MesaLabs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
MesaLabs Bundle
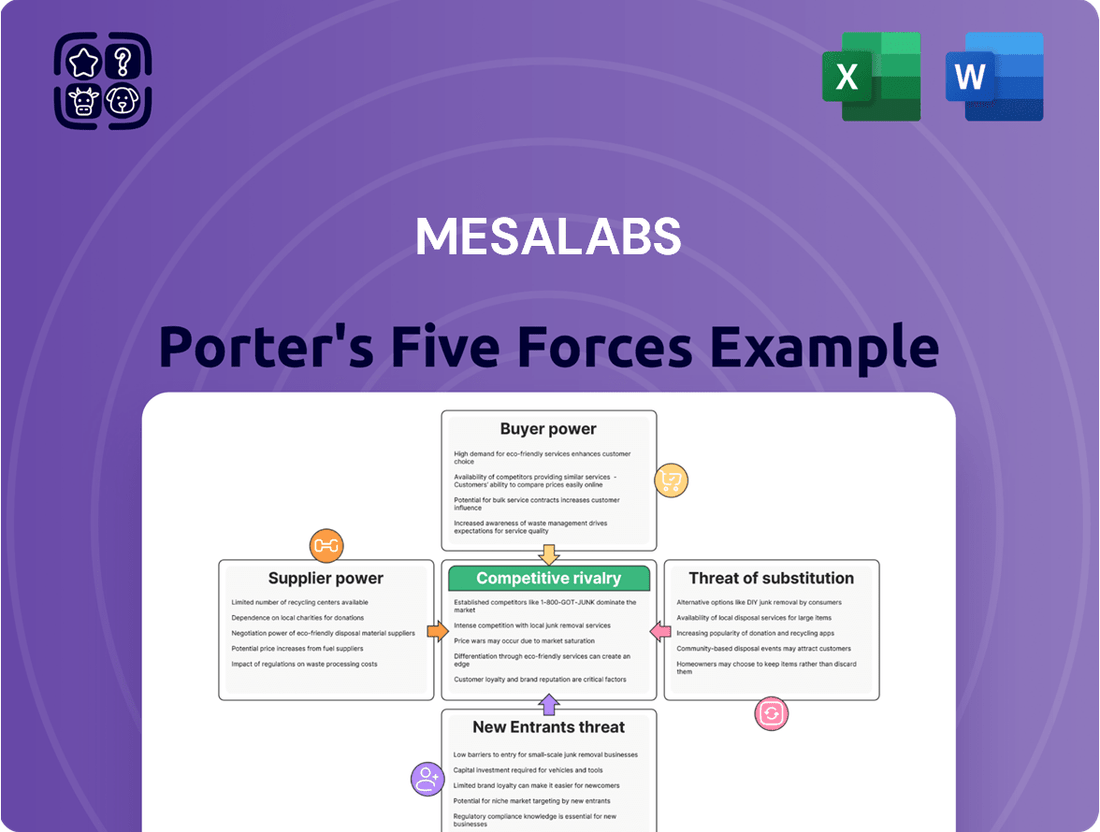
MesaLabs operates within a competitive landscape shaped by powerful industry forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview highlights key considerations, but the full analysis offers a comprehensive deep dive.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for MesaLabs unpacks each of these dynamics with detailed insights, providing a robust framework for assessing market attractiveness and competitive advantage. It's essential for anyone looking to gain a truly strategic perspective on MesaLabs's industry.
Don't just skim the surface of MesaLabs's market. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore MesaLabs’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Mesa Labs frequently depends on specialized components and raw materials, especially given its operations within regulated sectors. The scarcity or proprietary nature of these inputs can significantly bolster supplier leverage. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for advanced instrumentation, experienced continued supply chain challenges, with lead times for certain critical chips extending to over a year, a factor that would directly impact Mesa Labs' production costs and availability.
Suppliers in the healthcare, pharmaceutical, and medical device industries face significant regulatory compliance hurdles. These stringent standards, covering everything from manufacturing processes to material sourcing, can limit the pool of qualified vendors. For instance, suppliers must often meet FDA regulations for medical device components or Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical ingredients.
These compliance demands translate into higher operational costs for suppliers, including investment in specialized equipment, quality assurance personnel, and ongoing audits. Consequently, Mesa Labs might encounter increased material costs as suppliers pass on these expenses to maintain their certifications and ensure adherence to regulations like ISO 13485 for medical devices.
Mesa Labs faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. Changing suppliers for critical components isn't a simple matter; it involves substantial expenses and time for requalification, regulatory re-certification, and potential modifications to production lines. These hurdles make it difficult for Mesa Labs to easily shift sourcing, thus strengthening the leverage of their current suppliers.
The stringent validation processes required for new suppliers and materials, particularly in regulated industries like those adhering to FDA or ICH standards, act as a significant barrier to easily changing sourcing partners. For instance, the validation of a new chemical reagent or a critical sensor can take months and incur substantial testing fees, reinforcing the dependence on established suppliers.
Supplier Concentration
Supplier concentration significantly impacts Mesa Labs' bargaining power. If the market for critical inputs is dominated by a small number of suppliers, these suppliers gain leverage, potentially dictating terms and pricing. For instance, in the specialized medical device components sector, a few manufacturers might hold patents or unique production capabilities, making Mesa Labs reliant on them.
This reliance can translate into less favorable contract terms or higher costs for Mesa Labs. Consider the broader market for specific diagnostic reagents or sterile packaging materials; if only a handful of companies can meet Mesa Labs' quality and volume requirements, those suppliers are in a strong position. In 2024, reports indicated that in certain niche laboratory equipment consumables, supplier consolidation led to price increases of 5-10% for buyers facing limited alternatives.
- Supplier Concentration: If key input markets are concentrated, suppliers gain power over Mesa Labs.
- Market Dominance: A few dominant suppliers can command higher prices or impose stricter terms.
- Reliance on Niche Suppliers: Mesa Labs' dependence on specialized component or material providers increases supplier leverage.
- Impact on Costs: Supplier concentration can directly lead to increased operational expenses for Mesa Labs.
Technological Advancements by Suppliers
Suppliers who pioneer proprietary or cutting-edge technologies vital for Mesa Labs' offerings, like enhanced sensor tech for data loggers or innovative biological indicator formulations, gain leverage to charge premium prices. For instance, a supplier developing a novel, highly sensitive sensor could significantly increase the cost of a key component. Mesa Labs might find itself reliant on these technologically superior suppliers to uphold its competitive advantage and ensure optimal product functionality.
This dependency can shift the balance of power, as Mesa Labs may have fewer alternatives for acquiring these critical, advanced components. The market for specialized biotechnology components, for example, often sees a limited number of suppliers, intensifying their bargaining strength. In 2024, the specialty chemicals sector, which includes many suppliers of advanced materials, saw price increases averaging 5-7% due to raw material costs and innovation investment, directly impacting companies like Mesa Labs.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, patented technologies hold significant power.
- Component Criticality: If a component is essential for Mesa Labs' product performance, supplier power increases.
- Limited Alternatives: A small number of suppliers for advanced components reduces Mesa Labs' negotiation options.
- Innovation Costs: Suppliers investing heavily in R&D for new technologies often pass these costs to buyers.
Mesa Labs' reliance on specialized inputs, coupled with the high costs and regulatory hurdles associated with switching suppliers, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. The concentration of suppliers in key input markets and the critical nature of proprietary technologies further consolidate this leverage, potentially leading to increased costs and reduced negotiation flexibility for Mesa Labs.
| Factor | Impact on Mesa Labs | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased leverage for dominant suppliers. | Niche laboratory consumables saw 5-10% price hikes due to consolidation in 2024. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers can command premium prices for critical, advanced components. | Specialty chemicals sector prices rose 5-7% in 2024 due to R&D investment. |
| Switching Costs | High requalification and regulatory costs lock Mesa Labs into existing suppliers. | Validation of new medical device components can take months and incur substantial testing fees. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Suppliers pass on increased operational costs from standards like FDA and ISO 13485. | Stringent manufacturing and sourcing standards limit qualified vendors. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for MesaLabs thoroughly examines the industry's competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a strategic overview of MesaLabs' market position.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Mesa Labs' customer base, heavily concentrated in sectors like healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage, operates within intensely regulated environments. These industries impose rigorous quality control and validation mandates, meaning customers absolutely require high levels of reliability and adherence to standards from their suppliers.
While this inherent need for strict compliance might seem to dilute customer bargaining power, it actually amplifies it in a different way. Customers in these fields demand not just products, but validated solutions that ensure their own compliance, giving them significant leverage to push for top-tier performance and unwavering regulatory adherence from Mesa Labs.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, the cost of non-compliance can be astronomical, including product recalls and severe penalties, which translates to customers being very sensitive to any perceived risk. This regulatory pressure forces Mesa Labs to consistently invest in maintaining the highest quality and compliance standards, directly influencing customer negotiations.
Mesa Labs faces considerable bargaining power from its customers, particularly due to the consolidation within the healthcare and food and beverage sectors. Large healthcare systems, major pharmaceutical companies, and prominent food and beverage conglomerates wield significant purchasing power because of their sheer scale and volume of business. For instance, the top 10 largest hospital systems in the US collectively manage billions in annual spending, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms on laboratory equipment and services.
This concentration of buyers means that a few key customers can exert substantial leverage over Mesa Labs. They can demand customized solutions tailored to their specific operational needs, pushing Mesa Labs to adapt its product offerings and service models. In 2024, the trend of consolidation continued, with several mergers and acquisitions occurring in the healthcare industry, potentially increasing the concentration of Mesa Labs' customer base and amplifying their collective bargaining strength.
Once customers integrate Mesa Labs' instruments, software, and services into their critical quality control processes, switching to a competitor can be costly. This involves expenses like re-validation of equipment and processes, retraining staff, and the potential for significant operational disruption. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, regulatory compliance alone makes switching complex and time-consuming.
These integration challenges create a form of customer lock-in, effectively reducing the immediate bargaining power of individual customers. Mesa Labs reported that in 2023, its recurring revenue from services and consumables represented a significant portion of its total revenue, underscoring the stickiness of its customer relationships and the costs associated with changing providers.
Importance of Quality and Safety
For Mesa Labs' customers, particularly those in healthcare and life sciences, the unwavering demand for product quality and patient safety significantly influences their purchasing decisions. Regulatory mandates and the imperative to safeguard brand reputation mean that reliability and accuracy often outweigh price considerations. This focus on critical performance attributes somewhat mitigates the customers' direct price-bargaining power.
Mesa Labs operates in sectors where failures can have severe consequences, making them highly sensitive to product integrity. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, deviations in sterilization monitoring can lead to costly recalls and reputational damage. This inherent need for dependable solutions allows Mesa Labs to command a certain premium, as customers are willing to invest in certainty and compliance rather than risk the downstream costs of substandard products.
- Regulatory Compliance: Customers must adhere to stringent regulations like FDA requirements, making validated and reliable products essential.
- Patient Safety: In healthcare applications, product accuracy directly impacts patient well-being, a non-negotiable factor for buyers.
- Brand Reputation: For Mesa Labs' clients, using trusted products is crucial for maintaining their own credibility and market standing.
- Risk Mitigation: The cost of a product failure, including potential litigation and loss of business, far exceeds the savings from a lower price point.
Availability of Multiple Providers
Customers in the quality control and validation market benefit from a wide array of choices, as numerous providers offer comparable instruments, software, and services. This abundance of alternatives empowers buyers to readily compare pricing and feature sets.
The ability to easily switch between providers or leverage competing offers significantly enhances customer bargaining power, particularly for more standardized products where differentiation is minimal. For instance, in 2024, the market for laboratory validation equipment saw an estimated 15% increase in new entrants, further fragmenting the supplier landscape.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: With multiple providers, customers can solicit and compare quotes, driving down prices for standard validation services and equipment.
- Demand for Customization: While standardization favors price comparison, the availability of multiple vendors also allows customers to seek tailored solutions, potentially increasing their leverage if a provider is uniquely positioned to meet specific needs.
- Information Asymmetry Reduction: Online platforms and industry reports in 2024 made it easier for customers to access information on product performance and pricing, diminishing the advantage previously held by suppliers.
Mesa Labs' customers, particularly those in regulated industries like healthcare and pharmaceuticals, possess significant bargaining power due to the critical nature of their operations. The need for unwavering reliability and strict regulatory compliance means customers demand validated solutions, giving them leverage to insist on top-tier performance. This is amplified by industry consolidation, where larger entities can negotiate more favorable terms. For example, the continued mergers in the healthcare sector in 2024 likely increased buyer concentration, thus strengthening their collective negotiating position.
While integration costs can create customer lock-in, reducing individual bargaining power, the sheer number of alternative providers in the market, with an estimated 15% increase in new entrants in 2024, allows customers to easily compare pricing and features. This increased competition, especially for more standardized offerings, drives price sensitivity and demands for customization.
| Factor | Impact on Mesa Labs | Customer Leverage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Large hospital systems' significant spending power allows for negotiation of better terms. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate (due to integration) | Pharmaceutical companies face complex re-validation processes, limiting immediate switching. |
| Market Competitiveness | High | Increased new entrants in 2024 (est. 15%) provide more choices for customers. |
| Regulatory Demands | Mitigates price sensitivity | Need for FDA compliance means customers prioritize reliability over lower cost. |
Same Document Delivered
MesaLabs Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the precise MesaLabs Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape. You're looking at the actual document, meticulously compiled to provide actionable insights into the industry's dynamics. Once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this exact, fully formatted file, ready for your strategic planning. No mockups or samples; the document you see here is precisely what you’ll be able to download and utilize without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Mesa Labs thrives in specialized segments of the quality control market, including sterilization monitoring, process validation, and data logging. These niches, while potentially lucrative, are populated by a multitude of focused competitors, intensifying rivalry within each specific area.
The data logger market exemplifies this dynamic, experiencing robust growth and attracting numerous new entrants. For example, in 2023, the global data logger market was valued at approximately $3.6 billion and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 10.2%. This expansion fuels competition as companies vie for market share.
The competitive landscape for Mesa Labs is intensely shaped by a relentless pursuit of innovation and technological advancement. Companies vie for market share by developing products with superior features, enhanced accuracy, greater automation, and seamless integration into digital ecosystems. This constant drive pushes the boundaries of what's possible in laboratory diagnostics and monitoring.
Firms that successfully deploy cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence for sophisticated data analytics, real-time monitoring capabilities, and flexible cloud-based solutions, are positioned to capture significant market advantages. For instance, advancements in AI-powered diagnostic tools can lead to faster and more precise results, a critical factor for healthcare providers and researchers.
In 2024, the market for laboratory automation and digital integration is experiencing robust growth. Reports indicate the global laboratory automation market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of around 7.5% through 2030. This underscores the direct correlation between technological investment and competitive strength within the sector.
Mesa Labs must therefore prioritize its research and development efforts to stay ahead. Investing in areas like machine learning for predictive diagnostics, IoT integration for remote sample tracking, and user-friendly software platforms will be crucial for maintaining and improving its competitive standing in this dynamic industry.
In the highly regulated life sciences and medical device sectors, Mesa Labs faces intense competitive rivalry where navigating complex regulatory landscapes is a significant differentiator. Companies excelling in FDA and EMA compliance, such as those offering sterilization validation or environmental monitoring services, directly compete by enabling clients to bring products to market faster and more reliably. This expertise is crucial, as evidenced by the ongoing scrutiny and evolving standards within these industries. For instance, the FDA's increased focus on cybersecurity for medical devices, a trend intensifying through 2024, means companies with robust compliance solutions in this area gain a distinct advantage.
Global Presence and Distribution Networks
Competitive rivalry in the life sciences instrumentation market intensely focuses on global presence and the robustness of distribution networks. Mesa Labs operates manufacturing facilities in North America and Europe, complemented by a worldwide sales force. However, rivals with more extensive or deeply entrenched international operations can leverage their reach to capture market share.
This geographic advantage translates into quicker product delivery, more localized customer support, and potentially better access to emerging markets. For instance, a competitor with a stronger presence in Asia-Pacific might be better positioned to capitalize on the region's rapidly growing demand for diagnostic and research tools.
Consider the impact on sales strategies. A company with a broad global distribution network can offer a more comprehensive suite of products and services to a wider customer base, creating a significant competitive edge. This often involves establishing local partnerships or subsidiaries to navigate diverse regulatory environments and customer needs.
- Global Footprint Advantage: Competitors with broader international manufacturing and sales networks can offer more competitive pricing and faster delivery times worldwide.
- Distribution Network Strength: The effectiveness of a company's sales and distribution channels directly impacts its ability to reach and serve customers across different geographies.
- Market Access: A wider global presence allows companies to tap into diverse customer segments and emerging markets, potentially driving higher revenue growth.
- Customer Support Reach: Competitors with a stronger international support infrastructure can provide more responsive and localized assistance, enhancing customer loyalty.
Acquisitions and Consolidation
The life sciences and diagnostics industry, where MesaLabs operates, has experienced significant consolidation. In 2023, the sector saw a notable increase in merger and acquisition (M&A) activity as companies aimed to broaden their product offerings and enhance their market presence. For instance, deals like the acquisition of Cytiva by Danaher, valued at approximately $21.4 billion in 2020, illustrate the trend of larger entities absorbing smaller ones to gain scale and technological advancements.
This ongoing M&A trend intensifies competitive rivalry. Larger, well-capitalized players such as STERIS and Danaher can leverage their financial strength and market dominance to acquire innovative technologies or expand into new geographic regions. This strategic move often aims to achieve economies of scale, thereby creating a more formidable competitive barrier for smaller, independent companies like MesaLabs.
- Increased M&A Activity: The life sciences sector experienced a surge in mergers and acquisitions throughout 2023 as companies sought to consolidate market share and expand capabilities.
- Strategic Acquisitions by Larger Players: Companies like Danaher and STERIS have actively pursued acquisitions to bolster their product portfolios and technological offerings.
- Competitive Advantage through Scale: Larger entities can leverage their financial resources and operational scale, gained through acquisitions, to outcompete smaller rivals.
- Impact on Smaller Companies: This consolidation creates a more challenging environment for independent companies, necessitating strategic partnerships or niche specialization to remain competitive.
Mesa Labs faces intense rivalry from numerous specialized competitors within its niche markets. The drive for innovation is constant, with companies competing on product features, accuracy, and digital integration. For example, the global data logger market, a key area for Mesa Labs, was valued at $3.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly.
The competitive landscape is also shaped by regulatory expertise, with firms excelling in FDA and EMA compliance gaining an edge, especially with increasing scrutiny on areas like medical device cybersecurity in 2024. Furthermore, companies with extensive global manufacturing and distribution networks can offer advantages in pricing and delivery, impacting Mesa Labs' market access and customer support reach.
Consolidation within the life sciences sector, marked by significant M&A activity in 2023, further intensifies rivalry. Larger players like Danaher and STERIS leverage acquired scale and technology to outcompete smaller, independent firms, making strategic specialization or partnerships crucial for companies like Mesa Labs.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Manual or traditional quality control methods can act as a substitute, particularly for smaller businesses or less critical product lines where automation might be cost-prohibitive. For instance, a small craft brewery might rely on visual inspection and taste tests rather than sophisticated laboratory equipment for their quality assurance. This offers a lower-cost alternative to Mesa Labs' advanced solutions.
However, for industries where Mesa Labs operates, such as healthcare and industrial manufacturing, the demand for stringent accuracy and regulatory compliance significantly limits the appeal of these manual substitutes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for example, enforces strict guidelines for sterile processing and environmental monitoring, making manual checks insufficient and highly risky. In 2024, the global market for quality control software was projected to reach over $30 billion, indicating a strong preference for automated and data-driven solutions.
Large pharmaceutical and healthcare companies, especially those with substantial R&D budgets, may develop proprietary in-house solutions for quality control and compliance. This is particularly true if they have highly specialized or unique testing requirements that off-the-shelf products from companies like Mesa Labs don't perfectly address. For instance, a major pharmaceutical firm might invest millions in creating custom software and automated testing equipment to streamline their specific drug development processes, thereby reducing their need for external instrumentation.
The threat of substitutes for Mesa Labs' quality assurance solutions stems from entirely different technologies or methodologies that can achieve similar objectives. For instance, as of 2024, advancements in predictive analytics are increasingly being used for quality control in manufacturing, potentially reducing reliance on traditional monitoring instruments. New biological testing methods also offer alternative pathways for quality assurance in certain sectors, impacting the demand for established validation products.
Generic or Lower-Cost Alternatives
While Mesa Labs targets specialized, high-margin sectors, the presence of generic or substantially cheaper instruments and services, especially from developing economies, presents a significant threat. These alternatives can offer a more budget-friendly option, even if they lack some of Mesa Labs' sophisticated functionalities.
For instance, in the life sciences and healthcare sectors where Mesa Labs operates, the market for laboratory equipment and calibration services is increasingly seeing price-sensitive players emerge. These competitors can undercut established players by simplifying product designs or leveraging lower manufacturing costs.
- Cost-Conscious Competitors: Emerging market manufacturers are increasingly capable of producing instruments with comparable core functionalities at a fraction of the cost.
- Feature Trade-offs: While not always matching Mesa Labs' advanced features, these substitutes often provide sufficient performance for less demanding applications, appealing to budget-constrained institutions.
- Market Erosion: The availability of these lower-cost options can gradually erode Mesa Labs' market share, particularly in segments where advanced features are not the primary purchasing driver.
Outsourcing to Contract Organizations
The threat of substitutes for Mesa Labs' offerings is significant, particularly from specialized Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs). These entities can offer integrated quality control and validation services, effectively replacing the need for Mesa Labs' standalone instruments and services. The medical device and bioprocessing sectors are increasingly relying on these outsourcing partners, demonstrating a clear shift in customer preference.
This trend is fueled by the growing complexity and regulatory demands within these industries. For instance, the global CRO market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. Similarly, the CMO market for pharmaceuticals and medical devices is experiencing robust expansion, with forecasts indicating continued strong growth through 2030.
- Integrated Solutions: CROs and CMOs often provide end-to-end services, encompassing testing, validation, and manufacturing, which can be more convenient than managing multiple vendors or in-house processes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For some companies, outsourcing to specialized organizations can be more cost-effective than investing in and maintaining their own quality control infrastructure.
- Expertise and Specialization: CROs and CMOs typically possess deep expertise and advanced technologies in specific areas of quality control and validation, offering a level of specialization that may be difficult for individual companies to replicate.
- Market Growth: The increasing outsourcing trend in bioprocessing, where precision and regulatory compliance are paramount, directly impacts the demand for Mesa Labs' products if customers opt for full-service providers.
The threat of substitutes for Mesa Labs' offerings is moderated by the high regulatory and accuracy demands in its target markets. While manual methods and basic generic instruments exist, they often fall short of the precision and compliance required by industries like healthcare and pharmaceuticals. For example, the stringent validation protocols mandated by the FDA in 2024 make less sophisticated alternatives risky. The growing market for advanced quality control software, projected to exceed $30 billion globally in 2024, further underscores the preference for robust, data-driven solutions over simpler substitutes.
Furthermore, the rise of specialized Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) presents a more significant substitute threat. These entities offer integrated quality control and validation services, potentially reducing the need for Mesa Labs' standalone products. The global CRO market, valued at roughly $50 billion in 2023, and the expanding CMO sector highlight a trend toward outsourcing these critical functions, especially in bioprocessing where precision and compliance are paramount.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Mesa Labs | Relevant Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual/Traditional Methods | Lower-cost, less precise quality checks. | Limited impact in highly regulated sectors. | Manual checks are insufficient for FDA compliance. |
| Generic Instruments | Budget-friendly alternatives with core functionality. | Potential market erosion in less demanding segments. | Emerging market manufacturers offer lower-cost options. |
| Proprietary In-house Solutions | Custom-developed systems by large firms. | Reduces demand for external providers for specific needs. | Major pharma may invest millions in custom automation. |
| Predictive Analytics | Data-driven quality forecasting. | Potential to reduce reliance on traditional monitoring. | Advancements are impacting demand for traditional instruments. |
| CROs/CMOs | Integrated outsourced quality services. | Significant threat via end-to-end service offerings. | Global CRO market valued ~ $50 billion (2023). |
Entrants Threaten
Entering MesaLabs' market for quality control instruments and software in regulated sectors demands immense upfront capital. Think significant investments in research and development to create sophisticated technology, plus the cost of building state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities. For instance, developing a new validated laboratory instrument can easily run into millions of dollars.
Beyond manufacturing, new players must also fund extensive compliance infrastructure to meet stringent industry standards, like FDA regulations. This financial hurdle alone deters many smaller companies.
The sheer scale of these capital requirements acts as a formidable barrier, protecting established players like MesaLabs from a flood of new competition.
New entrants in the medical device and diagnostics sector, like Mesa Labs, encounter significant regulatory challenges. Obtaining approvals such as FDA clearance or CE marking, alongside ISO certifications for quality management, demands substantial investment in time and resources. This complex process, often taking years and millions of dollars, acts as a powerful deterrent for potential new competitors.
Mesa Labs benefits significantly from its long-standing brand reputation and deeply ingrained customer loyalty, particularly within specialized sectors where regulatory compliance is paramount. This established trust makes it incredibly challenging for new players to gain traction, as they lack the proven track record and customer confidence that Mesa Labs has cultivated over decades. For instance, in the highly regulated biological safety cabinet market, where Mesa Labs holds a strong position, customers often prioritize reliability and adherence to strict standards, which can be difficult for newcomers to demonstrate convincingly.
Access to Distribution Channels and Expertise
New entrants often struggle to secure shelf space or partnerships with established distributors, especially in competitive sectors like diagnostics where existing relationships are crucial. For instance, a new molecular diagnostics company might find it difficult to get its tests listed by major hospital networks or clinical laboratories without significant investment in sales teams and marketing efforts. This access is vital for reaching end-users and generating revenue.
Building a team with the necessary scientific and technical proficiency presents another substantial hurdle. MesaLabs, for example, relies on a deep understanding of microbiology and quality control. A new competitor would need to attract highly skilled scientists and engineers, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive. In 2024, the demand for specialized talent in the life sciences sector remained high, with reported salary increases for experienced professionals in R&D and quality assurance.
- Distribution Channel Barriers Companies may face difficulties accessing established distribution networks, particularly in international markets or specialized niches.
- Expertise Requirements The need for specialized scientific and technical knowledge to develop, manufacture, and validate products acts as a significant entry barrier.
- Capital Investment Significant financial resources are often required to overcome both distribution and expertise challenges, creating a barrier for smaller or less-funded entrants.
- Regulatory Hurdles Navigating complex regulatory landscapes, such as FDA approvals for diagnostic devices, demands specialized knowledge and considerable investment.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Proprietary technology and existing patents represent significant hurdles for new entrants in the laboratory services sector. Established companies like MesaLabs often possess a portfolio of patents covering their unique instruments, testing methodologies, and biological indicators. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office continued to see a high volume of applications in biotech and medical device fields, underscoring the importance of IP protection. Developing comparable or advanced technology without infringing on these protected assets is a complex and costly undertaking for any new competitor aiming to enter the market.
These intellectual property barriers can severely limit the ability of newcomers to offer competitive products or services. MesaLabs, as of its latest reports, actively defends its patented technologies, which are crucial to its market position in areas like biological safety and environmental monitoring. The cost and legal expertise required to navigate existing patent landscapes and develop novel, non-infringing solutions can be prohibitive, effectively deterring many potential entrants.
- Patented Technologies: MesaLabs and its competitors hold numerous patents on specialized instrumentation and testing methods.
- Intellectual Property Barriers: Existing patents create significant legal and technical challenges for new market entrants.
- R&D Investment: Developing proprietary, non-infringing technology requires substantial research and development capital.
- Market Entry Costs: The financial and legal resources needed to overcome IP hurdles are a major deterrent.
The threat of new entrants for Mesa Labs is relatively low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and regulatory compliance, estimated in the millions for new instrument development, deter many. Furthermore, established brand loyalty and the need for specialized scientific expertise, with high demand for life science talent in 2024, create significant hurdles for newcomers.
Existing patents and proprietary technology also act as a formidable defense. Developing non-infringing innovations requires substantial investment and legal navigation, a costly endeavor for potential competitors. Access to established distribution channels and partnerships further solidifies Mesa Labs' market position, making it challenging for new players to gain traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Impact | Relevant Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and compliance. | Very High | New instrument development can cost millions; 2024 saw continued high investment in biotech R&D. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and lengthy approval processes (e.g., FDA, CE). | Very High | Approvals can take years and millions of dollars; stringent quality standards remain. |
| Brand Reputation & Loyalty | Established trust and proven track record. | High | Customers prioritize reliability in regulated sectors, a difficult trait for newcomers to build. |
| Intellectual Property | Patented technologies and trade secrets. | High | Significant legal and technical challenges to develop non-infringing technology; high patent application volume in biotech. |
| Distribution Access | Securing partnerships with established networks. | Moderate | Difficulty in gaining access to major hospital networks or clinical labs without significant sales investment. |
| Expertise Requirements | Need for specialized scientific and technical knowledge. | High | High demand for specialized talent in life sciences, with increased salaries for experienced professionals in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports, investor presentations, and proprietary market intelligence to deliver a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
