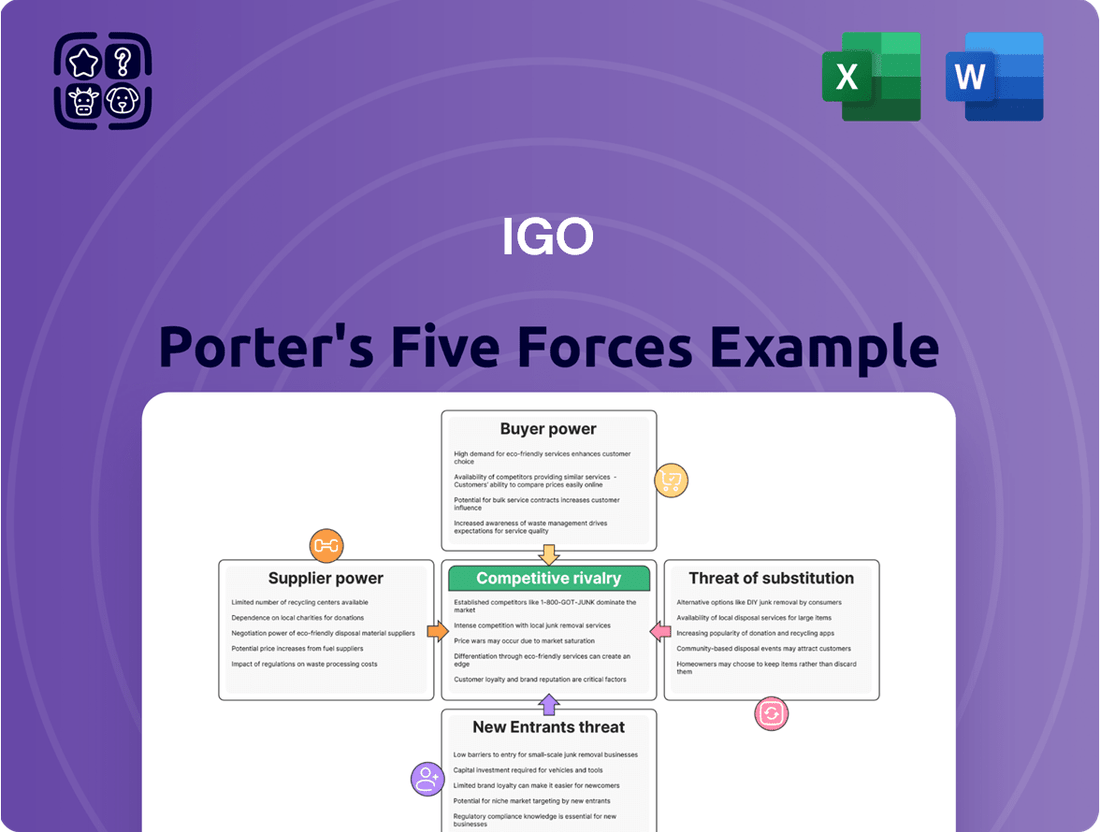
IGO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
IGO Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for IGO is crucial for any strategic decision. Porter's Five Forces provides a powerful framework to dissect these dynamics, revealing the underlying pressures that shape profitability and market opportunities.
This snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore IGO’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining industry's dependence on a small group of global manufacturers for critical, specialized machinery, like massive haul trucks and sophisticated underground drill rigs, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. This limited supplier base means mining companies have fewer options when acquiring essential, high-value equipment.
For instance, in 2024, the market for large mining haul trucks is dominated by a few key players, with Caterpillar and Komatsu holding substantial market shares. This concentration allows these suppliers to dictate terms, potentially driving up capital expenditures for mining operations due to the scarcity of viable alternatives and the high cost of developing new, competitive equipment.
The bargaining power of suppliers for critical mining inputs is a significant factor for IGO. Companies providing essential materials like explosives and advanced drilling technology are often concentrated among a few major global players. This limited number of suppliers means they hold considerable leverage, potentially driving up costs for IGO and affecting its access to vital resources needed for mining operations.
The availability of skilled labor, such as geologists, engineers, and experienced mine operators, significantly impacts supplier power in the mining industry. A scarcity of these specialized professionals can lead to increased labor costs and diminished operational flexibility for mining companies, effectively granting labor a stronger bargaining position.
Technological Advancements and Proprietary Solutions
Suppliers who offer cutting-edge and unique mining technologies, especially those that boost efficiency or sustainability, can charge more. This is because their solutions provide significant value and a competitive edge. For instance, AI-driven process improvements or advanced electric machinery are highly sought after. This trend is particularly impactful for companies like IGO, given their focus on clean energy metals and environmentally responsible operations.
The increasing demand for sustainable and efficient mining practices, driven by global decarbonization efforts, amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers providing these specialized technologies. Companies that can demonstrate a clear return on investment through reduced operational costs or enhanced resource recovery are in a strong position. For example, in 2024, the global mining technology market saw significant investment, with companies investing heavily in automation and AI to improve safety and productivity.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, patented technologies that offer substantial efficiency gains or environmental benefits hold significant leverage.
- Value-Added Solutions: Advanced solutions that directly address IGO's focus on clean energy metals and sustainability can command premium pricing.
- Competitive Advantage: Suppliers whose innovations provide a distinct competitive advantage to IGO in the market can negotiate more favorable terms.
- Industry Trends: The broader industry's push towards technological adoption in mining strengthens the position of suppliers at the forefront of innovation.
Logistics and Infrastructure Providers
For IGO, operating in Western Australia means the bargaining power of logistics and infrastructure providers is a significant factor. Limited availability or high demand for essential services like transportation, port access, and energy supply in remote mining areas can directly inflate operational costs. For instance, in 2024, the cost of road freight in Western Australia saw increases due to fuel price volatility and driver shortages, impacting companies like IGO that rely heavily on these services to move ore and equipment.
The concentration of providers in specific regions also plays a role. If only a few companies offer crucial services, they can exert greater influence over pricing and terms. This is particularly relevant for specialized mining logistics, where a smaller pool of experienced operators might exist. The cost of maintaining and upgrading infrastructure, such as rail links or port facilities, can also be passed on to users, further strengthening supplier power.
- Limited Provider Options: In remote Western Australian locations, the number of qualified logistics and infrastructure providers may be restricted, giving existing suppliers more leverage.
- Infrastructure Dependence: IGO's reliance on ports, rail, and road networks means disruptions or increased costs from infrastructure operators directly impact its supply chain efficiency and profitability.
- Energy Costs: The cost and reliability of energy supply, whether from the grid or independent providers, are critical operational expenses that can be influenced by supplier bargaining power.
Suppliers with proprietary technology, especially those offering unique solutions for efficiency or sustainability, hold significant leverage, allowing them to command premium prices. This is particularly true for innovations that provide a distinct competitive advantage, aligning with industry trends towards technological adoption. For instance, in 2024, the mining technology market saw substantial investment in AI and automation, enhancing the power of suppliers in these advanced areas.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when they offer value-added solutions directly addressing a company's strategic focus, such as IGO's commitment to clean energy metals. This strong alignment allows suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, especially when their innovations contribute to reduced operational costs or improved resource recovery. The increasing demand for sustainable mining practices further strengthens the position of suppliers at the forefront of such advancements.
The concentration of suppliers for critical inputs like specialized machinery or essential materials means they possess considerable leverage, potentially increasing costs and impacting access to vital resources. This is evident in the 2024 haul truck market, where a few dominant players like Caterpillar and Komatsu can dictate terms due to limited alternatives and high development costs for competitors.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Proprietary Technology | High | AI-driven process improvements in mining |
| Supplier Concentration | High | Dominance of Caterpillar/Komatsu in haul trucks |
| Value-Added Solutions | High | Advanced electric machinery for clean energy metals |
| Scarcity of Skilled Labor | Moderate to High | Increased costs for specialized geologists and engineers |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting IGO's market, including supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers is significantly amplified by the inherent volatility in global commodity prices, particularly for key materials like nickel, lithium, and copper. These price swings, driven by supply and demand imbalances and geopolitical events, directly affect IGO's revenue potential. For instance, in early 2024, nickel prices experienced notable fluctuations, trading in a range influenced by global production levels and demand from the electric vehicle sector. This makes it challenging for IGO to lock in stable pricing, granting buyers considerable leverage.
The clean energy sector's demand for critical metals is surging, yet a few dominant players, like major battery manufacturers and electric vehicle (EV) producers, represent the primary customer base. For instance, in 2024, the global EV market is projected to surpass 16 million units, with companies like Tesla and BYD being significant consumers of battery materials.
These high-volume purchasers can wield considerable bargaining power. If these key customers have established multiple supply sources or possess substantial financial clout, they can effectively negotiate for lower prices on essential clean energy metals, impacting supplier margins.
Customers in the clean energy sector, especially those purchasing battery-grade materials, have exceptionally high standards for quality and specific product attributes. For instance, battery manufacturers demand consistent purity levels and precise chemical compositions to ensure optimal performance and safety in their products.
Meeting these exacting demands often requires IGO to implement more rigorous processing steps and enhanced quality control measures. This can lead to increased operational costs for IGO, as seen in the premium pricing often associated with high-purity battery materials compared to less refined commodities.
The ability of customers to dictate these specific product attributes, driven by their own manufacturing needs and end-product performance requirements, significantly strengthens their bargaining power. This means IGO must be highly responsive to customer specifications to secure and maintain these valuable relationships.
Potential for Direct Investment or Vertical Integration by Customers
Large customers, especially in the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) and battery manufacturing industries, are increasingly looking to secure their own supply chains. This often involves direct investment in mining operations or pursuing vertical integration strategies.
This strategic shift by major buyers directly impacts their bargaining power. By gaining more control over raw material sourcing, they become less dependent on existing suppliers like IGO. For instance, in 2024, several major automotive manufacturers announced significant investments in lithium mining projects, aiming to secure long-term supply for their battery production needs.
- EV Manufacturers' Direct Investment: Companies like Tesla and BYD have been actively exploring or investing in upstream mining assets to control lithium and cobalt supplies.
- Battery Giants' Vertical Integration: Major battery producers are also looking to integrate backward into raw material extraction to mitigate supply risks and price volatility.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: As customers invest directly, their ability to negotiate pricing and terms with traditional suppliers like IGO strengthens considerably.
- Impact on IGO's Pricing Power: This trend can erode IGO's pricing power and potentially reduce its profit margins if it cannot adapt its supply chain or value proposition.
Geographic Concentration of Downstream Processing
The geographic concentration of downstream processing, particularly in refining and smelting critical minerals, significantly influences the bargaining power of customers. For companies like IGO, this means that while the demand for their extracted materials is global, the actual purchasers of these processed goods are often concentrated in a few key regions.
This concentration, notably in countries like China and Indonesia, which dominate global refining capacity for many critical minerals, grants these processing hubs considerable leverage. Buyers in these concentrated markets can exert pressure on pricing and terms, knowing that alternative processing options for IGO's specific materials might be limited in the short to medium term. For instance, China processed approximately 60% of the world's refined nickel and 70% of refined cobalt in 2023, creating a bottleneck and a powerful customer base.
- Limited Processing Options: The scarcity of advanced refining and processing facilities outside of major hubs restricts the number of immediate buyers for IGO's raw or semi-processed materials.
- Dominant Market Players: A few large processing companies in concentrated geographic areas can dictate terms due to their significant market share and control over essential processing steps.
- Price Sensitivity: High concentration can lead to price wars among suppliers attempting to secure processing contracts, ultimately benefiting the few dominant processors.
Customers in the critical minerals sector, particularly large battery manufacturers and electric vehicle (EV) producers, possess significant bargaining power. This is due to their substantial purchasing volumes and increasing efforts towards vertical integration, aiming to secure their own raw material supplies. For example, in 2024, major automakers are investing heavily in lithium mining projects, reducing their reliance on external suppliers like IGO and strengthening their negotiation stance.
The concentration of downstream processing, especially in refining and smelting, further enhances customer leverage. Regions like China, which refined a substantial portion of global nickel and cobalt in 2023, become powerful purchasing hubs. This geographic concentration limits alternative buyers for IGO's materials, allowing these dominant processors to dictate terms and prices.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Illustrative Example (2024/2023 Data) |
| High Purchasing Volume | Enables negotiation for lower prices and favorable terms. | Major EV manufacturers like Tesla and BYD are key consumers of battery materials. |
| Vertical Integration Efforts | Reduces dependence on suppliers, increasing leverage. | Automakers investing in lithium mining projects to secure supply chains. |
| Geographic Concentration of Processing | Limits alternative buyers, empowering dominant processors. | China processed ~60% of refined nickel and ~70% of refined cobalt in 2023. |
| Demand for Specific Product Attributes | Requires suppliers to incur higher costs to meet stringent quality standards. | Battery manufacturers demand precise purity levels and chemical compositions. |
Full Version Awaits
IGO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for IGO, offering a thorough examination of competitive intensity and industry attractiveness. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate utility. You'll gain access to a professionally formatted analysis ready for immediate application in your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Major global mining companies such as Rio Tinto and BHP are significant players in the critical minerals sector. These diversified giants possess immense financial strength and extensive existing operations, allowing them to exert considerable competitive pressure on IGO, particularly when vying for promising exploration and development projects.
The clean energy metals market, especially for lithium and nickel, has seen considerable price swings. For instance, lithium prices experienced a dramatic drop of over 70% in 2023 from their 2022 peaks. This volatility fuels fierce price competition as producers battle to secure market share and profitability when commodity prices decline.
This price pressure intensifies rivalry, forcing companies to optimize production costs and explore efficiency gains to remain competitive. Producers that can manage their cost structures effectively are better positioned to weather these downturns and capitalize on price rebounds.
Competitive rivalry in the mining sector is significantly shaped by access to high-quality mineral deposits. Companies that secure and control economically viable ore bodies, such as IGO Limited with its stake in the Greenbushes lithium project, possess a distinct advantage. This advantage stems from lower extraction costs and the ability to produce at a competitive price point, a crucial factor in a market driven by commodity prices.
Technological and Operational Efficiency
Companies that achieve higher operational efficiency and lower production costs, often by leveraging advanced mining technologies, gain a significant competitive edge. IGO's strategic emphasis on operational excellence and technological integration, including the use of artificial intelligence for exploration, is vital for maintaining its position in this dynamic sector.
This focus allows IGO to potentially reduce its cost per tonne of metal produced, a key metric in the mining industry. For instance, in the 2023 financial year, IGO reported a cost of sales of AUD 2.1 billion, and improvements in efficiency directly impact this figure, enhancing profitability and competitiveness.
- Technological Adoption: Companies investing in and effectively deploying technologies like AI, automation, and advanced data analytics can optimize resource extraction and reduce waste.
- Operational Cost Management: Lowering production costs per unit of output directly translates to higher profit margins and a stronger competitive stance.
- Exploration Efficiency: AI-driven exploration can identify promising deposits more quickly and cost-effectively, giving early movers an advantage.
- Sustainability Integration: Efficient operations often align with sustainability goals, which is increasingly important for investor relations and market access.
Sustainability and ESG Performance
Competitive rivalry is increasingly being shaped by a company's sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance. Businesses demonstrating strong ESG practices can gain a significant edge by attracting more favorable investment, fostering robust partnerships, and cultivating stronger customer relationships.
This differentiation is crucial in today's market, where stakeholders are keenly aware of a company's impact. For instance, in 2024, the global sustainable investment market continued its upward trajectory, with assets under management in ESG funds reaching new highs, indicating a clear investor preference for responsible companies.
- ESG as a Competitive Differentiator: Companies with superior ESG scores often see lower costs of capital and improved brand reputation.
- Investor Demand: In Q1 2024, ESG-focused ETFs saw net inflows of over $20 billion globally, highlighting strong investor appetite.
- Talent Attraction: A commitment to sustainability can also be a key factor in attracting and retaining top talent, further enhancing competitive advantage.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Evolving regulations globally are also pushing companies to prioritize ESG, intensifying rivalry in this area.
The competitive landscape in the critical minerals sector is intense, driven by a few large, diversified players and volatile commodity prices. Companies like Rio Tinto and BHP, with their substantial financial resources and existing infrastructure, exert significant pressure on smaller entities like IGO. This rivalry is further amplified by the fluctuating prices of key commodities such as lithium and nickel; for example, lithium prices saw a sharp decline of over 70% in 2023 from their previous year's highs, forcing producers to compete aggressively on cost and market share to maintain profitability.
Securing access to high-quality mineral deposits is a primary battleground, with companies like IGO leveraging their stakes in projects such as Greenbushes to gain a cost advantage. Operational efficiency and technological adoption are also crucial differentiators. For instance, IGO's focus on AI in exploration aims to streamline discovery and reduce extraction costs, a vital strategy when production costs, such as IGO's reported AUD 2.1 billion cost of sales in FY23, are under scrutiny.
Sustainability and ESG performance are increasingly becoming key competitive factors. In 2024, investor demand for ESG-focused funds remained strong, with significant inflows into related ETFs, signaling a preference for companies with robust environmental and social practices. This trend means that strong ESG credentials can lead to lower capital costs and enhanced brand reputation, creating a competitive edge.
| Metric | 2023 Data Point | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Price Change (2023 vs 2022 peak) | -70% | Intensified price competition and focus on cost efficiency. |
| IGO Cost of Sales (FY23) | AUD 2.1 billion | Drives need for operational efficiency to improve margins. |
| ESG ETF Inflows (Q1 2024) | >$20 billion (Global) | Highlights ESG as a differentiator attracting investment and talent. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for lithium and nickel in battery production is significant, primarily driven by advancements in alternative battery chemistries. Research and development into technologies such as solid-state batteries and sodium-ion batteries are actively progressing, aiming to reduce or eliminate the reliance on these specific metals. For instance, by mid-2024, several companies have announced breakthroughs in sodium-ion battery technology, with some projecting cost reductions of up to 30% compared to current lithium-ion batteries, directly impacting the demand for lithium.
Recycling and circular economy initiatives are emerging as significant substitute threats for primary mineral extraction. As these processes mature, they offer an alternative source of critical minerals, potentially reducing reliance on newly mined materials. For instance, by 2024, the global recycling market for electronics, a key source of many critical minerals, is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating the growing scale of this substitute.
The increasing efficiency and economic viability of recycling critical minerals mean that companies may opt for recycled content over virgin materials. This shift directly impacts the demand for newly extracted resources, presenting a long-term challenge to traditional mining operations. The European Union's Critical Raw Materials Act, for example, aims to boost domestic recycling rates to secure supply chains, highlighting a strategic move towards substitutes.
Technological advancements in material science present a significant threat of substitution for IGO. Continuous innovation could lead to the development of clean energy technologies that require fewer critical metals, potentially impacting IGO's core business. For instance, breakthroughs in battery chemistry might reduce reliance on cobalt or nickel, metals IGO heavily extracts.
Design changes in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems are already exploring alternative materials. Reports from 2024 indicate ongoing research into solid-state batteries and sodium-ion batteries, which could decrease the demand for lithium and cobalt. This shift could mean that IGO's current supply of these metals becomes less valuable if substitute technologies gain widespread adoption.
Energy Storage Alternatives
The threat of substitutes for IGO's core metals, particularly those used in energy storage, is a significant consideration. Beyond traditional lithium-ion batteries, alternative storage technologies are gaining traction and could reduce demand for lithium and nickel. For instance, advancements in hydrogen fuel cells offer a different pathway for energy storage and transportation, potentially impacting the market for battery metals.
Emerging grid-scale storage solutions that do not rely on lithium-ion chemistry also present a substitute threat. These could include flow batteries, compressed air energy storage, or other innovative approaches. As of early 2024, the global energy storage market is experiencing rapid growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% through 2030, indicating a dynamic landscape where technological shifts can occur quickly.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: While still developing, hydrogen's potential as a clean energy carrier and storage medium could displace battery electric vehicles in certain segments, impacting demand for lithium and cobalt.
- Advanced Grid Solutions: Technologies like pumped hydro storage, though established, and newer concepts like gravity-based storage, offer alternatives for grid stabilization, potentially reducing the need for electrochemical storage at scale.
- Alternative Battery Chemistries: Sodium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries, and other chemistries are being developed that may use fewer or no critical minerals currently supplied by companies like IGO, posing a direct substitute threat.
- Energy Efficiency and Demand Management: Improvements in energy efficiency and sophisticated demand-side management systems can reduce the overall need for energy storage, indirectly affecting the market for storage metals.
Policy and Regulatory Shifts
Government policies and regulations can significantly alter the threat of substitutes. For instance, subsidies or tax credits favoring specific technologies, like those for electric vehicles powered by non-lithium-ion batteries, could accelerate the adoption of alternatives, thereby increasing the substitute threat for lithium-based products.
Mandates for recycling rates or the use of sustainable materials also play a crucial role. Stricter environmental regulations might push industries to explore and adopt materials that are easier to recycle or have a lower environmental footprint, potentially displacing existing options. In 2024, many governments are reviewing and updating their environmental policies, with a notable focus on circular economy principles.
Consider the automotive sector's push towards sustainability. By mid-2024, several major economies have announced targets for increasing the use of recycled materials in vehicle production. This regulatory push could directly impact the demand for virgin materials and encourage the development and adoption of substitute materials with better recyclability profiles.
- Policy Impact: Government incentives for green technologies can boost substitute adoption.
- Regulatory Influence: Mandates for recycling and sustainable materials can favor alternatives.
- 2024 Trends: Increased focus on circular economy principles by governments worldwide.
- Sector Example: Automotive industry faces policy pressure to use more recycled and alternative materials.
The threat of substitutes is a critical factor for companies like IGO, particularly concerning the metals they extract for battery technology. Advancements in alternative battery chemistries, such as sodium-ion and solid-state batteries, are progressing rapidly. By mid-2024, several companies have announced significant breakthroughs in sodium-ion technology, projecting cost reductions of up to 30% compared to current lithium-ion batteries, directly impacting lithium demand.
Recycling initiatives are also emerging as a substantial substitute threat. As recycling processes mature, they offer an alternative source of critical minerals, lessening the need for newly mined materials. The global electronics recycling market, a key source of many critical minerals, is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2024, illustrating the growing scale of this substitute.
Technological innovation in material science poses a significant risk. Breakthroughs could lead to clean energy technologies requiring fewer critical metals, potentially affecting IGO's core business. For instance, advancements in battery chemistry might reduce the reliance on cobalt or nickel, metals IGO heavily extracts.
| Substitute Technology | Key Impact on IGO's Metals | Projected Market Impact (2024 Data/Projections) |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium-ion Batteries | Reduced demand for lithium | Potential 30% cost reduction vs. Li-ion |
| Solid-state Batteries | Reduced demand for lithium, cobalt, nickel | Active development by major automotive and tech firms |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cells | Displacement of battery EVs in certain segments | Growing interest in heavy transport and industrial applications |
| Advanced Grid Storage (e.g., Flow Batteries) | Reduced need for electrochemical storage at scale | Global energy storage market CAGR projected over 20% through 2030 |
| Recycling Initiatives | Decreased demand for virgin materials | Global electronics recycling market worth hundreds of billions |
Entrants Threaten
The mining sector presents a formidable threat of new entrants due to its exceptionally high capital intensity. Developing a new mine can easily cost billions of dollars, encompassing everything from initial geological surveys and land acquisition to the construction of extraction infrastructure and processing facilities. For instance, the development of a large-scale copper mine can require upfront investments exceeding $5 billion, making it a daunting prospect for newcomers without substantial financial backing.
Furthermore, the extended lead times inherent in the mining industry act as a significant deterrent. It often takes a decade or more from the initial discovery of a viable mineral deposit to the commencement of commercial production. This lengthy gestation period, coupled with the massive upfront capital, means that potential entrants face prolonged periods of risk and uncertainty before any revenue is generated, effectively shielding established players from immediate competitive pressure.
Securing access to economically viable, high-grade mineral deposits presents a significant barrier for new companies looking to enter the mining sector. Established players, such as IGO, often possess vast landholdings with proven reserves, making it challenging for newcomers to identify and acquire competitive resources. For instance, in 2024, the global discovery rate of new, economically viable mineral deposits continued to be a concern, with many of the most accessible and richest deposits already being exploited by incumbents.
The mining industry faces significant hurdles from new entrants due to stringent regulatory and permitting complexities. Obtaining environmental, social, and operational permits is a lengthy and expensive undertaking, often requiring years of detailed studies and stakeholder consultations. For example, in 2024, the average time to secure major mining permits in jurisdictions like Canada could extend beyond five years, with associated costs easily reaching millions of dollars, effectively acting as a substantial barrier.
Technological Expertise and Operational Know-how
The mining sector, particularly for critical minerals powering the clean energy transition, presents a high barrier to entry due to the intense need for specialized technological expertise and deep operational know-how. Successfully extracting and processing complex ores, such as those containing lithium, cobalt, or rare earth elements, requires advanced geological understanding, sophisticated extraction techniques, and efficient refining processes. For instance, developing commercially viable methods for processing low-grade lithium spodumene or extracting rare earths from challenging geological formations can take years and substantial investment in research and development.
New companies looking to enter this space must overcome the significant hurdle of acquiring or developing this specialized knowledge. This isn't just about having the capital; it's about possessing the intellectual property, the skilled workforce, and the proven operational track record that established players have cultivated over decades. Without this, a new entrant risks inefficient operations, lower yields, and ultimately, an inability to compete on cost or quality. For example, the learning curve for implementing advanced tailings management or employing novel hydrometallurgical processes can be steep, demanding experienced engineers and geologists.
- High R&D Investment: Companies like Lynas Rare Earths have invested hundreds of millions of dollars in developing proprietary processing technologies to efficiently separate rare earth elements.
- Operational Scale and Efficiency: Achieving economies of scale in mining and processing is crucial; a new entrant must demonstrate it can operate at a competitive cost per tonne, often requiring large-scale, automated operations.
- Environmental and Permitting Expertise: Navigating complex environmental regulations and securing permits for mining operations requires specialized knowledge and experience, a process that can take many years and significant financial outlay.
Market Volatility and Price Risk
The inherent volatility in commodity prices for metals like nickel, lithium, and copper presents a significant threat to new entrants in the mining sector. For instance, the London Metal Exchange (LME) nickel price saw dramatic swings in 2024, at times exceeding $20,000 per tonne before falling back, illustrating the unpredictable nature of these markets.
New entrants, lacking established revenue streams or diversified portfolios, are particularly vulnerable to these market downturns. A sudden drop in metal prices can quickly erode the profitability of a new project, making it difficult to recoup initial capital expenditures. This price risk can deter potential investors from entering the market, thereby reducing the threat of new competition.
- Nickel Price Volatility: LME nickel prices experienced significant fluctuations in 2024, highlighting the inherent market risk.
- Lithium Price Uncertainty: While demand for lithium remains strong due to EVs, price stabilization is a key concern for new projects.
- Copper Market Dynamics: Copper prices, influenced by global infrastructure spending and supply chain issues, also pose a risk to new mine developers.
- Impact on New Entrants: Companies without diversified operations or strong financial backing are more exposed to these price shocks.
The threat of new entrants in the mining sector is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Developing a new mine often demands billions of dollars for exploration, infrastructure, and operational setup, a sum that deters many aspiring companies. For example, the average cost to develop a new copper mine in 2024 was estimated to be between $3 billion and $6 billion, a substantial barrier for any newcomer.
Furthermore, the long lead times, typically a decade or more from discovery to production, coupled with regulatory hurdles and the need for specialized expertise, create formidable entry barriers. Securing access to viable mineral deposits is also challenging, as established players often control significant landholdings with proven reserves. In 2024, the scarcity of new, high-grade discoveries meant that acquiring prospective land was increasingly competitive and expensive.
The mining industry also faces considerable regulatory and permitting complexities, with obtaining necessary approvals often taking several years and costing millions. This protracted process, along with the need for advanced technological know-how for extraction and processing, particularly for critical minerals, further solidifies the position of incumbents. For instance, the average time to secure major mining permits in Canada in 2024 could exceed five years.
Commodity price volatility, as seen with nickel and lithium in 2024, also acts as a deterrent. New entrants, often lacking diversified revenue streams, are particularly vulnerable to price downturns, making it difficult to recoup initial investments and discouraging market entry.
| Barrier | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Extremely high upfront investment required for mine development. | Average cost to develop a new copper mine: $3-6 billion. |
| Lead Times & Risk | Long periods from discovery to production, involving prolonged risk. | Typically 10+ years from discovery to commercial production. |
| Access to Deposits | Difficulty in acquiring economically viable, high-grade mineral resources. | Increasing competition for prospective land due to scarcity of new discoveries. |
| Regulatory & Permitting | Complex, lengthy, and expensive processes to obtain necessary approvals. | Average time for major mining permits in Canada: 5+ years. |
| Specialized Expertise | Need for advanced technical knowledge in extraction, processing, and operations. | Developing efficient rare earth processing techniques requires significant R&D investment. |
| Commodity Price Volatility | Fluctuations in metal prices pose a risk to profitability and investment recovery. | Nickel prices on the LME experienced significant swings in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data, including industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from public companies, and regulatory filings from relevant government bodies. This blend of sources allows for a robust understanding of competitive intensity, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
