Howmet Aerospace Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Howmet Aerospace Bundle
Howmet Aerospace operates within a complex aerospace and defense landscape, where supplier power can be significant due to specialized materials and components. Understanding the intensity of competition and the threat of new entrants is crucial for navigating this market effectively.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Howmet Aerospace’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Howmet Aerospace's reliance on suppliers for highly specialized advanced engineered materials, like titanium and nickel-based superalloys, significantly impacts its bargaining power. These materials are absolutely critical for producing high-performance aerospace components, making their availability and cost a key concern.
The stringent quality standards and unique properties demanded by the aerospace industry often mean that only a select few suppliers can meet these requirements. This limited supplier base naturally grants those suppliers greater leverage in negotiations, as Howmet has fewer alternatives for these essential inputs.
The global market for advanced aerospace materials is expected to see robust growth. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5% for the aerospace materials market through 2030, suggesting sustained and increasing demand for these specialized inputs, further reinforcing supplier power.
Suppliers in the aerospace sector, particularly those providing complex components to Howmet Aerospace, often leverage proprietary and intricate manufacturing processes. These advanced techniques, such as specialized forging and precision casting, are not easily replicated by new market entrants. This inherent complexity effectively raises the barrier to entry, strengthening the negotiating position of established suppliers who possess the necessary expertise and equipment. For instance, in 2024, the lead time for certain high-temperature alloy components, a critical input for aerospace engines, could extend to over 18 months due to the specialized nature of their production.
Howmet's reliance on these highly engineered, often customized parts means that switching suppliers is not a simple matter. The investment in qualifying a new supplier, retooling, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems is substantial, both in terms of time and financial outlay. This switching cost reinforces the bargaining power of existing suppliers, as they are aware of the significant disruption and expense involved for Howmet to seek alternatives. In 2023, the cost of re-qualifying a single critical aerospace component supplier for a major airframer averaged over $5 million and could take up to two years.
The aerospace and defense sector, including companies like Howmet Aerospace, has grappled with persistent supply chain disruptions. These include shortages of critical components and a lack of skilled labor, which naturally gives suppliers more leverage to set prices and terms. For instance, in 2023, the aerospace industry continued to experience delays in engine components and airframe structures, directly impacting production schedules and costs for manufacturers.
Geopolitical events and evolving trade policies further amplify supplier bargaining power. Fluctuations in the availability and cost of essential raw materials, such as titanium and specialty alloys, are often influenced by international relations and trade disputes. This can lead to increased input costs for aerospace firms, forcing them to absorb higher prices or pass them on to customers.
In response, aerospace manufacturers are making significant investments in supply chain resilience. This involves diversifying their supplier base, exploring nearshoring or reshoring options, and building stronger relationships with key partners. For example, by 2024, many major aerospace companies were actively seeking to reduce reliance on single-source suppliers for critical materials and components to better manage these risks.
Long-Term Supplier Relationships
Howmet Aerospace often fosters long-term partnerships with its critical component suppliers, a necessity given the rigorous qualification procedures in the aerospace sector. These deep-rooted connections can foster mutual reliance, but also grant suppliers leverage. This is primarily due to the substantial costs and inherent risks involved in switching to a new provider, especially when consistent quality and unwavering reliability are non-negotiable requirements.
The aerospace industry's demand for specialized, high-performance materials and precision-engineered parts means suppliers who can consistently meet these stringent standards often hold significant sway. For instance, suppliers of advanced alloys or complex engine components might have fewer alternatives, increasing their bargaining power. Howmet's reliance on these specialized suppliers, who have invested heavily in the necessary technology and expertise, reinforces this dynamic.
- Supplier Specialization: Many suppliers provide highly specialized components or materials, making it difficult and costly for Howmet to find alternative sources.
- High Switching Costs: The extensive testing, qualification, and integration processes required for new aerospace suppliers represent significant financial and time investments.
- Industry Standards: The aerospace sector's strict quality and safety regulations mean that established suppliers with proven track records are often preferred, limiting Howmet's options.
- Supplier Concentration: In certain niche markets for aerospace materials or components, there may be a limited number of qualified suppliers, concentrating bargaining power among them.
Technological Advancements in Materials
Suppliers who invest in and develop next-generation materials, such as advanced lightweight composites and novel alloys, possess considerable leverage. These suppliers offer critical solutions that directly contribute to enhanced aircraft performance, improved fuel efficiency, and greater sustainability, making their innovations highly sought after.
As the aerospace sector relentlessly pursues innovation, suppliers leading the charge in material science advancements are in a strong position to negotiate higher prices and more advantageous contract terms. The market for cutting-edge aerospace materials is experiencing rapid innovation across composites, specialized alloys, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
- Supplier Investment: Companies like Solvay are heavily investing in advanced materials, with their specialty polymers segment reporting significant revenue growth, indicating a strong demand for their innovative offerings.
- Performance Gains: The adoption of materials like carbon fiber composites can reduce aircraft weight by up to 20%, leading to substantial fuel savings over the aircraft's lifecycle.
- Market Trends: The global aerospace materials market is projected to reach over $20 billion by 2028, driven by advancements in additive manufacturing and high-performance alloys.
Howmet Aerospace faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the highly specialized nature of aerospace materials and components. Suppliers of critical inputs like titanium and nickel-based superalloys often operate in concentrated markets, limiting Howmet's alternatives and allowing these suppliers to command higher prices and more favorable terms. This dynamic is exacerbated by the substantial costs and lengthy timelines associated with qualifying new suppliers in the aerospace industry, reinforcing the leverage of established providers.
The demand for advanced, high-performance materials in aerospace is projected to grow, further solidifying supplier influence. For example, the aerospace materials market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6.5% through 2030. This sustained demand means suppliers who can meet stringent quality and performance specifications, often backed by proprietary manufacturing processes, hold considerable negotiation power. In 2024, lead times for some critical alloy components could exceed 18 months, highlighting supplier control.
Switching suppliers for specialized aerospace parts incurs significant costs and risks, estimated in 2023 to average over $5 million and take up to two years for re-qualification. This high switching cost strengthens the position of existing suppliers. Furthermore, industry-wide supply chain disruptions and geopolitical factors in 2023, such as shortages of components and skilled labor, have also given suppliers increased leverage in setting prices and contract conditions.
| Factor | Impact on Howmet Aerospace | Supporting Data/Example |
| Supplier Specialization | Limited alternatives for critical materials | Proprietary manufacturing processes for alloys |
| High Switching Costs | Disincentive to change suppliers | Estimated $5M+ cost and 2-year re-qualification in 2023 |
| Industry Standards & Concentration | Preference for established, qualified suppliers | Limited number of qualified suppliers for niche materials |
| Market Growth & Innovation | Increased demand for advanced materials | Aerospace materials market CAGR of ~6.5% through 2030 |
What is included in the product
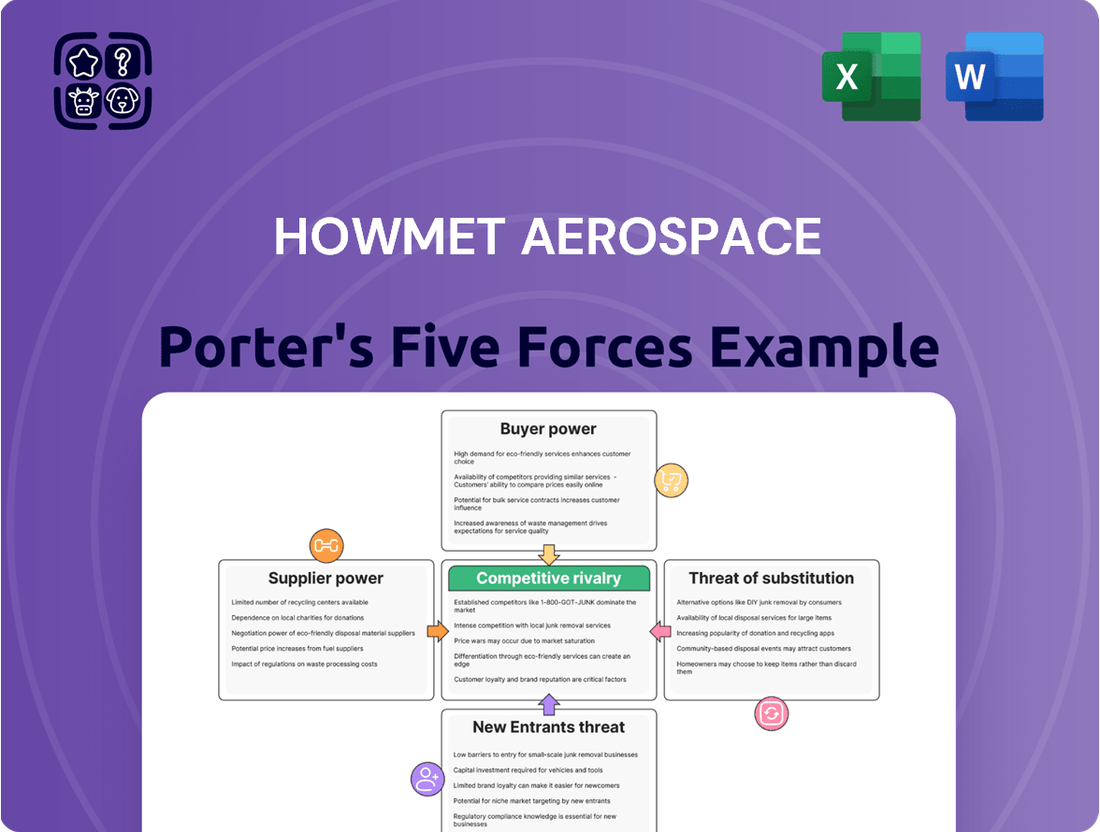
This analysis delves into the competitive landscape for Howmet Aerospace, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the potential for substitute products.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart, visualizing Howmet Aerospace's competitive landscape.
A clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making and identifying key pain points in the aerospace market.
Customers Bargaining Power
Howmet Aerospace's customer base is notably consolidated, primarily consisting of large, established aerospace and defense original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). This concentration means that a few key clients, such as GE Aerospace and RTX, represent a significant portion of Howmet's revenue. In 2024, these major players continue to drive Howmet's growth in critical aerospace segments, underscoring their substantial purchasing power.
Customers in the aerospace and defense industries have exacting demands for quality and reliability, necessitating lengthy qualification and certification procedures for all components. This intense scrutiny means that once a supplier like Howmet Aerospace is approved, the costs for a customer to switch to a new provider are substantial, involving extensive re-testing and re-certification. For instance, the FAA certification process for new aircraft components can take years and cost millions of dollars, significantly raising switching costs.
The bargaining power of customers is somewhat limited for Howmet Aerospace due to substantial original equipment manufacturer (OEM) backlogs in commercial aviation. Despite ongoing production challenges, demand for new aircraft significantly exceeds current delivery rates, creating a multi-year order book for manufacturers.
This sustained high demand for new aircraft and critical engine spare parts positions Howmet favorably in negotiations. Its essential components are vital for OEMs to fulfill these extensive backlogs, giving Howmet leverage.
Looking ahead to 2025, Howmet anticipates strong growth in its spares segment. This is largely attributed to the considerable needs arising from both older and currently produced engine programs, further solidifying its negotiating stance.
Criticality of Howmet's Products
Howmet Aerospace's products, including critical airframe and engine components, fastening systems, and turbine airfoils, are indispensable to the aerospace industry. For instance, in 2024, Howmet remained a global market leader in turbine blades, a highly specialized and essential component for jet engines. This criticality significantly diminishes customer bargaining power.
The specialized nature and high performance requirements of Howmet's offerings mean that customers, such as major aircraft manufacturers, have very limited alternative suppliers for these mission-critical parts. This lack of readily available substitutes restricts their ability to switch providers or exert significant downward pressure on pricing for essential components.
- Mission-Critical Components: Howmet's products are vital for aircraft and spacecraft functionality and safety.
- Limited Alternatives: The specialized engineering and manufacturing processes create few viable substitute suppliers.
- Global Market Leadership: As a leader, particularly in turbine blades, Howmet commands a strong position with few direct competitors for comparable quality.
- Reduced Customer Leverage: The indispensable nature of these parts limits customers' ability to negotiate aggressively on price or terms.
Customer Focus on Fuel Efficiency and Performance
Customers, particularly airlines, are intensely focused on fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance. This drive is fueled by the need to lower operational expenses and comply with increasingly stringent environmental mandates. For instance, by 2024, airlines are continually seeking ways to reduce their carbon footprint, making fuel savings a paramount concern.
Howmet Aerospace's advanced technologies directly address these customer priorities. By developing lighter, more durable components, Howmet enables manufacturers to build aircraft that consume less fuel, thereby offering significant value to their airline customers. This technological edge can bolster Howmet's bargaining power.
The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its development of critical parts for demanding aerospace applications. These specialized components, often protected by patents or requiring unique manufacturing expertise, reduce the number of viable alternative suppliers, further enhancing Howmet's negotiating position.
- Customer Demand for Efficiency: Airlines prioritize aircraft that minimize fuel burn to control operating costs and meet environmental targets.
- Howmet's Value Proposition: Differentiated technologies in lightweight materials and advanced engine components directly contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance.
- Technological Differentiation: Howmet's innovative solutions for critical aerospace applications create unique value, potentially reducing customer reliance on alternative suppliers.
Howmet Aerospace's bargaining power with its customers is generally strong, largely due to the mission-critical nature of its specialized aerospace components and the high switching costs involved. The concentration of its customer base among major aerospace OEMs, while significant, is counterbalanced by the essentiality and limited substitutability of Howmet's offerings. Furthermore, substantial OEM backlogs in commercial aviation, a trend continuing into 2024 and projected for 2025, bolster Howmet's position by ensuring consistent demand for its vital parts.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Howmet's Position (2024-2025 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High potential for leverage by major OEMs like GE Aerospace and RTX. | Mitigated by the essential nature of Howmet's products and high switching costs. |
| Switching Costs | Very high due to extensive qualification, certification, and re-testing requirements. | Significantly limits customer ability to switch suppliers for critical components. |
| OEM Backlogs | Creates strong demand and reduces customer leverage for essential parts. | Positive outlook driven by multi-year order books in commercial aviation. |
| Product Criticality & Differentiation | Howmet's specialized components (e.g., turbine blades) have few alternatives. | Global market leadership in key segments enhances negotiating strength. |
Full Version Awaits
Howmet Aerospace Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Howmet Aerospace, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The aerospace and defense sector presents formidable barriers to entry. Significant capital is required for advanced manufacturing and research, alongside the need for intricate technological expertise. For instance, Howmet Aerospace, a key player, boasts nearly 1,300 granted and pending patents, highlighting its deep technological moat and the difficulty for new entrants to replicate such innovation.
Howmet Aerospace thrives in specialized niches, leading in advanced engineered solutions for airframe, engine components, and fastening systems. This leadership, exemplified by its global dominance in turbine blades, means competition centers on product innovation and quality, not just price. In 2024, Howmet demonstrated robust performance by outgrowing each of its key markets, underscoring its competitive strength within these focused segments.
Competitive rivalry in the aerospace sector is intensely fueled by relentless innovation across materials science, manufacturing techniques, and product capabilities. Howmet Aerospace strategically positions itself by prioritizing technological advancements to offer highly precise, engineered solutions, a crucial element in sustaining its market advantage.
The aerospace industry is currently experiencing a profound shift, largely propelled by significant advancements in materials science, with companies like Howmet investing heavily in R&D. For instance, Howmet's commitment to developing advanced alloys and additive manufacturing processes directly addresses the industry's demand for lighter, stronger, and more efficient components, as evidenced by their continuous product development pipelines.
Long-Term Customer Contracts
Major aerospace programs, like those for new commercial aircraft or defense platforms, are characterized by extensive, long-term customer contracts. These agreements lock in suppliers like Howmet Aerospace for years, providing predictable revenue. However, the initial competition to win these design and production contracts is fierce, as suppliers vie for crucial early involvement that dictates future business.
Howmet Aerospace's growth is significantly bolstered by these long-term customer agreements. For instance, in 2023, the company reported that approximately 70% of its revenue was derived from long-term agreements, underscoring the stability these contracts provide. This reliance on extended partnerships intensifies the rivalry among component manufacturers to secure these foundational relationships.
- Long-term contracts provide revenue stability for Howmet Aerospace.
- Competition is high to win initial design and production agreements.
- Approximately 70% of Howmet's 2023 revenue stemmed from long-term agreements.
Global Market and Defense Spending
The global aerospace and defense market is characterized by fierce competition, intensified by rising defense expenditures worldwide. While this growing demand offers opportunities, companies like Howmet Aerospace face significant rivalry as they compete for contracts across diverse regions and defense initiatives.
In 2024, the defense aerospace sector proved to be a robust segment for Howmet, a trend anticipated to persist into 2025. This sustained strength highlights the importance of this segment amidst the broader competitive landscape.
- Global Defense Spending Growth: Projections indicated a continued upward trend in global defense spending through 2025, creating a larger, albeit more contested, market.
- Key Competitors: Major players such as GE Aerospace, Rolls-Royce, and Safran are direct rivals, particularly in engine components and systems.
- Program-Specific Competition: Bidding for major defense programs, like new fighter jet development or modernization efforts, often involves intense competition among established suppliers.
- Regional Market Dynamics: Competition also varies by region, with strong domestic players in Europe and Asia posing challenges in their respective markets.
Competitive rivalry within the aerospace sector is intense, driven by a few large, established players vying for significant, long-term contracts. Companies like Howmet Aerospace compete not just on price but on technological superiority and the ability to deliver highly specialized, engineered solutions. This dynamic is further amplified by the high barriers to entry, which limit the number of direct competitors but intensify the battle among existing ones.
In 2024, Howmet Aerospace's performance demonstrated its ability to outpace its key markets, indicating strong competitive positioning. This suggests that its focus on innovation and specialized niches allows it to effectively navigate the rivalry. The defense aerospace sector, in particular, showed robust growth in 2024, a trend expected to continue, making it a critical arena for competitive engagement.
| Competitor | Primary Focus Areas | 2024 Market Performance Indication |
|---|---|---|
| GE Aerospace | Engine components, systems | Strong competitor across engine segments |
| Rolls-Royce | Engine components, systems | Key rival in commercial and defense engines |
| Safran | Engine components, systems, landing gear | Significant player, particularly in European markets |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing use of advanced materials like carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) presents a significant threat. These composites, offering better strength-to-weight ratios, are displacing traditional metal parts in aircraft, impacting demand for Howmet's legacy products.
By 2024, the aerospace industry's adoption of composites for primary structures continued to grow, with some estimates suggesting composites could account for over 50% of new aircraft airframe weight. This trend directly challenges the market share of metallic components that have historically been Howmet's stronghold.
However, Howmet Aerospace is also a key player in producing advanced titanium and nickel-based superalloys, demonstrating its ability to adapt and capitalize on these material shifts. This dual capability mitigates the threat by positioning Howmet to supply components for both traditional and advanced material airframes.
The threat of substitutes for Howmet Aerospace's fastening systems is influenced by technological advancements. Digitalization in manufacturing and the rise of smart fastening technologies present potential alternatives that could offer enhanced efficiency or novel functionalities.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of composite materials in aerospace, particularly carbon-fiber skins, is driving demand for specialized fasteners. The projected rapid growth of composite-compatible polymer fasteners signifies a direct substitute threat, as these may offer weight savings and corrosion resistance advantages over traditional metallic fasteners.
The emergence of new propulsion systems, such as hybrid-electric and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) compatible engines, presents a significant threat of substitution for conventional aerospace components. As the aviation industry increasingly prioritizes environmental sustainability and fuel efficiency, these alternative technologies could directly impact the demand for parts designed for traditional jet engines. For instance, the shift towards SAF could necessitate changes in material compatibility and engine design, potentially rendering existing components obsolete or requiring costly redesigns.
The drive for reduced emissions is a powerful catalyst for this shift. By 2025, many major airlines are expected to significantly increase their SAF usage, with some aiming for 10% or more of their fuel supply. This growing adoption of SAF, coupled with advancements in hybrid-electric technology, means that companies reliant on manufacturing parts for current engine architectures face a substantial risk of their products becoming less relevant. The investment in research and development for these new propulsion systems by major players like GE Aerospace and Rolls-Royce underscores the potential for a substantial market disruption.
High Performance and Safety Requirements
The aerospace industry's exceptionally high performance and safety demands create a formidable barrier to substitutes for critical components. For instance, the rigorous certification process for new materials in aviation can take years and cost millions, as demonstrated by the extensive testing required for advanced composites. This inherent difficulty in replacing established, certified parts significantly reduces the immediate threat of substitutes for companies like Howmet Aerospace.
Howmet's strategic focus on precision-engineered solutions tailored to these stringent industry requirements further solidifies its position. By consistently meeting and exceeding the demanding specifications for safety and performance in aerospace applications, Howmet makes it exceptionally challenging for alternative, unproven solutions to gain traction. The company's commitment to quality and reliability directly addresses the core concerns that limit the viability of substitutes.
- Stringent Aerospace Standards: Aviation regulations mandate exhaustive testing and validation for new materials, often spanning many years and significant investment, effectively deterring rapid substitution.
- High Switching Costs: The expense and time involved in re-certifying aircraft components with new materials or technologies represent a substantial barrier for potential substitutes.
- Howmet's Value Proposition: Howmet Aerospace thrives by delivering highly engineered, reliable components that meet the non-negotiable safety and performance benchmarks of the aerospace sector.
- Limited Substitute Viability: The combination of rigorous certification, high costs, and Howmet's specialized offerings means that direct, immediate substitutes for its core products are scarce.
Howmet's Diversified Product Portfolio
Howmet Aerospace’s broad product range, spanning critical components for airframes, engines, fastening systems, and forged wheels, acts as a significant buffer against the threat of substitutes. This diversification means that even if a substitute emerges for one product line, the company’s other divisions remain robust. For instance, its strong position in aerospace engine components, a sector with high barriers to entry and long development cycles, is less susceptible to immediate substitution.
The company's commitment to research and development further solidifies its defenses. By continuously innovating and improving its offerings, Howmet makes it more difficult for substitutes to gain traction. This focus on technological advancement is crucial in the aerospace industry, where performance and reliability are paramount. Howmet's investment in R&D is directly tied to securing future growth through customer contracts, ensuring its products remain competitive and essential.
Howmet's strategic approach involves actively investing in growth, underpinned by secured customer contracts. This forward-looking investment strategy, particularly in areas like advanced materials and manufacturing processes, directly addresses and mitigates the threat of substitutes. For example, as of their latest reports, Howmet has been securing multi-year contracts with major aerospace manufacturers, demonstrating a clear path for continued demand and reducing the immediate impact of potential alternative solutions.
Consider these points regarding Howmet's mitigation of substitute threats:
- Diversified Portfolio: Operations across airframe, engine, fastening, and forged wheel segments reduce reliance on any single product category vulnerable to substitution.
- R&D Investment: Continuous innovation in materials and manufacturing processes creates a technological moat, making substitutes less appealing.
- Customer Contracts: Long-term agreements with key aerospace players lock in demand and provide a stable revenue stream, limiting the space for substitute products to penetrate.
- Industry Barriers: The aerospace sector's stringent regulatory requirements and high capital intensity naturally limit the emergence and adoption of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Howmet Aerospace is somewhat limited due to the highly specialized and regulated nature of the aerospace industry. However, advancements in materials science, such as the increasing use of composites, and the development of new propulsion systems pose potential challenges. The high cost and time associated with certifying new materials or technologies for aircraft significantly deter rapid substitution, providing Howmet with a degree of protection.
Howmet's strategic investments in research and development, coupled with its diversified product portfolio, serve as key defenses against substitutes. By continuously innovating and securing long-term contracts with major aerospace manufacturers, Howmet solidifies its market position and reduces the immediate impact of alternative solutions.
The aerospace sector's stringent safety and performance standards, along with high switching costs for airlines and manufacturers, create substantial barriers for potential substitutes. Howmet's ability to meet these demanding requirements through precision engineering and reliable component supply further strengthens its competitive advantage against less proven alternatives.
By 2024, the aerospace industry's continued integration of advanced composites into primary structures highlights a key area where substitutes for traditional metallic components are gaining traction. For example, the projected growth in composite airframe content, potentially exceeding 50% of new aircraft weight, directly impacts the market for metallic parts where Howmet has historically excelled.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the advanced engineered solutions market for aerospace and defense demands substantial capital investment. This includes building cutting-edge manufacturing plants, acquiring specialized equipment, and funding extensive research and development. Howmet Aerospace's 2024 capital expenditures of $321 million highlight the scale of investment needed to maintain and grow capabilities in this sector, presenting a significant hurdle for new competitors.
Howmet Aerospace's robust intellectual property, boasting nearly 1,300 granted and pending patents, creates a significant barrier to entry. This proprietary technology shields its advanced engineered solutions, making it incredibly challenging for newcomers to replicate its offerings without substantial research and development expenditure and the risk of legal action.
The aerospace and defense sectors present a formidable barrier to new entrants due to exceptionally stringent regulatory and certification requirements. These industries demand meticulous adherence to safety and performance standards, necessitating extensive testing and validation for every component. For instance, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) certification process for new aircraft parts can span several years and involve millions of dollars in development and testing, significantly deterring new players.
Howmet Aerospace, a key supplier of critical components for aircraft and spacecraft, benefits from these high entry barriers. New companies attempting to enter this market would face a steep learning curve and substantial upfront investment to navigate and satisfy these complex regulatory landscapes, making it difficult to compete with established firms like Howmet that have already invested heavily in compliance and quality assurance systems.
Established Customer Relationships and Supply Chains
Established aerospace and defense manufacturers like Howmet Aerospace benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). These partnerships, forged over years of reliable performance and trust, create significant barriers for new entrants. For instance, Howmet's collaborative work with leading airframe and engine producers means new competitors would face immense difficulty in displacing these existing, high-stakes supply chain integrations.
The complexity and critical nature of aerospace supply chains further fortify this barrier. Newcomers would need to navigate rigorous qualification processes, demonstrate exceptional quality control, and build a track record of dependability, which can take years and substantial investment. In 2024, the aerospace industry continued to emphasize long-term supplier agreements, underscoring the value of established partnerships.
- Deeply integrated relationships with OEMs: Howmet's long-standing collaborations with companies like Boeing and Airbus represent a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Struggle to displace established relationships: New competitors would find it challenging to break into a market where trust and proven performance are paramount.
- Integration into complex supply chains: The technical and logistical demands of aerospace manufacturing require extensive experience and existing infrastructure, which new entrants lack.
- Howmet's close work with leading manufacturers: This direct engagement ensures Howmet remains a preferred supplier, making it harder for others to gain a foothold.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the aerospace sector, like Howmet Aerospace, benefit significantly from economies of scale and a well-established experience curve in precision engineering and advanced manufacturing. This translates to lower per-unit production costs and enhanced operational efficiency, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers aiming to compete on price or operational prowess. For instance, Howmet Aerospace reported robust financial performance throughout 2024, culminating in record revenue and profit figures in the second quarter of 2025, underscoring the advantages of their scale and experience.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by these entrenched advantages. New companies would face considerable difficulty matching the cost efficiencies and specialized knowledge that established firms possess. This dynamic is crucial for understanding competitive pressures within the industry.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale production allows for bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized manufacturing processes, driving down costs.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated knowledge and refined techniques in complex manufacturing lead to greater efficiency and higher quality over time.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: New entrants lack the established infrastructure and operational history, forcing them to operate at higher costs initially.
- Howmet's 2024-2025 Performance: Howmet Aerospace's record revenue and profit in Q2 2025 demonstrates the tangible benefits of their scale and experience in a competitive market.
The threat of new entrants into the aerospace and defense engineered solutions market is significantly low. This is due to the immense capital required for advanced manufacturing and R&D, as evidenced by Howmet Aerospace's 2024 capital expenditures of $321 million. Furthermore, Howmet's extensive patent portfolio of nearly 1,300 patents creates a strong intellectual property barrier.
Stringent regulatory environments, like the multi-year and multi-million dollar FAA certification process for new aircraft parts, also deter new players. Howmet's deeply integrated relationships with major OEMs, built on years of trust and proven performance, are difficult for newcomers to penetrate. The complexity of aerospace supply chains and the need for established quality control further solidify these barriers.
Economies of scale and the experience curve provide established firms like Howmet with significant cost advantages. Howmet Aerospace's record revenue and profit figures in Q2 2025 underscore the efficiencies gained from their scale and accumulated expertise, making it challenging for new entrants to compete on cost or operational efficiency.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Howmet Aerospace Example |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in advanced manufacturing and R&D. | Significant financial hurdle. | $321 million in 2024 capital expenditures. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technology and patents. | Difficulty in replicating offerings without infringement risk. | Nearly 1,300 granted and pending patents. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict safety and performance certifications. | Lengthy and costly compliance processes. | FAA certification can take years and cost millions. |
| Supplier Relationships | Established trust and integration with OEMs. | Challenging to displace existing, high-stakes partnerships. | Long-standing collaborations with leading airframe and engine producers. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs and operational efficiency. | Cost disadvantage for new entrants. | Record revenue and profit in Q2 2025. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Howmet Aerospace Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of data from company annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and competitor press releases to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.
