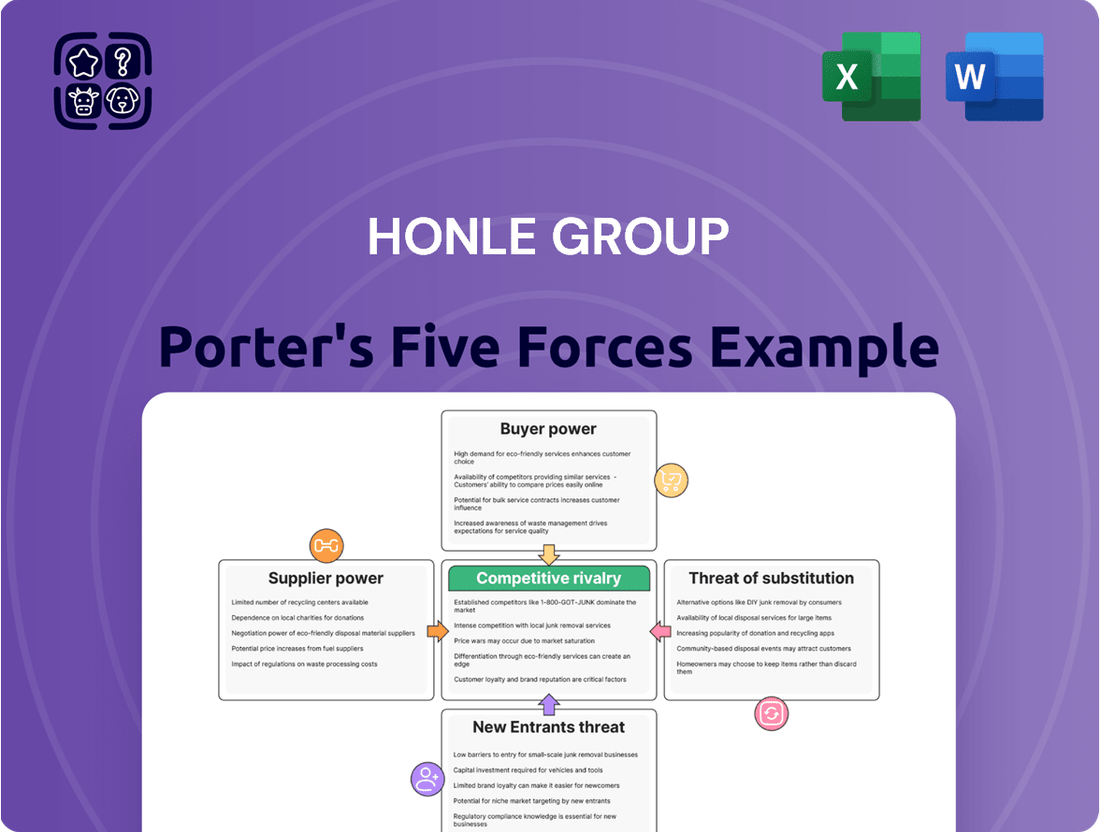
Honle Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Honle Group Bundle
The Honle Group operates within a dynamic market, and a Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the underlying competitive pressures. We've identified the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp Honle Group's strategic landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Honle Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The industrial UV technology market, where Honle Group operates, depends heavily on specialized components such as UV lamps (traditional and LED), electronic power supplies, and reflectors. Suppliers of these niche, high-performance parts can exert considerable bargaining power because there are few alternative sources that meet the stringent specifications for advanced UV systems.
For instance, companies like Honle Group might choose to produce critical components, like the core UV or IR lamps, in-house. This vertical integration strategy can effectively reduce the influence of external suppliers by maintaining control over quality and ensuring a consistent supply of essential parts.
Switching suppliers for critical components like UV lamps or LED modules presents significant hurdles for Honle Group, directly impacting their bargaining power with current vendors.
These switching costs are substantial and multifaceted. They encompass the expense and time required for redesigning existing systems that are calibrated for specific supplier components. Furthermore, Honle would need to re-tool production lines, a process that involves capital investment and potential downtime.
Beyond the physical aspects, re-qualifying new components is a crucial and often lengthy undertaking. This involves rigorous testing to ensure that alternative parts meet Honle's stringent performance benchmarks and comply with relevant industry regulations. For instance, in the UV technology sector, even minor variations in lamp spectrum or LED output can necessitate extensive validation.
The presence of these high switching costs effectively bolsters the bargaining power of Honle's existing suppliers. When it is costly and time-consuming for Honle to find and integrate a new supplier, the current suppliers can command more favorable terms, potentially leading to higher prices or less flexible contract conditions.
The Honle Group, while manufacturing some critical components in-house, relies on external suppliers for raw materials and specialized parts. The presence of readily available substitute inputs for these sourced items significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If alternative materials or components are scarce or less cost-effective, suppliers gain leverage.
For example, if a key semiconductor component for Honle's laser systems has limited alternative suppliers or substitute technologies, those suppliers can command higher prices. In 2024, the global semiconductor shortage, though easing, still impacted supply chains, potentially increasing the bargaining power of suppliers in that sector.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
Suppliers who provide highly differentiated or proprietary components, particularly in specialized areas like advanced UV LED technology or unique optical solutions, wield considerable bargaining power over Honle Group. This leverage stems from the difficulty Honle would face in finding comparable alternatives or in-house replication without substantial time and financial investment.
For instance, in 2024, the UV LED market saw continued innovation, with key players differentiating through enhanced spectral purity and longevity. Companies specializing in these niche segments can command premium pricing and favorable terms due to the limited availability of equivalent substitutes.
- Supplier Differentiation: Honle's reliance on suppliers with unique UV LED or optical technologies increases supplier power.
- Replication Difficulty: The cost and time to replicate proprietary components limit Honle's alternative sourcing options.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the specialized UV LED sector showed limited suppliers for cutting-edge spectral purity and longevity, enhancing their leverage.
- Pricing Power: Suppliers of these differentiated components can negotiate higher prices, impacting Honle's cost structure.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant challenge to Honle Group's bargaining power. If suppliers of critical components, such as specialized UV lamps or optical systems, possess the capability and incentive to produce complete UV systems themselves, their leverage over Honle Group would substantially increase. This potential shift could necessitate Honle Group maintaining strong supplier relationships and possibly offering favorable terms or concessions to secure essential inputs.
This scenario is particularly concerning for companies like Honle Group, which rely on specialized components. For instance, if a key supplier of advanced UV-C emitters decided to enter the finished UV disinfection system market, they could directly compete with Honle Group. This would not only disrupt Honle's supply chain but also create a formidable competitor who understands the component's intricacies intimately. In 2024, the global UV disinfection market saw significant investment in component innovation, with some suppliers reportedly exploring vertical integration to capture more value.
- Supplier Capability: Assess if suppliers have the technical expertise and manufacturing infrastructure to produce finished UV systems.
- Market Incentives: Evaluate if the profit margins and market demand for complete UV systems would incentivize suppliers to integrate forward.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze how many critical suppliers exist and the concentration of power among them.
- Honle's Dependence: Determine the degree to which Honle Group relies on specific suppliers for unique or proprietary components.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Honle Group is significant due to the specialized nature of components like UV lamps and LED modules. High switching costs for Honle, involving redesign, re-tooling, and rigorous re-qualification, strengthen suppliers' leverage. In 2024, continued innovation in UV LED technology meant fewer suppliers offered cutting-edge spectral purity, allowing them to command premium pricing.
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to the Honle Group's position in the UV technology market.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Customers Bargaining Power
Honle Group's diverse customer base across electronics, printing, automotive, and medical technology means bargaining power can vary. In sectors like automotive, where a few major manufacturers represent substantial revenue streams, these large customers wield significant influence. For instance, if a single automotive giant accounts for over 10% of Honle's sales, their ability to negotiate price or terms increases considerably.
Customers adopting Honle's UV systems for industrial processes, such as adhesive bonding or curing coatings, often encounter significant switching costs. These costs can encompass reconfiguring complex production lines, retraining skilled personnel on new equipment, and ensuring seamless integration and compatibility with existing or new ancillary systems. These financial and operational hurdles effectively diminish the bargaining power of customers, making them less likely to switch to a competitor. For instance, in the automotive sector, where UV curing is prevalent for coatings, the cost of recalibrating a complete paint line for a different UV emitter technology could run into hundreds of thousands of euros, if not millions, thereby solidifying customer loyalty to established suppliers like Honle.
Customers considering Honle Group's UV solutions often have access to alternative technologies. For instance, traditional thermal curing methods or various disinfection techniques present viable substitutes. While UV technology frequently boasts superior efficiency and environmental advantages, the mere existence of these alternatives grants customers leverage.
This availability of substitutes directly impacts Honle's bargaining power with its clientele. If customers perceive other options as sufficiently effective, they can more readily negotiate pricing or demand better terms. For example, in the industrial drying sector, while UV curing offers speed and precision, the established infrastructure and lower initial investment of thermal systems can still present a competitive challenge, especially for budget-conscious buyers.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers for Honle Group. In sectors where cost is a major driver, like high-volume printing or specific manufacturing operations, customers are likely to be very attuned to price. This makes them more inclined to switch suppliers if a better deal is available, especially if Honle's offerings are viewed as interchangeable rather than unique.
For instance, in the global printing industry, which saw revenues around $750 billion in 2024, price competition is often fierce, particularly for standard printing services. If Honle operates within such segments, its customers would exert substantial pressure on pricing. This means Honle needs to continually assess how its product differentiation stacks up against competitors to mitigate this power.
- Price Sensitivity in Printing: The printing industry, a key area for potential Honle Group operations, is highly competitive, with customers frequently prioritizing cost savings.
- Commoditization Risk: If Honle's products or services are perceived as commodities, customers gain leverage by easily comparing prices and switching to cheaper alternatives.
- Impact on Margins: High customer price sensitivity can directly lead to lower profit margins for Honle, as it may be forced to reduce prices to maintain market share.
- Diverting from Commodity: Honle's strategy to counter this power would involve emphasizing unique features, superior quality, or value-added services that differentiate its offerings from generic alternatives.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
Large industrial customers, especially those with strong research and development departments, could potentially explore creating their own UV curing or disinfection systems. This capability, though technically challenging, provides them with significant bargaining power when dealing with Honle Group.
The threat of backward integration by major clients is a key factor influencing pricing and service agreements. For instance, a large automotive manufacturer developing its own UV coating processes could reduce its reliance on external suppliers like Honle, potentially leading to demands for lower prices or customized solutions.
- Customer Leverage: Significant R&D investment by major clients can enable them to develop in-house UV solutions, increasing their negotiation strength.
- Potential Cost Savings: Customers integrating backward aim to reduce costs associated with purchasing external UV technology and services.
- Market Dynamics: The ability of customers to produce their own UV systems directly impacts Honle Group's pricing power and market share.
The bargaining power of customers for Honle Group is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, availability of substitutes, price sensitivity, and the potential for backward integration.
In 2024, the automotive sector, a key market for UV technology, continued to see consolidation, meaning a few large players could command significant negotiation power. For example, if a single automotive OEM represented over 10% of Honle's revenue in 2024, their ability to influence pricing and terms would be substantial. High switching costs for industrial UV systems, often involving significant retooling and integration expenses, typically mitigate this power. However, the presence of alternative curing technologies, such as thermal or electron beam curing, provides customers with a degree of leverage, especially in price-sensitive segments like certain printing applications where cost is a primary concern.
| Factor | Impact on Honle Group | 2024 Context/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration amplifies customer power. | Large automotive OEMs could exert significant influence if they represented a large portion of sales. |
| Switching Costs | High costs reduce customer bargaining power. | Reconfiguring industrial UV lines can cost hundreds of thousands, deterring switching. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Alternative technologies empower customers. | Thermal curing remains a viable, though often less efficient, alternative in some industrial applications. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity increases customer leverage. | The global printing industry, valued at approximately $750 billion in 2024, often faces intense price competition. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for customers to develop in-house solutions. | Major clients with strong R&D could develop proprietary UV systems, reducing reliance on suppliers like Honle. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Honle Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Honle Group meticulously details the competitive landscape, offering insights into industry rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of substitute products. You'll gain a clear understanding of the strategic forces shaping the Honle Group's market position. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is exactly what you get—professionally formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial UV technology market is quite crowded, featuring a mix of large, established corporations and smaller, highly specialized firms. This diversity means Honle Group must contend with a broad spectrum of competitors, each with different strengths and market focuses.
Key players challenging Honle Group include Better Place and Tomi Environmental Solutions, who are active in related UV disinfection sectors. Additionally, companies like Cantel Medical and KREMPEL operate within the broader UV technology landscape, presenting varied competitive pressures.
The competitive field also extends to lighting specialists such as Lucent Lighting and British Electric Electric Lamps, alongside significant UV light manufacturers like Heraeus Noblelight and LightSources. This broad competitive base necessitates continuous innovation and strategic positioning for Honle Group.
The UV curing and UV LED sectors are in a high-growth phase. The global UV curing market is anticipated to hit USD 29.98 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 19.00% starting in 2025. Similarly, the UV LED market is projected to reach USD 6.99 billion by 2035, with a CAGR of 19.4%.
This robust expansion often tempers competitive rivalry. When markets are growing quickly, companies tend to concentrate on capturing new customers and expanding their operations rather than engaging in intense battles for the existing customer base.
Honle Group actively pursues product differentiation in its UV systems and lamps, notably with innovations like AI-supported SMARTcure technology. This focus on advanced features, energy efficiency, and tailored solutions helps them stand out from competitors, reducing the pressure for direct price competition.
The company's commitment to R&D, evidenced by its continuous development of new UV applications and system enhancements, creates a barrier for rivals. For instance, their investment in specialized UV-A lamps for medical applications, which require precise wavelength control, illustrates this differentiation strategy.
By offering highly customized and technologically superior products, Honle Group can command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty. This makes it harder for competitors with more standardized offerings to directly challenge their market position through price alone.
Exit Barriers
Honle Group likely faces significant competitive rivalry due to high exit barriers. Specialized assets, such as advanced UV curing equipment and proprietary chemical formulations, can make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market. For instance, if a competitor has invested heavily in unique manufacturing processes for UV-reactive coatings, divesting those assets without substantial loss would be challenging, compelling them to remain active even in less favorable economic conditions.
These entrenched positions mean that even during industry slowdowns, companies are often reluctant to exit, leading to sustained pressure on pricing and market share. This can be particularly true in niche segments of the UV technology market where economies of scale are harder to achieve and specialized knowledge is paramount. The need to recoup substantial investments in research and development for new UV-LED curing systems or advanced materials further solidifies these barriers.
Consider the impact of long-term supply contracts, another common exit barrier. If Honle Group’s competitors are locked into multi-year agreements for raw materials or distribution channels, their ability to pivot away from the UV market is severely restricted. This forces them to continue competing, potentially at lower profit margins, thereby intensifying the rivalry for all players involved.
The specialized nature of UV technology itself, often requiring specific environmental controls and highly trained personnel, also contributes to high exit barriers.
- High Capital Investment: The development and manufacturing of specialized UV equipment can involve millions in capital expenditure, making divestiture difficult.
- Proprietary Technology: Significant investment in R&D for unique UV formulations or application processes creates a barrier to entry and exit.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers or customers in the UV sector can tie companies to the market for extended periods.
- Skilled Workforce Dependence: The need for specialized technical expertise in UV applications means that exiting the market might lead to a loss of valuable human capital.
Strategic Stakes
The industrial UV technology market represents a critical segment for many participants, including Honle Group, meaning companies have significant vested interests at play. This translates into an intensely competitive environment where firms are driven to protect and expand their market share. For example, in 2024, the global UV curing market was valued at approximately USD 4.8 billion, with projections indicating continued robust growth, underscoring the market's strategic importance.
Companies are therefore compelled to engage in aggressive tactics to maintain their competitive edge. This includes strategic pricing adjustments to capture market share, continuous investment in research and development for innovative solutions, and the formation of strategic alliances to enhance product offerings and distribution networks. These actions collectively escalate the rivalry among existing players.
- High Strategic Importance: The industrial UV technology market is a core revenue driver for companies like Honle Group, making market position highly valuable.
- Aggressive Defense Tactics: Expect intensified competition through price wars, rapid product innovation, and strategic collaborations as firms protect their turf.
- Market Growth Fueling Rivalry: The projected growth of the UV curing market, estimated to reach over USD 8.5 billion by 2030, incentivizes aggressive competition for future market share.
Competitive rivalry in the industrial UV technology market is significant due to the presence of numerous established players and specialized firms, all vying for market share. Honle Group faces competition from diverse entities, including those in UV disinfection and broader UV light manufacturing sectors.
Despite rapid market growth, which can temper rivalry, companies like Honle Group differentiate through advanced technologies such as AI-supported SMARTcure and specialized UV-A lamps, aiming for premium pricing and customer loyalty. This focus on innovation and customization creates barriers for competitors relying on standardized offerings.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial capital investment in specialized equipment, proprietary technology, and long-term contracts, compel companies to remain active, intensifying competition. The strategic importance of the UV market, with the global UV curing market valued around USD 4.8 billion in 2024, further fuels aggressive tactics like price adjustments and R&D investment.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Competitive Pressure on Honle Group |
|---|---|---|
| Large Established Corporations | Heraeus Noblelight, LightSources | Significant, due to scale and market reach |
| Specialized Firms | Better Place, Tomi Environmental Solutions | High in niche segments, driven by specific expertise |
| Lighting Specialists | Lucent Lighting, British Electric Electric Lamps | Indirect, through broader lighting solutions |
| UV Curing/LED Innovators | (Various emerging players) | Intense, due to high growth and technological advancements |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For curing applications, traditional thermal curing, solvent-based adhesives, and other chemical processes represent significant substitutes to UV curing. These methods, while potentially slower or less energy-efficient, have established market presence and customer familiarity.
In the realm of disinfection, traditional methods such as chemical disinfectants, filtration systems, and heat treatments offer alternatives to UV disinfection. While UV technology boasts benefits like rapid action, reduced energy consumption, and environmental advantages, these established methods remain competitive, particularly in specific use cases or for customers prioritizing familiarity over newer technologies.
The market for adhesives and sealants, where UV curing plays a role, is substantial. For instance, the global adhesives and sealants market was valued at approximately $60 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating the scale of existing, non-UV alternatives that customers can readily adopt.
While Honle Group leverages UV LED technology, the threat of substitutes remains a consideration. Emerging alternative curing and disinfection technologies, even those not directly UV-based, could offer comparable performance in certain applications. For instance, electron beam (EB) curing and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) represent potential long-term substitutes that might challenge the dominance of UV solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Hönle Group's UV solutions hinges on their cost-effectiveness compared to Hönle’s offerings. If alternative technologies, like traditional curing methods or emerging UV-LED systems from competitors, can match Hönle's performance at a lower price point, customers might consider switching. This is particularly relevant if the substitutes offer a good enough performance, even with minor compromises in process speed or environmental benefits, making the cost savings a primary driver for adoption. For instance, a competitor’s UV-LED system might require a higher initial investment but offer lower running costs, creating a compelling trade-off for certain customer segments by 2024.
Customer Perception and Adoption Barriers
Customer perception regarding the effectiveness, safety, and user-friendliness of alternative technologies significantly influences the threat of substitutes for Honle Group's UV-C disinfection solutions. For instance, a perceived lack of robust scientific backing or user-friendly interfaces for emerging disinfection methods could deter adoption, leaving traditional approaches more attractive.
High upfront costs associated with advanced UV systems, coupled with the necessity for specialized training to operate them effectively, present substantial adoption barriers. These financial and knowledge hurdles can make established, albeit less efficient, disinfection methods appear more palatable to potential customers, particularly small to medium-sized businesses or those with limited technical expertise.
Consider the market for water purification. While UV-C offers a chemical-free solution, potential buyers might be hesitant due to the initial investment in UV equipment compared to readily available and cheaper chemical treatments. This perception gap, especially if not effectively addressed by Honle Group through clear value propositions and educational resources, strengthens the threat of substitutes.
- Customer perception of efficacy: Surveys indicate that a significant portion of consumers still trust chemical disinfectants more than UV-C for certain applications, creating a perception barrier.
- Initial investment costs: For example, industrial-scale UV-C systems can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, a considerable outlay for many businesses.
- Need for specialized training: Proper maintenance and operation of UV-C equipment often require trained personnel, adding an ongoing cost and complexity that substitutes may avoid.
- Ease of use: If alternative methods are perceived as simpler to implement and manage without specialized knowledge, they become more appealing despite potential long-term drawbacks.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Increasing regulatory scrutiny around environmental impact and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions significantly boosts UV curing technologies as a preferred substitute for traditional solvent-based solutions. For instance, by 2024, many regions have tightened VOC limits, making compliant solvent-based formulations more complex and expensive. This shift directly benefits UV curing, which typically emits negligible VOCs, thereby reducing compliance burdens for manufacturers and presenting a favorable substitution threat to older technologies.
However, the landscape is dynamic. The emergence of new, non-UV curing technologies driven by further environmental mandates or performance enhancements could introduce a greater threat of substitution. If future regulations specifically target the energy consumption of UV lamps or chemical compositions within UV-curable resins, alternative curing mechanisms, such as electron beam (EB) curing or even advanced water-based coatings with faster drying times, could gain traction. This potential for disruptive innovation in curing technologies necessitates ongoing monitoring to assess the evolving threat of substitutes for Honle Group's UV-based offerings.
- Environmental Regulations Favor UV Curing: Stricter VOC emission standards, like those implemented across the EU in recent years, make solvent-based alternatives less attractive due to higher compliance costs and formulation challenges.
- UV Curing's Low VOC Profile: UV-curable materials typically emit near-zero VOCs, positioning them as a significantly more environmentally friendly and regulatory-compliant option.
- Potential for New Substitutes: Emerging non-UV curing technologies, driven by future environmental or performance demands, could challenge UV curing's dominance.
- Market Adaptability: Honle Group must remain agile, adapting to potential shifts in regulatory focus that might favor alternative curing methods over current UV technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Honle Group's UV solutions is moderate, primarily due to established alternatives in both curing and disinfection markets. While UV technology offers advantages like speed and reduced VOCs, traditional methods such as thermal curing or chemical disinfection remain prevalent, especially where cost or user familiarity are paramount. For instance, the global adhesives market, a key area for UV curing, was valued at around $60 billion in 2023, indicating the scale of existing non-UV alternatives. Emerging technologies like electron beam curing also represent potential future substitutes.
Customer perception and initial investment costs significantly influence the adoption of UV technologies, thereby impacting the threat of substitutes. High upfront costs for industrial UV systems, sometimes reaching tens of thousands of dollars, can make cheaper, though less efficient, traditional methods more appealing. Furthermore, the need for specialized training for UV equipment operation can deter adoption, especially for smaller businesses. For example, in water purification, the initial cost of UV systems might push buyers towards more familiar chemical treatments, despite UV’s chemical-free benefits.
Environmental regulations are increasingly favoring UV curing by penalizing VOC emissions from solvent-based alternatives. By 2024, stricter VOC limits make compliant solvent-based formulations more complex and expensive, boosting UV curing's appeal. However, future regulations could also target UV technology itself, potentially opening doors for new substitutes like advanced water-based coatings or electron beam curing if they offer better environmental profiles or performance enhancements.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial UV technology market, particularly in manufacturing UV systems and lamps, demands considerable financial outlay. This includes significant investment in research and development, establishing specialized production facilities, and building out robust distribution networks. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art cleanroom for lamp manufacturing alone can cost millions, a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
Established players like Honle Group benefit from a robust portfolio of intellectual property, encompassing patents for their advanced UV lamp designs, intricate system integrations, and specialized application technologies. This strong IP foundation serves as a significant hurdle for potential new entrants, effectively deterring market entry by those unable to navigate or license existing patent protections without risking infringement.
Economies of scale present a significant barrier for new entrants into the Honle Group's market. Established competitors leverage their substantial production volumes to achieve lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, raw material procurement, and research and development. For instance, in 2023, leading players in the photonics industry, a sector where Honle operates, reported manufacturing cost efficiencies that were, on average, 15% lower than smaller, emerging companies due to their scale of operations.
This cost advantage makes it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete on price. Without the capacity to generate comparable sales volumes, new entrants face higher production costs. This disparity in cost structures means that any attempt by a new player to undercut existing firms on price would likely result in unsustainable profit margins, effectively deterring their market entry.
Access to Distribution Channels
For industrial UV systems, securing reliable distribution and service networks is a significant hurdle for newcomers. Honle Group, with its established global presence, has cultivated deep relationships with a wide array of industrial clients spanning multiple sectors. This intricate web of trust and proven delivery is not easily replicated. For instance, in 2024, the industrial UV equipment market saw continued growth, driven by demand in sectors like water treatment and printing, highlighting the importance of established channels for market penetration.
New entrants would struggle to replicate Honle Group's extensive network, which is crucial for providing timely support and maintenance for complex industrial UV systems. Building these customer relationships across diverse geographies and industries takes considerable time and investment. The ability to offer comprehensive after-sales service, a hallmark of established players like Honle, is a key differentiator that new entrants would find challenging to match quickly. In 2023, customer service satisfaction was a significant factor in B2B purchasing decisions for capital equipment, underscoring the value of existing, trusted relationships.
- Established Global Reach: Honle Group benefits from existing distribution and service infrastructure, making it harder for new entrants to compete on accessibility.
- Customer Trust and Relationships: Years of reliable service have fostered strong customer loyalty, a significant barrier to entry for newcomers.
- Complexity of Industrial Networks: The diverse needs of industrial clients across various sectors require specialized knowledge and established channels to serve effectively.
- Service and Support Requirements: Industrial UV systems demand robust after-sales support, which new entrants would find costly and time-consuming to build from scratch.
Brand Loyalty and Industry Experience
In specialized industrial markets, brand reputation, reliability, and long-standing customer relationships are critical barriers to entry. Honle Group, boasting over 40 years of operational history, has cultivated significant trust and customer loyalty. This established goodwill presents a substantial challenge for new entrants aiming to secure market acceptance and build a comparable reputation.
New competitors must overcome the ingrained preference for proven performance and dependable service that Honle Group offers. The company's extensive experience translates into a deep understanding of customer needs and regulatory landscapes, which is difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly. As of the latest available data, Honle Group's consistent delivery of high-quality industrial solutions has solidified its market position, making it a formidable competitor for any emerging player.
- Established Brand Reputation: Honle Group's decades of operation have built a strong and recognizable brand synonymous with quality and reliability in specialized industrial sectors.
- Long-Standing Customer Relationships: The company has nurtured deep, trust-based relationships with its clientele over many years, creating loyalty that is hard for new entrants to disrupt.
- Industry Experience Advantage: With over 40 years in the field, Honle Group possesses invaluable institutional knowledge and expertise that new companies lack, impacting their ability to effectively serve complex market needs.
- Market Acceptance Hurdle: New entrants face the significant challenge of gaining market trust and acceptance when faced with an incumbent like Honle Group, which has a proven track record and established customer base.
The threat of new entrants for Honle Group in the industrial UV technology market is moderately high, primarily due to significant capital requirements and established intellectual property. While the initial investment in R&D and specialized manufacturing facilities, potentially running into millions for cleanroom setups, acts as a substantial barrier, the strong patent portfolio of established players like Honle further deters newcomers who risk infringement.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, production facilities, and distribution networks. | Significant hurdle, requiring substantial funding. | Setting up specialized manufacturing can cost millions. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on advanced UV lamp designs and system integrations. | Deters entry without licensing or risking infringement. | Established players hold numerous patents protecting core technologies. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established players due to high production volumes. | Makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. | Companies with higher output often achieve 15% lower manufacturing costs. |
| Distribution & Service Networks | Established global reach and customer relationships. | New entrants struggle to replicate the accessibility and support infrastructure. | Industrial UV equipment market growth in 2024 emphasizes the need for reliable channels. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Decades of operation and proven reliability. | New entrants face a challenge gaining market acceptance and loyalty. | Customer service satisfaction remained a key factor in B2B capital equipment purchases in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Honle Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial disclosures. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.
