Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Standard Chartered Bundle
Standard Chartered navigates a complex global financial landscape, shaped by distinct competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of buyer power, the threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of suppliers is crucial for any stakeholder. Furthermore, the presence of substitutes and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector significantly impact Standard Chartered's strategic options.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Standard Chartered’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Standard Chartered's dependence on technology providers for its digital banking, cybersecurity, and data analytics means these suppliers can wield significant influence. If their offerings are unique, highly specialized, or if migrating to a different provider incurs substantial costs and disruption for Standard Chartered, their bargaining power increases.
For instance, the global cloud computing market, a critical area for many banks, was valued at over $600 billion in 2023, with major players like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud often holding considerable leverage. The cost and complexity of transferring vast amounts of sensitive banking data and applications to a new cloud provider can be immense, making Standard Chartered's switching costs high.
This reliance underscores the need for Standard Chartered to cultivate strong, strategic relationships with its technology vendors. Proactive vendor management, including clear service level agreements and exploring multi-vendor strategies where feasible, is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with this supplier power.
The bargaining power of suppliers in human capital is significant for Standard Chartered, especially concerning skilled professionals in AI, data analytics, and cybersecurity. A global shortage of these specialized talents, particularly in key markets like Asia and the Middle East, amplifies their leverage. For instance, demand for AI specialists often outstrips supply, pushing up salaries and benefits.
To counter this, Standard Chartered needs robust talent acquisition and retention strategies. Investing in upskilling current employees and offering competitive compensation packages are crucial to securing access to essential expertise. This focus on human capital is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Financial market infrastructure providers, such as payment networks and clearing houses, wield considerable bargaining power. Their services are absolutely essential for banks like Standard Chartered to function, facilitating billions in daily transactions. For instance, SWIFT, a major financial messaging network, processed an average of 42 million messages per day in 2023, highlighting its critical role and limited substitutability for global banks.
The high barriers to entry for establishing and operating these critical systems mean there are few alternatives available to Standard Chartered. This inherent dependency limits the bank's ability to negotiate favorable terms or pricing, often resulting in standardized agreements for access to these vital operational components.
Data and Information Providers
Standard Chartered's reliance on high-quality financial data, market intelligence, and risk assessment tools places significant bargaining power with data and information providers. Companies that offer unique, comprehensive, or proprietary datasets can command higher prices or dictate terms. For instance, the global market for financial data and analytics services was projected to reach over $60 billion in 2024, indicating a substantial and concentrated supplier base in certain niches.
The bank must actively manage this relationship by implementing strong data governance practices and diversifying its data sources. This strategy helps mitigate the risk of over-dependence on a single supplier, which could otherwise lead to unfavorable contract negotiations or disruptions in service. Exploring alternative data providers and developing in-house analytical capabilities are key tactics.
- High data costs: Specialized financial data feeds can be extremely expensive, with some premium subscriptions costing tens of thousands of dollars annually.
- Limited alternatives: For certain niche market data, there may be only one or two dominant providers, increasing their leverage.
- Data quality and exclusivity: Providers with demonstrably superior data accuracy or exclusive datasets hold considerable sway.
- Integration challenges: Switching data providers can involve significant IT investment and integration effort, creating a barrier for the bank to move away from existing suppliers.
Regulatory Bodies and Central Banks
Regulatory bodies and central banks, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, wield significant power over Standard Chartered by shaping its operational framework. For instance, in 2024, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) continued to emphasize enhanced oversight of globally systemic banks, impacting capital adequacy and liquidity ratios for institutions like Standard Chartered.
Their influence is absolute; non-compliance with directives from entities such as the Bank of England or the Monetary Authority of Singapore can result in substantial fines, severe reputational damage, and even the suspension of critical banking activities. Standard Chartered's proactive engagement and adaptation to these evolving regulatory requirements, particularly in areas like digital asset regulation and anti-money laundering (AML) frameworks throughout 2024, are crucial for its continued stability and growth.
- Regulatory Influence: Central banks and financial regulators dictate capital requirements, operational standards, and compliance protocols, directly impacting profitability and strategy.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to stringent regulations, such as those related to Know Your Customer (KYC) and AML, incurs significant operational expenses for Standard Chartered.
- Strategic Adaptation: Banks must continuously adjust business models and technology investments to meet evolving regulatory demands, as seen with the focus on cybersecurity and data privacy in 2024.
- Reputational Risk: Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and irreparable damage to a bank's reputation, affecting customer trust and market position.
Standard Chartered's reliance on specialized technology providers for critical functions like cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics significantly enhances supplier bargaining power. The substantial costs and operational disruptions associated with switching major vendors, such as cloud service providers where the global market exceeded $600 billion in 2023, create high switching costs, limiting Standard Chartered's leverage.
The bank faces considerable bargaining power from financial market infrastructure providers, like payment networks and clearing houses, given their essential role and limited substitutability. For example, SWIFT's average daily message volume of 42 million in 2023 highlights its critical infrastructure dominance, making it difficult for Standard Chartered to negotiate terms or find alternatives.
Suppliers of essential financial data and analytics also hold significant leverage, especially those offering unique or proprietary information. With the global financial data and analytics market projected to exceed $60 billion in 2024, providers with superior data quality or exclusive datasets can command premium pricing, forcing Standard Chartered to manage these relationships carefully through diversification and internal capabilities.
What is included in the product
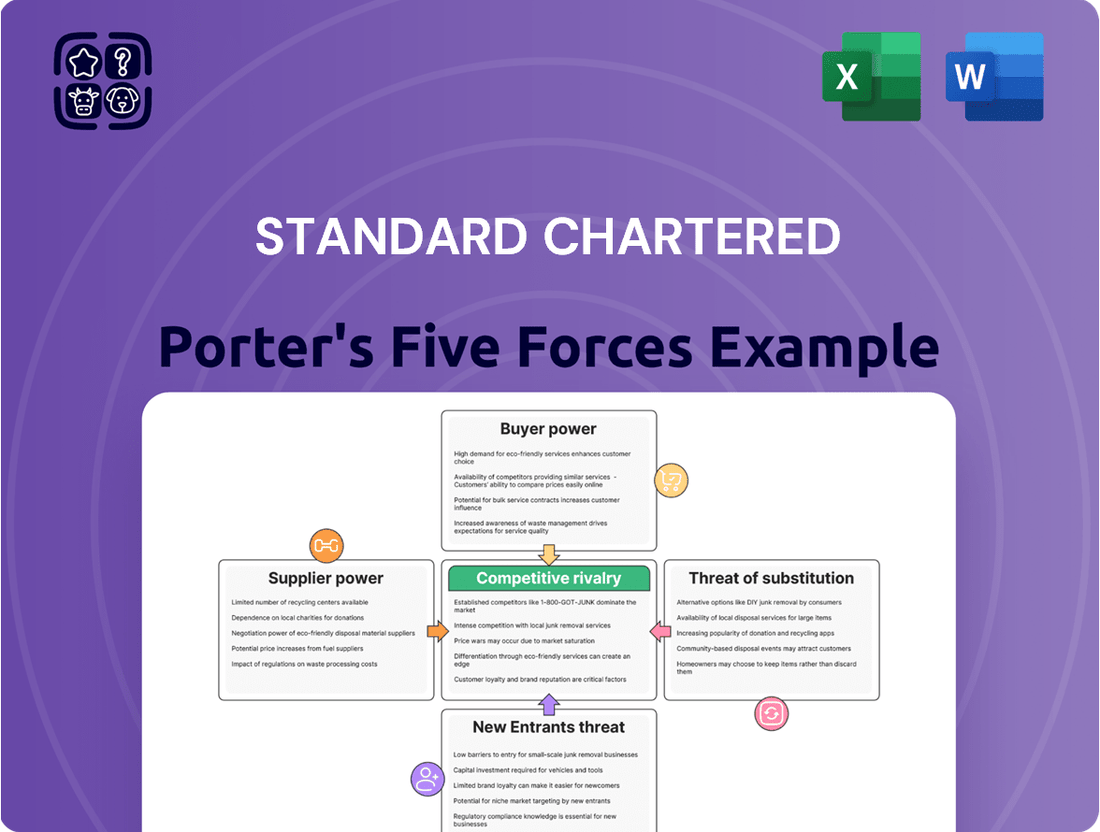
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Standard Chartered, providing insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, new entrant threats, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly assess competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for rapid identification of threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large corporate and institutional clients hold considerable sway over Standard Chartered. Their substantial transaction volumes and complex financial requirements mean they can often negotiate better rates and terms. For instance, in 2023, Standard Chartered reported significant revenue from its Corporate & Institutional business, highlighting the importance of these relationships.
These sophisticated clients are less likely to be locked into a single provider, fostering multi-banking relationships. This competitive landscape empowers them to seek out and secure more favorable pricing and bespoke service packages, directly impacting Standard Chartered's profit margins.
Affluent and High-Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) wield significant bargaining power within Standard Chartered's wealth management services. Their diverse investment needs and access to numerous financial advisors mean they can readily switch providers if service quality, personalization, or returns don't meet expectations. This segment is particularly discerning, demanding tailored solutions and competitive performance.
Standard Chartered recognizes this influence and is actively investing in its wealth management capabilities. The bank's strategy includes expanding its team of relationship managers, enhancing their advisory skills, and developing more sophisticated, personalized offerings. This focus aims to retain and attract HNWIs by demonstrating a commitment to meeting their sophisticated financial requirements and delivering superior value.
Retail banking customers, while individually possessing limited bargaining power due to smaller transaction volumes and generally low switching costs, collectively wield significant influence. The sheer volume of accounts across a bank's customer base means that even small changes in customer behavior can have a noticeable impact. For instance, in 2024, a slight shift in customer preference towards digital-only banks could pressure traditional institutions to enhance their online services.
The ongoing digitalization trend has dramatically reshaped customer expectations in retail banking. Customers now demand intuitive, personalized, and readily accessible services, pushing banks to compete fiercely on user experience and the breadth of their digital capabilities. This heightened expectation means that banks failing to offer cutting-edge digital platforms risk losing customers to more digitally adept competitors.
Access to Information and Digital Alternatives
The widespread availability of digital banking platforms and fintech innovations has significantly boosted customer bargaining power. For instance, by mid-2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, offering consumers a vast array of alternative financial services. This ease of access to information allows customers to readily compare offerings, fees, and service quality across traditional banks and newer digital players.
Customers are now better equipped to demand superior value due to increased financial literacy and the sheer volume of available choices. They can effortlessly research and switch providers, putting pressure on incumbent institutions like Standard Chartered to offer competitive rates and enhanced services. This dynamic is evident in the growing adoption of digital-only banks, which often attract customers with lower fees and more user-friendly interfaces.
- Increased Information Accessibility: Customers can easily research and compare financial products and services online, reducing information asymmetry.
- Rise of Fintech Alternatives: The proliferation of fintech companies provides consumers with more choices beyond traditional banks.
- Digital Platform Adoption: Growing use of digital banking platforms facilitates customer switching and comparison shopping.
- Enhanced Price Sensitivity: Greater transparency in fees and interest rates makes customers more sensitive to pricing differences.
Low Switching Costs for Certain Services
For many basic banking services, customers can switch providers with relative ease. This is particularly true with the growth of digital-only banks and the implementation of open banking, which facilitates data sharing and makes it simpler for customers to move their accounts. For instance, in 2024, the number of customers using challenger banks continued to grow, demonstrating this trend.
This low switching cost directly impacts Standard Chartered, as it necessitates a constant focus on improving its offerings. The bank must work harder to retain its customers by providing a superior value proposition, excellent customer service, and attractive loyalty programs. Failing to do so could lead to a higher rate of customer attrition.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily move their accounts for basic banking services, especially with digital banks.
- Impact on Standard Chartered: This pressure requires continuous enhancement of services and customer experience to retain clients.
- Digitalization Trend: The rise of digital-only banks in 2024 highlights the increasing ease of customer mobility.
- Competitive Necessity: Banks like Standard Chartered must invest in loyalty programs and value-added services to counter this customer power.
The bargaining power of Standard Chartered's customers is substantial, driven by increased information accessibility and the proliferation of fintech alternatives. Customers, particularly in the retail segment, can easily compare services and switch providers, especially with the growth of digital-only banks. This necessitates that Standard Chartered consistently offers competitive pricing and superior customer experiences to retain its client base.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Standard Chartered |
|---|---|---|
| Large Corporate & Institutional Clients | High transaction volumes, complex needs, ability to negotiate terms | Pressure on pricing, need for tailored solutions |
| Affluent & High-Net-Worth Individuals | Diverse investment needs, access to multiple advisors, demand for personalization | Need for superior service, competitive returns, and bespoke offerings |
| Retail Banking Customers | Low switching costs, digital platform adoption, price sensitivity | Pressure to enhance digital services, offer competitive rates, and improve user experience |
Preview Before You Purchase
Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the precise Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll obtain immediately after completing your purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing components. You're viewing the actual, comprehensive document, meticulously crafted and formatted, which will be instantly accessible for your review and utilization upon successful transaction. This is not a sample or placeholder; the detailed analysis of competitive forces impacting Standard Chartered, as displayed here, is precisely what you will receive, ready for immediate application. Rest assured, the document presented is the complete, professionally developed analysis that will be yours to download and leverage without delay after your purchase is finalized.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Standard Chartered operates in a highly competitive landscape, facing robust rivalry from both global banking giants and formidable regional institutions. These competitors, particularly in its core Asian, African, and Middle Eastern markets, offer a comparable suite of financial services.
The intensity of this competition is evident in the ongoing battle for market share, especially within lucrative segments like corporate and investment banking, as well as wealth management. For instance, in 2023, major players like HSBC reported pre-tax profits exceeding $24 billion, underscoring the scale and financial clout of direct competitors.
This fierce environment means Standard Chartered must constantly innovate and differentiate its offerings to attract and retain customers. The constant pressure from rivals necessitates strategic pricing, superior customer service, and cutting-edge digital solutions to maintain a competitive edge.
The competitive landscape for Standard Chartered is significantly shaped by fintech companies and digital-only banks. These agile players are disrupting traditional banking by offering innovative, often cheaper, and highly specialized services. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, demonstrating the scale of this challenge.
These new entrants excel at targeting specific market segments, such as peer-to-peer lending or digital payments, forcing established institutions like Standard Chartered to adapt. Their digital-first approach allows for lower overheads, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing on services. This pressure compels incumbents to accelerate their digital transformation efforts to remain relevant.
Examples like Revolut, which boasts over 40 million customers globally as of early 2024, highlight the rapid customer acquisition these digital banks can achieve. Such growth puts direct pressure on traditional banks to enhance their digital offerings and customer experience to compete effectively in areas like international money transfers and retail banking.
Competitive rivalry in banking hinges on differentiation. Standard Chartered highlights its extensive network across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East as a key advantage, allowing it to facilitate complex cross-border transactions. For instance, in 2023, the bank reported significant growth in its transaction banking services, a testament to its specialized capabilities in supporting international trade flows.
Furthermore, the bank's commitment to sustainable finance is a growing differentiator. As of the first half of 2024, Standard Chartered has been actively involved in advising on and underwriting a substantial volume of green and sustainable bonds, signaling a strategic move to capture market share in this expanding sector.
The push towards advanced digital platforms also intensifies competition. Standard Chartered's investments in digital banking solutions aim to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency, directly competing with fintechs and other traditional banks leveraging technology to offer streamlined services and innovative products.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Costs
The banking sector is heavily regulated, and this trend is only intensifying. For instance, in 2024, banks are facing heightened scrutiny and evolving requirements around Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations. These ongoing updates necessitate substantial investments in technology and personnel to ensure compliance.
These compliance costs, including those related to data privacy like GDPR and cybersecurity mandates, can indeed create barriers for new entrants. However, for established players like Standard Chartered, these costs also intensify competition. Banks must allocate significant capital to build and maintain robust compliance frameworks, which directly impacts their operational expenses and, consequently, their profitability and competitive standing.
- Increased Investment in Compliance: In 2024, global banks are projected to spend upwards of $30 billion annually on AML compliance alone, a figure expected to grow as regulations become more stringent.
- Data Privacy Mandates: Compliance with evolving data privacy laws, such as those being updated in various jurisdictions in 2024, requires continuous adaptation of data handling and security protocols, adding to operational overhead.
- Cybersecurity Expenditure: The escalating threat landscape means banks are increasing their cybersecurity budgets, with many allocating over 10% of their IT spend to security measures to meet regulatory expectations and protect customer data.
Market Growth and Consolidation
While some emerging markets present growth avenues, the overall market expansion in established banking sectors is projected to be moderate. For instance, in 2024, the global banking industry's growth rate was anticipated to be around 3-5%, a slight uptick from previous years but still indicative of maturity.
This scenario intensifies rivalry as institutions aggressively vie for existing customer bases. The pursuit of scale and operational efficiencies becomes paramount, driving industry consolidation. In 2023, the banking sector saw significant M&A activity, with major deals in the US and Europe aimed at creating larger, more resilient entities capable of weathering economic shifts and investing in technological advancements.
- Moderate Growth: Mature banking markets are expected to see subdued growth in 2024, estimated between 3-5% globally.
- Intensified Competition: Slower growth fuels aggressive competition for market share and customer retention.
- Consolidation Trend: Banks are increasingly merging to achieve economies of scale and enhance competitiveness, as evidenced by numerous M&A deals in 2023.
- Efficiency Drive: Consolidation is driven by the need for greater operational efficiency and the ability to invest in digital transformation.
Standard Chartered faces intense competition from established global banks and agile fintechs, particularly in its key emerging markets. The pressure to innovate is constant, driving the need for superior digital offerings and customer service to maintain market share. In 2024, the banking sector's moderate growth, estimated at 3-5% globally, intensifies this rivalry, pushing for consolidation and efficiency gains.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators / Challenges | Example (2023-2024 Data) |
| Global Banking Giants | Scale, financial clout, broad service offerings | HSBC pre-tax profits exceeding $24 billion (2023) |
| Regional Institutions | Deep local market knowledge, established networks | Strong performance in specific Asian and African markets |
| Fintech & Digital Banks | Agility, lower overheads, specialized services, customer acquisition | Revolut with over 40 million customers globally (early 2024); Global fintech market valued at ~$2.4 trillion (2023) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech payment solutions presents a substantial threat to traditional banking. Mobile payment apps, digital wallets, and P2P platforms from non-bank providers are increasingly popular due to their convenience, lower costs, and speed. For instance, by the end of 2024, global mobile payment transaction volume is projected to exceed $10 trillion, demonstrating a clear shift away from traditional methods.
Embedded finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) significantly heighten the threat of substitutes for traditional banking. These models allow non-financial companies to offer financial products, like payments or loans, directly within their customer journeys. For instance, a retail platform might offer point-of-sale financing, bypassing traditional lenders entirely.
This integration disintermediates banks, shifting the customer relationship away from the financial institution. The market for embedded finance is projected for substantial growth; estimates suggest it could reach $7 trillion globally by 2030, according to some industry reports from late 2023/early 2024. This growth signifies a direct challenge to banks’ traditional roles.
BaaS providers, in particular, enable fintechs and other businesses to offer regulated financial services, effectively creating alternative channels for banking products. This makes it easier for new players to enter the market, offering specialized or more convenient financial solutions that substitute for those provided by incumbent banks.
Direct lending platforms and crowdfunding initiatives present a significant threat of substitutes for Standard Chartered's traditional banking services. For corporate and SME clients, these alternatives offer a path to financing that bypasses conventional bank loans, often with greater speed and flexibility. For instance, in 2024, the global alternative lending market, which includes direct lending and crowdfunding, continued its robust growth, with volumes exceeding hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating a clear shift in client preference for non-bank financing options.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Services
While still maturing, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are emerging as potential substitutes for core traditional banking services. These include functions like cross-border remittances, payment processing, and even aspects of asset management. The decentralized nature of these technologies challenges the necessity of traditional financial intermediaries.
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, platforms are at the forefront of this disruptive potential. They aim to offer a wide array of financial services, from lending and borrowing to trading, entirely without relying on conventional banks. This presents a significant long-term threat to established banking models by offering alternative, often more efficient, avenues for financial transactions and management.
- Market Growth: The global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024, indicating substantial user adoption and transaction volume.
- DeFi Transactions: DeFi protocols processed over $1 trillion in transactions in 2023, demonstrating a growing preference for non-custodial financial services.
- Remittance Costs: Traditional international remittances can incur fees of 5-10%, while crypto-based transfers often cost less than 1%, highlighting a cost-based substitute.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: While growing, the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies remains varied, impacting the speed and scale of their adoption as direct banking substitutes.
Internal Corporate Treasury Management
The threat of substitutes for Standard Chartered's internal corporate treasury management services is growing as large corporate clients bring more treasury functions in-house. This trend means fewer companies are outsourcing tasks like cash flow optimization, foreign exchange management, and investment decisions to external banks. For instance, a significant portion of major corporations now employ sophisticated treasury management systems (TMS) to handle these operations internally, reducing their reliance on traditional banking products and advisory services.
This shift directly impacts the revenue streams for banks like Standard Chartered, particularly in areas such as transactional banking and foreign exchange services. As of 2024, many multinational corporations have invested heavily in treasury technology, enabling them to achieve greater efficiency and cost savings. This internal capability acts as a direct substitute for the services previously offered by financial institutions.
- Growing adoption of Treasury Management Systems (TMS) by large corporates.
- Reduced reliance on external banks for FX hedging and cash management.
- Internal optimization of investment and liquidity portfolios.
- Potential decline in fee-based revenue for banks from core treasury services.
The increasing availability of alternative financial solutions directly challenges Standard Chartered's core offerings. From peer-to-peer lending platforms to embedded finance solutions within non-banking applications, customers have more choices than ever. For instance, the global alternative lending market, encompassing direct lending and crowdfunding, was projected to exceed $1.5 trillion in volume by the end of 2024, illustrating a significant shift away from traditional bank loans.
This trend is amplified by the rise of fintechs offering specialized services, often at lower costs and with greater convenience. Consider the embedded finance market, which some analysts predicted could reach $7 trillion by 2030, allowing companies like retailers to offer financing directly at the point of sale, effectively bypassing incumbent banks. These substitutes erode the traditional banking model by offering specialized, user-friendly, and often cheaper alternatives for services like payments, lending, and remittances.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Banks | Example Data (2024 Projections/Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Payment Solutions | Convenience, Lower Costs, Speed | Reduced transaction fees, customer disintermediation | Global mobile payment transaction volume to exceed $10 trillion |
| Embedded Finance / BaaS | Integration into non-financial customer journeys | Loss of direct customer relationships, reduced product penetration | Embedded finance market potentially reaching $7 trillion by 2030 |
| Direct Lending & Crowdfunding | Faster access to capital, flexible terms for businesses | Loss of loan origination and interest income | Global alternative lending market exceeding hundreds of billions of dollars |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Decentralized, lower remittance costs, alternative asset management | Potential disruption of payment systems, reduced need for intermediaries | Global crypto market cap around $2.5 trillion (early 2024); DeFi transactions over $1 trillion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including operations like Standard Chartered's, faces significant hurdles for new entrants due to stringent regulatory and capital requirements. Globally, banks must maintain substantial capital reserves, often mandated by Basel III and its subsequent iterations, to absorb potential losses. For instance, in 2024, major banks are expected to meet a Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio well above 10%, a significant barrier to entry.
Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations is also a major cost and operational challenge. These extensive legal frameworks demand sophisticated systems and ongoing investment in personnel and technology. Establishing these robust risk management frameworks requires considerable upfront and continuous expenditure, effectively deterring many potential new competitors from entering the market.
In the financial services sector, trust and reputation are not just desirable; they are essential. For a company like Standard Chartered, built on decades of consistent service, security, and stability, this is a significant barrier to entry for newcomers. New entrants, particularly those from non-traditional banking backgrounds, must overcome the immense hurdle of establishing the trust and credibility needed to attract substantial deposits and high-value clients.
Established banks like Standard Chartered possess immense customer bases, built over decades, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction. For example, as of the end of 2023, Standard Chartered served millions of retail and corporate clients globally.
These deep-rooted relationships translate into significant customer loyalty and trust, which are difficult and costly for newcomers to acquire. The perceived stability and established reputation of incumbents act as a powerful deterrent.
Furthermore, network effects, particularly in areas like payments and interbank lending, benefit existing players. Standard Chartered's extensive correspondent banking relationships and presence in key emerging markets create a powerful network that new entrants would struggle to match.
The high switching costs for customers, especially in business banking where integrated services are crucial, further solidify the position of incumbents. These factors combine to create a substantial barrier to entry.
Technological Investment and Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants in the banking sector is significantly influenced by the substantial technological investments and robust infrastructure required. While nimble fintech startups often leverage existing platforms or cloud services, establishing a fully compliant, secure, and scalable banking technology stack, encompassing advanced cybersecurity measures, demands immense capital and specialized knowledge. For instance, a new entrant would need to consider the significant outlays for core banking systems, data analytics platforms, and regulatory compliance technology, which can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
Building this infrastructure from the ground up or integrating with third-party providers presents considerable cost and complexity barriers. Consider the ongoing expenditure for maintaining and upgrading these systems to meet evolving customer expectations and regulatory mandates. In 2024, the global spending on financial technology is projected to reach substantial figures, highlighting the scale of investment needed for new players to even compete on the technological front.
Here’s a breakdown of key considerations:
- Core Banking Systems: Implementing or licensing modern core banking platforms can cost upwards of $50 million, with ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs.
- Cybersecurity Investment: Financial institutions are increasingly investing in cybersecurity, with average spending on cybersecurity solutions and services in the financial sector reaching tens of millions annually to combat sophisticated threats.
- Data Analytics and AI: Building out data infrastructure and AI capabilities for personalized services and risk management requires significant investment in hardware, software, and talent.
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech): Compliance with stringent financial regulations necessitates dedicated RegTech solutions, adding further to upfront and operational costs.
Niche Digital Banks and Fintechs
While traditional banking faces high entry barriers, the rise of niche digital banks and fintechs presents a distinct threat to incumbents like Standard Chartered. These agile players often leverage technology to target specific, underserved customer segments or offer specialized services, effectively bypassing some of the established hurdles.
These new entrants, though not directly replicating Standard Chartered's comprehensive offerings, can erode profitability by capturing lucrative niches. For instance, by 2024, the digital banking sector continued its rapid expansion, with many fintechs securing significant funding rounds, enabling them to invest heavily in customer acquisition and product development. This allows them to offer competitive rates or tailored experiences that appeal to specific demographics, thereby chipping away at the larger bank's market share in those areas.
- Digital-first models allow for lower operational costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar banks.
- Fintechs are adept at identifying and serving niche markets, such as small businesses or specific demographic groups, that may be less profitable for larger institutions.
- In 2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $2.4 trillion, indicating substantial growth and investment in this disruptive sector.
- These specialized players can gain traction by focusing on superior customer experience and user-friendly interfaces, drawing customers away from more complex legacy systems.
The threat of new entrants for Standard Chartered remains moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and extensive regulatory compliance, such as Basel III, which demand significant upfront investment. For example, in 2024, maintaining a Common Equity Tier 1 ratio above 10% presents a substantial financial barrier.
Building trust and brand reputation is a lengthy and costly process for newcomers, as customers prioritize security and stability in banking. Furthermore, established network effects and high customer switching costs, particularly in corporate banking, solidify the position of incumbents like Standard Chartered, which served millions of clients globally by the end of 2023.
While traditional entry barriers are high, agile fintechs and digital banks pose a growing threat by leveraging technology to target niche markets and offer superior customer experiences, contributing to the projected over $2.4 trillion global fintech market in 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Standard Chartered Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, financial statements, and investor presentations to understand internal capabilities and strategic positioning.
We supplement this with insights from reputable industry research reports, market intelligence platforms, and news archives to gauge external competitive pressures and market dynamics.
