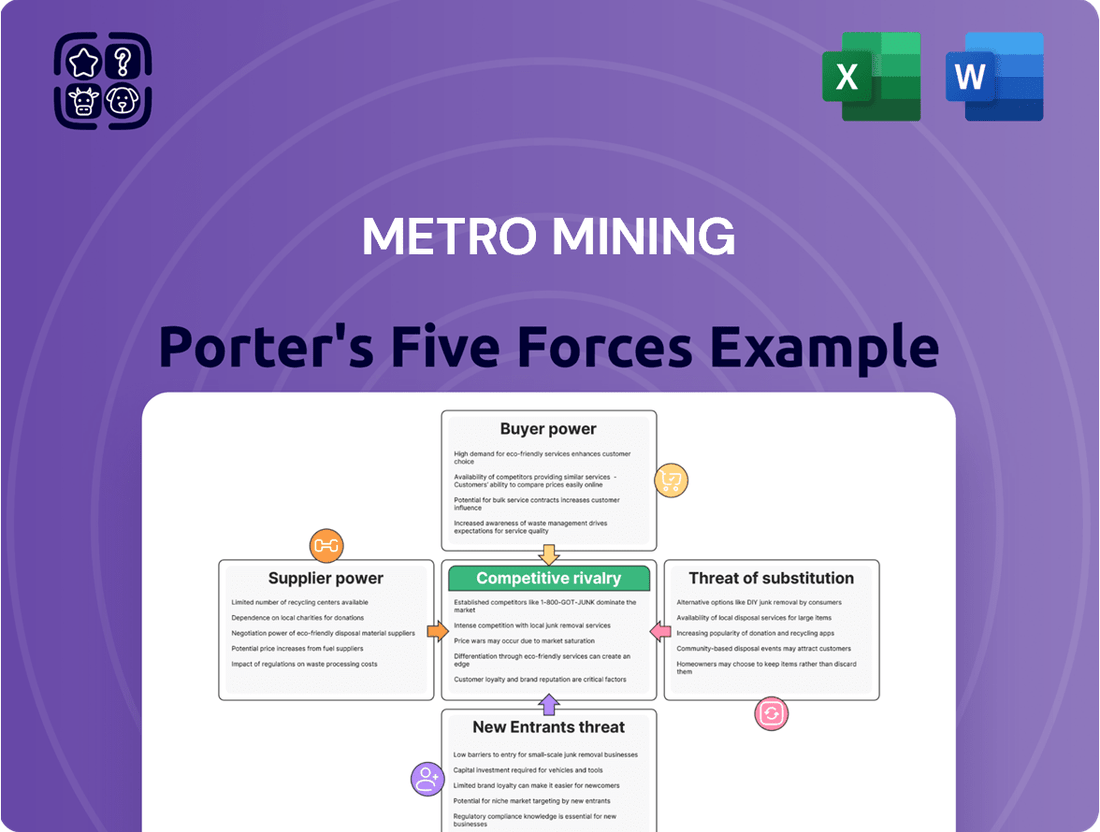
Metro Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Metro Mining Bundle
Metro Mining faces a complex competitive landscape, with significant pressure from buyers and a moderate threat from new entrants. The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration, influencing production costs and profitability. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the mining sector.
The threat of substitute products, while currently low, could evolve with technological advancements. Intense rivalry among existing players further shapes Metro Mining's strategic options. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Metro Mining’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Metro Mining's bargaining power. For specialized inputs crucial to bauxite extraction, such as advanced drilling equipment or proprietary chemical reagents, a limited number of suppliers means those suppliers hold considerable sway. For instance, in 2024, the global market for high-performance mining excavators, essential for bauxite operations, is dominated by a handful of manufacturers, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing.
Switching costs for Metro Mining can range dramatically depending on the supplier's product or service. For instance, replacing specialized mining equipment or mission-critical software can incur substantial expenses. These might include significant costs for new training programs for employees, extensive reconfigurations of existing operational systems, and potential downtime during the transition period.
Conversely, for more basic or commoditized inputs, such as standard raw materials or office supplies, the costs associated with switching suppliers are typically quite low. This low switching cost for these items means Metro Mining can readily move to a different provider if a better deal or quality is found, thereby diminishing the bargaining power of suppliers in these segments.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for Metro Mining. If a supplier provides proprietary technology or a highly specialized service essential for efficient bauxite extraction and processing, their leverage increases substantially. For instance, if a key piece of mining equipment is only available from a single manufacturer, that manufacturer can command higher prices.
Conversely, when inputs are standardized and readily available from numerous suppliers, Metro Mining's bargaining power strengthens. In 2024, the global supply of common mining consumables like lubricants and basic steel components remained robust, with many competitive providers, thus limiting the pricing power of individual suppliers in these categories.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into bauxite mining for Metro Mining is notably low. Establishing and operating a bauxite mine demands an astronomical capital outlay, often in the billions of dollars, far beyond the typical resources of most raw material suppliers. For instance, the initial capital expenditure for a new large-scale bauxite mine in Australia can easily exceed $2 billion, according to industry reports from early 2024.
Furthermore, bauxite mining requires highly specialized geological expertise, advanced extraction technologies, and a deep understanding of environmental regulations. These are significant barriers to entry that most suppliers in the value chain, such as those providing processing chemicals or transportation services, do not possess. This lack of capability limits their ability to directly compete with Metro Mining in its core business, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
- Immense Capital Requirements: Developing a bauxite mine necessitates billions in upfront investment, a scale rarely achievable by suppliers.
- Specialized Expertise Gap: Mining operations demand unique geological and engineering skills that most suppliers lack.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex mining permits and environmental compliance is a significant barrier for potential forward integrators.
- Limited Supplier Capability: The specialized nature of mining restricts suppliers to their existing roles, weakening their leverage over Metro Mining.
Importance of Metro Mining to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers to Metro Mining is influenced by the proportion of Metro Mining's business each supplier represents. If Metro Mining constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier's leverage is diminished. For example, if a key equipment manufacturer relies heavily on Metro Mining for a significant percentage of its sales, they will be more inclined to offer favorable terms to maintain that crucial business relationship.
Conversely, Metro Mining's bargaining power weakens when it is a small customer for a large, diversified supplier. In such scenarios, the supplier has less incentive to concede on pricing or terms, as Metro Mining's business is not critical to their overall financial health. This dynamic is common with suppliers of specialized mining equipment or bulk commodity inputs where Metro Mining may be one of many clients.
- Supplier Dependence: Metro Mining's importance as a customer directly impacts supplier leverage.
- Client Size Matters: A large, diversified supplier can exert more power over a smaller client like Metro Mining.
- Revenue Share: If Metro Mining accounts for a significant percentage of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power is reduced.
- Market Concentration: The availability of alternative suppliers for critical inputs also shapes this power dynamic.
Metro Mining faces moderate supplier bargaining power, primarily driven by the concentration of suppliers for specialized inputs. When inputs are unique or critical, like advanced drilling technology, a few dominant suppliers can dictate terms. However, for commoditized inputs such as standard lubricants, numerous suppliers offer competitive pricing, thus reducing their leverage.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is minimal due to the immense capital and specialized expertise required for bauxite mining. For instance, establishing a new bauxite mine in 2024 can cost upwards of $2 billion, a barrier most suppliers cannot overcome. This significantly limits their ability to compete directly with Metro Mining.
| Factor | Impact on Metro Mining | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High for specialized inputs, low for commoditized ones | Few manufacturers dominate the high-performance mining excavator market. |
| Switching Costs | High for specialized equipment, low for basic supplies | Replacing proprietary software involves significant training and system reconfiguration costs. |
| Input Uniqueness | High leverage for unique, essential inputs | Single-source proprietary technology for extraction can command premium pricing. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Very Low | Capital expenditure for a new bauxite mine can exceed $2 billion. |
| Customer Dependence | Supplier power reduced if Metro Mining is a key client | A supplier heavily reliant on Metro Mining for revenue will offer more favorable terms. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the mining sector, focusing on Metro Mining's specific industry dynamics and strategic positioning.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual breakdown of industry forces, empowering strategic action.
Customers Bargaining Power
Metro Mining's customer base is heavily concentrated, primarily serving large global alumina refineries and aluminum producers such as Chalco and Emirates Global Aluminium (EGA). This consolidation among buyers means they often purchase significant volumes, which inherently grants them greater leverage in price negotiations and contract terms.
The fact that Metro Mining has secured multi-cargo contracts with these major players for 2025 underscores the importance of these key customer relationships. Such agreements highlight the substantial volume commitment from these concentrated buyers, further amplifying their bargaining power within the industry.
Individual customers in the aluminum industry frequently purchase bauxite in substantial quantities. This high-volume purchasing power significantly enhances their importance and leverage, enabling them to negotiate better terms, such as pricing and delivery timelines.
Metro Mining's projected shipments of 6.5 to 7 million wet metric tonnes for 2025 highlight the considerable scale of demand from their customer base. Such large orders give these buyers considerable sway in their dealings with suppliers like Metro Mining.
The bargaining power of customers within the mining sector, particularly for bauxite, is influenced by relatively low switching costs for alumina refineries. Because bauxite is largely a commodity, refineries can often find alternative suppliers without significant disruption or investment. This commodity nature means that for many refineries, the cost and complexity of changing bauxite sources are minimal, empowering them to negotiate more aggressively on price.
Threat of Backward Integration
Large aluminum producers, a key customer segment for bauxite suppliers like Metro Mining, possess a significant threat of backward integration. This means they can potentially start their own mining operations if they deem it more cost-effective or strategically advantageous. For example, major aluminum giants often have direct ownership or strong alliances with bauxite mines, giving them the leverage to bypass external suppliers.
This capability directly enhances customer bargaining power. If the terms of bauxite supply from companies like Metro Mining become unfavorable, these large customers can simply choose to produce their own bauxite. This ability to self-supply acts as a powerful check on pricing and contract terms for bauxite producers.
Consider Rio Tinto, a significant player in the aluminum value chain, which operates substantial bauxite mines in Australia. This operational presence exemplifies the credible threat of backward integration within the industry, directly impacting the bargaining power of its customers by offering an alternative source of supply.
- Bauxite Supply Control: Aluminum producers can exert greater control over bauxite supply by integrating backward.
- Cost Management: Backward integration can lead to cost savings for aluminum producers by internalizing extraction costs.
- Market Influence: The ability to mine bauxite enhances the market influence of large aluminum companies.
Price Sensitivity and Product Differentiation
Bauxite, the primary raw material for Metro Mining, is largely a commoditized product. This means that the quality among different suppliers is fairly consistent, making it difficult for Metro Mining to differentiate its offering based on product features. Consequently, buyers of bauxite tend to be highly sensitive to price, as they can often switch between suppliers with minimal disruption.
This lack of differentiation and strong price sensitivity directly translates into significant bargaining power for Metro Mining's customers. Buyers are primarily focused on securing bauxite at the lowest possible cost while ensuring a reliable and consistent supply chain. This focus gives them considerable leverage when negotiating terms with Metro Mining, as Metro Mining relies on these large-scale purchases for its revenue.
- Price Sensitivity: Bauxite buyers are highly focused on cost, often comparing prices across multiple suppliers.
- Lack of Differentiation: The standardized nature of bauxite limits Metro Mining's ability to command premium pricing.
- Buyer Leverage: Customers can exert significant pressure on Metro Mining due to the availability of alternative suppliers.
- Supply Chain Importance: Consistent and reliable bauxite supply is critical for downstream industries, reinforcing buyer power.
Metro Mining's customers, primarily large alumina refineries and aluminum producers, wield significant bargaining power due to the commoditized nature of bauxite and their substantial purchasing volumes. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, as alternative suppliers are readily available with minimal switching costs.
The concentrated nature of Metro Mining's customer base, including entities like Chalco and Emirates Global Aluminium (EGA), further amplifies buyer leverage. These major players often secure multi-cargo contracts, such as those for 2025, committing to large volumes that give them considerable sway in negotiations.
Furthermore, the threat of backward integration, where large aluminum producers could potentially develop their own bauxite mining operations, acts as a potent check on Metro Mining's pricing power. Companies like Rio Tinto, with existing bauxite mining assets, exemplify this capability.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Metro Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Large Refineries/Producers (e.g., Chalco, EGA) | High volume purchases, commodity nature of bauxite, threat of backward integration | Strong price negotiation, demand for favorable contract terms |
| Overall Bauxite Market | Low switching costs for buyers, price sensitivity due to standardization | Limited ability to differentiate pricing, reliance on competitive cost structures |
Full Version Awaits
Metro Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use Metro Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape. What you're previewing is precisely the same professionally formatted document that will be available to you instantly after purchase. This analysis thoroughly examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the Metro Mining industry. You'll receive this exact, comprehensive strategic tool for immediate application.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global bauxite market is characterized by the presence of a few very large, established players such as Rio Tinto and Alcoa, alongside a more fragmented landscape of smaller, regional producers. This concentration of significant global entities means that any company, including Metro Mining, faces a highly competitive environment. For instance, in 2024, these major players continue to dominate production and pricing, making market entry and expansion challenging for smaller entities.
Metro Mining, while a notable player within Australia, must contend with these global giants, intensifying the competitive rivalry. The sheer scale and established market share of companies like Rio Tinto and Alcoa provide them with significant advantages in terms of cost, logistics, and access to capital. This makes the global bauxite market a space where competition is not just about resource extraction but also about operational efficiency and market influence.
Key bauxite-producing nations such as Guinea, Australia, and China further shape the competitive dynamics. Guinea, for example, holds a substantial portion of the world's bauxite reserves, and its production levels directly impact global supply and, consequently, competition. Australia, with its advanced mining infrastructure, also plays a crucial role. Understanding the production capacity and strategies of these major producing countries is vital for assessing the competitive landscape.
The global bauxite market is showing robust expansion, with consumption anticipated to reach 449 million tons in 2024. This steady growth is a key factor influencing competitive dynamics within the industry.
While a growing market generally moderates intense rivalry, the sheer size of the bauxite sector means competition for market share remains a significant challenge. Companies are vying for dominance in a market that's expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 2.66% between 2025 and 2033.
Bauxite, the primary ore for aluminum production, is largely considered a commodity. This means there's very little to distinguish one supplier's bauxite from another's, beyond basic quality metrics like its alumina content or the level of reactive silica. For example, in 2024, the global average grade of bauxite typically ranges from 45% to 60% alumina, with lower silica content being more desirable.
Because bauxite is so similar across different mines, competition often boils down to price. Buyers, such as aluminum smelters, can easily switch their sourcing from one producer to another if there's a better deal available. This dynamic puts significant pressure on Metro Mining to maintain cost-efficient operations to remain competitive in the market.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the mining sector, like those faced by Metro Mining, are exceptionally high. Companies are often locked into operations due to immense capital sunk into mine development, specialized equipment, and extensive infrastructure. For instance, a new underground mine can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars to establish, making a swift exit financially unviable.
These substantial fixed costs, coupled with long-term supply contracts and significant environmental rehabilitation obligations post-closure, create a strong disincentive to exit. These rehabilitation costs can run into tens of millions, depending on the scale and nature of the mining operation. Consequently, mining firms may persist in operations even when profitability dips, leading to a more intense competitive environment as they strive to recover their initial investments.
The reality of high exit barriers means that:
- Companies remain in operation longer, potentially extending competitive pressure.
- Capital tied up in mines is difficult to recoup, discouraging new entrants who consider the potential for stranded assets.
- Environmental bond requirements, which can be substantial (e.g., millions of dollars per site), add to the financial burden of exiting.
- The necessity to fulfill existing long-term contracts can force continued production, even in unfavorable market conditions.
Cost Structure of Competitors
Competitors with lower operating costs, often stemming from larger scale, superior ore grades, or streamlined logistics, possess a distinct advantage in navigating price volatility. For instance, in 2023, major diversified miners like BHP and Rio Tinto reported all-in sustaining costs (AISCs) for iron ore significantly below the industry average, allowing them greater flexibility during market downturns. This cost advantage enables them to absorb price dips more effectively than Metro Mining, potentially leading to market share gains if Metro Mining's cost structure is less competitive.
Metro Mining's strategic emphasis on cost leadership is a crucial countermeasure. By securing long-term contracts for essential inputs and investing in infrastructure upgrades, such as port facilities and haulage systems, the company aims to build a cost base that can rival or surpass its peers. These initiatives are designed to reduce per-unit production costs, thereby enhancing Metro Mining's resilience against competitive pricing pressures and improving its overall market standing.
- Scale Advantages: Larger competitors often benefit from economies of scale in mining operations, processing, and transportation, leading to lower per-unit costs.
- Resource Quality: Access to higher-grade mineral reserves can significantly reduce processing costs and increase the efficiency of extraction.
- Logistical Efficiency: Optimized supply chains, including proximity to ports and efficient rail or truck networks, directly impact transportation expenses.
- Technological Adoption: Investment in advanced mining technology and automation can drive down labor and operational costs over the long term.
Competitive rivalry in the bauxite market, where Metro Mining operates, is intense due to the presence of global giants like Rio Tinto and Alcoa. These established players, with their vast scale and market share, present significant advantages in cost and capital access. For instance, in 2024, these major entities continue to dictate production and pricing, creating substantial hurdles for smaller companies aiming to expand.
Bauxite's commodity nature means competition largely centers on price, as buyers can easily switch suppliers. This price sensitivity, coupled with high exit barriers in mining due to massive sunk capital, compels companies to maintain operations even during downturns, further intensifying rivalry. Metro Mining must therefore focus on cost efficiency to remain competitive against larger, more established players.
Key factors influencing competitive rivalry include scale advantages, resource quality, logistical efficiency, and technological adoption. Companies with lower operating costs, often a result of these factors, are better positioned to weather price volatility. For example, in 2023, diversified miners reported significantly lower all-in sustaining costs, granting them greater market flexibility.
The global bauxite market's growth, projected to reach 449 million tons in 2024, moderates extreme rivalry but the sheer size of the sector ensures continued competition for market share, with an expected compound annual growth rate of 2.66% between 2025 and 2033.
SSubstitutes Threaten
While bauxite remains the primary source for alumina, the threat of substitutes is present. Researchers are exploring alternative aluminum-containing minerals like nepheline syenite, kaolin clay, and alunite. However, as of recent analyses, these alternatives are not yet economically competitive for commercial-scale alumina production.
Aluminum faces significant competition from substitutes like steel, plastics, and composites across key sectors such as automotive, construction, and packaging. For instance, in the automotive industry, while aluminum's lightweight properties are advantageous, steel remains a cost-effective alternative, especially in traditional vehicle designs. In 2024, the automotive sector’s continued reliance on steel for certain components, despite the push for lighter materials, underscores this competitive pressure.
However, the burgeoning demand for lightweight materials, particularly driven by the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, presents a counteracting force that benefits aluminum. EVs prioritize weight reduction to enhance battery range and efficiency. Global EV sales in 2024 are projected to exceed 15 million units, a substantial increase that directly fuels the demand for aluminum in vehicle bodies and battery enclosures, mitigating some of the threat from other materials.
The price-performance trade-off for substitutes often leans towards aluminum, particularly when considering its inherent properties. Aluminum offers a compelling blend of being lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and a good conductor, making it ideal for many demanding applications.
While certain alternatives might present a lower upfront cost, they frequently fall short when it comes to the overall performance package that aluminum provides. This is especially true in sectors requiring high-end capabilities.
For instance, in the automotive sector, while steel might be cheaper, the weight savings offered by aluminum contribute to improved fuel efficiency, a critical factor for consumers. In 2024, the average fuel economy standards in the US are pushing manufacturers to explore lighter materials, further enhancing aluminum's value proposition.
Similarly, in the construction industry, despite higher initial costs for some composite materials, aluminum's durability and low maintenance requirements can lead to a lower total cost of ownership over the lifespan of a building.
Switching Costs for End-Users
Switching costs for end-users can indeed be a substantial barrier for substitute materials trying to displace aluminum. Industries often face considerable expense and operational disruption when shifting away from established materials. These costs can involve significant investments in re-tooling manufacturing processes, which might require new machinery or modifications to existing lines. For instance, an automotive manufacturer accustomed to aluminum stamping might need entirely new press equipment to work with a different material like advanced composites.
Beyond manufacturing, product redesign is frequently necessary. This includes re-evaluating structural integrity, assembly methods, and even aesthetic considerations. Think about the aerospace industry, where the certification of materials is an incredibly rigorous and time-consuming process, often taking years and costing millions. This complexity naturally slows down the adoption of any new material, making it difficult for substitutes to gain rapid widespread traction against aluminum, which has decades of proven performance and established supply chains.
The economic impact of these switching costs is considerable. For example, in the packaging sector, a shift from aluminum cans to alternatives like glass or plastic could mean investing millions in new filling and sealing equipment, as well as redesigning packaging lines. In 2024, the global beverage can market, a major consumer of aluminum, is valued in the tens of billions of dollars, highlighting the scale of investment tied to current aluminum usage.
- Re-tooling Costs: Significant capital expenditure for new or modified manufacturing equipment.
- Product Redesign: Engineering effort and testing required to adapt existing products to new materials.
- Material Certification: Lengthy and expensive processes to gain approval for new materials in regulated industries.
- Supply Chain Adjustments: Establishing new supplier relationships and logistics for alternative materials.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Ongoing research and development in materials science is a significant factor that could introduce more viable and cost-effective substitutes for traditional mining products in the future. Innovations in areas like advanced composites or novel metal alloys might present a long-term competitive threat, although the immediate risk from non-bauxite sources for alumina production appears relatively contained for now.
Consider the advancements in lightweight materials, for instance. While aluminum remains a dominant material in many applications, the increasing sophistication of carbon fiber composites and high-strength plastics could gradually erode its market share in sectors like automotive and aerospace. For example, the automotive industry's push for fuel efficiency continues to drive the adoption of lighter materials; by 2024, the global automotive lightweight materials market was valued at over $200 billion, with composites playing an increasingly important role.
The threat of substitutes is not static. As technology progresses, what might be an uneconomical or inferior substitute today could become a formidable competitor tomorrow. For Metro Mining, this necessitates continuous monitoring of emerging material technologies and their potential applications, as well as investing in research and development to stay ahead of potential disruptions.
- Materials Science R&D: Continuous innovation could yield cheaper, more effective substitutes.
- Emerging Technologies: Advanced composites and new metal alloys pose a potential long-term threat.
- Current Threat Level: The immediate threat from non-bauxite sources for alumina remains low.
- Market Adaptability: Metro Mining must monitor and adapt to new material developments to mitigate future risks.
While bauxite is the primary source for alumina, research into alternatives like nepheline syenite, kaolin clay, and alunite continues, though these are not yet economically viable for large-scale production.
Aluminum faces competition from steel, plastics, and composites in sectors like automotive and construction, with steel remaining a cost-effective choice for certain automotive components in 2024, despite the drive for lighter materials.
The growing demand for lightweight materials, especially for electric vehicles (projected to exceed 15 million units sold globally in 2024), boosts aluminum's appeal for car bodies and battery enclosures, counteracting some substitution threats.
| Material | Key Sectors | Substitute Threat Level for Aluminum (2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive, Construction | Moderate | Cost-effective, but heavier than aluminum. |
| Plastics | Packaging, Automotive | Moderate | Lower cost, but can lack strength and thermal properties. |
| Composites (e.g., Carbon Fiber) | Aerospace, Automotive | Low to Moderate | High performance, but significantly higher cost and complex manufacturing. |
| Alternative Alumina Sources (Nepheline Syenite, etc.) | Alumina Production | Low | Not currently economically competitive for commercial scale. |
Entrants Threaten
The bauxite mining sector demands substantial upfront capital for exploration, mine establishment, and processing infrastructure. For instance, developing a new open-pit bauxite mine can easily cost hundreds of millions, even billions, of dollars, making it a formidable barrier for potential new players aiming to compete with established entities like Metro Mining.
Established mining giants like Metro Mining leverage massive economies of scale, significantly driving down their per-unit production, processing, and logistics costs. For instance, in 2024, major diversified mining companies often operated with capital expenditures in the billions, enabling them to secure bulk discounts on raw materials and optimize their supply chains.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the existing infrastructure and high-volume output that Metro Mining commands, a new competitor would find it exceedingly difficult to compete on price, as their initial operational costs per ton would be considerably higher.
This cost disadvantage for newcomers is a direct consequence of the established players’ ability to spread fixed costs over a much larger production base. For example, the development of a new, large-scale mine can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, a barrier that deters many potential entrants who cannot immediately achieve the necessary scale.
The threat of new entrants in the bauxite mining sector, particularly concerning access to raw materials and reserves, is significantly mitigated by established players like Metro Mining. Securing access to high-quality, economically viable bauxite reserves is a substantial hurdle. These reserves are often already controlled by major mining corporations or necessitate navigating intricate government approvals and land access agreements. Metro Mining's strategic advantage lies in its existing, well-developed Bauxite Hills Mine reserves, providing a solid foundation for its operations.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations present a substantial threat to new entrants in the mining sector, particularly in Australia. The industry operates under a rigorous web of rules, demanding comprehensive permits, stringent environmental impact assessments, and unwavering compliance with safety and social license requirements. For instance, as of 2024, the Australian government continues to refine its environmental protection legislation, making the approval process for new mining projects increasingly demanding and time-consuming. This complexity acts as a significant deterrent, requiring new companies to invest heavily in legal and compliance expertise before even breaking ground.
The financial burden associated with meeting these regulatory hurdles is considerable. New entrants must allocate significant capital towards securing necessary approvals and ensuring adherence to evolving standards, which can easily run into millions of dollars. This financial commitment, coupled with the lengthy timelines often involved in regulatory processes, creates a high barrier to entry.
- Permitting and Licensing: New mining operations require numerous federal, state, and local permits, often involving extensive environmental impact statements and community consultations.
- Environmental Standards: Adherence to strict environmental protection laws, including waste management, water usage, and rehabilitation obligations, adds significant operational costs and complexity.
- Safety Regulations: Compliance with rigorous mine safety legislation, such as the Work Health and Safety Act, necessitates substantial investment in training, equipment, and safety management systems.
- Social Responsibility: Growing expectations around Indigenous engagement, local employment, and community benefit sharing mean new entrants must develop robust social performance strategies.
Access to Distribution Channels and Offtake Agreements
Securing reliable distribution channels and long-term offtake agreements is a significant hurdle for new bauxite producers. Metro Mining has successfully navigated this by establishing crucial contracts with major customers such as Chalco and Emirates Global Aluminium (EGA). These existing relationships create a substantial barrier for potential new entrants looking to gain market access and secure consistent sales for their product.
For instance, in 2024, the global alumina market continued to see strong demand, underscoring the importance of these offtake agreements. Metro Mining's established partnerships mean that new competitors face the difficult task of not only producing bauxite but also finding buyers willing to commit to the volumes and quality required, often at prices that new entrants may struggle to match against established players with secure off-take deals.
- Existing Offtake Agreements: Metro Mining's contracts with Chalco and EGA provide guaranteed sales volumes, reducing their exposure to market price fluctuations and securing a stable revenue stream.
- Customer Loyalty and Relationships: Long-standing relationships with major alumina refineries foster loyalty, making it harder for new entrants to displace established suppliers.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: For new entrants, the bargaining power of large alumina refineries is immense; they can dictate terms and pricing, making it difficult to secure favorable agreements without a proven track record.
- Capital Investment in Logistics: Accessing efficient shipping and port facilities is critical for bauxite producers. Metro Mining’s established logistics infrastructure presents another barrier for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants in the bauxite mining sector is considerably low for Metro Mining. High capital requirements for exploration, mine development, and infrastructure, often in the hundreds of millions or billions of dollars, create a significant barrier. For example, establishing a new open-pit mine demands substantial investment, deterring many potential competitors.
Economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Metro Mining, who often have billions in capital expenditures in 2024, further solidify this advantage. This allows them to secure bulk discounts and optimize logistics, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price due to higher initial per-unit costs.
Access to prime bauxite reserves is also a major hurdle, with established companies like Metro Mining already controlling key resources such as its Bauxite Hills Mine. Navigating complex government approvals and securing land access agreements are additional significant deterrents for newcomers in 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Metro Mining Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and government mining regulations. This blend of primary and secondary sources ensures a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.
