Mallinckrodt Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Mallinckrodt Bundle
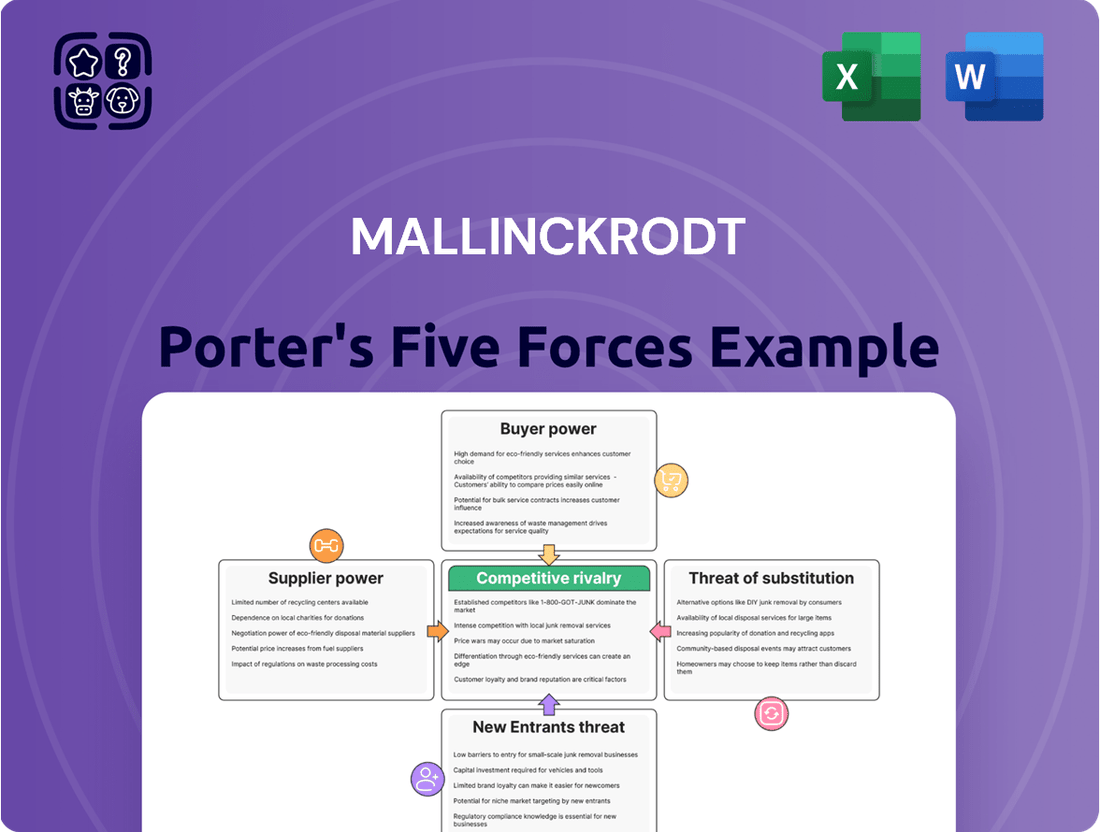
Mallinckrodt operates in a complex pharmaceutical landscape, facing significant pressure from powerful suppliers and intense rivalry with established competitors. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers is crucial for navigating this market.
The threat of substitute products also looms large, requiring Mallinckrodt to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these intricate dynamics.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Mallinckrodt’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you with actionable intelligence.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Mallinckrodt's reliance on highly specialized raw materials for products like Acthar Gel gives suppliers significant power. A limited number of suppliers for these complex, often biologics-based inputs means they can dictate pricing and control supply. This creates vulnerability for Mallinckrodt to cost increases and potential disruptions, especially after its 2022 restructuring. The highly regulated nature of these materials also imposes high switching costs, further strengthening supplier influence.
Mallinckrodt faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on third-party Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) suppliers, particularly for its specialty generics segment. While the company produces some APIs internally, external sourcing remains crucial. Global supply chain disruptions, as seen in recent years, heavily influence API availability and pricing, impacting production costs for 2024 operations. Any major interruption in API supply chains, such as those affecting key drug components, could severely impede Mallinckrodt's manufacturing output and sales volume.
Suppliers to the pharmaceutical industry, crucial for Mallinckrodt, must strictly adhere to stringent regulatory standards set by agencies like the FDA. The necessity for these suppliers to maintain continuous compliance adds a significant layer of complexity and risk to their operations. A supplier failing to meet these rigorous 2024 compliance benchmarks can directly lead to production halts for Mallinckrodt. This regulatory dependency elevates the bargaining power of compliant suppliers, as Mallinckrodt relies heavily on their adherence to avoid operational disruptions.
Contract Manufacturing Organization (CMO) Reliance
Mallinckrodt's reliance on Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) for specialized pharmaceutical production significantly elevates supplier bargaining power. These CMOs, like Catalent or Lonza, are crucial for operational efficiency and quality control, directly impacting Mallinckrodt's market access. The highly specialized and regulated nature of pharmaceutical manufacturing limits the pool of qualified CMOs, intensifying their leverage over pricing and terms. For instance, the global pharmaceutical CMO market was projected to reach over $100 billion by 2024, demonstrating the high demand for these services.
- Specialized pharmaceutical manufacturing limits CMO options.
- CMO operational efficiency directly impacts Mallinckrodt's market entry.
- High demand for CMO services strengthens their pricing power.
- The global pharmaceutical CMO market exceeded $100 billion in 2024.
U.S. DEA Quotas
Mallinckrodt's production of controlled substances, like its opioid-based pain medications, is critically dependent on procurement and production quotas granted by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). The DEA acts as a unique and powerful regulatory supplier, effectively controlling the right to manufacture these substances. This reliance on government-issued quotas creates a significant operational dependency and potential bottleneck for the company's revenue streams.
- For 2024, the DEA set specific aggregate production quotas (APQs) for Schedule II controlled substances, including 36,000 kg for oxycodone.
- These quotas directly impact manufacturers' ability to supply the market.
Mallinckrodt faces substantial supplier power, driven by its reliance on a concentrated base of specialized raw material, API, and CMO providers. The highly regulated nature of pharmaceutical inputs and limited alternative sources mean these suppliers can dictate terms and pricing. This elevates Mallinckrodt's operational costs and risks, particularly impacting its profitability margins in 2024. For instance, global pharmaceutical raw material prices saw an average increase of 3-5% in early 2024 due to supply chain pressures.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Driver | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Raw Materials | Limited Suppliers, High Switching Costs | Cost increases of 3-5% impacting COGS |
| API Manufacturers | Supply Chain Vulnerabilities, Quality Control | Potential production delays due to 2024 API shortages |
| CMOs | Specialized Capacity, Regulatory Expertise | Global CMO market exceeding $100 billion in 2024, indicating high demand |
What is included in the product
This analysis maps the competitive forces impacting Mallinckrodt, assessing supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its specific markets.
Visually diagnose competitive threats with an intuitive threat matrix, simplifying complex strategic positioning.
Quickly identify key competitive levers and areas of vulnerability to inform proactive strategy development.
Customers Bargaining Power
Mallinckrodt's customers, including large hospital networks, insurers, and pharmacy benefit managers, wield substantial bargaining power. These Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) and insurers purchase in immense volumes, granting them significant leverage to negotiate drug prices and demand favorable contract terms. For instance, major GPOs represent over 90% of US hospital purchasing volume, intensifying price pressure on pharmaceutical companies. This concentrated buying power can directly reduce Mallinckrodt's revenue and compress its profit margins, as seen in the broader pharmaceutical market where drug price negotiations remain a key focus in 2024.
Governmental bodies, particularly through programs like Medicare and Medicaid, remain major payers for Mallinckrodt's high-cost therapies, including Acthar Gel. These payers wield substantial power to influence pricing and reimbursement rates via legislative and regulatory actions. For instance, changes in federal healthcare policy or the Inflation Reduction Act's drug pricing provisions, effective 2024, directly impact the company's revenue streams. This significant customer concentration makes Mallinckrodt highly susceptible to cost-containment initiatives and shifts in public health policy. Their bargaining power is further amplified by their ability to dictate formulary inclusion and payment terms.
In the specialty generics market, customers exhibit high price sensitivity, significantly impacting Mallinckrodt. The availability of numerous generic alternatives for conditions like ADHD, where Mallinckrodt offers products such as generic Adderall XR, and pain management, empowers buyers. This ease of switching to lower-cost options intensifies competition, forcing Mallinckrodt to compete aggressively on price for these essential products. As of 2024, the broader generic drug market continues to experience downward pricing pressure due to increased competition and purchasing power from large pharmacy benefit managers and group purchasing organizations.
Informed Physicians and Patients
Informed physicians and patients significantly influence Mallinckrodt's market position. Both groups are increasingly well-versed in treatment options, their efficacy, and comparative costs. The availability of robust clinical data, especially for therapies like Acthar Gel, empowers them to choose alternatives, which can shift market share. For instance, Mallinckrodt's launch of the SelfJect injector for Acthar Gel aimed to enhance patient convenience and loyalty, a direct response to this bargaining power. This focus on patient experience is crucial as healthcare decisions become more patient-centric in 2024.
- Physicians and patients leverage comprehensive clinical data.
- Access to alternative therapies empowers choice.
- Patient convenience, as with SelfJect, is a key loyalty driver.
- Market share can shift based on informed decisions.
Consolidation of Customer Base
The healthcare industry has experienced significant consolidation among hospitals, pharmacies, and distributors, resulting in a smaller but more powerful customer base for companies like Mallinckrodt. This increased customer concentration enhances their negotiating leverage, allowing them to demand lower prices and more favorable terms for pharmaceutical products. Mallinckrodt's financial performance is notably susceptible to these customer concentration risks, especially given its reliance on a few key products, as indicated by its Q1 2024 financial reports highlighting revenue streams.
- Major pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) like CVS Caremark, Express Scripts, and OptumRx control a significant portion of the pharmaceutical purchasing volume in 2024.
- Hospital systems continue to merge, creating larger integrated delivery networks with stronger procurement power.
- Mallinckrodt’s 2024 revenue depends on maintaining relationships with these consolidated entities.
- Customer concentration risks were a factor in Mallinckrodt's recent restructuring efforts.
Customer consolidation across hospitals, pharmacies, and distributors significantly amplifies their bargaining power against Mallinckrodt.
Major pharmacy benefit managers like CVS Caremark and Express Scripts control substantial pharmaceutical purchasing volume in 2024.
This concentrated customer base demands lower prices and favorable terms, directly impacting Mallinckrodt's 2024 revenue streams and financial stability.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Factor | Impact on Mallinckrodt (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| PBMs (e.g., CVS Caremark) | High volume purchasing | Intense price pressure; formulary exclusion risk |
| Hospital Systems | Consolidation; GPO leverage | Demands for lower prices; contract terms |
| Government Payers | Regulatory changes; policy shifts | Reimbursement rate cuts; pricing caps |
Full Version Awaits
Mallinckrodt Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Mallinckrodt Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of competitive forces within the pharmaceutical industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning needs. This comprehensive analysis will equip you with insights into buyer power, supplier power, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry for Mallinckrodt. No mockups, no samples. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, offering a robust understanding of Mallinckrodt's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Mallinckrodt faces intense competitive rivalry for its specialty branded products, particularly Acthar Gel and INOmax. For instance, Acthar Gel's net sales were approximately $105.8 million in Q1 2024, reflecting ongoing pressure from alternative treatments and market dynamics. Competitors range from large pharmaceutical companies to smaller biotech firms actively developing innovative therapies for rare and autoimmune diseases. INOmax, specifically, navigates direct nitric oxide competition within the U.S. market, with other companies vying for share in this niche segment. This broad competitive landscape necessitates continuous innovation and strategic positioning for Mallinckrodt to maintain its market standing.
Mallinckrodt's branded pharmaceuticals face a constant threat from generic and biosimilar competitors, a significant aspect of competitive rivalry. The introduction of generic equivalents, such as for products like Acthar Gel, can lead to a rapid and substantial erosion of market share and pricing power, impacting revenue streams. This is a persistent risk, especially as high-revenue products approach or pass their patent expiration, requiring continuous innovation and portfolio diversification. For instance, the company has faced ongoing pressures from generic competition impacting sales of certain legacy products in 2024, highlighting this persistent vulnerability.
The specialty generics market is characterized by intense price competition, often leading to significant margin pressure across the board. Mallinckrodt competes directly with other large generic manufacturers, including Teva Pharmaceuticals and Endo International, who frequently leverage their substantial scale and cost advantages. For instance, generic drug pricing continued to face headwinds in 2024. Despite this, Mallinckrodt has historically maintained a competitive edge through its reliability of supply in this challenging segment.
Innovation as a Competitive Factor
The pharmaceutical industry demands continuous innovation to sustain competitive advantage. Companies relentlessly compete to develop new, more effective therapies and enhance existing products. For instance, Mallinckrodt has focused on advancements like the INOmax EVOLVE DS delivery system and the Acthar Gel SelfJect injector, crucial for maintaining product relevance.
Failure to innovate quickly can lead to a significant loss of market leadership and revenue, as evidenced by declining sales for older, less differentiated products in 2024. This constant push for novel solutions drives intense rivalry.
- R&D spending remains critical, with leading pharma companies investing over 20% of revenues in R&D in 2024.
- New drug approvals by the FDA influence market share significantly each year.
- Patent expirations force companies to innovate or face generic competition.
- Mallinckrodt’s 2024 focus includes lifecycle management for key brands.
Pricing Pressure and Scrutiny
The pharmaceutical sector, including Mallinckrodt, faces intense pricing scrutiny, particularly for high-cost drugs like Acthar Gel. This pressure limits pricing flexibility, directly eroding profitability as payers and policymakers push for significant cost reductions. In 2024, the focus remains on value-based care, compelling companies to demonstrate clear cost-effectiveness to maintain market access and competitiveness.
- Governmental initiatives, such as those enabled by the Inflation Reduction Act, continue to impact drug pricing negotiations.
- Mallinckrodt's revenue from Acthar Gel, for instance, has seen declines, with Q1 2024 sales reflecting ongoing market pressures.
- Payer pushback and formulary restrictions are intensifying, demanding stronger evidence of clinical and economic benefits.
- Increased generic and biosimilar competition for various therapeutic areas further intensifies the need for pricing justification across the industry.
Mallinckrodt faces fierce competitive rivalry across its specialty branded and generic portfolios. Key products like Acthar Gel saw Q1 2024 sales around $105.8 million amid challenges from generics and market alternatives. The industry's intense focus on innovation, with leading pharma spending over 20% of revenues on R&D in 2024, coupled with continuous pricing scrutiny, demands constant strategic adaptation to maintain market share.
| Rivalry Factor | 2024 Impact | Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Specialty Brands | Market Pressure | Acthar Gel Q1 2024 Sales: $105.8M |
| Generic Threat | Revenue Erosion | Ongoing for legacy products |
| Innovation | Critical for survival | Leading Pharma R&D >20% Revenue |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The market for autoimmune and rare diseases, central to Mallinckrodt's focus, faces significant threats from alternative therapies. Competitors are actively introducing next-generation biologics and novel treatments, directly challenging established drugs like Acthar Gel. For instance, in 2024, the continued development of new biologics for conditions such as multiple sclerosis and lupus provides physicians and patients with broader choices. This expanded availability of substitutes intensifies competitive pressure, potentially eroding Mallinckrodt's market share in these therapeutic areas.
In the specialty generics segment, the primary threat of substitution for Mallinckrodt stems from other generic versions of the same drug. Since these products are chemically equivalent, pharmacists can readily substitute a lower-cost generic, leading to minimal brand loyalty and intense price competition. This market dynamic is evident as Mallinckrodt itself produces generic alternatives for drugs like Mydayis and Vyvanse. The ease of substitution means that price becomes a dominant factor, potentially impacting Mallinckrodt's revenue streams from its branded generic portfolio as competitors introduce cheaper versions, a trend continuing into 2024.
The biopharmaceutical landscape is rapidly changing with gene therapy and advanced treatment pathways emerging as significant substitutes. These innovations, such as the expanding pipeline of over 2000 gene therapy clinical trials globally as of early 2024, pose a long-term disruption risk to Mallinckrodt's product portfolio. Specifically, conditions like rare diseases, which Mallinckrodt's products often address, are increasingly targets for novel, curative therapies. This technological progression creates a high threat of substitution, potentially impacting future revenue streams as patients opt for more advanced or less invasive alternatives.
Non-Pharmaceutical Alternatives
Non-pharmaceutical alternatives, such as lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, and certain physical therapies, can serve as substitutes for pharmaceutical interventions in managing some health conditions. While these are not direct replacements for Mallinckrodt’s specialty therapies in severe or critical cases, they can reduce the overall patient population needing drug treatment. For example, managing type 2 diabetes through diet and exercise can delay or reduce the need for certain medications. This threat is generally low for Mallinckrodt’s core specialty portfolio but remains present for indications where non-drug interventions are viable.
- Preventive care emphasizing lifestyle modifications saw increased focus in 2024, impacting demand for some chronic disease medications.
- The global wellness market, encompassing diet and exercise, was projected to exceed $5.8 trillion in 2024, reflecting a growing trend towards non-pharmacological health management.
- For conditions like hypertension, non-pharmacological interventions are often first-line treatments, potentially delaying or reducing drug prescriptions.
- Patient education on self-management strategies continues to expand, empowering individuals to explore alternatives before pharmaceutical reliance.
Lower-Cost Formulations
Mallinckrodt faces a significant threat from lower-cost formulations, especially within its active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) segment. Global competitors often produce similar ingredients at considerably reduced costs, eroding Mallinckrodt’s market share. This pressure is exemplified by the severe decline in their Acetaminophen (APAP) business, largely due to intense global competition and pricing pressures.
- The company has faced revenue erosion in generic segments due to intense pricing competition.
- Global suppliers can often produce bulk APIs at significantly lower manufacturing costs.
- The APAP business has been particularly vulnerable to these competitive dynamics.
- Mallinckrodt reported net sales of $1.86 billion in 2023, reflecting ongoing market pressures in certain areas.
Mallinckrodt faces substantial substitution threats from next-generation biologics and over 2,000 gene therapy clinical trials globally as of early 2024. Intense generic competition, particularly in the API segment, severely impacts pricing and market share, exemplified by pressures on their APAP business. While non-pharmaceutical alternatives, like the global wellness market exceeding $5.8 trillion in 2024, generally pose a lower threat to specialty drugs, they influence overall market demand. This diverse substitution landscape continually pressures Mallinckrodt's revenue streams.
| Threat Category | 2024 Impact | Key Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| New Biologics/Novel Therapies | Increased competition for Acthar Gel | Continued development in MS, lupus |
| Generic Competition | Price erosion in generic portfolio | Mallinckrodt's generic APAP business vulnerability |
| Gene Therapy/Advanced Treatments | Long-term disruption risk | >2,000 gene therapy clinical trials globally |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the specialty biopharmaceutical market, where Mallinckrodt operates, demands immense investment in research and development, often with a high risk of failure. The average cost to develop a new drug and bring it through clinical trials to market can exceed 2.6 billion USD, a figure that continues to rise into 2024. This substantial financial outlay is a significant deterrent for new companies considering entry. Such high R&D expenditures create a formidable barrier, protecting established players like Mallinckrodt from immediate competition.
The pharmaceutical industry faces exceptionally stringent regulatory hurdles, primarily from agencies like the FDA, making market entry challenging. Navigating these complex approval processes requires substantial expertise, time, and immense financial resources; for instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market can exceed 1 billion USD as of 2024. This extensive regulatory burden acts as a formidable barrier, effectively weakening the threat of new entrants into Mallinckrodt's specialized markets. New companies are deterred by the protracted development cycles and high capital requirements.
Established pharmaceutical companies like Mallinckrodt hold extensive patent portfolios, creating a formidable barrier for new entrants. These patents legally safeguard their branded products, preventing direct generic competition for a specified period, often 20 years from filing. This intellectual property wall forces potential new companies to invest heavily in developing novel, non-infringing therapies, a process that is both capital-intensive and time-consuming. For instance, Mallinckrodt’s 2024 intellectual property assets continue to protect key drugs, significantly increasing the development costs and regulatory hurdles for any aspiring competitor to enter the market. This makes the threat of new entrants exceptionally low due to the high costs and risks associated with overcoming existing patent protections.
Economies of Scale and Distribution
Large, established pharmaceutical companies benefit from immense economies of scale in manufacturing, marketing, and distribution, posing a significant barrier for new entrants. They possess deeply embedded relationships with Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs), hospitals, and pharmacies, which new firms struggle to replicate. A new entrant would find it exceedingly difficult to match this existing infrastructure and extensive market access, making competition on cost and reach nearly impossible.
- Top pharmaceutical companies collectively command over 60% of global market share as of 2024, demonstrating scale dominance.
- The cost of bringing a new drug to market can exceed $2 billion, a substantial barrier for startups.
- Established supply chains reduce per-unit costs for incumbents, giving them a pricing advantage.
- GPOs manage over $300 billion in annual healthcare purchasing, making established relationships crucial for market penetration.
Specialized Manufacturing and Expertise
Mallinckrodt faces a low threat from new entrants due to specialized manufacturing and expertise. The intricate processes for specialty pharmaceuticals, especially controlled substances and complex biologics, demand highly specialized facilities and a workforce with deep technical knowledge. This unique expertise is not easily replicated, creating a significant barrier for potential competitors. Furthermore, access to critical raw materials for controlled substances is tightly restricted by government quotas, making market entry exceedingly difficult for new players.
- Specialized facilities and skilled labor are critical barriers.
- Technical expertise in complex biologics is difficult to acquire.
- Government quotas for controlled substance raw materials limit new entrants.
- Mallinckrodt's established supply chains offer a competitive edge in 2024.
The threat of new entrants for Mallinckrodt remains low due to the immense capital required for R&D, often exceeding $2.6 billion per drug as of 2024. Stringent regulatory hurdles and extensive patent portfolios create formidable barriers. Established economies of scale and specialized manufacturing expertise, coupled with restricted raw material access, further deter new players. These factors collectively make market entry exceptionally difficult.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| R&D Costs | High financial outlay | >$2.6 Billion per drug |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex, time-consuming approvals | >$1 Billion drug approval cost |
| Economies of Scale | Cost and distribution advantages | Top firms >60% market share |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Mallinckrodt Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating insights from company annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports to thoroughly assess competitive dynamics.
We leverage data from financial databases, pharmaceutical industry trade journals, and regulatory agency disclosures to provide a comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping Mallinckrodt's competitive landscape.
