Iamgold Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Iamgold Bundle
Iamgold operates within a dynamic gold mining sector, facing significant pressures from powerful buyers and intense rivalry among established players. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry's complexities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Iamgold’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of key suppliers significantly impacts IAMGOLD's bargaining power. If only a handful of companies provide essential mining machinery, like large-scale excavators or sophisticated processing equipment, these suppliers can dictate terms and prices. For instance, in 2024, the global market for mining equipment saw continued consolidation, with major players like Caterpillar and Komatsu holding substantial market share, potentially increasing their leverage over mining companies like IAMGOLD.
IAMGOLD's suppliers gain leverage when they offer inputs that are distinct or require specialized expertise, making them hard for IAMGOLD to replace. This can manifest in proprietary mining equipment, advanced extraction technologies, or access to exceptionally skilled geologists and engineers crucial for exploration and operational efficiency.
The more specialized and difficult to substitute an input is, the greater the supplier's ability to dictate terms and pricing. For instance, a supplier of a unique, patented drilling fluid that significantly enhances ore recovery would possess considerable bargaining power over IAMGOLD.
IAMGOLD's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by switching costs. If IAMGOLD faces substantial expenses or operational hurdles when changing to a different provider for critical inputs like specialized mining equipment or essential chemicals, its ability to negotiate favorable terms with existing suppliers is diminished. This dependence grants suppliers greater leverage in dictating prices and contract conditions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into gold mining, thereby becoming direct competitors, is a significant factor influencing IAMGOLD's bargaining power. While typically less common for large equipment manufacturers, specialized service providers or technology firms with deep industry knowledge could potentially leverage their expertise to enter the mining sector directly. This would shift the competitive landscape, potentially increasing costs and reducing IAMGOLD's operational flexibility.
For instance, a key supplier of advanced drilling technology or specialized processing chemicals might consider establishing its own mining operations if the profit margins and market access appear attractive. Such a move would transform a supplier relationship into a competitive one, directly impacting IAMGOLD's market share and profitability. The feasibility of this threat often depends on the capital intensity and regulatory hurdles associated with gold mining.
Consider the following:
- Potential Competitors: Specialized technology or service providers could leverage their expertise to enter gold mining.
- Industry Entry Barriers: High capital requirements and complex regulations can deter suppliers from forward integration.
- Strategic Advantage: Successful forward integration by a supplier could disrupt IAMGOLD's supply chain and market position.
Importance of IAMGOLD to Suppliers
IAMGOLD's significance as a customer directly influences supplier leverage. If IAMGOLD constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's annual sales, that supplier may be less inclined to exert significant price pressure, prioritizing the continuation of the business relationship. For instance, if a key equipment provider relies on IAMGOLD for 25% of its revenue, they are likely to be more accommodating.
Conversely, for suppliers who serve a broad market and count IAMGOLD as a relatively minor client, their bargaining power increases. These suppliers are less dependent on IAMGOLD and can more readily dictate terms or seek alternative, potentially more lucrative, customers if negotiations falter. In 2023, IAMGOLD's total cost of sales was approximately $1.3 billion, meaning that for suppliers whose business is heavily concentrated with IAMGOLD, maintaining this relationship is crucial.
- Customer Dependence: IAMGOLD's revenue share for its suppliers is a critical factor.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with many clients have more leverage.
- 2023 Cost of Sales: IAMGOLD's $1.3 billion in cost of sales highlights its market presence.
- Relationship Value: High dependence on IAMGOLD limits supplier power.
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment and proprietary technologies hold significant bargaining power over IAMGOLD due to high switching costs and the difficulty of finding substitutes. In 2024, continued consolidation in the mining equipment sector, with companies like Caterpillar and Komatsu dominating, further strengthens supplier leverage. The threat of suppliers integrating forward into gold mining, while mitigated by high industry entry barriers, remains a potential concern, impacting IAMGOLD's operational flexibility and cost structure.
| Factor | Impact on IAMGOLD | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few key suppliers | Consolidation in mining equipment market |
| Input Differentiation | Stronger power for specialized inputs | Proprietary extraction technologies |
| Switching Costs | Reduced IAMGOLD negotiation power | High costs for changing equipment providers |
What is included in the product
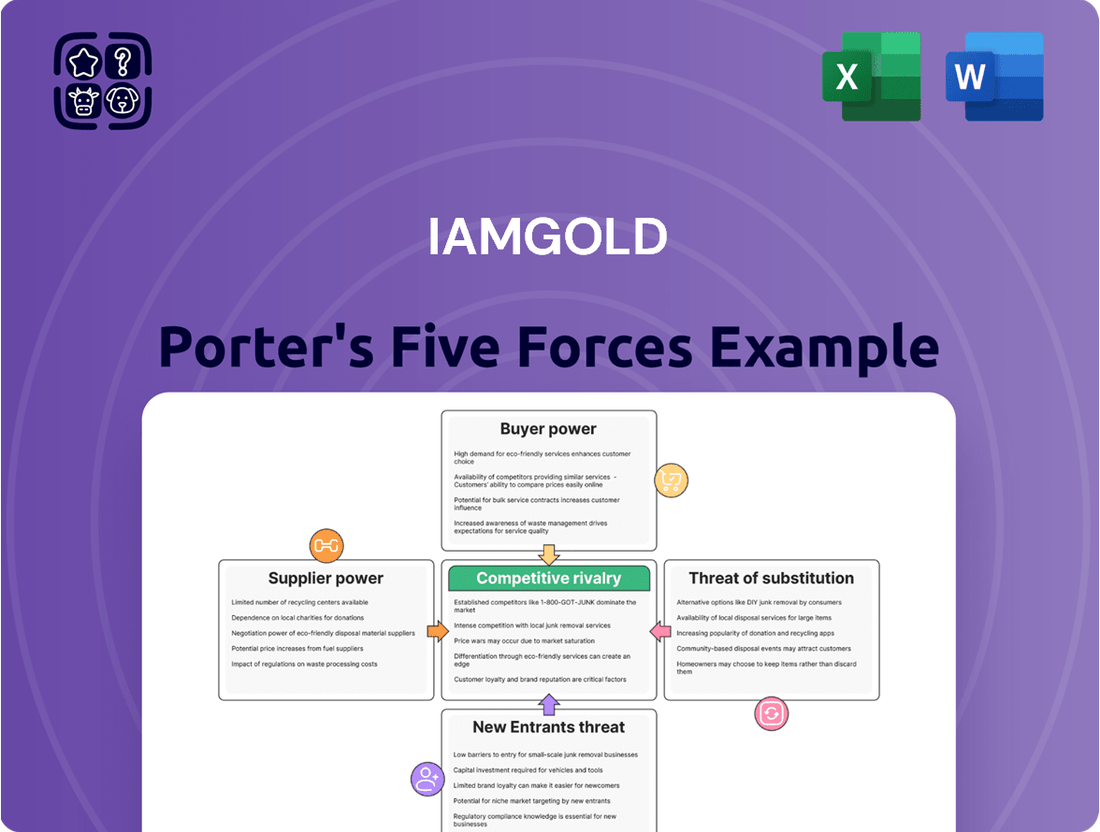
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Iamgold dissects the competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the gold mining industry.
Instantly visualize Iamgold's competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market pressures for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
The gold market's diverse customer base, encompassing investors, central banks, and industrial users, generally dilutes individual customer power. This broad distribution means that no single buyer typically represents a significant portion of IAMGOLD's sales, limiting their ability to dictate terms or prices.
The price sensitivity of customers for gold, a key factor in IAMGOLD's bargaining power, is quite varied. While gold's allure as a safe-haven asset, driven by geopolitical tensions, inflation fears, and currency fluctuations, can significantly dampen price sensitivity for investors and central banks, industrial and jewelry sectors exhibit more elastic demand. For instance, in 2024, gold prices have seen considerable volatility, influenced by central bank buying and investor sentiment, demonstrating this dual nature of demand.
While gold itself possesses unique qualities, investors and industrial users have a range of alternatives to consider. For instance, in 2024, silver prices saw significant fluctuations, presenting a potential hedge against inflation similar to gold, though with higher volatility. Other precious metals like platinum and palladium also offer diversification opportunities. Beyond metals, financial instruments such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) tracking various commodities or even bonds can serve as investment substitutes, providing different risk-return profiles.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating into gold production is typically low for a company like IAMGOLD. This is because establishing and operating a gold mine requires immense capital investment, specialized geological and engineering expertise, and navigating complex environmental and governmental regulations. These barriers make it highly improbable for most customers, such as jewelry manufacturers or industrial users of gold, to undertake such a venture themselves.
This limited likelihood of backward integration by customers significantly curtails their bargaining power. Customers cannot credibly threaten to produce their own gold, which would directly challenge IAMGOLD's core business. For instance, while some large industrial consumers might have substantial purchasing power, the sheer scale and complexity of gold mining mean they are unlikely to develop their own mining operations as a competitive tactic.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a new gold mine can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, a prohibitive expense for most downstream customers.
- Technical Expertise: Gold exploration, extraction, and processing demand specialized knowledge in geology, mining engineering, metallurgy, and environmental management.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining permits, adhering to environmental standards, and managing community relations are significant and time-consuming challenges in the mining sector.
- Limited Customer Capacity for Integration: The vast majority of IAMGOLD's customers operate in sectors far removed from primary resource extraction, making backward integration impractical and uneconomical.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers in the gold market, particularly large institutional investors and central banks, possess significant bargaining power due to their access to comprehensive market data. They can readily analyze global supply, demand dynamics, and price fluctuations, enabling them to make highly informed purchasing decisions. This transparency empowers them to negotiate more effectively with producers like IAMGOLD.
- Information Access: Institutional investors and central banks have access to real-time market data, analyst reports, and economic indicators influencing gold prices.
- Informed Decisions: This data allows them to predict price movements and identify optimal buying opportunities, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Market Influence: Large-scale buyers can significantly impact market demand, further enhancing their ability to bargain for better terms.
The bargaining power of customers for IAMGOLD is moderated by several factors. While large institutional buyers and central banks leverage their access to market data to negotiate effectively, the high capital and expertise required for gold mining make backward integration by customers highly improbable. This limits their ability to directly challenge IAMGOLD's production capabilities.
Customer price sensitivity varies, with investors and central banks often less sensitive to price due to gold's safe-haven status. However, industrial and jewelry sectors show more elastic demand. For instance, in 2024, gold prices have experienced notable swings, influenced by central bank acquisitions and investor sentiment, highlighting this varied responsiveness.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors & Central Banks | Lower (due to safe-haven appeal) | Access to market data, large purchase volumes |
| Industrial Users (e.g., electronics) | Moderate to High (depends on gold's role in product cost) | Potential for substitute materials, volume purchasing |
| Jewelry Manufacturers | Higher (price-sensitive consumer demand) | Brand reputation, ability to pass costs to consumers, potential for sourcing from multiple suppliers |
Full Version Awaits
Iamgold Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Iamgold Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. You're looking at the actual, professionally written document, so you can be confident in the quality and detail of the analysis. Once your purchase is complete, you'll gain instant access to this fully formatted and ready-to-use report, providing valuable insights into Iamgold's industry position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The gold mining sector is characterized by a substantial number of competitors, ranging from global giants to smaller, specialized firms. Major players such as Newmont Corporation and Barrick Gold Corporation dominate the market with significant production volumes and extensive global operations, creating a highly competitive environment.
IAMGOLD, as an intermediate gold producer, navigates this landscape by focusing on specific regions, notably West Africa and Canada. In these areas, the company contends with both large, established miners and a multitude of mid-tier and junior exploration companies, each vying for resources and market share.
For context, in 2023, Newmont reported gold sales of approximately 5.6 million ounces, while Barrick Gold sold around 4.5 million ounces, illustrating the scale of these leading competitors. IAMGOLD's production, while smaller, places it directly in competition for talent, capital, and prime mining concessions within its operational zones.
While global gold production has remained relatively stable or slightly declined due to resource depletion, the elevated gold prices experienced in 2024 and projected into 2025 are significantly boosting sector revenues. This financial incentive is drawing renewed interest and investment, which in turn is likely to intensify competition for exploration rights, mining concessions, and skilled labor.
Gold is fundamentally a commodity, offering limited inherent product differentiation. This means that competition within the gold mining sector, including for companies like IAMGOLD, often centers on operational advantages rather than unique product features.
Companies like IAMGOLD must therefore focus on cost efficiency, maximizing production volume, and ensuring operational reliability to stand out. IAMGOLD's strategic development of projects such as Côté Gold, which aims for significant production and cost advantages, directly addresses this competitive landscape.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers are a significant factor in the gold mining industry, often forcing companies to remain operational even when market conditions are unfavorable. These barriers include substantial sunk costs in specialized infrastructure, such as processing plants and mine shafts, which have limited alternative uses. For instance, the substantial capital investment required for a gold mine means that decommissioning it prematurely incurs massive losses.
Environmental reclamation obligations also contribute to these high exit barriers. Companies are legally required to restore mining sites to their original condition, a process that can be incredibly expensive and time-consuming, often running into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. These ongoing liabilities make it difficult for firms to simply walk away from a mine.
Consequently, these elevated exit barriers can intensify competitive rivalry. When firms are reluctant or unable to exit the market, they may continue to operate and compete fiercely for market share, even during periods of low gold prices. This can lead to price wars or a focus on cost reduction to maintain profitability, impacting overall industry dynamics.
- High Capital Investment: Gold mining operations require extensive upfront capital for exploration, development, and infrastructure.
- Environmental Reclamation Costs: Significant financial provisions are necessary for mine site closure and restoration, often spanning decades.
- Specialized Assets: Mining equipment and facilities are highly specialized and difficult to repurpose or sell, leading to substantial write-downs if operations cease.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining permits for mining operations and subsequent closure can be complex and costly, further deterring early exits.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors' strategic objectives, whether focused on production growth, cost leadership, or portfolio optimization through mergers and acquisitions, significantly shape the competitive landscape for IAMGOLD. For instance, major gold producers like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation have been actively pursuing strategies to enhance their operational efficiency and reduce all-in sustaining costs. In 2024, these larger players continue to demonstrate a strong focus on consolidating their asset bases, often through strategic divestments of non-core or higher-cost operations and acquisitions of promising new projects or existing mines with lower production costs.
The current period is characterized by a notable wave of consolidation within the mining sector, signaling aggressive strategic maneuvers by larger, well-capitalized entities. This trend is driven by a desire to achieve economies of scale, secure access to lower-cost reserves, and improve overall financial resilience in a volatile commodity market. For example, the ongoing pursuit of efficient operations and strategic M&A by industry leaders directly influences the pressure on companies like IAMGOLD to maintain competitive cost structures and explore similar portfolio adjustments.
- Production Growth: Many competitors aim to increase gold output year-over-year, often through expanding existing operations or developing new projects.
- Cost Leadership: A key objective for many is to become a low-cost producer, achieved through technological advancements and operational efficiencies.
- Portfolio Optimization: Companies are actively engaging in M&A to streamline their asset portfolios, divesting underperforming assets and acquiring those with higher potential or lower operating costs.
- Market Share: Larger players often seek to increase their market share through strategic acquisitions and organic growth, exerting greater influence on pricing and supply dynamics.
Competitive rivalry in the gold mining sector is intense, with numerous global and regional players vying for resources and market share. IAMGOLD, as an intermediate producer, faces pressure from larger entities like Newmont and Barrick, which possess greater scale and lower production costs. The commodity nature of gold means competition hinges on operational efficiency and cost management.
The sector's high capital requirements and environmental obligations create significant exit barriers, forcing companies to compete aggressively even in challenging market conditions. This dynamic is further amplified by ongoing consolidation trends as major players seek economies of scale and access to lower-cost reserves, directly impacting IAMGOLD's strategic positioning.
Elevated gold prices in 2024 and projected into 2025 are intensifying competition for exploration rights and skilled labor, as more capital flows into the sector. Companies are prioritizing production growth, cost leadership, and portfolio optimization through mergers and acquisitions to maintain a competitive edge.
| Company | 2023 Gold Sales (Million Ounces) | All-in Sustaining Costs (USD/oz) - Latest Available |
|---|---|---|
| Newmont Corporation | ~5.6 | ~1,267 (Q4 2023) |
| Barrick Gold Corporation | ~4.5 | ~1,340 (Q4 2023) |
| IAMGOLD Corporation | ~0.48 (2023) | ~1,449 (Q4 2023) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For Iamgold, the threat of substitutes is significant as investors have numerous alternative assets to consider. Gold directly competes with other precious metals like silver and platinum, which can offer similar diversification benefits. In 2024, while gold prices saw some volatility, the broader precious metals market also experienced shifts influenced by macroeconomic factors and industrial demand.
Beyond precious metals, gold faces competition from a vast array of financial instruments. Real estate, stocks, and bonds all present different risk-reward profiles that can attract capital away from gold, especially during periods of economic uncertainty or strong performance in other sectors. For instance, a robust stock market rally in 2024 might draw investment away from gold as investors seek higher growth potential.
The attractiveness of these substitutes is heavily influenced by prevailing market conditions and overall investor sentiment. When other asset classes are perceived as offering better returns or lower risk, demand for gold can diminish. This dynamic means Iamgold must constantly monitor not just the gold market but also the performance and appeal of a wide range of competing investment opportunities.
Technological progress in materials science presents a significant threat of substitution for gold, particularly in industrial sectors. For instance, advancements in ceramics and advanced polymers are creating viable alternatives in electronics and dentistry, areas historically reliant on gold’s conductivity and inertness.
In 2024, the demand for gold in industrial applications, while a smaller portion of the overall market compared to jewelry and investment, still represents a critical area where substitution can erode demand. The ongoing development of high-performance synthetic materials capable of matching gold's properties at a lower cost directly impacts its long-term market share in these specialized fields.
Shifting consumer tastes present a significant threat. For instance, a growing preference for lab-grown diamonds or alternative metals like platinum and titanium in 2024 could divert demand away from gold jewelry. This trend, fueled by ethical sourcing concerns and evolving fashion aesthetics, directly impacts a core market for gold producers.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly influence the perceived attractiveness of gold as an investment relative to other asset classes. Changes in monetary policy, such as adjustments to interest rates by central banks, can directly impact this dynamic. For instance, as of mid-2024, many central banks have maintained or slightly increased interest rates to combat inflation, making interest-bearing assets like bonds more competitive against gold, which does not offer a yield.
Furthermore, evolving investment regulations can alter the landscape for gold. Stricter capital controls or new taxation policies on precious metals could diminish gold's appeal. Conversely, policies that encourage diversification into tangible assets or provide tax incentives for gold ownership could bolster its attractiveness. The regulatory environment for mining operations, including environmental standards and permitting processes, also affects the supply side and, consequently, the price and availability of gold, indirectly impacting its role as a substitute.
- Monetary Policy Impact: Higher interest rates in 2024, for example, increase the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like gold, making alternatives such as government bonds more appealing to investors.
- Investment Regulation Changes: Shifts in regulations regarding capital flows or taxation on precious metals can alter gold's attractiveness compared to regulated financial instruments.
- Mining Regulations: Evolving environmental and operational regulations for gold mining can influence supply and price, affecting gold's competitive position against other commodities or investment options.
Perceived Value and Store of Wealth
The perceived value of gold as a safe haven and a store of wealth significantly influences its demand, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension. For instance, in 2023, gold prices saw considerable volatility, often reacting to inflation data and central bank policy shifts, underscoring its role as a perceived hedge.
Should global stability improve or compelling new alternative safe-haven assets gain traction, the demand for gold could face pressure. For example, the rise of certain digital assets or even shifts in sovereign debt attractiveness could divert investor capital away from traditional gold holdings.
- Gold's historical role as a store of value is a primary driver of its demand.
- Economic instability and geopolitical risks often increase investor interest in gold.
- Emergence of alternative safe-haven assets poses a potential threat to gold demand.
- In 2023, gold prices demonstrated sensitivity to inflation and monetary policy, highlighting its perceived hedging qualities.
The threat of substitutes for Iamgold is substantial, as investors have a wide array of alternative assets. Gold competes directly with other precious metals like silver and platinum, offering similar diversification benefits. In 2024, while gold experienced price fluctuations, the broader precious metals market also saw shifts influenced by macroeconomic conditions and industrial demand.
Beyond precious metals, gold faces competition from diverse financial instruments such as real estate, stocks, and bonds. These alternatives present different risk-reward profiles that can attract capital away from gold, particularly during economic uncertainty or when other sectors perform strongly. A robust stock market rally in 2024, for instance, could divert investment from gold as investors seek higher growth potential.
The appeal of these substitutes is heavily tied to market conditions and investor sentiment. When other asset classes appear to offer better returns or lower risk, demand for gold can decrease. This necessitates that Iamgold continuously monitors not only the gold market but also the performance and attractiveness of various competing investment opportunities.
Technological advancements in materials science introduce a significant threat of substitution for gold, especially in industrial applications. Innovations in ceramics and advanced polymers are yielding viable alternatives in electronics and dentistry, sectors historically reliant on gold's conductivity and inertness.
In 2024, industrial demand for gold, though a smaller market segment than jewelry and investment, remains a critical area where substitution can impact overall demand. The ongoing development of high-performance synthetic materials that can match gold's properties at a lower cost directly affects its long-term market share in specialized fields.
Shifting consumer preferences also pose a considerable threat. For example, a growing inclination towards lab-grown diamonds or alternative metals like platinum and titanium in 2024 could divert demand from gold jewelry. This trend, driven by ethical sourcing concerns and evolving fashion trends, directly affects a key market for gold producers.
Government policies and regulations significantly influence gold's attractiveness relative to other assets. Changes in monetary policy, such as central bank interest rate adjustments, directly impact this dynamic. As of mid-2024, many central banks have maintained or slightly increased interest rates to combat inflation, making interest-bearing assets like bonds more competitive against gold, which offers no yield.
Furthermore, evolving investment regulations can reshape the landscape for gold. Stricter capital controls or new taxation policies on precious metals could reduce gold's appeal. Conversely, policies encouraging diversification into tangible assets or offering tax incentives for gold ownership could enhance its attractiveness. Mining regulations, including environmental standards and permitting, also affect supply and price, indirectly impacting gold's competitive position.
The perceived value of gold as a safe haven and store of wealth is a primary driver of its demand, especially during economic uncertainty or geopolitical tension. In 2023, gold prices showed considerable volatility, often reacting to inflation data and central bank policy shifts, highlighting its role as a perceived hedge.
Should global stability improve or compelling new alternative safe-haven assets emerge, gold demand could face pressure. The rise of certain digital assets or shifts in the attractiveness of sovereign debt could divert investor capital from traditional gold holdings.
| Substitute Category | Key Factors Influencing Substitution | 2024 Market Dynamics & Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Other Precious Metals (Silver, Platinum) | Similar diversification benefits, price sensitivity to industrial demand and macroeconomic factors. | Experienced volatility in 2024, influenced by global economic trends. |
| Financial Instruments (Stocks, Bonds, Real Estate) | Risk-reward profiles, market performance, interest rate sensitivity, economic uncertainty. | Strong stock market rallies in 2024 could divert capital from gold; higher interest rates made bonds more competitive. |
| Industrial Materials (Ceramics, Polymers) | Technological advancements, cost-effectiveness, performance properties (conductivity, inertness). | Ongoing development of synthetic materials capable of matching gold's properties at lower costs impacts specialized industrial demand. |
| Alternative Consumer Goods (Lab-grown diamonds, other metals) | Ethical sourcing, fashion trends, perceived value, price. | Growing preference for alternatives in jewelry markets in 2024 could reduce demand for gold jewelry. |
| Alternative Safe-Haven Assets (Digital assets, Sovereign Debt) | Perceived stability, return potential, regulatory environment, investor sentiment. | Emergence of new safe-haven assets could siphon investment away from gold, especially during periods of improving global stability. |
Entrants Threaten
The gold mining industry demands immense capital, with significant upfront investments needed for exploration, mine development, and essential infrastructure. For instance, establishing a new gold mine can easily cost hundreds of millions, even billions, of dollars. This high capital intensity acts as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring many potential new entrants who lack the necessary financial backing to undertake such large-scale projects.
The mining industry, particularly for companies like IAMGOLD, faces significant regulatory hurdles that deter new entrants. Obtaining the necessary permits and navigating complex regulatory frameworks in jurisdictions such as Canada and West Africa is a time-consuming and arduous process. For instance, in 2023, the average time to secure a major mining permit in Canada could extend over several years, involving multiple levels of government and extensive environmental impact assessments.
The threat of new entrants into the gold mining sector, specifically concerning access to reserves and resources, is significantly dampened by the inherent scarcity and increasing difficulty in discovering high-quality gold deposits. Established companies like IAMGOLD benefit from their existing, proven reserves and extensive exploration portfolios, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers seeking economically viable and readily accessible gold assets. For instance, as of the end of 2023, IAMGOLD reported proven and probable gold reserves of 13.1 million ounces, a tangible asset that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly or cost-effectively.
Economies of Scale for Existing Players
Existing gold miners, like IAMGOLD, often leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs across larger production volumes, resulting in lower per-unit costs for extraction, processing, and even raw material procurement. For instance, major players can negotiate better terms for explosives, fuel, and equipment due to their sheer purchasing power, a benefit new entrants would find difficult to replicate quickly.
These cost advantages create a substantial barrier for new companies entering the gold mining sector. A new entrant would need to invest heavily to achieve comparable production levels and operational efficiencies. Without this scale, they would likely face higher operating costs per ounce of gold produced, making it challenging to compete on price with established, large-scale producers.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbent gold miners benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations, procurement, and processing.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: New players struggle to match cost efficiencies without significant production volumes, creating a competitive hurdle.
- Procurement Power: Established companies secure better pricing on essential supplies like fuel and equipment through bulk purchasing.
- Capital Intensity: Achieving competitive cost structures necessitates substantial upfront investment in infrastructure and technology, deterring smaller entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
Established gold mining companies benefit from significant brand loyalty and deep-rooted relationships within the industry. These existing connections with refiners, buyers, and financial institutions create substantial barriers for newcomers. For instance, major players often secure preferential terms and financing due to their long-standing partnerships, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, a company's reputation for ethical and sustainable mining practices, built over years, is a critical asset. Stakeholders, including investors and consumers, increasingly prioritize these aspects. New entrants must invest considerable time and resources to cultivate similar trust and demonstrate a commitment to responsible operations, a process that can take years to establish and gain market acceptance.
In 2023, the average cost for a new mining project to secure initial financing and establish supply chain agreements could easily run into tens of millions of dollars, reflecting the scale of investment required to overcome these relational hurdles. Companies like Barrick Gold and Newmont have spent decades solidifying these networks, making it a formidable challenge for any emerging competitor to gain comparable footing.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by:
- Strong existing relationships with refiners and buyers.
- Established reputations for responsible mining and ESG compliance.
- Difficulties in quickly replicating trust and securing favorable financial terms.
The threat of new entrants into the gold mining industry is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements, often in the hundreds of millions to billions of dollars for mine development, are a primary deterrent. Navigating complex and lengthy regulatory processes, which can take years for major permits as seen in Canada in 2023, further discourages newcomers.
Access to proven gold reserves is another significant hurdle. Established players like IAMGOLD, with 13.1 million ounces of proven and probable reserves as of year-end 2023, possess a distinct advantage over new entrants struggling to find and secure economically viable deposits.
Economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents, leading to lower per-unit production costs and strong procurement power for essential supplies, create a cost disadvantage for smaller, new operations. Additionally, established relationships with refiners, buyers, and financial institutions, coupled with reputations for responsible mining practices, are difficult for new entrants to quickly replicate.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment for exploration and mine development (e.g., hundreds of millions to billions USD). | Significant financial barrier; requires substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and time-consuming permitting processes; average major permit in Canada took several years in 2023. | Delays entry and increases project costs. |
| Access to Reserves | Scarcity of high-quality deposits; IAMGOLD reported 13.1 million ounces of reserves end of 2023. | Newcomers struggle to secure economically viable assets. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established large-scale producers. | New entrants face higher operating costs. |
| Established Relationships & Reputation | Strong ties with buyers, refiners, and financial institutions; years to build trust. | Difficult for new entrants to secure favorable terms and market access. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for IAMGOLD leverages data from company annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports to assess competitive intensity and strategic positioning.
