Jungheinrich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Jungheinrich Bundle
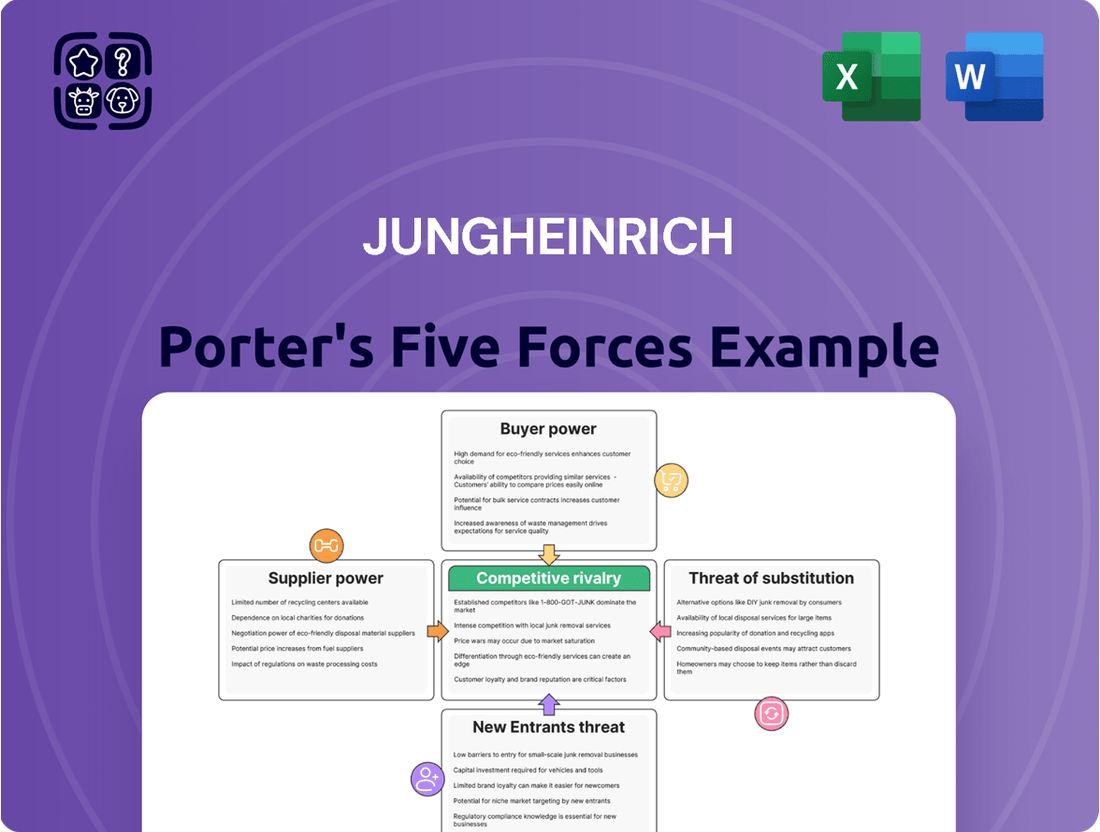
Jungheinrich faces moderate bargaining power from its buyers, as price sensitivity and product differentiation play crucial roles in the material handling equipment sector. The threat of substitutes, while present in the form of alternative logistics solutions, is generally low due to the specialized nature of Jungheinrich's offerings.
The intensity of rivalry within the industry is high, with several established global players competing on innovation, service, and price. Supplier power is also a significant consideration, as key component costs and availability can impact Jungheinrich's profitability.
The threat of new entrants is moderate, requiring substantial capital investment and technological expertise to compete effectively. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Jungheinrich’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration plays a crucial role in the bargaining power of suppliers within the intralogistics and material handling sector. Jungheinrich, like other players in this industry, depends on specialized components such as advanced batteries, particularly lithium-ion technology, sophisticated electronic control systems, and specific grades of steel.
When the supply of these critical inputs is dominated by a small number of manufacturers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This is because Jungheinrich, and its competitors, have fewer alternatives for sourcing these essential parts.
For instance, if a few key battery manufacturers hold a significant market share, they can dictate terms, potentially leading to higher prices or less favorable supply agreements for Jungheinrich. As of early 2024, the global lithium-ion battery market, crucial for electric forklifts and automated guided vehicles, is increasingly consolidated among a few major Asian producers.
Furthermore, Jungheinrich's reliance on any unique or patented technologies sourced from a limited number of specialized suppliers would inherently empower those suppliers. They could leverage this exclusivity to command higher prices or impose stricter conditions, directly impacting Jungheinrich's cost structure and operational flexibility.
High switching costs for Jungheinrich would significantly bolster supplier power. If Jungheinrich faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when changing component suppliers, such as the need for re-tooling production lines or re-certifying new parts, suppliers gain leverage. For example, if a specialized hydraulic system provider requires extensive integration and testing for any new equipment, Jungheinrich's reluctance to switch would benefit that supplier.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for Jungheinrich. When suppliers provide highly differentiated or proprietary components, particularly in advanced areas like automation software, AI algorithms, or specialized battery chemistries, they gain leverage. Jungheinrich's collaborations, such as its partnership with EP Equipment for lithium-ion powered vehicles, highlight reliance on suppliers with unique technological capabilities.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Jungheinrich's core business of material handling equipment manufacturing or intralogistics solutions can significantly bolster their bargaining power. This potential move would allow them to bypass Jungheinrich and engage directly with end-customers, capturing a larger portion of the value chain.
While this is a less frequent occurrence for component suppliers due to the intricate nature of final product assembly and the requirement for comprehensive after-sales service, the mere existence of this threat gives suppliers leverage. For instance, if a key supplier of advanced battery technology for electric forklifts were to develop its own integrated forklift solution, it could directly compete with Jungheinrich.
- Supplier Integration Threat: Suppliers entering Jungheinrich's market increases their power.
- Bypassing Jungheinrich: Direct sales to end-customers cut out the manufacturer.
- Complexity Barrier: High complexity in assembly and service often limits this threat for component suppliers.
- Industry Example: A hypothetical advanced battery supplier developing its own electric forklift line illustrates the risk.
Importance of Jungheinrich to Suppliers
Jungheinrich's significance as a customer directly impacts its bargaining power with suppliers. If Jungheinrich constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is likely more amenable to favorable pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, suppliers heavily reliant on the forklift and warehouse equipment sector, where Jungheinrich is a major player, would be more inclined to offer competitive pricing to retain this key client.
Conversely, if Jungheinrich represents a minor segment of a supplier's business, its leverage diminishes. A supplier serving a broad market with many customers would have less incentive to compromise on terms for a single, smaller client. This dynamic means Jungheinrich's negotiation strength is not absolute but is contingent on the supplier's own market position and dependency.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which suppliers depend on Jungheinrich for revenue is a critical factor in their willingness to negotiate.
- Market Share Concentration: If a supplier's market share is heavily concentrated with Jungheinrich, their bargaining power is reduced.
- Jungheinrich's Purchasing Volume: Higher purchasing volumes by Jungheinrich can increase its influence over suppliers.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with diverse customer bases may exhibit less flexibility when dealing with Jungheinrich.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Jungheinrich is influenced by the concentration of suppliers for critical components like advanced batteries and specialized electronics.
When only a few manufacturers supply essential parts, they can dictate terms, leading to higher costs for Jungheinrich, especially in the consolidated lithium-ion battery market as of early 2024.
High switching costs for Jungheinrich, such as re-tooling, also empower suppliers by making it expensive to change providers, giving them leverage over pricing and contract conditions.
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Jungheinrich's position in the material handling equipment industry.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visually intuitive framework—no more guessing where market pressures originate.
Customers Bargaining Power
Jungheinrich's customer base is quite broad, ranging from smaller enterprises to major global corporations and leading e-commerce players. This diversity generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power.
However, if a few very large clients represent a substantial percentage of Jungheinrich's total sales, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases significantly. For instance, if a single customer accounted for over 10% of revenue, they could leverage their purchasing volume to demand lower prices or specific product modifications.
While specific 2024 customer concentration figures for Jungheinrich are not publicly disclosed in detail, industry trends suggest that large logistics and automotive clients often represent significant revenue streams for industrial equipment manufacturers.
These major clients can also influence product development by requesting tailored solutions, which can be a double-edged sword, potentially increasing costs but also fostering stronger customer loyalty if managed effectively.
The degree to which Jungheinrich's products are standardized significantly influences customer bargaining power. For instance, basic pallet trucks, which are largely commoditized, allow customers to easily compare prices and switch suppliers, thereby amplifying their leverage.
Conversely, Jungheinrich's more sophisticated offerings, such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and integrated warehouse management systems, are highly customized and complex. This complexity, coupled with the significant investment required for implementation and integration, inherently reduces a customer's ability to switch easily, thus diminishing their bargaining power.
Switching costs for customers are a key factor in understanding their bargaining power. For businesses relying on Jungheinrich's equipment, the expense and disruption involved in replacing an entire fleet of forklifts, integrating new warehouse management software, or reconfiguring automated systems can be substantial. This complexity inherently limits their ability to easily switch to a competitor.
Jungheinrich's integrated approach, offering comprehensive service, maintenance, and rental solutions, further enhances these switching costs. For instance, a customer heavily invested in Jungheinrich's tailored maintenance plans for their fleet might face significant administrative and operational hurdles to switch providers, creating a strong element of customer lock-in.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor influencing Jungheinrich's bargaining power of customers. If material handling equipment constitutes a substantial part of a customer's operating expenses or if they operate in intensely competitive sectors with narrow profit margins, they will naturally be more attuned to pricing. This heightened sensitivity can pressure suppliers like Jungheinrich to offer more competitive terms.
The economic climate of 2024, marked by elevated interest rates, likely amplified this price sensitivity. For businesses considering significant investments such as new warehouse construction, the increased cost of capital makes the total cost of ownership, including equipment financing, a more critical decision point. This situation can lead customers to scrutinize prices more rigorously.
- High Operating Cost Impact: Customers for whom material handling equipment is a significant operational expense are more likely to seek the lowest possible prices.
- Competitive Industry Pressure: Businesses in industries with thin profit margins, such as retail or manufacturing, often pass cost savings onto their own customers, making them price-conscious.
- 2024 Economic Environment: Persistent high interest rates in 2024 increased the cost of financing new capital equipment, intensifying price sensitivity for large purchases like warehouse automation.
- Demand for Value: Customers are not just looking for the lowest price but also the best value, meaning they expect reliable equipment that minimizes downtime and operational inefficiencies.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, particularly those with significant logistical footprints like Amazon, possess the potential to develop their own material handling solutions or bring maintenance and system integration in-house. This threat, though facing high barriers to entry, directly enhances their bargaining power by presenting a viable alternative to relying solely on external suppliers like Jungheinrich.
For instance, as of 2024, major e-commerce players continue to invest heavily in automation and robotics for their warehouses. Amazon’s continued expansion of its own fulfillment center technology, including sophisticated sorting systems and autonomous mobile robots, illustrates this trend. This internal development capability reduces their dependence on third-party providers for core material handling functions, giving them leverage in negotiations for any Jungheinrich services or equipment they still procure.
- Customer Integration Potential: Large logistics companies can invest in developing proprietary material handling systems.
- Reduced Supplier Dependence: This capability creates a credible alternative to existing suppliers, increasing customer leverage.
- Market Impact (2024): Ongoing investments by major e-commerce firms in warehouse automation, like Amazon's robot fleets, exemplify this trend.
Jungheinrich's customers, especially large ones, wield considerable bargaining power due to their purchasing volume and the potential to develop in-house solutions. Factors like the commoditization of basic equipment and high switching costs for integrated systems also play a role.
The economic climate of 2024, with its higher interest rates, amplified customer price sensitivity, pushing them to demand more value and competitive pricing. This is particularly true for customers where material handling equipment represents a significant operational expense.
Major e-commerce players, such as Amazon, continue to invest in proprietary warehouse automation as of 2024, reducing their reliance on external suppliers and strengthening their negotiation position with companies like Jungheinrich.
Jungheinrich's ability to offer tailored, complex solutions like AGVs can mitigate customer bargaining power by increasing switching costs. However, the overall leverage is influenced by the proportion of standardized versus specialized equipment in a customer's portfolio.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Example |
| Customer Concentration | High for large clients, low for many small ones. | While specific figures are private, large logistics clients often represent significant revenue for industrial equipment makers. |
| Product Standardization | Higher for commoditized products, lower for specialized systems. | Basic pallet trucks are easily compared; AGVs and integrated systems have high switching costs. |
| Switching Costs | Substantial for integrated systems and large fleets. | Replacing a fleet or reconfiguring automated systems involves significant expense and disruption. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increased by high operating costs and competitive pressures. | 2024's elevated interest rates made financing capital equipment more expensive, heightening price scrutiny. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Credible for large, technologically advanced clients. | Amazon's continued investment in its own warehouse robotics (as of 2024) showcases this trend. |
Same Document Delivered
Jungheinrich Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It contains a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Jungheinrich, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company's market position. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the material handling equipment industry. This ready-to-use analysis is professionally formatted and directly applicable to your business strategy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The intralogistics sector is populated by a significant number of global contenders, such as KION Group, which reported €11.4 billion in revenue for 2023, Toyota Industries, and Crown Equipment. This array of established manufacturers, alongside a growing contingent of agile, specialized companies focusing on automation and robotics, means Jungheinrich faces robust competition.
While the intralogistics market, especially warehouse automation, is expected to see robust growth from 2025, it faced a slowdown in 2023 and weak growth in 2024. This subdued market environment intensifies competition as companies vie more aggressively for market share.
During these periods of slower expansion, expect heightened rivalry, which often translates into increased price pressure. Jungheinrich, as a key player, must navigate this landscape where competitors may resort to more aggressive pricing or promotional strategies to secure business.
Jungheinrich stands out by offering a broad spectrum of material handling equipment, advanced automated systems, sophisticated software, and a full suite of services. This includes pioneering work in lithium-ion technology and artificial intelligence applications, giving customers unique solutions.
The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its advancements in automation, robotics, and smart warehousing technologies. This focus on cutting-edge solutions helps to solidify its market position and lessen the impact of direct price competition from rivals.
For instance, Jungheinrich's ongoing development in autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and its integrated warehouse management systems provide distinct advantages. In 2024, the company continued to invest heavily in R&D, with a significant portion of its budget allocated to these future-oriented technologies, aiming to stay ahead of competitors.
Exit Barriers
Jungheinrich, like many in the industrial equipment sector, faces significant exit barriers. These are factors that make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market. For instance, specialized assets like dedicated forklift manufacturing plants represent substantial sunk costs. If a company were to cease operations, these facilities would be hard to sell or repurpose, locking capital in.
Furthermore, long-term customer contracts and the associated service agreements create another layer of commitment. Breaking these agreements can incur penalties and damage reputation. Jungheinrich's investment in R&D for advanced automation and intralogistics solutions also contributes to high exit barriers, as this knowledge and technology are specific to the industry and difficult to monetize elsewhere. In 2023, the capital expenditure for property, plant, and equipment for Jungheinrich amounted to €323 million, highlighting the significant investment in physical assets that contribute to these barriers.
- Specialized Assets: Manufacturing plants for forklifts and automated systems are highly specific and difficult to repurpose or sell, representing sunk costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing customer agreements for sales, leasing, and maintenance create ongoing obligations and switching costs for customers.
- R&D Investments: Significant expenditure in developing new technologies, such as autonomous forklifts and warehouse management systems, ties up resources and expertise.
- Brand and Reputation: The established brand name and service network are valuable assets that are costly to abandon, impacting future business opportunities.
Strategic Alliances and Acquisitions
Strategic alliances and acquisitions significantly reshape the competitive arena for material handling equipment manufacturers like Jungheinrich. These moves can consolidate market share, introduce innovative technologies, or create barriers to entry for smaller players. For instance, Jungheinrich's collaboration with EP Equipment for mid-tech electric forklifts, announced in 2023, aims to broaden its product offering and reach new market segments, directly impacting how it competes with other established brands and emerging suppliers.
Furthermore, Jungheinrich’s investment in Merantix, a specialist in artificial intelligence, underscores a strategic push into digital solutions and autonomous warehousing. This partnership, active through 2024, signals a commitment to leveraging AI for enhanced efficiency and new service models, intensifying rivalry among companies that are also investing heavily in Industry 4.0 technologies. Such strategic moves can lead to:
- Consolidation of market power: Larger players can acquire smaller, innovative firms to gain access to new technologies or customer bases.
- Accelerated innovation: Partnerships allow companies to pool resources and expertise, speeding up the development and deployment of advanced solutions, like AI-driven logistics.
- Shifting competitive advantages: Companies that successfully integrate new technologies through alliances or acquisitions can gain a significant edge over rivals.
- Increased R&D expenditure: The drive to partner or acquire forces competitors to also increase their investment in research and development to stay relevant.
Jungheinrich faces intense competition from established global players like KION Group, which achieved €11.4 billion in revenue in 2023, and Toyota Industries, alongside nimble specialized firms. This crowded market, particularly in warehouse automation, intensified rivalry in 2023 and 2024 due to a market slowdown, driving aggressive pricing and promotional activities as companies fight for market share.
Jungheinrich differentiates itself through a comprehensive offering of material handling equipment, automated systems, software, and services, including advancements in lithium-ion technology and AI. Its significant R&D investment in areas like autonomous mobile robots and integrated warehouse management systems in 2024 aims to maintain a competitive edge against rivals also focused on Industry 4.0 solutions.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by strategic alliances and acquisitions. Jungheinrich's 2023 collaboration with EP Equipment and its investment in AI specialist Merantix through 2024 illustrate a strategy to broaden product portfolios and integrate advanced technologies, directly influencing how it competes and potentially consolidating market power.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Jungheinrich's offerings exists from non-traditional material handling methods. For very small operations, manual labor might suffice, but this is increasingly impractical due to widespread labor shortages across industries. For instance, in 2024, Germany, a key market for Jungheinrich, continued to face significant skilled labor deficits, making manual solutions less viable.
Simpler, less automated equipment also presents a substitute threat. However, the growing emphasis on operational efficiency and cost reduction, driven by factors like rising energy prices and the need for faster throughput, often makes these less automated options less attractive in the medium to long term. Jungheinrich's focus on energy-efficient and automated solutions directly addresses these evolving market demands.
The threat of substitutes for Jungheinrich's advanced material handling solutions hinges on their price-performance ratio. If simpler, less technologically sophisticated alternatives can achieve a similar outcome for a fraction of the cost, the threat is elevated. For example, in certain low-volume or less demanding warehouse operations, manual pallet jacks or basic gravity roller conveyors might present a more budget-friendly option compared to Jungheinrich's automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or sophisticated reach trucks.
While these manual or simpler systems are indeed cheaper upfront, their operational efficiency and scalability are significantly lower. Jungheinrich's products are designed for high throughput, reduced labor costs, and optimized space utilization, benefits that often outweigh the initial investment for businesses with substantial material handling needs. For instance, a manual pallet jack might cost a few hundred dollars, whereas a Jungheinrich AGV can represent a significant capital expenditure, but delivers substantial savings in labor and operational time over its lifespan, a factor critical in 2024's competitive logistics landscape.
Customer propensity to substitute Jungheinrich's material handling equipment is influenced by several factors. Companies with tighter budgets or less demanding operational requirements might consider lower-cost alternatives, particularly if they perceive less long-term value in advanced automation or specialized features.
For instance, small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in 2024, especially those with simpler warehousing tasks, may find the initial purchase price of basic forklifts or manual pallet jacks from competitors to be a more attractive option than Jungheinrich's integrated, automated systems. This is often driven by a focus on immediate cost savings rather than total cost of ownership over many years.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are continuously introducing new ways to handle materials, posing a potential threat of substitution. For instance, sophisticated drones for inventory management or collaborative robots that offer more flexible solutions without requiring extensive system integration could offer alternatives to traditional Jungheinrich offerings.
These emerging technologies often require less initial capital investment and can be more adaptable to specific operational needs, directly challenging the value proposition of more integrated, capital-intensive solutions. Jungheinrich's own strategic investments in these very areas, however, mitigate this threat by allowing the company to be a leader in these evolving substitute markets rather than merely a victim of them.
- Emerging Drone Technology: Drones are increasingly capable of tasks like aerial inventory scanning, potentially reducing reliance on ground-based systems for certain warehousing functions.
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside humans, offering a more flexible and potentially lower-cost automation solution for specific material handling tasks compared to fully integrated robotic systems.
- Jungheinrich's Investment Strategy: Jungheinrich is actively developing and integrating these advanced technologies into its own product portfolio, aiming to capture market share in these evolving segments.
- Market Adaptability: The threat is partially neutralized as Jungheinrich aims to be a provider of these advanced solutions, turning a potential substitute into a new product category.
Outsourcing Logistics Functions
The threat of substitutes for material handling equipment, like that offered by Jungheinrich, emerges when customers opt to outsource their entire logistics operations. This means businesses might contract with third-party logistics (3PL) providers to manage their warehousing and distribution needs. While these 3PLs may utilize equipment from manufacturers such as Jungheinrich, the end customer’s decision to outsource bypasses the need for them to directly purchase or lease material handling equipment.
This shift to a service-based model presents a significant substitute. Instead of buying forklifts or automated storage systems, a company pays for the logistics service, which includes the use of necessary equipment. The global 3PL market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial portion of the logistics value chain is being handled by these external providers, thereby substituting direct equipment sales.
- Outsourcing Growth: The global 3PL market reached over $1.3 trillion in 2023, demonstrating a strong trend towards outsourcing logistics functions.
- Service Substitution: Customers can substitute direct equipment purchases with a comprehensive logistics service package from 3PLs.
- Reduced Direct Need: Outsourcing logistics reduces a company's direct requirement to invest in, manage, and maintain its own fleet of material handling equipment.
- Indirect Equipment Use: While 3PLs may use equipment from companies like Jungheinrich, the end-user's direct engagement with the equipment manufacturer is removed.
The threat of substitutes for Jungheinrich's advanced material handling solutions is present from simpler, less automated equipment and manual labor, especially for businesses with less demanding operational needs or tighter budgets. While these alternatives offer lower upfront costs, their long-term efficiency and scalability are often inferior, making them less attractive as operational demands increase or labor shortages persist, a trend evident in many European markets throughout 2024.
Emerging technologies like drones for inventory management and collaborative robots present new substitution avenues, offering flexibility and potentially lower initial investment. However, Jungheinrich's strategic investments in these very areas help to mitigate this threat by positioning the company as a provider of these evolving solutions.
Furthermore, the increasing trend of outsourcing logistics to third-party logistics (3PL) providers acts as a significant substitute. Companies opting for 3PL services bypass the need for direct investment in material handling equipment, as the service provider manages these needs. The global 3PL market's substantial growth, exceeding $1.3 trillion in 2023, underscores the significance of this service-based substitution.
Entrants Threaten
The intralogistics and material handling equipment sector, particularly for advanced automation and manufacturing, demands significant upfront capital. Jungheinrich, like other established players, invests heavily in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and extensive global distribution and service networks. These substantial capital requirements create a formidable barrier, deterring potential new entrants from easily entering the market.
Established players like Jungheinrich leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, enabling them to secure better material prices and achieve lower per-unit production costs. For instance, in 2023, Jungheinrich reported a revenue of €4.7 billion, reflecting their substantial operational capacity and purchasing power, which new entrants would struggle to match.
The extensive experience Jungheinrich possesses in developing and implementing sophisticated intralogistics systems creates a considerable barrier. This accumulated knowledge translates into optimized designs, efficient project execution, and a deeper understanding of customer needs, resulting in a steep learning curve for any new competitor entering the market.
Jungheinrich benefits from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and robust customer relationships. This is a significant barrier for new entrants. Their reputation for quality and comprehensive service, cultivated over years, fosters trust, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate this level of customer commitment. For instance, a substantial portion of Jungheinrich's revenue often comes from repeat business and long-term service contracts, indicating the strength of these existing ties.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Jungheinrich's established global network of direct sales and service operations, complemented by strategic dealer partnerships, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This extensive infrastructure ensures efficient product delivery and crucial after-sales support, a complex and costly system to replicate.
Building comparable distribution and service channels would require substantial upfront investment and time, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve the same market penetration and customer loyalty Jungheinrich enjoys. Furthermore, securing reliable and cost-effective supply chains for essential components presents another hurdle, as established players often benefit from economies of scale and strong supplier relationships.
Consider the sheer scale: in 2023, Jungheinrich reported a significant number of customer service operations worldwide, underscoring the depth of their support network. For instance, their ability to quickly service a diverse range of material handling equipment across various industries is a testament to this robust system.
- Extensive Global Reach: Jungheinrich's direct sales and service network offers unparalleled access to customers worldwide.
- After-Sales Support Dominance: The company's commitment to after-sales service builds strong customer relationships, a difficult feat for new entrants to match.
- Supply Chain Integration: Securing consistent and quality component supply chains is a challenge new companies face in a competitive market.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Jungheinrich's long-standing presence fosters trust, which new entrants must work hard to build.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
Regulatory and legal barriers significantly shape the threat of new entrants in the material handling equipment sector. The production and deployment of equipment like forklifts and automated systems are governed by stringent safety, environmental, and technical standards. For instance, in 2024, compliance with evolving emissions standards and advanced safety certifications requires substantial investment in research, development, and manufacturing processes. These requirements can escalate initial capital outlays for new market participants, making it more challenging to compete with established players who have already absorbed these costs.
New entrants must navigate a complex web of regulations that differ across jurisdictions. Obtaining necessary certifications and approvals for products, such as CE marking in Europe or EPA compliance in the United States, demands considerable time and financial resources. This regulatory burden acts as a deterrent, effectively raising the cost of entry and making it difficult for smaller or less capitalized firms to gain a foothold.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with ISO 3691 standards for forklift safety is mandatory, impacting design and manufacturing.
- Environmental Regulations: Meeting emissions targets, like those set by the EPA for internal combustion engines, adds R&D costs.
- Technical Certifications: Automated systems require rigorous testing and certification for operational reliability and safety, increasing development timelines and expenses.
- Market-Specific Compliance: Navigating varying national and regional regulations can add significant complexity and cost for global market entry.
The threat of new entrants in the intralogistics sector is generally considered moderate to low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investments required for research and development, manufacturing facilities, and establishing a global sales and service network. For instance, Jungheinrich's 2023 revenue of €4.7 billion highlights the scale of operations that new players must contend with.
Established brands like Jungheinrich benefit from significant economies of scale, strong brand loyalty, and extensive experience in developing complex intralogistics solutions. These factors create steep learning curves and high barriers to entry for newcomers, making it difficult to compete on cost and customer trust.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements, particularly concerning safety and environmental standards, add another layer of complexity and cost for potential entrants. Navigating these regulations across different markets demands significant resources and time, further solidifying the position of established players like Jungheinrich.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example for Jungheinrich (2023 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High | €4.7 billion revenue indicates substantial operational investment. |
| Economies of Scale | Challenging to achieve | Large-scale procurement and manufacturing lead to cost advantages. |
| Brand Loyalty & Experience | Difficult to replicate | Long-standing customer relationships and proven track record. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly and time-consuming | Meeting safety (e.g., ISO 3691) and environmental (e.g., EPA emissions) standards. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis of Jungheinrich's competitive landscape is built upon comprehensive data from Jungheinrich's annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports, alongside data from global financial databases and trade publications.
