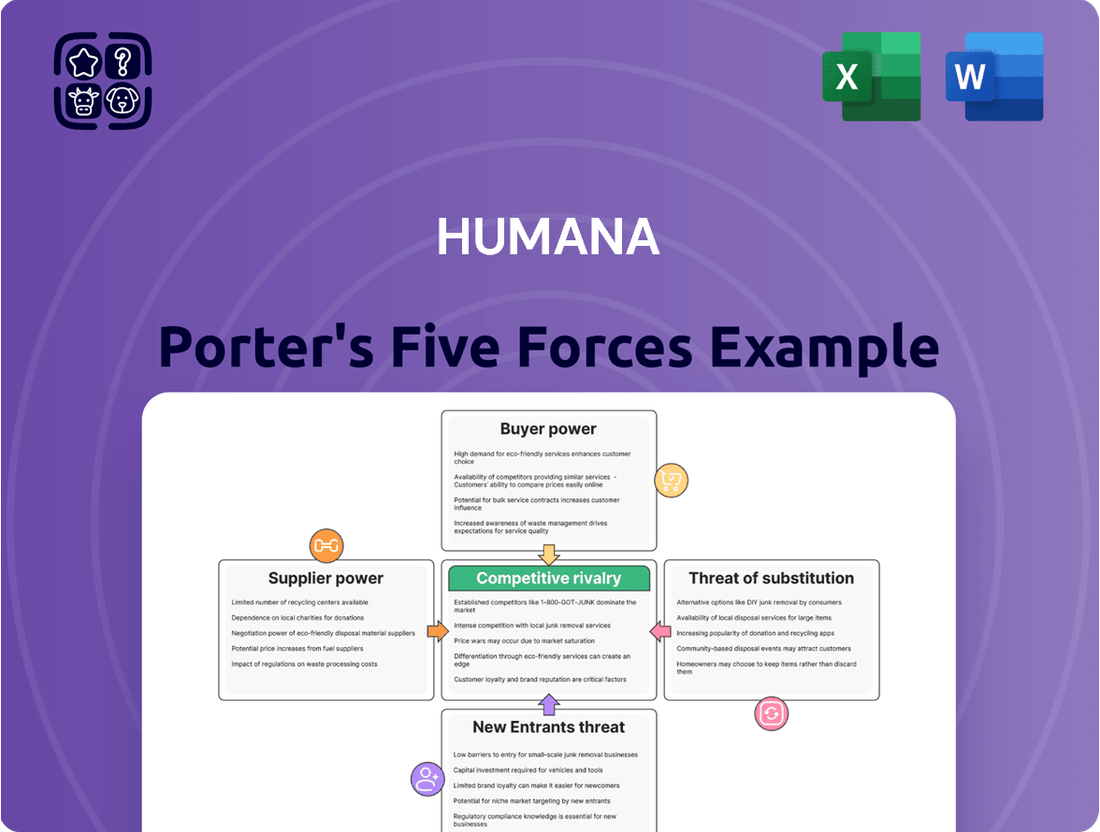
Humana Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Humana Bundle
Humana's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its customers to the intense rivalry among health insurers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the complex healthcare market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Humana’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Healthcare provider consolidation significantly boosts the bargaining power of these entities. As more hospitals and health systems merge, they gain a stronger collective voice when negotiating with insurers like Humana. This trend means providers can more effectively push for higher reimbursement rates, directly impacting Humana's operational costs.
The landscape of healthcare is increasingly dominated by larger players. By 2023, a substantial 60% of U.S. hospitals had integrated into larger health systems. This increased concentration of provider power translates into greater leverage during contract negotiations with payers, potentially squeezing profit margins for companies such as Humana.
Humana, like its peers in the health insurance sector, faces significant dependence on pharmaceutical companies for the medications it covers. This reliance is particularly pronounced for high-cost specialty drugs, which are crucial for treating complex conditions.
The bargaining power of suppliers, in this case, pharmaceutical firms, is amplified by the rising cost of prescription drugs. Projections indicate an average medicine cost increase of 10% globally in 2025, a trend that grants pharmaceutical companies considerable leverage.
This dynamic forces Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), often working on behalf of insurers like Humana, to actively negotiate for lower drug prices and meticulously manage drug formularies to mitigate these rising costs.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) like CVS Caremark, Express Scripts, and Optum Rx significantly influence the bargaining power of suppliers in the healthcare industry. These PBMs act as crucial intermediaries, negotiating drug prices directly with pharmaceutical manufacturers and also with pharmacies. Their concentrated market power is substantial, with approximately 80% of prescription claims being handled by these three major PBMs as of 2024, directly impacting Humana's pharmacy operations.
Specialized Services and Unique Offerings
Suppliers providing highly specialized medical services often have significant bargaining power because there are few, if any, readily available substitutes. This lack of alternatives allows them to dictate terms and prices more effectively. For example, the average cost for inpatient care reached around $10,000 per discharge in 2022, a figure that highlights the value placed on these essential, often unique, services.
This situation directly impacts companies like Humana, as it increases the pressure to manage healthcare expenditures while still guaranteeing members access to necessary, high-quality care. The specialized nature of these services means that providers can command higher prices, creating a challenge for payers in controlling overall costs.
- Specialized medical services lack direct substitutes, strengthening supplier leverage.
- The average inpatient care cost was approximately $10,000 per discharge in 2022.
- This necessitates careful cost management for payers like Humana.
Regulatory Changes Impacting Reimbursement
Changes in government regulations and reimbursement policies directly influence the bargaining power of suppliers within the healthcare sector. For instance, shifts in Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates can alter the financial leverage of medical equipment manufacturers or pharmaceutical companies when negotiating with healthcare providers like Humana.
In 2024, the healthcare landscape continues to be shaped by evolving reimbursement strategies. Hospitals, facing persistent cost inflation which saw the average hospital operating cost per patient day rise significantly in 2023, are likely to seek more favorable reimbursement terms from insurers during contract renewals. This push for higher rates to offset increased operational expenses can bolster the suppliers' negotiating position.
The regulatory environment, therefore, creates a dynamic where suppliers can leverage anticipated changes in payer behavior. For example, if new regulations mandate higher quality standards for medical devices, suppliers meeting these standards may command better prices, increasing their bargaining power.
- Regulatory Shifts: Government policies on healthcare reimbursement directly impact supplier leverage.
- Cost Inflation: Rising operational costs for providers (e.g., hospitals) in 2023-2024 drive demand for better reimbursement, indirectly aiding suppliers.
- Supplier Advantage: Suppliers who meet new regulatory quality standards can enhance their negotiating power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Humana is notably influenced by the consolidation within the healthcare provider market. As hospital systems merge, their collective strength increases, allowing them to negotiate more favorable reimbursement rates with insurers like Humana.
Pharmaceutical companies also wield considerable power, particularly concerning specialty drugs. The rising cost of medications, with global medicine costs projected to increase by 10% in 2025, gives these suppliers significant leverage.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) play a critical intermediary role, with the top three PBMs handling approximately 80% of prescription claims in 2024. This concentration of power among PBMs directly affects drug pricing negotiations with manufacturers.
Specialized medical services, lacking direct substitutes, also benefit from strong supplier bargaining power. The high average cost of inpatient care, around $10,000 per discharge in 2022, underscores the value and limited alternatives for these services.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Humana |
| Provider Consolidation | Increased mergers among hospitals and health systems | Strengthens provider negotiation leverage for higher reimbursement |
| Pharmaceutical Costs | Projected 10% global medicine cost increase in 2025 | Increases Humana's drug expenditure and necessitates PBM negotiation |
| PBM Market Concentration | Top 3 PBMs handle ~80% of claims (2024) | Concentrates negotiation power, influencing drug prices |
| Specialized Services | Lack of direct substitutes for unique medical treatments | Allows suppliers to command higher prices, increasing Humana's costs |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability of the health insurance industry for Humana, examining threats from new entrants, buyer and supplier power, substitutes, and existing rivals.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Humana's substantial reliance on Medicare Advantage and Medicaid places significant bargaining power in the hands of these government-sponsored program beneficiaries. In 2025, Medicare Advantage enrollment expanded by approximately 1.3 million individuals, bringing the total to 34.5 million. Humana, alongside UnitedHealth Group, represents nearly half of all Medicare Advantage enrollments across the country, underscoring the collective leverage of these large beneficiary groups.
While the total number of Medicare Advantage plans available is projected to see a slight decrease in 2025, beneficiaries still possess significant choice. For instance, in 2024, an estimated 3,140 Medicare Advantage plans were available, a figure that, while potentially adjusting slightly for 2025, still represents a substantial market. This continued availability of diverse options, coupled with the annual election period allowing beneficiaries to switch plans, directly amplifies their bargaining power.
The ability for customers to easily switch between different insurers and plans, especially when considering potential shifts in benefits or out-of-pocket expenses, grants them considerable leverage. Humana, recognizing this dynamic, actively provides a wide array of plan choices designed to meet varied individual needs and budgetary considerations, thereby catering to a broad customer base.
Recent regulatory shifts in Medicare Advantage for 2025 are causing significant changes for beneficiaries. We're seeing a reduction in plan options and benefit diversity, alongside an increase in out-of-pocket expenses for many. For instance, the median maximum out-of-pocket limit has seen an upward adjustment.
These changes directly impact Humana's customer bargaining power. With fewer choices and higher costs, customers are likely to become more discerning about the value they receive from their health plans. This heightened sensitivity means they will actively seek out plans that offer better terms and greater affordability, increasing their leverage in the market.
Demand for Value-Based Care and Integrated Services
Customers, particularly large government programs and employer groups, are increasingly prioritizing value-based care. This means they want healthcare that delivers better health outcomes and a more streamlined patient experience, rather than simply focusing on the volume of services. This growing demand significantly shifts power towards these customers.
Humana is responding to this by expanding its integrated care offerings, which include services like pharmacy benefits and in-home care. By combining these elements, Humana aims to provide the comprehensive, coordinated solutions that customers are actively seeking.
This customer-driven shift toward integrated, outcome-focused healthcare strengthens their bargaining power. They can now more effectively choose providers and plans that demonstrate clear value and improved patient well-being.
- Growing Demand for Value: In 2024, the healthcare industry continued its strong pivot towards value-based care models.
- Integrated Services Focus: Humana's strategy highlights the integration of pharmacy and home-based services to meet this demand.
- Customer Empowerment: The emphasis on better outcomes and simplified experiences gives customers greater leverage in selecting healthcare solutions.
Economic Uncertainty and Affordability Concerns
Economic uncertainty significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers in the health insurance market. During periods of economic slowdown, consumers, both individuals and employer groups, become acutely aware of their budgets. This heightened sensitivity to affordability means customers are more likely to scrutinize premiums and benefit packages, seeking out the most cost-effective options available.
For instance, in 2024, persistent inflation and a potentially slowing economy could lead more individuals to compare plans based purely on price, putting pressure on insurers like Humana to offer competitive rates. This trend encourages a focus on value, pushing companies to demonstrate the tangible benefits and cost savings their plans provide.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Economic downturns make customers more likely to switch to cheaper plans or delay coverage.
- Demand for Value: Customers expect more benefits for their money, forcing insurers to justify premium costs.
- Focus on Affordability: Humana faces pressure to offer a range of plans that cater to diverse economic circumstances.
The bargaining power of Humana's customers, particularly beneficiaries of government programs, remains a significant force. With 34.5 million Medicare Advantage enrollees in 2025, and Humana covering a substantial portion, these beneficiaries wield considerable collective influence. Their ability to switch plans annually, driven by factors like benefit changes and out-of-pocket costs, empowers them to demand greater value and affordability.
Economic pressures in 2024, including inflation, have amplified customer price sensitivity. This forces insurers like Humana to offer competitive rates and clearly demonstrate the value proposition of their plans. Customers are increasingly prioritizing integrated care models that deliver better health outcomes and a more streamlined experience, further strengthening their position to negotiate for comprehensive and cost-effective solutions.
| Customer Segment | Leverage Factors | Humana's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Medicare Advantage Beneficiaries | Large enrollment numbers (34.5M in 2025), annual switching, benefit/cost sensitivity | Wide plan variety, focus on integrated care |
| Medicaid Beneficiaries | Government program reliance, potential for state-level negotiation | Tailored benefit packages, compliance with regulations |
| Employer Groups | Negotiation for group rates, demand for cost-effective benefits | Customizable plan options, emphasis on preventative care |
What You See Is What You Get
Humana Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Humana's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the healthcare industry. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into Humana's strategic positioning and potential challenges.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Humana competes in a health insurance landscape marked by fierce rivalry, especially within the Medicare Advantage (MA) sector. As of 2024, while Humana maintains a substantial market presence, it contends with formidable competitors like UnitedHealth Group, Aetna, Anthem, Cigna, and Centene Corporation. This intense competition compels constant innovation and places downward pressure on both pricing and the benefits offered to beneficiaries.
The healthcare insurance landscape has seen significant consolidation, with the number of market players shrinking by 7.2% from 2022 to 2024. This reduction intensifies competition among the remaining large insurers, creating a more concentrated and fiercely contested market for every percentage point of market share.
While fewer players might seem like less rivalry, the opposite is true; it strengthens the market position of dominant entities like Humana. This means the competition becomes more direct and often more aggressive as these larger insurers vie for the same customer base.
Humana's strategic exits from certain Medicare Advantage markets, a move driven by profitability concerns and competitive pressures, directly fuel intensified rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the company announced plans to exit several states, creating openings for rivals like UnitedHealth Group and CVS Health to expand their member base in those vacated territories.
These strategic rebalancing acts by Humana underscore the fluid nature of competitive dynamics within the health insurance sector. Competitors are quick to capitalize on these shifts, actively seeking to acquire members that Humana is no longer serving, thereby raising the stakes for market share in those specific geographic areas.
Technological Investment and Digital Health Platforms
Competitive rivalry in the health insurance sector is intensifying, largely fueled by significant investments in technological advancements and the development of sophisticated digital health platforms. This technological arms race is a defining characteristic of the current competitive landscape.
Humana itself is a prime example of this trend, having strategically invested $425 million in digital health platforms during 2023. The company is actively harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to streamline its operations and enhance the quality of its customer service, aiming for greater efficiency and a more personalized member experience.
This focus on technology is not unique to Humana; its competitors are also channeling substantial resources into similar digital initiatives. This widespread investment means that technological differentiation has become a critical battleground, where innovation in digital health solutions can offer a significant competitive edge.
- Humana's 2023 Digital Health Investment: $425 million dedicated to advancing digital health platforms.
- Key Technology Focus: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) for operational efficiencies and improved customer service.
- Industry Trend: Competitors are also making substantial investments in digital health, escalating technological rivalry.
- Competitive Differentiator: Technological innovation in digital health platforms is a crucial factor in gaining market advantage.
Pricing and Benefit Design Competition
Insurers, including Humana, are locked in a fierce battle over both pricing and the design of benefits packages. This is particularly true within government-sponsored programs where consumers closely compare plan options and monthly premiums.
The competitive landscape is evident in the average Medicare Advantage premium for 2024, which stood at $18.50 per month. This figure highlights the pressure on insurers to offer attractive, cost-effective choices.
- Pricing Pressure: The low average Medicare Advantage premium demonstrates intense competition, forcing insurers to optimize costs and pricing strategies.
- Benefit Design: Insurers differentiate by offering a wide array of benefits, aiming to provide value beyond just cost.
- Humana's Strategy: Humana actively adjusts its plans to present affordable selections that also incorporate desirable benefits, responding directly to market demands.
Competitive rivalry within the health insurance sector, particularly in Medicare Advantage, remains exceptionally high. Humana faces intense competition from major players like UnitedHealth Group, Aetna, and Anthem, all vying for market share. This dynamic forces continuous innovation and keeps pricing and benefit offerings highly competitive, with the average Medicare Advantage premium in 2024 at $18.50 per month.
| Competitor | Estimated 2024 Medicare Advantage Enrollment (Millions) | Key Competitive Actions |
|---|---|---|
| UnitedHealth Group | ~9.5 | Aggressive market expansion, strong digital platform integration. |
| Humana | ~8.8 | Strategic market exits, focus on digital health investments ($425M in 2023). |
| Aetna (CVS Health) | ~5.2 | Leveraging retail presence for member acquisition, integrated care models. |
| Anthem (Elevance Health) | ~4.5 | Broadening benefit offerings, emphasis on value-based care. |
| Centene Corporation | ~2.1 | Focus on government-sponsored programs, expanding provider networks. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many individuals, particularly those enrolled in government-sponsored health insurance programs, direct substitutes for comprehensive health coverage are scarce. Regulatory mandates and the fundamental need for healthcare access significantly limit the appeal of alternatives. This inherent demand for robust coverage inherently weakens the threat of substitutes for established health insurance providers like Humana.
Large employers increasingly self-insure their health benefits, bypassing traditional insurance providers like Humana. This strategy allows them to directly manage financial risk and gain more control over benefit design, acting as a significant substitute offering. For instance, in 2024, a notable portion of large employers continued to explore or expand self-insurance options to curb rising healthcare costs.
This shift is driven by a desire to cut expenses and customize employee health plans. If health insurance premiums continue their upward trajectory in 2024 and beyond, more employers will likely consider self-insurance as a cost-saving measure, potentially reducing Humana's market share in the commercial segment.
The rise of direct primary care (DPC) and concierge medicine presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance. These models, often cash-pay, cater to individuals seeking more personalized and accessible routine care, potentially diverting a segment of the market away from conventional insurance plans. For instance, DPC practices reported an average membership growth of 15% in 2023, indicating increasing consumer interest.
While these direct care options offer benefits like reduced wait times and direct physician access, they generally do not provide coverage for major medical events or catastrophic illnesses. Therefore, their ability to fully substitute insurance is limited, especially for individuals with chronic conditions or those who prioritize comprehensive protection against high-cost medical emergencies.
Government Healthcare Programs (Original Medicare, Medicaid)
Government healthcare programs, specifically Original Medicare and Medicaid, represent a significant threat of substitutes for Humana's private Medicare Advantage and Medicaid managed care offerings. For eligible individuals, these government-sponsored fee-for-service options provide an alternative to managed care plans, particularly if private plans experience benefit reductions or perceived shortcomings.
The availability of Original Medicare and Medicaid means that beneficiaries are not solely reliant on Humana's managed care products. This choice becomes more pronounced when private plans face pricing pressures or changes in their benefit structures.
- 2024 Medicare Advantage Enrollment: As of early 2024, over 31 million beneficiaries were enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans, indicating a substantial portion of the eligible population opting for private managed care.
- Medicaid Managed Care Penetration: Medicaid managed care plans cover a significant majority of Medicaid beneficiaries, with states increasingly relying on managed care to control costs and improve care coordination.
- Fee-for-Service Appeal: While managed care is prevalent, a segment of the Medicare population still prefers the traditional fee-for-service model, highlighting the enduring appeal of direct provider choice without managed care restrictions.
Wellness Programs and Preventive Health Initiatives
The increasing focus on wellness and preventive health, often bolstered by technology and employer-sponsored programs, presents a significant threat of substitution. These initiatives aim to keep individuals healthier, potentially reducing their reliance on traditional, comprehensive health insurance for certain services.
For instance, in 2024, employer spending on wellness programs continued to rise, with many companies investing in digital health platforms and personalized health coaching. This trend could indirectly substitute for some aspects of health insurance by addressing health issues proactively. Humana itself is actively involved in these population health management strategies, recognizing their potential to improve member outcomes and manage costs.
- Growing Wellness Investment: Employers are increasing their investment in wellness programs, seeing them as a way to improve employee health and reduce long-term healthcare costs.
- Technology Integration: Digital health tools and platforms are becoming more common in wellness initiatives, offering personalized health tracking and support.
- Preventive Focus: The emphasis on preventing illness rather than just treating it can reduce the perceived need for extensive medical interventions covered by insurance.
- Humana's Role: Humana's own commitment to population health management demonstrates an understanding of this shifting landscape and its potential impact on the insurance market.
While direct substitutes for comprehensive health coverage are limited for many, especially those on government plans, alternatives are emerging. Large employers increasingly self-insure, and direct primary care models are gaining traction, offering different approaches to healthcare access and cost management.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Humana | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employer Self-Insurance | Employers manage their own health benefits, bypassing insurers. | Reduces Humana's commercial market share. | Continued exploration by large employers to manage costs. |
| Direct Primary Care (DPC) | Cash-pay models offering personalized routine care. | May divert individuals from traditional insurance for primary services. | Reported 15% average membership growth in 2023. |
| Government Programs (Medicare/Medicaid Fee-for-Service) | Original Medicare and Medicaid as alternatives to managed care. | Offers choice to beneficiaries, especially if private plans change benefits or pricing. | Over 31 million enrolled in Medicare Advantage as of early 2024; Medicaid managed care covers most beneficiaries. |
Entrants Threaten
The health insurance sector presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Establishing a presence necessitates substantial investments in sophisticated technology for claims processing and member management, alongside building and maintaining expansive networks of healthcare providers. For example, initial capital investments in this industry can easily surpass $10 million, acting as a significant deterrent for potential newcomers.
The health insurance industry faces a formidable threat from new entrants due to its incredibly complex regulatory landscape. Navigating federal and state-level rules, including licensing, solvency standards, and compliance mandates, demands substantial investment and expertise. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) imposes rigorous oversight on Medicare Advantage plans, a core business for Humana, requiring adherence to detailed operational and financial guidelines that can deter smaller, less capitalized new players.
Humana, like other established health insurers, benefits from considerable brand loyalty. Millions of members have come to trust Humana for their healthcare needs, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction. This loyalty translates into high switching costs for consumers who value the continuity and familiarity of their current coverage.
Need for Extensive Provider Networks
New entrants into the health insurance market face a significant barrier due to the critical need for extensive provider networks. Building a competitive health plan requires establishing relationships with a vast array of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers, a process that is both complex and incredibly time-consuming.
Established companies like Humana already possess long-standing contracts and deep relationships with a broad spectrum of providers. This existing network effect provides a substantial competitive advantage, making it difficult for newcomers to offer comparable coverage and access to care. For instance, in 2024, major health insurers often boast networks covering tens of thousands of physicians and hundreds of hospitals across multiple states, a scale that is challenging to replicate quickly.
- Network Scale: Competitors need to match the sheer size of existing provider networks to be viable.
- Contractual Relationships: Securing favorable contracts with providers is a lengthy and resource-intensive undertaking.
- Provider Loyalty: Existing insurers benefit from established trust and payment histories with providers.
Market Consolidation by Incumbents
The health insurance sector is witnessing significant consolidation, with established companies like Humana actively acquiring smaller competitors. This trend, which was particularly active in 2024 with several notable deals, intensifies the challenge for new entrants. As market share becomes concentrated among a few dominant players, the barriers to entry rise considerably, making it increasingly difficult for newcomers to establish a competitive presence.
This ongoing consolidation means fewer attractive acquisition targets remain for aspiring entrants looking to gain immediate market access. Consequently, the bargaining power of existing, larger firms like Humana is amplified, as they control a greater proportion of the market and can leverage economies of scale to their advantage.
- Market Consolidation: The health insurance industry is consolidating, with larger entities acquiring smaller ones.
- Increased Barriers: This consolidation strengthens incumbents and raises entry barriers for new companies.
- Reduced Targets: Fewer independent companies are available for acquisition, limiting a common entry strategy.
- Concentrated Power: Market power is increasingly held by a few dominant firms, making competition tougher for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants for Humana is moderately low. High capital requirements, stringent regulations, and established brand loyalty create significant hurdles. Furthermore, the need for extensive provider networks and the ongoing industry consolidation further solidify the position of incumbents, making it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Humana's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Very High | Established financial strength |
| Regulatory Complexity | High | Expertise in compliance |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | High | Large, loyal member base |
| Provider Network Scale | High | Extensive, established relationships |
| Industry Consolidation | High | Market leadership and economies of scale |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Humana Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Humana's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and Statista. We also incorporate data from healthcare regulatory bodies and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
