Olympic Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Olympic Steel Bundle
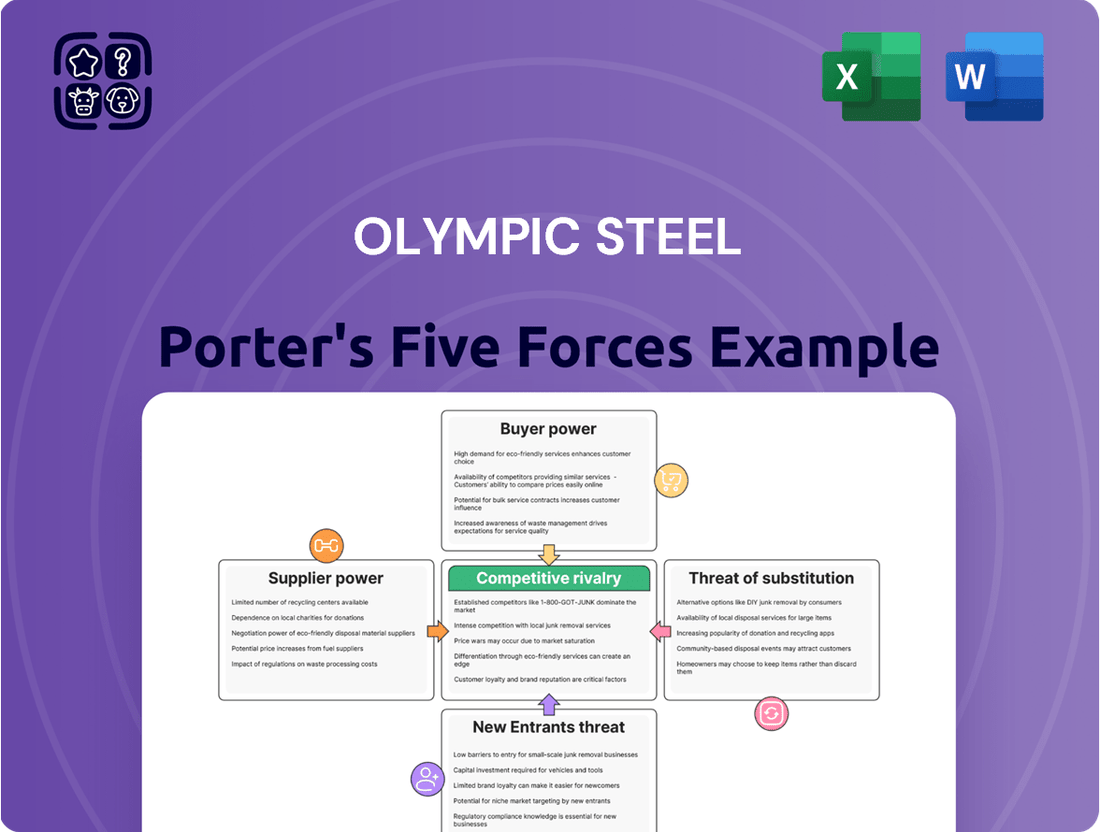
Olympic Steel navigates a competitive landscape shaped by significant buyer power, particularly from large industrial customers who demand competitive pricing and customized solutions. The threat of new entrants, while moderated by capital intensity and established relationships, remains a factor.
The bargaining power of suppliers, especially for raw materials like steel scrap and finished steel products, can impact Olympic Steel's cost structure. Furthermore, the availability of substitute products, such as aluminum and advanced composites, presents a constant challenge to market share.
Rivalry among existing competitors in the steel distribution and processing industry is intense, often leading to price wars and a focus on operational efficiency. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision-making.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Olympic Steel’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Olympic Steel is notably influenced by the concentration of its primary raw material sources: large steel mills and aluminum producers. These suppliers frequently operate within oligopolistic structures, especially for niche metals, granting them considerable sway over pricing and availability.
This supplier concentration means that fluctuations in the cost of steel and aluminum directly affect Olympic Steel's operational expenses. For instance, while steel prices saw a downward trend in 2024, aluminum costs remained high, illustrating the varied impact of different raw material markets on Olympic Steel's input costs.
Olympic Steel faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the substantial costs associated with switching major metal suppliers. These costs can include the extensive process of qualifying new materials, recalibrating specialized processing equipment, and the potential disruption to established, and often intricate, supply chain operations.
Furthermore, Olympic Steel's reliance on long-term contracts or the need for materials with very specific technical requirements can further entrench relationships with particular suppliers. This situation effectively locks the company into existing partnerships, thereby bolstering the suppliers' leverage in negotiations. For instance, in 2024, the automotive and construction sectors, key markets for Olympic Steel, continued to demand highly specific steel grades, reinforcing supplier dependency.
The quality and consistency of raw materials are absolutely critical for Olympic Steel to deliver the high-specification processed metals that its diverse customer base expects. If a supplier offers unique or demonstrably superior quality material, their leverage naturally grows, as this directly impacts Olympic Steel's capacity to satisfy customer needs and uphold its reputation for excellence.
This dynamic is particularly pronounced when dealing with specialized alloys, often essential for demanding, high-performance applications where material integrity is paramount. For instance, during 2024, the global market for specialized steel alloys saw significant price volatility, with some niche suppliers commanding premium prices due to constrained production and high demand from sectors like aerospace and advanced manufacturing.
Limited Forward Integration by Suppliers
While some major steel mills possess their own distribution networks, direct forward integration by these primary metal producers into the comprehensive value-added services that Olympic Steel provides is generally constrained. This limitation means that suppliers often depend on specialized service centers, such as Olympic Steel, to manage crucial functions like processing, maintaining inventory, and distributing products directly to a diverse and often fragmented customer base. This dynamic reduces the direct competitive pressure suppliers can exert within the steel service center market.
This reliance on service centers enhances Olympic Steel's position by ensuring suppliers need their expertise for market access. For instance, in 2024, the steel industry continued to see consolidation among large producers, making it less feasible for them to build out the niche processing and distribution capabilities that service centers offer. Olympic Steel's 2024 revenue of $2.6 billion demonstrates its significant role in this supply chain, processing and distributing a wide array of steel products, from hot-rolled coil to specialized alloys, which many mills find uneconomical to handle directly.
- Limited Scope of Supplier Integration: Primary steel producers typically focus on raw material sourcing and initial production, not the intricate processing and just-in-time delivery required by end-users.
- Value-Added Services as a Differentiator: Olympic Steel's ability to offer services like slitting, cutting, and coating creates a barrier to entry for suppliers wanting to replicate these functions.
- Market Access for Suppliers: Service centers provide suppliers with access to a broad and often dispersed customer base that direct sales might not efficiently reach.
- Cost Efficiency for Mills: For mills, outsourcing processing and distribution to specialists like Olympic Steel is often more cost-effective than developing these capabilities internally.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics and Tariffs
Geopolitical events and evolving trade policies, such as tariffs, significantly shape the bargaining power of suppliers within the global steel industry. For instance, the imposition of tariffs on imported steel and aluminum in 2018, and their subsequent adjustments, directly impacted U.S. manufacturers by increasing input costs. This made domestic steel sources more attractive, thereby bolstering the negotiating leverage of domestic suppliers.
These trade dynamics create a complex environment where supply-demand imbalances can further amplify supplier power. When global demand outstrips supply, or when specific regions face production disruptions, suppliers can command higher prices. For example, in early 2024, persistent supply chain bottlenecks and a rebound in industrial activity contributed to elevated steel prices, giving suppliers a stronger hand in negotiations with customers like Olympic Steel.
- Tariff Impact: Tariffs on imported steel can force U.S. companies to rely more on domestic suppliers, increasing their bargaining power.
- Supply-Demand Imbalances: Fluctuations in global supply and demand directly influence pricing and supplier leverage.
- Geopolitical Factors: International relations and trade agreements play a crucial role in determining supplier costs and availability.
- Cost Pressures: Increased input costs for suppliers can translate to higher prices for buyers, strengthening the supplier's position.
Olympic Steel faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, primarily large steel and aluminum producers, due to the concentrated nature of raw material sourcing and high switching costs. These suppliers often operate in oligopolistic markets, giving them considerable influence over pricing and availability, as evidenced by the varied price trends of steel versus aluminum in 2024.
The company's reliance on specialized materials and the substantial investment required to change suppliers further solidifies supplier leverage. For instance, the continued demand for specific steel grades in key 2024 markets like automotive and construction reinforced this dependency, making it costly for Olympic Steel to shift sourcing.
Furthermore, Olympic Steel's revenue of $2.6 billion in 2024 highlights its crucial role in providing value-added services that many primary mills find uneconomical to perform. This reliance on service centers like Olympic Steel for market access and specialized processing inherently strengthens suppliers' negotiating positions.
| Factor | Impact on Olympic Steel | 2024 Relevance |
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for fewer suppliers | Continued reliance on major mills for core materials. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers | Significant investment in material qualification and equipment recalibration. |
| Value-Added Services | Reduces supplier integration into processing | Mills depend on Olympic Steel for specialized processing, enhancing Olympic's market access role. |
| Geopolitical/Trade Policies | Influences domestic vs. import costs | Tariffs and supply chain disruptions in 2024 impacted raw material costs and supplier leverage. |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Olympic Steel, this analysis dissects the competitive forces of buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalry within the steel industry.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Olympic Steel Porter's Five Forces analysis, reducing the pain of understanding market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Olympic Steel's customer base is quite varied, serving sectors like construction, automotive, and general manufacturing with its processed steel and aluminum. This diversity means customers have different needs and specifications for products such as carbon, coated, and stainless flat-rolled steel.
While some major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) might represent substantial order volumes, the sheer breadth of industries and customer types means no single customer segment holds overwhelming sway. This fragmentation inherently dilutes the bargaining power of any individual customer or even a specific industry segment, as Olympic Steel can often shift focus or sales to other areas if one segment becomes too demanding.
The metals service center industry, despite some consolidation, remains quite fragmented. This means customers often have numerous options when choosing a supplier. For instance, in 2024, the industry continued to see a mix of large national players and many smaller, regional service centers operating across various geographic areas.
This wide availability of alternative service centers directly empowers customers. If Olympic Steel were to increase prices or if a customer found the service lacking, they could more easily find another provider. This competitive landscape puts pressure on service centers to maintain competitive pricing and high service standards.
Consider the sheer number of players; while exact 2024 figures are still being compiled, the industry has historically featured hundreds of companies, many of which serve specific local or regional markets. This depth of choice for buyers is a significant factor in their bargaining leverage.
Olympic Steel's extensive processing services, like leveling, cutting, and slitting, alongside its supply chain management solutions, significantly reduce customer bargaining power. These value-added offerings make it difficult for customers to switch to competitors without compromising on specialized needs or efficient material flow. For instance, in 2023, Olympic Steel reported net sales of $1.5 billion, underscoring its substantial market presence and the depth of its service integration.
By providing these integrated solutions, Olympic Steel effectively raises switching costs for its clients. Customers who rely on these specialized services are less likely to seek out alternative suppliers, as replicating the same level of processing and logistical efficiency would be a considerable undertaking. This integration positions Olympic Steel as a strategic partner rather than just a commodity supplier.
Price Sensitivity Due to Commodity Nature
The fundamental nature of steel and aluminum as commodities means Olympic Steel's customers are inherently sensitive to price changes. Even with value-added services, the core product's fungibility places significant leverage in the hands of buyers, particularly during market downturns. For instance, in early 2024, fluctuating raw material costs led to increased price negotiations across the metals industry, directly impacting companies like Olympic Steel.
This price sensitivity intensifies when market conditions favor buyers. If metal prices decline, customers are more likely to push for lower pricing from Olympic Steel, squeezing profit margins. This was evident in periods of oversupply observed in late 2023 and continuing into 2024, where buyers could readily source comparable materials from competitors, amplifying their bargaining power.
- Commodity Pricing Pressure: Steel and aluminum are largely undifferentiated, making price the primary competitive factor for many customers.
- Impact of Market Downturns: Declining metal prices in 2023-2024 increased customer pressure for lower costs, affecting Olympic Steel's margins.
- Value-Added Services Offset: While Olympic Steel offers processing and fabrication, the core commodity nature of its products remains a significant driver of customer price sensitivity.
Customer's Ability to In-Source Processing
For very large customers of Olympic Steel, there's a theoretical possibility they could bring their metal processing in-house. This would mean they'd no longer need the services provided by steel service centers, effectively removing their demand.
However, the reality of this threat is significantly limited by substantial barriers. Setting up in-house metal processing requires a massive capital outlay for specialized equipment and facilities. The logistical challenges and the need for skilled personnel also present considerable hurdles.
For instance, establishing a fully operational metal processing facility can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, a cost prohibitive for most companies. Olympic Steel's significant investment in advanced processing technologies, such as their coil processing lines and fabrication capabilities, creates a competitive advantage that is difficult and expensive for customers to replicate.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up in-house processing requires millions in specialized machinery.
- Specialized Equipment Needs: Customers would need to acquire sophisticated cutting, shaping, and finishing tools.
- Logistical Complexities: Managing raw material sourcing, inventory, and finished product distribution adds significant overhead.
- Operational Expertise: Developing the in-house knowledge and skilled labor force for efficient processing is a major undertaking.
The bargaining power of customers for Olympic Steel is moderate, primarily due to the commodity nature of steel and aluminum and the fragmented supplier base. While Olympic Steel provides value-added services that can increase switching costs, price sensitivity remains a significant factor, particularly when market conditions favor buyers, as seen with fluctuating raw material costs in 2024.
Customers can often find alternative suppliers in the fragmented metals service center industry, intensifying price competition. While the threat of customers bringing processing in-house is limited by high capital and operational barriers, their ability to negotiate prices based on market fluctuations is a key aspect of their power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Olympic Steel's Position |
| Product Differentiation | Low (Steel/Aluminum as commodities) | Offers value-added processing to differentiate |
| Supplier Fragmentation | High (Numerous service centers) | Faces competition from large and small players |
| Price Sensitivity | High (Especially with commodity pricing) | Must manage costs to remain competitive |
| Switching Costs | Moderate (Due to value-added services) | Leverages integrated solutions to retain customers |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low (High capital/operational barriers) | Benefits from customers' inability to process in-house |
What You See Is What You Get
Olympic Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Olympic Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for the company, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the steel industry. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, offering a comprehensive and actionable strategic assessment. You can trust that the insights provided are directly applicable to understanding Olympic Steel's market position and future challenges. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate use, providing a clear framework for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The metals service center industry in the U.S. is characterized by significant fragmentation and a high number of players. As of 2025, there are over 7,800 businesses operating within the metal wholesaling sector, indicating a highly competitive landscape.
While the industry has seen some consolidation, larger entities like Olympic Steel still face competition from a vast array of smaller, regional service centers. This dynamic forces intense rivalry, particularly on factors such as pricing and customer service, as companies vie for market share.
The global metal service centers market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 4.37% between 2025 and 2033. This growth is primarily fueled by increasing demand across key sectors like construction, automotive, and general manufacturing.
However, the market is not without its challenges. For instance, 2023 saw a downturn in sales volumes and pricing for many service centers. Such periods of contraction can significantly heighten competitive rivalry as companies aggressively pursue market share amidst slower overall growth.
Olympic Steel stands out by offering a comprehensive suite of processing services, including leveling, cutting, slitting, and forming, alongside a diverse product portfolio that spans carbon, coated, stainless, and aluminum. This extensive offering, coupled with robust supply chain management solutions, helps to insulate the company from intense price wars.
By providing specialized processing and a wide variety of materials, Olympic Steel builds strong customer relationships and reduces the likelihood of customers switching to competitors solely based on price. This differentiation is a key factor in its ability to maintain healthy profit margins in a competitive landscape.
In 2023, Olympic Steel reported net sales of $3.0 billion, demonstrating its significant market presence. The company's ability to offer value-added services alongside its core product offerings directly contributes to this revenue generation and competitive standing.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Olympic Steel operates in a capital-intensive industry where significant upfront investments in processing equipment, warehousing facilities, and inventory are standard. This high fixed-cost structure creates pressure on companies to maintain high operational capacity to spread those costs. For instance, the metals service center sector typically demands millions in machinery for cutting, slitting, and shaping metal products.
This necessity for high utilization rates can lead to aggressive pricing strategies, especially during economic downturns, as companies strive to cover their fixed costs. Even if margins are thin, keeping machines running is often preferred to complete idleness. This dynamic directly fuels competitive rivalry within the industry.
Furthermore, exit barriers can exacerbate this rivalry. Specialized processing equipment and established logistical networks represent assets that are difficult and costly to liquidate or repurpose. Consequently, even underperforming competitors may remain in the market, continuing to exert competitive pressure, rather than incurring substantial losses from exiting.
- Capital Intensity: The metals service center business requires substantial investment in plant, property, and equipment (PP&E), making it difficult for new entrants and keeping existing players heavily invested.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant fixed costs encourage companies to operate at high utilization levels, potentially leading to price competition to cover overheads.
- Exit Barriers: Specialized machinery and established infrastructure make exiting the market costly, potentially trapping less efficient firms and intensifying competition.
Acquisition and Diversification Strategies
Olympic Steel's competitive rivalry is notably shaped by its aggressive acquisition strategy. The company has integrated eight acquisitions over the last seven years, a significant move that bolsters its market position. The most recent, Metal Works, was acquired in late 2024, underscoring a continuous effort to expand its footprint and capabilities.
This proactive acquisition approach serves multiple strategic objectives. It’s designed to improve overall profitability, broaden the company's product and service portfolio, and extend its geographic reach. By consolidating operations and expanding into new markets, Olympic Steel can increase its market concentration in specific segments.
- Acquisition Pace: Eight acquisitions completed in the past seven years.
- Recent Acquisition: Metal Works acquired in late 2024.
- Strategic Goals: Enhance profitability, diversify offerings, and expand geographic reach.
- Impact on Rivalry: Increased market concentration potentially reduces rivalry in niche markets.
The diversification and geographic expansion resulting from these acquisitions can lead to a more consolidated industry landscape. As Olympic Steel grows through strategic purchases, it may gain greater pricing power and reduce the intensity of competition in certain areas, potentially softening the overall competitive rivalry.
The competitive rivalry within the metals service center industry is intense, driven by a fragmented market and high capital investment. Companies like Olympic Steel face constant pressure from numerous smaller players, necessitating a focus on value-added services to differentiate beyond price. Periods of industry contraction, such as the sales volume and pricing downturn experienced in 2023, further amplify this rivalry as firms fight for market share.
Olympic Steel's strategy of acquiring competitors, completing eight acquisitions in the last seven years, including Metal Works in late 2024, aims to increase market concentration and potentially lessen overall rivalry in specific segments. This consolidation, alongside a broad product and service offering, helps the company navigate the competitive pressures inherent in this capital-intensive sector.
| Metric | Value | Source Year |
| U.S. Metal Wholesaling Businesses | Over 7,800 | 2025 |
| Global Metal Service Centers Market CAGR | 4.37% | 2025-2033 |
| Olympic Steel Net Sales | $3.0 billion | 2023 |
| Olympic Steel Acquisitions | 8 | Last 7 years |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for steel is a real concern, particularly from plastics and advanced composites. These materials are increasingly making inroads into applications where steel traditionally dominated, especially when lightweighting or enhanced corrosion resistance are key. For instance, polymers are actively replacing aluminum in building products, and composites can offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to both aluminum and steel in certain high-performance scenarios. This trend directly impacts demand for steel in sectors like automotive and construction, forcing steel producers to innovate and focus on value-added products to remain competitive.
The threat of substitutes for Olympic Steel's products is influenced by the price-performance trade-off. While alternative materials exist, their adoption hinges on offering a compelling balance between cost and functional benefits. For example, advanced composites like carbon fiber provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, but their significantly higher cost restricts their use to specialized applications where performance is paramount, not as broad replacements for steel or aluminum in general construction or manufacturing.
Customers might consider bringing some processing in-house rather than using service centers like Olympic Steel. This would involve investing heavily in new equipment, training staff, and managing larger inventories. For many businesses, these upfront costs and ongoing operational complexities make this a less appealing alternative.
For instance, the cost of industrial processing machinery can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, a significant barrier for many potential in-house operations. Furthermore, maintaining the necessary skilled workforce and ensuring efficient inventory turnover adds to the complexity and expense, thereby limiting the threat of widespread in-house processing.
Technological Advancements in Material Science
Ongoing advancements in material science are continually introducing novel materials and enhancing existing ones, presenting potential substitutes for traditional metals. For instance, the automotive sector is increasingly exploring high-strength, low-weight aluminum alloys, such as those used in advanced vehicle construction, which could reduce reliance on steel. In 2023, the global advanced materials market was valued at approximately $235 billion, with significant growth projected in composites and lightweight alloys.
These innovations can significantly impact industries that are historically heavy users of steel, like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. For example, the development of carbon fiber composites offers a compelling alternative for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios. The aerospace industry, in particular, has seen a growing adoption of composite materials, with some estimates suggesting composites could account for over 50% of an aircraft's structure in future designs.
- Material Science Innovations: Development of new alloys and composites.
- Industry Impact: Automotive and aerospace sectors are key areas for substitution.
- Market Data: Global advanced materials market valued around $235 billion in 2023.
- Aerospace Trends: Increasing adoption of composite materials in aircraft structures.
Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
The increasing focus on environmental regulations and sustainability presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional steel products. As governments and consumers push for greener alternatives, materials with lower carbon footprints or enhanced recyclability gain traction.
While steel boasts strong recycling capabilities, the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions could see novel substitutes emerge and gain market share in specific applications. For instance, in 2024, the global market for sustainable building materials is projected to reach over $350 billion, indicating a strong consumer and regulatory pull towards alternatives.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter emissions standards and waste management policies can increase the cost of steel production, making substitutes more competitive.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Corporate sustainability goals often drive material selection towards options perceived as more environmentally responsible, potentially impacting steel demand in key sectors like automotive and construction.
- Material Innovation: Research and development in advanced composites, bio-based materials, and improved aluminum alloys offer viable alternatives with potentially lower lifecycle environmental impacts.
The threat of substitutes for Olympic Steel is moderate, primarily driven by advancements in materials science and increasing environmental consciousness. While steel's durability and cost-effectiveness remain strong, alternatives like advanced plastics, composites, and high-strength aluminum alloys are gaining traction in specific, performance-driven applications. For example, the automotive industry's push for lightweighting has led to increased use of aluminum, with its global market expected to see continued growth. Furthermore, a growing emphasis on sustainability and reduced carbon footprints could favor materials with lower embodied energy or superior recyclability in the long term.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Threat Level (Moderate) | Olympic Steel Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Plastics & Composites | Lightweight, corrosion resistance, design flexibility | Increasing | Impacts automotive, construction, appliance sectors |
| High-Strength Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio | Growing | Direct competitor in automotive and building applications |
| Engineered Wood Products | Sustainability, renewable resource | Niche | Minor threat in some construction segments |
| Concrete & Advanced Ceramics | Durability, specific performance characteristics | Niche | Limited impact, strong in specialized construction |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a metals service center, much like Olympic Steel, demands a significant capital outlay. This includes the costs associated with acquiring land, building state-of-the-art facilities, and investing in specialized processing machinery such as leveling, cutting, and slitting equipment. Furthermore, maintaining a robust inventory of raw materials and finished goods represents another substantial financial commitment, creating a formidable barrier for any new player looking to enter the market.
Established players like Olympic Steel enjoy significant cost advantages due to economies of scale. This means they can produce more steel at a lower per-unit cost by spreading fixed expenses across a larger output. For instance, in 2023, Olympic Steel reported net sales of $1.4 billion, indicating a substantial operational volume that new entrants would find hard to match initially.
The experience curve is another barrier. As companies like Olympic Steel produce more over time, they learn to optimize processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency, leading to lower costs. This accumulated knowledge and refined operational expertise are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly, creating a cost disadvantage for any new competitor entering the market.
These scale and experience advantages directly impact pricing power. New entrants would face a steep uphill battle to compete on price with established firms like Olympic Steel, which can leverage their lower cost structures. This makes it challenging for new companies to gain market share without substantial upfront investment and a long-term commitment to building scale and expertise.
Olympic Steel’s deep-rooted customer relationships and strong industry reputation act as significant barriers to new entrants. For instance, the company's ability to consistently serve a broad customer base, from automotive to heavy equipment manufacturers, showcases a level of trust and reliability that is difficult for newcomers to replicate. New market entrants would struggle to gain the same market penetration and secure the consistent order volumes that Olympic Steel has cultivated over years of dependable service and product quality.
Complex Supply Chain and Logistics Expertise
Operating a national network of facilities and offering comprehensive supply chain management solutions demands intricate logistics, robust inventory control, and specialized transportation capabilities. For instance, in 2024, the chemical distribution industry, which shares similar logistical complexities, saw companies investing heavily in advanced tracking and warehouse management systems to optimize efficiency. New entrants would need to build or purchase this complex infrastructure and cultivate the necessary expertise, presenting a significant barrier to entry.
Developing the sophisticated logistics, inventory management, and transportation prowess required to operate a national network is a substantial undertaking. New companies would face considerable upfront investment and a steep learning curve to match established players' operational efficiency. This complexity is a key factor that deters potential new entrants from challenging incumbents.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing a national footprint requires sophisticated route optimization and carrier management.
- Inventory Management: Maintaining optimal inventory levels across multiple locations is crucial for cost control and customer satisfaction.
- Transportation Expertise: Navigating diverse freight regulations and securing reliable transportation are essential.
- Infrastructure Investment: Building or acquiring the necessary warehousing and transportation assets represents a significant capital expenditure.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The metals processing industry faces significant regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning environmental compliance and safety standards. New companies entering this sector must navigate intricate permitting processes, which can be time-consuming and costly. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain environmental permits for industrial facilities often exceeded 18 months, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
These compliance measures require considerable capital investment. New entrants would need to allocate significant funds towards pollution control equipment, waste management systems, and adherence to workplace safety regulations. Failure to meet these standards can result in hefty fines and operational shutdowns, deterring potential competitors. For example, environmental compliance costs for new industrial plants can add 10-15% to initial capital expenditures.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for environmental controls and safety infrastructure.
- Lengthy Permitting Processes: Navigating complex and time-consuming regulatory approval pathways.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Continuous expenditure on monitoring, reporting, and equipment upgrades.
- Risk of Penalties: Potential for substantial fines and operational disruptions due to non-compliance.
The threat of new entrants for Olympic Steel is moderate, primarily due to the high capital requirements and established economies of scale that create significant barriers. Building and equipping a metals service center, along with maintaining substantial inventory, demands millions in upfront investment. For instance, in 2023, Olympic Steel's capital expenditures were $63.7 million, illustrating the scale of investment needed in this industry.
Existing players benefit from experience curves and deep customer relationships, making it challenging for newcomers to compete on cost or service. Olympic Steel’s net sales of $1.4 billion in 2023 underscore its market presence and ability to leverage scale. Furthermore, the intricate logistics and regulatory compliance, particularly environmental standards, add further complexity and cost, deterring many potential entrants.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of facilities, machinery, and inventory. | Significant upfront investment needed, limiting the pool of potential entrants. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | New entrants start with higher costs, making price competition difficult. |
| Customer Relationships & Brand Loyalty | Established trust and long-term contracts with clients. | New entrants struggle to secure initial orders and build market share. |
| Logistical & Operational Complexity | Managing national networks, supply chains, and specialized processing. | Requires substantial expertise and infrastructure investment, a steep learning curve. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to environmental and safety standards. | Adds significant costs and time delays through permitting and compliance measures. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Olympic Steel is built upon a foundation of verified data, including Olympic Steel's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and S&P Global Market Intelligence.
