Roku Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Roku Bundle
Roku navigates a dynamic streaming landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers. Intense rivalry among established players and the growing influence of suppliers shape its competitive environment. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategizing.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Roku’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Roku's reliance on a concentrated group of suppliers for critical hardware, such as semiconductors and specialized chipsets, grants these suppliers substantial bargaining power. This is especially true when components are proprietary or in high demand, as seen in the global semiconductor shortage that impacted many electronics manufacturers throughout 2021 and 2022, leading to increased costs and production delays.
Major content studios and providers wield significant sway over Roku, particularly concerning popular and exclusive programming. These content owners can negotiate for larger portions of revenue generated from their content on the platform, or demand more advantageous distribution agreements and prominent display slots. For instance, in 2023, major media companies continued to leverage their intellectual property to secure favorable terms in streaming deals, impacting platform economics.
Roku's reliance on third-party software, codecs, and intellectual property for its platform functionality grants these providers significant bargaining power. When these suppliers offer specialized or patented technologies essential for the streaming experience, their leverage escalates. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing development and licensing costs for advanced video compression codecs, critical for high-quality streaming, can represent a substantial portion of operational expenses for platform providers. This dynamic underscores the strategic importance of negotiating favorable terms and exploring in-house development to mitigate dependence on external software intellectual property.
Advertising Technology Partners
Advertising technology partners hold significant bargaining power over Roku, given that advertising is Roku's primary revenue source. These partners, including ad tech platforms, data analytics firms, and measurement services, are crucial for delivering effective advertising campaigns on Roku's platform. Specialized vendors with unique technologies or strong market positions can leverage this importance to negotiate favorable terms.
The bargaining power of these suppliers can directly impact Roku's financial performance. If key ad tech partners demand higher fees or more favorable revenue splits, it can reduce Roku's advertising revenue margins. For instance, in 2023, Roku faced challenges with its ad platform, highlighting the dependency on these partners and the potential for their demands to influence pricing and targeting capabilities, which are core to Roku's value proposition to advertisers.
- High dependency on ad tech: Roku relies heavily on third-party ad tech for its advertising business, giving these partners leverage.
- Specialized capabilities: Vendors with unique targeting or measurement solutions can command better terms.
- Impact on margins: Supplier demands can squeeze Roku's advertising revenue margins, affecting profitability.
- Market concentration: A few dominant ad tech players can exert considerable influence over pricing and service terms.
TV Manufacturing Partners for OS Licensing
Roku's bargaining power with TV manufacturing partners for its OS licensing is influenced by the manufacturers' alternatives. While Roku boasts a significant user base, which is a strong draw, TV makers like TCL, Hisense, and others are not without options. They can invest in their own proprietary smart TV platforms or forge alliances with other major tech players. This dynamic provides manufacturers with considerable leverage when negotiating licensing fees and the specifics of operating system integration.
In 2024, the smart TV market continues to be competitive, with operating system choice playing a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions. Roku's strategy of partnering with numerous TV manufacturers has allowed it to scale its platform rapidly. For instance, by the end of 2023, Roku OS was available on over 30 different TV brands. This broad adoption, however, also means that individual manufacturers, especially larger ones, can exert pressure on Roku for more favorable terms. They understand that their volume of sales can make them a significant contributor to Roku's overall ecosystem growth.
- Manufacturer Alternatives: TV manufacturers can develop in-house OS or partner with competitors like Google (Android TV/Google TV) or Amazon (Fire TV).
- Roku's Value Proposition: Roku's extensive content library and familiar user interface are key selling points for manufacturers seeking to enhance their smart TV offerings.
- Negotiation Leverage: The volume of units a manufacturer ships directly impacts their bargaining power for licensing agreements and revenue share.
- Market Share Dynamics: As Roku aims for broader smart TV market penetration, it must balance the desire for high licensing fees with the need to secure partnerships with high-volume manufacturers.
The bargaining power of Roku's suppliers is a significant factor in its operational landscape. Key component providers, particularly for specialized semiconductors, can exert considerable influence due to market concentration and demand. Additionally, content providers and intellectual property licensors wield substantial leverage, negotiating for favorable revenue shares and distribution terms. In 2024, ongoing supply chain dynamics and the value of exclusive content continue to empower these suppliers.
| Supplier Category | Key Suppliers | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Roku |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Components | Semiconductor Manufacturers (e.g., Broadcom, MediaTek) | Concentrated market, proprietary technology, supply chain volatility | Increased costs, production delays, potential feature limitations |
| Content Providers | Major Studios & Streaming Services (e.g., Netflix, Disney+) | Popularity of content, exclusive rights, negotiation for revenue share | Higher content acquisition costs, revenue allocation pressure |
| Software & IP | Codec developers, OS component providers | Patented technology, essential functionality, licensing fees | Ongoing licensing expenses, potential for dependence |
What is included in the product
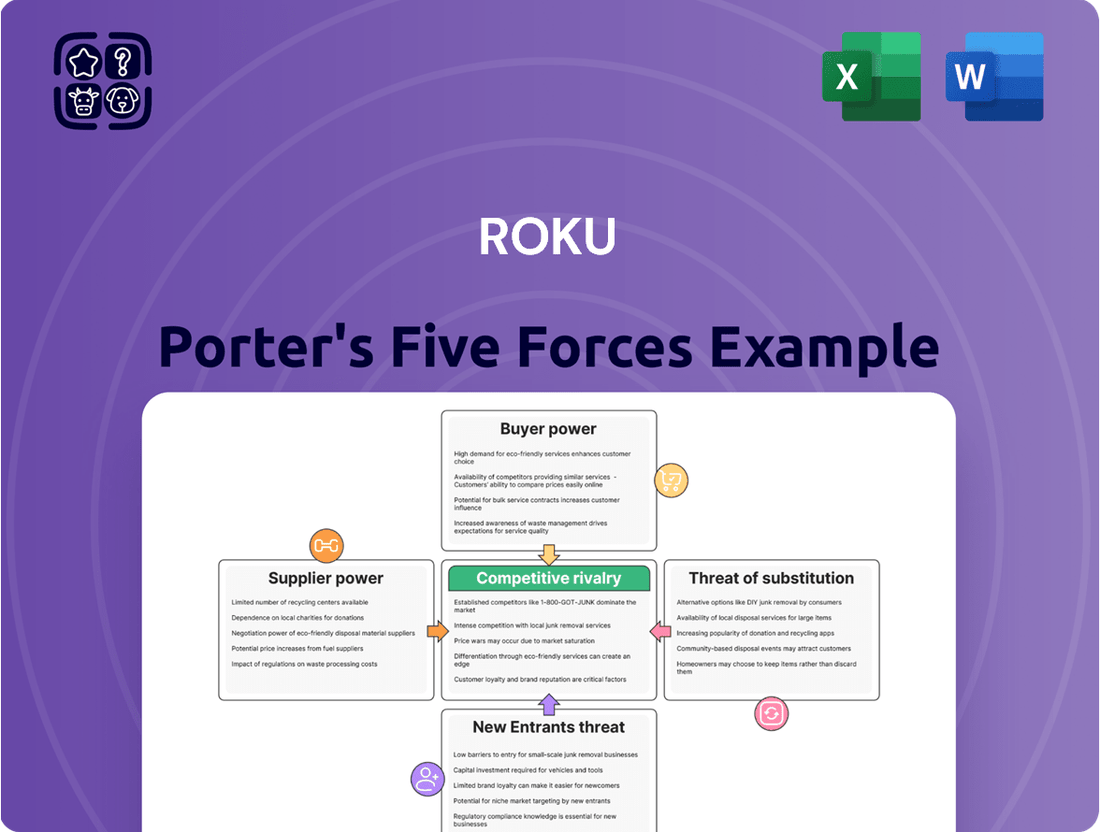
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Roku's ecosystem, examining supplier and buyer power, new entrant threats, substitute products, and rivalry within the connected TV market.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity across the streaming landscape with a dynamic spider chart, instantly highlighting Roku's strategic positioning and potential threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual consumers, the primary buyers of Roku streaming devices and integrated Roku TVs, wield considerable bargaining power. This strength stems from the wide array of readily available alternatives in the streaming market, such as Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV, and Google TV. Consumers can effortlessly shift their allegiance if Roku’s pricing, product features, content selection, or overall user experience falls short of expectations, compelling Roku to maintain competitive offerings.
Advertisers wield substantial bargaining power over Roku, as they are the primary drivers of platform revenue. Their ability to shift advertising spend to numerous competing channels, including other CTV platforms and digital giants like Google and Meta, puts pressure on Roku to offer compelling value propositions. For instance, in 2024, the digital advertising market is projected to reach over $800 billion globally, highlighting the intense competition for advertiser dollars.
Advertisers demand robust audience reach and granular targeting capabilities, alongside clear demonstrations of return on investment (ROI). This necessitates Roku to continuously innovate its ad technology and provide transparent performance metrics. Roku's success in retaining and attracting advertisers in 2024 hinges on its ability to deliver superior ad formats and cost-effectiveness compared to alternatives, which often offer comparable reach.
Content publishers and app developers are crucial customers for Roku, seeking access to its vast user base for distribution and monetization. Their bargaining power is significant because they can choose to distribute their content across multiple platforms or even directly to consumers, limiting Roku's exclusivity.
The value that unique and popular content brings to the Roku platform directly enhances Roku's appeal. This leverage allows publishers and developers to negotiate more favorable revenue-sharing agreements and promotional terms, impacting Roku's platform economics.
In 2023, Roku reported that over 100 content publishers and app developers generated more than $1 million in gross revenue on its platform, highlighting the significant financial stake these partners have and their resulting negotiating leverage.
While Roku provides a valuable distribution channel, the ability of these content creators to diversify their reach means they can exert pressure on Roku to maintain competitive terms, particularly regarding ad revenue splits and platform fees.
TV Manufacturers Licensing Roku OS
TV manufacturers that license Roku's Smart TV operating system represent a significant customer base for Roku. These companies, such as TCL, Hisense, and Sharp, have the power to choose alternative operating systems or develop their own, which directly impacts their negotiation leverage with Roku. Their purchasing decisions are driven by factors like licensing costs, the ease of integrating Roku's platform, and the perceived consumer demand for Roku-enabled televisions. This ability to switch or opt for self-development grants them considerable bargaining power in securing favorable licensing terms and the level of ongoing support Roku provides.
The bargaining power of these TV manufacturers is substantial. For instance, in 2023, TCL, a major Roku TV partner, continued to be a significant volume driver for Roku's platform. Manufacturers consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees and the resources required for integration, when evaluating operating system partners. The availability of competing platforms, such as Google TV or Amazon Fire TV, further strengthens their position, allowing them to pit different OS providers against each other. This dynamic means manufacturers can negotiate not only on price but also on features, update cycles, and the degree of customization Roku allows.
- Significant Customer Base: Major TV brands like TCL and Hisense license Roku OS, making them crucial clients whose preferences influence Roku's strategy.
- Alternative Options: Manufacturers can choose from competing operating systems (e.g., Google TV, Fire TV) or develop proprietary platforms, increasing their leverage.
- Key Decision Factors: Licensing costs, ease of integration, and consumer demand for Roku-enabled TVs are critical elements in their negotiation calculus.
- Negotiation Leverage: The ability to switch OS providers or develop in-house solutions empowers manufacturers to secure better terms and support from Roku.
Subscription Service Providers
Subscription video-on-demand (SVOD) and ad-supported video-on-demand (AVOD) services, while partners, also act as customers for Roku. They depend on Roku for user acquisition and seamless billing integration, giving them a degree of leverage. Major streaming giants, particularly those with substantial subscriber numbers or exclusive content libraries, wield significant bargaining power.
These content providers can negotiate favorable terms regarding platform integration, revenue-sharing agreements, and prominent promotional placement on Roku's interface. For instance, a service like Netflix or Disney+ could leverage its massive global subscriber base to demand better placement or lower commission rates from Roku. In 2024, the streaming market continues to be highly competitive, with services actively seeking to expand their reach and subscriber numbers, further amplifying their customer power when dealing with distribution platforms like Roku.
- Content providers with large, dedicated subscriber bases hold significant sway.
- Exclusive content can be a powerful bargaining chip for streaming services.
- Negotiations often center on revenue splits and platform visibility.
- The competitive streaming landscape in 2024 empowers these content partners.
Individual consumers have substantial bargaining power due to the abundance of streaming alternatives like Amazon Fire TV and Apple TV. This forces Roku to maintain competitive pricing and product offerings to retain its user base.
Advertisers, a key revenue driver for Roku, can easily shift their spending to other digital platforms. Roku must offer compelling value, robust targeting, and demonstrable ROI to secure advertising dollars amidst a global digital ad market exceeding $800 billion in 2024.
Content publishers and app developers, crucial for Roku's platform appeal, possess significant leverage. They can distribute content elsewhere or directly to consumers, enabling them to negotiate favorable revenue shares and promotional terms, especially as over 100 publishers generated more than $1 million in gross revenue on Roku in 2023.
TV manufacturers licensing Roku's OS, like TCL and Hisense, hold considerable power by having alternative OS options or the ability to develop their own. This allows them to negotiate favorable licensing fees and support, considering the total cost of ownership in a competitive market where Google TV and Amazon Fire TV are viable alternatives.
What You See Is What You Get
Roku Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Roku's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these forces is crucial for assessing Roku's strategic position and future profitability in the streaming industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry in the streaming device sector is fierce, with Roku constantly vying against formidable opponents like Amazon's Fire TV, Apple TV, and Google's Chromecast with Google TV. These players frequently introduce new hardware, often with competitive pricing strategies, and benefit from their established technology ecosystems and strong brand recognition among consumers.
The battle for market share is fueled by a continuous drive for innovation, focusing on enhancing user interfaces, introducing novel features, and ensuring smooth integration with a wide array of digital services. For instance, Amazon's Fire TV devices saw significant sales momentum, capturing a substantial portion of the market in 2024, further intensifying the competitive landscape for Roku.
Roku's smart TV operating system faces intense competition from major players like Google TV, Samsung's Tizen, and LG's webOS. These established platforms are frequently pre-loaded onto a vast array of smart TVs, intensifying the struggle for market dominance and crucial partnerships with TV manufacturers.
This robust rivalry directly influences Roku's capacity to grow its presence in the integrated smart TV sector and secure prime on-screen real estate. For instance, in 2024, Google TV continued its expansion, powering a significant portion of Android TV-based sets, while Tizen and webOS remained deeply embedded in Samsung and LG's extensive television lineups, respectively.
Roku faces significant competitive rivalry from content aggregators and streaming services. While Roku provides a platform for many third-party services, it also directly competes with them for viewer engagement and advertising revenue, notably through its own Roku Channel. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, Roku reported that The Roku Channel reached 136 million people in the U.S., showcasing its growing user base and competitive push.
Competitors like Pluto TV, Tubi, and Amazon's Freevee offer comparable free, ad-supported content, directly challenging Roku's model and user acquisition strategies. This proliferation of options in the streaming market intensifies the battle for consumer attention, making it crucial for Roku to retain users and maximize viewing hours across its diverse content offerings.
Tech Giants with Ecosystem Strategies
Roku faces intense rivalry from tech giants like Amazon, Apple, and Google. These companies leverage their extensive resources and deeply integrated ecosystem strategies, encompassing hardware, software, content, and a wide array of services. Their goal is to solidify their presence across the consumer's digital life, making it harder for users to switch platforms. This pervasive ecosystem competition forces Roku to constantly innovate and differentiate its platform to maintain user engagement and loyalty.
These tech behemoths are not just competing on device sales but on the entire digital experience. For instance, Amazon's Fire TV ecosystem is deeply tied to its Prime Video streaming service, its e-commerce platform, and Alexa voice assistant. Similarly, Apple's strategy with Apple TV is part of its broader Apple One bundles and device integration, from iPhones to iPads. Google's Android TV and Google TV are similarly integrated with its search, advertising, and other cloud-based services.
The sheer scale of these competitors presents a significant challenge. In 2024, Amazon's global e-commerce sales are projected to exceed $700 billion, demonstrating its vast financial capacity. Apple's Services segment alone generated over $85 billion in revenue in fiscal year 2023, showcasing its ability to monetize its ecosystem. Google's advertising revenue continues to be a dominant force, providing substantial resources for platform development and user acquisition.
- Amazon's Fire TV integrates seamlessly with its Prime Video, Kindle, and vast e-commerce empire, aiming for a holistic consumer experience.
- Apple's TV strategy is intrinsically linked to its entire hardware and software ecosystem, including the App Store and Apple Music.
- Google's Android TV/Google TV leverages its dominance in search, advertising, and cloud services, offering a deeply integrated smart home and entertainment platform.
- These competitors' ability to cross-subsidize offerings within their ecosystems allows them to aggressively price hardware and content, putting pressure on Roku's margins.
Traditional Media and Cable Companies
Traditional media and cable companies remain a significant competitive force for Roku, even as the media landscape shifts. Many of these legacy players, such as Warner Bros. Discovery and Paramount Global, are actively developing and promoting their own streaming services, like Max and Paramount+, to retain viewers and advertising revenue. This evolution means they are directly competing for consumer attention and advertising dollars that might otherwise flow to streaming platforms like Roku.
The rivalry isn't just about direct competition; it's about adapting to changing consumer habits. These companies are leveraging their extensive content libraries and brand recognition to draw audiences to their digital offerings. For instance, major networks continue to invest heavily in exclusive content for their apps, directly challenging the appeal of aggregated streaming on Roku. This strategic adaptation by traditional players means they are not merely incumbents but evolving competitors in the digital entertainment space.
- Content Investment: Major media companies are dedicating billions to original content for their streaming platforms, a direct challenge to Roku's content aggregation model.
- Brand Loyalty: Established media brands benefit from existing consumer loyalty, which can be a powerful draw for their own streaming services.
- Advertising Budgets: Traditional media still commands a substantial portion of advertising spend, which Roku also seeks to capture.
- Bundling Strategies: Some legacy companies are exploring bundling their streaming services with other offerings, creating attractive packages that could divert consumer spending.
The competitive rivalry in the streaming device market is intense, with Roku facing strong competition from Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV, and Google Chromecast. These rivals frequently launch new hardware, often at competitive price points, and benefit from their established technology ecosystems and brand recognition.
Roku's smart TV operating system also contends with deeply embedded platforms like Google TV, Samsung's Tizen, and LG's webOS, which are pre-installed on many smart TVs, complicating Roku's access to integrated smart TV market share and prime on-screen placement.
The competition extends to content aggregation and free, ad-supported streaming services like Pluto TV and Tubi, which directly challenge Roku's user engagement and advertising revenue streams, particularly as Roku itself expands its own ad-supported content offerings.
| Competitor | Key Strengths | 2024 Market Impact/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Fire TV | Ecosystem integration (Prime Video, e-commerce, Alexa), vast resources | Continued strong sales momentum, aggressive pricing |
| Apple TV | Hardware/software ecosystem integration, App Store, Apple Music | Focus on premium user experience and service bundles |
| Google TV (Android TV) | Search dominance, advertising, cloud services, smart home integration | Expanding platform presence on Android TV-based sets |
| Traditional Media (e.g., Max, Paramount+) | Extensive content libraries, brand loyalty, advertising budgets | Investing heavily in exclusive streaming content, bundling strategies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers have a vast array of substitutes for Roku devices, significantly impacting its competitive landscape. Smart TVs from major manufacturers like Samsung and LG, equipped with their own integrated operating systems, offer direct access to streaming services, bypassing the need for a separate streaming box. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 60% of US households owned a smart TV.
Beyond smart TVs, gaming consoles such as PlayStation and Xbox, along with mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, and even personal computers, all function as effective substitutes. These devices provide robust streaming capabilities, allowing users to access content without a dedicated Roku player. This widespread availability of alternative streaming pathways puts pressure on Roku’s market position.
Despite the rise of streaming, traditional broadcast and cable television continue to be a viable substitute for Roku. Many households still rely on these formats for familiar entertainment, especially for live events, news, and sports. This accessibility, often without requiring an internet connection or a dedicated streaming device, appeals to a segment of the market.
In 2024, while streaming services continue to gain traction, linear TV still commands a significant audience. For instance, in the US, while cord-cutting accelerated, a substantial portion of households still subscribe to cable or satellite TV. This enduring presence means traditional television remains a competitive force, offering a distinct value proposition centered on established viewing habits and guaranteed access to certain content.
While less prevalent today, physical media like DVDs and Blu-rays, alongside offline activities such as reading, board games, and outdoor pursuits, function as substitutes for streaming services. These alternatives provide distinct engagement methods and appeal to varied leisure preferences, drawing consumer time and focus away from digital platforms. For instance, the home video market, though declining, still held some relevance, with Blu-ray sales contributing to the physical media landscape. These offline options represent a wider spectrum of leisure choices that compete for consumer attention and discretionary spending.
Direct-to-Consumer Content Applications
The threat of substitutes for platforms like Roku is growing as more content providers bypass aggregators. Many major studios and networks, including Disney (Disney+), Warner Bros. Discovery (Max), and Paramount Global (Paramount+), now offer direct-to-consumer streaming applications. This allows users to subscribe and watch content on any internet-connected device, such as smart TVs, smartphones, and tablets, without needing a specific hardware platform like Roku. In 2023, the global direct-to-consumer streaming market was valued at over $100 billion, indicating a significant shift in consumer behavior towards standalone services.
This trend directly impacts Roku's position as an aggregator. While Roku devices provide access to these direct-to-consumer apps, the underlying technology is often available on competing smart TV operating systems or even through devices like Amazon Fire TV sticks and Apple TVs. The ease of downloading an app on a different platform diminishes the unique necessity of relying solely on Roku for content consumption. For example, a user wanting to watch content from Netflix or Hulu can do so via a web browser on a computer or a dedicated app on a mobile device, bypassing the need for a Roku box altogether.
- Content Independence: Consumers can access services like Netflix, HBO Max, and Disney+ directly without a Roku device.
- Device Proliferation: Smart TVs, gaming consoles, and mobile devices offer native app stores, providing alternative avenues for streaming.
- Bundling Strategies: Content providers increasingly bundle services or offer standalone subscriptions, reducing reliance on third-party platforms.
- Cost Considerations: Some consumers may opt for direct subscriptions or free ad-supported streaming services (FAST) as substitutes for aggregated platforms.
Alternative Forms of Digital Entertainment
Beyond direct streaming competitors, any digital activity that occupies a consumer's leisure time can be considered a substitute for Roku's core offering. This encompasses extensive use of social media platforms, video gaming, web browsing, consuming podcasts, or engaging with other digital content not primarily focused on video streaming.
Roku competes for a finite amount of consumer attention and time. For instance, in 2024, the average global internet user spent approximately 6 hours and 37 minutes online daily, with a significant portion dedicated to social media and gaming. This directly siphons off potential viewing hours from streaming services available on Roku devices.
- Social Media Dominance: Platforms like TikTok and Instagram continue to capture significant user engagement, offering short-form, endlessly scrollable content that competes directly for leisure time.
- Video Gaming Growth: The global video game market is projected to reach over $250 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial allocation of consumer time and discretionary spending towards interactive entertainment.
- Podcast Popularity: The podcast industry has seen remarkable growth, with millions of active podcasts available and a substantial portion of the population regularly tuning in, providing an alternative audio-visual or purely audio entertainment option.
- User-Generated Content: The proliferation of platforms like YouTube and Twitch, where users create and consume a vast array of content, also presents a strong substitute to professionally produced streaming video.
The threat of substitutes for Roku is substantial and multifaceted, impacting its market position. Consumers have numerous alternatives for accessing streaming content, ranging from integrated smart TV operating systems to gaming consoles and mobile devices. By late 2023, over 60% of US households already owned a smart TV, offering a built-in streaming solution.
Content providers increasingly offer direct-to-consumer (DTC) services, allowing users to subscribe and watch via any internet-connected device, bypassing the need for a third-party aggregator like Roku. The global DTC streaming market exceeded $100 billion in 2023, highlighting this shift. Furthermore, traditional linear TV remains a competitor, with a significant portion of households still relying on cable or satellite services, especially for live events.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Roku |
| Integrated Smart TVs | Samsung Tizen, LG webOS | Reduces demand for separate streaming devices. |
| Gaming Consoles & Mobile Devices | PlayStation, Xbox, Smartphones, Tablets | Offer native app support and alternative streaming pathways. |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Services | Disney+, Max, Paramount+ | Diminishes Roku's role as an essential aggregator. |
| Traditional TV | Cable, Satellite | Appeals to users preferring established viewing habits and live content. |
| Digital Leisure Activities | Social Media, Gaming, Podcasts | Compete for consumer attention and time, diverting from streaming. |
Entrants Threaten
Developing, manufacturing, and distributing streaming devices like those Roku offers demands a significant upfront investment. This includes substantial spending on research and development to create competitive hardware and software, alongside the costs associated with building and managing a robust supply chain. For instance, in 2024, the global market for streaming devices was valued at over $25 billion, with R&D often consuming a considerable percentage of revenue for leading companies.
New companies entering this space would encounter substantial financial barriers. They would need to match the capital outlay of established players like Roku, who already possess advantages such as economies of scale in production and established relationships with manufacturers. Roku's extensive distribution networks, built over years, also represent a costly hurdle for any newcomer to overcome, making direct competition in the hardware segment particularly challenging.
Roku's established brand recognition and its expansive streaming ecosystem present a significant barrier to new entrants. Building this kind of trust and comprehensiveness, which includes a vast app store and strong content partnerships, requires substantial time and capital. For instance, as of early 2024, Roku boasted over 80 million active accounts, a testament to its user base that new players would find incredibly difficult to replicate quickly.
Roku's robust intellectual property portfolio, particularly its proprietary streaming operating system, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. Developing a comparable, feature-rich platform from the ground up would demand immense investment in research and development, estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars for a comparable ecosystem.
Licensing Roku's established technology is also a costly proposition, requiring new players to secure rights to a proven and reliable OS. This is especially true for those aiming to partner with TV manufacturers, where a mature and widely adopted platform is crucial for market penetration.
In 2024, the value of intellectual property in the streaming device market continues to climb, with companies actively seeking to protect their innovations. Roku's patent filings related to streaming optimization and user interface design underscore the depth of its IP moat, making it economically challenging for newcomers to replicate or circumvent.
Network Effects in Advertising Business
Roku's advertising business thrives on powerful network effects. A growing base of viewers naturally draws in more advertisers seeking access to that audience. This increased advertiser demand fuels Roku’s revenue, allowing for reinvestment in exclusive content and platform enhancements, which then attracts even more users, creating a virtuous cycle.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this dynamic. It's incredibly challenging to simultaneously build a substantial user base and attract a critical mass of advertisers needed to generate competitive ad revenue. This dual requirement acts as a robust barrier to entry.
- Network Effect: Roku's platform benefits from a two-sided market where more users attract more advertisers, and more advertiser investment can lead to better content, attracting more users.
- Barrier to Entry: New entrants must overcome the significant challenge of building both a large, engaged user base and a compelling advertiser ecosystem simultaneously.
- Data Point: In Q1 2024, Roku reported that its platform reached 101.3 million active accounts, a key metric for advertisers.
- Advertiser Appeal: The sheer scale of Roku's audience in 2024 makes it a highly attractive channel for advertisers, a position difficult for new entrants to quickly achieve.
Existing Partnerships and Distribution Channels
Roku's established partnerships act as a significant barrier to entry. The company has invested years in building strong ties with TV manufacturers, content creators, and advertising firms. These deep relationships translate into preferential treatment, better terms, and extensive reach for Roku's platform.
New competitors entering the streaming device market would find it incredibly challenging to replicate Roku's network of alliances. Securing comparable distribution agreements and access to essential channels is a formidable task, particularly as major industry players are often committed to long-term arrangements with Roku. For instance, in 2024, Roku announced expanded partnerships with manufacturers like TCL and Hisense, further solidifying its market presence.
- Deeply Ingrained Relationships: Roku's years of cultivation with TV OEMs, content providers, and ad agencies create a robust ecosystem.
- Preferential Treatment and Terms: These partnerships often include favorable terms and priority access, which are difficult for newcomers to match.
- Distribution Channel Lock-in: Key stakeholders are frequently bound by existing, long-term agreements, limiting opportunities for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the streaming device market, where Roku operates, is significantly dampened by substantial capital requirements. Developing and manufacturing competitive hardware, coupled with establishing extensive distribution networks, demands immense financial resources. For example, in 2024, the sheer scale of investment needed to build a comparable ecosystem, including R&D and supply chain management, easily runs into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars for any aspiring player.
Economies of scale and established relationships also present formidable barriers. Roku benefits from lower per-unit production costs due to its high volume, a feat difficult for newcomers to match. Furthermore, securing prime shelf space and favorable terms with retailers and content providers, as Roku has achieved by 2024, requires years of negotiation and proven market performance, creating a substantial hurdle for nascent companies.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Roku's Advantage (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Discourages new players due to upfront investment needs. | Established infrastructure and scale lead to lower per-unit costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower production costs due to high sales volume. | New entrants struggle to compete on price. | Roku's market leadership allows for significant cost advantages. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to retail shelf space and pre-installation on TVs. | Newcomers face difficulty securing broad market access. | Roku has deep partnerships with major TV manufacturers and retailers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Roku leverages data from company investor relations sites, competitor announcements, market share data, and industry research reports to inform each aspect of the analysis.
