Hanwha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hanwha Bundle
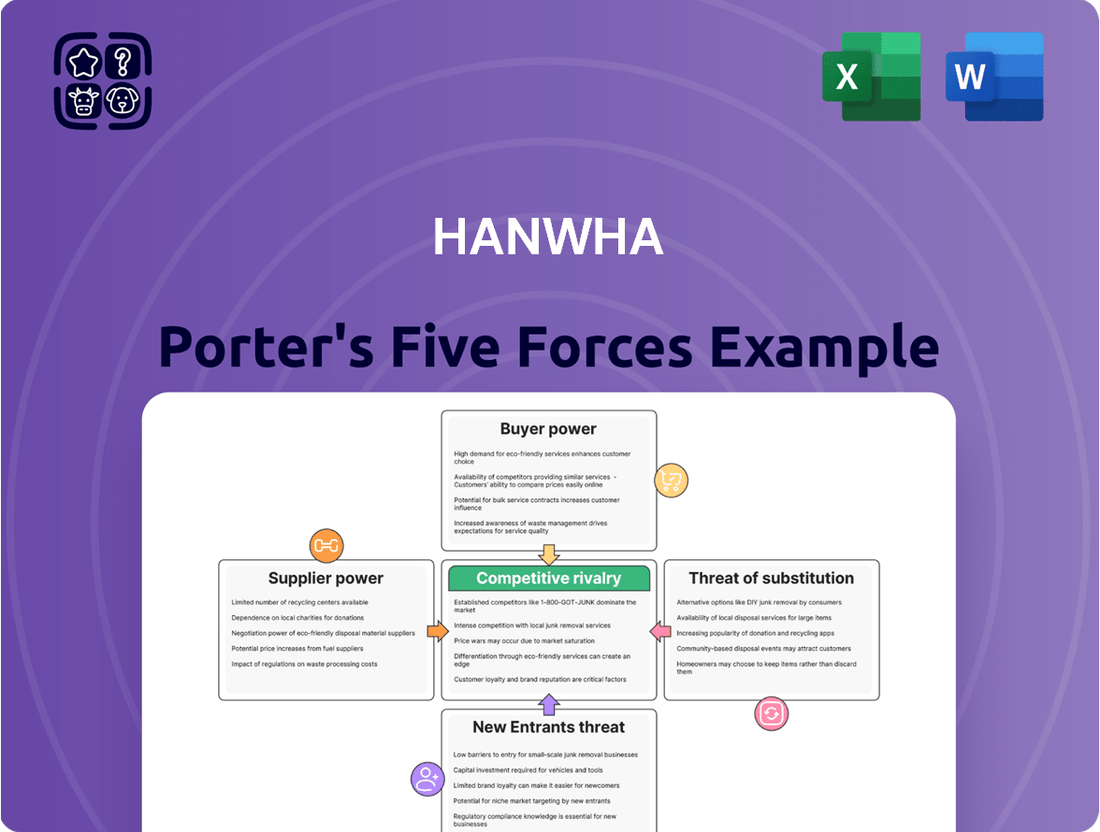
Hanwha operates in a dynamic landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and significant buyer power. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive, data-driven examination of Hanwha's market position, revealing specific strategies to leverage its strengths and mitigate threats.
Ready to gain a deeper strategic advantage? Unlock the complete analysis to uncover actionable insights and make informed decisions about Hanwha's future.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
In Hanwha's diverse operations, especially within its aerospace and defense sectors, a limited number of highly specialized suppliers for critical components and advanced technologies can significantly amplify supplier bargaining power. This scarcity of alternatives for proprietary parts grants these suppliers considerable leverage over pricing and contract terms.
For instance, in the aerospace industry, the development of advanced materials or unique electronic systems often involves a small, select group of manufacturers. If Hanwha relies heavily on these specialized suppliers for its defense systems, the suppliers can dictate terms more readily. This was evident in 2024 discussions around the supply chain for next-generation fighter jet components, where a few key firms controlled essential technologies.
To counter this, Hanwha actively cultivates strategic alliances and invests in developing its internal manufacturing capabilities. By fostering strong relationships with key suppliers and building in-house expertise for critical technologies, Hanwha aims to reduce its dependence on any single source, thereby moderating supplier influence.
The quality and reliability of components are critical for Hanwha's advanced products, including its aerospace systems and cutting-edge materials. Suppliers whose inputs directly affect the performance or safety of these high-tech offerings wield considerable influence.
For instance, a supplier of specialized alloys for Hanwha's aerospace division, where even minor material imperfections can have severe consequences, would possess significant bargaining power. Hanwha's commitment to rigorous quality assurance and fostering enduring partnerships with its key suppliers are essential strategies to effectively navigate and mitigate this supplier leverage.
Switching suppliers presents significant hurdles for Hanwha. For instance, in its aerospace and defense divisions, re-tooling manufacturing lines and obtaining new certifications can cost millions, directly impacting production timelines and budgets. Similarly, in its advanced materials segment, specialized chemical suppliers may require extensive re-training of Hanwha's workforce to handle new compounds or processes.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers possessing unique technologies or critical resources could threaten Hanwha by integrating forward into its markets. This means they might start producing and selling the final products themselves, bypassing Hanwha. For instance, a supplier of advanced battery components for electric vehicles, if they also developed the expertise to assemble entire EV packs, could become a direct competitor.
The risk of forward integration is particularly high for suppliers of essential, high-value components that are difficult for Hanwha to source elsewhere. If a supplier controls a proprietary material or a crucial manufacturing process, they have a stronger incentive and capability to move up the value chain. This could significantly impact Hanwha's market share and profitability.
Hanwha mitigates this threat through several strategies. A primary approach is investing heavily in its own research and development (R&D) and manufacturing capabilities. By staying at the forefront of technological innovation and maintaining efficient production, Hanwha reduces its reliance on any single supplier and strengthens its competitive position. For example, Hanwha's continued investment in solar technology R&D, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs, lessens the leverage of component suppliers.
Furthermore, Hanwha actively cultivates strategic alliances and partnerships. These collaborations can secure supply chains, share risks, and foster joint innovation, thereby discouraging suppliers from pursuing disruptive forward integration. By building strong, mutually beneficial relationships, Hanwha can ensure a stable supply of critical inputs while maintaining its own competitive edge.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers with unique technologies or critical resources may enter Hanwha's markets directly.
- Impact on Hanwha: This poses a risk to Hanwha's market share and profitability, especially for suppliers of high-value, difficult-to-source components.
- Mitigation Strategies: Hanwha invests in its own R&D and manufacturing to reduce supplier reliance and maintain competitiveness.
- Strategic Alliances: Forming partnerships helps secure supply chains and discourages suppliers from integrating forward.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
When suppliers offer highly differentiated or patented materials and technologies, their bargaining power increases significantly. This is particularly true in specialized sectors like advanced chemicals or unique aerospace components. For instance, a supplier holding exclusive rights to a critical, high-performance material for Hanwha's solar panel production would command greater leverage.
Hanwha's strategic response to this involves a commitment to continuous innovation and the active diversification of its supply chain. By developing alternative materials or fostering relationships with multiple suppliers for key components, Hanwha aims to mitigate dependence on any single provider, thereby strengthening its own negotiating position.
- Supplier Differentiation: High differentiation, such as patented materials in advanced chemicals or specialized aerospace components, grants suppliers significant bargaining power.
- Hanwha's Mitigation Strategy: Hanwha actively combats this by investing in continuous innovation and diversifying its supplier base to reduce reliance on any single entity.
- Impact on Hanwha: This strategy is crucial for maintaining cost control and ensuring supply chain resilience, especially as Hanwha expands its presence in sectors like renewable energy and defense, where specialized inputs are common.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration for Hanwha, particularly when dealing with specialized components in sectors like aerospace and advanced materials. A concentrated supplier base for critical technologies can lead to higher input costs and less favorable contract terms for Hanwha.
In 2024, Hanwha's defense sector, for example, faced increased supplier leverage due to the limited availability of certain advanced electronic components. This scarcity meant that a few key suppliers could dictate pricing, impacting Hanwha's production costs for next-generation defense systems.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Hanwha | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base (e.g., Aerospace Electronics) | Increased input costs, less favorable terms. In 2024, specialized component suppliers in defense saw pricing power rise. | Developing internal capabilities, strategic alliances. |
| High Switching Costs (e.g., re-tooling, certifications) | Reduced flexibility, potential production delays. Re-tooling for new aerospace components can cost millions. | Long-term partnerships, supplier performance monitoring. |
| Supplier Differentiation (e.g., patented materials) | Higher prices for unique inputs. Suppliers of advanced alloys for aerospace can command premiums. | Supply chain diversification, investment in R&D for alternatives. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Hanwha's industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. It provides strategic insights into Hanwha's market position and potential vulnerabilities.
Easily identify and prioritize competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of each force, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
In Hanwha's defense and aerospace businesses, a key factor impacting customer bargaining power is the concentrated nature of its client base. Often, these customers are limited to a few government defense agencies or major prime contractors. This limited pool of buyers grants them significant influence over pricing, contract conditions, and product specifications, creating a substantial bargaining advantage.
For example, in the defense sector, a single major government contract can represent a significant portion of revenue. This dependence means Hanwha must carefully negotiate terms to maintain profitability and secure future business. In 2023, global defense spending reached an estimated $2.4 trillion, highlighting the scale of these markets but also the power wielded by major purchasers within them.
Hanwha actively counters this by focusing on product differentiation, emphasizing technological superiority, and pursuing expansion into diverse global markets. By offering unique capabilities and reducing reliance on any single customer or region, Hanwha aims to dilute the bargaining power of individual large clients and strengthen its overall market position.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Hanwha across its diverse business segments. For instance, in the highly competitive solar energy market, customers, particularly in regions with a strong presence of lower-cost Chinese manufacturers, demonstrate considerable price sensitivity. This was evident in 2024, where global solar panel prices saw fluctuations, putting pressure on margins for all players, including Hanwha Qcells.
Hanwha Qcells, in response to this price sensitivity, differentiates itself by focusing on superior product quality, higher energy conversion efficiency, and offering comprehensive, integrated solar solutions. This strategy aims to justify a premium price by delivering greater long-term value and reliability to customers, mitigating the direct impact of price-based competition.
The sheer availability of substitute products significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. For example, in the solar energy sector, Hanwha's customers can readily switch between a multitude of panel manufacturers, each offering comparable technologies. Similarly, the financial services landscape presents consumers with an abundance of choices for banking, insurance, and investment products, allowing them to easily compare and leverage better terms.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
Large customers, particularly those with substantial procurement needs across various industrial sectors, can sometimes consider backward integration. This means they might explore producing key components or services in-house rather than relying on external suppliers like Hanwha. While not a widespread threat for Hanwha's primary, highly specialized product lines, this possibility does exist in certain industrial segments where component manufacturing is more standardized.
Hanwha counters this potential threat by focusing on its operational efficiency and the unique value proposition of its specialized offerings. By consistently delivering high-quality, technologically advanced products and maintaining competitive pricing, Hanwha aims to make in-house production less attractive for its clients. For instance, in 2024, Hanwha Solutions' Chemical Division reported strong performance, driven by optimized production processes and a focus on high-demand specialty chemicals, reinforcing its competitive edge.
- Customer Integration Threat: Large buyers may consider backward integration to produce components or services themselves, particularly in industries with significant procurement volumes.
- Hanwha's Counter-Strategy: The company leverages operational efficiency and specialized product offerings to maintain its competitive advantage and deter customer integration.
- Market Focus: While not a universal concern, this threat is more relevant in specific industrial segments where component production is more commoditized.
- 2024 Performance Indicator: Hanwha Solutions' Chemical Division's strong 2024 results, attributed to efficiency and specialty product focus, highlight its ability to retain customers through superior value.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, allowing them to easily compare Hanwha's product pricing, performance metrics, and available alternatives across the market. This digital transparency significantly amplifies their ability to negotiate better terms.
For instance, in the solar panel industry, a sector Hanwha is active in, online comparison tools and customer reviews readily provide detailed performance data and price points. A report from late 2023 indicated that over 70% of consumers conduct extensive online research before making a significant purchase, directly impacting supplier selection and pricing leverage.
- Increased Information Access: Digital platforms empower customers with pricing, performance, and competitor data.
- Enhanced Negotiation Leverage: Transparency allows customers to demand competitive pricing and better value.
- Hanwha's Strategic Imperative: Maintaining competitive pricing and transparent operations is crucial for market share retention.
- Customer Relationship Management: Building strong, trust-based relationships becomes a key differentiator.
The bargaining power of Hanwha's customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitutes and the ease with which they can switch suppliers. In sectors like solar energy, numerous manufacturers offer comparable products, giving customers considerable leverage to demand better pricing and terms. This is further amplified by the increasing transparency in pricing and product performance data readily available online, empowering buyers to make informed comparisons and negotiate effectively.
| Factor | Impact on Hanwha | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High | In the solar panel market, customers can easily switch between various manufacturers offering similar technologies, increasing price pressure. |
| Customer Information Access | High | Online comparison tools and reviews allow customers to easily benchmark Hanwha's offerings against competitors, enhancing their negotiation power. |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | In competitive markets like solar, customers are sensitive to price, especially with the presence of lower-cost alternatives. Global solar panel prices experienced fluctuations in 2024, impacting margins. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Hanwha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hanwha Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase. This comprehensive analysis is ready for immediate use, providing valuable strategic insights without any hidden elements or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hanwha faces significant competitive rivalry in sectors like aerospace and defense, where giants such as Lockheed Martin and Boeing dominate. In the chemicals market, it contends with established players like BASF and Dow. This high industry concentration means Hanwha must constantly innovate and strategically acquire companies to maintain and grow its market share.
Hanwha's established chemical divisions face a challenging landscape of slow industry growth, particularly in mature markets. This stagnation naturally fuels more intense rivalry as companies vie for a limited pool of existing demand. For instance, the global petrochemical market, a key area for Hanwha, is projected to see modest growth rates in the coming years, putting pressure on margins and market share.
In response to this competitive pressure, Hanwha must strategically pivot towards higher-value-added products and explore new market avenues. Diversifying its product portfolio and geographical reach becomes crucial to mitigate the risks associated with slow growth in legacy segments. This strategic imperative is underscored by the fact that companies prioritizing innovation and niche markets often outperform those relying solely on volume in mature industries.
Industries where Hanwha operates, such as chemicals and manufacturing, inherently involve substantial fixed costs. These substantial upfront investments, for example in plant and machinery, necessitate high levels of production to achieve economies of scale and recover these costs efficiently.
Consequently, companies in these sectors are driven to maintain high capacity utilization rates. This pursuit of efficiency can intensify competition, as firms may resort to aggressive pricing strategies to fill excess capacity, particularly when market demand softens or oversupply conditions emerge. For instance, in the global petrochemical market, which Hanwha participates in, capacity utilization rates can significantly influence pricing dynamics.
Product Differentiation and Innovation
Hanwha's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by its focus on product differentiation and innovation, especially within its key sectors like solar, aerospace, and defense. In these areas, technological advancements are not just a bonus; they are fundamental to staying ahead. For instance, in the solar industry, Hanwha Q CELLS consistently pushes for higher efficiency panels, a crucial differentiator in a market flooded with similar offerings. Their investment in research and development directly combats rivals who might offer lower-priced but less advanced alternatives.
The aerospace and defense segments demand even more rigorous innovation. Hanwha's development of advanced unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and sophisticated defense systems showcases this commitment. By investing heavily in R&D, Hanwha aims to create unique capabilities that competitors struggle to replicate quickly. This strategy is vital, as rivals are constantly seeking to match or surpass technological milestones, making continuous innovation a necessity for market leadership.
- Solar Efficiency Gains: Hanwha Q CELLS has consistently improved solar panel efficiency, with some of their latest modules reaching over 23% efficiency, a key differentiator against competitors.
- Aerospace R&D Investment: In 2023, Hanwha Aerospace reported significant R&D spending dedicated to next-generation propulsion systems and advanced materials for aircraft.
- Defense Technology Advancement: The company's focus on AI-driven defense solutions and advanced missile technology provides a distinct competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving global security landscape.
- Innovation Pipeline: Hanwha's commitment to innovation is evident in its robust product development pipeline, aiming to introduce novel solutions that address emerging market needs and create new demand.
Strategic Alliances and Acquisitions by Competitors
Competitors across Hanwha's varied industries are strategically forming alliances and pursuing mergers and acquisitions. These moves are designed to bolster market share, acquire advanced technologies, and broaden their operational capabilities. For instance, in the defense sector, rivals are consolidating to offer more comprehensive solutions, a trend that intensifies rivalry.
Hanwha is actively participating in this consolidation wave. A prime example is its acquisition of Philly Shipyard, which significantly enhances its shipbuilding capacity and market position. Furthermore, Hanwha is forging strategic partnerships within the defense industry, aiming to secure new contracts and technological leadership, directly responding to competitive pressures.
- Increased Consolidation: Competitors are merging or acquiring to achieve economies of scale and scope, presenting a more formidable challenge to Hanwha.
- Technological Arms Race: Alliances are often formed to share R&D costs and accelerate the development of cutting-edge technologies, forcing Hanwha to innovate rapidly.
- Market Share Shifts: Successful acquisitions by rivals can lead to a direct loss of market share for Hanwha in specific segments.
The competitive rivalry within Hanwha's operating sectors is intense, driven by a mix of established global players and emerging innovators. In the solar energy market, Hanwha Q CELLS faces fierce competition from companies like JinkoSolar and LONGi Solar, all vying for market share through technological advancements and cost efficiencies. The aerospace and defense sectors see Hanwha competing against behemoths such as Hyundai Rotem and KAI, where significant R&D investment and government contracts are key battlegrounds.
High fixed costs in manufacturing, particularly in chemicals and shipbuilding, compel companies to operate at high capacity, often leading to price competition to fill production lines. For instance, the global shipbuilding market, where Hanwha has a presence, experienced fluctuating demand in 2023, putting pressure on pricing for new builds and repairs.
Hanwha's strategy of focusing on product differentiation through innovation, especially in high-efficiency solar panels and advanced defense systems, is crucial for navigating this rivalry. Their investment in R&D, exemplified by the development of next-generation propulsion systems in aerospace, aims to create a technological edge that competitors find difficult to match quickly.
The trend of consolidation and strategic alliances among competitors further heightens rivalry. Companies are merging to gain scale, acquire new technologies, and expand their market reach, forcing Hanwha to be agile and strategic in its own M&A activities and partnerships to maintain its competitive standing.
| Industry Sector | Key Competitors | Competitive Dynamics | Hanwha's Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | JinkoSolar, LONGi Solar, Trina Solar | Price competition, technological innovation (efficiency), supply chain management | Focus on high-efficiency panels, R&D investment, vertical integration |
| Aerospace & Defense | Hyundai Rotem, KAI, Lockheed Martin, Boeing | Technological superiority, government contracts, R&D spending, strategic alliances | Advanced technology development (UAVs, missile tech), strategic partnerships |
| Chemicals | BASF, Dow, LG Chem | Economies of scale, product specialization, sustainability initiatives | Diversification into specialty chemicals, cost optimization |
| Shipbuilding | Hyundai Heavy Industries, Samsung Heavy Industries | Order backlog, technological capabilities, cost competitiveness | Acquisition of shipbuilding assets, focus on high-value vessels |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Technological advancements in alternative materials pose a significant threat to Hanwha's chemical and materials segments. Innovations in areas like bio-based polymers or advanced composites could offer comparable or superior performance to existing petrochemical-derived products, potentially eroding market share and pricing power. For instance, the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions is driving significant investment in biodegradable and compostable alternatives to traditional plastics, a core market for many chemical companies.
Hanwha actively addresses this threat by strategically investing in research and development focused on sustainable and high-performance materials. This forward-looking approach aims to not only counter potential substitutions but also to lead in emerging material categories. In 2024, Hanwha Solutions, a key subsidiary, continued to prioritize its advanced materials division, with R&D spending allocated to areas like eco-friendly plastics and next-generation battery materials, reflecting a commitment to staying ahead of material substitution trends.
Hanwha's solar energy business faces a significant threat from emerging alternative energy technologies. Innovations in advanced wind solutions, geothermal power, and especially more efficient battery storage systems can reduce the overall demand for solar panels, impacting Hanwha's core solar PV segment.
To counter this, Hanwha is strategically expanding its clean energy portfolio beyond solar. The company is investing heavily in green hydrogen production and advanced energy storage solutions, aiming to offer a more comprehensive suite of sustainable energy options and mitigate the direct threat of substitutes.
Evolving customer preferences are a significant threat. For instance, in 2024, global consumer spending on sustainable products saw a notable increase, with reports indicating a 15% year-over-year growth in the eco-friendly goods market. This shift directly pressures companies like Hanwha to adapt their product lines towards more environmentally conscious options, potentially making existing offerings less competitive if they don't align with these new demands.
Regulatory changes further amplify this threat. New environmental regulations, such as stricter emissions standards or mandates for recycled content, can rapidly alter the landscape. For example, the European Union's proposed regulations on plastic packaging, set to be fully implemented by 2025, could significantly impact industries reliant on traditional materials, encouraging a faster transition to substitutes that meet these new compliance requirements.
Hanwha must proactively address these trends by innovating its offerings. A strategic focus on developing and promoting eco-friendly products and embracing circular economy principles is crucial. This includes exploring biodegradable materials and implementing robust recycling programs, which can not only mitigate the threat of substitutes but also create new market opportunities.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitutes presents a significant threat to Hanwha, especially in its industrial and materials divisions. When alternative products or services provide similar utility at a substantially lower price point, customers are naturally inclined to switch. This dynamic is particularly acute in sectors where price is a primary driver of purchasing decisions.
For Hanwha, this necessitates a dual focus: relentless optimization of internal production costs to remain competitive and a clear articulation of the superior value proposition its offerings provide. By demonstrating enhanced performance, durability, or unique features, Hanwha can justify its pricing and mitigate the allure of cheaper substitutes.
- Price Sensitivity: In markets like basic chemicals or construction materials, where Hanwha operates, price is often the dominant factor. For instance, the global commodity chemical market, where Hanwha is active, saw price volatility in 2024, making lower-cost alternatives more attractive.
- Functionality Equivalence: If a substitute can perform the same core function as Hanwha's product, even with minor differences, the cost advantage becomes a powerful differentiator.
- Value Demonstration: Hanwha's strategy must emphasize total cost of ownership, reliability, and innovation to counter the immediate appeal of lower-priced, potentially less robust, alternatives.
Integrated Solutions vs. Component-Level Substitution
Hanwha's strategic focus on delivering integrated solutions, like end-to-end solar energy packages encompassing modules and Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) services, effectively mitigates the threat posed by substitute components. This approach aims to create a stickier customer base by offering a more complete and valuable proposition than sourcing individual parts.
By bundling services and products, Hanwha differentiates itself from competitors who might only offer basic components. This integration makes it more challenging for customers to switch to alternative, unbundled solutions, thereby strengthening Hanwha's market position.
- Integrated Solutions: Hanwha's offering of complete solar energy systems, including modules and EPC services, reduces reliance on individual component suppliers.
- Customer Lock-in: This comprehensive approach aims to increase customer loyalty and make it harder for them to switch to less integrated alternatives.
- Value Proposition: By providing a seamless, end-to-end experience, Hanwha enhances its value beyond just the hardware, making component-level substitution less appealing.
The threat of substitutes for Hanwha's products is multifaceted, stemming from technological advancements, evolving customer preferences, and regulatory shifts. Innovations in areas like bio-based polymers and advanced wind energy solutions directly challenge Hanwha's chemical and solar divisions, respectively. For instance, the 2024 market saw a continued surge in demand for sustainable packaging, pushing alternatives to conventional plastics. Furthermore, increasing global consumer spending on eco-friendly goods, estimated to have grown by 15% year-over-year in 2024, pressures Hanwha to adapt its offerings to align with these changing preferences.
Hanwha is actively mitigating these threats through strategic R&D and portfolio diversification. The company is investing in eco-friendly materials and expanding its clean energy offerings to include green hydrogen and advanced energy storage. This proactive approach aims to not only counter substitution but also to lead in emerging markets. For example, Hanwha Solutions' increased R&D allocation in 2024 towards eco-friendly plastics and battery materials underscores this commitment.
The cost-effectiveness of substitutes also poses a significant challenge, particularly in Hanwha's materials segments where price sensitivity is high. In 2024, the volatile global commodity chemical market made lower-cost alternatives more attractive to customers. Hanwha counters this by optimizing production costs and highlighting its products' superior value proposition, focusing on total cost of ownership and reliability to retain market share against cheaper, potentially less robust, alternatives.
| Threat Area | Impact on Hanwha | Mitigation Strategy | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements (Materials) | Erosion of market share in petrochemicals due to bio-based polymers, advanced composites. | R&D investment in sustainable and high-performance materials. | Growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. |
| Alternative Energy Technologies | Reduced demand for solar panels from advanced wind, geothermal, and battery storage. | Expansion into green hydrogen and advanced energy storage solutions. | Increased focus on comprehensive clean energy portfolios. |
| Evolving Customer Preferences | Pressure to adopt eco-friendly product lines; existing offerings may become less competitive. | Innovation and promotion of eco-friendly products; embracing circular economy principles. | 15% year-over-year growth in the eco-friendly goods market in 2024. |
| Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes | Customer switching due to lower price points in commodity chemical and construction material markets. | Production cost optimization; demonstrating superior value proposition (durability, performance). | Price volatility in the global commodity chemical market in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Hanwha's involvement in sectors like aerospace, defense, chemicals, and large-scale solar manufacturing necessitates immense capital outlays. For instance, establishing a new aerospace manufacturing facility can easily run into billions of dollars, covering advanced machinery, specialized tooling, and extensive testing infrastructure.
The sheer financial commitment for state-of-the-art facilities, ongoing research and development, and rigorous regulatory adherence presents a formidable hurdle for any new player. This high entry cost effectively deters potential competitors from entering these lucrative but capital-demanding markets.
Hanwha's significant economies of scale present a formidable barrier to new entrants. For instance, in its solar energy division, Hanwha Q CELLS achieved a global module production capacity of 12.4 GW in 2023, allowing for lower per-unit manufacturing costs that are difficult for smaller, newer companies to replicate.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. Having operated for decades across diverse sectors, Hanwha has honed its processes, leading to greater efficiency and reduced costs over time. A new player would need substantial initial investment and time to develop comparable operational expertise and cost structures.
Hanwha's established brand recognition and deep customer loyalty, especially within South Korea, act as a significant barrier to new entrants. Developing comparable trust and affinity in markets where Hanwha operates would require substantial investment and time, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
New players face significant challenges in establishing and accessing the distribution channels and supply chains that Hanwha has cultivated. For instance, Hanwha's involvement in sectors like aerospace and defense often necessitates long-term relationships with specialized suppliers and government entities, creating a high barrier to entry.
Securing reliable access to critical components, such as advanced semiconductors or specialized alloys, is another substantial hurdle. Hanwha's established procurement networks and bulk purchasing power allow it to negotiate favorable terms, making it difficult for newcomers to match these cost efficiencies.
- Established Networks: Hanwha's extensive global distribution network, built over decades, provides immediate market reach that new entrants would struggle to replicate.
- Supply Chain Control: Hanwha's strategic partnerships and vertical integration in certain areas of its supply chain offer a competitive advantage in terms of cost and reliability.
- Regulatory Hurdles: In many of Hanwha's key industries, such as defense, access to supply chains is often restricted by government regulations and security clearances, which are difficult for new companies to obtain.
Government Regulations and Policy Hurdles
Government regulations and policy hurdles significantly impact the threat of new entrants, particularly in sectors like defense, financial services, and specific chemical industries. These fields often demand extensive certifications, licenses, and rigorous adherence to safety and environmental standards, creating substantial barriers.
For instance, in the defense sector, companies must navigate complex export controls and security clearances. In 2024, the global defense market was valued at approximately $2.2 trillion, with stringent regulatory frameworks being a key characteristic that limits new players. Similarly, financial services in 2024 faced evolving compliance demands related to data privacy and anti-money laundering, adding to the cost and complexity of market entry.
- Defense Sector: High capital investment and lengthy approval processes deter new entrants.
- Financial Services: Evolving regulations like those concerning digital assets in 2024 increase compliance burdens.
- Chemical Industry: Strict environmental permits and safety protocols require significant upfront investment and expertise.
- Foreign Companies: Navigating diverse and often stringent national regulations presents a formidable challenge for international businesses seeking to enter these markets.
The threat of new entrants for Hanwha is generally low due to substantial capital requirements and significant economies of scale. For example, establishing advanced manufacturing facilities in aerospace or defense can cost billions, a prohibitive sum for most newcomers. Hanwha's global production capacity in solar, reaching 12.4 GW in 2023, allows it to achieve cost efficiencies that new entrants struggle to match.
Furthermore, established brand loyalty, intricate distribution networks, and control over supply chains present considerable barriers. In sectors like defense, stringent government regulations and security clearances, a common feature in the $2.2 trillion global defense market in 2024, also deter new participants. Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes requires substantial time, investment, and expertise.
Hanwha's deep experience curve, leading to optimized processes and reduced costs, also acts as a deterrent. New companies would need considerable time and investment to develop comparable operational efficiencies. The need for specialized knowledge and long-term relationships with suppliers and government entities in many of Hanwha's core industries further solidifies these entry barriers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hanwha leverages a robust combination of primary and secondary data. This includes Hanwha's official investor relations materials, annual reports, and competitor filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and macroeconomic data from reputable sources.
