Infineon Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Infineon Technologies Bundle
Infineon Technologies operates in a dynamic semiconductor landscape, facing significant pressures from powerful suppliers and intense rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Infineon Technologies’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
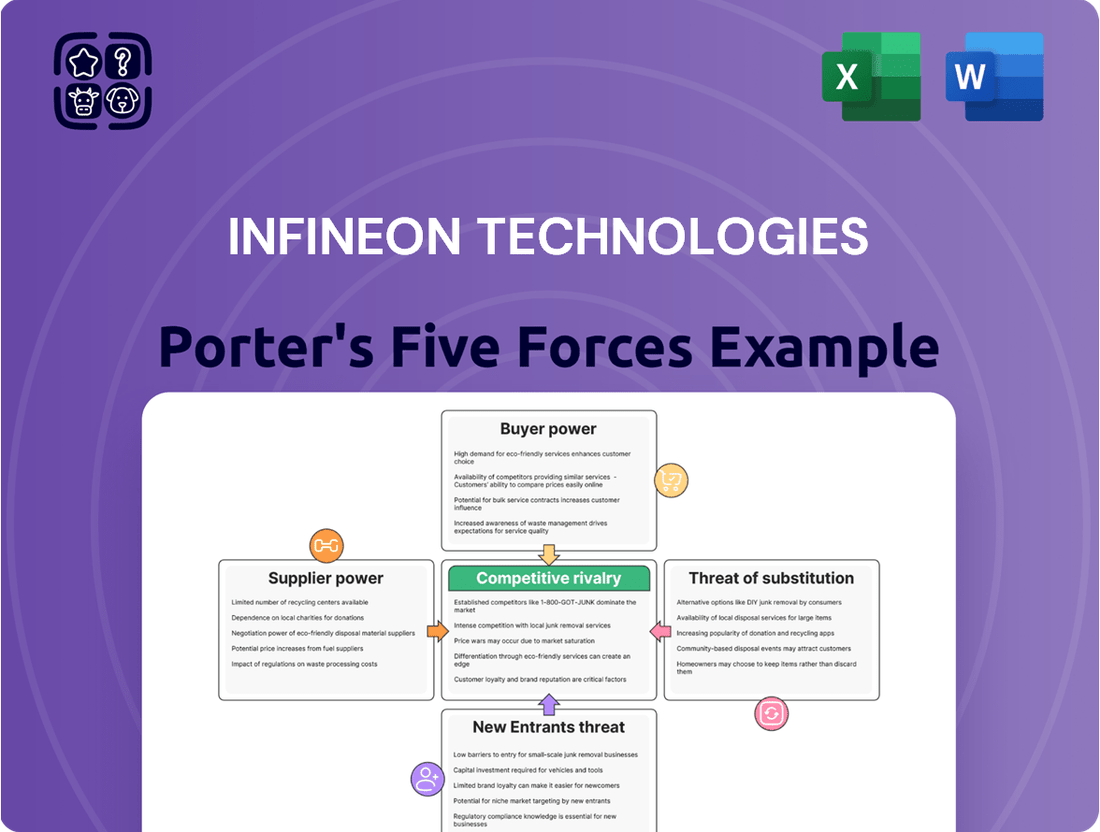
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The semiconductor industry, crucial for companies like Infineon Technologies, often features a limited number of specialized suppliers for essential materials and equipment. This concentration means a few key players control the supply of critical inputs such as silicon wafers, advanced manufacturing machinery, and specialized intellectual property. For instance, the production of wide-bandgap materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN), vital for power electronics, is dominated by a handful of highly technical firms.
This limited supplier base grants these companies considerable bargaining power. The high barriers to entry, including significant R&D investment and complex manufacturing processes, mean few competitors can emerge. Consequently, these concentrated suppliers can often dictate pricing and supply terms, impacting the cost structure and production schedules of semiconductor manufacturers like Infineon. In 2024, the demand for advanced semiconductor materials continued to outpace supply, further strengthening the position of these key suppliers.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly impacts Infineon's bargaining power with its suppliers. For advanced semiconductors like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), which are crucial for Infineon's high-performance products, the materials and manufacturing processes are highly specialized. Only a limited number of suppliers can meet these stringent requirements, giving those suppliers considerable leverage.
Switching suppliers in the semiconductor industry, including for a company like Infineon Technologies, is a costly and time-consuming endeavor. The rigorous qualification processes, potential need for re-engineering of existing designs, and the risk of production disruptions all contribute to these high switching costs. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see significant lead times for specialized components, meaning a supplier change could delay product launches by months.
Infineon, a leader in power semiconductors and system solutions, invests heavily in ensuring the reliability and compatibility of its suppliers' components. This deep integration into their complex manufacturing and product development cycles means that changing a supplier isn't just a matter of placing a new order; it involves extensive validation and potential redesigns. This commitment to quality and integration inherently strengthens the bargaining power of their established suppliers.
Consequently, the substantial expense and the potential for significant operational delays associated with transitioning to new suppliers grant existing suppliers considerable leverage. Infineon, like its peers, must weigh these considerable costs against the benefits of seeking alternative sources, often making it more economical to maintain relationships with proven suppliers, even if pricing power shifts.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into semiconductor manufacturing, while generally low, is a potential concern for companies like Infineon Technologies. This could occur if a supplier of highly specialized materials or equipment, crucial for chip production, decided to enter the chip manufacturing space themselves.
The significant barriers to entry in semiconductor fabrication, including the astronomical capital investment and the need for highly specialized expertise, make this a rare occurrence. For instance, building a new semiconductor fabrication plant, or fab, can cost upwards of $20 billion, a cost that few suppliers would readily undertake.
- High Capital Expenditure: Semiconductor fabs require billions of dollars in investment, deterring most suppliers from forward integration.
- Specialized Expertise: The complex nature of chip design and manufacturing demands highly specialized knowledge and skilled personnel.
- Limited Likelihood: Due to these barriers, the threat of direct forward integration by suppliers into chip manufacturing remains a low, though not entirely absent, risk for established players like Infineon.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Infineon's Cost Structure or Differentiation
The cost of raw materials and specialized equipment represents a substantial segment of Infineon's expenditures. For instance, in 2023, the cost of goods sold for Infineon was €13.4 billion, highlighting the significant impact of supplier pricing on its profitability.
Moreover, the caliber and novelty of components sourced from suppliers directly influence Infineon's capacity for product differentiation, particularly in rapidly expanding sectors such as automotive and industrial power management. This is crucial as Infineon aims to maintain its leadership in these competitive markets.
The escalating need for energy-efficient technologies and chips powered by artificial intelligence further elevates the importance of high-performance materials from suppliers. These advanced inputs are essential for Infineon to sustain its competitive advantage and meet evolving market demands.
- Significant Material Costs: Infineon's cost of goods sold reached €13.4 billion in 2023, underscoring the supplier's impact on its overall cost structure.
- Quality Drives Differentiation: The quality of supplier inputs is directly linked to Infineon's ability to offer differentiated products, especially in high-demand areas.
- Critical for Innovation: Advanced materials from suppliers are vital for Infineon's progress in energy efficiency and AI chip development.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Infineon Technologies is significant due to the concentrated nature of specialized input providers in the semiconductor industry. Key suppliers of advanced materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), along with critical manufacturing equipment, are few in number. This limited supplier base, coupled with high barriers to entry, allows these entities to exert considerable influence over pricing and supply terms, directly impacting Infineon's cost structure and production timelines. In 2024, the ongoing demand for advanced semiconductor materials continued to strengthen the leverage of these crucial suppliers.
The uniqueness and specialized nature of the inputs required for Infineon's high-performance products further amplify supplier leverage. Switching suppliers involves substantial costs, including rigorous qualification processes, potential redesigns, and the risk of production delays, making it often more economical to maintain existing relationships. For instance, in 2024, extended lead times for specialized components underscored the difficulty and cost of supplier transitions within the semiconductor sector.
Suppliers' ability to dictate terms is also influenced by Infineon's deep integration with their components, which necessitates extensive validation and potential redesigns for any supplier change. The threat of forward integration by suppliers into chip manufacturing is minimal due to the immense capital expenditure and specialized expertise required, with new fab construction costing upwards of $20 billion. However, the substantial material costs, exemplified by Infineon's €13.4 billion cost of goods sold in 2023, highlight the significant financial impact of supplier pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Infineon | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High Bargaining Power | Limited number of suppliers for critical materials (SiC, GaN) and equipment. |
| Input Uniqueness & Specialization | High Bargaining Power | Specialized materials and processes require few capable suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High Bargaining Power | Costly qualification, redesigns, and risk of production delays; extended lead times in 2024. |
| Supplier Integration | Low Threat | High capital expenditure (>$20B for a fab) and specialized expertise deter forward integration. |
| Cost of Goods Sold | Significant Impact | Infineon's COGS was €13.4 billion in 2023, showing supplier pricing's financial weight. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the semiconductor industry's competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes, specifically for Infineon Technologies.
Instantly visualize Infineon's competitive landscape with a clear, actionable breakdown of each force, enabling rapid identification of key strategic levers.
Customers Bargaining Power
The concentration of Infineon's customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. Serving large, consolidated industries like automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics means a few dominant players often dictate terms.
For example, Infineon is a key supplier to a select group of major car manufacturers and Tier 1 automotive suppliers. This limited customer base allows these significant buyers to exert considerable influence over pricing and contract conditions, particularly when market inventories are high.
Infineon's major customers, particularly in the automotive sector, frequently place very large volume orders for semiconductors and integrated system solutions. For example, in 2024, the automotive segment continued to be a significant revenue driver, with major car manufacturers relying on Infineon for critical components like power semiconductors and microcontrollers. These substantial order volumes grant these clients considerable bargaining power during price and contract negotiations, as their business is vital to Infineon's overall financial performance and market share.
Switching semiconductor suppliers can be a significant undertaking for Infineon's customers. The deep integration of Infineon's components into their product designs necessitates extensive re-design, rigorous qualification processes, and carries the risk of supply chain disruptions. For example, in the automotive sector, a single semiconductor change can trigger months of re-testing and validation, impacting time-to-market. While these switching costs are substantial, customers facing intense cost pressures or finding superior technological alternatives might still explore supplier changes.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customers in the automotive and industrial sectors, while prioritizing performance and reliability, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is largely driven by the intense competition they face in their respective end markets, pushing them to seek cost-effective solutions. For Infineon, this translates into a constant need for efficient cost management and competitive pricing strategies to maintain market share.
The impact of economic headwinds and ongoing inventory adjustments within these sectors can further heighten customer price sensitivity. For instance, during periods of economic slowdown, purchasing decisions become even more scrutinized for cost-effectiveness. Infineon's ability to offer competitive pricing, even amidst fluctuating market conditions, is therefore crucial for its success in these key segments.
- Automotive and Industrial Sector Sensitivity: Customers in these vital sectors are not just looking for quality; they are actively seeking value due to competitive pressures in their own supply chains.
- Cost Management Imperative: Infineon's operational efficiency and cost control are directly linked to its ability to meet the price expectations of these discerning customers.
- Economic and Inventory Fluctuations: Broader economic trends and the need for inventory optimization by customers can amplify the focus on price, making it a critical decision factor.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts Infineon Technologies' bargaining power with its customers. Customers can readily turn to competitors such as NXP Semiconductors, STMicroelectronics, and Renesas Electronics for similar semiconductor solutions. For instance, in the automotive sector, where Infineon is a leader, NXP and STMicroelectronics also offer a broad range of microcontrollers and power management ICs, providing viable alternatives.
While Infineon boasts strong market positions, particularly in power semiconductors and automotive applications, the existence of these capable substitutes empowers customers. This means customers have choices and can switch suppliers if pricing, features, or service levels are not met. In 2023, the global automotive semiconductor market, a key segment for Infineon, was valued at approximately $60 billion, with significant competition across various product categories.
- Customer Choice: Competitors like NXP, STMicroelectronics, and Renesas offer comparable semiconductor products, giving customers alternatives.
- Market Competition: In the automotive sector, a key market for Infineon, these competitors provide a wide array of microcontrollers and power management ICs.
- Supplier Leverage: The presence of these alternatives enhances customer bargaining power, allowing them to seek better terms or switch suppliers.
- Market Dynamics: The global automotive semiconductor market, valued around $60 billion in 2023, illustrates the competitive landscape where substitutes are prevalent.
Infineon's customers, especially in the automotive and industrial sectors, possess considerable bargaining power due to their large order volumes and the significant switching costs involved in changing suppliers. For example, major car manufacturers, a key customer base for Infineon, often place orders worth hundreds of millions of dollars for critical components, giving them leverage in price negotiations. The deep integration of Infineon's chips into complex product designs means that switching can incur substantial re-engineering and validation expenses, potentially delaying product launches.
| Customer Segment | Order Volume Impact | Switching Cost Impact | Price Sensitivity Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturers | High (Large, recurring orders) | High (Deep product integration) | Intense market competition |
| Industrial Equipment Makers | Moderate to High | Moderate to High | Cost-efficiency demands |
| Consumer Electronics Brands | Variable (Depends on product cycle) | Moderate | Rapid innovation and cost pressures |
Same Document Delivered
Infineon Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Infineon Technologies, detailing the competitive landscape, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalry within the semiconductor industry. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, offering actionable insights into Infineon's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The semiconductor industry is densely populated, featuring numerous global competitors of varying sizes. Infineon Technologies faces substantial competition from established giants like NXP Semiconductors, STMicroelectronics, Renesas Electronics, Texas Instruments, and Onsemi. These well-capitalized companies contribute to a highly competitive environment.
The semiconductor industry is poised for robust expansion, with artificial intelligence and automotive applications acting as key growth drivers. However, not all of Infineon's specific market segments are expected to mirror this rapid ascent. Some end markets are projected to see a more subdued business trajectory in 2025, with AI being a notable exception.
In periods of slower industry-wide growth, competitive pressures tend to escalate significantly. Companies within these markets often engage in more aggressive strategies to capture or defend their market share, which can impact pricing and profitability for all players, including established firms like Infineon.
Infineon Technologies thrives on product differentiation, particularly in high-growth areas like energy efficiency, mobility, and security. Their significant investment in research and development, which reached €1.1 billion in fiscal year 2023, fuels innovation in power semiconductors and advanced materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN). This focus allows them to offer specialized solutions that command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty, directly impacting competitive rivalry.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The semiconductor industry, including players like Infineon Technologies, is characterized by exceptionally high fixed costs. Building and equipping a modern semiconductor fabrication plant, or fab, can easily run into billions of dollars. For instance, TSMC's new fabs are reported to cost upwards of $20 billion each. This massive capital expenditure creates a significant barrier to entry and necessitates high capacity utilization to spread these costs and achieve profitability.
These substantial fixed costs, coupled with the highly specialized nature of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, lead to formidable exit barriers. Once a company invests heavily in R&D and manufacturing infrastructure, it is difficult and costly to divest or repurpose these assets. Consequently, firms are often compelled to continue competing, even in challenging market conditions, to recoup their investments, intensifying rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Outlay: Semiconductor manufacturing requires billions in upfront investment for R&D and advanced fabrication facilities.
- Economies of Scale Imperative: Companies must operate at near-full capacity to make these high fixed costs economically viable.
- Specialized Assets: The unique and specialized nature of manufacturing equipment makes exiting the industry extremely difficult and costly.
- Sustained Competitive Pressure: High exit barriers mean companies are less likely to leave the market, leading to persistent competition, especially during industry downturns.
Strategic Stakes
The semiconductor industry, a cornerstone of digitalization, decarbonization, and the burgeoning AI revolution, presents incredibly high strategic stakes. This intense importance fuels a fierce competitive landscape where companies like Infineon Technologies are heavily incentivized to invest and innovate aggressively. Infineon's focus on critical segments such as automotive and power management underscores the drive to secure and maintain market leadership, which is paramount for sustained growth and profitability.
This strategic imperative translates into continuous and robust competitive efforts. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor market was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the immense value and the intense battle for market share. Companies are pouring billions into research and development and expanding manufacturing capacity to meet demand and stay ahead.
- High Industry Value: The global semiconductor market is a multi-hundred-billion-dollar industry, making market share extremely valuable.
- Strategic Importance: Semiconductors are critical enablers for key growth trends like AI, electric vehicles, and renewable energy.
- Investment in R&D: Companies like Infineon invest heavily in research and development to maintain a technological edge.
- Capacity Expansion: Significant investments are being made in new fabrication plants (fabs) to meet escalating demand.
Infineon operates in a highly competitive semiconductor market, facing rivals like NXP, STMicroelectronics, and Texas Instruments. The industry's immense value, projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, fuels aggressive competition for market share. Companies like Infineon invest heavily, with R&D spending reaching €1.1 billion in fiscal year 2023, to maintain a technological edge and secure leadership in critical growth areas such as automotive and AI.
| Competitor | Key Market Segments | Approximate R&D Spending (2023, if available) |
|---|---|---|
| NXP Semiconductors | Automotive, Industrial, IoT | $1.8 billion (FY23) |
| STMicroelectronics | Automotive, Industrial, Personal Electronics | $1.6 billion (FY23) |
| Texas Instruments | Analog, Embedded Processing | $3.5 billion (FY23) |
| Onsemi | Automotive, Industrial, Cloud Power | $1.4 billion (FY23) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for Infineon's advanced semiconductor solutions are often older, less efficient silicon-based technologies or alternative system-level approaches. While these substitutes might present a lower upfront cost, they typically lag significantly behind Infineon's specialized power semiconductors and microcontrollers in terms of performance, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities. This is particularly evident in high-demand sectors such as electric vehicles and AI data centers, where the total cost of ownership and operational efficiency are paramount.
Customer propensity to substitute for Infineon's semiconductor solutions is typically low, especially in demanding sectors like automotive and industrial. This is because Infineon's offerings often provide crucial advantages in efficiency, miniaturization, unwavering reliability, and advanced functionality that are hard for competitors to replicate quickly. For instance, the automotive industry's stringent safety and performance requirements mean that switching suppliers for critical components like microcontrollers or power semiconductors carries significant risk and development cost.
Switching to a fundamentally different technology or system architecture would involve substantial re-design, testing, and validation costs for Infineon's customers. These high switching costs act as a significant barrier to substitution. For instance, in the automotive sector, where Infineon has a strong presence, development cycles can span several years, locking customers into existing designs and making a shift to a substitute product financially prohibitive.
Rate of Improvement of Substitute Technologies
While traditional silicon semiconductor technologies are quite mature, ongoing advancements in alternative materials and system-on-chip (SoC) integration present a potential long-term threat. For instance, the increasing efficiency and performance of compound semiconductors could eventually displace silicon in certain high-power or high-frequency applications.
However, Infineon Technologies is proactively addressing this by heavily investing in and integrating next-generation materials such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN). This strategy effectively mitigates the threat from these specific substitutes by incorporating them into Infineon's own product roadmap and offerings.
- SiC and GaN Adoption: Infineon's commitment to SiC and GaN technologies positions them to capitalize on the shift towards higher performance semiconductors, rather than being disrupted by them.
- Market Growth for Wide Bandgap Semiconductors: The market for SiC and GaN devices is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion driven by demand in electric vehicles, renewable energy, and 5G infrastructure. For example, the SiC power semiconductor market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 30% through 2030.
- System-on-Chip (SoC) Integration: While SoC integration can offer advantages in terms of miniaturization and power efficiency, Infineon's expertise in power management and its ability to integrate various functionalities into its own solutions helps to manage this threat.
Indirect Substitution through System-Level Changes
Substitution isn't always about a direct competitor offering a similar product. Sometimes, customers can bypass the need for certain components entirely by adopting different technological approaches. This is particularly relevant in the semiconductor industry where system-level changes can significantly alter component demand. For instance, a shift towards highly integrated System-on-Chips (SoCs) in automotive electronics could consolidate functions previously requiring multiple discrete semiconductors. This trend could directly impact demand for individual chips that Infineon Technologies supplies, as fewer separate components are needed within a single integrated solution.
Consider the automotive sector's increasing reliance on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment. While these systems drive demand for sophisticated chips, the architecture often favors integration. For example, a single SoC might handle sensor fusion, processing, and communication, reducing the need for separate microcontrollers, memory chips, and power management ICs that Infineon also offers. This indirect substitution through system-level integration presents a significant threat, as it fundamentally alters the bill of materials for end products.
- System-on-Chip (SoC) Integration: The increasing prevalence of SoCs in automotive and consumer electronics reduces the need for discrete components.
- Architectural Shifts: Customers may adopt new design philosophies that consolidate functionality, thereby lowering the demand for individual semiconductor parts.
- Impact on Infineon: This indirect substitution threatens demand for Infineon's discrete components, even as the overall complexity of electronic systems grows.
The threat of substitutes for Infineon's semiconductor products is generally low due to high switching costs and the specialized performance advantages Infineon offers, particularly in sectors like automotive and industrial. While alternative technologies exist, they often fall short in efficiency and reliability, making them impractical for demanding applications. For instance, the automotive industry's rigorous safety standards and long development cycles create significant barriers to adopting substitute components.
However, advancements in alternative materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) present a potential long-term challenge, especially in high-power applications. Infineon is proactively addressing this by investing heavily in these wide bandgap technologies, integrating them into its own product portfolio. The market for SiC and GaN is projected for substantial growth; for example, the SiC market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% through 2030, demonstrating a clear shift in the semiconductor landscape.
Furthermore, system-level integration through System-on-Chips (SoCs) can act as an indirect substitute, consolidating functions and reducing demand for discrete components. While this trend impacts the need for individual chips, Infineon's strategic focus on advanced integration and power management solutions helps to mitigate this threat by offering comprehensive solutions rather than just individual components.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Impact on Infineon | Mitigation Strategies | Key Data Point |
| Older Silicon Technologies | Less efficient, lower performance alternatives. | Low, due to performance gaps and high switching costs in critical sectors. | Highlighting superior efficiency, reliability, and total cost of ownership. | Automotive development cycles can span several years, increasing switching costs. |
| Alternative System-Level Approaches (e.g., SoCs) | Consolidation of functions, reducing need for discrete components. | Moderate, as it can reduce demand for individual chips. | Focusing on integrated solutions and power management expertise. | Increased SoC prevalence in automotive and consumer electronics. |
| Emerging Materials (SiC, GaN) | Higher performance in specific high-power/high-frequency applications. | Potential long-term threat if not adopted. | Investing in and integrating SiC and GaN into product roadmap. | SiC market expected to grow at over 30% CAGR through 2030. |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor industry, where Infineon Technologies operates, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its staggering capital requirements. Building and equipping a state-of-the-art fabrication plant, or fab, can easily cost tens of billions of dollars. For instance, Intel announced in 2021 plans for new fabs in Arizona with an initial investment of $20 billion, highlighting the immense scale of necessary funding.
This colossal financial hurdle means that only a handful of established global players can afford to enter or expand significantly in the market. The upfront investment for research, development, and manufacturing infrastructure is so substantial that it effectively deters most potential new competitors, offering a degree of protection for existing companies like Infineon.
Established players like Infineon Technologies benefit immensely from significant economies of scale in their advanced manufacturing processes, a factor that is crucial in the capital-intensive semiconductor industry. These scale advantages translate directly into lower per-unit production costs, a hurdle new entrants would find incredibly difficult to overcome. For instance, in 2023, Infineon's revenue was approximately €16.3 billion, indicating a substantial operational footprint that smaller, newer companies cannot easily replicate.
Furthermore, Infineon possesses a deep and extensive experience curve, honed over decades of semiconductor design, development, and production. This accumulated knowledge allows for optimized processes, higher yields, and superior product quality. A new entrant would need years, if not decades, to build a comparable level of expertise, making it challenging to compete on both cost efficiency and technological sophistication, thereby posing a significant barrier to entry.
Infineon Technologies' extensive portfolio of proprietary technologies and patents, especially in power semiconductors and microcontrollers, creates a significant barrier to entry. This deep know-how makes it challenging and costly for newcomers to develop comparable products, often requiring substantial investment in research and development to avoid patent infringement.
Access to Distribution Channels
Infineon Technologies benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with major customers and extensive distribution networks, particularly in the high-stakes automotive and industrial sectors. Newcomers struggle to replicate this established trust and access, as these markets often involve lengthy design-in periods and demand unwavering reliability, creating a significant barrier.
For instance, in the automotive semiconductor market, a segment where Infineon holds a strong position, securing partnerships with leading car manufacturers is crucial. These relationships are built over years, involving rigorous qualification processes and a demonstrated track record of performance. A new entrant would need substantial investment and time to even begin challenging Infineon's established market presence and customer loyalty.
The difficulty in accessing these critical distribution channels means that potential new competitors face an uphill battle. Without established routes to market and the necessary customer confidence, even innovative technologies may struggle to gain traction. This is particularly true for sectors where product lifecycles are long and switching costs for established suppliers are high.
Key challenges for new entrants regarding distribution channels include:
- Building trust with long-term customers: Infineon's history of reliability in demanding applications like automotive electronics makes it difficult for new players to gain immediate acceptance.
- Navigating complex sales cycles: The extended design and qualification phases in sectors such as automotive require significant upfront investment and patience, which new entrants may lack.
- Establishing global distribution networks: Replicating Infineon's widespread reach across key geographical markets and industry segments is a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
- Meeting stringent industry standards: Sectors like automotive demand adherence to rigorous quality and safety standards, a hurdle that new entrants must clear before even accessing distribution.
Government Policy and Regulation
Governments are increasingly prioritizing semiconductor manufacturing, with significant policy shifts impacting potential new entrants. For instance, the US CHIPS and Science Act, enacted in 2022, allocated over $52 billion to boost domestic chip production and research. This creates both opportunities and hurdles for new companies. While subsidies can lower entry barriers, navigating the complex regulatory environment and securing government favor, often tilted towards established players with proven track records, remains a significant challenge.
The evolving regulatory landscape, driven by national security concerns and supply chain resilience efforts, can act as a deterrent. New entrants must contend with varying national standards, export controls, and intellectual property protection laws across different regions. For example, the European Union's Chips Act, aiming to double its market share in semiconductors by 2030, involves substantial funding but also mandates adherence to specific environmental and labor standards, adding layers of compliance for any new player.
- Government Subsidies: The US CHIPS Act ($52 billion) and EU Chips Act provide significant financial incentives, potentially lowering capital requirements for new entrants.
- Regulatory Complexity: New players must navigate diverse national regulations, export controls, and intellectual property laws, increasing operational costs and time-to-market.
- Established Player Advantage: Government support programs often favor existing companies with established infrastructure and market presence, creating an uneven playing field.
- Supply Chain Security Focus: Policies aimed at securing domestic supply chains may prioritize domestic sourcing and collaboration with existing, trusted manufacturers.
The threat of new entrants in the semiconductor industry, impacting Infineon Technologies, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital investment required. Building a modern semiconductor fabrication facility can cost upwards of $20 billion, as seen with Intel's Arizona expansion plans announced in 2021. This financial barrier effectively limits the number of companies capable of entering the market, protecting established players.
Furthermore, economies of scale and a steep learning curve present substantial challenges for newcomers. Infineon's 2023 revenue of approximately €16.3 billion demonstrates its operational scale, allowing for lower per-unit costs that new entrants would struggle to match. Decades of experience also contribute to process optimization and product quality, creating a knowledge gap that new companies must overcome.
Infineon's strong customer relationships, particularly in demanding sectors like automotive, and its extensive patent portfolio also act as significant deterrents. These established ties and proprietary technologies require substantial time and investment for new entrants to replicate or circumvent, further solidifying Infineon's market position.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Infineon Technologies is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Infineon's own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research reports from firms like Gartner and IDC.
