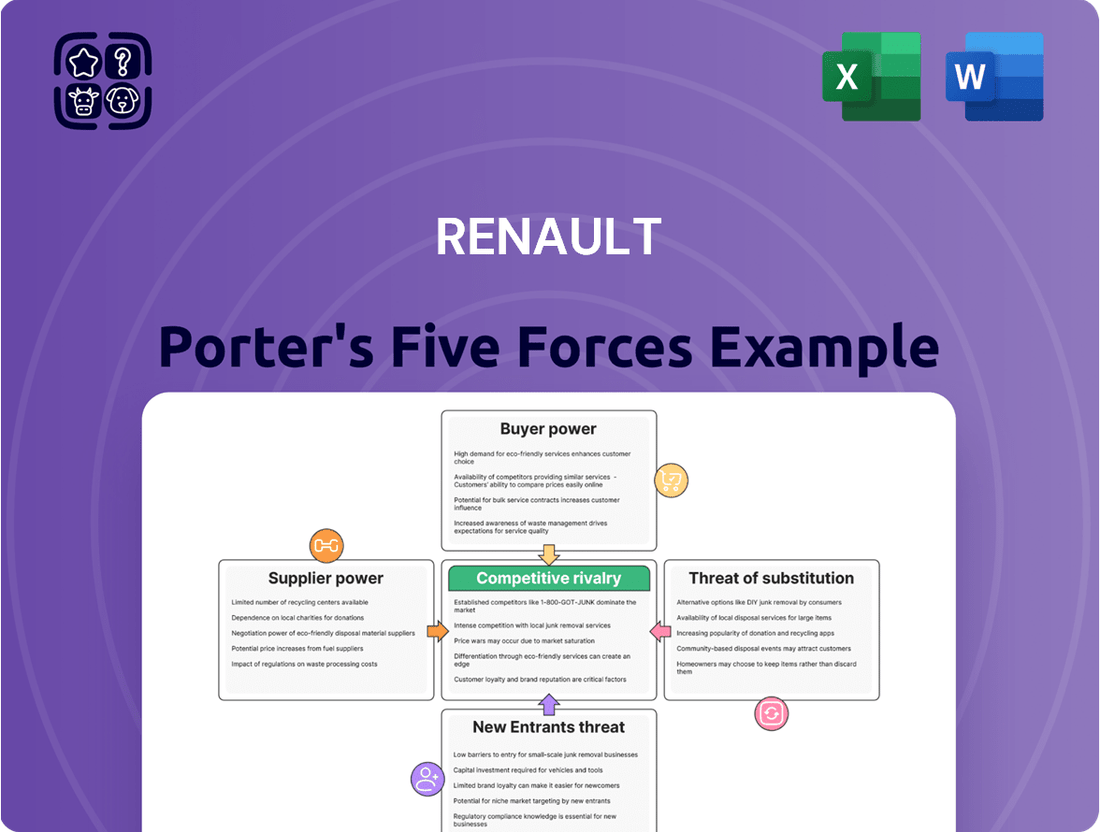
Renault Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Renault Bundle
Renault's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals a dynamic automotive landscape. High threat of new entrants is tempered by significant capital requirements, while buyer power is considerable due to brand loyalty and product differentiation challenges. The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly for specialized components, presents a notable force.
The intensity of rivalry among established automotive giants is fierce, impacting pricing and innovation. Furthermore, the threat of substitutes, from public transport to emerging mobility solutions, demands constant adaptation. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Renault’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The automotive sector, including major players like Renault, continues to grapple with the scarcity of vital raw materials. This includes essential items like semiconductors, which are critical for modern vehicle electronics, and lithium, a cornerstone for electric vehicle batteries. The ongoing global demand and sometimes limited production capacity for these components significantly bolster the bargaining power of their suppliers.
When these key materials become scarce, suppliers can dictate higher prices. For Renault, this translates directly into increased production costs. For example, the average price of lithium carbonate saw significant fluctuations in 2023, with spot prices reaching highs that would directly impact battery manufacturing costs for automakers. This situation can force Renault to absorb these higher costs or pass them on to consumers, potentially affecting sales volume.
Furthermore, these supply chain disruptions can lead to substantial production delays. In 2023, many automakers reported production cuts due to semiconductor shortages, with some estimates suggesting millions of vehicles were not produced globally. For Renault, such delays mean lost revenue and a weakened ability to meet market demand, giving suppliers even more leverage in negotiations.
Suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary technologies, such as those for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or electric vehicle (EV) battery components, wield considerable bargaining power over Renault. These innovators are critical for Renault's ability to stay competitive and adapt to changing market trends and stricter environmental regulations. For instance, in 2024, the global ADAS market was projected to reach over $45 billion, highlighting the significant value and dependence on specialized tech providers.
Consolidation within the automotive supply chain significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. As fewer, larger entities emerge, manufacturers like Renault face a reduced pool of potential partners, granting these dominant suppliers greater leverage in negotiations. This can translate into less favorable pricing structures and stricter contract terms for Renault, impacting its cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
Switching Costs for Renault
Switching suppliers for critical automotive components presents significant challenges for Renault, directly impacting the bargaining power of its suppliers. The intricate nature of automotive supply chains means that replacing a supplier involves substantial costs and potential disruptions. These costs are not merely financial; they include the time and resources needed for new supplier qualification, retooling, and ensuring seamless integration of new parts into existing production lines.
The automotive industry demands rigorous quality control and adherence to specific technical standards. When Renault considers changing a supplier, it must undertake extensive testing and validation processes for new components, which can take months or even years. This lengthy qualification period, coupled with the risk of production delays if the new supplier fails to meet expectations, creates a strong incentive for Renault to maintain relationships with established, reliable suppliers, thereby strengthening supplier power.
- High Integration Costs: Replacing specialized components requires significant investment in new tooling and re-engineering existing systems.
- Stringent Quality Assurance: The automotive sector's demanding quality standards necessitate lengthy and expensive validation processes for new suppliers.
- Long Qualification Cycles: The time required to vet and approve new suppliers can disrupt production schedules and add considerable expense.
- Risk of Production Downtime: A poorly managed supplier transition can lead to manufacturing halts, incurring substantial financial losses for Renault.
Labor and Logistics Costs
Rising labor costs significantly influence the bargaining power of suppliers to Renault. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry, including component manufacturers, faces upward pressure on wages due to inflation and skilled labor shortages. This can lead suppliers to increase their prices, directly impacting Renault's production costs.
Volatile global logistics expenses also bolster supplier leverage. Shipping rates, influenced by fuel prices and geopolitical events, can fluctuate dramatically. In late 2023 and early 2024, disruptions in key shipping lanes and increased energy costs have contributed to higher freight expenses, which suppliers will likely pass on to automotive manufacturers like Renault.
- Labor Cost Impact: In 2024, many European countries experienced average wage growth of 3-5%, directly affecting suppliers' operational expenses.
- Logistics Cost Volatility: The cost of shipping a container globally saw significant increases throughout 2023, with some routes doubling in price, a trend that continued into early 2024.
- Supplier Pricing Power: These increased input costs empower suppliers to negotiate higher prices for parts and materials, potentially squeezing Renault's profit margins.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Renault's ability to absorb or mitigate these rising costs depends on its supplier relationships and its own cost-management strategies.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Renault is considerably high due to the scarcity of critical raw materials like semiconductors and lithium, impacting production costs and timelines. Suppliers of specialized technologies and consolidated supply chain entities also wield significant leverage. High integration costs, stringent quality assurance, and long qualification cycles make switching suppliers a challenging and expensive endeavor for Renault, further empowering existing suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Renault | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Scarcity | Increased production costs, potential delays | Lithium carbonate prices fluctuated significantly in 2023; semiconductor shortages led to millions of lost vehicle production globally in 2023. |
| Specialized Technologies | Dependence on key tech providers for competitiveness | Global ADAS market projected to exceed $45 billion in 2024. |
| Supplier Consolidation | Reduced negotiation options, less favorable terms | Industry trend leading to fewer, larger suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | Incentive to maintain existing relationships | Qualification cycles can take months/years; significant investment in retooling. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Renault's light commercial vehicle segment. It analyzes the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitutes and new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry within the Porter's Five Forces framework.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the Renault Porter's Five Forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the automotive market are highly price-sensitive, especially when considering brands like Renault. The internet has made it incredibly easy for buyers to compare prices, features, and available incentives across numerous manufacturers. For instance, data from early 2024 indicated that average new car prices in many key markets remained elevated, pushing consumers to seek the best value, which directly amplifies their bargaining power.
This readily available information empowers customers to negotiate more effectively, as they can easily identify if a competitor offers a similar vehicle at a lower price or with better terms. Renault, like other automakers, must contend with this heightened price transparency, which can pressure profit margins if not managed strategically. The ability to quickly compare deals means customers can walk away from a less competitive offer, forcing manufacturers to be more accommodating.
The automotive market, including Renault's segment, is characterized by a vast selection of vehicle models and brands. In 2024, consumers have access to offerings from established giants, niche manufacturers, and increasingly, new entrants, providing a wealth of alternatives. This abundance directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers, as they can readily explore and switch to competitors if Renault's pricing or product features are not to their liking.
For instance, the sheer number of available compact SUVs, a key segment for Renault, means a customer dissatisfied with a Renault Captur could easily consider a Volkswagen T-Cross, a Peugeot 2008, or even an electric option like the MG ZS EV. This ease of comparison and switching significantly amplifies customer leverage, forcing manufacturers like Renault to remain competitive in terms of features, quality, and price to retain market share.
As new car inventory levels rebound, especially in markets like the United States, the bargaining power of customers is on the rise. Following periods of significant scarcity in 2022 and 2023, where inventory hovered around critically low levels, many manufacturers are now seeing a build-up. For instance, in early 2024, the days' supply of new vehicles in the U.S. has been steadily climbing, offering buyers more choice and less pressure to commit quickly.
This increase in available stock directly translates into greater leverage for consumers. With more vehicles on dealership lots, the need for immediate purchases diminishes, allowing customers to negotiate more effectively. We're likely to see a return of more competitive pricing and incentives, as dealerships work to move these growing inventories, further tipping the scales in favor of the buyer.
Growing Demand for EVs and Connectivity
The increasing consumer interest in electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced connectivity features significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. Buyers are becoming more discerning, demanding better range, faster charging, and seamless integration of digital services. This influences manufacturers like Renault to prioritize these aspects to remain competitive.
Customers can leverage their preferences in several ways:
- Demand for Extended Range: As EV technology progresses, consumers expect longer driving ranges on a single charge, pushing manufacturers to invest in battery advancements. For instance, by mid-2024, the average EV range in many markets is approaching or exceeding 300 miles, setting a new benchmark.
- Charging Infrastructure Expectations: The availability and speed of charging infrastructure are critical purchasing factors. Customers are less willing to compromise on this, prompting automakers to collaborate on charging networks or develop proprietary solutions.
- Connectivity and Software Features: Integrated infotainment systems, over-the-air updates, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are increasingly becoming non-negotiable. Renault's investment in its "Software Defined Vehicle" strategy directly addresses this, aiming to meet consumer desires for smart, connected mobility.
- Price Sensitivity and Competition: While demand is growing, price remains a significant factor. The expanding number of EV models from various manufacturers intensifies competition, giving customers more options and leverage to negotiate prices or seek better value propositions.
After-Sales Service and Brand Loyalty
The bargaining power of customers for Renault is significantly influenced by the after-sales service, warranty offerings, and the perceived resale value of their vehicles. Customers can exert pressure by demanding better terms on maintenance, repairs, and extended warranties. A robust service network and reliable product can foster brand loyalty, thereby reducing customer power.
Renault's efforts in customer retention are crucial, as a single negative experience with after-sales support can lead to customer defection. For instance, in 2023, customer satisfaction scores related to after-sales service played a key role in repeat purchase decisions for many automotive brands. Renault's focus on improving service quality and transparent pricing directly addresses this customer leverage.
- After-Sales Service Impact: Customers leverage their need for ongoing service and repairs to negotiate better terms or seek alternative providers.
- Brand Loyalty as a Mitigator: Strong brand loyalty, built on positive ownership experiences and reliable after-sales support, can significantly lessen customer bargaining power.
- Resale Value Influence: A strong resale value enhances customer confidence and can reduce their willingness to switch brands, thereby diminishing their bargaining leverage.
- Customer Satisfaction Metrics: Renault monitors customer satisfaction surveys, which often highlight after-sales service as a critical factor in brand loyalty and future purchasing decisions.
Customers possess substantial bargaining power due to the automotive industry's inherent nature and evolving market dynamics. High price sensitivity, fueled by readily available online price comparisons and the sheer volume of competitive models, empowers buyers to negotiate favorable terms. For example, in early 2024, increased new car inventory levels across many markets meant consumers had more choice and less urgency, strengthening their position to demand better pricing and incentives.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data (Early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity & Transparency | High - Easy access to competitor pricing online. | Elevated average new car prices drove demand for best value. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High - Numerous brands and models across segments. | Abundance of compact SUVs meant easy switching between brands like Renault, VW, Peugeot. |
| Inventory Levels | Increasingly High - Rebounding stock provides more choice. | Rising days' supply of new vehicles in the U.S. offered consumers more negotiation leverage. |
| EV & Technology Demands | High - Specific expectations for range, charging, connectivity. | Average EV range approaching 300 miles set a new benchmark, influencing manufacturer R&D. |
| After-Sales Service & Resale Value | Moderate to High - Influences loyalty and future purchases. | Customer satisfaction with after-sales service in 2023 was a key driver of repeat purchases. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Renault Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our comprehensive Five Forces Analysis of the Renault Porter meticulously details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global automotive sector, including Renault's operating environment, is crowded with numerous established manufacturers and a surge of new entrants, especially in the electric vehicle (EV) space. This high number and diversity of competitors means Renault constantly contends with a broad spectrum of rivals, from legacy automakers to agile EV startups.
In 2024, the competitive intensity remains a defining characteristic. For instance, the Volkswagen Group, a major global competitor, reported a significant increase in vehicle deliveries, showcasing the scale of operations against which Renault must compete. Likewise, the rapid expansion of Chinese EV manufacturers like BYD, which saw substantial sales growth through 2024, adds another layer of diverse competitive pressure, forcing Renault to innovate and adapt quickly.
The automotive market anticipates modest global growth, yet established regions like Europe are experiencing maturity and slower expansion. This maturity fuels an intensified battle for market share among established players, including Renault, pushing them to compete more aggressively for every sale.
In 2023, global light vehicle sales reached approximately 89.2 million units, a 7% increase from 2022, signaling continued demand but also highlighting regional variations. Mature markets are particularly competitive, with companies vying for incremental gains, making pricing and product innovation critical for success.
The automotive industry, including major players like Renault, is characterized by massive fixed costs associated with research, development, and manufacturing facilities. These high upfront investments necessitate high production volumes to spread costs and achieve profitability. For instance, the average cost to develop a new car model can exceed $1 billion.
This inherent need for high sales volumes to offset substantial fixed costs and achieve economies of scale directly intensifies competitive rivalry. Manufacturers are compelled to push for market share, often through aggressive pricing and promotional activities, to ensure their production lines run at optimal capacity.
Companies like Renault, operating in this environment, face constant pressure to sell vehicles. If a plant operates significantly below its capacity, the per-unit cost increases dramatically, eroding profit margins. In 2024, the global automotive industry continued to grapple with overcapacity in many segments, further fueling price wars and intense competition for every sale.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Race
Competitive rivalry in the automotive sector, including for Renault, is intensely driven by a relentless innovation race across electric powertrains, autonomous driving capabilities, in-car connectivity, and evolving vehicle design. Renault's strategy heavily relies on substantial R&D investment and the consistent introduction of new models to distinguish its products and maintain market relevance. This is exemplified by their proactive product offensive, aiming to capture market share in key segments.
The pressure to innovate is palpable, with rivals frequently launching cutting-edge technologies. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry saw significant advancements in battery technology, leading to increased range and faster charging times for electric vehicles, a critical area for Renault's competitiveness. The market is saturated with offerings, forcing companies to invest heavily in differentiation to avoid commoditization.
- Innovation Hotspots: Electric powertrains, autonomous driving, connectivity, and vehicle design are key battlegrounds.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in research and development is essential for differentiation.
- Product Offensive: Renault's product offensive aims to introduce a stream of new models to capture market share.
- Competitive Intensity: High rivalry necessitates constant adaptation and technological advancement to remain competitive.
Geopolitical and Regulatory Pressures
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can significantly disrupt supply chains and market access for automotive manufacturers like Renault. For instance, ongoing trade friction between major economic blocs can lead to increased tariffs, making it more expensive to import or export vehicles and components, thereby intensifying competitive pressures. Renault, with its global manufacturing footprint, must navigate these complex and often unpredictable international relations.
Evolving environmental regulations, particularly around CO2 emissions, are a critical factor shaping the competitive landscape. The European Union, for example, has ambitious targets, with a goal to reduce CO2 emissions from cars by 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels, and aims for a 100% reduction by 2035, effectively banning the sale of new petrol and diesel cars. This necessitates substantial investment in electric vehicle (EV) technology and production, creating a competitive race among automakers to develop and market compelling EV models. Companies that fail to adapt quickly risk falling behind and losing market share.
The need to comply with varying regulatory standards across different markets creates an uneven playing field. Renault must invest in adapting its vehicle designs and production processes to meet diverse requirements, from safety standards to emissions controls, in countries where it operates. This adds complexity and cost, potentially impacting the price competitiveness of its offerings compared to rivals with simpler market focuses.
- Global Regulatory Divergence: Different countries impose distinct emission standards and safety regulations, requiring automakers to tailor production and product lines, impacting economies of scale.
- EV Mandates: Increasingly stringent CO2 emission targets, like those in the EU aiming for a 55% reduction by 2030 and a ban on new internal combustion engine sales by 2035, compel rapid investment in electric vehicle technology.
- Trade Policy Impact: Tariffs and trade agreements directly influence the cost of imported components and finished vehicles, altering competitive pricing and supply chain strategies.
- Geopolitical Instability: Regional conflicts or political shifts can disrupt manufacturing operations, access to raw materials (like battery components), and consumer demand in affected markets.
Competitive rivalry within the automotive sector is extremely high, with numerous global manufacturers and emerging EV startups vying for market share. This intensity is fueled by substantial fixed costs, requiring high production volumes and often leading to aggressive pricing and promotional activities. Renault faces constant pressure to innovate, with rivals like Volkswagen and Chinese EV makers such as BYD making significant advancements.
The race for technological leadership, particularly in electric powertrains and autonomous driving, is fierce. For example, in 2024, significant improvements in battery technology by competitors mean Renault must invest heavily in R&D to remain competitive and avoid product commoditization. The global market, while showing growth in 2023 with approximately 89.2 million light vehicle sales, is also characterized by regional maturity, intensifying the battle for every sale.
| Competitor Example | 2023 Sales (Units - approx.) | Key Competitive Action/Trend |
| Volkswagen Group | 9.2 million | Increased deliveries, strong EV push |
| BYD | 3.02 million (New Energy Vehicles) | Rapid global expansion, aggressive pricing in EV segment |
| Renault Group | 2.9 million (FY23) | Product offensive with new models, focus on electrification |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rising accessibility and convenience of public transportation systems, coupled with the boom in ride-sharing and car-sharing services, directly challenge the necessity of personal vehicle ownership. In many urban centers, these alternatives offer cost-effective and flexible mobility solutions. For instance, by 2023, ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft saw continued strong user engagement, with global revenue projected to surpass $100 billion. This trend directly impacts automakers like Renault by potentially dampening demand for new car sales, particularly among younger, urban demographics.
For short urban commutes, bicycles, e-bikes, and various micro-mobility options like scooters present a growing threat to Renault's smaller vehicle sales. These alternatives are often more cost-effective and quicker than traditional cars in congested city centers. For instance, the global e-bike market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial shift in personal transportation preferences.
The surge in telecommuting and remote work, significantly accelerated by global events and technological advancements, directly impacts the automotive industry by reducing the daily need for personal transportation. As more employees work from home, the frequency of car usage for commuting drops, potentially extending the lifespan of existing vehicles and decreasing demand for new car sales. This trend, evident in the continued strength of hybrid work models throughout 2024, means fewer miles are driven on average, lessening the urgency for vehicle replacement.
Walking and Active Transportation
Urban planning initiatives focused on enhancing walkability and creating pedestrian-friendly infrastructure are increasingly offering viable alternatives to short-distance car trips for many individuals. These developments directly substitute for personal vehicle use, contributing to a gradual shift in transportation habits.
The growing emphasis on active transportation, supported by infrastructure investments, presents a tangible threat to car manufacturers and related industries. For instance, cities like Paris have actively expanded their pedestrian zones and cycling networks, aiming to reduce car dependency.
- Increased Walkability: Cities globally are investing in pedestrian infrastructure, making walking a more attractive option for short journeys.
- Cycling Infrastructure Growth: The expansion of bike lanes and bike-sharing programs provides a cost-effective and healthy alternative to driving.
- Public Health Initiatives: Campaigns promoting active lifestyles further encourage walking and cycling, indirectly reducing demand for automotive transport.
- Reduced Vehicle Miles Traveled (VMT): A rise in active transportation can lead to a decrease in overall VMT, impacting fuel sales and vehicle maintenance.
Evolution of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
The rise of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms presents a substantial threat by offering integrated, on-demand transportation solutions. These platforms bundle public transit, ride-sharing, bike-sharing, and scooter services into a single subscription, directly challenging traditional car ownership models. For instance, by mid-2024, many European cities are seeing increased adoption rates of MaaS apps, with some reporting over 20% of urban commuters utilizing these integrated services. This shift encourages a move from owning a vehicle to subscribing to mobility, impacting long-term automotive sales.
The convenience and cost-effectiveness of MaaS can significantly reduce the perceived need for personal vehicle ownership. Consumers can access a variety of transport options through one app, often at a lower overall cost than maintaining a car, especially in urban environments. In 2024, studies indicated that for frequent urban travelers, a comprehensive MaaS subscription could be up to 30% cheaper than owning and operating a private vehicle. This makes it a very attractive substitute for car manufacturers like Renault.
- Integrated Mobility: MaaS platforms combine multiple transport modes, offering a seamless user experience.
- Subscription Models: Shifting consumer preference from ownership to access-based mobility services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: MaaS can offer a more economical alternative to private car ownership, particularly in cities.
- Environmental Factors: MaaS often promotes more sustainable transport options, aligning with growing eco-consciousness.
The threat of substitutes for Renault is significant, driven by evolving urban mobility trends and technological advancements. Alternatives like ride-sharing, public transit, and micro-mobility options directly challenge the necessity of personal car ownership, especially in densely populated areas. These substitutes offer convenience and cost savings, impacting traditional automotive sales models.
The increasing adoption of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms further amplifies this threat. By consolidating various transportation modes into a single, often subscription-based, offering, MaaS provides a comprehensive and potentially more economical alternative to owning a vehicle. For instance, by mid-2024, reports indicated that in many European cities, over 20% of commuters were utilizing MaaS apps, demonstrating a clear shift in consumer behavior away from private car dependency.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Renault | 2023/2024 Data Points |
| Ride-Sharing/Car-Sharing | Convenience, cost-effectiveness, reduced ownership burden | Decreased demand for new car purchases, especially in urban areas | Global ride-sharing revenue projected to exceed $100 billion in 2023. |
| Micro-mobility (Bikes, E-bikes, Scooters) | Cost-efficiency, speed in congested areas, environmental appeal | Threatens sales of smaller, urban-focused vehicles | Global e-bike market valued at approx. $25 billion in 2023, with strong growth forecasts. |
| Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) | Integrated transport, subscription models, flexibility | Shifts focus from ownership to access, potentially reducing long-term vehicle sales | Over 20% commuter adoption in some European cities by mid-2024; potential 30% cost savings vs. car ownership in urban settings. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive sector, including major players like Renault, faces a substantial threat from new entrants due to incredibly high capital requirements. Establishing a new automotive manufacturing operation demands billions of dollars for research and development, state-of-the-art factories, building a complex global supply chain, and extensive marketing campaigns. For instance, setting up a new EV battery plant alone can cost upwards of $2 billion. This financial hurdle acts as a significant deterrent, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold against established giants.
Established brand loyalty significantly deters new entrants in the automotive sector, a prime example being Renault. Incumbent manufacturers like Renault have cultivated deep customer relationships over decades, fostering trust and repeat business. This loyalty is often reinforced by extensive and well-established dealer networks, providing crucial sales, service, and parts accessibility that new players struggle to replicate. For instance, as of late 2023, Renault maintained a robust presence with thousands of dealerships globally, a critical asset for customer retention.
The automotive sector, including major players like Renault, faces substantial threats from new entrants due to rigorous regulatory hurdles. New companies must comply with demanding safety regulations, such as those set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the US, and stringent emissions standards, like Euro 7 in Europe, which are constantly evolving and require significant R&D investment. Meeting these requirements necessitates advanced engineering and substantial capital, acting as a powerful deterrent for potential newcomers.
Technological Complexity and Expertise
The automotive industry, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and connected car technology, presents significant technological hurdles for new entrants. Designing, engineering, and manufacturing these sophisticated vehicles demands specialized expertise and intricate production capabilities that are difficult and time-consuming to acquire. This high degree of technical complexity acts as a substantial barrier, deterring many potential new players from entering the market. For instance, developing battery technology for EVs alone requires immense R&D investment and specialized knowledge, a capital outlay that can easily run into billions of dollars.
Newcomers must bridge substantial knowledge gaps in areas like software integration, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and autonomous driving technologies. The learning curve is steep, and the investment in skilled personnel and advanced research facilities is considerable. Companies like Tesla demonstrated this by investing heavily in proprietary software and battery management systems, setting a high bar for competitors. The ongoing evolution of automotive software, which now constitutes a significant portion of a vehicle's value, further elevates this technical barrier.
- High R&D Costs: Developing cutting-edge automotive technology, especially for EVs and autonomous systems, can cost billions, deterring smaller entrants.
- Specialized Skillsets: The industry requires highly skilled engineers in areas like battery chemistry, AI, and software development, which are in high demand and short supply.
- Complex Manufacturing Processes: Modern automotive production involves sophisticated robotics, precision engineering, and intricate supply chain management, demanding significant capital investment and operational expertise.
- Intellectual Property: Existing players hold extensive patents in critical areas, making it challenging for new entrants to innovate without infringing on intellectual property rights.
Rise of EV-Focused Startups and Chinese Manufacturers
The automotive industry's pivot to electric vehicles (EVs) has significantly altered the landscape, creating new avenues for entry. Despite substantial capital requirements for manufacturing, the specialized nature of EV technology has, in some ways, lowered traditional barriers for newcomers focused solely on this segment. This has led to a surge in EV-focused startups and, notably, well-capitalized Chinese manufacturers who are rapidly expanding their global reach.
These agile entrants often possess inherent cost advantages, particularly in battery production and streamlined manufacturing processes. For established players like Renault, this presents a growing competitive threat. For instance, BYD, a leading Chinese EV manufacturer, saw its revenue surge by 42% in 2023, reaching approximately $83.5 billion, and has rapidly ascended to become a dominant force in the global EV market, challenging incumbent automakers.
- EV Startups: Companies like Tesla have demonstrated the viability of new entrants disrupting the market.
- Chinese Manufacturers: BYD, NIO, and XPeng are aggressively expanding into European markets, offering competitive pricing and advanced technology.
- Cost Advantages: Chinese EV makers often benefit from lower production costs and government support, enabling aggressive pricing strategies.
- Market Share Gains: In 2023, Chinese brands captured a significant portion of the EV market share in several European countries, pressuring traditional automakers.
While established automakers like Renault face high capital and regulatory barriers, the shift to electric vehicles (EVs) has opened doors for new, agile competitors. Chinese manufacturers, in particular, are leveraging cost advantages in battery production and streamlined processes to gain significant market share. This trend is evident in BYD's impressive 2023 revenue growth of 42%, reaching approximately $83.5 billion, highlighting the competitive pressure on traditional players.
| Emerging Competitor Type | Key Advantage | 2023 Market Impact Example |
| Chinese EV Manufacturers | Cost-efficient battery production, streamlined manufacturing | BYD revenue grew 42% to ~$83.5 billion |
| EV Startups | Agile innovation, direct-to-consumer models | Tesla continues to set benchmarks in EV technology and sales |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Renault leverages data from annual reports, industry expert interviews, and automotive market research databases to understand competitive dynamics.
We gather insights from competitor financial statements, government automotive statistics, and trade association publications to assess the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
