Nojima Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Nojima Bundle
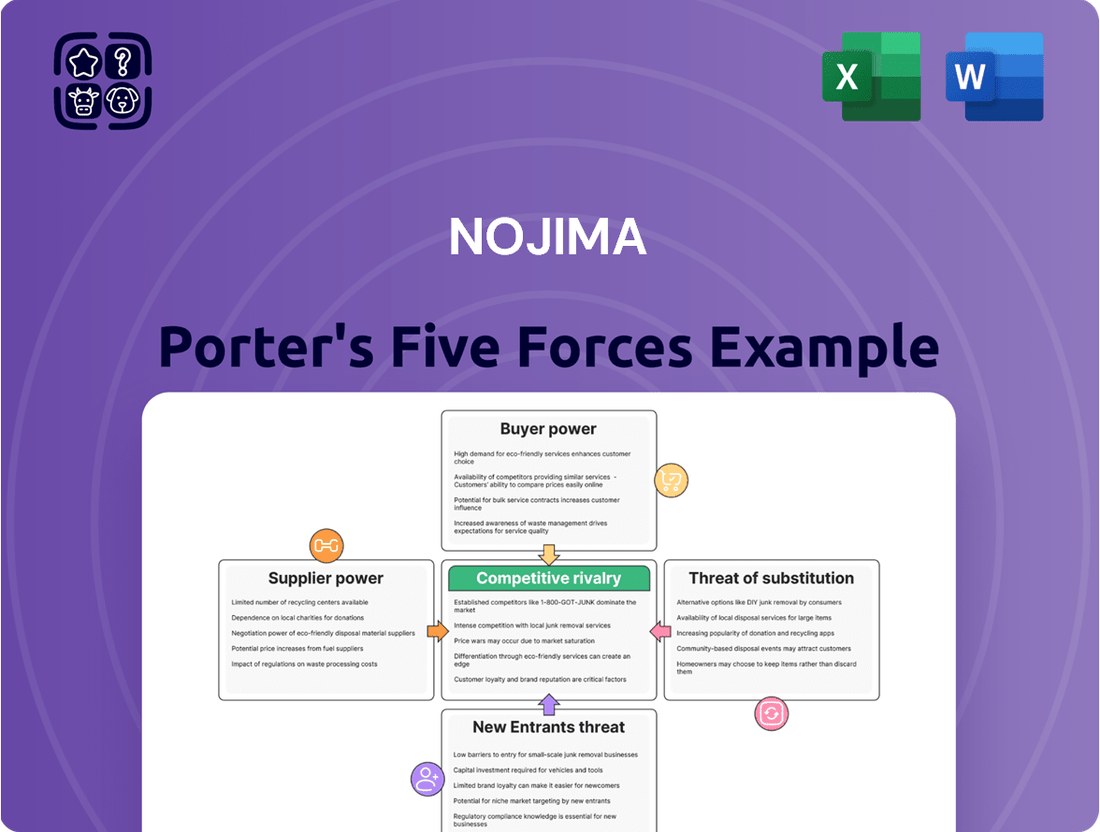
Nojima operates within a dynamic retail landscape, facing pressures from both established competitors and emerging digital players. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for navigating this market effectively. Furthermore, the availability of substitute products and the collective power of buyers significantly shape Nojima's strategic options and profitability.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Nojima’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers in the consumer electronics sector grants considerable bargaining power. Nojima Corporation, like many retailers, faces a landscape where a few dominant global manufacturers, including giants such as Sony and Apple, dictate much of the product availability and terms. These leading brands, boasting strong brand loyalty and advanced technology, can exert significant influence over retailers.
This supplier concentration means Nojima’s ability to negotiate favorable pricing or terms is somewhat limited. For instance, in 2024, major component shortages, particularly for semiconductors, demonstrated how a few key chip manufacturers could dictate supply and prices across the entire electronics industry, directly impacting retailers like Nojima.
The uniqueness of electronic products significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power for retailers like Nojima. High-demand items, such as the newest smartphone models or specialized home appliances, often boast proprietary technology or strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for Nojima to substitute suppliers without impacting sales. For instance, a supplier of a unique, cutting-edge gaming console could command higher prices and dictate terms due to limited alternatives.
While basic electronic components might be easily sourced from multiple vendors, innovative or premium products inherently grant suppliers more leverage. This is particularly true in fast-evolving sectors where differentiation is key. Consider the market for high-fidelity audio equipment; manufacturers with patented sound technologies can exert considerable influence over retailers.
Nojima's strategic acquisition of VAIO, a personal computer manufacturer, directly addresses this. By bringing a product line in-house, Nojima aims to gain greater control over its PC offerings and lessen its reliance on external PC component suppliers, thereby reducing their bargaining power in that specific segment.
Switching costs for Nojima are substantial, encompassing more than just renegotiating contracts. Adjusting intricate inventory management systems and adapting marketing strategies to new product lines can be a significant undertaking. Furthermore, training staff on potentially unfamiliar products from new or smaller suppliers adds another layer of expense and time commitment, reinforcing the loyalty of existing relationships.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a significant concern for retailers like Nojima. Many major electronics manufacturers have already established direct-to-consumer sales channels, including robust online platforms and their own branded physical stores. This allows them to bypass traditional retail intermediaries. For instance, in 2024, many leading tech brands continued to expand their D2C offerings, capturing a larger share of end-customer revenue. If these suppliers intensify their direct sales strategies, it could directly siphon sales away from Nojima, diminishing its revenue streams and weakening its negotiating position. This trend necessitates Nojima’s focus on providing value beyond mere product accessibility, such as superior customer service, expert advice, or unique in-store experiences.
This competitive pressure from supplier forward integration means Nojima must constantly innovate its business model. The increasing prevalence of D2C channels by manufacturers, a trend that saw significant growth in 2023 and continued into 2024, directly impacts retailer margins and market share. For Nojima, this translates into a need to differentiate itself.
- Manufacturer D2C Expansion: Major electronics brands are increasingly investing in and expanding their own online and physical retail presence.
- Bypassing Retailers: This direct sales approach allows manufacturers to capture the full retail margin and customer relationship.
- Impact on Nojima: Reduced sales volume and weakened bargaining power for Nojima if suppliers prioritize their own direct channels.
- Competitive Imperative: Nojima must offer compelling value propositions beyond product availability to retain customers and suppliers.
Importance of Volume to Suppliers
Nojima, as a dominant consumer electronics retailer in Japan, wields considerable influence with suppliers due to its substantial purchase volumes. This scale allows Nojima to negotiate favorable terms and potentially secure bulk discounts, enhancing its bargaining position.
However, the power dynamic is nuanced. Many electronics manufacturers operate on a global scale, meaning Nojima's orders, while large domestically, might represent a smaller fraction of a supplier's overall international revenue. For instance, a major component supplier might generate billions in global sales, making even Nojima's significant Japanese orders a relatively minor portion of their business.
This global reach of suppliers can therefore temper Nojima's absolute bargaining power. Suppliers may have alternative markets for their products, reducing their dependence on any single retailer, even one as prominent as Nojima in its home market.
- Volume Leverage: Nojima's large order quantities provide leverage for price negotiations and preferential treatment.
- Supplier Diversification: Global manufacturers may mitigate Nojima's power by having a broad customer base.
- Market Share Impact: The proportion of Nojima's orders relative to a supplier's total global sales is a key determinant of bargaining strength.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of alternative buyers for suppliers can influence their willingness to concede to Nojima's demands.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the consumer electronics sector, particularly for Nojima, is influenced by supplier concentration and product uniqueness. Major global manufacturers like Sony and Apple hold significant sway due to brand loyalty and technological advancements, limiting Nojima's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
Component shortages, such as those seen in 2024 with semiconductors, underscore how concentrated suppliers can dictate prices and availability. Moreover, the proprietary nature of many electronic products, like cutting-edge gaming consoles, means Nojima struggles to find substitutes, further empowering these suppliers.
Nojima's acquisition of VAIO is a strategic move to mitigate this by controlling its PC offerings in-house. However, the threat of supplier forward integration, with brands expanding direct-to-consumer channels, continues to pressure retailers like Nojima, necessitating a focus on differentiated customer experiences.
| Factor | Impact on Nojima | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Few dominant manufacturers dictate terms. |
| Product Uniqueness | High | Proprietary technology limits substitution. |
| Switching Costs | Substantial | Inventory, marketing, and training adjustments. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Significant | D2C channels by manufacturers reduce retailer margins. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Nojima's specific business environment.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces with intuitive color-coding.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in Japan's consumer electronics sector, Nojima's primary market, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is fueled by readily available online price comparison tools and extensive product reviews, allowing consumers to easily identify the most attractive offers. For instance, as of early 2024, a significant portion of Japanese consumers actively utilize price comparison websites before making electronics purchases.
This heightened transparency directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers, compelling Nojima to focus on competitive pricing strategies. The proliferation of e-commerce giants like Amazon.co.jp further intensifies this pressure by providing an easily accessible benchmark for pricing, making it harder for retailers to command premium prices without strong value propositions.
The bargaining power of customers at Nojima is significantly influenced by the wide availability of substitutes and alternatives. Consumers can readily turn to competitors such as Yamada Denki, Bic Camera, and Yodobashi Camera, all established players in Japan's electronics retail market. Furthermore, the pervasive reach of online marketplaces like Amazon Japan and Rakuten provides an even broader spectrum of choices, often with competitive pricing and convenient delivery options.
This abundance of alternatives empowers customers to easily switch their purchasing decisions. If Nojima's prices are perceived as too high, its service quality falters, or product availability is limited, customers have immediate recourse to other retailers. For instance, in 2023, the Japanese e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with online sales accounting for a substantial portion of total retail, underscoring the competitive pressure from digital channels.
For many consumer electronics, the cost for a customer to switch from one retailer to another is practically zero. The only hurdle is the minor inconvenience of going to a different store or website. This ease of switching significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
Customers can readily compare prices and product offerings across numerous retailers, leveraging this competition to their advantage. For instance, in 2024, online price comparison tools made it effortless for consumers to find the best deals, further diminishing the loyalty retailers could expect solely based on product availability.
This low switching cost means customers face no substantial penalties for taking their business elsewhere. They can easily switch brands or suppliers if they find better prices, superior service, or a wider selection, putting pressure on retailers like Nojima to remain competitive on multiple fronts.
Customer Knowledge and Differentiation
Modern consumers are increasingly informed, often researching product specifications and features extensively online. This readily available information diminishes their dependence on sales staff for basic product understanding. In 2024, for instance, studies indicated that over 70% of consumers conduct thorough research before making electronics purchases, directly impacting their negotiation stance.
Nojima attempts to counter this by focusing on consulting-style sales and robust after-sales service. However, the inherent nature of many electronics products means the core offerings can be quite similar across brands. This standardization makes it challenging for Nojima to cultivate lasting customer loyalty solely through product differentiation.
- Informed Consumers: Customers in 2024 possess significant product knowledge, reducing reliance on retailers for basic information.
- Standardized Products: Many electronic goods have similar core features, limiting differentiation based on the product itself.
- Nojima's Strategy: Consulting-based sales and after-sales support are key differentiators for Nojima against informed, less brand-loyal customers.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The ease of comparing similar products online contributes to lower switching costs for customers, strengthening their bargaining power.
Impact of Online Retail and Second-hand Market
The bargaining power of customers is significantly amplified by the robust growth of e-commerce in Japan. In 2024, the online retail share in consumer electronics continued its upward trajectory, offering consumers a vast array of choices and competitive pricing. This digital landscape, coupled with an expanding second-hand market, provides consumers with more purchasing options than ever before, directly impacting companies like Nojima.
This increasing customer leverage is evident in several key areas:
- Increased Price Sensitivity: With numerous online platforms and resale options readily available, customers can easily compare prices and find the best deals, making them less tolerant of higher prices from traditional retailers.
- Shift in Purchasing Habits: The convenience and accessibility of online shopping, a trend that has solidified in recent years, has fundamentally altered consumer behavior, favoring channels that offer greater flexibility and often lower costs.
- Access to Information: Online reviews and product comparisons empower customers with extensive knowledge, enabling them to make more informed purchasing decisions and negotiate from a stronger position.
- Growth of the Used Goods Market: The thriving second-hand market provides a viable and often significantly cheaper alternative for consumers, further pressuring new product pricing and availability.
Customers in Japan's consumer electronics market possess considerable bargaining power, largely due to heightened price transparency and the ease of accessing comparable products. This is exacerbated by the widespread use of online price comparison tools, which as of early 2024, are routinely used by a significant portion of Japanese shoppers before making electronics purchases. This environment compels retailers like Nojima to maintain competitive pricing to attract and retain customers.
The bargaining power of Nojima's customers is further amplified by the low cost of switching between retailers. With numerous established competitors such as Yamada Denki, Bic Camera, and Yodobashi Camera, alongside major e-commerce platforms like Amazon Japan and Rakuten, consumers can easily shift their patronage if they find better prices, service, or product availability. This ease of transition, a trend that saw Japanese e-commerce sales continue their robust growth in 2023, means customer loyalty is less assured.
Informed consumers, a growing demographic in 2024 with over 70% conducting extensive online research before buying electronics, also exert significant influence. This readily available product knowledge reduces their dependence on sales staff, allowing them to negotiate from a stronger position. While Nojima counters with consulting-style sales and after-sales support, the inherent standardization of many electronic products makes it challenging to build loyalty purely on product differentiation.
| Factor | Impact on Nojima | Customer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Requires competitive pricing strategies. | Utilize price comparison websites. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Faces pressure from numerous competitors. | Easily switch to alternative retailers. |
| Low Switching Costs | Customer loyalty is not guaranteed. | Move business to better offers with minimal effort. |
| Informed Consumers | Reduces reliance on sales expertise. | Negotiate based on researched product knowledge. |
Full Version Awaits
Nojima Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is your complete Nojima Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the electronics retail sector. This preview accurately represents the professionally formatted and insightful document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing elements. You're not looking at a sample; this is the actual, ready-to-use analysis designed to provide actionable strategic insights for Nojima. Gain immediate access to this comprehensive report and leverage its detailed breakdown of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Nojima operates in the intensely competitive Japanese consumer electronics retail sector. Major rivals such as Yamada Denki, Bic Camera, Yodobashi Camera, and EDION command significant market share through extensive physical store networks.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the robust growth of online retailers, presenting a dual threat to Nojima's traditional brick-and-mortar model. This diverse array of competitors, spanning both established giants and agile e-commerce players, necessitates continuous strategic adaptation for Nojima.
In 2023, the Japanese electronics retail market saw continued dominance by these major players, with companies like Yamada Denki reporting substantial revenues, highlighting the scale of competition Nojima faces.
The Japanese consumer electronics market's growth rate in retail volume for 2024 has been characterized as fairly stagnant, with certain product categories experiencing declines. This environment, where expansion is limited, naturally fuels more intense rivalry among existing players as they fight to capture a larger portion of the existing pie. Consequently, companies like Nojima must differentiate themselves and innovate to gain market share rather than simply benefiting from a growing market.
Competitive rivalry in the consumer electronics sector is intense, often characterized by similar product offerings that drive price-based competition. For instance, during 2024, many retailers engaged in aggressive promotional pricing on popular electronics. Nojima strives to stand out by focusing on consulting-based sales, offering product installation, repair services, and comprehensive after-sales support. This approach aims to elevate the customer experience beyond mere product transactions.
While Nojima emphasizes its service-oriented differentiation, it's important to note that other prominent retailers also invest significantly in customer service initiatives. Many major competitors in 2024 bolstered their loyalty programs and expanded their service portfolios, including extended warranties and in-store technical assistance. This means Nojima's differentiation strategy faces a strong counter-response from rivals who also aim to capture customer loyalty through service and added value.
Exit Barriers
High fixed costs are a major hurdle for companies looking to exit the consumer electronics retail industry. Think about the massive investments in large retail stores, the significant capital tied up in inventory, and the complex, established supply chains. These aren't easily shed assets.
Because of these substantial exit barriers, companies are often compelled to remain in the market and continue competing, even when profits are thin. Shutting down operations would mean realizing substantial losses on these fixed assets. For instance, a large electronics retailer might have millions invested in physical store leases and fixtures, making a clean exit incredibly costly.
This situation intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies are reluctant to leave, leading to a crowded marketplace where players fight harder for market share.
- High Capital Investment: Significant outlays in prime retail locations, extensive inventory, and sophisticated logistics create substantial sunk costs.
- Inventory Write-downs: Disposing of unsold electronics inventory often results in steep discounts and significant financial losses, deterring quick exits.
- Brand and Reputation: A poorly managed exit can damage a brand's reputation, impacting future business ventures.
- Employee Severance and Lease Obligations: Companies face costs related to employee termination packages and fulfilling ongoing lease agreements for retail spaces.
Price Competition and Promotions
Price competition is a defining characteristic for electronics retailers like Nojima. The market often sees aggressive pricing strategies, especially for products that have become commodities, leading to frequent price wars. Retailers commonly engage in price matching to retain customers, and promotional discounts are a regular tactic to drive sales volume. This intense rivalry can significantly compress profit margins across the entire industry.
- Price wars: In 2024, many consumer electronics retailers reported margin pressures directly linked to aggressive price matching and promotional sales events.
- Promotional activities: Major sales periods, such as Black Friday and holiday seasons, often witness retailers offering discounts of 20% or more on popular electronics, further intensifying competition.
- Margin squeeze: The constant need to compete on price means that even successful retailers can find their gross profit margins on individual items reduced, often falling into the single digits for highly competitive product categories.
- Customer acquisition cost: While promotions attract customers, the cost of these discounts contributes to a higher customer acquisition cost, making profitability a challenge.
Nojima faces a fierce competitive landscape in Japan's consumer electronics retail sector, battling established giants like Yamada Denki and Bic Camera, alongside a growing online retail threat. The market's limited growth in 2024, with stagnant retail volume, forces intense rivalry as companies vie for existing market share. This environment necessitates differentiation beyond price, as many competitors also enhance services and loyalty programs.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx. JPY Billion) | Key Competitive Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| Yamada Denki | ~1,500 | Extensive store network, private brands, online sales |
| Bic Camera | ~800 | Loyalty programs, diverse product categories, airport stores |
| Yodobashi Camera | ~700 | Strong online presence, private label products, premium service |
| EDION | ~600 | Regional strength, home appliance focus, repair services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales by electronics manufacturers presents a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional retailers like Nojima. Companies are increasingly leveraging their own online platforms and physical flagship stores to reach customers directly, cutting out intermediaries.
This shift means consumers can bypass Nojima and purchase directly from brands, potentially securing competitive pricing or exclusive product bundles. For instance, Apple's robust D2C strategy, which includes its online store and Apple Stores, allows it to control the customer experience and data, making it a strong substitute for purchasing through a third-party retailer.
In 2023, the global D2C e-commerce market was valued at over $130 billion, with significant growth projected in the electronics sector as manufacturers seek to strengthen brand loyalty and capture higher margins. This trend directly erodes the value proposition of traditional retail channels.
As more manufacturers invest in their D2C capabilities, Nojima faces pressure to differentiate its offerings beyond mere product availability, focusing on value-added services, expert advice, and a superior in-store experience to counter this substitute threat.
The rise of multi-functional devices like smartphones, which now combine cameras, music players, and even gaming capabilities, significantly impacts traditional electronics retailers like Nojima. These all-in-one gadgets diminish the need for customers to purchase separate, specialized devices. For instance, in 2024, the global smartphone market continued its robust growth, with unit shipments projected to reach over 1.2 billion, indicating a strong consumer preference for integrated solutions.
Furthermore, the expanding smart home ecosystem, where devices seamlessly communicate and offer combined functionalities, presents another substitute threat. Consumers are increasingly opting for integrated systems that manage lighting, security, and entertainment, reducing their reliance on individual component purchases. This trend is evidenced by the projected 15% year-over-year growth in the global smart home market in 2024, reaching an estimated value of $150 billion.
Emerging subscription and rental models present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional product sales in the electronics sector. Services like cloud-based software, streaming entertainment platforms, and device leasing programs offer consumers access to functionality without the need for outright ownership. For instance, the global device-as-a-service market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a shift in consumer preference away from perpetual ownership.
Second-hand and Refurbished Markets
The burgeoning second-hand and refurbished electronics market in Japan presents a significant threat of substitutes for Nojima. This segment offers consumers a more affordable alternative to purchasing new devices, directly impacting Nojima's sales of new products, especially among price-conscious buyers. The expansion of this secondary market means consumers have readily available, lower-cost options, diverting potential revenue away from Nojima's core business.
Japan's second-hand electronics market has seen substantial growth, indicating its increasing appeal. For example, the market for used smartphones alone was valued at approximately ¥400 billion in 2023 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory. This trend suggests that a growing number of consumers are opting for pre-owned or refurbished goods, thereby reducing their demand for brand-new items typically sold by Nojima.
- Growing Market Share: The second-hand market is capturing an increasing share of consumer spending on electronics.
- Price Sensitivity: Cost-conscious consumers are increasingly turning to refurbished options as a viable substitute.
- Competitive Pressure: This alternative channel directly competes with Nojima's new product sales, potentially eroding market share.
- Availability of Alternatives: The ease of access to quality refurbished electronics provides a strong substitute for new purchases.
Cloud-based Services and Digital Alternatives
The increasing adoption of cloud-based services and digital alternatives poses a significant threat of substitution for Nojima Corporation. As consumers increasingly opt for streaming music, movies, and games, the demand for physical media like CDs and DVDs, along with dedicated playback devices, diminishes. This trend directly impacts Nojima’s traditional electronics retail business, as cloud storage and digital distribution reduce the need for local hardware. For instance, the global cloud computing market size was estimated to reach over $1 trillion in 2024, indicating a substantial shift away from on-premise solutions and physical media.
This shift represents a long-term substitute threat to Nojima's hardware sales. Consumers are less inclined to purchase high-capacity hard drives or powerful local processors when cloud storage and streaming services offer convenient, often subscription-based, alternatives. This can lead to a decline in sales for components and devices that were once core to Nojima's offerings.
- Cloud adoption: The global cloud computing market is projected for substantial growth, with forecasts suggesting it will continue to expand rapidly through 2024 and beyond, impacting hardware demand.
- Digital media consumption: Streaming services have become the dominant mode for accessing music and video content, with platforms like Spotify and Netflix reporting billions of active users.
- Reduced hardware dependency: Consumers are increasingly relying on smartphones and smart TVs for media consumption, lessening the need for separate media players or specialized gaming consoles.
- Shift in consumer spending: A growing portion of consumer electronics budgets is being allocated to software subscriptions and digital content rather than physical devices.
The increasing prevalence of subscription and rental models in electronics presents a significant substitute threat for Nojima. These services provide access to technology without the burden of ownership, appealing to consumers who prefer flexibility and lower upfront costs. This shift directly challenges Nojima's traditional sales model.
Device-as-a-service (DaaS) and leasing programs allow consumers to use the latest gadgets for a monthly fee, often including maintenance and upgrades. This model is gaining traction as it offers predictable expenses and access to cutting-edge technology, diminishing the appeal of outright purchase from retailers like Nojima. The global DaaS market is experiencing robust growth, projected to expand significantly in the coming years.
Emerging digital platforms also act as substitutes for physical media and dedicated devices. For instance, the continued dominance of streaming services for music and video, alongside cloud gaming, reduces the need for consumers to purchase CDs, DVDs, or even specialized gaming consoles, impacting Nojima's sales of these product categories.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Nojima | 2024 Market Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Sales | Bypasses traditional retail channels, potentially lower prices for consumers. | Global D2C e-commerce market valued over $130 billion (2023), with continued growth. |
| Multi-functional Devices | Reduces demand for separate specialized electronics. | Global smartphone shipments projected over 1.2 billion units (2024). |
| Subscription/Rental Models | Offers access without ownership, impacting outright sales. | Device-as-a-Service (DaaS) market showing significant expansion. |
| Second-hand & Refurbished Market | Provides affordable alternatives to new products. | Japanese used smartphone market valued around ¥400 billion (2023). |
| Cloud Services & Digital Media | Decreases need for physical media and local storage. | Global cloud computing market estimated over $1 trillion (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
Entering Japan's consumer electronics retail sector demands a considerable financial outlay. Establishing a physical store presence, managing inventory, and building efficient logistics networks represent significant upfront costs, deterring many potential new players.
For instance, securing prime retail locations in major Japanese cities can involve millions of dollars in leasehold improvements and rent. Add to this the cost of stocking a wide range of products, from high-end televisions to small accessories, and the capital barrier becomes even more imposing.
In 2024, the average cost to open a medium-sized electronics store in Japan, including initial inventory and fit-out, could easily exceed ¥50 million to ¥100 million (approximately $320,000 to $640,000 USD), making it a substantial hurdle for aspiring competitors.
This high capital requirement effectively limits the number of new companies that can realistically challenge established retailers like Nojima, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants.
Existing major electronics retailers in Japan, such as Nojima, Yamada Denki, and Bic Camera, have cultivated significant brand loyalty and strong customer relationships over many years. For instance, Nojima, a prominent player, reported net sales of ¥832.4 billion for the fiscal year ending March 2024, indicating its substantial market presence and customer base.
New entrants face a considerable challenge in replicating this ingrained trust and familiarity that consumers associate with these established brands. The sheer decades of consistent service and product offerings have solidified their positions, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly gain consumer preference.
Competing against these deeply rooted brand loyalties requires new entrants to invest heavily in marketing and customer acquisition strategies. The established retailers benefit from repeat business and positive word-of-mouth, creating a significant barrier to entry for any aspiring competitor.
Building a robust supply chain and distribution network in Japan, as Nojima has, is a formidable barrier for new entrants. It requires establishing strong relationships with major electronics manufacturers, a process that can take years and significant investment. For instance, securing favorable terms and guaranteed stock from leading brands like Sony or Panasonic is a prerequisite for competitive pricing and availability.
The logistical complexity of distributing a wide range of electronics across Japan’s diverse geography further elevates this barrier. New players would need to invest heavily in warehousing, transportation, and last-mile delivery infrastructure. In 2024, the Japanese logistics market saw continued growth, with e-commerce driving demand for efficient delivery, but also increasing operational costs for newcomers.
Nojima's established network, honed over decades, provides them with economies of scale and preferential treatment from suppliers that are difficult for emerging competitors to replicate. This existing infrastructure allows for faster inventory turnover and reduced shipping costs per unit, directly impacting their price competitiveness.
Regulatory Hurdles and Market Knowledge
Navigating Japan's unique business landscape presents a significant threat of new entrants, particularly concerning regulatory hurdles and the deep understanding of market knowledge required. Companies must grapple with specific Japanese business regulations, stringent consumer protection laws, and intricate cultural nuances prevalent in the retail sector.
Foreign entrants often face substantial challenges in overcoming these deeply ingrained regulatory and cultural barriers. For instance, understanding and complying with the Act on Specified Commercial Transactions or the nuances of customer service expectations in Japan demands considerable investment in local expertise and adaptation. In 2023, Japan’s retail sales reached approximately ¥156.7 trillion (around $1.1 trillion USD), highlighting a massive market but one with high entry barriers.
- Regulatory Complexity: Japan's legal framework, including consumer safety standards and advertising guidelines, requires meticulous adherence.
- Cultural Nuances: Understanding Japanese consumer behavior, service expectations, and business etiquette is critical for success.
- Market Knowledge Imperative: Extensive research and on-the-ground experience are vital to effectively compete in the Japanese retail market.
- High Initial Investment: New entrants must allocate significant resources to legal compliance, market research, and cultural training.
Expected Retaliation from Incumbents
In Japan's fiercely competitive consumer electronics sector, established companies like Sony, Panasonic, and Sharp possess substantial resources. They are known to respond aggressively to new entrants, often initiating price wars or significantly boosting marketing spend to protect their market share. For example, in 2023, major players continued aggressive promotional campaigns, particularly during key sales periods like Obon and year-end, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold without considerable capital investment.
This anticipated strong retaliation acts as a significant deterrent, discouraging many potential new companies from entering the market. The high cost of matching incumbent marketing budgets and the risk of price erosion make the Japanese consumer electronics market a challenging environment for startups.
The potential for incumbents to leverage their existing customer loyalty and distribution networks further solidifies this threat. Newcomers must be prepared for a robust defense from established players.
Key retaliatory strategies observed include:
- Price reductions on popular product lines.
- Increased advertising and promotional activities.
- Bundling of products or enhanced after-sales service.
- Aggressive product innovation cycles.
The threat of new entrants into Japan's consumer electronics retail sector is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements for establishing operations and inventory. Additionally, formidable brand loyalty cultivated by incumbents like Nojima, coupled with the complexities of building robust supply chains and navigating regulatory landscapes, presents substantial barriers. Established players also possess the resources to engage in aggressive retaliation against newcomers, further deterring market entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Estimated Cost/Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Opening a medium-sized electronics store in Japan, including initial inventory and fit-out, could exceed ¥50 million to ¥100 million (approx. $320,000-$640,000 USD). | High |
| Brand Loyalty | Established retailers like Nojima have decades of customer trust, making it difficult for new entrants to gain consumer preference. Nojima’s net sales were ¥832.4 billion in FY ending March 2024. | Significant |
| Supply Chain & Logistics | Building relationships with manufacturers and establishing efficient nationwide distribution networks is complex and costly. | Challenging |
| Regulatory & Cultural Barriers | Navigating Japan's specific business regulations, consumer laws, and cultural nuances requires considerable expertise and adaptation. Japan's retail sales reached approximately ¥156.7 trillion in 2023. | Formidable |
| Retaliation from Incumbents | Established firms can initiate price wars or boost marketing spend, making market entry financially risky for new companies. | Likely |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Nojima Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports from Nojima Corporation and its competitors, as well as market research reports from firms like Euromonitor International and Statista.
We also leverage industry-specific trade publications and government economic indicators to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and external influences affecting Nojima.
