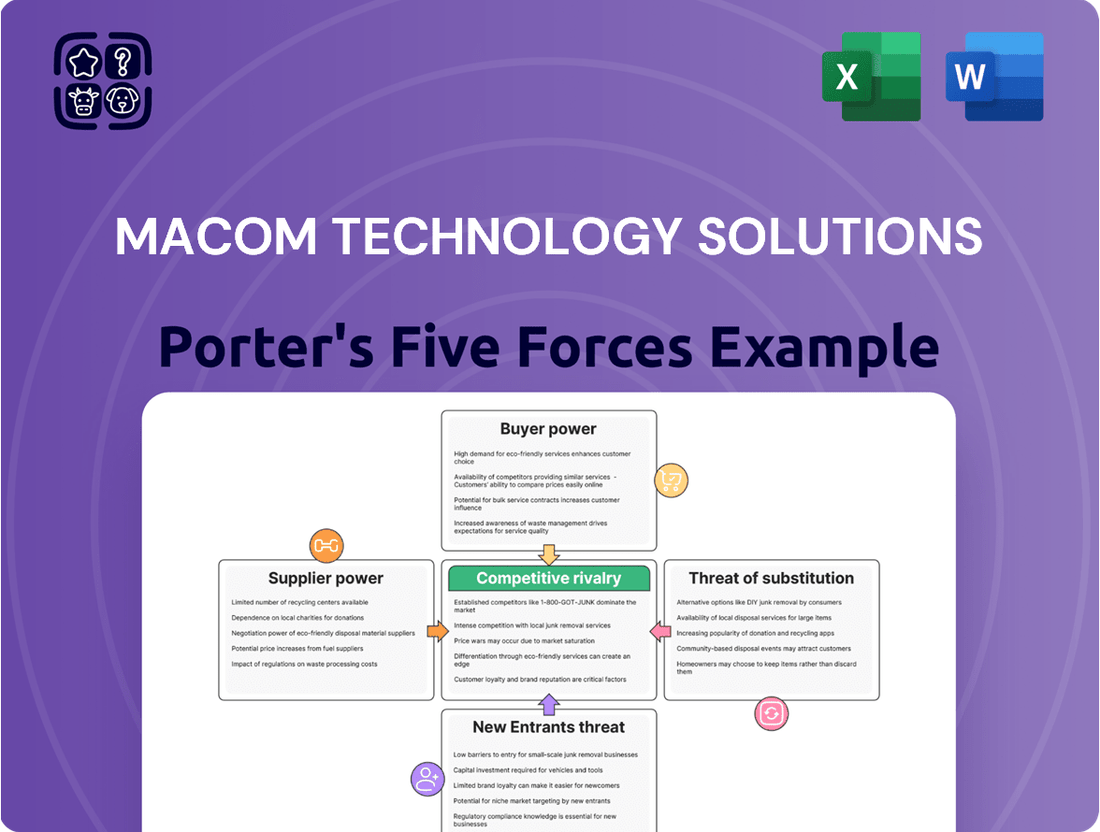
Macom Technology Solutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Macom Technology Solutions Bundle
Macom Technology Solutions operates in a dynamic semiconductor market, where intense competition, powerful suppliers, and evolving customer demands significantly shape its strategic landscape. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for navigating this complex industry.
The threat of new entrants is moderate, as high capital requirements and technological expertise act as barriers, yet innovative startups can disrupt established players. The bargaining power of buyers, primarily large electronics manufacturers, is substantial, driving price pressures and demanding customized solutions.
Conversely, the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly for specialized raw materials and manufacturing equipment, can be considerable, impacting Macom's cost structure. The threat of substitutes is also present, as alternative technologies or components could emerge, offering similar functionalities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Macom Technology Solutions’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Highly specialized component suppliers wield considerable influence over MACOM Technology Solutions. MACOM's dependence on a select group of providers for critical semiconductor wafers and sophisticated RF components means these suppliers can dictate terms. For instance, the semiconductor industry saw wafer prices increase by approximately 5-10% in late 2023 and early 2024 due to strong demand and limited foundry capacity, directly impacting companies like MACOM.
The immense technical knowledge and massive capital outlay needed to establish advanced semiconductor fabrication plants present formidable barriers for potential new entrants. This scarcity of alternative suppliers for essential materials amplifies the existing suppliers' leverage, potentially forcing MACOM into less favorable pricing or facing disruptions in its supply chain.
MACOM Technology Solutions' reliance on suppliers possessing proprietary technology or unique intellectual property significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. When these specialized components or processes are essential for MACOM's advanced semiconductor solutions, substituting suppliers becomes difficult and costly. This limited substitutability means suppliers can command higher prices or impose stricter contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry faced ongoing supply chain challenges, particularly for advanced materials and specialized fabrication services, giving suppliers with unique capabilities substantial leverage.
Switching suppliers in the semiconductor industry, particularly for a company like MACOM, involves significant hurdles. These can include the substantial costs of redesigning components and the lengthy, rigorous re-qualification processes required to ensure new parts meet stringent performance standards. Furthermore, any switch can lead to potential production delays, impacting MACOM's ability to meet market demand.
These high switching costs effectively reduce MACOM's flexibility in sourcing critical materials and components. This limitation, in turn, significantly strengthens the bargaining power of MACOM's existing, incumbent suppliers. They are aware that MACOM faces considerable challenges and expenses if it attempts to move to a different supplier, giving them leverage in negotiations.
The sheer amount of time and resources that MACOM must invest to onboard any new supplier acts as a strong disincentive to make a change. Even if more attractive or cost-effective alternatives become available in the market, the practical difficulties and upfront investment often make it more prudent to stick with established relationships, even if less favorable.
Supplier Concentration and Market Share
The semiconductor industry, crucial for MACOM's operations, is characterized by a high degree of supplier concentration. A limited number of dominant wafer manufacturers control a substantial portion of the market. This structure significantly bolsters the bargaining power of these few key suppliers, directly impacting MACOM's ability to negotiate favorable terms for essential components.
For example, in 2024, the top three global semiconductor foundries accounted for over 60% of wafer manufacturing revenue, illustrating this concentration. This limited supplier pool means MACOM has fewer alternatives for critical materials, giving these suppliers considerable leverage over pricing and supply availability. Such market dynamics restrict MACOM's negotiating flexibility.
- High Supplier Concentration: A few dominant players in semiconductor wafer manufacturing hold a significant majority of the market share.
- Limited Alternatives: MACOM faces restricted options for sourcing critical components due to this concentrated supply base.
- Pricing and Availability Leverage: Dominant suppliers can dictate terms, impacting MACOM’s cost structure and production schedules.
- Reduced Negotiating Power: MACOM's ability to negotiate aggressively on price and delivery is diminished in this supplier-dominated environment.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Dynamics
Global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions significantly empower suppliers in the semiconductor industry, leading to increased demand and potentially higher input costs for companies like MACOM. This leverage is amplified when specific manufacturing processes are concentrated among a few key providers.
MACOM's reliance on external foundry partners in Asia, with 85% of its manufacturing outsourced, places it in a vulnerable position. This high dependency means that disruptions or price increases from these Asian foundries can directly impact MACOM's production and profitability. For instance, during 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to grapple with the aftermath of earlier supply chain shocks, with lead times for certain components remaining extended, giving suppliers considerable pricing power.
Government initiatives, such as the CHIPS Act enacted in the US, aim to address these vulnerabilities by incentivizing the growth of domestic semiconductor manufacturing. While these efforts are designed to build more resilient supply chains and reduce reliance on overseas partners over the long term, their immediate impact on mitigating supplier bargaining power for companies like MACOM in 2024 was still developing.
- Supplier Concentration: MACOM's 85% dependence on external Asian foundries highlights a significant concentration risk, granting these partners substantial bargaining power.
- Market Volatility: Ongoing global supply chain issues and geopolitical instability in 2024 continued to favor suppliers by increasing demand and limiting production capacity.
- Policy Impact: Legislation like the CHIPS Act seeks to diversify manufacturing locations, potentially reducing supplier leverage for companies like MACOM in the future, though its immediate 2024 impact was nascent.
The bargaining power of suppliers for MACOM Technology Solutions is substantial, driven by industry concentration and the specialized nature of components. MACOM's reliance on a few key providers for critical semiconductor wafers and RF components means these suppliers can exert significant influence over pricing and terms, a situation exacerbated by ongoing global supply chain dynamics evident throughout 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on MACOM | 2024 Context |
| Supplier Concentration | A few dominant wafer manufacturers control a large market share. | Limits MACOM's sourcing options and negotiating leverage. | Top 3 foundries held >60% of wafer revenue in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and time for redesign and re-qualification. | Reduces MACOM's flexibility to change suppliers. | Ongoing lead times for specialized parts in 2024 reinforced this. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers possess unique IP and specialized processes. | Increases supplier leverage due to limited substitutability. | Unique capabilities remained crucial for advanced semiconductors in 2024. |
| External Manufacturing Dependence | MACOM outsources 85% of manufacturing, primarily in Asia. | Vulnerability to price hikes and disruptions from foundries. | Extended lead times persisted for some components in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for MACOM Technology Solutions by examining the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Pinpoint and mitigate competitive threats with a detailed breakdown of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and new entrant barriers.
Instantly assess the threat of substitutes and rivalry intensity to inform proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
MACOM's diverse customer base across telecommunications, industrial, defense, and data centers helps to spread out risk and lessen the leverage of any single customer. This broad market reach means that no one segment holds overwhelming power over the company.
However, within specific sectors like telecom infrastructure and hyperscale data centers, a few large customers can account for significant order volumes. Their substantial purchasing power allows them to negotiate for better pricing and tailored product specifications.
For instance, a major telecom equipment manufacturer, representing a large portion of MACOM's revenue in a given quarter, could exert considerable pressure on pricing. This is a common dynamic in industries where consolidation leads to fewer, larger buyers.
In 2024, MACOM's financial reports indicated that a single customer did not represent more than 10% of total revenue, demonstrating a degree of customer diversification that mitigates individual customer power.
MACOM's products are fundamental for customers' high-speed communication and sensing applications, meaning they are crucial for the performance and functionality of their own offerings. This reliance suggests that customers might have less power initially. However, the market dynamics for these specialized components can shift.
While MACOM's technology is advanced, the potential for certain components to become commoditized or for customers to find viable, even if less advanced, alternative solutions can empower buyers. This availability of substitutes directly influences how much leverage customers have in negotiations.
Customers, particularly those in high-volume sectors, consistently seek a balance between the high performance and reliability MACOM provides and the need for cost-effectiveness. For instance, in the telecommunications infrastructure market, where MACOM is a key supplier, cost pressures are significant, potentially driving customers to seek more budget-friendly options if available.
Customers in key markets like telecommunications and data centers are highly attuned to pricing, always looking for ways to reduce their expenses. This means MACOM faces constant pressure to offer competitive prices, even for its highly engineered solutions.
For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor industry, which MACOM operates within, saw average selling prices fluctuate, with some segments experiencing downward pressure due to increased supply and demand shifts. This environment directly impacts MACOM’s ability to command premium pricing.
The relentless pursuit of cost optimization by these customers can squeeze MACOM's profit margins, as they may be less willing to pay a premium for innovation if a slightly less advanced but cheaper alternative exists.
This price sensitivity means MACOM must continuously balance its investment in advanced technology with the market's willingness to pay, impacting its overall profitability and competitive strategy.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Components
Customers who possess strong in-house design and integration skills can significantly influence suppliers like MACOM. This is because they have the option to source components from various vendors or even develop solutions internally, thereby reducing their dependence on a single provider and increasing their bargaining power. For instance, a large aerospace or defense contractor with a sophisticated engineering team might explore alternatives if MACOM's pricing or terms become unfavorable.
However, the highly specialized nature of MACOM's analog RF, microwave, millimeterwave, and photonic products often creates a barrier to entry for internal development. These technologies demand deep expertise and significant investment in research and development. MACOM's catalog for 2024 includes advanced solutions for 5G infrastructure and satellite communications, areas where developing comparable in-house capabilities would be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for most customers.
The bargaining power of customers in this segment is therefore somewhat tempered by the technical complexity and the specialized nature of MACOM's offerings.
- High customer integration capabilities can lead to reduced reliance on MACOM.
- MACOM's specialized product portfolio (RF, microwave, millimeterwave, photonic) makes internal development difficult for many customers.
- The cost and expertise required for in-house development of such advanced components limit customer integration power.
- MACOM's 2024 product lines cater to industries where specialized components are critical, further strengthening MACOM's position.
Market Concentration of Key Customer Segments
MACOM serves a broad range of customers, but a significant portion of its revenue can be tied to a few major players in sectors like telecommunications and data centers. For instance, in 2023, a substantial percentage of MACOM's sales were concentrated among its top customers, indicating a potential leverage point for these buyers.
This concentration means that large clients, by virtue of their substantial order volumes, can negotiate more favorable pricing and terms. Their ability to switch suppliers, though potentially costly, remains a factor in their bargaining strength.
- Customer Concentration: Key customers in telecom and data center markets can exert significant influence due to their purchasing volume.
- Negotiation Leverage: Large clients can use their scale to demand better pricing and contract conditions from MACOM.
- Supplier Switching Costs: While MACOM aims to create sticky customer relationships through specialized solutions, the underlying potential for customers to seek alternatives exists.
- Relationship Management: MACOM's strategy relies heavily on maintaining strong, collaborative relationships and offering highly tailored product roadmaps to mitigate this customer power.
While MACOM benefits from a diversified customer base, significant revenue concentration in sectors like telecommunications and data centers grants large clients considerable bargaining power. These major customers, due to their substantial order volumes, can negotiate for better pricing and tailored product specifications, as evidenced by MACOM's 2023 revenue concentration among its top clients.
This leverage is further amplified when customers possess strong in-house engineering capabilities, allowing them to explore alternative suppliers or even internal development, though the highly specialized nature of MACOM's RF, microwave, and photonic products often makes direct internal replication challenging and cost-prohibitive.
Customers consistently seek cost optimization, pressuring MACOM to maintain competitive pricing even for advanced solutions. The semiconductor industry's price fluctuations in 2023 highlight this dynamic, where supply-demand shifts can impact average selling prices and MACOM's ability to command premiums.
| Customer Segment | Key Influencing Factors | MACOM's Mitigating Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications & Data Centers | High volume purchasing, cost sensitivity, potential for supplier diversification | Product specialization, strong customer relationships, tailored roadmaps |
| Industrial & Defense | Critical component reliance, long-term contracts, specialized application needs | High-performance solutions, reliability, deep technical expertise |
Same Document Delivered
Macom Technology Solutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for MACOM Technology Solutions details the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these forces is crucial for MACOM to strategize effectively in the semiconductor industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
MACOM operates in high-performance analog RF, microwave, millimeterwave, and photonic semiconductor markets, where competition is incredibly fierce. These specialized areas demand constant innovation, making it a battleground for market share.
Key rivals such as Analog Devices, Skyworks Solutions, and Qorvo are formidable players with established reputations and substantial market penetration. Their presence means MACOM must consistently outperform to maintain and grow its position.
For instance, the semiconductor industry, particularly in advanced components, sees significant R&D investment. Companies like Analog Devices, with reported revenues of over $13 billion in fiscal 2023, demonstrate the scale of resources dedicated to staying ahead.
The critical nature of these components in sectors like 5G infrastructure and advanced defense systems further intensifies this rivalry, as performance and reliability are paramount for customers.
Competitive rivalry in the semiconductor industry, particularly for MACOM Technology Solutions, hinges significantly on product differentiation and the speed of innovation. Companies actively compete by offering unique features, superior performance, and pioneering new technologies.
MACOM's strategic emphasis on research and development fuels its ability to introduce advanced solutions for rapidly evolving markets. For instance, its commitment to developing high-performance components for 5G infrastructure, artificial intelligence applications, and next-generation 1.6T data center optical connectivity is a direct response to this competitive dynamic. This constant push for innovation allows MACOM to maintain a distinct advantage.
The pace at which MACOM can conceptualize, develop, and bring these cutting-edge products to market serves as a critical differentiator. In 2024, the demand for faster, more efficient semiconductor solutions continues to accelerate, making rapid product deployment essential for capturing market share and staying ahead of competitors who are also investing heavily in R&D.
While the markets MACOM Technology Solutions operates in are competitive, they are also experiencing robust growth, especially in areas like 5G infrastructure, data centers, and defense. This expansion presents significant opportunities for all participants, but it naturally fuels a more intense competition for market share. Companies are actively working to capture demand for faster connectivity and sophisticated sensing technologies.
For instance, the global data center market was valued at approximately $277.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $571.6 billion by 2027, according to Statista. Similarly, the 5G infrastructure market is expected to grow substantially, with revenues projected to increase from $47.5 billion in 2024 to $106.9 billion by 2029, as per MarketsandMarkets. This dynamic environment means that while there's ample room for growth, players must innovate and execute effectively to gain and maintain their positions.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
The semiconductor industry's competitive intensity is significantly amplified by a constant drive for strategic acquisitions and partnerships. Companies actively pursue these avenues to broaden their product offerings, capture greater market share, and secure access to vital technologies. MACOM Technology Solutions itself has engaged in such strategies, notably acquiring ENGIN-IC, a move designed to bolster its presence in high-growth sectors like artificial intelligence and data center semiconductors. This consolidation trend means rivals are also likely to pursue similar M&A activities to remain competitive.
These strategic maneuvers are not just about inorganic growth; they are critical for staying ahead in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. By integrating new capabilities or expanding market reach through alliances, companies can more effectively counter competitive threats and capitalize on emerging opportunities. For instance, MACOM's focus on AI and data center solutions, bolstered by acquisitions, positions it to compete against larger, more diversified players. The industry's dynamic nature necessitates continuous adaptation, with M&A and collaborations serving as key tools.
- MACOM's acquisition of ENGIN-IC in 2023 aimed to enhance its portfolio in high-performance analog and mixed-signal components crucial for AI and data center applications.
- The CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, while not a direct acquisition, fosters strategic partnerships and investments, indirectly influencing competitive dynamics by supporting domestic semiconductor manufacturing and R&D.
- Competitors frequently engage in similar M&A activities to consolidate market position, acquire key intellectual property, and expand their technological capabilities.
- The success of these strategic moves can lead to significant shifts in market share and technological leadership within the semiconductor sector.
Global Presence and Regional Focus
MACOM Technology Solutions operates in a highly competitive landscape where a global presence is crucial for reaching diverse customer bases. Many competitors maintain extensive networks of design centers and sales offices across key regions like North America, Europe, and Asia to effectively serve these markets. MACOM's strategic placement of its own facilities in these areas allows it to engage directly with customers and adapt to regional demands, a vital factor in securing international business.
The competitive rivalry is intensified by the varying strengths and market penetration of global players. For instance, companies with established supply chains and strong brand recognition in specific geographic areas can leverage these advantages. MACOM's approach, which includes focusing on domestic manufacturing with support from the U.S. government, offers a distinct competitive edge in segments like defense, where national security and localized production are prioritized. This can translate into preferential treatment or access to specific contracts not available to purely foreign-based competitors.
- Global Reach: Competitors often boast extensive global networks, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and market penetration.
- Regional Specialization: Success hinges on understanding and catering to the unique needs and regulations of different regional markets.
- MACOM's Footprint: MACOM supports its global competitiveness with design centers and sales offices strategically located in North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Domestic Advantage: U.S. government support for domestic manufacturing provides MACOM with a competitive edge, particularly in defense-related sectors.
The competitive rivalry in MACOM's specialized semiconductor markets is intense, driven by innovation and the presence of major players like Analog Devices and Skyworks. Companies must continuously differentiate through superior performance and rapid product development to capture market share in high-growth areas such as 5G and data centers.
For example, Analog Devices reported revenues exceeding $13 billion in fiscal 2023, highlighting the significant resources invested by competitors. The global data center market's projected growth to $571.6 billion by 2027 and the 5G infrastructure market's expansion to $106.9 billion by 2029 underscore the high stakes.
Strategic moves like MACOM's acquisition of ENGIN-IC in 2023, aimed at bolstering its AI and data center offerings, reflect the industry trend of consolidation. These actions are crucial for staying competitive against rivals who also pursue M&A and partnerships to expand capabilities and market reach.
MACOM's global presence, with design centers and sales offices in key regions, is essential for competing against rivals with established international networks. Its focus on domestic manufacturing, supported by initiatives like the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, provides a distinct advantage, particularly in defense sectors prioritizing localized production.
| Competitor | Key Markets | Reported Revenue (FY2023 Est.) | Strategic Focus |
| Analog Devices | RF, Microwave, Data Converters, Power Management | >$13 billion | Broad portfolio expansion, AI integration |
| Skyworks Solutions | Mobile Connectivity, IoT, Automotive | ~$4.7 billion | 5G solutions, expanding into new verticals |
| Qorvo | Mobile, Infrastructure, Defense | ~$4.4 billion | Advanced RF for 5G and emerging applications |
SSubstitutes Threaten
MACOM's high-performance semiconductors face a threat from alternative technologies that can achieve similar high-speed communication and sensing functions. For instance, advancements in optical interconnects outside of MACOM's direct photonics focus, or even evolving wireless communication standards, could provide comparable performance at a lower cost or with different advantages. This competitive pressure is a constant driver for MACOM to invest in research and development.
While MACOM excels in analog RF, microwave, and millimeterwave technologies, the landscape of high-speed data transmission is dynamic. Emerging solutions in areas like advanced digital signal processing or novel materials could potentially offer substitutes that meet the performance demands of sectors like 5G infrastructure or data centers. Staying ahead requires constant adaptation and innovation in their core competencies.
As technology marches forward, there's a growing possibility of merging various functions into single chips or modules. This integration could lessen the demand for separate, high-performance parts, creating substitute solutions that offer simpler designs, reduced system costs, and better power efficiency.
MACOM is actively addressing this threat by focusing on the development of its own integrated solutions. For instance, the company’s recent investments in advanced semiconductor manufacturing, including its acquisition of Qorvo’s optical business in late 2023 for $400 million, bolster its capacity to deliver these more consolidated offerings.
Software-defined networking (SDN) and virtualization are indeed emerging as potential substitutes in certain communication and networking sectors, impacting hardware demand. These technologies abstract network functions from physical hardware, allowing for more flexible and programmable infrastructure. For instance, the growth of cloud-based network functions, which rely heavily on virtualization, could reduce the need for some specialized, purpose-built hardware components that companies like MACOM supply.
While not a direct replacement for semiconductors themselves, the shift towards software-defined solutions can alter the value proposition. This means that instead of selling discrete hardware components, MACOM might need to focus on providing enabling technologies for these virtualized environments. The market for network function virtualization (NFV) infrastructure, for example, was projected to reach over $100 billion by 2027, indicating a significant trend away from purely hardware-centric solutions.
Material Science Advancements
Material science advancements represent a potential threat of substitutes for MACOM Technology Solutions. Breakthroughs in novel materials, moving beyond established semiconductor substrates like silicon, gallium arsenide (GaAs), gallium nitride (GaN), and indium phosphide (InP), could introduce devices with enhanced performance or more favorable cost structures. For instance, research into 2D materials like graphene or transition metal dichalcogenides continues, aiming for faster switching speeds and lower power consumption, which could directly challenge current semiconductor capabilities.
While MACOM actively works with a diverse material portfolio, a truly disruptive material innovation could redefine the market. Companies investing heavily in fundamental material research, such as those exploring quantum dot technology or advanced organic semiconductors, could emerge with superior alternatives. The ongoing global investment in materials research, with significant funding allocated to nanotechnology and advanced materials, underscores the dynamic nature of this threat.
- Material Innovation: Continued R&D into alternative materials is crucial to anticipate and counter potential substitute threats.
- Performance Metrics: New materials offering superior speed, power efficiency, or thermal management capabilities pose the greatest risk.
- Cost Competitiveness: Substitutes that achieve comparable or better performance at a lower manufacturing cost will gain market traction.
- Industry Investment: Significant global investment in material science R&D highlights the potential for disruptive advancements.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs and Customer Choices
The threat of substitutes for MACOM Technology Solutions is influenced by cost-performance trade-offs. Customers might choose less advanced, cheaper alternatives if their specific needs don't demand MACOM's high-performance products, especially when budget is a primary concern. For instance, in certain telecommunications infrastructure projects, if the required data speeds or signal integrity are not at the absolute cutting edge, a more economical component could be selected.
MACOM operates in markets where high performance is often a key differentiator, but a shift in customer priorities towards cost savings could elevate the risk from less sophisticated substitutes. Consider the enterprise networking segment where a business might assess if the marginal performance gain from MACOM’s latest chipsets justifies the higher price compared to a competitor offering adequate, though not top-tier, functionality.
- Cost Sensitivity: A significant portion of the market may prioritize lower upfront costs over marginal performance gains, especially in emerging markets or for less critical applications.
- Performance Thresholds: Applications with less demanding performance requirements, such as basic IoT connectivity or certain industrial control systems, are more susceptible to substitution by lower-cost components.
- Technological Maturation: As substitute technologies mature and their performance improves, they can become viable alternatives for a broader range of MACOM's target applications, increasing competitive pressure.
The threat of substitutes for MACOM's high-performance semiconductor solutions is significant and multifaceted. While MACOM specializes in areas like analog RF, microwave, and millimeterwave technologies, alternative approaches in digital signal processing and novel materials could offer comparable performance, potentially at a lower cost or with different advantages. For instance, advancements in optical interconnects and evolving wireless communication standards present ongoing challenges, compelling MACOM to continually invest in research and development to maintain its competitive edge.
The rise of software-defined networking (SDN) and virtualization also acts as a substitute threat by abstracting network functions from physical hardware. This trend, exemplified by the projected growth of the network function virtualization (NFV) infrastructure market, which was anticipated to surpass $100 billion by 2027, suggests a market shift away from purely hardware-centric solutions. Consequently, MACOM must adapt by focusing on providing enabling technologies for these virtual environments rather than solely relying on discrete hardware components.
Material science innovations represent another critical substitute threat. Breakthroughs in areas like 2D materials, quantum dots, or advanced organic semiconductors could yield devices with superior performance or cost structures, directly challenging MACOM's existing semiconductor capabilities. Given the substantial global investment in materials research, particularly in nanotechnology, the potential for disruptive advancements remains high.
| Technology Area | Potential Substitute | Impact on MACOM | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Communication | Advanced Optical Interconnects | Reduced demand for certain RF components | Competes on speed and potential integration |
| Networking Infrastructure | Software-Defined Networking (SDN) & Virtualization | Shift from hardware to software enablement | NFV market projected over $100B by 2027 |
| Semiconductor Materials | 2D Materials (e.g., Graphene), Quantum Dots | Potential for superior performance/cost | Significant global R&D investment |
| Data Processing | Advanced Digital Signal Processing (DSP) | May reduce need for specialized analog components | Improves efficiency and flexibility |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the high-performance semiconductor sector, especially in specialized areas like analog RF and millimeterwave technologies, demands substantial upfront capital. Consider the costs associated with research and development, building state-of-the-art fabrication plants, and acquiring sophisticated manufacturing equipment. These hefty financial requirements present a formidable hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete. For instance, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication facility can easily run into billions of dollars.
The semiconductor industry, where MACOM operates, is characterized by extremely high barriers to entry, particularly due to the immense need for continuous, cutting-edge research and development. New companies must commit significant capital and time to R&D to even begin competing, a hurdle that naturally deters many potential entrants.
To succeed, a new player would need to cultivate a deep pool of specialized engineering talent and possess advanced technological expertise. This isn't something that can be acquired overnight; it requires years of experience and substantial investment in human capital, making it difficult for newcomers to match established players like MACOM.
MACOM's advantage is underscored by its 'Trusted Foundry' status, a testament to its proven track record and deep-seated expertise in semiconductor manufacturing. This established credibility and long history in the field represent a significant barrier for any new entrant attempting to gain market traction.
MACOM Technology Solutions and its peers possess robust patent portfolios, a significant deterrent to new entrants. These patents cover crucial semiconductor designs and manufacturing techniques, making it challenging for newcomers to enter without infringing on existing intellectual property. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor industry saw significant R&D spending, with major players investing billions, underscoring the high cost of developing proprietary technology.
Developing novel, non-infringing technologies or securing licenses for existing intellectual property represents a substantial financial and temporal hurdle for potential competitors. This barrier is amplified by the fact that patent litigation can be extremely expensive, often running into millions of dollars, further discouraging new market participants in the specialized semiconductor space.
Established Customer Relationships and Supply Chains
MACOM's deep roots in the telecommunications, industrial, defense, and data center sectors mean years have been invested in building trust and strong relationships with its clientele. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this established credibility and reliability. These long-standing partnerships are often reinforced by intricate, integrated supply chain arrangements that are difficult for new entrants to penetrate.
The company's extensive reach, serving over 6,000 customers annually, underscores its deep market penetration and the loyalty it has cultivated. Displacing these incumbent suppliers requires not just competitive pricing but also a proven track record of dependability and a seamless integration into existing operational workflows, which MACOM possesses.
- Years of customer relationship building in key markets.
- Established credibility and reliability of incumbent suppliers.
- Difficulty for new entrants to displace integrated supply chains.
- MACOM's extensive customer base of over 6,000 annually.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The threat of new entrants for MACOM Technology Solutions is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory hurdles and the need for specialized certifications. Particularly in sectors like defense and aerospace, obtaining approvals such as Category 1A Trusted Foundries is a lengthy and complex process, creating a high barrier for new players. This stringent requirement limits the number of companies capable of meeting the rigorous standards for sensitive applications, thereby protecting existing market participants like MACOM.
These regulatory demands translate into considerable upfront investment and technical expertise. New entrants must navigate a labyrinth of compliance requirements, which can delay market entry for years and necessitate substantial financial commitment. For instance, the lead times for obtaining certain defense-related certifications can extend beyond 18-24 months, representing a significant deterrent.
Consequently, the pool of potential competitors equipped to serve high-security and mission-critical markets is inherently small. MACOM benefits from this, as the specialized nature of its end markets, which often demand adherence to standards like those from the U.S. Department of Defense, naturally filters out less prepared entrants.
- High Capital Requirements: The cost associated with meeting advanced manufacturing and security certifications can run into millions of dollars, acting as a substantial barrier.
- Lengthy Approval Cycles: Obtaining necessary certifications, especially for defense contracts, can take upwards of two years, delaying market entry for new firms.
- Specialized Expertise: New entrants need to demonstrate deep technical knowledge and a proven track record in secure manufacturing processes, which is difficult to replicate quickly.
- Limited Market Access: The need for specific, often government-mandated, certifications restricts access to lucrative segments for companies that haven't invested in compliance.
The threat of new entrants for MACOM Technology Solutions is low due to significant capital requirements, the need for specialized talent, and strong customer relationships. Established patent portfolios and regulatory hurdles further deter new players. For instance, in 2023, semiconductor R&D spending by leading firms exceeded billions, highlighting the immense investment needed to compete.
| Barrier | Description | MACOM's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Establishing semiconductor fabrication facilities costs billions. | MACOM has existing, advanced infrastructure. |
| R&D Intensity | Continuous innovation requires substantial, ongoing investment. | MACOM's deep R&D commitment creates a technological moat. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protect proprietary designs. | MACOM's robust patent library deters infringement. |
| Customer Loyalty | Long-standing relationships and integrated supply chains are hard to disrupt. | MACOM serves over 6,000 customers, built on trust and reliability. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Specialized certifications, like 'Trusted Foundry', are time-consuming and costly. | MACOM's established certifications provide access to sensitive markets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for MACOM Technology Solutions is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate data from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
