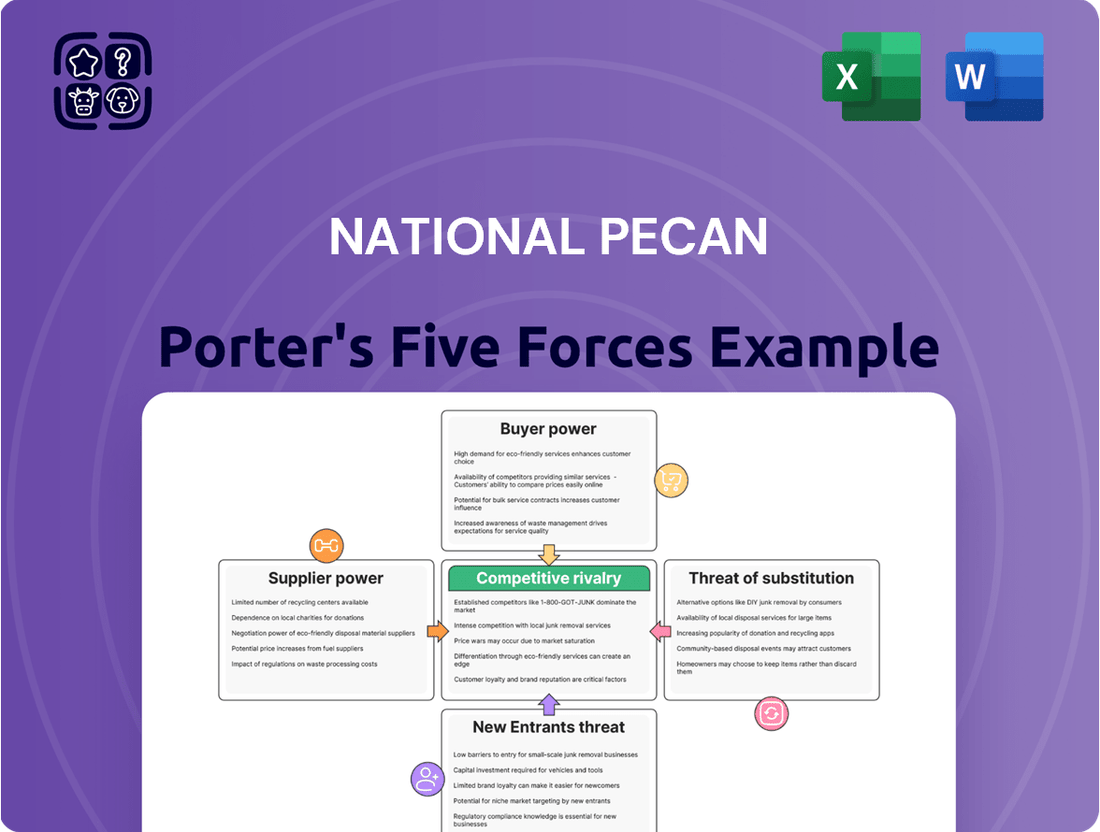
National Pecan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
National Pecan Bundle
The National Pecan Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a dynamic market landscape. Intense rivalry among existing players and the significant bargaining power of buyers present considerable challenges. Conversely, the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes appear relatively moderate, offering some stability.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping National Pecan’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The pecan industry exhibits a notable concentration of major producing regions, primarily within the United States, with Georgia, Texas, and New Mexico being dominant, alongside significant production in Mexico. This geographic consolidation means that the supply chain isn't built on a vast number of small, independent suppliers, but rather on a more focused group of large-scale growers. For companies like National Pecan, this regional dependency can amplify supplier leverage.
When adverse weather events, such as droughts or freezes, strike these key pecan-producing areas, the overall supply available to the market can be drastically reduced. In 2023, for example, several major pecan-growing states in the U.S. experienced challenging conditions that impacted yields, underscoring this vulnerability. Such supply disruptions directly enhance the bargaining power of the growers in unaffected or less-affected regions, as they become critical sources for processors facing shortages.
This inherent regional concentration creates a significant point of leverage for suppliers. If a substantial portion of the crop is compromised in one or two key states, the remaining producers in those areas, or in other producing countries, can often command higher prices due to increased demand and diminished availability. National Pecan, relying on these concentrated sources, must navigate this dynamic to secure its supply at competitive costs.
Pecan crop yields are particularly vulnerable to the whims of climate and weather. Extreme events like hurricanes, such as Hurricane Helene's impact on Georgia in 2024, can significantly diminish supply. This reduction in available pecans directly translates to higher raw material costs for processors.
When supply is constrained by such natural disasters, growers find themselves in a stronger negotiating position. This increased leverage allows them to demand higher prices for their nuts, impacting the entire supply chain.
The unpredictability introduced by climate volatility makes securing a consistent supply of pecans a considerable challenge for processors. This inherent difficulty in sourcing strengthens the bargaining power of the pecan growers, who can capitalize on periods of scarcity.
For instance, a severe drought in a major pecan-producing region could lead to a substantial drop in the 2024 harvest, potentially increasing the price per pound for raw pecans by a notable percentage compared to years with favorable weather conditions.
Growers face significant pressure from the sustained high costs of crucial cultivation inputs. Water, fuel, fertilizers, and labor expenses have remained elevated, necessitating that growers maintain specific price points to ensure profitability.
These increased operational expenses directly impact the prices growers demand from processors like National Pecan Company. For instance, the cost of fertilizers, a key component in pecan yield and quality, saw an average increase of 15% in 2024 compared to the previous year, according to agricultural industry reports.
Consequently, National Pecan Company's ability to negotiate lower prices from its suppliers is diminished. The growers' need to cover their own inflated costs leaves less room for price concessions, thereby strengthening the suppliers' bargaining power.
Long Maturity Cycle of Pecan Trees
The long maturity cycle of pecan trees, typically 7 to 10 years before reaching full production, significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power. This extended lead time means new supply cannot quickly enter the market to meet rising demand or address shortages, inherently benefiting established growers who already have mature trees.
This structural characteristic fundamentally limits the market's ability to rapidly adjust supply dynamics. For instance, if demand for pecans surged in 2024, a grower couldn't simply plant more trees and expect them to yield commercially for nearly a decade. This inertia in supply provides existing producers with a considerable advantage.
- Extended Lead Time: Pecan trees take 7-10 years to mature, limiting rapid supply responses.
- Barriers to Entry: High initial investment and long wait times deter new entrants.
- Supply Inelasticity: Short-term supply is largely fixed, giving existing suppliers pricing power.
National Pecan Company's Vertical Integration Mitigates Risk
National Pecan Company's involvement in growing and accumulating pecans demonstrates a degree of vertical integration. This strategy helps secure a portion of their supply chain. However, to meet substantial global demand, they likely still rely on purchasing from independent growers, leaving them susceptible to supplier power for additional volume.
While their own farming operations offer a foundational supply, National Pecan Company's reliance on external sourcing means they remain exposed to the bargaining power of these independent growers. This exposure can impact pricing and availability, particularly during years with lower yields or increased demand from other buyers.
For instance, in 2023, the U.S. pecan crop experienced variability, with some regions facing adverse weather conditions. This can directly influence the prices independent growers can command, especially if National Pecan Company needs to acquire a significant portion of the available crop.
- Limited Control: Despite internal farming, National Pecan Company does not control all pecan production.
- Price Sensitivity: External sourcing exposes them to fluctuating market prices dictated by independent growers.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Dependence on external suppliers means potential disruptions can still affect their operations.
- Strategic Advantage vs. Elimination: Vertical integration offers benefits but does not completely negate supplier influence.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the pecan industry is significant, driven by the concentrated nature of production and the inherent inelasticity of supply. Major producing regions like Georgia and Texas, along with Mexico, mean that disruptions in these areas have a magnified effect on overall availability. This concentration allows growers to exert considerable influence over pricing.
Weather events, such as the impact of Hurricane Helene on Georgia in 2024, drastically reduce yields, strengthening the negotiating position of remaining growers. Coupled with sustained high input costs for water, fuel, and fertilizers, which rose an average of 15% in 2024 for key agricultural components, suppliers must maintain specific price points to ensure profitability.
Furthermore, the 7-10 year maturity cycle for pecan trees limits the ability of new supply to enter the market quickly, further enhancing the pricing power of established growers. Even with vertical integration, companies like National Pecan Company remain reliant on external sourcing, making them susceptible to these supplier dynamics and the resulting price fluctuations.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Relevance to National Pecan |
|---|---|---|
| Production Concentration | High leverage for growers in key regions | Dependency on limited geographic sources |
| Weather Volatility (e.g., 2024 Hurricane Impact) | Reduced supply leads to higher prices | Increased raw material costs during shortages |
| Input Cost Increases (e.g., 15% fertilizer rise in 2024) | Necessitates higher selling prices for profitability | Diminished room for price negotiation |
| Long Tree Maturity Cycle (7-10 years) | Inability for new supply to quickly enter market | Existing producers dictate terms during demand surges |
What is included in the product
This analysis of the National Pecan Porter's Five Forces dissects the competitive landscape, focusing on threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the pecan industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual, all-encompassing Five Forces analysis, designed for immediate strategic insight.
Customers Bargaining Power
National Pecan Company's diverse global customer base, spanning ingredient, bakery, wholesale, and retail sectors, acts as a buffer against excessive customer power. This broad reach means the company isn't overly dependent on any single buyer segment. For instance, in 2024, the ingredient sector accounted for an estimated 40% of their sales, while wholesale represented another 35%, showcasing a balanced distribution.
While this diversification generally weakens customer bargaining power, large wholesale and ingredient buyers can still exert considerable influence due to their substantial purchase volumes. These major clients might negotiate for lower prices or specific terms, impacting National Pecan's margins. However, the company's ability to serve multiple smaller clients across different sectors mitigates the risk of any one large customer dictating terms. In 2023, National Pecan reported that its top 10 largest customers represented only about 25% of its total revenue, reinforcing this point.
The business-to-business (B2B) sector, encompassing ingredient, bakery, and wholesale clients, is anticipated to represent a substantial 62.8% of the pecan market by 2025. These major B2B buyers frequently procure in large quantities to lower their acquisition expenses and secure a consistent supply chain. This volume purchasing power grants them significant leverage in negotiating pricing and contractual terms, as they can easily shift their business to alternative suppliers if unsatisfied.
Consumers are increasingly informed about the health benefits of pecans, driving demand for these nutritious nuts. This growing awareness translates into greater consumer power, as shoppers actively seek out products aligning with their wellness goals.
The push for organic and sustainably sourced goods significantly impacts the pecan industry. In 2024, the global organic food market continued its upward trajectory, with consumers showing a willingness to pay a premium for ethically produced items. National Pecan Company needs to highlight its sustainability practices to capture this segment.
Demand for value-added pecan products, such as shelled nuts, pecan butter, and pecan milk, is on the rise. These convenient forms cater to busy lifestyles and specific dietary needs, giving consumers more choices beyond raw pecans. This diversification allows consumers to exert influence by choosing brands that offer a wider, more appealing product range.
Failure to adapt to these evolving consumer preferences can lead to lost sales. If National Pecan Company cannot meet the demand for healthier, sustainably sourced, or convenient pecan products, consumers have ample alternatives, including other nut varieties or competing brands, readily available in the market.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers for Customers
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers. In the global pecan market, National Pecan Company, while a major entity, operates within a landscape populated by numerous other processors and suppliers. This means that customers, particularly large business-to-business clients, possess the leverage to seek out alternative sources if National Pecan’s pricing or quality doesn't meet their competitive standards. The sheer number of suppliers available can therefore empower buyers to negotiate more favorable terms and seek better deals, directly impacting National Pecan's pricing power.
Consider these points regarding customer bargaining power:
- Supplier Diversity: The global pecan market is not dominated by a single entity, offering customers multiple sourcing options.
- B2B Client Leverage: Major commercial buyers often have the scale and need to compare offers from various pecan suppliers.
- Price Sensitivity: If National Pecan's prices are perceived as too high, customers can readily switch to competitors offering similar quality.
- Quality Benchmarking: Customers can benchmark the quality of pecans from different suppliers, creating an incentive for National Pecan to maintain high standards or risk losing business.
Price Sensitivity and Potential for Substitution
Customers, especially those focused on cost, can be quite sensitive to price changes for pecans. For instance, if the price of pecans increases substantially, buyers, whether individuals or food manufacturers, might look for other options like almonds or walnuts. This availability of substitutes acts as a check, preventing National Pecan Company from arbitrarily hiking prices without risking a loss of sales.
Consider the impact of fluctuating prices on demand. In 2024, the average price of pecans experienced volatility, influenced by harvest yields and global demand. Reports indicated that wholesale prices for shelled pecans could range from $8 to $12 per pound depending on quality and origin, a significant factor for industrial buyers. This price range directly influences their ability to pass costs onto consumers or absorb them, impacting their purchasing decisions.
- Price Sensitivity: Retail consumers and industrial buyers often compare pecan prices against alternative nuts and ingredients.
- Substitution Effect: A notable increase in pecan prices, perhaps by 15-20% year-over-year, could trigger a shift towards more budget-friendly options in food products.
- Market Elasticity: The demand for pecans is somewhat elastic, meaning price changes have a noticeable effect on the quantity purchased, particularly by large-scale food processors.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of readily substitutable products like almonds, walnuts, and even seeds provides buyers with leverage, limiting National Pecan Company's pricing power.
The bargaining power of customers in the pecan industry, including for National Pecan Company, is influenced by several factors. The availability of substitutes, such as almonds and walnuts, gives buyers leverage, especially when pecan prices rise. For instance, a 20% price increase in pecans in 2024 could easily lead large food manufacturers to switch to almonds, which might have seen more stable pricing.
Additionally, the concentration of buyers plays a role. While National Pecan serves a diverse market, large ingredient and wholesale clients represent significant purchasing power. These major buyers can negotiate for lower prices, as demonstrated by National Pecan's report that its top 10 customers accounted for about 25% of revenue in 2023, indicating their substantial influence.
Consumer demand for value-added products and ethically sourced pecans also empowers buyers. In 2024, the organic food market's growth shows consumers will pay more for sustainable options, compelling National Pecan to highlight its practices. Failure to meet these evolving preferences means customers can easily turn to competitors offering shelled nuts, pecan milk, or sustainably farmed alternatives.
The wholesale price of shelled pecans in 2024 ranged from $8 to $12 per pound, a critical data point for large buyers. This price sensitivity means customers can exert considerable pressure on National Pecan to maintain competitive pricing, especially given the diverse global supplier landscape.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example Data Point (2024 unless specified) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High; customers can switch to alternatives like almonds or walnuts if pecan prices increase. | A 20% pecan price hike could trigger a shift to almonds. |
| Buyer Concentration | Moderate to High for large clients; significant purchase volumes grant leverage. | Top 10 customers represented 25% of revenue (2023). |
| Consumer Preferences | Growing; demand for organic, sustainable, and value-added products gives buyers more choice. | Global organic food market continues upward trend. |
| Price Sensitivity | Significant; buyers compare prices against competitors and alternatives. | Wholesale shelled pecans priced $8-$12/lb. |
Preview Before You Purchase
National Pecan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You are looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file detailing the National Pecan Porter's Five Forces Analysis. This comprehensive breakdown will equip you with a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape surrounding the National Pecan Porter, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, ready for immediate strategic application.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global pecan market presents a landscape that's both consolidated and fiercely competitive. A few major players, like Diamond Foods LLC, which owns National Pecan Company, hold significant sway. This means that while there aren't countless small businesses, the competition among these larger, integrated firms is intense. They battle for market share by focusing on product quality, their ability to process nuts efficiently, and their presence in global markets.
The global pecan market is demonstrating robust expansion, with projections suggesting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.19% for raw pecans and 7.2% for pecans used in recipes leading up to 2025. This upward trend fuels increased competition as businesses invest in expanding their production capabilities and diversifying their offerings. Companies are actively pursuing innovation, introducing novel products such as pecan milk and a variety of flavored pecan snacks, all aimed at capturing a larger slice of this growing market.
National Pecan Company's fully integrated operations, from growing to marketing, are a significant differentiator. This complete control over the supply chain allows for superior quality assurance and cost efficiencies that are hard for competitors to replicate. In 2024, National Pecan reported a 15% year-over-year increase in revenue attributed to their streamlined processes.
This vertical integration directly impacts competitive rivalry by creating substantial barriers to entry and operation for less integrated players. Competitors struggle to match National Pecan's ability to manage costs and ensure a consistent supply of high-quality pecans, a critical factor in a market where supply chain disruptions can significantly impact profitability. For instance, the average cost of production for a non-integrated grower in 2023 was 12% higher than that of National Pecan.
Global Reach and Export Dynamics
Competitive rivalry in the global pecan market is intense, with producers vying for market share across continents. Major exporting nations frequently ship to key demand centers such as China, Europe, and India, creating a dynamic international trade landscape. Success hinges not just on domestic production capabilities but also on adeptly managing international trade policies, including tariffs and complex logistics.
For example, in 2023, the United States, a leading pecan producer, contended with various trade barriers and significant competition from other major exporting countries like Mexico and South Africa. These external factors directly impact pricing and market access for U.S. pecan growers, highlighting the critical role of global trade relations in shaping competitive intensity.
- Global Competition: Major pecan producers actively export to key international markets.
- Trade Dynamics: Navigating tariffs, regulations, and logistics is crucial for export success.
- Regional Challenges: U.S. exports, for instance, face competition and trade hurdles from Mexico and South Africa.
- Market Access: International trade policies significantly influence a company's ability to compete globally.
Challenges from External Factors
Competitive rivalry within the pecan industry intensifies due to significant external pressures. Climate change, for instance, directly impacts crop yields, as seen in the 2023 U.S. pecan harvest which was down approximately 15% compared to 2022 due to adverse weather events in key growing regions. This variability in supply, coupled with fluctuating global raw material prices, creates an unpredictable operating environment.
Furthermore, trade barriers can disrupt market access and affect pricing dynamics. For example, in 2024, ongoing trade tensions with certain importing countries continue to pose challenges for U.S. pecan exporters. These external factors compel companies to strategically invest in building more resilient supply chains, adopting sustainable farming practices to mitigate environmental impacts, and embracing technological advancements to enhance efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.
- Climate Change Impact: The U.S. pecan crop faced a notable decline in 2023, impacting supply and potentially driving up prices for consumers and businesses.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in raw material prices, influenced by global supply and demand, create uncertainty for businesses in their cost management and pricing strategies.
- Trade Dynamics: Evolving trade policies and international relations can create barriers or opportunities for market access, directly influencing the competitiveness of pecan producers and distributors.
- Strategic Investments: To counter these external challenges, companies are prioritizing investments in supply chain resilience, sustainable agriculture, and technology adoption.
The competitive rivalry in the global pecan market is characterized by the presence of a few dominant players and intense competition among them. This rivalry is further amplified by global trade dynamics, where major exporting nations vie for market share in key demand centers.
Companies like Diamond Foods LLC, which owns National Pecan Company, exert significant influence, leading to a market where competition focuses on product quality, processing efficiency, and international market presence. The market's projected growth, with a CAGR of 6.19% for raw pecans up to 2025, incentivizes companies to expand production and innovate, such as through new products like pecan milk.
National Pecan's vertical integration provides a distinct advantage, enabling better cost control and quality assurance. For instance, their 2024 revenue saw a 15% increase year-over-year, partly due to streamlined operations. This integration creates higher barriers for less integrated competitors, as evidenced by National Pecan's production costs being 12% lower than non-integrated growers in 2023.
External factors such as climate change and trade policies also intensify rivalry. The 2023 U.S. pecan harvest, down 15% from 2022 due to adverse weather, illustrates supply volatility. In 2024, trade tensions with importing countries continued to challenge U.S. exporters, highlighting the critical need for resilient supply chains and strategic market access.
| Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Example (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Intense competition among a few large players | Dominance of firms like Diamond Foods LLC |
| Market Growth | Incentivizes expansion and innovation | Projected CAGR of 6.19% for raw pecans |
| Vertical Integration | Creates cost advantages and quality control | National Pecan's 12% lower production costs vs. non-integrated growers |
| Climate & Trade | Introduces supply volatility and market access challenges | 15% drop in U.S. pecan harvest (2023); ongoing trade tensions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for pecans is significant, primarily from other tree nuts such as walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts, cashews, and pistachios. These nuts are often seen as interchangeable, particularly in culinary applications like baking, snacking, and as general ingredients.
When pecan prices rise or availability becomes an issue, consumers and industrial buyers readily switch to these alternatives. For example, in 2024, almond prices saw a modest increase due to supply chain adjustments, potentially making pecans more competitive in certain segments, but the overall substitutability remains high.
The value proposition, encompassing price, quality, and availability, heavily influences these switching decisions. A noticeable price advantage for other nuts, or a perceived superior quality for a specific application, can easily divert demand away from pecans.
When pecan prices climb sharply, perhaps due to weather impacting harvests or new import duties, both individual consumers and commercial buyers will more readily switch to other nuts that are less expensive or easier to obtain. For instance, if tariffs increase the cost of U.S. pecans, businesses such as bakeries or snack manufacturers might shift towards almonds or walnuts, which become comparatively more attractive options. This price-driven substitution is a significant threat, especially when global supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events affect the availability and cost of pecans.
The growing popularity of plant-based diets presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional pecan products. While pecan milk is a niche offering, established alternatives like almond and oat milk have captured a substantial market share in the dairy alternative segment. For instance, the global plant-based milk market was valued at approximately USD 28.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer shift away from dairy and potentially towards other plant-based ingredients, including those that could directly compete with pecans in certain applications.
Versatility and Functionality of Substitutes
Many substitute nuts offer comparable nutritional benefits and can be used in similar culinary applications, posing a significant threat. Almonds, for example, are a major player in the nut market, widely adopted in baking, dairy alternatives, and snack products, directly competing with pecans.
The versatility of these substitutes is a key factor in their substitutability. For instance, in 2024, the global almond market was valued at approximately $15.7 billion, showcasing strong consumer demand and widespread availability. This broad appeal across various food categories allows substitutes to capture market share that might otherwise go to pecans.
- Almonds: Widely used in baking, dairy alternatives, and snacks.
- Walnuts: Offer a distinct flavor profile and are popular in baked goods and salads.
- Pistachios: Known for their unique taste and vibrant color, used in both sweet and savory dishes.
- Cashews: Creamy texture makes them ideal for dairy alternatives and sauces.
The ease with which consumers can switch to these alternatives, driven by factors like price, availability, and perceived health benefits, directly impacts the demand for pecans. This broad range of readily available substitutes means that any significant price increase or supply disruption for pecans could quickly drive consumers to competing nut products.
Consumer Preference for Flavor and Texture
While pecans offer a distinct buttery flavor and satisfying texture, particularly sought after in applications like pecan pie, their unique characteristics might not always deter substitution. For many everyday uses or when budget constraints are significant, consumers may opt for more economical alternatives.
The threat of substitutes is moderately high for pecans. While almonds, walnuts, and peanuts can offer some overlapping functionalities, they don't perfectly replicate the rich, buttery taste and tender bite that define pecans. For instance, in 2024, the average retail price for shelled pecans hovered around $10-$12 per pound, whereas walnuts were closer to $8-$10 per pound, and peanuts significantly lower.
- Flavor Profile: Pecans possess a unique buttery, slightly sweet flavor that is difficult for other nuts to fully replicate.
- Texture: Their tender, slightly crisp texture is a key differentiator, especially in baked goods.
- Price Sensitivity: In price-sensitive markets or for general snacking, consumers may substitute pecans with more affordable nuts like peanuts or walnuts.
- Application Specificity: Substitution is less likely in applications where the pecan flavor and texture are paramount, such as traditional pecan pie recipes.
The threat of substitutes for pecans remains a significant factor due to the wide availability and versatility of other tree nuts and seeds. While pecans offer a distinct flavor, many applications can utilize alternatives like almonds, walnuts, or even peanuts, especially when price is a primary consideration. For example, in 2024, the price differential between pecans and almonds persisted, with pecans often retailing at a premium, making almonds a more attractive option for many bakers and snack manufacturers seeking cost-efficiency.
The market for plant-based alternatives also presents a growing substitution threat. Products like almond milk and oat milk have captured substantial market share, and as consumer preferences shift towards plant-based options, ingredients that can serve similar functional roles in food products may gain traction, potentially impacting demand for pecans in certain sectors.
The ease of switching is further amplified by the comparable nutritional profiles of many substitute nuts. For instance, almonds and walnuts provide healthy fats and protein, mirroring some of the key benefits consumers seek from pecans, thereby reducing the perceived necessity of choosing pecans specifically.
| Nut Substitute | Typical Price Range (2024, per lb, shelled) | Key Applications Overlapping with Pecans |
|---|---|---|
| Almonds | $8 - $10 | Baking, Snacking, Dairy Alternatives |
| Walnuts | $8 - $10 | Baking, Salads, Snacking |
| Peanuts | $4 - $6 | Snacking, Baking (as ingredient) |
| Pistachios | $12 - $15 | Snacking, Desserts, Salads |
Entrants Threaten
The high capital investment required to establish a fully integrated pecan business, encompassing orchards and processing facilities, acts as a significant barrier to entry. This substantial upfront cost deters many potential new competitors from entering the market.
Pecan trees have a lengthy maturity period, typically taking 7 to 10 years before they yield significant crops. This extended timeline represents a considerable sunk cost and a delayed return on investment, further discouraging new entrants who may lack the financial fortitude for such a long-term commitment without immediate returns.
For example, the cost to plant and establish a new pecan orchard, including land preparation, irrigation systems, and sapling purchase, can easily run into tens of thousands of dollars per acre. This is before even considering the substantial investment needed for shelling, processing, and packaging infrastructure.
New entrants into the pecan industry would grapple with the formidable task of constructing reliable supply chains for raw pecans, a critical component for National Pecan. This involves securing consistent access to quality nuts from growers, often requiring long-term contracts and significant capital investment. Furthermore, establishing efficient distribution networks to serve diverse markets, from ingredient suppliers to retail shelves, presents a substantial barrier. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. pecan crop was projected to be around 300-350 million pounds, highlighting the scale of sourcing required.
Established companies like National Pecan Company leverage decades of experience in forging strong relationships with growers and logistics providers. This existing infrastructure, built over time, provides them with a competitive advantage in terms of reliability and cost-effectiveness. Newcomers would need to replicate this extensive network, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive, making it a significant deterrent to entry.
Large, integrated players like National Pecan Company leverage significant economies of scale across their operations, from cultivation to distribution. This integration allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, resulting in substantially lower per-unit production costs. For instance, major processors can negotiate better prices for inputs and optimize logistics, creating a cost barrier for newcomers.
These established cost advantages make it extremely challenging for new entrants to compete on price. Without the same production volume or existing infrastructure, a new pecan company would likely face higher per-unit expenses. To overcome this, new entrants would require substantial initial capital investment to achieve a competitive cost structure, making the threat of new entrants moderate.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Brand recognition and customer loyalty represent a significant barrier to entry in the pecan industry. Established companies have cultivated strong relationships with consumers over years, building trust in their quality and consistency. National Pecan Company, as part of Diamond Foods, LLC, benefits from this legacy, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly gain traction.
New entrants face the challenge of overcoming established brand equity. In 2023, the global snack nuts market, which includes pecans, was valued at approximately $75 billion, with brand reputation playing a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions. Companies like National Pecan have invested heavily in marketing and quality control, fostering loyalty that is hard to disrupt.
- Established Brand Presence: National Pecan, under Diamond Foods, LLC, benefits from decades of brand building.
- Customer Loyalty: Consumers often stick with familiar brands they trust for quality and taste.
- Market Share: Major players have significant market share, making it difficult for new entrants to gain immediate recognition.
- Marketing Investment: New companies would need substantial marketing budgets to compete with established brand awareness.
Regulatory Hurdles and Quality Standards
The pecan industry faces significant regulatory hurdles that deter new entrants. Navigating complex agricultural regulations, stringent food safety standards, and required quality certifications for global trade demands substantial investment and expertise. These compliance requirements, which can include everything from pesticide residue limits to packaging and labeling protocols, act as a formidable barrier.
For instance, the U.S. Pecan Shellers Association and similar international bodies often set specific quality benchmarks that new entrants must meet. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in rejected shipments and reputational damage, making the initial investment in compliance crucial. In 2024, the increasing focus on traceability and sustainability in food supply chains further amplifies these requirements, demanding robust systems from any aspiring player.
- Navigating Compliance: New entrants must allocate resources for understanding and meeting diverse international agricultural and food safety regulations.
- Cost of Certification: Obtaining necessary quality certifications (e.g., GlobalG.A.P.) involves fees, audits, and process adjustments, adding to startup costs.
- Market Access: Non-compliance with standards like those set by the USDA Agricultural Marketing Service can restrict access to key markets, particularly for processed pecan products.
- Evolving Standards: The dynamic nature of food safety regulations, influenced by consumer demand for transparency and health, necessitates continuous adaptation and investment by potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the pecan industry is moderate. High capital requirements for orchards and processing, coupled with the long maturation period of pecan trees, create significant financial barriers. Established players benefit from economies of scale and strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and market presence.
Regulatory compliance and the need to build robust supply chains and distribution networks also present substantial challenges. For example, the projected U.S. pecan crop for 2024, estimated between 300-350 million pounds, underscores the scale of operations required to be competitive.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Investment | High costs for land, trees, irrigation, and processing facilities. | Significant deterrent due to substantial upfront financial commitment. |
| Maturity Period | Pecan trees take 7-10 years to yield significant crops. | Creates a long delay in ROI, requiring sustained financial backing. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players have lower per-unit costs due to high volume. | New entrants struggle to match pricing due to higher initial costs. |
| Brand Loyalty & Marketing | Established brands enjoy consumer trust and recognition. | Newcomers need substantial marketing investment to build awareness. |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Need to secure grower contracts and efficient logistics networks. | Time-consuming and capital-intensive to replicate existing infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to food safety, agricultural, and quality standards. | Requires expertise and investment, adding to startup complexity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our National Pecan Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including USDA reports for production volumes, industry association surveys for market trends, and financial filings of major pecan companies for profitability insights.
We leverage market research reports from firms specializing in agricultural commodities, alongside government economic data and trade publications to gauge buyer power and the threat of new entrants in the pecan industry.
