Grupo Inbursa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grupo Inbursa Bundle
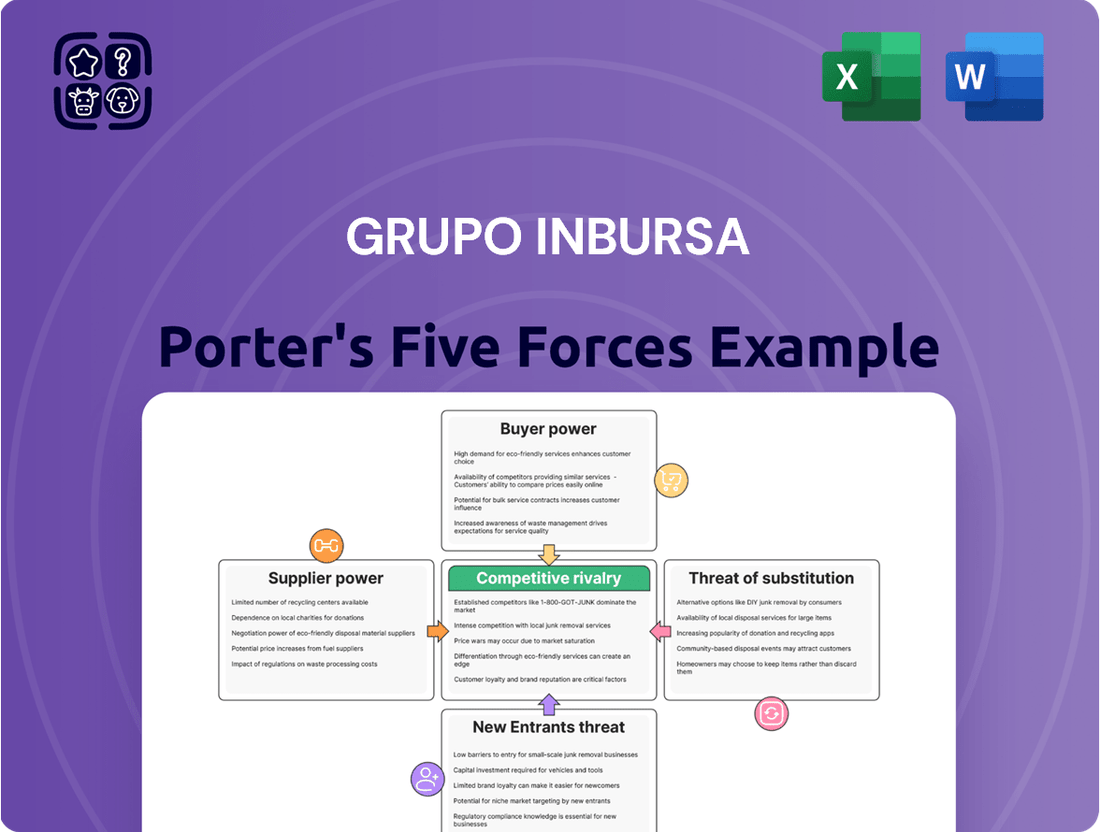
Grupo Inbursa operates within a dynamic financial services landscape, facing moderate bargaining power from both suppliers and buyers. The threat of new entrants is significant due to regulatory hurdles and capital requirements, while the intensity of rivalry among existing players, particularly in insurance and banking, shapes competitive strategies.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Grupo Inbursa’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Grupo Inbursa's access to capital is largely secured through a substantial base of retail deposits and institutional funding. By March 2025, retail deposits had surged to MXN 392,283 million, demonstrating Inbursa's considerable capacity to draw funds from individual customers.
Despite this strong retail presence, institutional lenders and large-scale depositors hold significant bargaining power. They can leverage their capital by demanding higher interest rates or more favorable terms, which directly influences Inbursa's overall cost of capital and profitability.
Grupo Inbursa's reliance on technology means software and IT vendors wield significant influence. The company's digital operations are extensive, with 94.2% of transactions occurring digitally as of March 2025. This high digital adoption rate amplifies the bargaining power of vendors offering critical infrastructure and specialized software solutions, especially those with proprietary technologies.
The specialized nature of these technological offerings and the substantial costs associated with migrating integrated systems create high switching costs for Inbursa. Consequently, vendors providing these essential, often unique, IT and cybersecurity solutions are in a strong position to negotiate terms, impacting Inbursa's operational efficiency and costs.
Grupo Inbursa's reliance on skilled human capital in finance, technology, risk management, and compliance significantly influences supplier power. A tight labor market, particularly for specialized financial professionals, can empower these employees, driving up recruitment and retention expenses for Inbursa. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity experts in the financial sector saw salary increases of up to 15% in key markets, directly impacting Inbursa's operational costs.
Regulatory Bodies and Central Bank
Regulatory bodies such as Banco de México and the National Banking and Securities Commission (CNBV) exert significant influence over Grupo Inbursa. These entities establish capital adequacy, risk management, and consumer protection standards that directly shape Inbursa's operational strategies and associated costs. For instance, Mexico's adherence to Basel III international standards necessitates robust compliance measures, impacting how Inbursa manages its balance sheet and capital reserves.
The bargaining power of these regulatory bodies is substantial, as non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and operational restrictions. In 2024, financial institutions in Mexico, including Inbursa, continued to navigate evolving regulatory landscapes. For example, the CNBV's ongoing focus on cybersecurity and data protection mandates additional investment in technological infrastructure and compliance protocols.
- Regulatory Mandates: Banco de México and CNBV set operational rules, influencing costs and strategic decisions.
- Compliance Requirements: Adherence to international standards like Basel III impacts capital management and risk frameworks.
- Enforcement Power: Penalties for non-compliance can be substantial, reinforcing regulatory authority.
- 2024 Focus Areas: Cybersecurity and data protection are key areas of regulatory scrutiny for financial institutions.
Credit Rating Agencies
Credit rating agencies wield considerable power over Grupo Inbursa. Their assessments directly influence Inbursa's borrowing costs and the market's perception of its financial health. For instance, in November 2024, AM Best affirmed an A (Excellent) rating for Seguros Inbursa, a testament to its strong financial standing. This favorable rating allows Inbursa to secure capital at more competitive interest rates.
A downgrade in credit rating by agencies like S&P Global Ratings could significantly increase Inbursa's funding expenses. It might also restrict its ability to access capital markets, impacting its expansion and operational flexibility. Such agencies act as gatekeepers, shaping Inbursa's access to and cost of debt financing.
- Favorable Ratings: Agencies like AM Best and S&P Global Ratings provide crucial assessments that affect Inbursa's cost of borrowing.
- Impact on Capital Access: A strong credit rating, such as the A (Excellent) affirmed for Seguros Inbursa in November 2024, facilitates access to capital markets at competitive rates.
- Risk of Downgrades: Conversely, a lower rating can lead to higher funding costs and diminished access to necessary capital.
Grupo Inbursa faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly in specialized technology and skilled labor. While the company benefits from a strong retail deposit base, institutional lenders can negotiate favorable terms. The high digital transaction rate of 94.2% in March 2025 amplifies the influence of IT vendors, especially those with proprietary solutions, due to high switching costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Grupo Inbursa is influenced by several factors. Critical IT and cybersecurity vendors hold significant sway due to the specialized nature of their offerings and the substantial costs associated with system migration. Furthermore, the demand for specialized financial and technology talent in 2024, leading to potential salary increases of up to 15% for cybersecurity experts, empowers skilled employees and increases Inbursa's recruitment and retention expenses.
| Supplier Type | Key Influences | Impact on Inbursa |
| Institutional Lenders/Large Depositors | Capital size, demand for higher rates | Increased cost of capital, potential impact on profitability |
| IT & Software Vendors | Proprietary technology, high switching costs | Negotiating power on terms, potential impact on operational efficiency and costs |
| Skilled Labor (Finance, Tech, Risk) | Tight labor market, specialized skills demand | Higher recruitment and retention costs, impacting operational expenses |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Grupo Inbursa, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive breakdown of Grupo Inbursa's Porter's Five Forces, empowering proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail and SME customers, while individually small, possess significant collective bargaining power. This power stems from their ability to easily switch between the increasing number of financial service providers available. The digital landscape makes comparing services and rates straightforward, effectively reducing the cost and effort associated with changing providers.
Grupo Inbursa's retail loan portfolio saw a substantial 27.1% growth in Q1 2025, demonstrating a strong customer base. However, this growth also highlights the necessity for Inbursa to maintain competitive offerings to retain these customers in a market where switching is increasingly frictionless.
Large corporate and institutional clients wield significant bargaining power over Grupo Inbursa. Their substantial business volumes and the strategic nature of their financial relationships allow them to negotiate highly customized financial products, often securing preferential interest rates and reduced service fees. This leverage is critical for Inbursa to maintain and grow its market share in the wholesale banking segment.
The importance of these powerful clients is underscored by Inbursa's financial performance. For instance, the company’s wholesale loan portfolio experienced a notable 13.7% growth in the first quarter of 2025. This expansion demonstrates Inbursa's commitment to meeting the demands of these key clients, which is essential for their continued business and profitability.
Customers across Grupo Inbursa's various segments demonstrate a notable sensitivity to price, especially for standard banking and insurance offerings. For instance, in 2023, the average interest rate spread for Mexican banks hovered around 5%, a figure that directly impacts customer choices for loans and deposits, pressuring Inbursa to remain competitive.
The proliferation of online comparison platforms and increased financial literacy among consumers significantly boosts transparency in the financial services market. This means customers can easily benchmark Inbursa's pricing against competitors, forcing the company to offer attractive rates and potentially squeezing profit margins on its core products.
Low Switching Costs in Digital Channels
The increasing prevalence of digital platforms in banking and insurance significantly lowers the barriers for customers to switch providers. This ease of transition, driven by readily available online comparison tools and streamlined onboarding processes, directly impacts the bargaining power of customers.
Grupo Inbursa's strong digital presence, evidenced by 98.0% of new contracts originating digitally as of March 2025, highlights this dynamic. While a digital-first approach is a competitive advantage, it simultaneously empowers customers to more readily explore and compare offerings from rival financial institutions, thereby increasing their leverage.
- Reduced Friction: Digital channels minimize the effort and perceived cost customers associate with changing financial service providers.
- Increased Transparency: Online comparison sites and readily available product information allow customers to easily assess alternatives.
- Inbursa's Digital Penetration: 98.0% of new contracts originated digitally in March 2025 underscores the accessibility of Inbursa's services but also the ease with which customers can switch away.
Access to Diverse Financial Products
Customers today enjoy a significantly wider selection of financial products and services. Beyond the traditional offerings from banks like Grupo Inbursa, the market now includes innovative solutions from fintech companies and specialized lending institutions. This increased accessibility to diverse financial tools empowers customers, allowing them to seek out and customize solutions that best fit their specific needs from a variety of providers.
This heightened customer choice directly translates into increased bargaining power. When faced with numerous alternatives, customers are less reliant on any single provider and can more readily switch to competitors offering better terms, rates, or service. For instance, the growth of digital lending platforms in Mexico, which saw a substantial increase in loan origination volume in 2024, presents a direct alternative for many of Inbursa's potential or existing clients.
- Expanded Product Landscape: Fintechs and specialized lenders offer alternatives to traditional banking services, increasing customer options.
- Customization and Choice: Customers can now tailor financial solutions from a broader market, enhancing their ability to negotiate.
- Competitive Pressure: The availability of diverse providers forces established institutions like Inbursa to remain competitive in pricing and product offerings.
- Customer Retention Imperative: Inbursa must continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain its customer base in this dynamic environment.
The bargaining power of customers within Grupo Inbursa's operations is substantial and growing, driven by increased market transparency and reduced switching costs. Customers can easily compare rates and services across numerous providers, especially through digital channels, which makes them less loyal to any single institution.
In 2024, the financial services sector in Mexico saw a significant increase in digital adoption, with many customers leveraging online platforms to find the best deals. This trend, coupled with a wider array of fintech and specialized lenders offering competitive products, means Inbursa must consistently provide attractive pricing and superior service to retain its client base.
| Factor | Impact on Inbursa | Customer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Comparison Platforms | Increased price sensitivity | Easily compare rates and fees |
| Fintech Competition | Pressure on margins | Switch to alternative providers for better terms |
| Customer Financial Literacy | Demand for transparency | Negotiate for lower interest rates and fees |
What You See Is What You Get
Grupo Inbursa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders, detailing Grupo Inbursa's Porter's Five Forces analysis. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial services sector. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use upon purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Mexican financial landscape presents a curious duality: while approximately 70 insurers actively compete, a concentrated core of just ten entities commands nearly 70% of the total market share. This dynamic signifies that despite a large number of participants, the competitive intensity is largely dictated by a few major players. Grupo Inbursa, for instance, maintained a 3.4% stake in this insurance market as of March 2025, illustrating its position within this concentrated structure.
Competition is particularly fierce in high-growth segments like retail banking and insurance. Grupo Inbursa's total loan portfolio expanded by 17.9% year-over-year in Q1 2025, highlighting the dynamic nature of the market where numerous players are actively pursuing loan growth. This intense rivalry frequently translates into compressed profit margins as institutions compete on pricing and service offerings.
While many financial products are becoming similar, companies like Grupo Inbursa aim to stand out. They achieve this through excellent customer service, cutting-edge digital tools, and unique financial solutions tailored to specific needs.
Inbursa's impressive efficiency ratio of 17.0% as of March 2025 is a key differentiator. This high level of operational efficiency suggests they can manage costs effectively, potentially translating into more attractive product offerings and competitive pricing for their customers.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Competitive rivalry within the financial services sector is intensifying as key players pursue strategic acquisitions and partnerships. This consolidation aims to bolster market share, integrate new technologies, and unlock operational efficiencies. For instance, Grupo Inbursa's March 2024 acquisition of 80% of Cetelem Mexico underscores this strategic maneuver, signaling a significant push to expand its footprint in consumer and commercial auto financing. This move is expected to enhance Inbursa's competitive standing by leveraging Cetelem's established presence and expertise in the automotive lending space.
These strategic moves are not isolated incidents; they reflect a broader industry trend where companies are actively seeking alliances and mergers to gain a competitive edge. By combining resources and capabilities, firms can achieve greater economies of scale, which translates into more competitive pricing and service offerings. This dynamic environment means that companies like Inbursa must constantly evaluate and adapt their strategies to remain relevant and profitable amidst aggressive competition.
The impact of such consolidation on competitive rivalry can be substantial:
- Increased Market Concentration: Acquisitions can lead to fewer, larger players dominating specific market segments, intensifying the pressure on remaining independent entities.
- Enhanced Service Offerings: Merged entities often combine complementary services, presenting customers with more comprehensive solutions and forcing competitors to innovate or partner.
- Price Competition: Economies of scale achieved through acquisitions can enable larger firms to engage in more aggressive pricing strategies, challenging smaller competitors.
Digital Transformation and Fintech Impact
The financial sector's swift digital evolution, fueled by fintech advancements, significantly escalates competitive rivalry for Grupo Inbursa. Traditional institutions are pouring resources into digital platforms to counter agile fintech disruptors, creating a dynamic and often aggressive market. This digital push means established players must constantly innovate to retain market share.
Mexico's fintech scene is particularly vibrant, leading Latin America with over 500 startups as of early 2024. This proliferation of new digital financial services intensifies competition, forcing companies like Inbursa to adapt rapidly. The sheer number of innovative solutions entering the market means customer choices are expanding, and loyalty can be harder to maintain.
- Fintech Startups in Mexico: Over 500, leading Latin America.
- Digital Investment: Traditional banks are increasing spending on digital channels.
- Disruption: Fintechs are challenging established banking models.
The competitive rivalry in Mexico's financial sector is intense, driven by a mix of established players and a burgeoning fintech scene. Despite a large number of insurers, a few dominant entities control a significant market share, leading to fierce competition, especially in retail banking and insurance. Grupo Inbursa's 3.4% insurance market share as of March 2025 and a 17.9% loan portfolio growth in Q1 2025 highlight its active participation in this dynamic environment.
Strategic acquisitions and digital innovation are key battlegrounds. Grupo Inbursa's acquisition of 80% of Cetelem Mexico in March 2024 demonstrates a move to consolidate and expand its reach in auto financing. Simultaneously, the rapid growth of over 500 fintech startups in Mexico by early 2024 forces traditional institutions like Inbursa to heavily invest in digital platforms to maintain relevance and customer engagement.
| Metric | Grupo Inbursa (Q1 2025) | Industry Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Market Share | 3.4% | Concentrated; top 10 hold ~70% |
| Loan Portfolio Growth (YoY) | 17.9% | High growth in retail banking |
| Efficiency Ratio | 17.0% (Mar 2025) | Key differentiator for competitive pricing |
| Fintech Startups in Mexico | N/A | Over 500 (early 2024), driving digital competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech lending platforms present a significant threat of substitution for Grupo Inbursa. These platforms offer quicker, more adaptable, and often more accessible credit compared to traditional banking, directly impacting Inbursa's loan business for both consumers and companies.
Mexico's fintech industry has experienced robust growth, expanding by 30% annually since 2017, indicating a substantial shift in how credit is accessed and provided.
The rise of digital payment systems and e-wallets presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services offered by Grupo Inbursa. These platforms, like Mercado Pago and SPEI transfers in Mexico, provide increasingly seamless and cost-effective alternatives for everyday transactions, bypassing conventional banking channels. The FinTech Mexico Festival 2025 underscored the rapid adoption and innovation in this space, indicating a growing consumer preference for these digital solutions.
Online brokerage platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitution for Grupo Inbursa's investment services. These digital platforms offer individuals direct access to a wide array of investment opportunities, frequently with considerably lower fees and minimum investment requirements compared to traditional financial institutions. For instance, in 2024, the growth of digital investment platforms continued to accelerate, with many reporting substantial increases in user acquisition and assets under management, directly competing for Inbursa's customer base.
This accessibility empowers customers to independently manage their investment portfolios or utilize automated advisory services, bypassing the need for traditional intermediaries like Inbursa. The convenience, cost-effectiveness, and user-friendly interfaces of these substitutes allow individuals to take greater control of their financial futures, thereby reducing their reliance on established financial groups for investment management.
Self-Insurance and Captive Companies
Large corporations with significant financial reserves can opt to self-insure or establish captive insurance companies. This strategy allows them to retain risk internally rather than transferring it to external insurers like Grupo Inbursa, potentially lowering costs and enhancing control over their risk management. For instance, in 2024, the global captive insurance market continued its growth trajectory, with many large enterprises leveraging these structures to manage specific liabilities.
This alternative directly competes with Inbursa's traditional insurance offerings, particularly for comprehensive coverage packages. By managing risks in-house, these corporations bypass the premium payments and administrative overhead associated with purchasing policies from third-party providers. The feasibility of self-insurance or captives is directly tied to a company's financial strength and its ability to absorb potential losses.
The availability of these internal risk management solutions acts as a significant threat of substitutes for Grupo Inbursa. Companies that choose this path reduce their reliance on the broader insurance market, thereby limiting Inbursa's potential customer base and revenue streams. This is especially true for specialized or high-volume risks where internal expertise and capital can be effectively deployed.
Key considerations for this threat include:
- Financial Capacity: The ability of a corporation to absorb potential large-scale losses is paramount for self-insurance.
- Risk Management Expertise: Companies need internal capabilities to effectively assess, manage, and mitigate risks.
- Regulatory Environment: Captive insurance companies operate within specific regulatory frameworks that can influence their attractiveness.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Corporations weigh the potential savings against the risks and administrative burdens of self-insuring.
Alternative Retirement Fund Management
Beyond traditional Afores, individuals increasingly consider alternative long-term savings and investment vehicles. These substitutes, such as private investment funds or direct real estate investments, can fulfill similar financial planning needs. For instance, Mexico’s private equity market saw significant growth, with investments reaching approximately $2.5 billion USD in 2023, offering potential returns that could compete with retirement fund performance.
These alternatives present a credible threat to established retirement fund administrators like Grupo Inbursa. For example, the rise of fintech platforms offering diversified investment portfolios directly to consumers provides accessible options. In 2024, investment in fintech solutions for wealth management in Latin America was projected to exceed $1 billion USD, indicating a strong shift towards these substitute channels.
- Growing Accessibility: Fintech platforms democratize access to investment vehicles previously reserved for institutional investors.
- Diversification Options: Alternatives like real estate or private equity offer diversification beyond traditional equity and bond portfolios managed by Afores.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Some substitute investments, while carrying higher risk, promise superior returns, attracting investors seeking to maximize their retirement nest egg.
- Investor Preference Shift: A growing segment of the population, particularly younger generations, shows a preference for self-directed investment strategies and alternative assets.
Fintech lending platforms offer a significant substitute for Grupo Inbursa's loan products. These platforms provide faster, more flexible, and often more accessible credit, directly impacting Inbursa's consumer and corporate lending business. Mexico's fintech lending sector saw substantial growth in 2024, with new entrants continually challenging traditional banking models.
Digital payment systems and e-wallets are increasingly substituting traditional banking transactions for Grupo Inbursa. Platforms like Mercado Pago and various SPEI-linked services offer convenient and cost-effective alternatives for everyday financial activities. The increasing adoption of these digital solutions in Mexico highlights a growing consumer preference for bypassing conventional banking channels.
Online brokerage and robo-advisory services are strong substitutes for Grupo Inbursa's investment management offerings. These platforms provide direct, low-cost access to investment opportunities, attracting customers seeking greater control and lower fees. In 2024, digital wealth management platforms in Mexico experienced a notable surge in user engagement and assets under management.
Large corporations can self-insure or establish captive insurance entities, acting as a direct substitute for Grupo Inbursa's insurance products. This allows them to retain risk internally, potentially reducing costs and enhancing control. The captive insurance market continued its expansion in 2024, with many large enterprises leveraging these structures to manage specific liabilities.
Alternative savings and investment vehicles, such as private equity and direct real estate investments, pose a threat to Grupo Inbursa's traditional retirement fund and investment services. These options offer diversification and potentially higher returns, attracting investors seeking to supplement or replace traditional Afore offerings. Mexico's private equity market saw continued investment growth in 2023, indicating a robust alternative investment landscape.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into Mexico's financial services sector is significantly dampened by substantial regulatory and capital barriers. Aspiring institutions must navigate a complex web of compliance, including adherence to international standards like Basel III and a host of domestic banking and securities regulations. These rigorous requirements, coupled with extensive licensing procedures, create a formidable entry hurdle.
Grupo Inbursa's robust financial standing, exemplified by its Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio of 22.69% in 2024, underscores the immense capital depth necessary to compete effectively. Such high capital requirements and the intricate licensing processes effectively deter many potential newcomers, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants and solidifying the position of established players.
Established brand recognition and trust are significant barriers for new entrants aiming to compete with Grupo Inbursa. Decades of operation have allowed Grupo Inbursa to cultivate deep customer loyalty and a strong reputation for reliability in the financial services sector. For instance, as of early 2024, Grupo Inbursa consistently ranks among Mexico's leading financial institutions, a testament to its enduring market presence and customer confidence, making it difficult and costly for newcomers to gain comparable market acceptance.
Existing financial giants like Grupo Inbursa leverage significant economies of scale, optimizing costs across banking, insurance, and investment services. This broad operational base allows them to spread fixed costs, like technology infrastructure and regulatory compliance, over a larger volume of business, making their per-unit costs lower. For instance, in 2024, Inbursa's consolidated revenue reached approximately MXN 120 billion, demonstrating the scale of their operations.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without an established, large customer base and a diversified product portfolio, they cannot achieve the same per-transaction or per-customer cost advantages. This makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price or offer the same breadth of services as established players without incurring significantly higher operating expenses.
Access to Distribution Networks
New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating Grupo Inbursa's established distribution networks, which encompass both extensive physical branch presence and a highly developed digital infrastructure. Building such a comprehensive system demands substantial capital investment and considerable time, acting as a strong deterrent.
While digital channels can theoretically reduce entry barriers, creating a widespread and trusted digital presence, akin to Inbursa's, still requires immense resources and sophisticated technological capabilities. For instance, Inbursa reported a substantial increase in digital transactions in 2024, underscoring the scale and effectiveness of their existing digital network.
- Significant Capital Outlay: Establishing physical branches or a robust digital platform requires millions in investment.
- Time and Brand Trust: Building a widespread and trusted distribution network takes years, a significant barrier for newcomers.
- Digital Reach Advantage: Inbursa's high digital transaction volume in 2024 highlights their established and efficient digital distribution capabilities.
Incumbent Response and Innovation
Established financial institutions like Grupo Inbursa are far from passive in the face of potential new entrants. They actively invest in and develop their own innovative digital platforms and services. This proactive stance, which includes strategic acquisitions, directly counters the threat of new companies disrupting the market.
A prime example of this is Inbursa's acquisition of Cetelem Mexico, a move designed to bolster its digital offerings and customer reach. By integrating new technologies and business models, incumbents like Inbursa can effectively raise the barrier to entry for newcomers, making it significantly more challenging for them to carve out a competitive niche.
- Incumbent Innovation: Grupo Inbursa actively develops digital solutions, not just reacting but leading.
- Acquisition Strategy: The acquisition of Cetelem Mexico demonstrates a proactive approach to market consolidation and digital enhancement.
- Barrier Raising: These actions by established players make it harder for new entrants to gain market share and differentiate.
The threat of new entrants into Mexico's financial sector is low due to high capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles, which demand significant investment and adherence to complex compliance standards. Grupo Inbursa's strong capital position, evidenced by its 22.69% CET1 ratio in 2024, highlights the substantial financial depth needed to compete, effectively deterring many potential newcomers.
Established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, both physical and digital, further solidify Inbursa's market position, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction. For instance, Inbursa's consolidated revenue of approximately MXN 120 billion in 2024 showcases the economies of scale that new players struggle to match, impacting their ability to compete on cost.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for licensing and operations. | Significant financial barrier; Inbursa's 2024 CET1 ratio of 22.69% indicates high capital needs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex licensing and adherence to banking laws. | Time-consuming and costly process, deterring less capitalized entrants. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established customer loyalty and reliability. | Difficult for new entrants to build comparable trust and market acceptance. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational volume. | New entrants struggle to match Inbursa's cost efficiencies; 2024 revenue ~MXN 120 billion. |
| Distribution Networks | Extensive physical and digital reach. | High investment and time needed to replicate Inbursa's established networks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Grupo Inbursa is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Grupo Inbursa's official annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific publications and market research reports from reputable firms.
