Onto Innovation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Onto Innovation Bundle
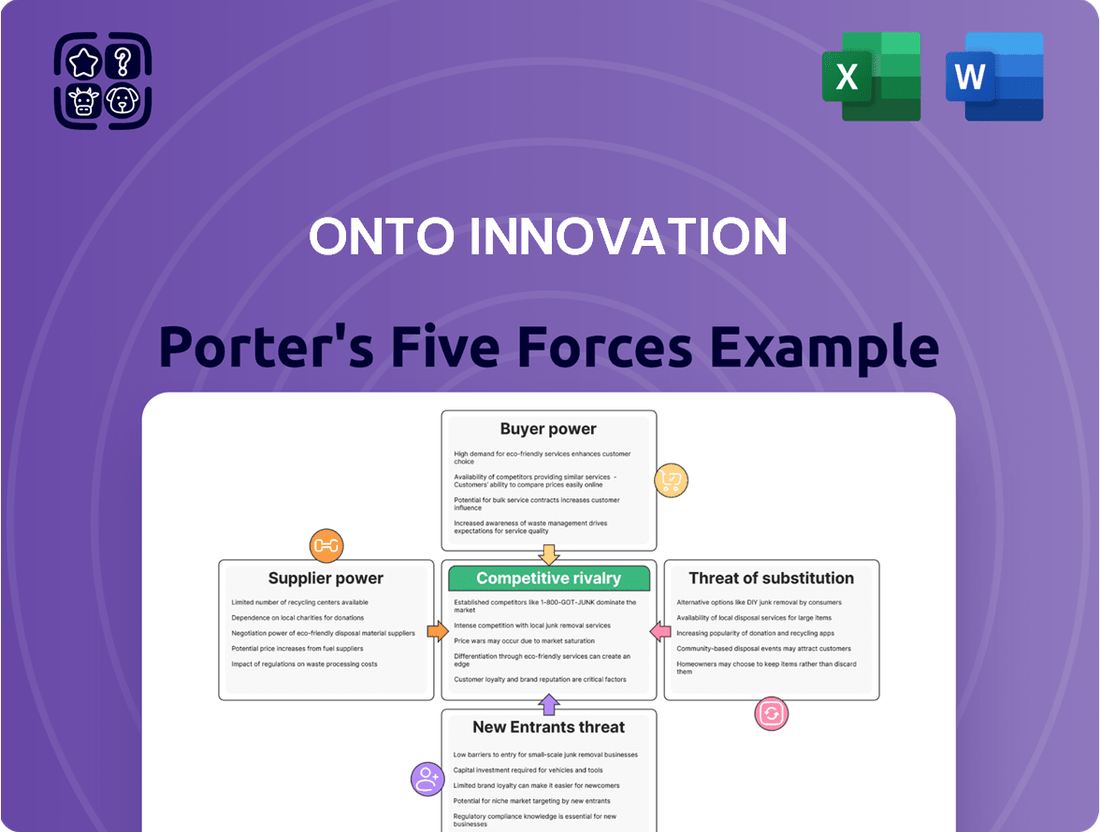
Onto Innovation operates in a dynamic semiconductor equipment sector, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for its strategic positioning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these intricate market forces.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Onto Innovation’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you with a comprehensive view of its industry landscape.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Onto Innovation's reliance on specialized components, like those for its advanced semiconductor inspection and metrology systems, means it often deals with a small pool of highly capable suppliers. For example, the intricate optics and advanced sensor technologies critical for sub-nanometer measurement precision are not readily available from multiple sources.
This scarcity is compounded by the fact that these specialized components require significant research and development investment, creating high barriers to entry for new competitors. Consequently, existing suppliers, having perfected these niche technologies, possess considerable bargaining power.
This situation can translate into higher input costs for Onto Innovation. While specific financial data on supplier cost increases isn't publicly detailed for 2024, industry trends in advanced manufacturing components suggest upward pressure on pricing due to the specialized nature and limited supply base.
The limited number of suppliers also introduces potential supply chain risks. Disruptions at a key supplier, whether due to production issues or strategic decisions, could directly impact Onto Innovation's ability to manufacture and deliver its sophisticated equipment, highlighting the suppliers' leverage.
Onto Innovation faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs associated with critical, custom-designed components essential for semiconductor manufacturing. Developing or adapting new components requires extensive re-engineering, rigorous testing, and lengthy qualification periods, making it costly and time-consuming to change suppliers.
These substantial switching costs inherently limit Onto Innovation's flexibility and deepen its reliance on its current supplier network. For example, if a key supplier of specialized metrology equipment parts were to increase prices, Onto Innovation would likely absorb these costs due to the prohibitive expense and time involved in finding and integrating an alternative supplier.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or holding patents for critical components can establish a near-monopoly, granting them significant leverage. This technological exclusivity allows them to dictate pricing and terms, as Onto Innovation relies on these specialized inputs for its advanced semiconductor metrology and inspection solutions. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see tight supply chains for advanced materials and specialized manufacturing equipment, highlighting the potential for supplier power.
Input Importance to Product Quality and Performance
The quality and performance of Onto Innovation's sophisticated process control equipment hinge directly on the precision and reliability of the components it sources. Substandard inputs can significantly compromise device yield and manufacturing productivity for Onto's customers, directly impacting the value proposition Onto offers. This critical dependence on high-quality inputs grants suppliers considerable leverage, often making Onto Innovation amenable to paying a premium for assured quality, thereby increasing supplier power.
Suppliers of specialized, high-precision components for the semiconductor industry, such as advanced metrology sensors or critical optical elements, wield substantial bargaining power. These suppliers often operate in niche markets with limited competition, and the stringent specifications required for semiconductor manufacturing mean few alternative suppliers can meet Onto's exacting standards. For instance, if a key supplier of advanced lithography optics experiences production disruptions, it could directly impact Onto's ability to deliver its inspection and metrology systems, highlighting the supplier's critical role.
- Supplier Specialization: Many suppliers provide highly specialized components that are difficult to substitute, such as custom-designed optical filters or advanced semiconductor sensor modules.
- Limited Supplier Base: The market for these highly specialized components often consists of a small number of qualified vendors, concentrating power among them.
- Impact on Onto's Value: The performance and reliability of Onto's equipment are directly tied to the quality of these inputs; therefore, Onto is incentivized to maintain strong relationships with these suppliers, even if it means higher costs.
- Potential for Price Increases: Due to the critical nature of their products and limited alternatives, these suppliers may be able to command higher prices, especially if demand for Onto's equipment increases.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Onto Innovation's equipment manufacturing, while uncommon, represents a theoretical bargaining chip. If a supplier holds highly specialized or critical intellectual property for key components, they could potentially leverage this to enter the market directly as a competitor. This possibility, however remote, can strengthen a supplier's negotiating position when dealing with Onto Innovation.
Consider these points regarding this potential threat:
- Theoretical Risk: Suppliers with unique technology might explore manufacturing their own equipment rather than just supplying components.
- Intellectual Property Leverage: Critical patents or proprietary knowledge held by suppliers could be the basis for such a move.
- Negotiating Power: Even the possibility of forward integration can give suppliers increased leverage in pricing and contract discussions with Onto Innovation.
Onto Innovation faces a considerable threat from the bargaining power of its suppliers, particularly for specialized components essential to its advanced semiconductor inspection and metrology systems. The limited number of suppliers capable of producing these high-precision parts, coupled with the significant investment and expertise required, concentrates leverage in the hands of these vendors.
This dynamic is amplified by the high switching costs for Onto Innovation; transitioning to new suppliers for custom-designed components involves extensive re-engineering, testing, and qualification, making it both costly and time-consuming. Consequently, suppliers of critical inputs, such as advanced optics or sensor technology, can command higher prices and dictate terms, impacting Onto's cost structure.
For example, the semiconductor industry's continued demand for cutting-edge materials and equipment in 2024 meant that suppliers of specialized components often experienced strong pricing power. Onto Innovation's reliance on these high-quality, precisely manufactured parts directly influences its product performance and customer value, reinforcing the suppliers' leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Onto Innovation | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High dependence on niche, custom-made parts. | Suppliers have few competitors meeting exact specifications. |
| High Switching Costs | Significant financial and time investment to change suppliers. | Limits Onto's flexibility and ability to negotiate aggressively. |
| Proprietary Technology | Reliance on suppliers' unique intellectual property. | Suppliers can dictate terms and pricing due to technological exclusivity. |
| Quality Dependence | Product performance and customer satisfaction rely on input quality. | Onto is willing to pay a premium for assured, high-quality components. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Onto Innovation, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes within the semiconductor industry.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling faster, more informed strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Onto Innovation's customer base is highly concentrated, primarily consisting of major global semiconductor manufacturers and foundries. These large-scale players, like Intel, Samsung, and TSMC, are crucial to Onto Innovation's sales, often accounting for substantial portions of revenue. Their significant order volumes and strategic importance grant them considerable bargaining power, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. For instance, a single large foundry's decision to shift a portion of its business could significantly impact Onto Innovation's financial performance, highlighting the customers' leverage in the supply chain.
While customers hold significant sway, the semiconductor industry faces a unique challenge: high switching costs for process control equipment. For manufacturers, moving from one vendor to another isn't a simple swap. It demands extensive re-qualification of new machinery, intricate integration into existing, highly complex production lines, and rigorous testing protocols. This process can easily take months, impacting production schedules.
These substantial barriers mean that once a semiconductor manufacturer has invested in and integrated Onto Innovation's equipment, their immediate bargaining power is somewhat diminished. The cost and disruption associated with switching vendors after initial implementation can deter customers from seeking alternative suppliers, thereby strengthening Onto Innovation's position.
Semiconductor manufacturers are relentless in their pursuit of higher yields and more efficient production, a dynamic that positions Onto Innovation's offerings as indispensable. This pressure means customers have significant leverage, demanding not just advanced performance but a clear return on their investment.
Consequently, these customers can wield considerable power when negotiating crucial aspects like product features, the specifics of service level agreements, and ultimately, pricing. For instance, in 2024, the average semiconductor manufacturing cost per wafer can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars, making yield improvements directly impactful to profitability and thus, customer negotiation strength.
To thrive, Onto Innovation must consistently prove its ability to deliver superior value, ensuring it remains the preferred partner for these discerning and high-stakes clients.
Customer Knowledge and Technical Sophistication
Onto Innovation's customer base, primarily comprised of leading semiconductor manufacturers, possesses substantial technical knowledge and deep insights into their intricate production processes. This sophistication enables them to rigorously assess and compare the performance and value of various equipment and software solutions, directly influencing their negotiation leverage.
Their ability to conduct thorough technical evaluations and understand the nuances of equipment capabilities means customers can effectively challenge pricing and demand specific performance metrics. This informed approach significantly bolsters their bargaining power.
- High Customer Sophistication: Customers are technically proficient, understanding Onto Innovation's product functionalities and their impact on manufacturing yields.
- Informed Negotiation: This expertise allows customers to negotiate effectively on pricing and technical specifications, leveraging their knowledge of alternative solutions.
- Rigorous Evaluation: Customers' capacity for detailed product assessment empowers them to demand superior performance and value, increasing their purchasing influence.
- Market Awareness: A deep understanding of the semiconductor industry's needs and available technologies grants customers significant leverage in procurement discussions.
Cyclical Nature of Semiconductor Industry Investment
The semiconductor industry's inherent cyclicality significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When global demand for electronics softens, capital expenditures for new manufacturing equipment tend to decrease sharply. For instance, industry-wide semiconductor capital expenditure was projected to grow by around 10-15% in 2024, a notable rebound from a slight contraction in 2023, indicating the volatile nature of investment cycles.
During these downturns, customers, such as chip manufacturers, often postpone or scale back their equipment orders. This reduced demand gives them more leverage to negotiate prices and favorable terms with suppliers like Onto Innovation. The competition for a smaller pool of available orders intensifies, forcing equipment makers to be more accommodating to secure business.
This dynamic can lead to price concessions, as suppliers vie for market share. The cyclical nature means that periods of high demand and robust pricing can be followed by periods of intense price competition, directly impacting Onto Innovation's revenue and profitability. Companies in this sector must navigate these fluctuations carefully, managing inventory and production capacity to mitigate the impact of customer bargaining power during troughs.
- Cyclical Demand Impact: Downturns in the semiconductor cycle lead to reduced customer orders, increasing their negotiating leverage.
- Price Negotiation: Customers can demand price concessions during periods of lower industry-wide capital expenditure.
- Competitive Pressure: Onto Innovation faces intensified competition from other equipment suppliers when demand falters.
- 2024 Outlook: While 2024 projected capital expenditure growth, the underlying cyclicality still presents opportunities for customer bargaining power.
Onto Innovation's customers, predominantly large semiconductor manufacturers, possess considerable bargaining power due to their significant order volumes and the critical nature of Onto's solutions to their production yields. These customers, including industry giants, can leverage their purchasing influence to negotiate pricing and favorable terms, making them key stakeholders in Onto's revenue streams.
The high costs and complexity associated with switching equipment vendors in the semiconductor industry, involving extensive re-qualification and integration, serve to somewhat temper immediate customer bargaining power once systems are in place. However, the continuous drive for efficiency and yield improvements means customers remain influential in demanding superior performance and clear return on investment.
The semiconductor industry's cyclical nature significantly amplifies customer bargaining power during downturns, as reduced capital expenditures lead to increased competition for fewer orders. For instance, while 2024 saw projected growth in semiconductor capital expenditures, the inherent volatility means periods of weak demand empower customers to negotiate price concessions and more favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on Onto Innovation's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
| Customer Concentration | High | Key customers like Intel, Samsung, TSMC represent substantial revenue portions. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate (after initial integration) | Months-long re-qualification and integration processes create inertia. |
| Technical Sophistication | High | Customers possess deep process knowledge, enabling informed negotiation on performance and value. |
| Industry Cyclicality | High (especially during downturns) | Reduced CapEx during slumps increases customer leverage for price concessions. 2024 CapEx growth projected around 10-15% but industry remains cyclical. |
What You See Is What You Get
Onto Innovation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Onto Innovation Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the semiconductor equipment industry. The document you see is the exact, professionally formatted report you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility for your strategic planning. It thoroughly dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate download and application, providing actionable insights into Onto Innovation's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The semiconductor equipment sector, where Onto Innovation operates, demands substantial upfront capital. We're talking about massive investments in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and the global service networks needed to support complex machinery. This inherently creates a competitive landscape where companies are driven to achieve high sales volumes to justify these enormous fixed costs.
This necessity to recoup significant investments fuels aggressive competition. Companies like Onto Innovation are constantly battling for market share, as failing to do so means those high fixed costs become a heavier burden. For instance, leading players in the semiconductor equipment market often report R&D expenditures representing a significant percentage of their revenue, frequently in the double digits, underscoring the continuous innovation race.
Onto Innovation faces intense competition from established global players in the semiconductor manufacturing equipment sector. Companies like Applied Materials, Lam Research, and KLA Corporation, all significantly larger with more diversified offerings, directly challenge Onto Innovation for market share.
These competitors provide comparable inspection, metrology, and lithography solutions, creating a highly competitive environment for securing significant customer contracts. For instance, KLA Corporation, a dominant force in process control, consistently invests heavily in R&D, posing a continuous threat to Onto Innovation's market positioning.
The need to differentiate is paramount. Onto Innovation must leverage its specialized expertise, particularly in areas like advanced packaging inspection, to stand out. Building and maintaining strong, collaborative relationships with key semiconductor manufacturers is crucial for retaining customers and winning new business in this crowded space.
In 2023, the semiconductor equipment market saw significant activity, with KLA Corporation reporting revenues of over $10 billion, highlighting the scale of the larger competitors Onto Innovation contends with. This underscores the strategic imperative for Onto Innovation to carve out and defend its niche.
Competitive rivalry in the semiconductor metrology and inspection market, where Onto Innovation operates, is heavily driven by product performance and technological advancements. Companies vie for market share by demonstrating superior capabilities in improving device yield and manufacturing productivity. This intense competition necessitates continuous innovation to stay ahead.
Onto Innovation distinguishes itself by leveraging proprietary algorithms, cutting-edge optics, and the development of integrated solutions. These elements are crucial for providing customers with tangible improvements in their manufacturing processes. The company's focus on these areas aims to create a distinct value proposition in a crowded market.
The sector is characterized by a relentless pursuit of technological leadership, which inherently fuels robust rivalry and rapid innovation. For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced packaging technologies, like chiplets, is pushing the boundaries of inspection and metrology, requiring even more sophisticated solutions. Companies that can offer faster, more accurate, and more comprehensive data analysis will likely gain a competitive edge.
Global Market Reach and Customer Relationships
Onto Innovation's success hinges on its global reach, mirroring the semiconductor industry's dispersed manufacturing base. Effective support requires a worldwide sales and service network, crucial for building trust with major fabrication plants (fabs). This global presence, combined with deep customer relationships, acts as a significant competitive advantage, making it challenging for less established players to compete. For instance, in 2023, Onto Innovation reported revenue from diverse geographic regions, underscoring their international footprint.
The company actively cultivates long-term partnerships with leading foundries, understanding that technological innovation alone is insufficient. Responsiveness and consistent support are paramount, solidifying Onto Innovation's position. These established relationships are not just about current sales but also about future opportunities and collaborative development, presenting a substantial hurdle for new entrants aiming to secure similar levels of access and trust.
- Global Service Network: Essential for supporting semiconductor manufacturers across various continents.
- Customer Relationship Strength: A key differentiator in a market where trust and reliability are paramount.
- Barrier to Entry: The established global presence and deep customer ties make it difficult for new competitors to gain traction.
Consolidation and Strategic Acquisitions in the Industry
Competitive rivalry in the semiconductor equipment sector is notably high, fueled by ongoing consolidation. Larger companies frequently acquire smaller, specialized firms to bolster their technological capabilities and broaden their market presence. This strategy intensifies competition by creating more formidable, diversified players. Onto Innovation's own formation through a merger exemplifies this industry trend, underscoring the continuous pursuit of scale and operational synergies.
- Market Consolidation: The semiconductor equipment industry has experienced significant consolidation, with major players acquiring smaller, innovative companies to enhance their product offerings and market share.
- Onto Innovation's Merger: Onto Innovation was formed through the merger of Nanometrics and Rudolph Technologies, a move that consolidated expertise in metrology and inspection, demonstrating the industry's drive for scale.
- Increased Competition: Such consolidations lead to the emergence of larger, more resource-rich competitors, intensifying the competitive landscape for all participants.
- Technological Advancement: Acquisitions are often driven by the need to quickly integrate new technologies, further accelerating the pace of innovation and raising the bar for competitive performance.
Competitive rivalry is intense in the semiconductor equipment sector, driven by significant R&D investments and the need for high sales volumes to offset substantial fixed costs. Onto Innovation competes directly with larger, more diversified players like Applied Materials, Lam Research, and KLA Corporation, who possess greater financial resources and broader product portfolios.
These competitors offer similar inspection, metrology, and lithography solutions, leading to a fierce battle for customer contracts. For example, KLA Corporation's substantial R&D spending in 2023, exceeding $10 billion in revenue, demonstrates the scale of the competition. This necessitates Onto Innovation's focus on specialized areas like advanced packaging inspection and strong customer relationships to maintain its market position.
The industry also sees ongoing consolidation, where larger firms acquire smaller ones to enhance technological capabilities and market reach, further intensifying competition. Onto Innovation’s own formation via a merger highlights this trend. In 2024, advancements in chiplet technology are driving demand for more sophisticated metrology and inspection, rewarding companies with superior data analysis and faster, more accurate solutions.
| Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Product Areas |
| Applied Materials | ~25 | Semiconductor manufacturing equipment, including deposition, etch, and ion implantation |
| Lam Research | ~16 | Wafer fabrication equipment, specializing in deposition and etch processes |
| KLA Corporation | ~10 | Process control, metrology, and inspection solutions |
| Onto Innovation | ~1.4 | Metrology, inspection, and data analytics for semiconductor manufacturing |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While highly specialized, major semiconductor manufacturers sometimes develop their own internal solutions for specific process control challenges, especially for delicate or unique manufacturing steps. This internal development, although expensive and demanding on resources, can act as an alternative to buying equipment from outside suppliers.
For instance, a large chipmaker might invest in building its own metrology tools for a particularly niche application. This capability, however, is often prohibitively costly compared to leveraging the expertise and economies of scale offered by established vendors like Onto Innovation, making external partnerships the more practical choice for most.
The threat of substitutes in process control metrology is a long-term consideration, with potential for entirely new scientific breakthroughs to emerge. While Onto Innovation currently leverages advanced optical and electron-beam technologies, future developments in areas like AI-driven predictive analytics or novel material characterization could offer alternative inspection methodologies. These emerging techniques, however, typically require substantial research and development investment, making them more of a future threat than an immediate one.
Advances in semiconductor manufacturing, like enhanced process control and stricter design rules, could theoretically lessen the reliance on specific inspection and metrology equipment. If manufacturing becomes more stable and defect-free, the demand for certain defect detection tools might decline.
For instance, if a wafer fabrication process consistently yields fewer critical defects, the need for advanced optical inspection systems could be reduced. This would represent a direct substitution threat, where improved upstream processes make downstream equipment less essential.
However, the increasing complexity of integrated circuits, with smaller feature sizes and more intricate designs, often counteracts this potential reduction. The drive for higher yields and greater precision in advanced nodes, such as those below 5 nanometers, frequently necessitates *more* sophisticated metrology and inspection, thereby mitigating the threat of substitution from process optimization alone.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued investment in advanced process control and yield enhancement technologies. Companies are focusing on reducing variability at every stage, but the relentless push for miniaturization and performance means that while some specific inspection steps might be streamlined, the overall demand for advanced metrology solutions, a core area for Onto Innovation, remains robust due to the inherent complexity of cutting-edge chip manufacturing.
Generic or Lower-Cost Equipment from Emerging Markets
The threat of substitutes for Onto Innovation's advanced semiconductor metrology and inspection solutions comes from generic or lower-cost equipment originating from emerging markets. While these alternatives may not match Onto's cutting-edge precision, they can capture market share among customers with less demanding technical specifications or more budget-conscious needs. For instance, while Onto Innovation focuses on critical process steps in advanced node manufacturing, some smaller foundries or assembly houses might opt for less sophisticated, imported equipment for less sensitive stages of production. This segment of the market, while not directly competing for Onto's core customers, represents a potential erosion of broader market presence. For example, in 2023, the global semiconductor equipment market saw significant growth, but this also attracted a wider array of suppliers, including those offering more basic solutions.
These less advanced substitutes typically lack the sophisticated algorithms, advanced optical systems, and deep integration capabilities that Onto Innovation provides for leading-edge semiconductor manufacturing. However, for applications where extreme precision and rapid throughput are not the absolute highest priorities, these lower-cost options become a viable alternative. This is particularly true for older technology nodes or for specific back-end semiconductor processes. For example, while Onto Innovation's systems are crucial for sub-7nm node development, simpler inspection tools might suffice for packaging or testing of less advanced chips.
- Lower Cost Appeal: Emerging market equipment can offer a significantly lower price point, attracting budget-constrained manufacturers.
- Segment Targeting: These substitutes cater to market segments with less stringent performance requirements, such as older technology nodes or non-critical process steps.
- Performance Trade-off: While not matching Onto's precision and throughput, they provide a functional alternative for specific, less demanding applications.
- Market Diversification: The availability of these substitutes increases the overall competitive landscape, potentially impacting market share in non-premium segments.
Software-Based Predictive Maintenance and Yield Management
The increasing sophistication of software-driven analytics presents a potential threat of substitutes for traditional metrology and inspection services. Advanced AI and machine learning algorithms can predict equipment malfunctions and yield deviations in manufacturing processes before they manifest physically. For instance, in 2024, investments in industrial AI solutions for predictive maintenance saw significant growth, with some reports indicating a global market size exceeding $10 billion, demonstrating a clear trend towards software-based solutions.
While these software tools often complement hardware, highly advanced predictive capabilities could diminish the need for frequent, hands-on physical inspections or reliance on specific metrology equipment. This shift could impact companies like Onto Innovation, whose core business involves providing such physical inspection and measurement solutions. The threat lies in software evolving to a point where it can accurately forecast and potentially even guide adjustments, thereby reducing the demand for the physical touchpoints Onto Innovation currently offers.
Onto Innovation itself recognizes this evolving landscape and actively integrates advanced software and AI into its own product portfolio. This strategy aims to mitigate the threat of substitution by becoming a provider of these integrated solutions, rather than being solely reliant on hardware-based metrology. By embedding predictive analytics, Onto Innovation can offer enhanced value and retain its market position in a changing technological environment.
Key considerations regarding this threat include:
- Advancements in AI for predictive analytics: The ability of software to accurately forecast equipment failures or yield issues is a direct substitute for manual or hardware-dependent inspection.
- Integration of software with existing hardware: While often complementary, sophisticated software can reduce the *frequency* of reliance on physical checks.
- Onto Innovation's proactive strategy: The company's move to incorporate AI and software into its offerings is a direct response to this evolving threat.
- Market growth of industrial AI: The significant and growing market for AI in manufacturing underscores the potential for these software solutions to displace traditional methods.
While internal development by chipmakers can offer bespoke solutions, it’s often cost-prohibitive compared to specialized vendors. Future breakthroughs in AI-driven analytics or novel characterization techniques could also present alternative inspection methods, though these require substantial R&D, making them a longer-term concern.
The semiconductor industry’s ongoing pursuit of miniaturization and enhanced precision, particularly in nodes below 5nm, inherently drives the need for more sophisticated metrology, thereby counteracting any potential substitution threat from process optimization alone. In 2024, despite efforts to streamline processes, the demand for advanced metrology solutions for cutting-edge chip manufacturing remained strong.
Lower-cost equipment from emerging markets can capture market share for less demanding applications or older technology nodes, representing a threat to Onto Innovation’s broader market presence. While these substitutes may not match Onto's precision, they offer a functional alternative for specific, less critical process steps, as seen in the broader semiconductor equipment market growth attracting diverse suppliers in 2023.
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor equipment sector, where Onto Innovation operates, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to exceptionally high capital investment and research and development (R&D) requirements. Developing advanced inspection and metrology solutions, crucial for modern chip manufacturing, necessitates billions of dollars in upfront investment and sustained R&D over many years. For instance, the development cycle for new lithography systems alone can easily exceed $1 billion, creating a substantial financial hurdle. This immense financial commitment effectively limits the number of new players capable of entering and competing effectively in this space.
The extensive intellectual property and patent landscape is a significant barrier to new entrants in the semiconductor metrology and inspection industry, an area where companies like Onto Innovation operate. This complex web of patents, developed over many years by incumbents, protects their proprietary technologies and innovations.
Developing new, competitive technologies without infringing on these existing patents presents a formidable challenge for any potential new player. For instance, Onto Innovation itself holds a substantial portfolio of patents covering various aspects of its advanced inspection and metrology solutions, crucial for semiconductor manufacturing processes.
The sheer volume and complexity of intellectual property mean that new entrants would likely face significant legal hurdles and substantial costs to navigate or design around existing patents. This intellectual property barrier effectively deters many from entering the market, reinforcing the position of established companies.
Developing new semiconductor equipment is an incredibly long game, often spanning multiple years. This is just the first hurdle. After the equipment is built, it faces lengthy and rigorous customer qualification cycles, which can drag on for months, or even years, depending on the complexity and criticality of the process. For example, qualifying a new metrology tool for advanced node manufacturing can be an extensive process involving numerous validation runs and data analysis.
New entrants often struggle because they lack the established track record and inherent trust that established players like Onto Innovation have built with semiconductor manufacturers. These manufacturers are inherently risk-averse, especially when dealing with processes that are critical to their chip production yields. The sheer time and investment required to get a new product through development and customer validation presents a significant barrier to entry.
Need for Deep Technical Expertise and Talent Pool
The semiconductor equipment industry, including players like Onto Innovation, demands an exceptionally deep well of technical expertise. Designing, manufacturing, and supporting sophisticated equipment for chip production requires mastery in fields like optics, physics, advanced software development, materials science, and ultra-precision engineering. New companies entering this arena face a formidable challenge in assembling a workforce with this specialized knowledge.
Building and retaining such a highly skilled talent pool is not only difficult but also incredibly expensive. The scarcity of professionals possessing this niche expertise acts as a significant barrier to entry for potential new competitors. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of semiconductor engineers was estimated to be around 200,000, highlighting the intense competition for qualified personnel.
- Specialized Knowledge: Expertise in optics, physics, software, materials science, and precision engineering is critical.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants face high costs and significant challenges in recruiting and retaining specialized talent.
- Talent Scarcity: A limited pool of qualified professionals creates a substantial barrier to entry.
- Impact on Innovation: The difficulty in accessing talent can slow down innovation and product development for new companies.
Established Customer Relationships and Brand Reputation
Established players like Onto Innovation have forged strong, enduring connections with leading semiconductor manufacturers. These relationships are built on a foundation of demonstrated performance, consistent reliability, and trusted service, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to break in. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continues to be characterized by long-term supply agreements and deep integration between equipment providers and fabs.
Dislodging these deeply entrenched relationships and building the requisite brand trust and credibility presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. The semiconductor equipment market, in particular, demands a proven track record and a reputation for innovation and support. In 2023, capital expenditures by the top semiconductor companies exceeded $150 billion, highlighting the scale of investment and the importance of reliable partners.
Furthermore, the substantial switching costs associated with changing equipment suppliers in the semiconductor fabrication process act as a powerful barrier. These costs encompass not only financial outlays but also the time and effort required for qualification, process integration, and retraining of personnel. This inertia strongly favors incumbents like Onto Innovation, as demonstrated by the extended lifecycles of critical process equipment in many fabs.
- Deeply entrenched customer relationships with major semiconductor fabs, built over years of proven performance and reliable service.
- Significant brand reputation and credibility required for new entrants to challenge established players.
- High switching costs for customers, involving financial and operational complexities, further solidifying incumbent positions.
- Long-term supply agreements and integration are common in the semiconductor industry, creating sticky customer bases.
The threat of new entrants into the semiconductor equipment sector, where Onto Innovation operates, is generally low due to several significant barriers. These include massive capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, a complex intellectual property landscape, lengthy customer qualification processes, and the need for highly specialized technical expertise. Established customer relationships and high switching costs further solidify the positions of incumbents.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Billions required for R&D and advanced manufacturing facilities. | Extremely high hurdle; limits the number of capable entrants. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protect existing technologies. | Requires costly navigation or design-around, increasing risk. |
| Customer Qualification | Lengthy and rigorous validation cycles for new equipment. | Significant time and resource commitment before revenue generation. |
| Technical Expertise | Need for specialized skills in optics, physics, software, etc. | Difficult and expensive to acquire and retain top talent; talent scarcity is a key issue, with an estimated global semiconductor engineer shortage of 200,000 in 2024. |
| Customer Relationships & Switching Costs | Deeply entrenched partnerships and high costs to change suppliers. | Makes it hard for newcomers to gain initial traction and displace incumbents. In 2023, semiconductor capital expenditures exceeded $150 billion, indicating the scale of investment and reliance on trusted partners. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Onto Innovation leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and financial analyst evaluations.
We combine insights from competitor financial statements, trade publications, and macroeconomic data to comprehensively assess the competitive landscape, supplier power, buyer bargaining, threat of substitutes, and new entrants.
