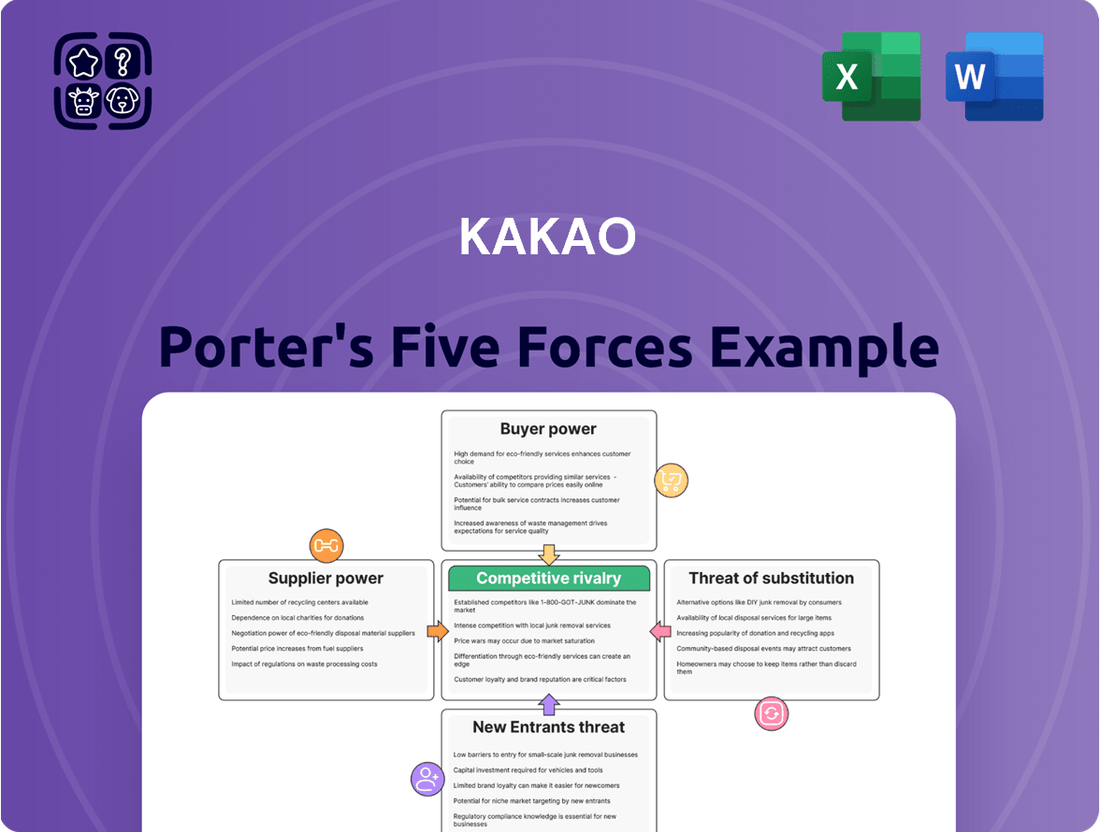
Kakao Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Kakao Bundle
Kakao operates in a dynamic digital landscape where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, and the intensity of rivalry reveals the core challenges and opportunities Kakao faces.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Kakao’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Kakao's reliance on a concentrated group of technology suppliers for cloud infrastructure, AI models, and hardware presents a significant bargaining power challenge. If these suppliers are few and hold dominant positions, they can dictate terms and increase prices for essential services, impacting Kakao's operational costs and innovation capabilities. For example, their partnership with OpenAI for advanced AI capabilities underscores this dependence. In 2023, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $596.8 billion, with a few major players dominating the infrastructure landscape, giving them considerable leverage.
In the digital content arena, Kakao's dependence on creators and IP holders significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, in the competitive webtoon market, popular artists can leverage their appeal for more favorable revenue splits, directly impacting Kakao's profitability. The global expansion of Kakao Entertainment, including strategic alliances in 2024 with major players like NetEase for gaming and Billboard for music-related ventures, underscores the necessity of securing premium content and the leverage these creators hold.
Kakao's reliance on payment gateway providers for its vast fintech and e-commerce activities means these infrastructure partners can wield considerable bargaining power. This leverage is amplified by the critical need for secure and efficient transaction processing, a non-negotiable for Kakao's operations.
In 2024, the digital payment segment in South Korea continued its robust growth, capturing a substantial market share. This expanding market, while offering opportunities, also means that specialized providers of essential payment gateway services hold a degree of influence over terms and pricing.
Mobility Service Providers (Drivers)
The bargaining power of drivers within Kakao Mobility's ride-hailing services is a significant consideration. A shortage of drivers, which can be influenced by economic conditions or the attractiveness of competing platforms, directly strengthens their negotiating position. For instance, in many urban centers globally, driver shortages in 2024 have led to increased incentives and commission rates offered by ride-hailing companies to attract and retain drivers.
The presence of strong driver unions or associations can further amplify this power. These groups can collectively bargain for better commission structures, improved working conditions, and more favorable terms of service, potentially impacting Kakao Mobility's operational costs and profitability. Reports from late 2023 and early 2024 have highlighted increased unionization efforts among gig economy workers, including ride-share drivers, across various regions.
Moreover, the availability of alternative platforms offering superior benefits or higher earning potential directly challenges Kakao Mobility. If drivers can easily switch to competitors, Kakao Mobility may be forced to offer more competitive terms to prevent attrition. This dynamic is particularly relevant as new mobility service providers enter or expand in markets where Kakao Mobility operates.
- Driver Supply: Fluctuations in driver availability directly impact their bargaining power, with shortages increasing their leverage.
- Unionization: Organized driver groups can collectively negotiate for better terms, potentially raising operational costs for platforms.
- Competition: The presence of alternative platforms offering better incentives can draw drivers away, forcing existing platforms to improve their offers.
- Regulatory Environment: Kakao Mobility has faced scrutiny regarding its relationships with taxi operators, suggesting potential regulatory influence on driver-platform dynamics.
Talent and Human Capital
For Kakao, a technology-driven company, the bargaining power of suppliers in the realm of talent and human capital is substantial. Highly skilled professionals such as software engineers, AI specialists, product managers, and cybersecurity experts are critical inputs. The intensely competitive technology talent market within South Korea significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these individuals. This can translate into upward pressure on wages and increased expenses related to talent acquisition and retention for Kakao.
Kakao's commitment to talent development and securing skilled personnel is evident in its sustainability initiatives. For instance, in its 2023 ESG report, Kakao detailed investments in training programs and efforts to foster a competitive employee value proposition. The demand for specialized tech skills in 2024 remains high, with reports indicating a shortage in areas like AI development, further strengthening the position of qualified candidates.
- Critical Talent: Software engineers, AI specialists, product managers, and cybersecurity experts are essential suppliers.
- Market Dynamics: South Korea's competitive tech talent market grants these individuals significant bargaining power.
- Cost Implications: This bargaining power leads to higher wage demands and increased recruitment costs for Kakao.
- Company Initiatives: Kakao's ESG reports highlight ongoing efforts in talent acquisition and training to mitigate these pressures.
Kakao's reliance on specialized technology suppliers for critical infrastructure like cloud computing and advanced AI models grants these providers significant leverage. As the global cloud market, valued at nearly $600 billion in 2023, is dominated by a few major players, these entities can dictate terms, impacting Kakao's operational expenses and future innovation capacity.
The bargaining power of content creators, particularly in Kakao's webtoon and music divisions, is substantial. Popular artists and IP holders can negotiate more favorable revenue splits, directly affecting profitability. Kakao's strategic partnerships in 2024, such as with NetEase for gaming, highlight the importance of securing premium content and the influence these creators wield.
Payment gateway providers hold considerable sway due to the essential nature of secure and efficient transaction processing for Kakao's fintech and e-commerce operations. The robust growth of South Korea's digital payment sector in 2024 further solidifies the influence of specialized providers within this critical infrastructure.
In Kakao Mobility, driver supply is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. Shortages, driven by economic conditions or competitor incentives in 2024, strengthen drivers' negotiating positions, leading to increased costs for ride-hailing platforms. Organized driver groups can amplify this power through collective bargaining for better terms.
What is included in the product
Kakao Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry to understand Kakao's strategic position and profitability drivers.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing Kakao's bargaining power with suppliers and buyers.
Streamline strategic planning by rapidly assessing the threat of new entrants and substitutes in Kakao's ecosystem.
Customers Bargaining Power
KakaoTalk's dominance in the South Korean messaging market, boasting over 93% of users in 2023 and a projected 97% in 2025, presents a complex dynamic for customer bargaining power. While such high user concentration might initially suggest limited individual leverage, the platform's very strength lies in its extensive network effects.
This means that while one user might have little individual power, the collective power of its 48.95 million domestic monthly active users (as of Q4 2024) is substantial. A mass exodus, however unlikely, would cripple the platform, giving users a latent, albeit rarely exercised, form of collective bargaining power.
While Kakao's integrated ecosystem aims for user stickiness, customers possess significant bargaining power due to low switching costs for individual services. For instance, a user can effortlessly opt for a different music streaming platform, a dedicated payment app, or an alternative ride-hailing service without leaving the Kakao ecosystem entirely. This ability to cherry-pick best-in-class alternatives for specific needs grants users considerable leverage.
This ease of switching for individual components directly impacts Kakao's ability to retain users across all its offerings. In South Korea's dynamic e-commerce landscape, this is evident in the high rate of 'multi-homing,' where consumers actively use multiple platforms for different needs, diminishing the lock-in effect of any single integrated service.
Advertisers and merchants leverage their ad spend and sales volume on Kakao's platform, giving them significant bargaining power. This allows them to negotiate for better terms, enhanced analytics, and potentially lower transaction fees, particularly if viable alternative platforms exist to reach their customer base.
Kakao's revenue streams heavily rely on advertising and e-commerce services, making these businesses crucial partners. For instance, in 2023, Kakao's advertising revenue saw a notable increase, underscoring the importance of these clients to their financial performance. Their ability to shift their spending to competing services or to demand more favorable arrangements directly impacts Kakao's profitability.
Content Consumers' Price Sensitivity
Consumers of digital content, such as music, webtoons, and games, are generally quite sensitive to price. This means Kakao faces a challenge when trying to increase prices for its content services, as users might easily switch to competitors offering similar content or free alternatives. For instance, the digital media market in South Korea is expanding, with video content being the most dominant segment, indicating a diverse and competitive landscape where pricing is a critical factor.
This price sensitivity directly impacts Kakao's bargaining power. With numerous free options and competing subscription models available, users have a low switching cost. In 2023, the South Korean digital content market was valued at approximately 11.5 trillion KRW (around $8.5 billion USD), with video content accounting for a significant portion of this, underscoring the intense competition and the importance of competitive pricing strategies.
- Price Sensitivity: Users of digital content like music, webtoons, and games are highly aware of pricing and readily explore free or cheaper alternatives.
- Competitive Landscape: The growing digital media market, particularly in video, offers consumers many choices, intensifying pressure on Kakao to maintain competitive pricing.
- Risk of Churn: Aggressively raising prices could lead to a noticeable exodus of users to rival platforms, impacting Kakao's revenue streams.
- Market Dynamics: The overall growth of the digital media sector in South Korea, projected to continue its upward trend, highlights the need for Kakao to balance profitability with user retention through strategic pricing.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Consumer Advocacy
Increased regulatory oversight, especially in South Korea's digitally integrated environment, amplifies customer influence through robust consumer protection statutes and anti-monopoly enforcement. These regulations ensure fairer market practices, giving consumers a stronger voice.
Regulatory bodies can actively intervene to protect consumers from dominant platform behavior. For instance, Kakao Mobility faced penalties for unfair practices, demonstrating how regulators can curb monopolistic tendencies and consequently bolster the bargaining power of customers.
- Consumer Protection Laws: South Korea's stringent consumer protection laws empower individuals by providing recourse against unfair business practices.
- Anti-Monopoly Actions: Government agencies actively monitor and penalize companies exhibiting monopolistic behavior, thereby leveling the playing field for consumers.
- Regulatory Fines: In 2024, Kakao Mobility was fined approximately 10 billion KRW (roughly $7.5 million USD at the time) for alleged unfair practices, a clear signal of regulatory intervention benefiting consumers.
- Enhanced Consumer Leverage: Such regulatory actions directly translate into increased bargaining power for customers, who can now expect more transparent and equitable service terms.
Kakao's vast user base, exceeding 48.95 million monthly active users in South Korea by Q4 2024, creates a unique dynamic for customer bargaining power. While individual users have minimal sway, the sheer collective number of users represents a formidable latent power, capable of impacting the platform through mass migration, though this is highly improbable.
Customers exhibit significant bargaining power due to low switching costs for individual services within Kakao's integrated ecosystem. Users can easily opt for alternative providers for music, payments, or ride-hailing without abandoning Kakao entirely, diminishing the platform's overall lock-in effect.
Advertisers and merchants, key revenue drivers for Kakao, leverage their significant ad spend and sales volume. This allows them to negotiate favorable terms, better analytics, and potentially reduced transaction fees, especially with the availability of competing platforms to reach consumers.
The digital content market, valued around 11.5 trillion KRW in 2023, features highly price-sensitive consumers. Kakao faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing for services like music and webtoons, as users can readily switch to free or cheaper alternatives, impacting Kakao's revenue streams.
Regulatory oversight, including consumer protection laws and anti-monopoly enforcement, further empowers customers. For instance, Kakao Mobility's 2024 fine of approximately 10 billion KRW (around $7.5 million USD) for unfair practices highlights how regulations can enhance consumer leverage and ensure fairer market practices.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Kakao | Example/Data Point |
| Network Effects vs. Collective Power | High user concentration creates network effects but also a latent collective bargaining power. | Lowers individual power, but mass defection, however unlikely, could be detrimental. | 48.95 million domestic MAU (Q4 2024). |
| Low Switching Costs (Individual Services) | Users can easily switch to competitors for specific services (e.g., music, payments). | Reduces user stickiness and increases the incentive to "cherry-pick" best alternatives. | Ease of using separate payment apps or music streaming services. |
| Bargaining Power of Advertisers/Merchants | Key clients leverage ad spend and sales volume. | Enables negotiation for better terms, lower fees, and improved analytics. | Kakao's advertising revenue increased in 2023, highlighting client importance. |
| Price Sensitivity of Digital Content Consumers | Users are sensitive to prices for music, webtoons, and games. | Limits Kakao's ability to raise prices and increases risk of user churn. | South Korean digital content market valued at ~11.5 trillion KRW (2023). |
| Regulatory Environment | Consumer protection laws and anti-monopoly enforcement. | Empowers consumers and limits monopolistic practices, increasing customer leverage. | Kakao Mobility fined ~10 billion KRW in 2024 for unfair practices. |
Full Version Awaits
Kakao Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Kakao Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase. It details Kakao's competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This document is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering a complete and accurate assessment without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Kakao faces fierce competition across its diverse business verticals. In the core messaging and social media space, while KakaoTalk remains dominant, Instagram is gaining traction, especially among younger demographics, signaling a shifting user preference. This intensity is mirrored in other key areas of Kakao's operations.
The rivalry is particularly pronounced when facing domestic powerhouse Naver, which competes directly in search, webtoons, and fintech services. Globally, Kakao contends with tech giants like Google, whose YouTube platform is a major force in digital content, and Meta, whose Instagram and WhatsApp are formidable in social communication and messaging. These broad-reaching competitors create a complex competitive landscape.
In specialized sectors, Kakao's fintech arm competes with local disruptors like Toss, which has rapidly expanded its user base and service offerings. Similarly, its mobility services are challenged by international players such as Uber, alongside local alternatives like TADA, all vying for market share in the burgeoning ride-sharing and transportation sectors.
Kakao's competitive landscape is a dynamic interplay between its expansive ecosystem and the disruptive force of specialized niche players. This rivalry is most acutely felt in its competition with Naver, another dominant South Korean tech giant, as both companies vie to integrate more aspects of daily life into their respective platforms.
While Kakao leverages its integrated services, such as KakaoTalk, Kakao Pay, and Kakao Mobility, to foster user loyalty and convenience, niche players can excel by offering more refined or innovative solutions within specific service areas. For instance, a specialized delivery app might offer faster or more diverse options than Kakao's integrated delivery service, potentially drawing users away from Kakao's broader offering for that particular need.
Kakao's strategic response to this competitive pressure involves deepening the integration of its diverse services, aiming to create a sticky, seamless user experience that discourages users from seeking alternatives. This approach seeks to capitalize on network effects and user habituation, making it more convenient for users to stay within the Kakao universe for multiple daily tasks.
The South Korean market for Kakao's core services, such as messaging and its portal, is highly saturated. With internet penetration already at very high levels, growth opportunities are scarce, forcing intense competition for user attention and revenue. This dynamic means Kakao primarily gains ground by taking market share from rivals or by venturing into less crowded business areas.
Evidence of this intense rivalry is seen in user engagement trends. KakaoTalk experienced a slight dip in monthly active users in early 2024. Furthermore, in December 2023, YouTube overtook KakaoTalk as the most frequently used mobile application in South Korea, highlighting the challenge Kakao faces in maintaining its dominance in its core messaging service.
Aggressive Pricing and Innovation
Competitors in the South Korean fintech space, including players like Naver Pay and Toss, frequently engage in aggressive pricing strategies and introduce innovative features. This intense rivalry means Kakao Pay must constantly invest in research and development, alongside marketing efforts, to safeguard its market share and user loyalty. For instance, many platforms offer substantial cashback or discount promotions to attract new users, a trend that has intensified throughout 2024.
Strategic alliances are also a common tactic, allowing competitors to broaden their service offerings and reach. This dynamic environment, characterized by rapid technological advancements, is projected to drive significant growth in South Korea's fintech market. Kakao's response involves not only matching competitor innovations but also anticipating future market needs to maintain its leadership position.
- Aggressive Pricing: Competitors often use price wars and promotional offers to gain market share.
- Feature Innovation: Continuous introduction of new services and user experience enhancements is a key battleground.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with other businesses are crucial for expanding reach and service capabilities.
- R&D Investment: Kakao must allocate significant resources to innovation to keep pace.
- Market Growth: The South Korean fintech market is expected to expand, fueled by ongoing technological progress.
Regulatory Intervention Shaping Competition
Government regulations and antitrust actions are actively reshaping the competitive dynamics within the ride-hailing sector. The Korea Fair Trade Commission (KFTC) has demonstrated a proactive stance, investigating and penalizing dominant players to foster a more equitable market. This regulatory intervention, including significant fines, signals a commitment to preventing monopolistic practices and ensuring fairer competition for emerging players.
Recent actions, such as the KFTC's investigation and potential fines against Kakao Mobility in 2023, exemplify this trend. These interventions aim to curb market dominance and create opportunities for smaller competitors to gain traction. Such regulatory scrutiny can significantly alter the competitive intensity by imposing constraints on established companies and encouraging a more diverse market structure.
- Government oversight: The KFTC's active role in monitoring and enforcing fair competition laws directly impacts market dynamics.
- Antitrust actions: Fines and investigations against dominant players like Kakao Mobility level the playing field.
- Market leveling: Regulatory intervention aims to prevent monopolistic practices, benefiting smaller competitors.
- Increased scrutiny: Ongoing investigations create uncertainty and can influence strategic decisions of major market participants.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force impacting Kakao across its various business segments. In its core messaging platform, while KakaoTalk remains a leader, it faces increasing competition, notably from Instagram, which is gaining traction with younger users in South Korea. This indicates a dynamic shift in user preferences that Kakao must actively address.
The intensity of this rivalry is amplified by domestic giant Naver, a direct competitor in search, webtoons, and fintech. Globally, Kakao contends with tech titans like Google and Meta, whose platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and WhatsApp present formidable challenges in digital content and social communication. These broad-based competitors create a complex and demanding competitive environment for Kakao.
Within specialized sectors, Kakao's fintech services compete with agile domestic players like Toss, which has rapidly expanded its user base and service offerings. Similarly, its mobility division faces pressure from international giants such as Uber, alongside local alternatives like TADA, all vying for market share in the competitive ride-sharing industry. This demonstrates Kakao's need for continuous innovation and strategic adaptation to maintain its market position.
| Competitor | Primary Competitive Area | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Instagram (Meta) | Social Media, Messaging | Targeting younger demographics, visual content focus |
| Naver | Search, Webtoons, Fintech | Ecosystem integration, diverse service offerings |
| Digital Content (YouTube) | Dominant platform, content creator ecosystem | |
| Toss | Fintech | User-friendly interface, aggressive promotions |
| Uber | Mobility | Global brand recognition, technological advancement |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Kakao's integrated digital services is significant, stemming from users' ability to piece together a suite of specialized applications. Instead of relying on Kakao's all-encompassing platform, consumers can opt for individual apps that excel in specific functionalities.
For instance, while KakaoTalk remains a dominant force in messaging, users readily adopt alternatives like Telegram or WhatsApp for communication. Similarly, for music streaming, services such as Spotify or YouTube Music offer robust libraries, and for payments, Toss and Naver Pay provide specialized financial solutions.
This fragmentation means that even though Kakao offers a broad range of services, users are not locked into its ecosystem for every need. The availability of best-in-class single-purpose apps directly challenges Kakao's proposition of convenience through integration.
In 2024, the ride-hailing market, for example, saw continued competition from platforms like TADA, directly impacting Kakao Mobility's market share in that specific segment, further illustrating the threat of specialized substitutes.
Despite the growing digital landscape, traditional offline alternatives continue to pose a threat to some of Kakao's services. For instance, cash payments remain a viable substitute for mobile payment solutions, and traditional taxis still compete with ride-hailing platforms like Kakao T. Similarly, physical media can be an alternative to digital content consumption. In 2023, cash transactions still accounted for a notable portion of consumer spending in South Korea, although mobile payments are steadily gaining ground.
New technologies, particularly in artificial intelligence, pose a significant threat by enabling substitute services that could bypass Kakao's core offerings. Imagine AI-powered virtual assistants deeply integrated into smartphones, handling many communication tasks currently managed through KakaoTalk. This could reduce reliance on a dedicated messaging app for a portion of user interactions.
Kakao is actively exploring these advancements, notably through its partnership with OpenAI to integrate AI into its ecosystem. This strategic move aims to leverage emerging technologies, but it also highlights the industry's shift towards AI-centric solutions that could redefine user communication habits and potentially fragment the market for traditional messaging platforms.
Social Media Platforms as Communication Substitutes
Other social media platforms are increasingly offering messaging and community features that directly compete with KakaoTalk's core social functions. This is particularly evident among younger users who are drawn to platforms like Instagram for its integrated messaging and growing community-building capabilities. For instance, Instagram's user base in South Korea has seen consistent growth, indicating a shift in how younger demographics prefer to communicate and connect online, potentially eroding KakaoTalk's traditional stronghold.
These evolving user preferences mean that while KakaoTalk remains dominant, the threat of substitution is becoming more pronounced. The ability of platforms like Instagram to bundle messaging with content sharing and community engagement presents a compelling alternative. As these platforms enhance their communication features, they siphon away users, especially for casual social interactions.
Here's a breakdown of how substitutes challenge KakaoTalk:
- Direct Messaging Competition: Platforms like Instagram Direct and Facebook Messenger offer robust messaging features, directly substituting for KakaoTalk's primary communication function.
- Community Features: Instagram's Stories and evolving group features allow for community building and content sharing, mimicking some of KakaoTalk's group chat functionalities.
- Demographic Shifts: Younger users, in particular, are showing a preference for integrated social experiences, where messaging is seamlessly part of a broader social media engagement.
- Market Share Trends: Instagram's increasing share of the social networking market in Korea signals a growing willingness among users to adopt alternative platforms for their social communication needs.
Global Platforms with Localized Offerings
Global tech giants are increasingly tailoring their services to the South Korean market, presenting a strong threat of substitution for Kakao. For instance, platforms like Google and Meta are investing heavily in local content and features, aiming to capture user attention. If these global players successfully integrate compelling localized offerings, it could lead to a gradual migration of users away from Kakao's established ecosystem.
The competitive landscape in South Korea is intensifying, with global technology behemoths posing a growing challenge to domestic players like Kakao. These international companies leverage their vast resources and technological prowess to introduce services that directly compete with Kakao's core offerings.
- Increased Competition: Global platforms like Google, with its extensive search and advertising capabilities, and Meta, with its social media dominance, are expanding their localized services in South Korea.
- Localized Content and Features: These global players are actively developing or acquiring local content and features to resonate with South Korean users, potentially drawing them away from Kakao.
- User Migration Risk: A compelling user experience and attractive localized offerings from global competitors could lead to a significant substitution threat, impacting Kakao's market share and user engagement.
- Market Dynamics: By mid-2024, global digital advertising spending in South Korea was projected to reach approximately $5.5 billion, indicating the significant market presence and potential influence of these international platforms.
The threat of substitutes remains a critical factor for Kakao, as users can assemble a diverse set of specialized applications to fulfill their needs. This means users aren't necessarily "locked in" to Kakao's ecosystem for every service, with alternatives readily available. For instance, in 2024, while Kakao Pay is popular, alternative fintech solutions like Toss continue to gain traction, offering specialized financial services that directly compete.
Furthermore, emerging technologies like advanced AI assistants could fundamentally alter how people communicate and access information, potentially replacing functions currently served by KakaoTalk. Even traditional offline methods, like cash transactions, which accounted for roughly 20% of consumer spending in South Korea in 2023, still represent a substitute for Kakao's digital payment services.
The increasing sophistication of other social media platforms, such as Instagram, which offers integrated messaging and community features, also poses a substitution threat, particularly for younger demographics. This trend is highlighted by Instagram's consistent user growth in South Korea, indicating a preference for bundled social experiences that can detract from Kakao's core messaging dominance.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into Kakao's diverse markets is significantly mitigated by the high capital requirements and the necessity for substantial infrastructure investment. Developing and maintaining a robust technological backbone, including advanced data centers and expansive service networks, demands considerable financial outlay. For instance, building a comprehensive mobile platform with integrated services, akin to Kakao's ecosystem, requires immense capital resources, acting as a substantial barrier to entry.
Kakao's own capital expenditure patterns illustrate this point. The company reported a decrease in capital expenditure in the fourth quarter of 2024, largely due to the completion of significant data center investments. This ongoing need for capital-intensive infrastructure development means that new players would face immediate and substantial financial hurdles to compete effectively with Kakao's established operational capacity.
KakaoTalk's formidable presence in South Korea, boasting a staggering 97% market share as of recent data, creates incredibly strong network effects. This means that the more people use KakaoTalk, the more valuable it becomes for everyone else, making it exceptionally challenging for new messaging applications to gain a foothold.
The sheer number of active users on KakaoTalk acts as a significant barrier to entry for any would-be competitor in the communication space. As the platform becomes the default for a vast majority of the population, the cost and effort for a new entrant to replicate this user base and its associated value are immense.
Furthermore, KakaoTalk has solidified its position as the primary channel for businesses to engage with consumers in South Korea. This strategic integration means that companies are heavily reliant on KakaoTalk for customer interaction and marketing, further cementing its dominance and discouraging alternatives.
Kakao has built substantial brand loyalty, making it difficult for new competitors to attract users. Consider that in 2023, KakaoTalk remained the dominant messaging app in South Korea, boasting over 47 million monthly active users. This deeply embedded user habit and trust in Kakao's services presents a significant barrier to entry.
New entrants face the immense task of not only matching Kakao's functionality but also convincing users to switch from their established routines. This requires substantial investment in marketing and product differentiation to even approach Kakao's entrenched position.
Kakao's strength lies in its integrated ecosystem, seamlessly connecting various aspects of daily life, from communication and finance to transportation and entertainment. This creates a powerful network effect that new entrants would struggle to replicate.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Costs
Operating in sectors where Kakao is active, such as fintech and mobility, presents significant regulatory challenges for new entrants. Navigating complex compliance requirements, including financial regulations, data privacy laws like the Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA), and obtaining necessary industry-specific licenses, demands substantial investment in time and resources. For instance, obtaining a payment gateway license in South Korea can take several months and involve rigorous scrutiny of business practices and financial stability.
The South Korean government's stance on fostering fintech innovation, as evidenced by initiatives like the fintech regulatory sandbox, can mitigate some barriers. However, the inherent complexity and cost of compliance remain a substantial deterrent for potential new players aiming to compete with established entities like Kakao.
- Regulatory Burden: New entrants face extensive compliance requirements in areas like financial services and data handling.
- Licensing Costs: Obtaining necessary operating licenses, especially in fintech, incurs significant fees and time.
- Data Privacy: Strict adherence to data protection laws, such as PIPA, adds to operational expenses and complexity.
- Government Support vs. Reality: While regulatory sandboxes exist, the overall cost and time for full compliance remain high.
Access to Talent and Strategic Partnerships
New entrants into Kakao's market face substantial hurdles in acquiring skilled personnel and forging crucial business alliances. The competition for top-tier tech talent in South Korea is intense, making it difficult for newcomers to attract and retain the expertise needed to challenge established players like Kakao, which boasts a strong brand and significant financial backing.
Building a comprehensive ecosystem, essential for competing with Kakao's integrated services, requires securing strategic partnerships with content creators, service providers, and various merchants. This process is inherently challenging for new entrants who lack Kakao's existing network and proven track record. Kakao has demonstrated its ability to secure such partnerships, notably with companies like OpenAI and NetEase, enhancing its service offerings and market position.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: New entrants must compete with Kakao's established employer brand, which can attract and retain highly skilled tech professionals in South Korea's competitive labor market.
- Partnership Formation Difficulty: Establishing the broad network of content providers, merchants, and other businesses necessary to replicate Kakao's ecosystem is a significant barrier for newcomers.
- Kakao's Strategic Alliances: Kakao's existing partnerships, such as those with OpenAI for AI development and NetEase for gaming content, provide it with distinct competitive advantages that are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants to Kakao's core markets is significantly diminished by the immense capital investment required for infrastructure and platform development. Kakao's established network effects, particularly with KakaoTalk's dominant 97% market share in South Korea, create a formidable barrier, as replicating such a vast user base is prohibitively difficult and costly for newcomers. Furthermore, Kakao's strong brand loyalty and integrated ecosystem, spanning finance to mobility, present substantial challenges for any new player attempting to gain traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for infrastructure (data centers, networks) and platform development. | Substantial financial hurdle, limiting entry to well-funded organizations. |
| Network Effects | KakaoTalk's dominant user base (over 47 million MAU in 2023) increases its value with each new user. | Makes it extremely difficult for new communication apps to attract users away from the established platform. |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Deeply embedded user habits and trust in Kakao's integrated services. | New entrants must overcome inertia and offer significant advantages to persuade users to switch. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Complex compliance in fintech and data privacy (e.g., PIPA) requires time and investment. | Adds significant operational expenses and potential delays for new businesses. |
| Talent & Partnerships | Competition for skilled tech talent and difficulty in replicating Kakao's strategic alliances. | Newcomers struggle to acquire necessary expertise and build a comparable ecosystem. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Kakao Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Kakao's official investor relations materials, financial statements, and publicly available earnings calls. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research reports and market analysis firms specializing in the Korean tech sector.
