Natera Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Natera Bundle
Understanding Natera's competitive landscape is crucial for strategic planning. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Natera’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Natera’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Natera’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Our full Porter's Five Forces report goes deeper—offering a data-driven framework to understand Natera's real business risks and market opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Natera relies on a limited number of specialized suppliers for essential laboratory instruments and critical chemical reagents. The genetic testing industry, including Natera, depends heavily on highly specialized inputs like next-generation sequencing machines and proprietary assay kits. This reliance on a concentrated supplier base for components, which represented a significant portion of Natera's cost of revenue in 2024, grants these suppliers substantial leverage in dictating pricing and contract terms. Securing these vital inputs remains a core operational challenge, impacting Natera's cost structure and supply chain stability.
Suppliers providing unique or patented technologies, like specific gene sequencing platforms, wield significant power over Natera. Natera and its rivals often depend on these advanced technologies to conduct their diagnostic tests. For instance, if a supplier owns critical patented sequencing chemistries, they can dictate pricing and contractual terms. This leverage is a defining characteristic within the competitive biotechnology and diagnostics sector, where intellectual property is paramount for test development and commercialization.
Switching to alternative suppliers for Natera's specialized laboratory equipment and reagents involves substantial costs and time. The validation of new instruments and processes is critical, requiring rigorous testing to meet stringent accuracy and regulatory standards, like those from CLIA and CAP. This extensive validation process, often taking months, locks Natera into its current supplier relationships, thereby enhancing the bargaining power of these key suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the investment in validating a new high-throughput sequencing platform could easily run into millions of dollars, encompassing equipment, training, and extensive quality control runs.
Supplier Consolidation
The market for essential genomic sequencing technologies, crucial for Natera, is heavily consolidated, with a few dominant players like Illumina holding significant control. This high supplier consolidation gives them considerable pricing power and control over the supply chain for Natera's core operations. Natera's dependence on these large suppliers, particularly for 2024 operations, exposes it to their strategic decisions and potential price increases for vital equipment and consumables.
- Illumina remains a primary supplier of sequencing platforms and reagents.
- Supplier concentration limits Natera's negotiation leverage.
- Potential for increased operational costs due to supplier pricing power.
Regulatory Requirements for Suppliers
Suppliers to Natera must meet stringent regulatory standards, such as ISO 13485 certification, for components used in clinical diagnostic tests. This significantly shrinks the pool of qualified suppliers, empowering those who have already achieved these crucial certifications. The rigorous validation processes required for medical device components further reduce Natera's flexibility in easily substituting suppliers, making compliant and validated materials essential.
- ISO 13485 compliance is a critical barrier to entry for new suppliers.
- The limited supplier base enhances the bargaining leverage of established, certified vendors.
- Natera's reliance on validated materials for its 2024 diagnostic pipeline restricts sourcing options.
Natera faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated base of specialized vendors for critical genomic sequencing equipment and reagents. High switching costs, including extensive 2024 validation processes for new instruments, further entrench these relationships. Key suppliers, often holding patented technologies and operating in a consolidated market, can dictate terms and pricing, directly impacting Natera's operational expenses and supply chain resilience.
| Supplier Power Factor | Impact on Natera (2024) | Level of Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Few dominant players (e.g., Illumina) control key inputs. | High |
| Switching Costs | Validation of new suppliers costs millions, takes months. | High |
| Proprietary Technology | Reliance on patented sequencing platforms. | High |
What is included in the product
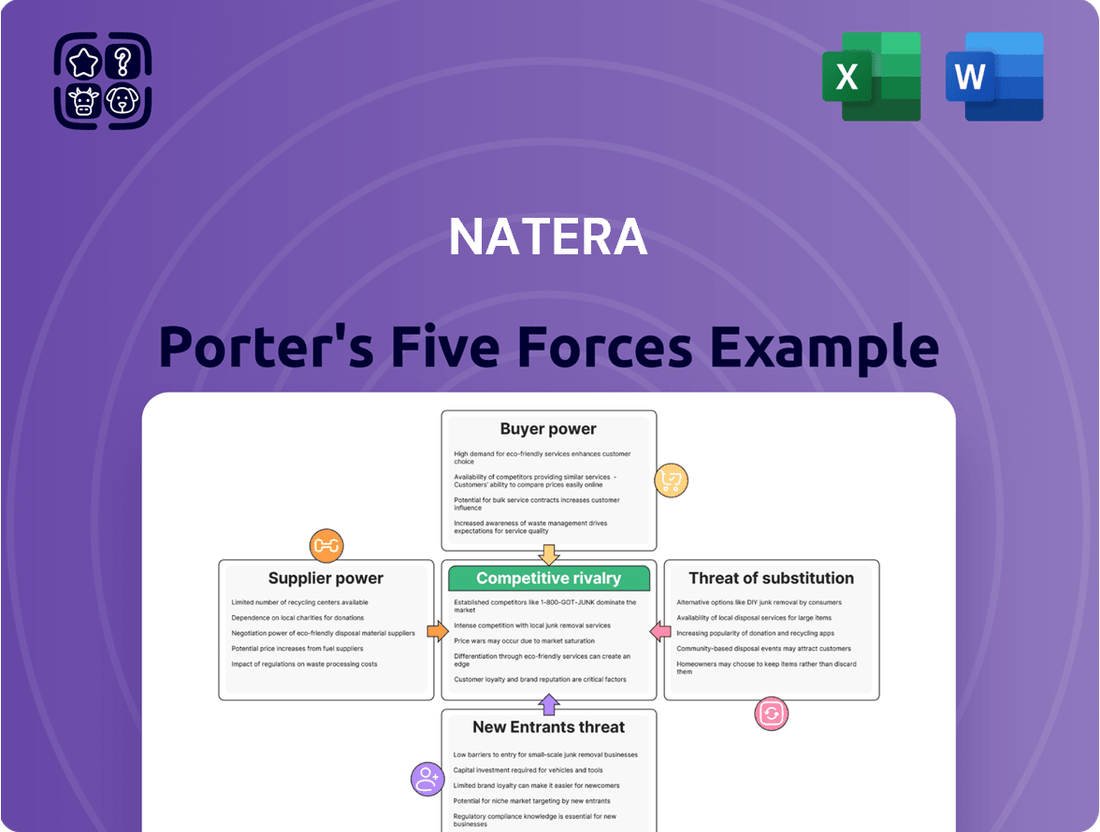
Natera's Porter's Five Forces Analysis examines the intensity of competition, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all specifically within the diagnostic testing and genetic screening market.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, simplifying complex market dynamics for faster strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
A significant portion of Natera's revenue depends on reimbursement from third-party payers like private insurance companies and government programs such as Medicare. These large institutional buyers, including major insurers, wield substantial power to negotiate reimbursement rates and coverage policies for Natera's diagnostic tests. For instance, in 2024, changes in Medicare's coverage for certain genetic tests could directly impact Natera's revenue streams. Such policy shifts can significantly affect Natera's financial performance and profitability.
Clinicians, hospitals, and extensive medical networks serve as Natera's primary customers, wielding substantial bargaining power. These organized buyers, including integrated delivery networks representing significant patient volumes, can negotiate volume discounts on Natera's genetic tests. Their influence extends to determining which tests become part of the standard of care, crucial for adoption and sustained test volume. For example, large networks often consolidate purchasing, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing for specialized diagnostic services like Natera's non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and oncology offerings, impacting revenue streams in 2024.
While many of Natera's tests are insurance-covered, patients paying out-of-pocket exhibit significant price sensitivity, especially for discretionary offerings like certain genetic screenings not yet standard of care. This sensitivity is heightened as information becomes more accessible, with patient advocacy groups increasingly empowering individuals to question the cost-effectiveness of tests. For instance, in 2024, patient co-pays and deductibles remain a notable concern, driving demand for transparent pricing and potentially lower-cost alternatives, impacting Natera's volume for non-mandated tests.
Low Switching Costs for Clinicians
For clinicians, the costs of switching between genetic testing providers are relatively low. They often have multiple options, like Quest Diagnostics or LabCorp, offering similar prenatal or oncology tests. This competitive landscape, with numerous labs vying for business, gives clinicians significant leverage. As of 2024, the market continues to see new entrants and evolving test offerings, intensifying competition on both price and service quality.
- The competitive genetic testing market includes companies like Natera, Invitae, and various hospital labs.
- Clinicians often evaluate providers based on factors such as turnaround time, test menu breadth, and reimbursement support.
- Ease of integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems can also influence provider choice, but this is often manageable across vendors.
- This flexibility means providers must continuously offer superior value to retain their clinical clients.
Increasing Patient Awareness and Choice
Increasing patient awareness empowers customers in the genetic testing market. Through direct-to-consumer marketing and accessible online resources, patients are becoming more educated about their options. This heightened awareness leads them to actively participate in decision-making, often requesting specific tests or questioning provider choices, which adds a layer of consumer-driven pressure on companies like Natera.
- The global direct-to-consumer genetic testing market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023.
- Patient engagement through digital health platforms increased by over 20% in 2024.
- Online searches for genetic testing options rose 15% year-over-year by mid-2024.
- Approximately 70% of patients research health options online before consulting a provider.
Customers, including powerful third-party payers and large medical networks, exert significant bargaining power over Natera by negotiating reimbursement rates and volume discounts. Clinicians face low switching costs between genetic testing providers, fostering intense competition on price and service quality. Patient price sensitivity, especially for out-of-pocket tests, combined with increasing digital awareness, further empowers consumers. These factors collectively pressure Natera's pricing and revenue streams, with patient engagement through digital platforms rising over 20% in 2024.
| Customer Segment | Key Influence | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Third-Party Payers | Reimbursement Rates, Coverage | Medicare policy shifts directly impact revenue. |
| Medical Networks | Volume Discounts, Test Adoption | Consolidated purchasing dictates pricing terms. |
| Clinicians/Patients | Switching Costs, Price Sensitivity | Demand for transparent pricing for non-mandated tests. |
What You See Is What You Get
Natera Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Natera Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the diagnostics industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that will be available to you instantly after purchase. It delves into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products for Natera. You're looking at the actual document, ensuring no surprises or placeholders, just the valuable strategic insights you need.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and oncology testing markets are intensely competitive, featuring large, established diagnostics companies and specialized biotech firms. In women's health, Natera faces strong rivals like Illumina, LabCorp, and Quest Diagnostics. For oncology, key competitors include Guardant Health and Exact Sciences. This intense rivalry, evident in 2024 market dynamics, drives continuous innovation in testing methodologies but simultaneously puts significant pressure on pricing strategies across the industry.
The Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) market is dominated by a few key players, including Natera, Illumina, and Roche, who have secured significant market shares. As of 2024, Natera holds a leading position, driven by its widely adopted Panorama test. This concentration of market power among a few firms fuels intense strategic maneuvering for competitive dominance and innovation within the NIPT space.
Competitive rivalry in the diagnostics sector is intense, driven by continuous technological innovation, superior test accuracy, and robust clinical data. Natera leverages its extensive validation, supported by over 250 peer-reviewed publications, to differentiate its offerings in areas like oncology and women's health. The ongoing race to publish supportive clinical data and develop more advanced, comprehensive tests, such as Natera's Prospera for transplant assessment and Signatera for cancer recurrence, is a central feature of the competitive landscape. This constant pursuit of enhanced diagnostic capabilities and clinical evidence defines market leadership as of 2024.
Aggressive Legal and Patent Strategies
The genetic testing industry, especially for Natera, is marked by intense competitive rivalry often manifesting as aggressive legal and patent strategies. Companies frequently engage in litigation over intellectual property and alleged patent infringement, with Natera actively defending its innovations and challenging competitors to solidify its market standing. For instance, in 2024, ongoing legal disputes related to non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) patents continue to incur significant legal expenditures across the sector. This litigious environment undeniably adds a substantial layer of operational risk and financial burden, impacting profitability margins.
- Natera's legal expenses often represent a notable portion of its SG&A, reflecting an industry-wide trend where patent defense and enforcement are critical competitive tools.
- The cost of patent litigation can reach millions of dollars per case, directly impacting companies' R&D budgets and market development.
- As of 2024, the genetic testing market sees continuous intellectual property disputes, particularly in high-growth segments like oncology and reproductive health.
- Successful patent defense or challenge can grant a company, like Natera, a significant competitive edge or protect its revenue streams from infringing products.
Expanding Test Menus and Market Segments
Competitive rivalry intensifies as Natera's peers consistently broaden their test menus, venturing deeper into women's health, oncology, and organ health. This includes expanding non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) to screen for more conditions, with competitors like Illumina and Exact Sciences actively developing new liquid biopsy applications. The push to offer a comprehensive suite of diagnostic tests heightens competition across all of Natera’s key markets in 2024.
- Competitors continually expand NIPT panels, impacting Natera's market share in prenatal screening.
- Rivals are aggressively pursuing new liquid biopsy applications for early cancer detection and treatment monitoring.
- The drive for comprehensive diagnostic portfolios pushes innovation, increasing competitive pressure on Natera's product development.
- Market entries into organ health by competitors diversify their revenue streams and challenge Natera’s focus areas.
The diagnostics sector, particularly for Natera, faces intense competitive rivalry from established players and biotech firms. This rivalry, evident in 2024, drives continuous innovation in testing and aggressive patent litigation, impacting profitability. Competitors consistently broaden their test menus, including NIPT and liquid biopsy applications, increasing pressure across all of Natera’s key markets.
| Market | Key Rivals | 2024 Trend |
|---|---|---|
| NIPT | Illumina, Roche | Intense market share battles |
| Oncology | Guardant Health, Exact Sciences | Aggressive liquid biopsy expansion |
| IP Litigation | Various | High legal expenses, defense focus |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional prenatal screening methods, like maternal serum screening and ultrasound, remain a significant substitute for Natera's NIPT. These established tests, while generally less accurate for chromosomal abnormalities, are considerably less expensive, often costing under $200 in 2024 compared to NIPT prices that can exceed $800. For patients with specific risk profiles or in certain clinical scenarios, their lower cost and widespread availability make them a preferred initial approach. This represents a robust, lower-cost alternative, impacting NIPT adoption rates.
Invasive procedures like amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS) present a significant substitute threat to Natera's non-invasive screening tests. While Natera's tests provide risk assessments, these invasive methods offer definitive chromosomal diagnoses, crucial for high-risk pregnancies, despite a reported miscarriage risk of around 0.1% for amniocentesis in 2024. For patients with concerning screening results, these diagnostic procedures are often the necessary next step in the clinical pathway, directly competing with the need for further non-invasive analysis. This definitive diagnostic capability makes them a strong substitute, particularly when precision is paramount over risk avoidance.
Alternative cancer diagnostics pose a notable threat to Natera's Signatera, as traditional tissue biopsies remain the gold standard for initial diagnosis and tumor characterization, with millions performed globally in 2024. Imaging techniques, such as CT scans and MRIs, are also widely utilized for staging and monitoring, representing a market valued over $40 billion in 2023. While liquid biopsies offer non-invasive monitoring, established methods are still the primary standard of care in many clinical guidelines. The choice of diagnostic tool ultimately hinges on the specific cancer type, its stage, and the clinical objective.
Different Technological Platforms for Genetic Analysis
Natera faces a significant threat from substitute molecular diagnostic technologies. Other methods of DNA analysis, like microarrays or PCR-based tests, can detect genetic abnormalities, serving as direct alternatives to Natera's specific platforms. The rapid evolution in diagnostic technology means that new, potentially more efficient substitute platforms are constantly emerging, impacting market dynamics in 2024.
- The global molecular diagnostics market is projected to reach $37.5 billion by 2024, indicating a vast landscape of competing technologies.
- Alternative platforms include array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) and various quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays.
- Emerging technologies, such as advanced CRISPR-based diagnostics, could offer faster or more cost-effective genetic analysis.
- Natera's reliance on specific sequencing methods could be challenged by these diverse and evolving diagnostic tools.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Genetic Tests
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) genetic tests, such as those from 23andMe and AncestryDNA, are emerging as substitute products by raising consumer awareness of genetic information. While not clinical diagnostics, these tests offer health-related insights, potentially diverting some consumers seeking general genetic data from the clinical testing market. The global DTC genetic testing market was valued at approximately 2.5 billion in 2024, indicating a growing alternative for consumers exploring their genetic makeup without clinical necessity.
- 23andMe reported approximately 14.5 million customers by early 2024.
- AncestryDNA has accumulated over 23 million customers as of 2024.
- The DTC genetic testing market is projected to grow significantly through 2025.
- These tests increase general public engagement with genetic information.
Natera faces significant substitute threats across its diagnostic portfolio. Traditional prenatal screenings, costing under $200 in 2024, and invasive procedures offer cheaper or definitive alternatives to NIPT. For oncology, standard tissue biopsies and imaging, alongside a diverse $37.5 billion molecular diagnostics market in 2024, compete with Signatera. Even direct-to-consumer genetic tests, like 23andMe with 14.5 million customers, subtly impact market dynamics.
| Substitute Type | Key Examples | 2024 Impact Data |
|---|---|---|
| Prenatal Screening | Maternal serum, Ultrasound | Costs under $200 |
| Invasive Diagnostics | Amniocentesis, CVS | Miscarriage risk ~0.1% |
| Molecular Diagnostics | aCGH, qPCR, CRISPR | Market projected $37.5B |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a CLIA-certified and CAP-accredited laboratory for advanced genetic testing, like Natera's, requires significant upfront capital investment in infrastructure and specialized equipment. Beyond initial setup, the ongoing commitment to research and development for new test validation is immense. For instance, Natera's Q1 2024 R&D expenses reached $135.2 million. These substantial financial barriers make it exceptionally difficult for new companies to enter the market at scale. This high cost of entry limits the threat from new competitors.
New entrants into the genetic testing market, like Natera's, face formidable regulatory hurdles. The industry is heavily scrutinized by bodies such as the FDA and CMS under CLIA, with evolving rules for laboratory-developed tests (LDTs) posing a significant challenge. For instance, the VALID Act, if enacted in 2024, could introduce more stringent FDA premarket review requirements for LDTs, escalating the compliance burden. New companies must navigate these complex pathways, incurring substantial upfront compliance costs and needing specialized legal and scientific expertise, which can easily reach millions of dollars annually for a comprehensive regulatory framework.
Incumbent companies like Natera benefit from deeply established relationships with major insurance payers and healthcare providers. As of 2024, Natera’s Panorama non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) achieved over 90% coverage for insured lives in the United States, showcasing extensive payer integration. Securing these crucial reimbursement contracts with large insurers and integrating into the complex workflows of major hospital systems presents a formidable barrier for new companies. Without such pre-existing networks and trust, a new entrant faces immense difficulty competing effectively in the diagnostic testing market.
Strong Brand Recognition and Intellectual Property
The threat of new entrants for Natera is significantly mitigated by strong brand recognition and intellectual property. Leading companies like Natera have cultivated deep trust among clinicians and patients through years of reliable performance and extensive marketing efforts. Natera, for example, reported a 28% year-over-year revenue growth in Q1 2024, underscoring its established market presence. Additionally, existing players hold vast patent portfolios protecting their proprietary technologies and test methodologies, making it extremely difficult for newcomers to compete without infringing on these rights.
- Natera's established brand equity creates high customer loyalty.
- The company possesses a robust intellectual property portfolio, including over 400 issued and pending patents as of early 2024.
- Significant R&D investments by incumbents raise the financial barrier for new entrants.
- Regulatory hurdles and clinical validation costs further deter new market participants.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established diagnostic laboratories, like Quest Diagnostics and LabCorp, leverage significant economies of scale, processing a vast volume of tests at a substantially lower cost per unit. Their extensive operational history also grants them an experience curve advantage, having optimized complex laboratory and logistical processes over decades. New entrants into the genetic testing market, including those competing with Natera, face a considerable cost disadvantage, as achieving comparable scale and efficiency requires substantial initial investment and time. This barrier is further reinforced by the high capital expenditure needed for advanced genetic sequencing equipment, which can exceed $1 million per machine, making it difficult for smaller players to compete on price in 2024.
- Large labs handle over 1 billion tests annually, driving down per-test costs.
- Operational efficiencies from experience reduce processing times and error rates.
- New entrants face initial capital outlays for equipment, often exceeding $1 million.
- Achieving competitive cost structures can take years, hindering market penetration.
The threat of new entrants for Natera is low due to the immense capital needed for CLIA/CAP labs and R&D, with Natera's Q1 2024 R&D reaching $135.2 million. Significant regulatory hurdles, including potential 2024 VALID Act changes, and high compliance costs deter new companies. Natera's established payer relationships, like over 90% US coverage for Panorama in 2024, and strong brand recognition create formidable market entry barriers. Additionally, incumbent intellectual property, such as Natera's 400+ patents, and economies of scale further limit new competition.
| Factor | Description | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High R&D and infrastructure costs | Natera Q1 2024 R&D: $135.2 million |
| Regulatory Burden | Complex compliance requirements | VALID Act (potential 2024 impact) |
| Market Access | Established payer and provider networks | Natera Panorama US coverage: >90% |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios | Natera patents: >400 (issued/pending) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Natera Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Natera's own investor relations disclosures, SEC filings, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and analyses from reputable financial institutions to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
