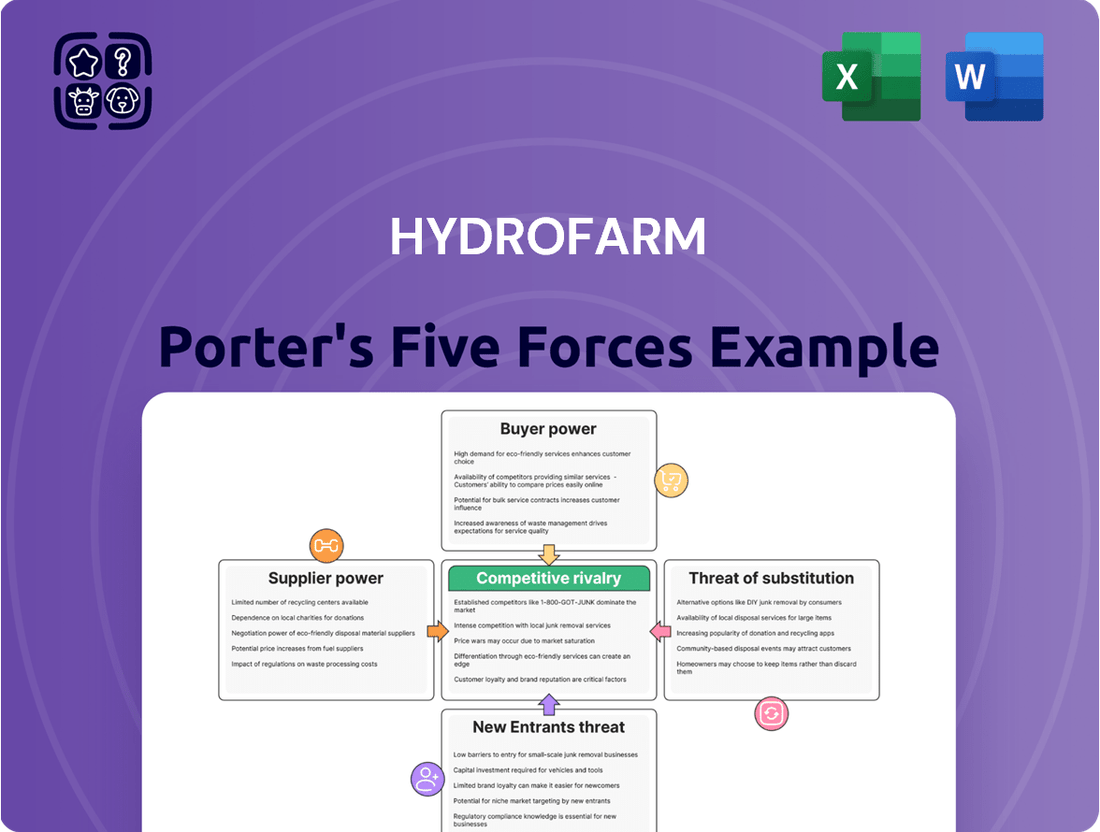
Hydrofarm Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hydrofarm Bundle
Hydrofarm operates in a dynamic market shaped by significant buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes in the indoor gardening sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Hydrofarm delves into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the barriers to entry for potential competitors. This comprehensive view is essential for navigating the industry landscape effectively.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Hydrofarm’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration significantly impacts Hydrofarm's bargaining power. If only a few companies provide essential items like specialized grow lights or advanced climate control systems, those suppliers gain leverage. This means they can potentially charge Hydrofarm more for these critical inputs, squeezing profit margins.
For instance, in 2024, the market for high-efficiency LED grow lights, a key component for many hydroponic setups, saw consolidation with leading manufacturers expanding market share. This concentration means Hydrofarm has fewer alternatives for sourcing these advanced technologies, potentially increasing their cost and reducing Hydrofarm's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
Hydrofarm's switching costs from its current suppliers are a critical factor in assessing supplier power. If Hydrofarm needs to retool its manufacturing processes or requalify materials from a new supplier, these actions represent significant expenses and time investments. For example, if Hydrofarm relies on highly specialized components for its hydroponic systems, finding and integrating an alternative supplier could involve substantial R&D and testing, potentially costing millions of dollars and delaying product launches.
The complexity of switching also plays a role. If Hydrofarm's supply chain is deeply integrated with existing suppliers, including long-term contracts and unique technical specifications, the effort to transition can be immense. In 2024, many manufacturers faced disruptions due to supply chain vulnerabilities, highlighting the cost of switching. For Hydrofarm, a smooth transition might involve extensive training for its staff on new supplier systems or the need to redesign packaging to meet new material requirements, all of which contribute to higher switching costs and thus greater supplier leverage.
The uniqueness of inputs is a critical factor in assessing supplier bargaining power for Hydrofarm. If suppliers provide highly differentiated or proprietary components, especially those with no easy substitutes, their leverage increases significantly. For instance, specialized nutrient blends or unique lighting technologies developed by a single supplier could give that supplier considerable power over Hydrofarm.
In 2024, the agricultural technology sector saw continued innovation, with some suppliers offering patented grow media or advanced sensor technologies. Companies that successfully differentiate their offerings can command higher prices and more favorable terms. Conversely, if Hydrofarm can source its essential inputs like growing mediums, nutrients, and lighting from multiple providers offering standardized products, its ability to negotiate better pricing and terms is enhanced, thereby reducing supplier power.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by Hydrofarm's suppliers, such as those providing LED lighting or nutrient solutions, could significantly alter the competitive landscape. If these suppliers were to start selling directly to retailers or even end-users, they would effectively become direct competitors, leveraging their existing product knowledge and manufacturing capabilities.
This is particularly concerning if suppliers possess strong brand equity or established distribution networks, as seen with some major agricultural technology providers who have expanded their offerings. For instance, in 2024, several companies that traditionally supplied components for controlled environment agriculture (CEA) began offering integrated systems, blurring the lines between supplier and solution provider.
- Supplier Integration Risk: Key suppliers may leverage their expertise to enter Hydrofarm's market directly.
- Increased Bargaining Power: If suppliers can reach Hydrofarm's customers, their negotiation leverage grows.
- Brand and Distribution Factors: Supplier brand recognition and existing distribution channels amplify this threat.
- Market Trends: The 2024 market saw some component suppliers moving towards offering complete CEA solutions, increasing this risk.
Importance of Hydrofarm to Supplier
The significance of Hydrofarm's business to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Hydrofarm constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier may be more inclined to offer favorable pricing and terms to retain Hydrofarm as a key client. Conversely, if Hydrofarm is a minor customer for a supplier, the supplier likely holds greater leverage in negotiations.
For instance, in 2023, the horticultural supply chain saw varying levels of supplier dependence on major distributors like Hydrofarm. While specific revenue breakdowns for individual suppliers are often proprietary, the general market trend indicates that suppliers with diversified customer bases are less susceptible to pressure from any single buyer. This means that for suppliers who also serve other significant players in the agriculture and hydroponics sectors, Hydrofarm's individual order volume might not dictate their entire negotiation strategy.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers whose revenue heavily relies on Hydrofarm may concede on price or terms.
- Market Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base have less incentive to offer significant concessions to Hydrofarm.
- Contractual Agreements: Long-term contracts can lock in terms, reducing immediate supplier bargaining power.
- Input Costs: Fluctuations in raw material costs for suppliers can influence their willingness to negotiate on Hydrofarm's behalf.
The bargaining power of Hydrofarm's suppliers is a key factor in its profitability, influenced by supplier concentration and the uniqueness of inputs. In 2024, the consolidation within the high-efficiency LED grow light market meant Hydrofarm faced fewer options for advanced technology, potentially increasing costs.
High switching costs, stemming from specialized components and integrated supply chains, also empower suppliers. For example, retooling manufacturing or requalifying materials for new suppliers can be a significant financial and time investment for Hydrofarm.
Furthermore, suppliers who offer patented or highly differentiated products, such as unique nutrient blends, can command higher prices. The 2024 agricultural technology sector saw continued innovation, with some suppliers providing patented grow media, thus strengthening their negotiating position.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, where they might start selling directly to Hydrofarm's customers, also increases their leverage. This trend was observed in 2024 as some component suppliers began offering complete controlled environment agriculture (CEA) solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Hydrofarm | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Reduces Hydrofarm's negotiation options, potentially increasing input costs. | Consolidation in the high-efficiency LED grow light market. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for Hydrofarm to change suppliers empower existing ones. | Significant investment required for retooling and material requalification. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Differentiated or patented products give suppliers pricing power. | Innovation in patented grow media and advanced sensor technologies. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers entering Hydrofarm's market directly increases their leverage. | Component suppliers offering integrated CEA solutions. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Hydrofarm, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the hydroponics market.
Visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, instantly highlighting areas of strategic vulnerability.
Gain clarity on industry dynamics with a pre-populated, yet customizable, Porter's Five Forces template, simplifying complex competitive analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hydrofarm's customer base is relatively diverse, encompassing commercial growers, home growers, and retailers. While specific customer concentration data for 2024 isn't publicly detailed, the presence of large commercial operations and established retail partnerships suggests some level of concentrated buying power. If a few major clients represent a substantial portion of Hydrofarm's revenue, they could leverage this to negotiate more favorable pricing or terms, impacting Hydrofarm's profitability.
The availability of substitutes significantly impacts Hydrofarm's customer bargaining power. Customers can readily find alternative grow lights, nutrient solutions, and environmental controls from numerous competitors, including both established brands and emerging players. For instance, the indoor gardening market in 2024 features a wide array of LED grow light manufacturers offering comparable spectrums and efficiency, directly challenging Hydrofarm's market share and pricing flexibility.
Hydrofarm faces varying degrees of price sensitivity across its customer base. Home growers, often operating with tighter budgets, tend to be more responsive to price fluctuations for basic hydroponic supplies. Conversely, large commercial agricultural operations, prioritizing yield and consistency, may exhibit lower price sensitivity when seeking specialized equipment or solutions that guarantee performance.
This differential sensitivity directly impacts Hydrofarm's ability to dictate pricing. For less differentiated products, such as standard nutrients or growing media, a highly price-sensitive customer segment can exert significant pressure for lower costs. For instance, a 10% price increase on a widely available nutrient solution might lead to a substantial shift in demand among hobbyists, whereas a commercial grower might absorb that increase if the product offers a proven advantage.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today possess a significant amount of information about product pricing, quality, and what competitors offer. This transparency, particularly amplified by online channels, means buyers can easily compare options. For instance, in the hydroponics market, online marketplaces and review sites allow consumers to quickly assess product features and prices from various suppliers. In 2024, the growth of e-commerce platforms dedicated to gardening and hydroponics has made price comparison more straightforward than ever.
This heightened customer awareness directly translates to increased bargaining power. When customers can readily identify lower-priced alternatives or products with superior features, they are less tied to a single supplier. This forces Hydrofarm to remain competitive in its pricing and product development to retain its customer base.
- In 2024, an estimated 75% of consumers researched products online before making a purchase, even for items bought in physical stores.
- The average consumer spends over 10 hours per month researching purchases.
- Online reviews and comparison websites are primary sources of information for over 60% of shoppers.
Threat of Backward Integration
The bargaining power of Hydrofarm's customers is influenced by the threat of backward integration, where customers might start producing their own hydroponics equipment. This is particularly relevant for large commercial growers or major retailers who have the scale and resources to consider manufacturing or distribution in-house. If they can credibly produce their own supplies, their negotiating leverage against Hydrofarm increases significantly.
This threat is often more pronounced for standardized products within the hydroponics sector, where the barriers to entry for manufacturing are lower. For instance, if a large agricultural cooperative can produce basic grow lights or nutrient solutions efficiently, they may reduce their reliance on suppliers like Hydrofarm, potentially driving down prices or demanding more favorable terms. In 2023, the global hydroponics market was valued at approximately $12.5 billion, indicating a substantial market where large players could indeed explore backward integration.
- Increased Leverage: Customers capable of backward integration gain more power to negotiate prices and terms with Hydrofarm.
- Standardized Products: The threat is higher for less complex, commoditized hydroponics equipment where manufacturing is more accessible.
- Market Size Impact: The substantial global hydroponics market size, estimated at $12.5 billion in 2023, provides ample incentive for large customers to consider in-house production.
- Competitive Pressure: If competitors' customers are backward integrating, Hydrofarm may face pressure to offer more competitive pricing or services.
Hydrofarm's customers possess considerable bargaining power, amplified by market transparency and the availability of substitutes. In 2024, with widespread online research, customers can easily compare Hydrofarm's offerings against numerous competitors, especially for standardized products like LED grow lights and nutrient solutions. This ease of comparison, coupled with a diverse customer base ranging from budget-conscious home growers to large-scale commercial operations, means Hydrofarm must remain highly competitive on price and product innovation to retain market share and influence terms.
| Factor | Impact on Hydrofarm's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Moderate to High for key accounts; low for fragmented base. | Specific concentration data not public, but large commercial growers represent significant revenue potential. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Numerous competitors offer comparable grow lights, nutrients, and environmental controls. The LED grow light market alone is highly competitive. |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by segment; higher for home growers, lower for commercial operations prioritizing yield. | Home growers may switch for small price differences; commercial clients may pay a premium for proven performance and reliability. |
| Customer Information/Transparency | High | Over 75% of consumers research online before purchasing; online reviews and comparison sites are key decision-making tools for over 60% of shoppers. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Moderate | Large commercial growers or cooperatives could potentially produce some supplies in-house, particularly for commoditized items. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hydrofarm Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hydrofarm Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring a transparent and accurate representation of the final deliverable. You'll gain instant access to this professionally formatted analysis, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The hydroponics equipment and supplies market is characterized by a moderate number of competitors, with a mix of large, established companies and numerous smaller, specialized firms. This fragmentation suggests a dynamic competitive landscape where smaller players can carve out niches, but larger entities often hold significant market share due to economies of scale and brand recognition.
In 2024, the global hydroponics market was valued at approximately USD 12.5 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. While specific market share data for individual companies is proprietary, industry analysis suggests that companies like Hawthorne Gardening Company (a subsidiary of Scotts Miracle-Gro) and General Hydroponics are significant players, alongside a substantial number of regional and online retailers offering a wide array of products.
The presence of both large and small competitors creates a multi-faceted rivalry. Large companies can leverage their resources for aggressive pricing and wider distribution, while smaller firms often compete on innovation, specialized product offerings, and customer service. This dynamic means that established players must remain vigilant against emerging threats and adapt to evolving market demands.
The controlled environment agriculture (CEA) and hydroponics industry is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 10-15% through 2025 and beyond. This expansion suggests a market that can absorb new entrants without immediate, cutthroat competition for market share.
This healthy growth rate generally tempers the intensity of competitive rivalry. As the overall market expands, companies can focus on capturing new customers and increasing their own production rather than aggressively poaching from competitors in a zero-sum game. However, as the industry matures, we may see increased consolidation and more targeted competitive strategies.
Hydrofarm's product differentiation is a key factor in its competitive landscape. While many competitors offer standard grow lights and hydroponic systems, Hydrofarm has focused on developing proprietary technologies and unique product features. For instance, their advanced LED grow lights often boast superior spectrum control and energy efficiency, setting them apart from more basic, commoditized offerings. This differentiation can lessen the pressure of direct price wars, as customers may be willing to pay a premium for perceived performance and innovation.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the hydroponics market can significantly influence competitive rivalry by making it difficult for companies to leave, even during periods of low profitability. These barriers often stem from substantial investments in specialized equipment and facilities, which have limited resale value outside the hydroponics sector. For instance, custom-built vertical farming systems or advanced climate control infrastructure represent significant sunk costs.
Companies might also be bound by long-term supply contracts or leases for specialized growing spaces, further complicating an exit. The high fixed costs associated with maintaining these operations mean that ceasing production can still incur substantial ongoing expenses. These factors collectively encourage existing players to remain in the market, intensifying competition as they strive to cover their costs, even if margins are thin.
Consider these specific exit barrier elements:
- Specialized Assets: Hydroponic systems, advanced lighting, and climate control technology are often highly specific and difficult to repurpose or sell, representing significant sunk costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers for nutrients, growing media, or energy, as well as customer sales agreements, can lock companies into operations.
- High Fixed Costs: Ongoing expenses like facility maintenance, depreciation of specialized equipment, and energy consumption remain even if production is scaled back or halted.
- Emotional and Managerial Investment: Founders and management teams often have deep personal and professional investment in their hydroponic businesses, making it emotionally challenging to walk away.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for Hydrofarm's customers appear to be relatively low, particularly for those using simpler hydroponic systems. This ease of switching intensifies competitive rivalry as customers can readily explore alternatives based on price or product features. For instance, many basic hydroponic kits require minimal specialized knowledge or equipment, making it straightforward to transition to a different brand if a competitor offers a more attractive price point or an innovative new feature.
The market for hydroponic supplies is broad, with numerous manufacturers offering comparable products. This accessibility means that if a customer finds Hydrofarm's pricing uncompetitive or its product offerings lacking, they can easily pivot to another supplier. For example, a customer looking to purchase grow lights or nutrient solutions can find a multitude of options from various online retailers and specialty stores, often with next-day delivery, further reducing the friction associated with switching.
- Low Switching Costs: Many hydroponic systems, especially entry-level ones, require minimal setup changes and offer readily available alternative brands.
- Intensified Rivalry: This ease of switching allows customers to quickly move between suppliers in response to price adjustments or new product introductions from competitors.
- Market Accessibility: The broad availability of hydroponic supplies from numerous manufacturers and retailers means customers face little difficulty in finding and adopting alternative products.
- Impact on Hydrofarm: Hydrofarm must remain competitive on price and innovation to retain customers who can easily opt for competing solutions.
Competitive rivalry within the hydroponics sector is shaped by a dynamic interplay of numerous players, ranging from large corporations to niche specialists. The global hydroponics market's estimated USD 12.5 billion valuation in 2024, with projected growth, indicates a market capable of supporting multiple competitors. However, the presence of established firms like Hawthorne Gardening Company and General Hydroponics, alongside a vast network of smaller suppliers, ensures that competition remains a significant factor.
The intensity of this rivalry is somewhat tempered by the industry's robust growth, estimated at a CAGR of 10-15% through 2025. This expansion allows companies to focus on capturing new market segments rather than solely on aggressive market share grabs. Nevertheless, Hydrofarm must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings, such as its advanced LED grow lights, to counter the low switching costs faced by customers who can easily opt for more competitively priced or feature-rich alternatives.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Intensity Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Grow Lights | Hawthorne Gardening Company, General Hydroponics, Mars Hydro, Spider Farmer | High (due to technological advancements and price sensitivity) |
| Hydroponic Systems | General Hydroponics, AeroGarden, Lettuce Grow, various DIY solutions | Moderate to High (depending on system complexity and brand loyalty) |
| Nutrients & Supplements | General Hydroponics, Advanced Nutrients, Botanicare, Earth Juice | High (commodity-like, with strong brand preference and price competition) |
| Growing Media | Oasis, Grodan, Sunshine Mix, various coco coir suppliers | Moderate (driven by product consistency and bulk purchasing power) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Alternative growing methods, like traditional outdoor farming or simpler hydroponic setups, can present a compelling price-performance trade-off. For instance, while Hydrofarm offers advanced controlled environment agriculture (CEA) solutions, a small-scale grower might find that a basic Dutch bucket system, costing significantly less upfront, can achieve comparable yields for certain crops, especially when considering labor costs. The market for DIY indoor growing kits, often assembled from readily available components, further intensifies this. In 2024, the global hydroponics market was valued at approximately $11.7 billion, with a significant portion driven by smaller, more accessible systems, indicating a strong customer segment prioritizing cost-effectiveness.
Hydrofarm's customers, particularly commercial growers, face a moderate threat from substitutes. While hydroponic systems offer efficiency, the significant investment in existing infrastructure and established cultivation practices can deter switching. For example, a large commercial greenhouse already equipped for soil-based or traditional hydroponic methods might find the cost and disruption of adopting entirely new systems prohibitive.
The threat of substitutes for Hydrofarm's hydroponics equipment is moderate but growing. Customers can turn to traditional soil-based gardening, which requires less initial investment and is familiar to many. For instance, the global home gardening market was valued at approximately $101.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $154.8 billion by 2030, indicating a strong alternative.
Relative Price of Substitutes
The relative price of substitute solutions significantly impacts Hydrofarm's competitive landscape. If alternatives, such as traditional soil-based gardening supplies or simpler hydroponic kits from less established brands, are priced considerably lower, customers may opt for these to save costs, even if the performance is slightly inferior. For instance, while Hydrofarm might offer advanced nutrient solutions and lighting systems, a DIY enthusiast could achieve basic plant growth with significantly cheaper, albeit less sophisticated, components.
This price sensitivity is a key consideration. If substitutes offer a comparable outcome at a substantially lower price, Hydrofarm faces pressure to either match those price points or clearly articulate the superior value proposition of its premium products. For example, in 2024, the average cost of a basic hydroponic starter kit from a direct-to-consumer online retailer was approximately $50, whereas comparable, feature-rich systems from established brands like Hydrofarm could range from $150 to $300 or more, depending on the complexity and scale.
- Price Gap: A substantial price difference between Hydrofarm's offerings and those of substitutes can drive customer migration.
- Value Demonstration: Hydrofarm must effectively communicate the benefits of its higher-priced products, such as increased yield, efficiency, or durability, to justify the premium.
- Market Segmentation: Understanding which customer segments are more price-sensitive versus those prioritizing performance and features is crucial for pricing strategy.
- Substitute Innovation: As substitute products become more sophisticated and offer better value, Hydrofarm needs to continuously innovate to maintain its competitive edge.
Perceived Value and Innovation of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Hydrofarm's products is amplified when new cultivation technologies are perceived by the market as offering significantly better benefits or simpler operation. For instance, advancements in aeroponics and aquaponics, which can streamline growing processes and boost crop yields, present compelling alternatives even if they necessitate different setups and expertise.
Hydrofarm faces a constant need to innovate to maintain its competitive edge against these evolving substitute methods. The market's willingness to adopt these new techniques, driven by perceived efficiency gains, directly impacts the demand for Hydrofarm's traditional hydroponic systems.
- Aeroponics and aquaponics are gaining traction for their potential to increase yields by up to 20% compared to traditional soil-based farming, according to industry reports from early 2024.
- The perceived ease of use and reduced water consumption of some newer systems can make them attractive alternatives, even with higher initial equipment costs.
- Hydrofarm's ability to integrate or offer solutions that match or exceed the perceived benefits of these substitutes will be crucial for mitigating this threat.
The threat of substitutes for Hydrofarm's offerings is moderate, primarily due to the significant capital investment and expertise often required for advanced hydroponic systems. However, simpler DIY hydroponic kits and traditional outdoor farming remain viable alternatives, especially for cost-conscious consumers. In 2024, the market saw a rise in accessible, lower-cost hydroponic solutions, underscoring the price sensitivity of a segment of the customer base.
Entrants Threaten
The hydroponics equipment manufacturing and distribution market demands substantial initial capital. Establishing production facilities with specialized machinery, securing a diverse inventory of components, investing in ongoing research and development for innovative solutions, and building robust distribution networks all require significant upfront investment. For instance, setting up a moderately sized manufacturing plant could easily run into millions of dollars, a considerable barrier for many aspiring entrepreneurs.
Existing players in the hydroponics market, like Hydrofarm, often leverage significant economies of scale in production, purchasing, and distribution. This means they can produce goods more cheaply per unit due to higher output volumes. For instance, bulk purchasing of raw materials like nutrients and lighting components can lead to substantial cost savings that smaller, new entrants cannot easily match.
These scale advantages create a considerable barrier to entry. A new company would need to invest heavily to achieve production volumes comparable to established firms to compete on price. Without achieving similar efficiencies, new entrants would likely face higher per-unit costs, making it difficult to attract price-sensitive customers and gain market share against incumbents like Hydrofarm.
Newcomers face significant hurdles in securing shelf space in established retail stores and gaining visibility on popular online marketplaces, which are crucial for reaching consumers. Hydrofarm's long-standing relationships with key distributors and retailers present a formidable barrier, as these channels are often saturated with existing products and prioritize proven sales performance.
For instance, in the competitive gardening supplies market, securing placement in major home improvement chains or specialized hydroponic shops requires substantial investment and proven demand, which new entrants typically lack. This limited access to distribution channels effectively raises the cost and complexity of entering the market, deterring potential competitors.
Product Differentiation and Brand Loyalty
Hydrofarm's established brand recognition and the loyalty it has cultivated among growers significantly deter new entrants. Customers often associate Hydrofarm with quality and reliability, making it difficult for newcomers to capture market share. For instance, in 2024, Hydrofarm continued to emphasize its commitment to innovation and customer support, reinforcing its brand image in a competitive landscape.
The degree to which Hydrofarm's products are perceived as unique or superior creates a substantial barrier. If consumers view Hydrofarm's hydroponic systems, lighting solutions, or nutrient lines as distinct and highly effective, new competitors must invest heavily in marketing and product development to persuade customers to switch. This differentiation is key to maintaining pricing power and market position.
New entrants must overcome the hurdle of building trust and convincing customers that their offerings are equivalent or superior to Hydrofarm's established reputation. This often translates into substantial upfront costs for advertising, promotions, and potentially lower initial pricing to gain traction. Without strong differentiation, new players struggle to carve out a niche.
- Brand Recognition: Hydrofarm's long-standing presence in the market has built significant brand equity.
- Customer Loyalty: Repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth contribute to a loyal customer base.
- Perceived Differentiation: Hydrofarm's product lines are often seen as offering unique features or performance advantages.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants need substantial capital to challenge Hydrofarm's established market presence.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies significantly influence the threat of new entrants in the hydroponics sector. For instance, stringent food safety regulations, such as those enforced by the FDA in the United States, require new hydroponic farms to implement rigorous quality control and traceability systems, increasing initial setup costs and operational complexity. In 2024, many regions are also exploring or implementing specific licensing requirements for controlled environment agriculture (CEA) operations, which can add administrative burdens and compliance expenses for newcomers.
Environmental regulations, particularly concerning water usage and waste disposal, can also act as a barrier. New hydroponic ventures must often demonstrate compliance with local water quality standards and sustainable waste management practices. For example, some jurisdictions mandate specific filtration and recycling systems for nutrient-rich wastewater, adding to the capital investment needed to start operations. Favorable government incentives, however, like grants for sustainable agriculture or tax breaks for investing in CEA technology, can effectively lower these entry barriers.
- Licensing and Permitting: Obtaining necessary permits for agricultural operations, water rights, and food production can be a time-consuming and costly process for new hydroponic businesses.
- Environmental Standards: Compliance with regulations on water discharge, nutrient runoff, and energy efficiency adds to the operational costs and technical expertise required for new entrants.
- Food Safety Certifications: Meeting stringent food safety standards, such as Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), often necessitates investments in specialized equipment and training, impacting initial capital outlay.
- Government Incentives: Subsidies for renewable energy use or grants for developing innovative hydroponic technologies can reduce the financial burden for emerging companies.
The threat of new entrants in the hydroponics market, particularly for companies like Hydrofarm, is moderately low due to significant capital requirements for manufacturing, R&D, and distribution. Economies of scale achieved by incumbents further solidify this barrier, making it challenging for newcomers to compete on price. Established brand recognition, customer loyalty, and the need for substantial marketing investment also deter new players from easily entering the market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hydrofarm Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and trade association publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
We incorporate insights from financial databases, competitor websites, and agricultural technology journals to accurately assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, as well as the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
