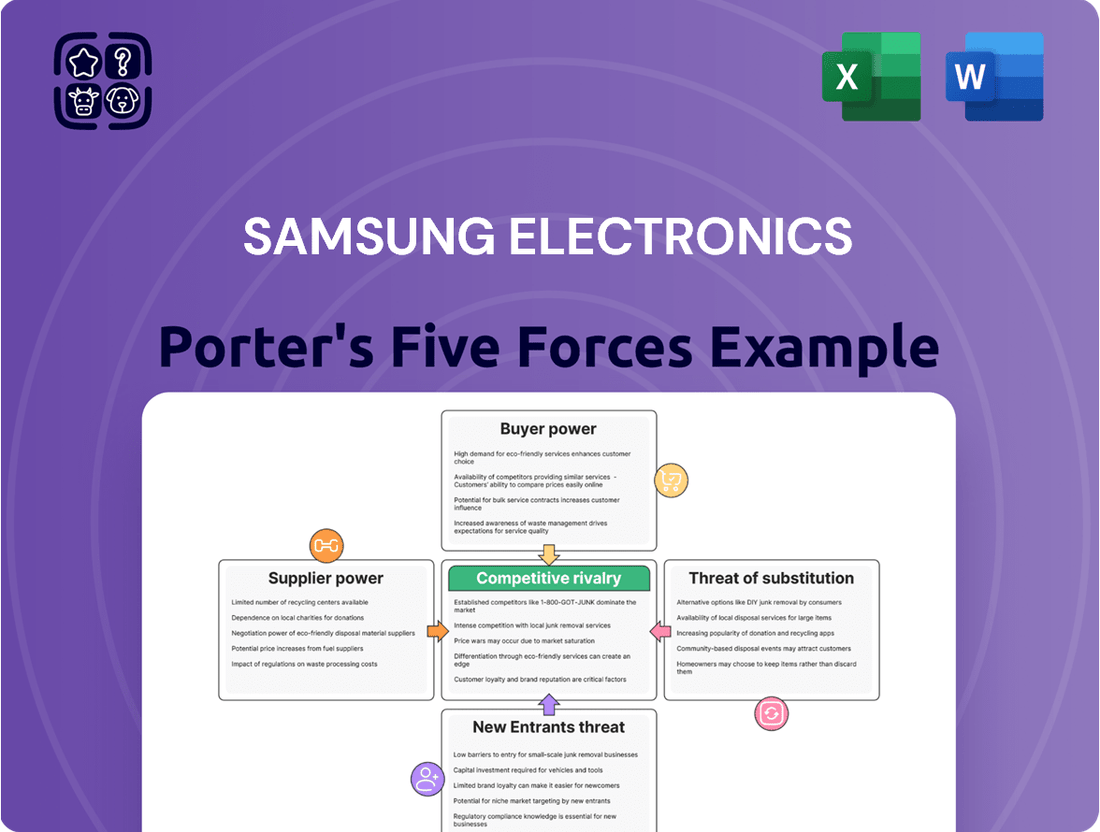
Samsung Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Samsung Electronics Bundle
Samsung Electronics operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, where the threat of new entrants is moderate due to high capital requirements but mitigated by established brand loyalty and technological expertise.
The bargaining power of buyers, particularly large retailers and enterprise clients, is significant, forcing Samsung to focus on innovation and value to maintain market share.
Suppliers, especially those controlling key components like advanced semiconductors, wield considerable influence, impacting Samsung's cost structure and product development timelines.
The threat of substitute products, such as emerging smart home ecosystems or alternative display technologies, requires constant vigilance and strategic adaptation from Samsung.
Intense rivalry among existing competitors, including giants like Apple and LG, drives aggressive pricing, rapid product cycles, and continuous R&D investment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Samsung Electronics’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The semiconductor industry, critical to Samsung, features highly concentrated suppliers for essential inputs like silicon wafers and rare earth elements. This concentration grants these suppliers significant influence over pricing and availability. Qualifying new suppliers is costly and protracted, typically taking 12-18 months and millions of dollars, such as the estimated $15-25 million for a new semiconductor material qualification in 2024. This substantial barrier further solidifies Samsung's reliance on its established supplier network.
Samsung significantly mitigates supplier power through extensive vertical integration, producing essential components like memory chips, displays, and batteries in-house. This strategy reduces its reliance on external suppliers for critical parts, enhancing control over its supply chain. For instance, Samsung Display's market share in small/medium OLED panels was approximately 61% in Q1 2024, demonstrating its internal capabilities. Furthermore, Samsung maintains a vast and geographically diversified network of over 2,500 primary suppliers globally, including key partners in Asia and the U.S. This broad base prevents over-dependence on any single supplier or region, fostering competitive pricing and supply stability.
For the broader electronics industry, switching suppliers for crucial components like advanced semiconductors involves significant costs, including technical certification and validation of new materials. This reality grants established suppliers substantial leverage, as integration into production processes is deep-seated. However, Samsung's immense scale, with 2024 capital expenditures projected to remain high for memory and foundry, helps mitigate this. Long-term relationships further counterbalance supplier power, securing vital components for devices like the Galaxy S24 series.
Supplier Dependence on Samsung
Many of Samsung's key suppliers are highly dependent on the company for a substantial portion of their revenue, which significantly diminishes their bargaining power. Losing Samsung as a client would severely impact their financial stability, making them less able to dictate terms. Samsung strategically fosters close, long-term relationships, often involving joint technology development and financial support, creating a mutually beneficial partnership with firms like ASML for lithography equipment. This interdependence allows Samsung to maintain favorable pricing and supply chain stability.
- Samsung's global market share in smartphones was approximately 20% in Q1 2024, driving significant demand for components.
- Key component suppliers, such as those for memory chips (e.g., Micron, SK Hynix) and OLED displays (e.g., LG Display), often rely on Samsung for a large percentage of their sales.
- Samsung's robust R&D investment, projected at over $15 billion in 2024, often includes collaborative projects with suppliers.
- The company's scale allows it to secure favorable terms, leveraging its purchasing volume for components like advanced processors and camera modules.
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Risks
Recent geopolitical tensions have significantly amplified the bargaining power of key suppliers for Samsung Electronics, particularly those in critical semiconductor and display component sectors. Events like the ongoing U.S.-China tech decoupling can restrict access to vital technologies and increase input costs, directly impacting Samsung's production efficiency. To mitigate these risks, Samsung is actively diversifying its supply chain, aiming to reduce reliance on single regions and enhance resilience against future disruptions. This strategic shift is crucial as global supply chain instability, seen in 2024, continues to pose challenges for major tech manufacturers.
- In 2024, Samsung's capex for semiconductors is projected to reach approximately 36.4 trillion Korean Won, emphasizing critical component sourcing.
- The company aims to localize more production, with plans to expand manufacturing capabilities outside traditional hubs.
- Supply chain resilience is a core focus, driven by lessons from recent global disruptions.
- Geopolitical risks necessitate increased inventory levels and diversified supplier relationships for key materials.
Suppliers of critical components like advanced semiconductors hold significant leverage due to their concentration and high switching costs, estimated at $15-25 million for new material qualification in 2024. However, Samsung mitigates this through extensive vertical integration, producing components like OLED displays, where its market share was 61% in Q1 2024. Its vast, diversified network and suppliers' dependence on Samsung's substantial purchasing volume for components like memory chips further reduce their power. Geopolitical tensions in 2024, however, are increasing supplier influence, prompting Samsung to diversify its supply chain.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High Leverage | $15-25M new qual. |
| Samsung Vertical Integration | Mitigates Power | 61% OLED Q1 2024 |
| Geopolitical Risks | Increase Power | Supply chain instability |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Samsung Electronics' diverse product portfolio and global operations.
Quickly assess competitive intensity and identify strategic vulnerabilities with a visually intuitive Porter's Five Forces analysis, streamlining complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Effortlessly adapt to shifting market landscapes by dynamically updating key drivers within the Five Forces framework, enabling agile strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the consumer electronics market, customers face a vast selection of alternatives, significantly enhancing their bargaining power. For instance, in the global smartphone market in Q1 2024, Samsung competed intensely with Apple, Xiaomi, and Huawei, all offering compelling devices. Similarly, in home appliances, LG and Whirlpool remain strong rivals, holding substantial market shares. This extensive choice allows consumers to easily switch brands if Samsung's pricing or features do not meet their expectations, putting pressure on the company.
For many of Samsung’s products, especially smartphones, customers face low switching costs, significantly increasing their bargaining power. Consumers can easily transition to competitor brands like Apple or Xiaomi due to the general similarity in Android ecosystems and readily available data transfer tools. This ease of movement means Samsung must consistently innovate and offer competitive pricing to retain its market share, which stood at approximately 20% of global smartphone shipments in Q1 2024. The minimal friction in moving between devices empowers buyers to seek better value or features elsewhere.
Consumers today are highly informed, leveraging online platforms for product reviews and real-time price comparisons, which empowers their purchasing decisions. This digital transparency puts significant pressure on Samsung to maintain competitive pricing across its diverse product range. In budget-conscious segments, such as the mid-range smartphone market, price remains a critical factor influencing choices. For instance, in Q1 2024, Samsung faced intense competition in these segments, highlighting consumer price sensitivity. This accessibility means consumers can easily switch to alternatives if prices are not aligned with perceived value.
Brand Loyalty and Ecosystem Effects
While switching costs for individual Samsung products can be low, the company strategically builds customer loyalty through its strong brand reputation and an expanding ecosystem. Features like SmartThings, which enable seamless integration across various Samsung devices, significantly increase customer stickiness. This interconnectedness makes it less appealing for customers to switch away entirely, even if a single product's alternative is cheaper. For high-value purchases like major home appliances, brand loyalty and the perceived quality of a trusted brand like Samsung, which held a leading 23.5% market share in global home appliance sales in 2023, effectively reduce customer bargaining power.
- Samsung's global smartphone market share was approximately 20% in Q1 2024, demonstrating strong brand presence.
- The SmartThings platform connects over 280 million registered users globally as of late 2023, enhancing ecosystem lock-in.
- Samsung held the largest share in the global home appliance market in 2023, reflecting significant consumer trust in its brand for durable goods.
- Brand perception surveys consistently rank Samsung among the top global brands for reliability and innovation in consumer electronics.
Differentiated Product Portfolio
Samsung's expansive product portfolio, spanning from premium Galaxy S24 Ultra smartphones to budget-friendly A-series models, significantly dilutes customer bargaining power. This differentiation caters to diverse market segments, allowing Samsung to capture demand across various price points and income levels. For instance, in Q1 2024, while premium models drove profitability, the broader range sustained market presence, ensuring customers have varied options within the Samsung ecosystem. This strategy reduces the leverage customers might gain from a market with numerous alternatives, as Samsung itself offers a spectrum of choices.
- Samsung's global smartphone market share was approximately 20% in Q1 2024, showcasing its broad appeal.
- The company's diverse product range includes high-end foldable phones, mid-range devices, and budget smartphones.
- This multi-tiered approach helps Samsung retain customers who might otherwise switch brands for specific price or feature needs.
- Samsung's ability to offer differentiated products across price points mitigates the power of individual customers to demand lower prices.
Customers wield significant power due to low switching costs and ample alternatives in Q1 2024, pressuring Samsung on pricing and features. Despite this, Samsung's strong brand, ecosystem, and diverse product range, including its ~20% global smartphone share in Q1 2024, mitigate some buyer leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Power | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Product Alternatives | High | Q1 2024 smartphone market competition |
| Switching Costs | Low | Easy Android transfers |
| Brand Ecosystem | Lowers | SmartThings (280M+ users) |
Preview Before You Purchase
Samsung Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for Samsung Electronics, providing an in-depth examination of its competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a professionally formatted and ready-to-use strategic overview. You'll gain actionable insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the electronics industry, all presented in this exact file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Samsung faces intense competition across its diverse product portfolio. In the premium smartphone segment, its primary rival remains Apple, with both companies aggressively vying for market share; for instance, Apple held a 20.1% global smartphone market share in Q4 2023, closely followed by Samsung. In the broader smartphone landscape, Chinese manufacturers like Xiaomi and Transsion are significant contenders, with Xiaomi securing 12.5% of the global market in 2024's first quarter. Furthermore, in home appliances and televisions, Samsung competes fiercely with established players such as LG and Sony, constantly innovating to maintain its leadership position.
The consumer electronics sector demands immense marketing and R&D outlays, fostering intense competitive rivalry for Samsung. Companies annually pour billions into brand awareness and product innovation; Samsung's marketing and selling expenses alone reached approximately 24.3 trillion KRW in 2023. This constant investment pressure, driving differentiation and technological advancements, ensures only financially robust players can sustain their market presence.
Samsung differentiates itself through relentless technological innovation, notably in foldable phones and cutting-edge display technology. This continuous innovation race is central to competitive rivalry, as companies vie for market share by offering the latest features. For instance, Samsung's foldable phone shipments are projected to reach 1.1 million units in Q1 2024, highlighting its leadership. This drive ensures they remain a top player in a fiercely contested global electronics market.
Global Market Share Battle
The global market share battle, especially in smartphones, presents intense rivalry for Samsung. While historically a leader, Samsung's position is continually challenged by Apple and rising Chinese brands like Xiaomi and Transsion. Market share can fluctuate significantly based on new product launches and evolving consumer preferences, impacting profitability and strategic direction.
- In Q1 2024, Samsung regained the top spot in smartphone shipments with 20.8% global market share.
- Apple followed closely with 17.3% share in the same period.
- Xiaomi secured 14.1% and Transsion (Tecno, Infinix, Itel) reached 9.9% market share in Q1 2024.
- This dynamic landscape highlights the constant pressure to innovate and capture consumer attention.
Price Wars and Diverse Product Ranges
Competitive rivalry for Samsung intensifies through price wars, especially in the mid-range and budget smartphone segments where Chinese brands like Xiaomi and Transsion Group hold significant sway. Samsung's broad product portfolio, spanning from premium foldable devices to affordable A-series phones, directly counters this pressure. This strategy allows Samsung to effectively compete across all price points, maintaining its market position against both high-end and value-oriented rivals in 2024. For instance, Samsung's global smartphone market share was approximately 20.8% in Q1 2024, slightly ahead of Apple.
- Samsung's global smartphone market share was 20.8% in Q1 2024.
- Chinese brands like Xiaomi and Transsion Group drove significant competition in budget segments in 2024.
- Samsung’s diverse product range, including the Galaxy A series, targets value-conscious consumers.
- The mid-range smartphone market experienced intense price competition throughout 2024.
Samsung faces fierce competitive rivalry across its diverse electronics portfolio, especially from Apple in premium smartphones and Xiaomi and Transsion in the broader market.
High R&D and marketing investments are crucial, with Samsung spending significantly to maintain its lead and innovate.
Price wars, particularly in the mid-range segment, intensify competition, pushing Samsung to leverage its broad product range.
This dynamic environment demands constant innovation and strategic market share battles to sustain profitability and leadership in 2024.
| Company | Q1 2024 Global Smartphone Share | Primary Rivalry Segment |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung | 20.8% | Premium, Mid-range, Budget |
| Apple | 17.3% | Premium Smartphones |
| Xiaomi | 14.1% | Mid-range, Budget Smartphones |
| Transsion (Tecno, Infinix, Itel) | 9.9% | Budget Smartphones |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat from indirect substitutes for Samsung Electronics remains low across its core product lines. For smartphones, a primary revenue driver, there are few single-device alternatives that match their comprehensive functionality. While a separate camera or computer can perform individual tasks, the integrated convenience of a smartphone, with Samsung holding a 20.8% global market share in Q1 2024, is hard to replicate. Similarly, major home appliances like refrigerators and washing machines face minimal indirect substitution, as no other product offers the same level of performance and essential convenience for daily living.
The most significant threat of substitution for Samsung Electronics comes from direct alternatives offered by competing brands within the same product category. A consumer seeking a new smartphone has numerous options from Apple, Google, and Chinese manufacturers like Xiaomi and Honor, which collectively captured a significant portion of the global smartphone market in early 2024. The low cost of switching between these brands further intensifies this threat, as consumers can easily move to a competitor's device. This competitive landscape demands continuous innovation from Samsung to retain its market position.
The growing market for used and refurbished smartphones presents a notable substitution threat for Samsung's new device sales. As smartphone durability improves, consumers extend their device replacement cycles, often holding onto phones for three to four years, up from two. This trend, coupled with the availability of professionally refurbished older models, provides a compelling lower-cost alternative. In 2024, the global refurbished smartphone market is projected to continue its expansion, with reports indicating it grew by 9% year-over-year in 2023, reaching 309.4 million units, a significant volume impacting new sales.
Integration and Ecosystem as a Defense
Samsung strategically mitigates the threat of substitutes by cultivating a deeply integrated ecosystem of devices and services. When consumers own multiple Samsung products, such as a 2024 Galaxy S24 smartphone, a Galaxy Watch, and a QLED TV, the seamless cross-device functionality significantly enhances user stickiness. This interconnected experience makes it less appealing for customers to switch to a competitor for individual products, reinforcing loyalty across the brand. Samsung's smart home platform, SmartThings, further solidifies this defense by connecting an expanding array of appliances and IoT devices.
- Samsung's SmartThings platform reported over 290 million registered users globally as of early 2024.
- Cross-device connectivity fosters higher customer retention rates, reducing churn.
- The integration of AI features across devices, like on the Galaxy S24 series, enhances ecosystem value.
- Samsung continues to expand its services, including Samsung Pay and Samsung Health, to bolster ecosystem engagement.
Innovation to Outpace Substitution
Continuous innovation is Samsung's core strategy to outpace potential substitutes. By consistently introducing new features and improving performance, like with its cutting-edge foldable phones, Samsung reduces the appeal of simpler or less advanced alternatives, including its own older models. This proactive approach ensures Samsung’s offerings remain compelling, minimizing the threat of customers switching to alternative technologies or brands. For instance, Samsung invested approximately KRW 28.34 trillion in research and development in 2023, reflecting its commitment to staying ahead.
- Samsung launched its Galaxy S24 series in January 2024, emphasizing AI capabilities.
- The company continues to lead the foldable phone market, with new models expected in 2024.
- Samsung's semiconductor innovations, like advanced memory solutions, reduce reliance on external suppliers.
- Their 2023 R&D investment highlights a strong commitment to future product differentiation.
The threat of substitutes for Samsung Electronics primarily stems from direct competitors offering similar products, with low switching costs intensifying this rivalry. The growing market for used and refurbished devices, which saw 309.4 million units in 2023, also presents a significant alternative to new sales. Samsung counters these threats by fostering an integrated ecosystem, evidenced by over 290 million SmartThings users in early 2024, and through continuous innovation, like the AI-focused Galaxy S24 series launched in 2024.
| Threat Type | Impact Level | 2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Competitors | High | Samsung's 20.8% global smartphone share (Q1 2024) amidst strong rivals |
| Refurbished Devices | Moderate | Refurbished market grew 9% in 2023, reaching 309.4M units |
| Indirect Substitutes | Low | Integrated smartphone functionality remains unique |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the consumer electronics and semiconductor industries demands immense capital investment. Samsung, for instance, reported capital expenditures of approximately 6.5 trillion Korean Won in Q1 2024, underscoring the scale needed for R&D and advanced manufacturing facilities. Established players like Samsung benefit from significant economies of scale, producing goods at a far lower cost per unit. This substantial financial outlay creates a formidable barrier, making it exceptionally difficult for new entrants to compete effectively.
Samsung boasts a powerful, globally recognized brand, valued at $91.4 billion by Interbrand in 2023, reflecting decades of massive marketing investments and consistent product quality. A new entrant would face immense difficulty and expense in 2024 to cultivate a comparable level of brand trust and customer loyalty. This established brand equity significantly deters potential new competitors from entering the market, given the high barriers to overcome consumer preference.
Establishing efficient global distribution and supply networks is incredibly complex and costly, posing a substantial barrier for new entrants. Samsung boasts an intricate network, including over 2,500 primary suppliers globally as of early 2024, alongside vast manufacturing facilities and retail partnerships. A new company would struggle immensely to replicate this scale, which cost Samsung billions in infrastructure over decades. This makes it difficult for newcomers to get products to market effectively and at competitive prices, hindering their ability to challenge Samsung's market presence.
Technological Expertise and Patents
The electronics sector thrives on innovation, heavily protected by extensive patent portfolios. Samsung Electronics holds a formidable array of patents, significantly hindering new entrants from replicating key technologies or manufacturing processes. The deep technical expertise, particularly in complex areas like advanced semiconductor fabrication, represents a substantial barrier to entry for any potential competitor. This institutional knowledge and the immense capital expenditure required are not easily acquired.
- Samsung's global patent count exceeded 97,000 as of 2024.
- Semiconductor fabrication facilities can cost tens of billions of dollars to build.
- New entrants face significant R&D investment and a steep learning curve.
- Legal challenges over patent infringement deter market entry.
Government Policies and Regulations
New entrants into the electronics market face substantial hurdles from global government policies and regulations, including international trade laws, tariffs, and stringent environmental and product safety standards. Established players like Samsung Electronics benefit significantly, possessing extensive experience and dedicated teams to navigate this complex landscape. For a new company, the immense cost and complexity of achieving compliance, such as adhering to the EU's Digital Markets Act or various national WEEE directives, form a formidable barrier to entry. This regulatory burden often requires substantial investment in legal, R&D, and production adjustments, making market penetration exceptionally difficult.
- Global trade tensions in 2024 necessitate complex supply chain compliance.
- EU environmental directives, like Ecodesign, demand significant R&D investment.
- Product safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE) add considerable testing costs.
- Regulatory compliance can exceed 10% of a new product's development budget.
New entrants face immense capital barriers, with Samsung's Q1 2024 capex at 6.5 trillion KRW highlighting the scale needed for R&D and manufacturing. Replicating Samsung's global brand, valued at $91.4 billion in 2023, and its complex supply network of over 2,500 suppliers is exceptionally costly and time-consuming. Samsung's vast patent portfolio, exceeding 97,000 in 2024, alongside deep technical expertise, creates significant intellectual property hurdles. Stringent 2024 global regulations and trade policies further complicate market entry, demanding substantial compliance investment.
| Barrier | Key Data (2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Samsung Q1 2024 Capex: 6.5 Trillion KRW | High financial outlay; prohibitive cost |
| Brand Equity & Scale | Samsung Brand Value: $91.4 Billion (2023) | Difficult to build trust; replicate global reach |
| IP & Regulations | Samsung Patents: 97,000+; EU DMA, WEEE | Legal hurdles; high compliance costs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Samsung Electronics leverages data from their annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and reputable financial news outlets to assess competitive intensity. We also incorporate market research reports and industry publications to understand buyer power and the threat of new entrants.
