newcomers.
STEC, as an established player, possesses a deep understanding and extensive experience in managing these intricate regulatory processes. This includes cultivating long-standing relationships with governmental bodies and regulatory agencies, which can expedite approvals and ensure compliance. Such established networks and proven track records are difficult for new entrants to replicate, thereby acting as a considerable barrier to entry.
Established Client Relationships and Reputation
Established client relationships and reputation act as a significant barrier to entry for new competitors in Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co Ltd's (STEC) sector, particularly within the public sector. For government entities and public works agencies, trust, reliability, and a demonstrable history of successful project delivery are non-negotiable requirements. STEC, with its extensive operational history and a portfolio of completed, complex infrastructure projects, has cultivated deep-seated relationships and a strong, reputable brand. This established credibility makes it challenging for new entrants to gain traction, as clients are inherently risk-averse when awarding large-scale, high-stakes projects to organizations without a proven track record.
New players find it difficult to overcome the entrenched trust STEC enjoys. For instance, public sector clients often prioritize long-term partnerships and a known quantity, making the initial hurdle for an unknown entity extremely high. This preference for reliability means that STEC can leverage its reputation to secure bids without necessarily competing solely on price, further deterring less established firms. The sheer weight of STEC's past performance, often backed by government commendations or industry awards, solidifies its position and discourages potential new entrants from even attempting to challenge its market share in these crucial segments.
- Proven Track Record: STEC's history of successful tunnel and infrastructure projects provides a tangible demonstration of capability.
- Public Sector Trust: Government clients prioritize reliability and established relationships, which STEC possesses.
- High-Value Projects: The significant investment and risk associated with major infrastructure projects favor experienced and trusted contractors.
- Brand Reputation: STEC's strong brand image, built over years of consistent performance, acts as a deterrent to new entrants.
Economies of Scale and Project Scale
Established players like Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. (STEC) leverage significant economies of scale. This advantage is evident in their ability to secure better pricing on materials and equipment due to bulk purchasing and their optimized project management processes honed over years of experience. In 2023, STEC's revenue reached approximately ¥75.5 billion, reflecting the substantial scale of operations it commands.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in matching STEC's cost efficiency. Without the same volume of business, they will likely incur higher per-unit costs for materials and labor, making it difficult to compete on price for large infrastructure projects. Furthermore, the capital required to undertake projects of the scale typically handled by STEC, such as major subway lines or complex tunnel systems, presents a significant financial barrier.
- Economies of Scale: STEC's large operational volume allows for cost reductions in procurement and project execution.
- Project Scale Barrier: The sheer size and complexity of infrastructure projects favor well-capitalized and experienced firms.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: Entrants operating at a smaller scale will face higher unit costs, impacting competitiveness.
- Capital Intensity: The substantial investment needed for large projects deters smaller, less-established companies.
The threat of new entrants for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. (STEC) remains moderate to low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for specialized equipment, like Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs) costing upwards of $50 million, and the need for extensive geotechnical expertise deter many potential competitors. Furthermore, navigating complex regulatory landscapes and securing necessary permits, which can take months in 2024, adds significant upfront investment and delay.
Established client relationships, particularly with public sector entities, and STEC's strong brand reputation built on a history of successful, large-scale projects, also create a significant hurdle for newcomers. The sector's reliance on proven track records and trust means new firms struggle to gain the confidence needed for high-value contracts. STEC's operational scale, evidenced by its approximately ¥75.5 billion revenue in 2023, allows for economies of scale that new entrants cannot easily match, leading to a cost disadvantage.
| Barrier Category | Specific Factor | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Cost of TBMs and heavy machinery | Very High |
| Technical Expertise | Need for specialized geotechnical and engineering knowledge | High |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Permitting processes and compliance standards | Moderate to High |
| Customer Relationships | Established trust and reputation with public sector clients | High |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from bulk purchasing and operational volume | High |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Co. Ltd. is built upon a foundation of rigorous data collection, drawing from the company's annual reports, official stock exchange filings, and reputable industry-specific research from organizations like IBISWorld.
