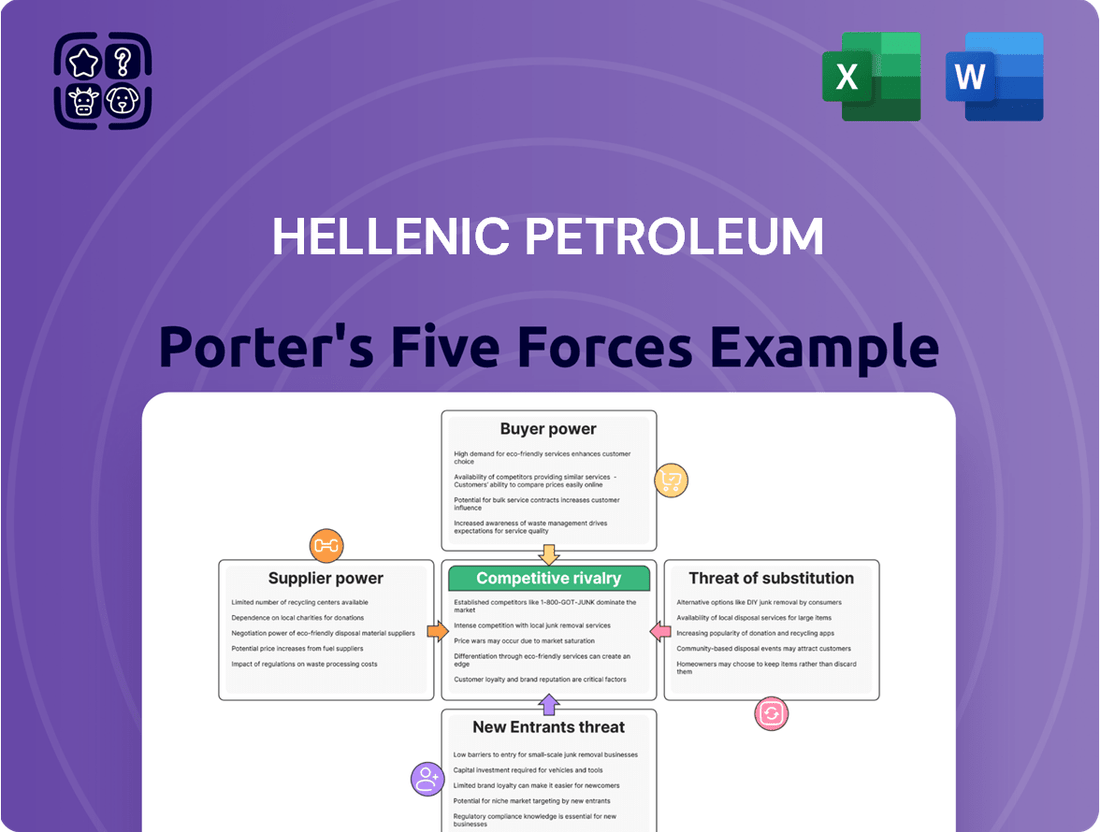
Hellenic Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hellenic Petroleum Bundle
Hellenic Petroleum operates in a dynamic energy sector, where the bargaining power of buyers, particularly large industrial clients and government entities, can significantly impact pricing and profit margins.
The threat of new entrants, while somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles, remains a consideration for long-term strategic planning.
The intensity of rivalry among existing oil and gas companies, including Hellenic Petroleum, is a key factor shaping market share and competitive strategies.
Suppliers, especially those controlling crude oil sources or specialized refining technologies, wield considerable influence over Hellenic Petroleum's operational costs and production capabilities.
The availability of substitute energy sources, such as renewables, presents a growing challenge to the traditional petroleum market, necessitating adaptation and diversification.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hellenic Petroleum’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The global crude oil market exhibits high supplier concentration, primarily dominated by OPEC+ nations, which significantly impacts HELLENiQ ENERGY. This allows them substantial control over supply and pricing, directly influencing HELLENiQ ENERGY's primary input costs. For instance, OPEC+ production cuts, like those extended through Q2 2024, directly limit supply. Geopolitical instability in key oil-producing regions, such as ongoing tensions in the Middle East in 2024, can create acute supply volatility. This concentration and volatility strengthen supplier bargaining power, making HELLENiQ ENERGY vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
Crude oil prices, the primary cost for refiners like HELLENiQ, are determined by global benchmarks such as Brent and WTI. This structure leaves very little room for individual negotiation, essentially making the company a price taker for its most critical raw material. For example, Brent crude oil prices generally hovered between 80 and 90 USD per barrel during much of early 2024, reflecting broad market forces. This standardized pricing mechanism inherently grants immense bargaining power to global oil suppliers, like OPEC+ nations who collectively control significant output. HELLENiQ's leverage is minimal against such consolidated supplier control.
Supplier power for Hellenic Petroleum is significantly amplified by ongoing geopolitical instability, particularly from conflicts and trade sanctions impacting major oil-producing regions. Such events, like those seen influencing global crude oil prices in early to mid-2024, can severely disrupt supply chains and inflate transportation costs. These external factors lead to sudden and unpredictable price hikes for raw materials, largely beyond HELLENiQ's direct control. For instance, shifts in global crude benchmarks directly affect their input costs, impacting profitability. This inherent vulnerability underscores the significant leverage held by global energy suppliers.
Specialized Technology and Equipment Providers
HELLENiQ Energy, for its refining processes and expansion into green energy, relies heavily on specialized technology and equipment suppliers. These providers often possess patents and unique expertise, such as those offering advanced catalysts or renewable energy components, giving them substantial bargaining power.
This power is evident in negotiations for new projects and essential maintenance, especially as HELLENiQ Energy plans significant capital expenditures in 2024 for strategic investments, including its energy transition. Such specialized suppliers can command higher prices due to their irreplaceable contributions to operational efficiency and strategic growth.
- HELLENiQ Energy's 2024 capex for strategic investments, including green energy, highlights reliance on high-tech suppliers.
- Suppliers of patented catalysts and specialized refining equipment hold strong negotiating leverage.
- Unique expertise in renewable technologies, critical for HELLENiQ's energy transition, increases supplier influence.
- Limited alternatives for advanced solutions empower these providers to dictate terms and pricing.
Moderate Switching Capability for Crude Types
While HELLENiQ Petroleum remains subject to global oil price fluctuations, its advanced refining infrastructure provides a crucial operational advantage. These sophisticated refineries possess the flexibility to process a diverse range of crude oil types, including both light and heavy crudes, which enhances their adaptability. This capability allows the company to strategically switch between various suppliers, thereby somewhat reducing the leverage of any single crude provider. For instance, in 2024, HELLENiQ continued to optimize its crude slate based on market availability and pricing, sourcing from over 20 different crude grades globally.
- HELLENiQ's refineries can process diverse crude types, including those from the Middle East, North Africa, and the Black Sea region.
- This flexibility allows for strategic sourcing based on price and availability, mitigating reliance on specific suppliers.
- Operational agility helps manage supply chain risks and optimize input costs for refined products.
- The company's investment in upgrading its facilities, such as the Aspropyrgos refinery, supports this multi-crude processing capability.
HELLENiQ ENERGY faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the concentrated global crude oil market, dominated by OPEC+ nations, which dictates prices. Geopolitical events in 2024 further amplify this by disrupting supply and inflating costs. Additionally, reliance on specialized technology and equipment suppliers, crucial for its energy transition, grants them substantial leverage. While HELLENiQ's flexible refining capability allows diverse crude processing, mitigating some specific supplier risks, overall supplier power remains high.
| Supplier Group | Key Influence | 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| OPEC+ Nations | Crude Oil Supply & Pricing | Production cuts, Brent crude 80-90 USD/bbl |
| Specialized Tech Providers | Refining & Green Energy Tech | Patented catalysts, high capex for energy transition |
| Global Market Dynamics | Geopolitical Stability | Supply chain disruptions, price volatility |
What is included in the product
Hellenic Petroleum's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense competition from global refiners and local distributors, the significant bargaining power of large industrial clients and crude oil suppliers, and the moderate threat of new entrants due to capital intensity and regulatory hurdles.
A clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces for Hellenic Petroleum—perfect for quick decision-making regarding competitive pressures.
Instantly understand strategic pressure on Hellenic Petroleum with a powerful spider/radar chart, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers exert significant bargaining power due to the commodity nature of fuel, making them highly sensitive to price changes. At the retail level, consumers often choose stations based primarily on the lowest price per liter, a trend continuing into 2024. This intense price sensitivity forces HELLENiQ Energy and its competitors to engage in fierce price competition across their networks. Such market dynamics severely restrict the ability of companies like HELLENiQ to increase their profit margins on petroleum products. For instance, even a small price difference can shift significant sales volumes.
Gasoline and diesel are largely undifferentiated commodities, meaning consumers perceive minimal distinction between fuel brands. While HELLENiQ Energy may invest in branding or specialized additives, the primary purchasing drivers for most customers in 2024 remain price competitiveness and station convenience. This low product differentiation significantly enhances customer bargaining power, as they can easily switch to competitors like Motor Oil Hellas or Shell based on minor price variations.
For Hellenic Petroleum, the bargaining power of customers is notably high due to minimal switching costs. Retail consumers, for instance, face virtually no barrier to choosing a competitor's fuel station, such as Shell or BP, given the ubiquitous nature of petrol stations across Greece in 2024. The product, gasoline or diesel, is largely undifferentiated, making price and convenience key drivers. Even large industrial and commercial clients, despite potential contracts, can easily negotiate with other suppliers like Motor Oil Hellas, leveraging the commoditized fuel market to secure better terms and pricing.
Bargaining Power of Large Industrial Buyers
Large industrial, aviation, and marine customers purchase fuel in significant volumes, giving them substantial bargaining power. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. Such negotiations pressure HELLENiQ's margins, particularly in these crucial B2B segments. For example, the aviation fuel market saw a 13.5% increase in demand in Greece in 2024, yet large airlines leverage their purchasing scale.
- Bulk purchases enable customers to demand price concessions.
- Contract terms often favor large buyers due to their volume commitment.
- This dynamic impacts HELLENiQ's profitability in key B2B sectors.
Increasing Availability of Information
The increasing availability of digital tools significantly empowers Hellenic Petroleum customers. Applications and online platforms provide real-time fuel price comparisons across various stations, intensifying competition. This transparency shifts power to consumers, who can easily identify the lowest price available, impacting purchasing decisions.
For instance, in early 2024, data from European fuel price monitoring services indicated a continued rise in consumer reliance on digital tools to compare prices, often leading to immediate shifts in demand towards more competitive stations.
- Real-time price transparency enables consumers to quickly compare Hellenic Petroleum prices against competitors.
- Digital platforms reduce search costs for customers, making it easier to find optimal deals.
- Increased information availability intensifies price sensitivity among fuel consumers.
- This dynamic forces fuel retailers like Hellenic Petroleum to maintain competitive pricing to retain market share.
Customers exert strong bargaining power over HELLENiQ Energy due to fuel being a commodity with low differentiation and minimal switching costs, a trend continuing into 2024. Retail consumers leverage digital tools for real-time price comparisons, intensifying competition. Large industrial and aviation clients use their significant purchase volumes to secure favorable terms and pricing, directly impacting HELLENiQ's profitability. This dynamic forces HELLENiQ to maintain competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on HELLENiQ | 2024 Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Lower margins | High, driven by digital tools | ||
| Switching Costs | Easy customer churn | Minimal for retail | ||
| Bulk Purchases | Negotiated discounts | Growing B2B leverage |
Full Version Awaits
Hellenic Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Hellenic Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the oil and gas sector. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing insights into industry rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This meticulously researched analysis is your deliverable, ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Greek energy market exhibits intense domestic competition, primarily between HELLENiQ ENERGY and Motor Oil Hellas, forming a duopoly. Their strategic moves in refining capacity, such as HELLENiQ ENERGY's 2024 production targets, and retail network expansion are closely monitored. Pricing strategies are highly competitive, reflecting the dynamic nature of this rivalry. Both companies consistently vie for market share in fuel distribution and petrochemical products across Greece.
The oil refining industry, exemplified by Hellenic Petroleum, is characterized by substantial exit barriers due to immense capital outlays for specialized, non-transferable assets such as refineries and extensive pipeline networks. These significant sunk costs, often running into billions for modern facilities, compel companies to remain operational and compete intensely. Even amidst periods of lower profitability, as experienced in parts of the European refining market in early 2024, the difficulty of divesting these assets forces continued market presence, thereby sustaining high competitive rivalry.
The European market for traditional petroleum products, a core for Hellenic Petroleum, is notably mature, showing slow to stagnant growth as of 2024. Increased energy efficiency initiatives, like the EU's 2024 target to reduce primary and final energy consumption, and the rising adoption of electric vehicles, act as significant substitutes. This environment intensifies competition among refiners, forcing aggressive battles for market share. Consequently, this leads to persistent pressure on pricing and ultimately compresses profit margins across the sector.
Competition from International Players
HELLENiQ faces intense competition from major international oil and gas companies operating across Southeast Europe, not just domestic rivals. These global players, like Shell and TotalEnergies, possess vast financial resources, allowing for significant investment in infrastructure and technology. Their established brands and extensive distribution networks, often spanning multiple countries, give them a competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, international firms continue to dominate regional market shares, leveraging their scale to optimize supply chains and pricing strategies.
- International players command significant capital for expansion.
- Global brands benefit from widespread recognition and trust.
- Extensive distribution networks enhance market penetration.
- Superior scale allows for competitive pricing and efficiency.
Strategic Shift to Renewables as a New Competitive Front
As HELLENiQ Energy and its rivals pivot towards renewable energy, a significant new front for competition is emerging. Rivalry intensifies in securing permits for crucial wind and solar projects, with HELLENiQ Energy aiming for 1 GW of RES capacity by 2025. Competitors are aggressively developing energy storage solutions and capturing market share in Greece's growing green energy sector, which saw substantial investment growth in 2024.
- HELLENiQ Energy targets 1 GW of renewables capacity by 2025.
- Rivalry focuses on securing wind and solar project permits.
- Competition is fierce in developing energy storage solutions in 2024.
HELLENiQ ENERGY faces intense rivalry from domestic duopoly partner Motor Oil Hellas and powerful international players like Shell. High exit barriers due to massive capital investments in refining sustain this competition despite market maturity. A new competitive front is rapidly emerging in renewable energy, where firms aggressively vie for market share and project permits. This dynamic environment includes fierce competition for Greece's growing green energy sector, which saw substantial investment growth in 2024.
| Rivalry Factor | 2024 Data Point | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Refining Output Targets | HELLENiQ ENERGY 2024 targets | Direct market share competition |
| RES Investment Growth | Greece's 2024 green energy investment | Intensified competition in renewables |
| European Refining Profitability | Early 2024 market conditions | Sustained rivalry despite pressure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for HELLENiQ ENERGY's traditional transportation fuels, like gasoline and diesel, is the rapidly expanding electric vehicle (EV) market. Government incentives across Europe, such as purchase subsidies and tax breaks, continue to accelerate EV adoption, with new EV sales in Greece showing a significant increase in 2024. Improvements in battery technology, offering longer ranges and faster charging, along with the continuous expansion of charging infrastructure, further reduce range anxiety for consumers. This growing shift directly threatens the long-term demand for refined petroleum products, as EV registrations are projected to climb, eroding a core revenue stream for companies like HELLENiQ.
The expanding use of natural gas for heating and industrial purposes, alongside the growing adoption of biofuels, presents a notable threat of substitution for Hellenic Petroleum. Biofuels, whether blended into traditional fuels or used independently, are gaining traction; for instance, the European Union is targeting a minimum 14% share of renewable energy in transport by 2030, driving demand. HELLENiQ, through its gas operations like DEPA Commercial, simultaneously contributes to the natural gas market while also hedging against the substitution risk to its oil refining business. In 2024, the push for cleaner energy solutions continues to reshape the energy landscape, influencing consumer choices and industrial shifts away from conventional petroleum products.
Strong regulatory pressures from the European Union and the Greek government, such as the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) with carbon prices around €60-€70 per tonne in early 2024, actively promote substitutes. Greece's updated National Energy and Climate Plan (NECP) targets 80% renewable energy in electricity generation by 2030, directly phasing out fossil fuels. These mandates create a deliberate and significant threat to HELLENiQ Energy's traditional refining business model. The company itself is targeting 1 GW of installed renewable capacity by 2030, reflecting this unavoidable strategic shift.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Efforts
Improvements in vehicle fuel efficiency, like the growing adoption of electric vehicles, and advancements in home insulation technology significantly reduce the demand for traditional fossil fuels. This societal push towards energy conservation acts as a potent substitute, directly impacting the volume of energy products sold by companies such as HELLENiQ. For instance, the European Union aims for a 11.7% reduction in final energy consumption by 2030 compared to 2020 levels, driven by such efficiency measures. This trend creates persistent downward pressure on the overall market for refined petroleum products, necessitating strategic adjustments for energy firms.
- In 2024, the global electric vehicle fleet continues rapid expansion, with projections for significant market share growth impacting gasoline demand.
- EU energy efficiency directives reinforce the push for better building insulation and reduced heating/cooling energy consumption.
- Conservation efforts collectively reduce the overall demand for HELLENiQ's core refined products.
- This shift mandates diversification and investment in renewable energy sources for traditional oil companies.
Rise of Alternative Power Generation
The rapid advancements and declining costs of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, pose a significant threat of substitution to Hellenic Petroleum's legacy fossil fuel-based power generation. As of 2024, the levelized cost of energy for new solar and wind projects continues to be highly competitive, making them increasingly attractive alternatives for electricity production. HELLENiQ ENERGY is actively mitigating this threat by strategically investing in its own portfolio of renewable energy projects. This internal diversification aims to shift its energy mix and secure future revenues in a decarbonizing market.
- Global solar PV capacity is projected to exceed 1,600 GW by 2024, demonstrating widespread adoption.
- HELLENiQ ENERGY aims for 1 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, with substantial progress expected by 2025.
- The cost of utility-scale solar PV has fallen over 80% in the last decade, enhancing its competitiveness.
The primary threat of substitutes for HELLENiQ ENERGY stems from the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles, directly eroding demand for refined fuels, with EV sales in Greece increasing in 2024. Expanding use of natural gas and biofuels further displaces conventional petroleum, driven by EU renewable energy targets like the 14% share for transport by 2030. Strong regulatory pressures, including the EU ETS carbon prices around €60-€70 per tonne in early 2024, actively promote cleaner alternatives. The declining cost and rapid deployment of solar and wind power also challenge fossil-fuel-based electricity generation.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Data Point | Impact on HELLENiQ |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Increased EV sales in Greece | Reduced gasoline/diesel demand |
| Biofuels/Natural Gas | EU 14% renewable transport target by 2030 | Displaces conventional fuels |
| Renewable Energy (Solar/Wind) | Competitive LCOE; Global solar PV >1,600 GW | Threatens fossil-fuel power generation |
Entrants Threaten
The capital outlay for constructing a modern, large-scale oil refinery and its essential logistical network is exceptionally high, often exceeding several billion euros. As of 2024, building a new complex refinery can easily cost upwards of €8-€10 billion. This massive financial barrier makes it incredibly challenging for any new market participant to enter the refining sector and compete with established players like Hellenic Petroleum. Such prohibitive costs significantly deter potential entrants, limiting the threat of new competition.
New entrants into the European energy sector, like those considering Hellenic Petroleum's market, confront formidable regulatory and environmental hurdles. Obtaining necessary permits, especially within the stringent European Union framework, is a multi-year process, often extending beyond five years for major projects. Furthermore, the rising political and social opposition to new fossil fuel infrastructure, evident in the EU's 2024 emissions reduction targets, creates a near-insurmountable barrier. This makes any significant investment in new refining or distribution capacity exceptionally risky and costly for potential newcomers.
New entrants face significant barriers due to established players like HELLENiQ benefiting from massive economies of scale. HELLENiQ, with its extensive refining capacity, which includes facilities like the Aspropyrgos refinery, processes millions of tons of crude oil annually, driving down per-unit costs in procurement, refining, and distribution. Their well-established brands, robust retail networks, boasting over 1,700 service stations across Greece and Southeastern Europe in 2024, and long-standing relationships with global suppliers and customers, are powerful advantages. A new entrant would find it incredibly challenging and capital-intensive to replicate such an integrated infrastructure and market presence.
Control over Distribution Channels
The control over extensive distribution channels presents a formidable barrier for new entrants in the Greek energy market. HELLENiQ ENERGY and its main competitors, like Motor Oil Hellas, own or control vast networks, including critical pipelines, storage terminals, and a significant number of retail fuel stations across Greece.
For instance, HELLENiQ ENERGY operates over 1,700 retail service stations, primarily under the EKO and BP brands, as of 2024, alongside substantial logistics infrastructure. A new entrant would face the monumental and capital-intensive challenge of either constructing a comparable new network from scratch or securing access to these established, proprietary systems, which is highly unlikely given the strategic nature of these assets.
- HELLENiQ ENERGY's retail network exceeds 1,700 service stations in Greece (2024 data).
- Building a new, nationwide fuel distribution network can cost billions of euros.
- Existing players control essential pipelines and storage, vital for market access.
- Regulatory hurdles and licensing for new infrastructure are complex and time-consuming.
Lower Barriers in Niche Renewable Markets
While establishing a traditional oil refinery presents significant barriers, the threat of new entrants is notably higher in specific downstream and renewable energy sectors where HELLENiQ Energy is expanding. New companies can emerge, focusing solely on developing electric vehicle (EV) charging networks or specialized biofuel production, potentially capturing significant market share. For instance, the market for distributed solar generation continues to grow, attracting new, agile players. These niche players can challenge HELLENiQ Energy's diversification efforts by offering specialized solutions.
- HELLENiQ Energy is actively investing in renewables, aiming for 1 GW of installed capacity by 2025.
- New entrants can quickly scale in EV charging, leveraging lower capital intensity compared to refining.
- Specialized biofuel producers benefit from evolving regulatory support and market demand in 2024.
- Distributed solar projects offer accessible entry points for smaller, focused energy companies.
The threat of new entrants in traditional refining is extremely low due to immense capital requirements, exceeding €8-€10 billion, and stringent 2024 EU environmental regulations. HELLENiQ ENERGY's vast economies of scale and control over 1,700 retail service stations and critical distribution networks create formidable barriers. However, the threat is higher in niche downstream and renewable sectors like EV charging and biofuels, where agile new companies can emerge. HELLENiQ ENERGY aims for 1 GW of renewables by 2025, facing competition from specialized players.
| Barrier Type | Impact Level | 2024 Data Point | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | Very High | >€8-€10 Billion (Refinery) | ||
| Regulatory Hurdles | High | 5+ Year Permitting | ||
| Market Share | High | HELLENiQ 1,700+ Stations | ||
| New Sector Entry | Moderate | EV Charging, Biofuels |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis of Hellenic Petroleum's competitive landscape leverages data from its annual reports and financial statements, alongside industry-specific research from reputable energy sector publications and market intelligence firms.
We also incorporate information from regulatory filings and macroeconomic data relevant to the oil and gas sector in Greece and the broader Mediterranean region to provide a comprehensive view.
