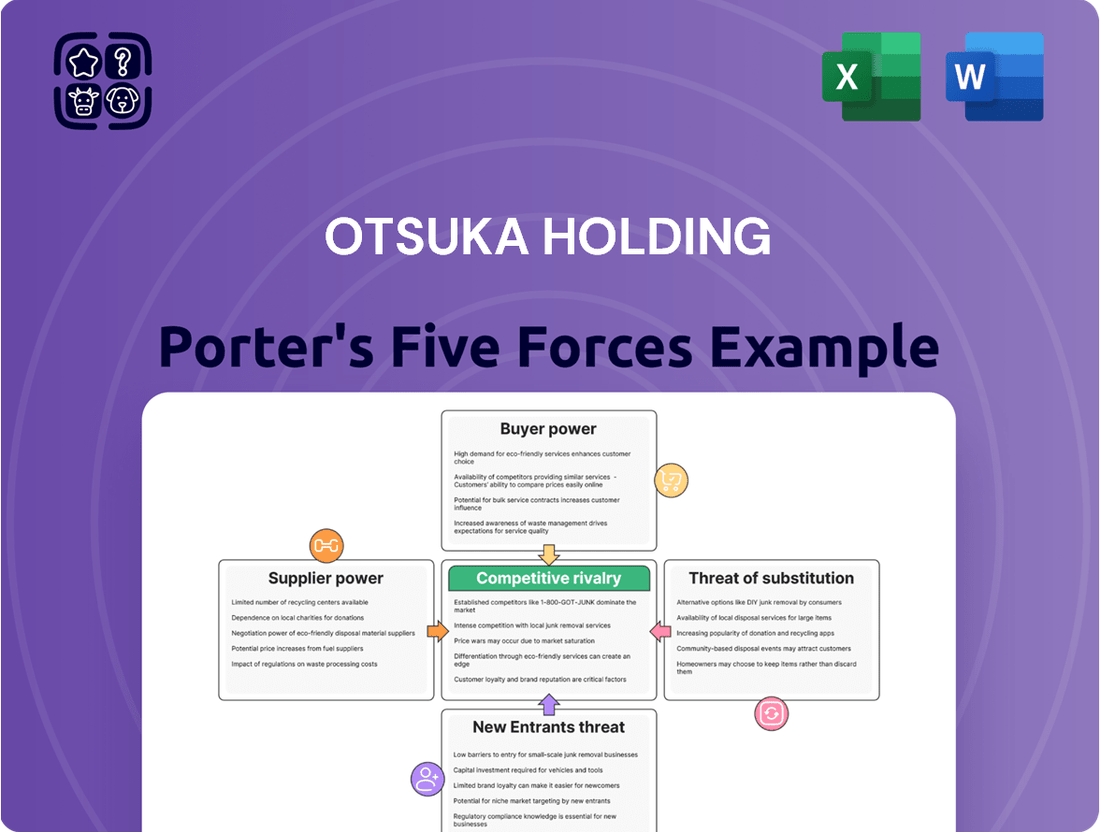
Otsuka Holding Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Otsuka Holding Bundle
Otsuka Holding navigates a complex pharmaceutical landscape, where the threat of new entrants is tempered by high R&D costs and regulatory hurdles. However, intense rivalry among established players and the bargaining power of buyers, particularly large healthcare systems, exert significant pressure.
The availability of substitutes, though limited in the highly specialized pharmaceutical sector, remains a constant consideration for Otsuka's product pipeline. Understanding the intricate interplay of these forces is crucial for strategic planning and sustained growth.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Otsuka Holding’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The pharmaceutical sector, including Otsuka, often depends on a narrow group of suppliers for highly specialized raw materials and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). This reliance is particularly pronounced with manufacturers located in Asia, creating a concentrated supply base. For instance, the global API market, valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023, shows significant concentration in countries like China and India, where many critical components originate.
This concentration grants these specialized suppliers considerable bargaining power. If a few key suppliers decide to increase prices or face production disruptions, it can directly and significantly impact Otsuka's manufacturing costs and overall production schedules. The limited number of sources for essential pharmaceutical components introduces a notable vulnerability into the supply chain, making it susceptible to external pressures.
Switching suppliers in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries carries significant financial and operational burdens for companies like Otsuka. These costs stem from rigorous regulatory approval processes, meticulous quality control, and extensive validation procedures required for any change in the supply chain. For example, changing an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) supplier necessitates a complete re-validation of the manufacturing process, a time-consuming and costly endeavor. This inherent friction discourages frequent supplier changes, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of established, approved suppliers.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts Otsuka's bargaining power with its suppliers. While Otsuka's pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products often rely on highly specialized ingredients or patented compounds, limiting direct substitutes, the broader landscape of raw materials can present alternatives. For instance, if a particular active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is not readily available from a specialized supplier, Otsuka might explore alternative APIs with similar therapeutic effects, though this often involves extensive research and development and regulatory hurdles.
Supplier's Forward Integration Threat
Suppliers to Otsuka Holding generally pose a minimal threat of forward integration into pharmaceutical or nutraceutical manufacturing. The significant capital investment, extensive research and development, and stringent regulatory approvals required for drug development and commercialization create substantial barriers.
While direct forward integration by suppliers is rare, consolidation within specialized chemical or biotech supply markets could indirectly enhance their bargaining power. For instance, if a key raw material supplier were to acquire a smaller competitor, it might gain more leverage over buyers like Otsuka by controlling a larger share of a niche market.
The intricate and highly regulated nature of the healthcare value chain generally dissuades suppliers from undertaking the complex process of direct forward integration into manufacturing.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities can cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
- R&D Intensity: The pharmaceutical industry's R&D spending as a percentage of sales was around 15% in 2024, a figure difficult for most suppliers to match.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating FDA, EMA, and other regulatory bodies requires specialized expertise and significant time investment.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Otsuka's Cost Structure
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor for Otsuka, particularly concerning raw material costs. For pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies like Otsuka, the price of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and other essential components heavily dictates their overall cost structure. This sensitivity means that any upward pressure on these inputs directly affects Otsuka's profitability.
The increasing cost of these vital raw materials is a significant concern. For instance, some manufacturers have reported raw material cost hikes of over 22% since 2022. Such substantial increases underscore the formidable pricing power that suppliers wield, directly impacting Otsuka's bottom line and strategic cost management.
- API and Raw Material Dominance: Raw material costs, especially for APIs, represent a substantial portion of Otsuka's production expenses, directly influencing profitability.
- Sensitivity to Price Hikes: Otsuka's profitability is directly linked to the cost of its inputs; therefore, it is highly vulnerable to supplier-driven price increases.
- Amplified Supplier Power: Recent data shows significant cost escalations, with some raw material prices surging by more than 22% since 2022, enhancing supplier leverage.
Suppliers of specialized pharmaceutical ingredients and raw materials hold significant sway over Otsuka, primarily due to the concentrated nature of this supply chain, especially with key manufacturers located in Asia. This concentration, coupled with the immense cost and regulatory complexity involved in switching suppliers, strengthens their hand considerably.
| Factor | Impact on Otsuka | Supporting Data (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High bargaining power due to limited specialized sources. | Global API market shows significant concentration in China and India. |
| Switching Costs | Substantial financial and operational burdens deter supplier changes. | Re-validation of manufacturing processes for API changes is time-consuming and costly. |
| Raw Material Price Sensitivity | Directly impacts Otsuka's profitability. | Some raw material costs increased by over 22% since 2022. |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Otsuka Holding, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive model that pinpoints strategic vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity at Otsuka varies significantly. For generic drugs and consumer nutraceuticals, buyers like healthcare systems and individuals are often quite sensitive to price. This means they actively compare options and look for the best value, which can put pressure on Otsuka's pricing for these less differentiated products.
However, Otsuka's innovative, patented pharmaceuticals, such as those for central nervous system disorders, tend to face less direct price pressure. These drugs offer unique therapeutic benefits, making customers less likely to switch based solely on price. For instance, the strong clinical data supporting Otsuka's treatments can justify higher price points.
Yet, the broader healthcare landscape is shifting towards cost containment. Insurers and governments are increasingly pushing for value-based purchasing, where drug prices are tied to their effectiveness and patient outcomes. This trend means even innovative drugs may eventually face scrutiny regarding their cost-effectiveness, influencing customer purchasing decisions over time.
In 2023, the global pharmaceutical market saw continued growth, but with an increasing focus on affordability. For example, the average drug price increase in the US, while still present, faced more pushback than in prior years, indicating a heightened awareness of cost among payers and patients alike. This environment underscores the importance of demonstrating value for Otsuka's products.
The availability of generic alternatives for Otsuka's off-patent drugs significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When patents expire, the landscape shifts, allowing lower-cost generic versions to enter the market. For instance, in 2024, the global generic drugs market was valued at over $400 billion, showcasing the substantial availability and consumer preference for these alternatives when available.
Furthermore, in Otsuka's nutraceutical and consumer health segments, customers face a vast array of competing products. This wide selection empowers consumers to easily switch brands if pricing or product features are not perceived as competitive. The sheer volume of options in the global health and wellness market, which continues to expand rapidly, forces companies like Otsuka to focus on strong product differentiation and value to retain customers.
Large healthcare systems and national health services are major purchasers of Otsuka's pharmaceutical products, wielding significant negotiating power due to their substantial order volumes. In 2023, for instance, the top 10 hospital systems in the US accounted for over $200 billion in pharmaceutical spending, demonstrating their collective clout.
Similarly, major pharmacy chains and large retail groups, as well as dominant online platforms for nutraceuticals and consumer goods, command considerable influence. Their aggregated purchasing power allows them to secure preferential pricing and terms from suppliers like Otsuka, impacting overall revenue realization.
Buyer's Backward Integration Threat
While individual consumers have minimal impact, large entities like major healthcare systems or pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) possess significant bargaining power. These powerful buyers could, in theory, consider backward integration into drug manufacturing or direct sourcing, a move that is exceedingly rare given the immense capital and technical expertise required. For instance, the global pharmaceutical market in 2024 is valued in the trillions, highlighting the scale of investment needed for such a venture.
However, their actual leverage comes from controlling drug formularies and negotiating reimbursement rates. This allows them to strongly influence pharmaceutical companies, including Otsuka, to offer more competitive pricing on their products. In 2023, PBMs played a crucial role in negotiating rebates and discounts, directly impacting drug manufacturers' revenue streams.
- High Capital Intensity: Drug manufacturing requires substantial investment in research, development, and production facilities, making backward integration a formidable barrier.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Entering pharmaceutical manufacturing involves navigating complex and stringent regulatory approvals, adding significant time and cost.
- Formulary Control: Healthcare providers and PBMs leverage their ability to dictate which drugs are covered and at what cost, exerting immense pressure on pricing.
- Reimbursement Negotiation: Their power in negotiating reimbursement policies with payers provides another critical avenue for influencing drug pricing and market access.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers increasingly have access to information, especially regarding drug pricing and health product details. Regulatory pushes and digital tools are making this information more transparent, allowing consumers to easily compare options and negotiate prices. This reduces the gap in knowledge between buyers and sellers, giving customers more leverage when making purchasing decisions from companies like Otsuka.
For example, in 2024, the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continued to enforce measures requiring price transparency from hospitals and insurers. While direct impacts on Otsuka's specific product negotiations might vary, the overall trend empowers consumers across the healthcare landscape. This heightened consumer awareness, fueled by readily available data, directly translates to increased bargaining power.
- Increased Price Transparency: Regulatory mandates and digital platforms are making drug and health product pricing more open.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Customers can now access and compare more data, leveling the playing field.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Better information allows consumers to choose products based on value and price.
- Enhanced Bargaining Power: Empowered customers can negotiate more effectively with suppliers like Otsuka.
Otsuka's customers, particularly large entities like healthcare systems and pharmacy benefit managers, wield considerable bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volumes and influence over drug formularies. The widespread availability of generic alternatives for off-patent drugs, with the global generic drug market exceeding $400 billion in 2024, further amplifies this pressure. Increased price transparency and readily accessible information empower individual consumers, enabling them to compare options and negotiate more effectively, especially in the competitive nutraceutical and consumer health segments.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Otsuka |
|---|---|---|
| Large Healthcare Systems/PBMs | High volume purchasing, Formulary control, Reimbursement negotiation | Pressure on pricing, demand for rebates and discounts |
| Individual Consumers (Generic/Nutraceuticals) | Price sensitivity, Availability of substitutes, Information access | Need for competitive pricing, strong value proposition |
| Patients (Innovative Pharmaceuticals) | Therapeutic need, Clinical data, Limited direct substitutes | Lower price sensitivity, but increasing scrutiny on value-based pricing |
Full Version Awaits
Otsuka Holding Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Otsuka Holding Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of industry competition and strategic positioning. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. It delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within Otsuka Holding's operational landscape. No mockups, no samples – the document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing immediate strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Otsuka Holdings navigates a crowded global landscape. In pharmaceuticals, it contends with giants like Pfizer, which reported over $58 billion in revenue for 2023, and Novartis, with approximately $45 billion in 2023 revenue. These established players possess vast R&D budgets and extensive distribution networks, intensifying the battle for market dominance and new drug approvals.
Beyond the pharmaceutical arena, Otsuka's nutraceutical and consumer product segments also face significant competition. Companies like Nestlé, a leader in consumer goods and health science with over $100 billion in 2023 sales, and Danone, a major player in dairy and plant-based products with around $28 billion in 2023 revenue, present formidable rivalry. This diversity of competitors, ranging from massive conglomerates to niche specialists, demands constant innovation and strategic agility.
The healthcare industry's growth rate presents a mixed picture for competitive rivalry. While segments like nutraceuticals are seeing robust expansion, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGR) between 6.4% and 11.3% through 2029, this can offer breathing room and opportunities for various companies, including Otsuka, to carve out their niches.
However, this growth doesn't uniformly reduce competitive pressure across the board. In more established pharmaceutical markets and specific therapeutic areas, where growth is more moderate, the struggle for market share becomes more intense. Competitors are more likely to aggressively vie for existing customers and revenue streams, directly impacting companies like Otsuka.
Otsuka Holding's strategy heavily relies on product differentiation, particularly in its pharmaceutical segment with innovative, original drugs. This approach aims to establish high switching costs for both patients and medical prescribers, thereby mitigating direct competition for its patented medications. For instance, the success of drugs like Abilify, a treatment for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, demonstrated the power of strong differentiation before patent expiry.
However, the competitive landscape shifts dramatically once patents expire. Generic manufacturers then enter the market, rapidly eroding the differentiation Otsuka initially established and intensifying price-based rivalry. This is a common challenge across the pharmaceutical industry, where the exclusivity of patented treatments is a temporary shield against competition.
In the nutraceutical sector, where Otsuka also operates with brands like CalorieMate, differentiation hinges on building brand loyalty and developing unique formulations. This strategy is crucial for standing out against a vast array of competitors offering similar health and wellness products. The ability to maintain unique product attributes and foster strong consumer recognition is key to sustaining market share in this crowded space.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The pharmaceutical sector, where Otsuka operates, is defined by immense fixed costs. These are driven by the enormous capital required for research and development (R&D), maintaining sophisticated manufacturing plants, and navigating stringent regulatory approvals. For instance, developing a new drug can cost billions of dollars, with the industry investing heavily in innovation year after year.
These substantial investments, especially in specialized equipment and intellectual property, erect significant exit barriers. Companies find it difficult to simply walk away from these sunk costs. This reality compels firms like Otsuka to continue competing, even in challenging economic periods, to amortize their investments and avoid substantial losses.
- High R&D Spending: In 2023, the top pharmaceutical companies spent tens of billions on R&D globally to bring new treatments to market.
- Capital Intensive Manufacturing: Building and maintaining pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities requires billions in upfront investment and ongoing operational expenditure.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The cost and time associated with gaining regulatory approval for new drugs represent a significant financial commitment and barrier to entry.
- Specialized Assets: Investments in proprietary technologies and highly specialized manufacturing equipment create significant switching costs and deter exit.
Strategic Stakes
The healthcare sector, including companies like Otsuka, faces intense rivalry due to its profound societal impact and substantial profit potential. This drives significant investment in research and development, as well as aggressive market expansion strategies. Companies are constantly vying for market share and long-term dominance through various means.
Strategic stakes are exceptionally high in healthcare, motivating companies to engage in fierce competition. The pursuit of groundbreaking treatments and therapies fuels a relentless drive for innovation and market leadership. This often translates into substantial financial commitments aimed at securing a competitive edge.
- High R&D Investment: In 2023, global pharmaceutical R&D spending reached an estimated $240 billion, underscoring the intense competition to develop new drugs.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: The healthcare industry saw significant M&A activity in 2023, with major deals aimed at consolidating portfolios and expanding market reach.
- Pipeline Competition: Companies are in a constant race to advance drug candidates through clinical trials, with success in late-stage development being a critical competitive differentiator.
- Market Exclusivity: Patent protection and market exclusivity for successful drugs create intense pressure to innovate and capture market share before competitors do.
Otsuka Holdings faces intense competition from global pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, which posted over $58 billion in revenue for 2023, and Novartis, with approximately $45 billion in 2023 revenue. These established players leverage massive R&D budgets and extensive distribution networks, intensifying the fight for market share and new drug approvals.
In its nutraceutical and consumer segments, Otsuka contends with companies such as Nestlé, a behemoth with over $100 billion in 2023 sales, and Danone, generating around $28 billion in 2023 revenue. This diverse competitive landscape, featuring both broad conglomerates and specialized firms, necessitates continuous innovation and strategic agility.
The competitive rivalry in the healthcare sector is particularly fierce due to its societal importance and significant profit potential, driving substantial R&D investments and aggressive market expansion. Companies are constantly striving for market dominance through innovation and strategic maneuvering.
The stakes are exceptionally high in healthcare, fueling intense competition as firms race to develop groundbreaking treatments and therapies, often involving substantial financial commitments to gain a competitive edge.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of generic drugs poses a substantial threat to Otsuka's pharmaceutical business. Once a patent on an Otsuka drug expires, cheaper generic alternatives can enter the market. These generics are designed to be therapeutically the same as the branded drug, meaning they offer the same health benefits.
The impact on revenue can be dramatic. Studies show that generic drugs can capture market share so quickly that they reduce a branded drug's revenue by as much as 70-80%. This significant price difference makes generics a highly attractive substitute for patients and healthcare providers alike.
The threat is particularly acute in the near term. With a considerable number of pharmaceutical patents expected to expire in 2024 and 2025, Otsuka faces intensified pressure. This environment necessitates a robust strategy of continuous innovation to bring new, patented drugs to market before existing ones lose their exclusivity.
In pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, alternative therapies like herbal medicines, acupuncture, and psychotherapy, alongside lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, pose a significant threat of substitutes for Otsuka's products. These alternatives can lessen the demand for conventional drugs and supplements, especially for managing chronic conditions or promoting general well-being. For instance, the global market for traditional and complementary medicine was estimated to reach over $200 billion by 2023, demonstrating a substantial consumer shift towards these options.
The rising consumer focus on preventative healthcare is a major catalyst for the growth of the nutraceutical sector, directly impacting Otsuka's presence in this market. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural and holistic approaches to health, often viewing supplements and lifestyle adjustments as more desirable than pharmaceutical interventions. This trend is supported by data showing a consistent year-over-year increase in consumer spending on dietary supplements, with the market projected to continue its upward trajectory through 2025.
The threat of substitutes for Otsuka Holding's products is significant, particularly concerning over-the-counter (OTC) and self-care options. Many conditions that prescription drugs address can be managed effectively with readily available OTC medications, especially for less severe health concerns. This broad accessibility means consumers have numerous choices for managing their well-being.
For Otsuka's consumer products and certain nutraceuticals, the market is awash with self-care alternatives found in pharmacies, supermarkets, and online retailers. To stand out, Otsuka must cultivate strong brand recognition and demonstrate clear efficacy. In 2023, the global OTC pharmaceutical market was valued at approximately $165 billion, highlighting the intense competition from these accessible substitutes.
Innovation in Competing Fields
Rapid advancements in competing fields pose a significant threat of substitution for Otsuka Holdings. Innovations in medical technology, diagnostics, and digital health are creating new treatment pathways that can bypass or replace traditional pharmaceutical approaches. For example, digital therapeutics are emerging as viable alternatives for managing chronic conditions, potentially reducing reliance on Otsuka's drug portfolio.
The rise of non-pharmacological interventions, such as advanced medical devices and personalized gene therapies, directly challenges the market position of many pharmaceutical products. Otsuka must actively monitor and potentially integrate these disruptive technologies to maintain its competitive edge. By 2024, the digital health market alone was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally, indicating the substantial scale of this substitution threat.
- Digital Therapeutics Market Growth: The global digital therapeutics market is experiencing rapid expansion, with projections suggesting continued double-digit growth through 2025.
- Advanced Medical Devices: Innovations in areas like minimally invasive surgery and wearable diagnostic devices offer alternatives to drug-based treatments for various conditions.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics and AI are enabling highly targeted therapies that may reduce the need for broad-spectrum pharmaceuticals.
- Integration Challenges: Otsuka faces the strategic challenge of either developing its own digital/device solutions or partnering with existing innovators to counter these substitutes.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitute products significantly impacts Otsuka's market position. Generic pharmaceuticals, for instance, offer substantial cost savings to both healthcare systems and patients compared to branded medications. This economic advantage can lead to a rapid shift in market share once patents expire.
In the nutraceutical sector, consumers frequently evaluate the price of premium products against their perceived health benefits. When cheaper, readily available alternatives offer comparable perceived value, consumers may readily switch, especially if the unique selling proposition of Otsuka's offerings isn't strongly established. For example, in 2024, the global nutraceutical market was valued at approximately $600 billion, with a significant portion driven by products where price is a key differentiator.
- Generic Drug Penetration: The availability and cost of generic versions of Otsuka's patented drugs directly challenge its pricing power and market share.
- Nutraceutical Value Proposition: Otsuka must continuously demonstrate superior efficacy or unique benefits in its nutraceuticals to justify premium pricing against lower-cost competitors.
- Consumer Price Sensitivity: In 2023, studies indicated that over 60% of consumers consider price a primary factor when choosing health and wellness products, highlighting the threat from more affordable substitutes.
- Healthcare System Budgets: Public and private healthcare payers are increasingly focused on cost containment, favoring less expensive pharmaceutical alternatives where clinically appropriate.
The threat of substitutes for Otsuka Holding is multifaceted, encompassing generic drugs, alternative therapies, and advancements in digital health and medical devices. The expiration of patents on Otsuka's key pharmaceuticals opens the door for lower-cost generics, which can rapidly erode market share, with revenue declines of 70-80% being common.
Beyond generics, non-pharmacological approaches like herbal medicines, lifestyle changes, and digital therapeutics are gaining traction, particularly for chronic conditions and general well-being. The global market for traditional and complementary medicine, valued at over $200 billion by 2023, underscores this shift.
Furthermore, innovative medical devices and personalized medicine approaches, fueled by genomics and AI, present a significant challenge to traditional drug-based treatments. The digital health market, projected to reach hundreds of billions globally by 2024, highlights the scale of these evolving substitutes.
The cost-effectiveness of these substitutes is a critical factor. Consumers, especially in the nutraceutical sector where price sensitivity is high, may opt for more affordable alternatives if Otsuka's products do not clearly demonstrate superior value. In 2024, the global nutraceutical market, approximately $600 billion, sees price as a key differentiator for a substantial portion.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors, particularly pharmaceuticals, necessitates substantial capital for research and development, extensive clinical testing, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and robust marketing campaigns. The sheer cost associated with bringing a new drug to market, often exceeding $2.6 billion according to some estimates, alongside the decade-long development timeline with no certainty of regulatory approval, creates a significant hurdle.
These high capital requirements effectively deter smaller, less-resourced entities, channeling potential new entrants towards well-capitalized startups or established, diversified corporations with the financial muscle to absorb such significant upfront investments and long gestation periods.
The pharmaceutical industry presents formidable barriers to entry due to exceptionally stringent regulatory requirements. Companies must navigate complex and costly clinical trials, adhere to rigorous Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and secure lengthy approvals from bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug exceeded $2.6 billion as of 2023, a significant deterrent for potential newcomers. This intricate regulatory landscape effectively filters out less resourced and experienced players, safeguarding established firms.
Intellectual property and patent protection represent a significant hurdle for new entrants in the pharmaceutical sector. Otsuka, for instance, holds numerous patents on its blockbuster drugs, safeguarding its market position and revenue streams for extended periods. This legal shield means newcomers cannot simply replicate existing successful products. Developing entirely new, patentable compounds is an immensely costly and uncertain undertaking, often requiring billions of dollars and years of research. Consequently, the threat of new entrants is substantially diminished by the robust intellectual property framework that favors established innovators.
Brand Loyalty and Established Distribution Channels
Otsuka's robust brand loyalty, cultivated across its diverse segments like pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and consumer goods, presents a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, their Pocari Sweat beverage has achieved widespread recognition and a loyal following, particularly in Asian markets, demonstrating the power of established brand equity.
New entrants must overcome the considerable hurdle of replicating Otsuka's extensive and deeply entrenched global distribution networks. Building comparable reach and efficiency requires substantial capital investment and time, making it difficult to compete directly with established players who can leverage existing infrastructure for product placement and sales.
The challenge for new entrants extends to gaining market acceptance and building brand trust against well-recognized companies like Otsuka. This necessitates significant marketing expenditure and a long-term strategy to erode existing consumer preferences and establish a competitive foothold.
Consider these points regarding brand loyalty and distribution channels:
- Otsuka's established brands, such as Pocari Sweat and Oronamin C, command high consumer recognition and loyalty, especially in key Asian markets.
- New entrants face the arduous task of building brand equity and consumer trust from scratch, a process that demands substantial marketing investments.
- Otsuka's global distribution infrastructure, built over decades, provides efficient access to diverse markets, a capability that is extremely costly and time-consuming for new companies to replicate.
- The sheer scale of marketing required to challenge established brands and distribution networks often deters potential new entrants due to the high upfront costs and uncertain returns.
Access to Specialized Knowledge and Talent
The pharmaceutical industry, a core area for Otsuka Holdings, demands exceptionally specialized knowledge. This includes deep scientific understanding for drug discovery, advanced medical expertise for clinical trials, and intricate technical skills for manufacturing and quality control. New entrants face a significant hurdle in acquiring this talent, as the pool of qualified scientists, researchers, and regulatory affairs specialists is often limited and highly competitive.
For instance, the global pharmaceutical market, projected to reach approximately $1.9 trillion by 2024 according to industry analyses, is driven by innovation that hinges on this specialized human capital. Companies like Otsuka invest heavily in attracting and retaining top-tier talent, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly build the necessary R&D and operational capabilities. This talent gap directly impacts a new entrant's ability to develop novel therapies and navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
- Specialized Expertise: Pharmaceuticals require deep scientific, medical, and technical knowledge.
- Talent Scarcity: Access to skilled scientists, researchers, and regulatory specialists is a significant challenge for new firms.
- R&D Intensity: Drug development is knowledge-intensive, requiring substantial upfront investment in human capital.
- Competitive Landscape: Established players like Otsuka have existing talent pools, creating a barrier for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Otsuka Holdings is considerably low, primarily due to the immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles inherent in its core pharmaceutical and nutraceutical businesses. Bringing a new drug to market can cost over $2.6 billion, a sum that deters most potential competitors.
Furthermore, Otsuka's strong patent portfolio and established brand loyalty, exemplified by products like Pocari Sweat, create significant barriers. Newcomers must also contend with the challenge of replicating Otsuka's extensive global distribution networks and specialized scientific expertise, making market entry a formidable undertaking.
The global pharmaceutical market, projected to exceed $1.9 trillion by 2024, is characterized by high R&D intensity and a need for specialized talent, further limiting the influx of new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Otsuka's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | Drug development costs exceed $2.6 billion. | High barrier, requires substantial funding. | Financial strength to sustain long R&D cycles. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex FDA approvals, GMP compliance. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate. | Established compliance infrastructure and expertise. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents protect key products. | Prevents replication of existing successful drugs. | Strong patent portfolio and ongoing innovation. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established brands (Pocari Sweat) and global networks. | Difficult to match market penetration and consumer trust. | Decades of brand building and efficient logistics. |
| Specialized Knowledge | Requires deep scientific and medical expertise. | Talent acquisition is a significant challenge. | Access to top-tier researchers and scientists. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Otsuka Holdings is built upon a foundation of verified data, drawing from annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and financial statements. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry publications and market research reports to ensure comprehensive and accurate competitive insights.
