Iron Mountain Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Iron Mountain Bundle
Iron Mountain operates in a market shaped by moderate buyer power and significant threat of substitutes, particularly digital solutions. The company's established infrastructure and service reputation offer some defense against new entrants.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Iron Mountain’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly impacts Iron Mountain's bargaining power. The information management sector, covering secure storage, data backup, and destruction, depends on suppliers like real estate providers for facilities, hardware and software vendors for digital services, and specialized equipment makers. When a few major suppliers dominate the market for essential inputs, their ability to dictate terms and prices to Iron Mountain grows, as alternative options become scarce.
The burgeoning data center market, for example, is a critical area where supplier concentration can be observed. As demand for digital infrastructure escalates, suppliers of data center space and related hardware may find themselves in a stronger position to negotiate pricing. This trend could translate into higher operational costs for companies like Iron Mountain if they cannot secure favorable long-term agreements with these key providers.
Iron Mountain's suppliers hold significant bargaining power if the company faces high switching costs. These costs can manifest in various forms, such as the expense and time involved in reconfiguring IT systems to accommodate new software, the logistical challenges and financial outlay of relocating physical assets between storage facilities, or the investment required to retrain employees on new equipment and processes. For instance, migrating substantial volumes of sensitive data from one cloud storage provider to another is a complex and often expensive undertaking, directly impacting Iron Mountain's ability to switch suppliers easily.
Suppliers who provide highly specialized or proprietary technology, like advanced data encryption or unique shredding equipment, wield significant bargaining power. When Iron Mountain finds it difficult to replicate or source alternatives for these distinct offerings, its reliance on these specific suppliers increases, particularly in the fast-moving areas of digital transformation and cybersecurity.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly bolsters their bargaining power against Iron Mountain. If key suppliers, such as large data center operators or specialized logistics providers, were to begin offering integrated information management services directly to Iron Mountain's clientele, they could effectively bypass Iron Mountain's core offerings. This would allow them to capture a larger share of the value chain and potentially dictate terms more aggressively.
Consider the scenario where a major cloud infrastructure provider, like Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure, expands its service portfolio to include physical records storage and lifecycle management. Such a move would directly compete with Iron Mountain's traditional business. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, indicating the substantial resources and reach these providers possess. If even a fraction of these players decided to enter the physical records management space, it would present a formidable competitive threat.
- Supplier Threat: Suppliers offering integrated information management services directly to Iron Mountain's customers increases their bargaining power.
- Example Scenario: A large data center provider entering the records management space, bypassing Iron Mountain.
- Market Context: The massive scale of cloud providers, with the global cloud market exceeding $600 billion in 2024, highlights the potential resources of forward-integrating suppliers.
Importance of Iron Mountain to the Supplier
The importance of Iron Mountain to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Iron Mountain constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier might have less leverage, as they depend heavily on Iron Mountain's continued business. Conversely, a supplier for whom Iron Mountain is a minor client would likely possess greater bargaining power.
Iron Mountain's immense scale, serving over 240,000 customers globally, including a remarkable 95% of the Fortune 1000 companies, indicates that for many suppliers, Iron Mountain is a significant and valuable client. This substantial customer base suggests that suppliers may be more inclined to offer favorable terms to maintain their relationship with Iron Mountain, thereby reducing the supplier's inherent bargaining power.
- Revenue Dependence: Suppliers heavily reliant on Iron Mountain's business are less likely to exert significant bargaining power.
- Client Significance: Iron Mountain's status as a major client for many suppliers diminishes their ability to dictate terms.
- Market Reach: Serving 95% of the Fortune 1000 highlights Iron Mountain's importance to suppliers' own market penetration and stability.
Suppliers' bargaining power is influenced by the availability of substitutes for their offerings. If Iron Mountain can easily find alternative providers for essential inputs like secure storage facilities or data management software, the existing suppliers' ability to command higher prices or impose unfavorable terms is significantly reduced.
The threat of backward integration by Iron Mountain also serves to curb supplier power. Should Iron Mountain decide to develop its own capabilities for certain inputs, such as building its own data centers or developing proprietary software, it would lessen its reliance on external suppliers, thereby decreasing their leverage.
The overall concentration of suppliers in the information management ecosystem plays a critical role. A fragmented supplier base, where numerous small providers exist, generally offers Iron Mountain more options and thus lessens individual supplier bargaining power. Conversely, a consolidated market with few dominant players empowers those suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Iron Mountain | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases bargaining power | Few dominant data center space providers |
| Switching Costs | Increases bargaining power | High cost of migrating large data volumes |
| Supplier Differentiation | Increases bargaining power | Proprietary encryption technology |
| Forward Integration Threat | Increases bargaining power | Cloud providers entering records management |
| Importance to Supplier | Decreases bargaining power | Iron Mountain is a major client |
What is included in the product
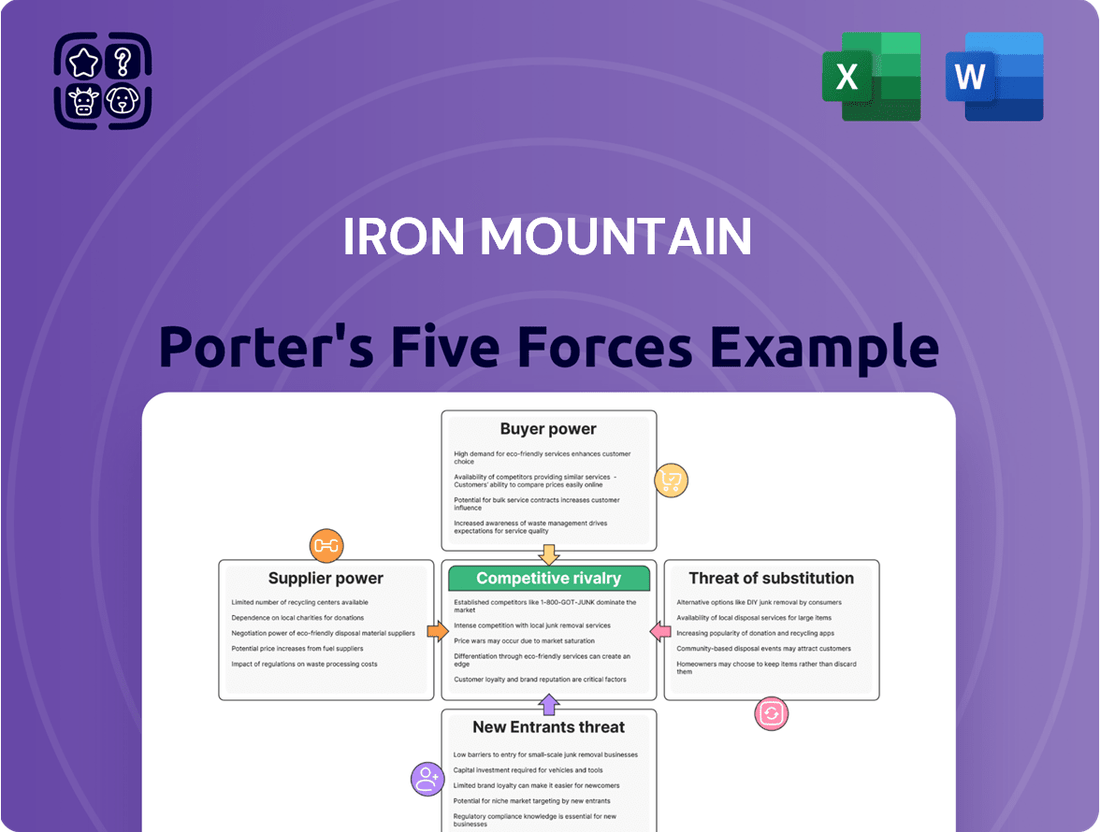
This analysis details the competitive forces impacting Iron Mountain, including buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and industry rivalry.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, allowing for rapid identification and mitigation of strategic threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
Iron Mountain's customer base is exceptionally broad, serving over 240,000 clients, with a remarkable 95% of Fortune 1000 companies among them. This wide reach generally weakens the bargaining power of any single customer.
However, if a few very large enterprise clients account for a disproportionately large share of Iron Mountain's revenue, their ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms would increase. The company's high customer retention rate of around 98% suggests strong customer loyalty, which can mitigate the impact of concentration.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in Iron Mountain's industry. For customers, moving their physical records or complex digital information management systems to a competitor can be quite costly. These expenses aren't just monetary; they often involve the sheer logistical effort of relocating vast amounts of physical documents, the technical hurdles of migrating sensitive data, and the potential for business disruptions during the transition.
These switching costs effectively act as a barrier, making it less appealing for customers to move to a rival service provider. This reduced ease of switching directly diminishes the bargaining power that customers hold. For instance, a company relying on Iron Mountain for secure, long-term physical document storage faces considerable expense and operational risk if they were to attempt to move that archive to another vendor.
Customers possess significant bargaining power when numerous substitute services are readily available for information management. These alternatives span from managing data internally to utilizing other third-party providers, including a wide array of cloud storage solutions and digital content management platforms.
The competitive landscape is notably shaped by the growing adoption of cloud-based solutions and broader digital transformation efforts across industries. For instance, by 2024, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $600 billion, illustrating the vast availability of alternative information management solutions.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers' willingness to pay for Iron Mountain's services is influenced by how crucial the information is, their available budget, and the perceived worth of the offerings. For instance, while secure storage and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable for many, budget-minded clients might explore cheaper options for data that isn't highly sensitive.
The market for managed information services is projected for significant expansion, with some forecasts indicating a compound annual growth rate of around 10-12% through 2028. However, this growth also attracts new competitors, potentially intensifying price competition and putting pressure on Iron Mountain's pricing strategies.
- Information Criticality: Critical business records and compliance data command higher prices than less sensitive information.
- Budget Constraints: Smaller businesses or those with tight budgets may prioritize cost over premium features for certain data types.
- Perceived Value: Customers weigh the benefits of security, compliance, and convenience against the cost of Iron Mountain's services.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of alternative providers, from local storage facilities to cloud-based solutions, can influence price sensitivity.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
Large enterprise clients, particularly those with significant IT infrastructure and internal expertise, might contemplate bringing certain information management functions in-house. This could involve managing their own data centers or digital archives, especially if they perceive cost savings or greater control. For instance, a major financial institution with a robust IT department could potentially manage its own secure physical record storage or digital data replication.
However, the specialized nature of Iron Mountain's services, such as secure destruction, complex data center operations, and regulatory compliance for physical records, often presents a significant barrier to full backward integration for most customers. The capital investment and ongoing operational expertise required are substantial. In 2023, data center construction costs could range from $10 million to over $100 million depending on scale and features, a prohibitive expense for many considering in-house solutions for specialized needs.
- Specialized Expertise: Many customers lack the niche skills for secure physical storage, certified destruction, and advanced data center management.
- Capital Investment: Building and maintaining secure, compliant facilities requires significant upfront and ongoing capital expenditure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex data privacy and destruction regulations is a continuous challenge that specialized providers like Iron Mountain manage effectively.
- Economies of Scale: Iron Mountain's vast infrastructure provides economies of scale that are difficult for individual companies to replicate cost-effectively.
Iron Mountain's broad customer base, including 95% of Fortune 1000 companies, generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power, though large clients could exert influence if they represent a significant revenue share. High customer retention, around 98%, indicates strong loyalty, which can offset concentration risks.
High switching costs for customers, encompassing logistical, technical, and business disruption risks associated with moving vast physical records or complex digital information, significantly reduce their leverage. The substantial expense and operational challenges involved in migrating sensitive data make switching providers less appealing.
The availability of numerous substitute services, from internal management to a wide array of cloud storage and digital content platforms, does present customers with alternatives, potentially increasing their bargaining power. For instance, the global cloud computing market's projected growth to over $600 billion by 2024 highlights the breadth of these alternatives.
Customers' willingness to pay is tied to information criticality, budget, and perceived value. While secure storage and compliance are essential, budget-conscious clients may seek less expensive options for less sensitive data, especially as the managed information services market grows at an estimated 10-12% CAGR through 2028.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context |
| Customer Concentration | Low to Moderate | 95% of Fortune 1000 served; 98% retention suggests loyalty mitigates concentration risk. |
| Switching Costs | Low | High logistical, technical, and operational risks for customers moving data. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate to High | Global cloud market >$600 billion (2024 est.); numerous internal and external alternatives exist. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate | Influenced by information criticality, budget constraints, and perceived value; market growth may increase price competition. |
Full Version Awaits
Iron Mountain Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, professionally written Iron Mountain Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, fully formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Iron Mountain faces intense competition from a broad spectrum of companies. This includes giants like Dell EMC and Hewlett Packard Enterprise, which offer extensive IT solutions, as well as specialized data center providers such as Digital Realty Trust. The rise of major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform further intensifies this rivalry, offering alternative storage and data management solutions.
The information management services industry, encompassing data centers and managed information services, is a rapidly expanding sector. The global data center market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 11.24% between 2025 and 2034. Furthermore, the managed information services market is projected to reach $443.38 billion by 2030, with an expected CAGR of 7.9%.
This robust industry growth generally serves to temper competitive rivalry, as it provides ample room for numerous companies to expand their operations. However, despite the overall expansion, intense competition for market share persists, particularly within high-growth segments such as data centers and advanced digital solutions.
Iron Mountain stands out through its vast global network, a reputation built on trust for security and regulatory adherence, and a diverse service offering that includes physical and digital record management, data centers, and equipment disposal. This comprehensive approach is a significant differentiator in a market where rivals might specialize in particular areas or emphasize cost-effectiveness.
While Iron Mountain offers a wide array of services, competitors often carve out their niches. Some may excel in cutting-edge digital solutions, leveraging artificial intelligence for data analytics, or focus on being the lowest-cost provider. For instance, companies specializing in cloud-based document management might offer more agile, tech-forward solutions for specific digital-native businesses.
In 2024, the information management sector continues to see innovation, with many competitors investing heavily in AI and automation to streamline data processing and enhance customer experience. This technological push presents a dynamic competitive landscape where Iron Mountain's established infrastructure and broad service portfolio are balanced against the agility and specialized offerings of its rivals.
Switching Costs for Customers
High switching costs significantly dampen competitive rivalry. For instance, customers heavily invested in Iron Mountain's specialized physical storage solutions, like secure vaults or climate-controlled archives, face substantial logistical and financial hurdles to move their sensitive materials. This inertia makes them less likely to explore alternative providers, thereby reducing the pressure on Iron Mountain to compete aggressively on price or service features solely to retain these clients.
The integration of Iron Mountain's digital solutions further solidifies customer loyalty. Once a business has embedded Iron Mountain's document management, e-discovery, or data backup services into its operational workflows, the process of migrating data, retraining staff, and reconfiguring systems for a new vendor becomes a complex and costly undertaking. This deep integration acts as a powerful deterrent against switching, contributing to a more stable competitive landscape.
In 2023, Iron Mountain reported that its total revenue reached $5.1 billion, showcasing the scale of its operations and the depth of its customer relationships. The company's strategic focus on recurring revenue streams, particularly within its digital transformation services, inherently builds in higher switching costs over time as these solutions become more integral to client operations.
- High initial investment: Customers often incur significant upfront costs for specialized infrastructure or software integration with Iron Mountain.
- Operational disruption: Migrating data and retraining personnel to a new provider can cause considerable business disruption.
- Data security concerns: The sensitive nature of many clients' data makes them reluctant to risk a transition to an unproven competitor.
- Long-term contracts: Many service agreements are structured to encourage long-term commitment, further increasing the effective switching cost.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like specialized assets and long-term contracts, can trap companies in the market even when unprofitable, thus fueling competitive rivalry. Iron Mountain's substantial investments in its global network of purpose-built storage facilities and data centers exemplify these barriers.
These significant capital outlays, coupled with the specialized nature of its infrastructure, make it costly and difficult for competitors to simply shut down operations. For instance, Iron Mountain reported capital expenditures of $1.3 billion in 2023, a significant portion of which is directed towards expanding and modernizing its physical and digital storage capabilities.
- Specialized Assets: Iron Mountain's extensive network of highly secure, climate-controlled storage facilities and advanced data centers are not easily repurposed or sold, locking in investment.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many of Iron Mountain's customer agreements are multi-year, creating ongoing commitments that discourage early exits for competitors tied to these arrangements.
- Brand and Reputation: The established trust and brand recognition built over decades in secure storage and information management also act as a barrier, as exiting would mean abandoning this hard-won market position.
Iron Mountain faces a competitive landscape populated by large IT solution providers like Dell EMC and HPE, alongside specialized data center operators such as Digital Realty Trust. The growing influence of major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud further intensifies this rivalry by offering alternative data storage and management solutions. The information management sector is expanding, with the global data center market projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.24% from 2025 to 2034, and the managed information services market expected to reach $443.38 billion by 2030. While this growth offers opportunities, intense competition for market share, particularly in digital solutions, persists.
Iron Mountain differentiates itself through its extensive global network, a strong reputation for security and compliance, and a broad service portfolio encompassing physical and digital records, data centers, and equipment disposal. Competitors often focus on specific niches, such as advanced digital solutions leveraging AI or cost-leadership strategies. In 2024, many competitors are investing in AI and automation, creating a dynamic environment where Iron Mountain's established infrastructure competes with the agility of specialized rivals.
High switching costs significantly reduce competitive rivalry for Iron Mountain. Customers invested in specialized physical storage or deeply integrated digital solutions face substantial logistical and financial hurdles when considering a change. For example, migrating sensitive data from secure vaults or reconfiguring embedded document management systems represents a complex and costly undertaking, fostering customer loyalty and market stability. In 2023, Iron Mountain's revenue of $5.1 billion reflects the depth of these customer relationships, with recurring revenue streams in digital services further solidifying these bonds.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Large IT Solutions Providers | Dell EMC, Hewlett Packard Enterprise | Broad IT infrastructure and services |
| Specialized Data Center Providers | Digital Realty Trust | Physical infrastructure and colocation |
| Cloud Service Providers | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform | Scalable, flexible cloud-based solutions |
| Niche Information Management | Various specialized software and service firms | Specific digital solutions, AI integration, cost leadership |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing shift towards digital transformation presents a significant threat of substitutes for Iron Mountain's core physical records storage business. Businesses are actively moving away from paper-based systems, embracing cloud storage solutions and digital document management platforms. This trend is driven by the desire for greater scalability, enhanced accessibility, and potential cost savings compared to maintaining physical archives.
By the end of 2023, global spending on cloud infrastructure services reached an estimated $266 billion, a substantial increase reflecting this digital migration. Companies are leveraging these cloud services for everything from data backup to active document collaboration, directly impacting the demand for traditional offsite physical storage.
Organizations might opt for in-house information management, especially for highly sensitive data or when possessing ample internal resources and expertise. This often translates to maintaining proprietary physical archives or constructing and operating private data centers, bypassing external service providers.
The cost-effectiveness of in-house solutions can be a significant driver, though it requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure and skilled personnel. For instance, a company with stringent compliance requirements for financial records might find it more secure and ultimately cheaper to manage these internally rather than outsourcing, avoiding potential data breach risks associated with third parties.
Generic cloud storage providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform present a substantial threat of substitution for Iron Mountain's digital storage solutions. These hyperscale cloud providers offer highly scalable, flexible, and often competitively priced alternatives for businesses looking to store and manage their digital data. For instance, AWS reported revenue of $62.4 billion for fiscal year 2023, highlighting its massive market presence and ability to attract customers with its extensive service offerings, including storage.
Managed IT Services and Software Solutions
Beyond physical storage, a significant threat comes from managed IT service providers and software solutions. These offerings, focused on enterprise content management (ECM) and document management systems (DMS), provide alternative ways for businesses to streamline information workflows. They allow companies to manage their digital assets and processes without necessarily needing Iron Mountain's extensive physical infrastructure.
These substitute solutions often leverage cloud-based platforms and advanced automation to achieve similar outcomes. For instance, companies might adopt platforms like Microsoft SharePoint, OpenText, or Box for their document management needs. These systems can handle version control, access permissions, and workflow automation, directly competing with aspects of Iron Mountain's digital information management services.
- Managed IT Services: Providers offering comprehensive IT solutions, including cloud storage and data management, present a direct substitute.
- ECM/DMS Software: Specialized software allows businesses to manage and automate document-centric processes internally or via cloud providers.
- Cloud Storage Providers: Companies like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer scalable and cost-effective alternatives for digital data storage and management.
- Digital Transformation Initiatives: Businesses undergoing digital transformation may opt for integrated digital solutions that bypass traditional information management models.
Alternative Data Destruction Methods
While Iron Mountain offers secure shredding, other data destruction methods exist. Businesses might consider in-house shredding, which can be cost-effective for smaller volumes but often lacks the robust security protocols and certifications of specialized services.
Burning is another option, particularly for paper records, but it presents environmental concerns and does not address electronic media. Degaussing is effective for magnetic media like hard drives, rendering data unrecoverable, but it requires specialized equipment and doesn't physically destroy the media, which may be a compliance requirement.
- In-house Shredding: Potentially lower cost for small volumes, but may lack security certifications.
- Burning: Suitable for paper, but has environmental implications and is not for electronic media.
- Degaussing: Effective for magnetic media, but requires specific equipment and doesn't physically destroy the media.
The threat of substitutes for Iron Mountain's physical storage services is significant, driven by the widespread adoption of digital solutions. Businesses are increasingly migrating to cloud storage and digital document management systems, seeking greater accessibility and scalability. This shift is underscored by the robust growth in cloud infrastructure spending, with global figures reaching an estimated $266 billion by the end of 2023, indicating a clear preference for digital alternatives.
Furthermore, companies may choose to manage their information in-house, particularly for sensitive data, bypassing third-party providers. This can involve maintaining proprietary physical archives or investing in private data centers. While requiring substantial initial investment, such in-house solutions can offer perceived benefits in security and control, especially for organizations with stringent compliance needs.
Generic cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer competitive digital storage solutions. For example, AWS alone reported $62.4 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2023, demonstrating its significant market penetration and ability to attract customers with extensive digital service offerings.
Managed IT service providers and specialized software, such as Enterprise Content Management (ECM) and Document Management Systems (DMS), also pose a threat. Platforms like Microsoft SharePoint, OpenText, and Box enable businesses to manage digital assets and workflows, directly competing with aspects of Iron Mountain's digital information management services.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Advantages | Market Trend Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage Providers | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud | Scalability, accessibility, cost-effectiveness | Global cloud infrastructure spending reached $266 billion in 2023 |
| ECM/DMS Software | Microsoft SharePoint, OpenText, Box | Workflow automation, digital asset management, version control | Growing adoption for streamlining business processes |
| In-house Management | Proprietary physical archives, private data centers | Enhanced security control, compliance adherence | Strategic decision for highly sensitive data |
Entrants Threaten
The information management sector, particularly for a company like Iron Mountain that offers a broad suite of services, demands substantial upfront capital. This is a major hurdle for potential newcomers.
Building and maintaining secure, climate-controlled physical storage facilities, along with investing in state-of-the-art data centers for digital records, requires tens of millions, if not hundreds of millions, of dollars. For instance, developing even a single advanced data center can easily cost over $100 million. This financial barrier significantly limits the number of new players who can realistically enter the market.
Iron Mountain enjoys substantial economies of scale, a significant barrier to new entrants. Its extensive network of over 1,400 facilities worldwide and a global workforce of 24,000 employees enable cost efficiencies in operations, logistics, and procurement that smaller competitors struggle to match. For instance, in 2023, Iron Mountain reported $5.1 billion in revenue, a testament to its operational capacity and market penetration.
Furthermore, Iron Mountain's economies of scope, achieved through its diverse service offerings including physical records management, data center solutions, and digital transformation services, create integrated value propositions. This broad service portfolio allows for cross-selling opportunities and operational synergies, making it more challenging for new entrants to replicate its comprehensive business model and achieve similar cost advantages.
Iron Mountain benefits from deeply entrenched brand loyalty, a significant barrier for new entrants. Its long history, particularly serving Fortune 1000 clients, has cultivated a reputation for unwavering security, compliance, and reliability in handling sensitive information. This established trust is not easily replicated, making it challenging for newcomers to quickly gain traction and market share against such a well-regarded incumbent.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The information management sector faces significant regulatory and compliance challenges. Stringent laws like GDPR and HIPAA mandate robust data privacy, security, and retention protocols. For instance, in 2024, companies handling sensitive data continued to invest heavily in compliance, with data privacy spending projected to reach billions globally.
Navigating these complex requirements presents a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. The cost and time associated with achieving and maintaining compliance can be prohibitive, effectively deterring many from entering the market.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Laws like GDPR and CCPA impose strict rules on data handling.
- Industry-Specific Compliance: Sectors like healthcare (HIPAA) and finance have unique, rigorous data management mandates.
- Security Standards: Adherence to standards like ISO 27001 is often expected, requiring significant investment.
- Cost of Compliance: Meeting these requirements can involve substantial expenditures on technology, personnel, and legal counsel.
Access to Distribution Channels and Technology
New competitors face significant hurdles in building out effective sales and distribution networks for both physical records and digital information services. Iron Mountain's established infrastructure, including its extensive network of storage facilities and logistics capabilities, presents a formidable barrier. For instance, as of 2024, Iron Mountain operates over 1,400 facilities globally, a scale that is difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate.
The technological landscape for information management is also a key entry barrier. Developing or acquiring the necessary cutting-edge technology for secure data storage, digital transformation, and advanced analytics requires substantial investment. The growing emphasis on artificial intelligence and machine learning in data management, a trend accelerating in 2024, further elevates the required technological sophistication for any new player aiming to compete effectively.
- Distribution Network: Iron Mountain's global footprint of over 1,400 facilities offers a significant advantage in reaching diverse customer bases.
- Technology Investment: The increasing demand for AI and machine learning in data management necessitates substantial R&D and capital expenditure for new entrants.
- Scalability Challenges: New companies must overcome the immense cost and time required to build comparable infrastructure and technological capabilities.
The threat of new entrants for Iron Mountain is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish a comparable infrastructure. Building a global network of secure storage facilities and advanced data centers, akin to Iron Mountain's over 1,400 locations, demands hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant deterrent for most aspiring competitors in 2024. This high initial investment, coupled with the need for sophisticated technology for digital transformation and analytics, creates a formidable barrier.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory compliance, including data privacy laws like GDPR and industry-specific mandates such as HIPAA, necessitates substantial ongoing investment in technology and expertise. New entrants must also overcome the challenge of building brand recognition and customer loyalty, which Iron Mountain has cultivated over decades, particularly with its established relationships with Fortune 1000 clients. The company's economies of scale and scope, derived from its vast operational capacity and diverse service offerings, further solidify its competitive position and make it difficult for newcomers to achieve similar cost efficiencies or integrated value propositions.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing global physical and digital infrastructure costs hundreds of millions. | High; limits number of potential entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to GDPR, HIPAA, and other data security standards is costly and complex. | High; requires significant investment in technology and legal expertise. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Iron Mountain's long-standing trust with large enterprises is difficult to replicate. | High; new entrants struggle to gain market share quickly. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Vast operational network and diverse services offer cost advantages. | High; new entrants face higher per-unit costs. |
| Technology Investment | Need for advanced AI, ML, and secure data management solutions. | High; requires substantial R&D and capital expenditure. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Iron Mountain Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Iron Mountain's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
