Immunocore Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Immunocore Bundle
Immunocore faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers shaping its market landscape. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Immunocore’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Immunocore's pioneering work with ImmTAC molecules, a unique form of T cell receptor bispecific immunotherapy, inherently ties it to a supply chain demanding highly specialized raw materials and reagents. The very nature of these advanced biotechnological inputs means that only a select few suppliers can meet the stringent quality and technical specifications required for their production.
This reliance on a narrow supplier base for critical components significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, the development and manufacturing of complex biological reagents or custom-synthesized chemical compounds essential for ImmTACs often involve proprietary processes and intellectual property, further consolidating supplier leverage. If these specialized inputs are not readily available from alternative sources, Immunocore faces the risk of increased procurement costs and potential disruptions, impacting its production timelines and overall operational efficiency.
The biologics contract manufacturing market is a vital ecosystem, featuring over 305 CMOs worldwide, but a concentrated few dominate the market's financial value. Immunocore, for its complex ImmTAC molecule production, likely relies on these specialized CDMOs.
This reliance grants significant leverage to CDMOs, especially as the demand for advanced therapies, like those Immunocore develops, continues to surge. Their specialized expertise is indispensable for ensuring efficient and regulatory-compliant manufacturing, making them powerful partners.
Switching contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) or suppliers for highly specialized biotechnology components involves significant expenses, lengthy timelines, and complex regulatory hurdles. This is especially true for novel therapeutic modalities like Immuno-oncology's ImmTacs, where manufacturing processes are highly specific and already validated with regulatory bodies.
For instance, the validation of a new manufacturing process for a biologic drug can take 12-18 months and cost millions of dollars. These substantial switching costs effectively increase the bargaining power of Immunocore's current manufacturing partners and specialized raw material providers, as the company faces considerable friction in seeking alternative sources.
Supplier Expertise and Proprietary Technologies
Many contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) and specialized suppliers hold unique expertise, proprietary technologies, and intellectual property vital for areas such as cell line development and bioprocess optimization. Immunocore's dependence on these specialized capabilities for its complex ImmTAC molecules significantly amplifies the suppliers' bargaining power. This is because these suppliers offer critical functionalities that are difficult to replicate internally or source from alternative vendors.
The specialized nature of manufacturing complex biologics, like Immunocore's ImmTAC molecules, means that only a limited number of CDMOs possess the necessary advanced technologies and skilled personnel. For instance, the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating high demand for specialized services. This scarcity of providers with proven track records in handling intricate manufacturing processes strengthens their position.
- Limited Pool of Specialized CDMOs: The number of CDMOs capable of handling complex biologics manufacturing, such as Immunocore's ImmTACs, is relatively small, concentrating power among these few.
- Proprietary Technology and IP: Suppliers often possess patented technologies or unique know-how in areas like cell culture, purification, and analytical testing, which are essential for producing high-quality biologics.
- High Switching Costs: Transitioning to a new supplier for complex manufacturing processes involves significant time, investment, and regulatory hurdles, making it costly and disruptive for Immunocore.
- Criticality of Supplier Performance: The quality and reliability of the supplier directly impact the efficacy and safety of Immunocore's drug candidates, making supplier choice paramount and increasing their leverage.
Limited Supplier Base for Niche Biologics
The market for specialized biologics manufacturing, particularly for complex modalities like TCR bispecifics, presents a concentrated supplier landscape for companies like Immunocore. While the broader biologics contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) sector is expanding, the niche requirements for advanced immunotherapies mean fewer players possess the necessary expertise and facilities. This limited supplier base can significantly enhance the bargaining power of these specialized CDMOs.
For instance, the global biologics CDMO market was valued at approximately $20.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. However, within this, the segment catering to cell and gene therapies, which includes advanced immunotherapies, is characterized by a smaller number of highly specialized providers. This scarcity of qualified manufacturers for cutting-edge treatments means Immunocore may have fewer alternative suppliers, increasing their reliance on existing partners.
- Limited Specialized Capacity: The technical complexity of manufacturing TCR bispecifics requires advanced analytical capabilities and specialized containment, restricting the number of CDMOs capable of meeting these demands.
- High Switching Costs: Transitioning manufacturing to a new CDMO involves significant time, investment in process validation, and regulatory hurdles, making it difficult for Immunocore to switch suppliers easily.
- Supplier Concentration: A few key CDMOs dominate the landscape for advanced biologics, giving them leverage in pricing and contract negotiations due to high demand for their services.
Immunocore's reliance on a limited number of specialized contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) and raw material suppliers for its unique ImmTAC molecules significantly enhances supplier bargaining power. These suppliers often possess proprietary technologies and specialized expertise crucial for the complex manufacturing processes involved in advanced immunotherapies.
The high switching costs associated with validating new manufacturing processes and securing regulatory approval for alternative suppliers create substantial friction for Immunocore. This dependence on existing partners for critical components and manufacturing capabilities grants these suppliers considerable leverage in negotiations.
The global biologics CDMO market, valued at approximately $20.5 billion in 2023, includes a segment for advanced therapies that is characterized by fewer, highly specialized providers. This scarcity of qualified manufacturers for cutting-edge treatments strengthens their negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on Immunocore | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Expertise & Technology | Essential for ImmTAC production; difficult to replicate | High |
| Limited Supplier Pool | Few CDMOs capable of advanced biologics manufacturing | High |
| High Switching Costs | Significant time, investment, and regulatory hurdles for new suppliers | High |
| Criticality of Inputs | Supplier quality directly impacts drug efficacy and safety | High |
What is included in the product
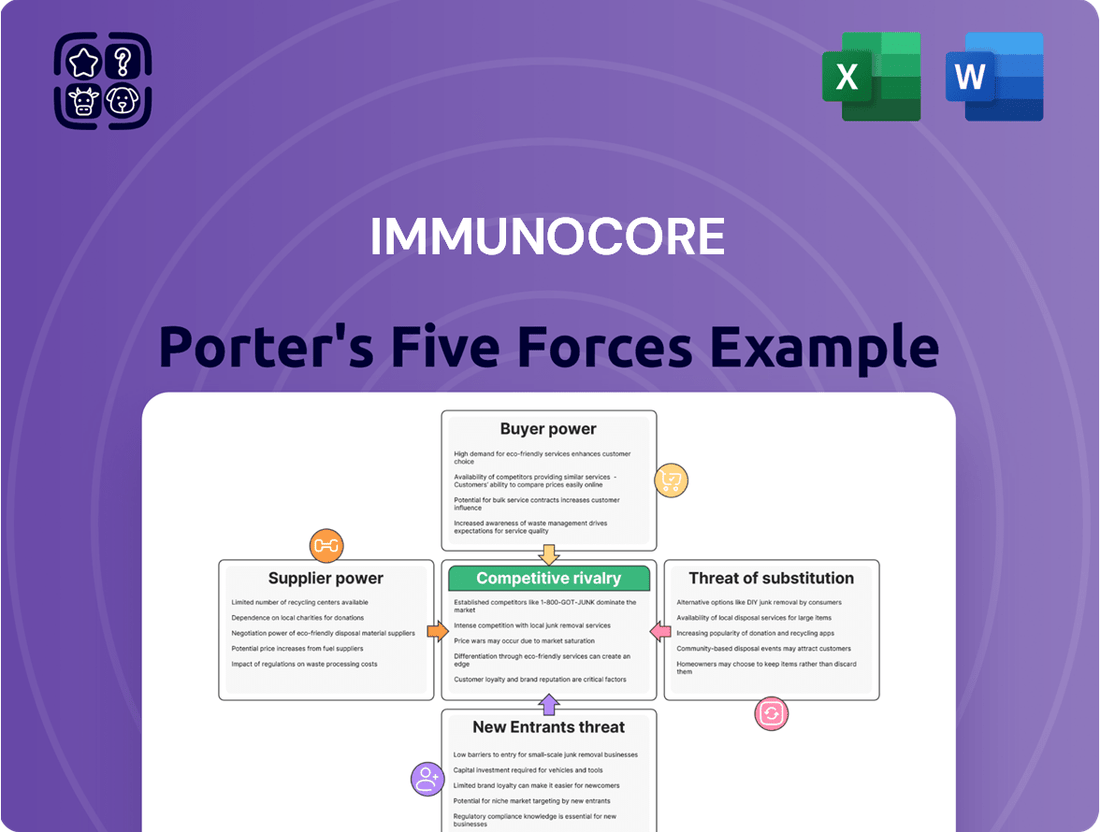
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Immunocore dissects the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its competitive environment.
A clear, one-sheet summary of Immunocore's competitive landscape—perfect for quickly identifying and addressing market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Healthcare payers, such as government programs and private insurers, hold significant sway over drug pricing and accessibility. Their decisions on reimbursement and inclusion in formularies directly impact a company like Immunocore's revenue potential, especially for expensive new treatments.
For novel, high-cost therapies like Immunocore's KIMMTRAK, payers are keenly focused on demonstrating value and controlling expenditures. This necessitates robust data on efficacy and cost-effectiveness to secure favorable reimbursement terms.
Securing positive reimbursement decisions is paramount. For instance, Immunocore's KIMMTRAK received a positive recommendation for funding in England by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in 2024, highlighting the crucial role these bodies play in market access and the financial viability of such therapies.
The high cost of novel therapies, particularly in areas like oncology, significantly boosts customer bargaining power. These treatments can cost hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars per patient, placing immense pressure on payers to control healthcare spending. For instance, CAR T-cell therapies, a leading example of advanced treatments, often carry price tags exceeding $400,000, making payers highly sensitive to value propositions.
While KIMMTRAK represents a significant advancement as the first FDA-approved T-cell receptor therapy for metastatic uveal melanoma, patients still have recourse to established treatments. These include radiation therapy and surgical interventions for the primary disease, alongside a range of systemic and investigational therapies being developed for metastatic instances.
The availability of these alternative treatment modalities, even if their efficacy varies across different patient groups, grants customers a degree of bargaining power. This leverage stems from the existence of options outside of Immunocore's KIMMTRAK, influencing pricing and market dynamics.
Demand for Real-World Evidence and Clinical Outcomes
Customers, especially payers and healthcare providers, are increasingly insistent on solid real-world evidence and clear clinical outcomes to validate the significant expense of novel pharmaceuticals. Immunocore's capacity to showcase the survival advantages and sustained effectiveness of KIMMTRAK is paramount for securing and broadening market access.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by this demand for data. For instance, in 2024, many health systems and insurers implemented stricter evidence requirements for new drug approvals, often looking beyond initial clinical trial data to long-term real-world performance metrics. Failure to furnish compelling data demonstrating KIMMTRAK's value proposition could indeed diminish Immunocore's leverage in negotiations with these influential entities.
- Demonstrating survival benefit is key to justifying KIMMTRAK's price.
- Payers and providers demand robust real-world evidence.
- Lack of data weakens Immunocore's negotiating position.
Patient Access and Formulary Restrictions
Payers, such as insurance companies, wield significant power by imposing formulary restrictions and prior authorization requirements. These measures directly influence patient access to Immunocore's therapies, effectively managing demand for its high-cost treatments. For instance, in 2024, many health plans continued to scrutinize specialty drug approvals, with some requiring step therapy or extensive documentation before covering new oncology treatments.
This intricate market access environment grants customers considerable leverage in shaping the availability and utilization of pharmaceuticals. The complex approval processes and potential for reimbursement limitations mean that Immunocore must actively engage with payers to ensure its innovative treatments reach patients, thereby demonstrating the substantial bargaining power held by these entities.
- Formulary Restrictions: Payers can limit which drugs are covered and at what tier, impacting patient out-of-pocket costs and physician prescribing habits.
- Prior Authorization: Many high-cost drugs, including those in the oncology space, require pre-approval from insurance companies, adding administrative hurdles and potential delays.
- Utilization Management: Strategies like step therapy (requiring patients to try less expensive drugs first) can reduce the immediate uptake of novel, high-priced medications.
- Impact on Demand: These customer-driven controls can effectively reduce the addressable market and revenue potential for pharmaceutical companies like Immunocore.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly healthcare payers and providers, is substantial for companies like Immunocore, especially with high-cost therapies. Payers exert influence through reimbursement decisions, formulary placement, and utilization management, all of which directly impact market access and revenue. For instance, in 2024, many insurers continued to implement stringent prior authorization requirements for specialty drugs, including those in oncology, demanding extensive clinical justification.
The existence of alternative treatments, even if less advanced, also grants patients and payers leverage. Immunocore's KIMMTRAK, while innovative, competes in a landscape where other therapeutic options, such as established chemotherapies or emerging immunotherapies, are available. This competitive environment means Immunocore must continually demonstrate KIMMTRAK's superior value proposition to justify its price point.
Robust real-world evidence is increasingly critical for securing favorable reimbursement. Payers in 2024 placed a higher emphasis on long-term data demonstrating sustained efficacy and survival benefits, moving beyond initial clinical trial results. Immunocore's ability to provide this data for KIMMTRAK is paramount for negotiating pricing and expanding access, as payers are highly sensitive to demonstrating cost-effectiveness to control healthcare spending.
| Customer Type | Leverage Mechanism | 2024 Trend Example | Impact on Immunocore |
| Healthcare Payers (Insurers, Government) | Reimbursement, Formulary Restrictions, Prior Authorization | Increased scrutiny on specialty drug approvals, step therapy requirements | Limits market access, revenue potential, requires strong value demonstration |
| Healthcare Providers (Hospitals, Clinics) | Treatment protocols, physician prescribing habits | Demand for cost-effective solutions and clear clinical pathways | Influences adoption rates, necessitates physician education |
| Patients | Treatment choice (with provider guidance) | Seeking value and improved outcomes, especially for high-cost therapies | Drives demand for demonstrable efficacy and quality of life improvements |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Immunocore Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Immunocore Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The uveal melanoma treatment market, projected to reach around $1,000 million in 2024, is a dynamic space. While Immunocore's KIMMTRAK is a notable player, it faces strong competition from established treatments like radiation therapy and surgery, which continue to command a substantial portion of the market.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the active development and commercialization efforts of other significant companies. Novartis AG, Eli Lilly and Company, and Delcath Systems, Inc. are all introducing novel targeted therapies and combination treatment strategies, directly challenging existing treatment paradigms and creating a more crowded competitive environment.
Immunocore is a pioneer in the niche area of TCR bispecific immunotherapies, a cutting-edge approach to cancer treatment. However, this specialized field is not without its competitors. Companies like Immatics are actively developing similar TCR bispecific and TCR-T therapies, creating a direct competitive landscape.
This head-to-head competition is particularly evident in the race to advance their respective pipelines and secure market approval for new TCR-based treatments across a range of diseases. For instance, as of early 2024, both Immunocore and Immatics have multiple TCR bispecific candidates in various stages of clinical development, targeting indications like melanoma and other solid tumors.
Immunocore's ambition to tackle various solid tumors means it's up against a crowded field of immunotherapy developers. This includes giants like Johnson & Johnson and Bristol-Myers Squibb, who are already strong in areas like PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors, as well as CAR-T cell therapies and other T-cell engagers. The oncology immunotherapy market is a hotbed of innovation and investment, with significant growth projected.
In 2024, the global cancer immunotherapy market was valued at approximately $100 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 12% through 2030, highlighting the intense competition for market share. Companies are pouring billions into R&D, with major players like AstraZeneca and Pfizer actively expanding their portfolios in this space, creating a dynamic and challenging competitive environment for Immunocore.
High R&D Investment and Pipeline Expansion
The pharmaceutical sector is characterized by substantial research and development expenditures, with leading companies allocating billions of dollars each year to pioneer novel oncology treatments. This robust R&D focus fuels a highly competitive landscape marked by rapid innovation and the consistent introduction of new drug approvals.
Immunocore actively broadens its pipeline, venturing into diverse therapeutic domains such as various solid tumors, infectious diseases, and autoimmune conditions. This strategic expansion broadens its competitive reach and intensifies rivalry across these crucial healthcare markets.
- R&D Spending: Major pharmaceutical companies often invest upwards of $10 billion annually in R&D.
- Pipeline Diversification: Immunocore's expansion into oncology, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders highlights a common strategy to mitigate risk and capture broader market share.
- Innovation Cycle: The industry's competitive intensity is driven by the constant need to bring differentiated, effective therapies to market, often through significant clinical trial investments.
Market Share and Patient Population Targeting
Competitive rivalry in the biopharmaceutical sector, particularly for niche indications like uveal melanoma, centers on both treatment effectiveness and strategic patient population targeting. Companies vie for market share by developing therapies that address specific genetic markers or patient subgroups. For instance, Immunocore's KIMMTRAK is approved for patients with the HLA-A*02:01 genetic mutation. This targeted approach creates an initial advantage but also invites competition from other developers aiming to capture broader patient segments or offer alternative treatment modalities.
The landscape is dynamic, with ongoing research into new therapies that could potentially broaden patient eligibility or offer different mechanisms of action. This intensifies the competition for patient access and influences prescription volume. For example, while KIMMTRAK's initial success is tied to its specific target population, the development of therapies with wider applicability could shift market dynamics. Companies must continuously innovate and adapt their strategies to maintain or expand their position within these evolving patient pools.
- Targeted Patient Populations: Companies differentiate by focusing on specific genetic markers or patient subgroups, such as Immunocore's HLA-A*02:01 targeting for KIMMTRAK in uveal melanoma.
- Broader Patient Group Competition: The development of treatments aimed at larger or different patient populations creates a competitive pressure for existing niche therapies.
- Market Share and Prescription Volume: Competition extends beyond efficacy to securing market share through patient access and influencing prescription decisions.
- Pipeline Development: Ongoing research and development of new therapies with potentially wider patient applicability are key drivers of future competitive rivalry.
The competitive rivalry for Immunocore is intense, particularly in the oncology immunotherapy space, which is valued at around $100 billion in 2024 and projected to grow significantly. Companies like Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Delcath are actively developing targeted therapies that directly challenge Immunocore's KIMMTRAK. Furthermore, the emergence of similar TCR bispecific therapies from competitors such as Immatics creates direct head-to-head competition in pipeline advancement and market approval.
Immunocore's strategy to expand into diverse therapeutic areas like infectious diseases and autoimmune conditions further intensifies rivalry, as it enters markets with established players. The pharmaceutical industry's substantial R&D spending, often exceeding $10 billion annually for major companies, fuels a rapid innovation cycle where differentiated treatments are crucial for market share. This environment necessitates continuous innovation to maintain a competitive edge.
| Competitor | Therapeutic Area Focus | Key Competitive Strategy |
| Novartis AG | Oncology, Targeted Therapies | Introduction of novel targeted therapies and combination treatments |
| Eli Lilly and Company | Oncology, Targeted Therapies | Development of novel targeted therapies and combination treatment strategies |
| Delcath Systems, Inc. | Oncology, Interventional Oncology | Commercialization of targeted therapies |
| Immatics | TCR Bispecifics, TCR-T Therapies | Developing similar TCR bispecific and TCR-T therapies |
| Johnson & Johnson | Oncology Immunotherapy (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4), CAR-T | Broad portfolio of established and emerging immunotherapies |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | Oncology Immunotherapy (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4), CAR-T | Strong presence in established immunotherapy markets |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For primary uveal melanoma, established treatments like radiation therapy (plaque brachytherapy, proton beam therapy) and surgical options (enucleation, local resection) remain prevalent and effective for local tumor control. These serve as significant substitutes to systemic therapies, particularly for early-stage disease. Radiation therapies are anticipated to maintain a substantial market share in 2025, reflecting their continued utility.
While KIMMTRAK stands as the sole FDA-approved therapy for metastatic uveal melanoma demonstrating improved overall survival, the landscape of systemic treatments is evolving. Several other systemic therapies are under active investigation, including novel combination strategies and agents specifically designed to target particular genetic mutations found in uveal melanoma.
These emerging treatments, if proven effective in clinical trials, could present viable alternative options for patients. Such advancements might lead to these new therapies substituting KIMMTRAK in specific patient populations or treatment scenarios, thereby increasing competitive pressure.
The threat of substitutes for Immunocore's pipeline candidates targeting solid tumors is significant. Established immunotherapies like PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors are widely used, with the global checkpoint inhibitors market projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027, offering a strong alternative.
Emerging options such as oncolytic viruses and other T-cell engagers also present competitive pathways. For instance, the oncolytic virus market is anticipated to grow substantially, indicating increasing adoption of these alternative approaches.
Targeted Therapies and Chemotherapy
While Immunocore's focus is on T-cell receptor (TCR) bispecifics, traditional targeted therapies and chemotherapy are still relevant for other solid tumors in their pipeline. For instance, in 2023, the global chemotherapy market was valued at approximately $167.6 billion, indicating its continued significance, even as newer modalities emerge. This presents a competitive landscape where established treatments, though potentially less effective for specific indications like uveal melanoma, still hold market share.
Furthermore, advancements in precision diagnostics are paving the way for highly personalized treatment plans. These plans may incorporate non-Immunocore T-cell engaging therapies or other novel approaches, creating a dynamic environment where the threat of substitutes is constantly evolving. The increasing sophistication of diagnostic tools means that treatment decisions are becoming more nuanced, potentially diverting patients from specific biologic therapies.
- Market Share: Traditional chemotherapy and targeted therapies still command significant portions of the oncology market, estimated to be worth hundreds of billions globally.
- Evolving Treatment Paradigms: Precision medicine and companion diagnostics are enabling more tailored treatment strategies, potentially reducing reliance on broad-spectrum therapies.
- Patient Stratification: The ability to identify specific patient populations who respond better to alternative treatments increases the threat of substitutes.
- Research & Development: Ongoing research into novel therapeutic modalities outside of bispecific antibodies continues to expand the range of available treatment options.
Emerging Cell and Gene Therapies
The broader landscape of advanced therapies, including CAR-T cell therapies and other cellular therapies, presents a long-term substitutive threat to Immunocore's ImmTAC technology. As of early 2024, CAR-T therapies have seen significant advancements, with several approved for hematological malignancies. For instance, Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) and Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel) continue to gain traction in treating specific blood cancers.
Research is actively exploring the application of these cellular modalities to solid tumors, which represent a significant portion of the oncology market. While challenges remain in solid tumor treatment, ongoing clinical trials and technological refinements suggest these therapies could become competitive alternatives for various oncology indications in the future. This evolution poses a potential threat as these approaches mature and expand their therapeutic reach.
- CAR-T Therapy Approvals: Multiple CAR-T therapies are approved for hematological cancers, indicating their established efficacy in certain indications.
- Solid Tumor Research: Significant investment and research are focused on adapting cellular therapies for solid tumors, a key area for Immunocore.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in cellular therapy manufacturing and delivery could enhance their competitiveness.
- Market Expansion: As cellular therapies become more accessible and broadly applicable, they represent a growing substitutive threat.
For uveal melanoma, established treatments like radiation and surgery remain strong substitutes, particularly for early-stage disease, and are expected to retain significant market share through 2025. While KIMMTRAK is the only FDA-approved systemic therapy for metastatic uveal melanoma, emerging systemic treatments targeting specific genetic mutations could offer viable alternatives, increasing competitive pressure.
The broader oncology market sees established therapies like chemotherapy, valued at approximately $167.6 billion in 2023, and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, with a market projected to exceed $60 billion by 2027, as significant substitutes. Additionally, advancements in precision diagnostics and the ongoing development of cellular therapies like CAR-T, which has multiple approvals for hematological cancers, present evolving substitutive threats, especially as research aims to adapt them for solid tumors.
| Therapeutic Modality | Estimated Market Value/Projection | Relevance as Substitute |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation Therapy (Uveal Melanoma) | Maintained substantial market share in 2025 | Primary substitute for early-stage uveal melanoma |
| Chemotherapy (Global Market) | Approx. $167.6 billion (2023) | Established alternative for various solid tumors |
| PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors (Global Market) | Projected >$60 billion (by 2027) | Key immunotherapy substitute in oncology |
| CAR-T Therapies | Growing market, multiple approvals for hematological cancers | Emerging cellular therapy substitute, research ongoing for solid tumors |
Entrants Threaten
The biotechnology sector, especially in the realm of novel immunotherapies, demands enormous investments in research and development. By 2024, the average cost for a major pharmaceutical company to bring a new drug to market had climbed to an staggering $2.23 billion. This significant financial hurdle presents a formidable barrier to entry for aspiring companies aiming to compete with established entities such as Immunocore.
The stringent regulatory approval process for novel therapies, such as ImmTAC molecules, acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector. Gaining approval from bodies like the FDA or EMA requires extensive preclinical research and multi-phase clinical trials, a journey that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market is estimated to be over $2 billion, with development timelines often exceeding a decade.
Immunocore's robust intellectual property (IP) portfolio presents a significant barrier to new entrants. The company's proprietary ImmTAC platform and its flagship product, KIMMTRAK, are shielded by extensive patent rights, making it difficult for competitors to enter the market without licensing or developing entirely new therapeutic approaches.
The successful market penetration and clinical validation of KIMMTRAK underscore the strength of Immunocore's established IP in the T-cell receptor (TCR) modality. This success not only validates the platform but also highlights the substantial IP advantage that new companies would need to overcome to compete directly.
Need for Specialized Scientific and Clinical Expertise
The development and commercialization of T cell receptor bispecific immunotherapies, like those pioneered by Immunocore, require a deep well of specialized scientific knowledge. This includes expertise in immunology, oncology, and protein engineering, along with robust clinical development infrastructure. For instance, the intricate design of bispecific molecules targeting specific tumor antigens and T cell receptors is a complex scientific undertaking.
Building this niche knowledge base and talent pool presents a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. The scarcity of professionals with the precise blend of skills needed for advanced immunotherapy research and development acts as a significant barrier to entry. The high cost of acquiring and retaining such specialized talent is a key factor.
- Specialized Scientific Expertise: Immunology, oncology, and protein engineering are critical fields for developing TCR bispecifics.
- Clinical Development Capabilities: Navigating complex regulatory pathways and conducting successful clinical trials require extensive experience.
- Talent Acquisition Difficulty: The limited pool of highly skilled scientists and clinicians makes it challenging for new companies to build necessary teams.
- High R&D Investment: Significant capital is needed to fund the research, development, and clinical testing of novel immunotherapies.
Access to Capital and Investor Confidence
While venture equity investment in life sciences saw a significant surge in 2024, securing the vast capital required for long-term drug development, particularly for companies like Immunocore, remains a formidable challenge. The sheer scale of investment needed for clinical trials, manufacturing, and regulatory approvals necessitates robust investor confidence. This confidence is directly tied to a company's demonstrated progress, intellectual property strength, and the perceived market potential of its therapies.
The threat of new entrants is influenced by the accessibility of capital and the prevailing investor sentiment in the biotechnology sector. Despite a generally positive investment climate in 2024, a downturn or a shift in investor risk appetite could quickly dry up funding avenues, making it harder for new players to emerge and challenge established companies. For instance, while the biotech sector saw substantial funding rounds in early 2024, the ability of new companies to attract similar levels of investment for complex, multi-year development programs remains a key barrier.
- Capital Intensity: Drug development requires billions of dollars over many years, a significant barrier for potential new entrants.
- Investor Confidence Fluctuations: The biotech market can be volatile; dips in investor confidence can severely limit new company funding.
- Demonstrated Progress: New entrants must show clear scientific and clinical milestones to attract the necessary capital.
The threat of new entrants in Immunocore's specialized immunotherapy space is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements for research and development. By 2024, the cost to bring a new drug to market averaged $2.23 billion, a figure that deters many potential competitors.
Furthermore, Immunocore's strong intellectual property portfolio, particularly around its ImmTAC platform and KIMMTRAK, creates a substantial barrier. New companies would need to navigate complex patent landscapes or develop entirely novel, equally defensible technologies.
The need for deep, specialized scientific expertise in areas like immunology and oncology, coupled with the difficulty in acquiring and retaining top talent, also limits new entrants. This talent scarcity, combined with high R&D costs, makes market entry exceptionally challenging.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Average cost to bring a drug to market (2024) | Formidable financial hurdle, requiring billions in investment. |
| Intellectual Property | Immunocore's proprietary ImmTAC platform and patents | Restricts competitors from utilizing similar technologies without licensing. |
| Specialized Expertise & Talent | Need for deep immunology, oncology, and clinical development skills | Limited pool of qualified professionals makes team building difficult and expensive. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent FDA/EMA approval processes for novel therapies | Time-consuming and costly, requiring extensive clinical trials and data. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Immunocore Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, SEC filings, and clinical trial databases to understand competitive dynamics.
