Hancock Whitney Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hancock Whitney Bundle
Hancock Whitney operates within a dynamic banking landscape, facing pressures from competitors and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the intricate web of influences shaping Hancock Whitney's market. Discover the true power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the strategic leverage of suppliers.
Ready to gain a competitive edge? Unlock the complete analysis to uncover actionable insights and make informed decisions about Hancock Whitney's future.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology and software providers, especially those specializing in core banking systems, cybersecurity, and AI, wield considerable influence over financial institutions like Hancock Whitney. These critical systems are the backbone of modern banking operations, making them indispensable. The complexity and expense involved in migrating from one vendor to another, particularly as banks invest heavily in digital transformation throughout 2024 and 2025, significantly increases switching costs and supplier leverage.
Suppliers of financial data, market intelligence, and analytics are essential for Hancock Whitney's operations. The quality and uniqueness of this information directly impact their ability to make sound decisions and manage risks effectively. For instance, in 2024, the global big data and business analytics market was projected to reach over $370 billion, highlighting the immense value placed on such services.
Hancock Whitney's competitive edge increasingly depends on timely and accurate data. Providers offering proprietary or highly specialized analytics can hold considerable sway. This is particularly true as the demand for data-driven insights continues to surge through 2025, allowing these suppliers to potentially dictate terms and pricing.
Hancock Whitney, like all financial institutions, operates within a heavily regulated environment. Staying compliant with ever-changing laws and guidelines is not just important; it's critical. This necessitates engaging specialized legal, audit, and consulting services. The banking sector, particularly in 2025, is experiencing significant shifts and increased scrutiny in areas like cybersecurity, data protection, and the governance of artificial intelligence.
These professional service providers, with their deep expertise and established reputations, wield considerable bargaining power. Their ability to help banks like Hancock Whitney navigate this complex and evolving regulatory landscape means their services are in high demand. For instance, the global regulatory compliance market was valued at approximately $70 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow significantly, underscoring the importance and value of these specialized consultants.
Human Capital (Skilled Labor)
The availability of skilled professionals, particularly in rapidly evolving fields like cybersecurity, data science, AI development, and digital banking, significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers within the financial sector. A scarcity of these specialized talents can directly lead to increased labor costs and hinder a bank's capacity for innovation and competitive positioning.
In 2024 and into 2025, the demand for these advanced skills within the financial industry is particularly robust. This high demand translates into considerable bargaining power for employees possessing these in-demand capabilities, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms, compensation, and benefits.
- Cybersecurity talent shortage: Reports from 2023 indicated a global cybersecurity workforce gap of approximately 3.4 million professionals, a figure expected to persist.
- Data Scientist demand: LinkedIn data from late 2023 and early 2024 consistently ranked data scientist roles among the most sought-after in the tech and finance sectors.
- AI development growth: The global AI market was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion by 2030, with significant investment in AI talent driving up demand and compensation for developers.
- Digital banking expertise: As banks increasingly invest in digital transformation, experienced professionals in digital product management and user experience design command premium salaries.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers like Visa and Mastercard hold significant bargaining power over banks such as Hancock Whitney. Their extensive networks and established brand recognition create strong network effects, making it difficult for new entrants to compete. This dominance allows them to dictate terms and fees for transaction processing, impacting Hancock Whitney's profitability in its card services division.
In 2024, the fees charged by these networks continue to be a key cost for financial institutions. For instance, interchange fees, a primary revenue source for banks, are largely determined by the payment networks. These fees can fluctuate based on network policies and market conditions, directly influencing Hancock Whitney's revenue streams from credit and debit card transactions.
- Network Dominance: Visa and Mastercard process a vast majority of card transactions, giving them leverage over financial institutions.
- High Switching Costs: Banks face substantial costs and operational challenges when attempting to switch payment networks.
- Fee Setting Power: Payment networks largely control the interchange fees and other service charges that banks incur.
- Impact on Profitability: These fees directly affect Hancock Whitney's net interest income and fee-based revenue from card services.
Suppliers of specialized technology and data, particularly those in cybersecurity and AI, possess significant leverage over financial institutions like Hancock Whitney. The high costs and complexity associated with switching these core systems, especially with ongoing digital transformation efforts in 2024-2025, solidify supplier influence.
Providers of essential financial data and analytics also wield considerable power, as the uniqueness and quality of their information directly impact a bank's decision-making and risk management capabilities. The global big data and business analytics market's projected growth to over $370 billion in 2024 underscores the value placed on these services.
The bargaining power of suppliers is further amplified by the critical need for specialized professional services, such as legal and compliance experts, to navigate the complex regulatory landscape of the banking sector. The global regulatory compliance market, valued around $70 billion in 2024, highlights the demand for these indispensable services.
Finally, the scarcity of skilled talent in areas like cybersecurity, data science, and AI development in 2024-2025 grants significant leverage to suppliers of human capital, allowing them to command higher wages and dictate terms, impacting overall operational costs for banks.
What is included in the product
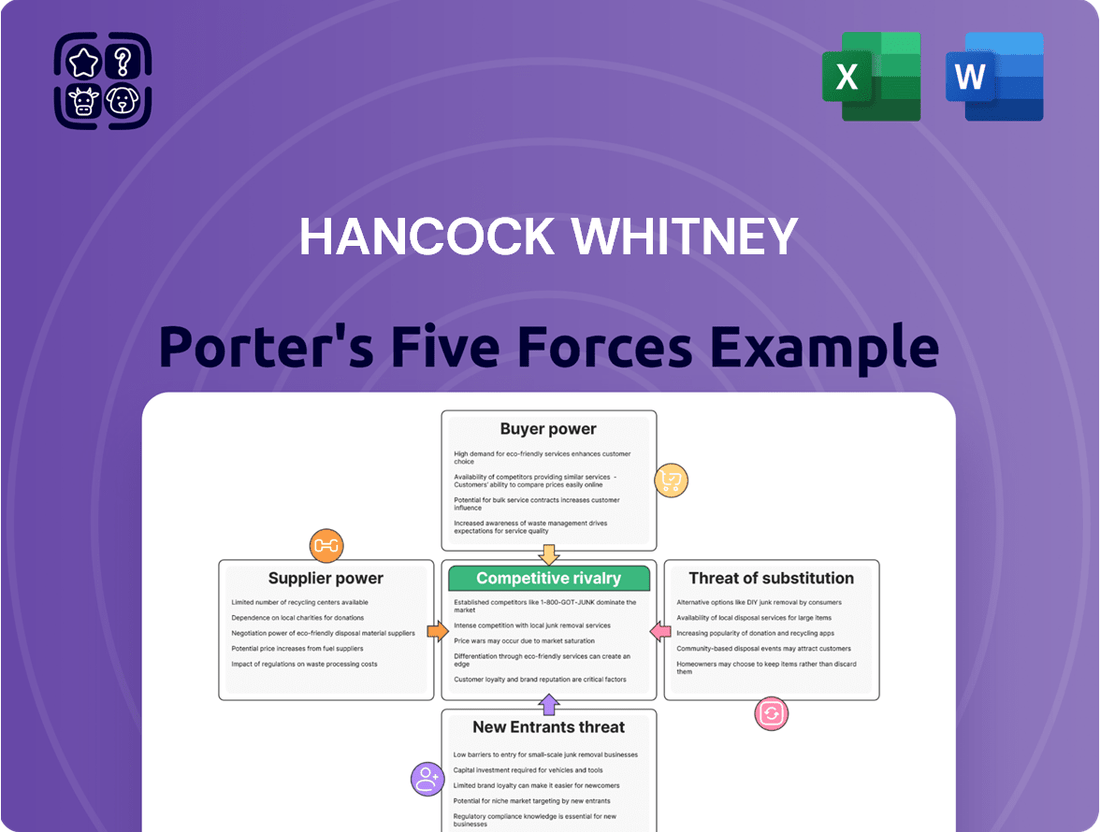
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Hancock Whitney, examining industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the influence of substitute products.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a clear, intuitive dashboard, simplifying complex market dynamics for faster, more informed strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
For typical banking needs like deposits and loans, individual and small business customers usually have a moderate ability to influence prices. While switching banks is an option, the hassle involved and existing ties can make them hesitant. However, the banking landscape in 2024 and 2025, with more digital banks and clearer fee structures, allows these customers to easily shop around. This makes it easier for them to push for better rates and service, increasing their bargaining power.
Larger commercial and corporate clients wield significant bargaining power, often driven by the substantial volume of business they bring to institutions like Hancock Whitney. These sophisticated clients frequently maintain relationships with several financial institutions, enabling them to negotiate more advantageous terms on crucial services such as loans and treasury management.
For Hancock Whitney, retaining and attracting these high-value clients hinges on its capacity to deliver customized financial solutions and maintain competitive pricing structures. In 2024, the banking sector saw continued emphasis on client retention, with fee income from corporate services remaining a key revenue driver for many regional banks.
Clients seeking private banking, trust, and investment management services typically possess considerable wealth. This substantial asset base translates into significant bargaining power, as they expect tailored services, strong investment returns, and competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, the average assets under management for high-net-worth individuals in the US were reported to be over $1 million, highlighting the financial clout of this demographic.
These affluent clients are discerning and demand personalized attention, superior investment performance, and transparent, attractive fee structures. Hancock Whitney’s strategic acquisition of Sabal Trust Company, finalized in 2025, directly addresses the need to bolster its capabilities in serving these influential clients, underscoring the competitive imperative to cater to their sophisticated requirements.
Digital-Savvy Customers
Digital-savvy customers wield significant power due to the widespread adoption of online and mobile banking. These customers expect seamless digital experiences, prioritizing convenience and access to a comprehensive suite of services through banking apps. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 70% of retail banking transactions in the US were conducted digitally, highlighting this shift.
Financial institutions like Hancock Whitney must continuously enhance their digital offerings to retain these customers. Failure to keep pace with technological advancements and user expectations can lead to customers migrating to competitors, including agile fintech companies that excel in digital service delivery. This ongoing investment in digital infrastructure is crucial for maintaining market share and customer loyalty.
- Digital Adoption: Over 70% of US retail banking transactions were digital by the close of 2023.
- Customer Expectations: Demand for convenience, seamless apps, and broad digital service access is high.
- Competitive Landscape: Fintechs pose a threat by offering superior digital experiences.
- Strategic Imperative: Continuous investment in digital platforms is essential for customer retention.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
In a dynamic interest rate climate, customers with substantial deposits or loan needs closely monitor offerings from various financial institutions. If Hancock Whitney's deposit rates lag behind competitors, there's a tangible risk of funds being redirected to other banks or investment products. For instance, as of early 2024, the Federal Reserve maintained a target federal funds rate range of 5.25%-5.50%, influencing deposit yields across the industry. This sensitivity directly impacts a bank's ability to retain core deposits, a crucial funding source.
Conversely, while attractive loan rates can draw in borrowers, this also exerts downward pressure on Hancock Whitney's net interest margin. The bank must balance offering competitive loan pricing to capture market share with maintaining profitability. In 2023, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage hovered around 6.8%, a figure that directly influences borrower decisions and bank lending strategies.
- Customer sensitivity to interest rates increases when rates fluctuate significantly.
- Non-competitive deposit rates can lead to customer attrition, impacting funding stability.
- Aggressive loan pricing, while attracting borrowers, can compress net interest margins.
- The Federal Reserve's monetary policy, such as the 5.25%-5.50% target rate in early 2024, directly influences customer behavior and bank profitability.
Customers, especially those with significant financial needs or digital savviness, possess considerable bargaining power. This is amplified by the ease of comparing services and rates in 2024, particularly with the rise of digital banking options. While switching costs exist, the increasing transparency and availability of alternatives empower customers to negotiate better terms, impacting Hancock Whitney's pricing and service delivery.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Hancock Whitney (2024-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Individual & Small Business | Ease of comparison, digital options, switching hassle | Moderate power; pressure on rates and service fees |
| Large Commercial & Corporate | High volume, multiple banking relationships, negotiation expertise | Significant power; demand for customized solutions and competitive pricing |
| Affluent (Private Banking) | Substantial wealth, demand for tailored services, investment performance | Considerable power; expectation of personalized attention and attractive fees |
| Digital-Savvy | Preference for convenience, seamless apps, fintech competition | High power; necessitates continuous digital platform investment |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hancock Whitney Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version of Hancock Whitney's Porter's Five Forces analysis. The document you see here is precisely the same comprehensive report that will be available to you instantly after completing your purchase, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hancock Whitney, a significant regional player across five Gulf Coast states, contends with robust competition from numerous other regional and community banks. This competitive landscape is shaped by factors like deep local market understanding, tailored customer service, and strong community relationships, which are crucial differentiators.
The intensity of this rivalry is evident as these institutions often compete on personalized service and community engagement. For instance, many community banks pride themselves on local decision-making and a direct connection with their customers, a stark contrast to larger, more centralized operations.
Looking ahead to 2025, the regional banking sector is anticipating a wave of mergers and acquisitions, alongside evolving regulatory environments. These dynamics could potentially empower smaller, more agile institutions, further intensifying the competitive pressures faced by larger regional banks like Hancock Whitney.
Hancock Whitney, while strong in its regional markets, faces significant competition from large national and global banks. These behemoths possess vast resources, enabling them to offer a wider array of products and services, from sophisticated wealth management to international trade finance.
These larger institutions often have a distinct advantage due to economies of scale and cutting-edge technology. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to invest heavily in digital transformation, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency, which smaller or regionally focused banks must constantly strive to match.
The competitive pressure from these national and global players is persistent. Their substantial marketing budgets allow them to reach a broader customer base and build brand recognition, creating a challenging landscape for regional banks like Hancock Whitney to navigate in terms of customer acquisition and retention.
The competitive landscape for Hancock Whitney is intensifying due to the surge of fintech companies and digital-first banks. These agile players, often unburdened by legacy systems, are rapidly gaining market share by offering streamlined digital experiences, competitive pricing, and innovative solutions in areas like payments and lending.
By 2024, the fintech sector is projected to process trillions in transactions globally, with digital banks consistently outperforming traditional institutions in customer acquisition and satisfaction metrics. For instance, neobanks have seen substantial growth in user bases, with some reporting over 10 million customers in key markets by early 2025.
Hancock Whitney faces direct competition in core banking services, forcing a strategic imperative to accelerate its own digital transformation. This includes enhancing mobile banking capabilities, optimizing online account opening processes, and potentially integrating AI-driven customer service to match the seamless, user-centric approach of these disruptors.
Product and Service Differentiation
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector is intensely focused on the breadth and quality of products and services. Hancock Whitney differentiates itself with a comprehensive suite that includes private banking, trust services, and investment management, aiming to attract a diverse clientele.
However, the competitive landscape is dynamic, with rivals consistently innovating. They introduce new banking products, enhance digital platforms, and offer more appealing terms to customers. This necessitates continuous adaptation from Hancock Whitney to maintain its competitive edge and customer engagement.
- Product Breadth: Hancock Whitney offers a wide range of services, from basic checking and savings to more complex offerings like wealth management.
- Service Quality: The bank emphasizes personalized customer service, a key differentiator in a commoditized industry.
- Digital Innovation: Competitors are rapidly improving online and mobile banking capabilities, forcing Hancock Whitney to invest in its own digital infrastructure.
- Pricing and Terms: Attractive interest rates on deposits and competitive loan terms are constantly being introduced by rivals, pressuring margins.
Geographic Market Concentration
Hancock Whitney's competitive rivalry is heavily influenced by its geographic concentration in the Gulf Coast states. This means that the intensity of competition for both deposits and loans can differ substantially from one local market to another. In areas where banking services are already plentiful, the struggle for customers can become quite aggressive, often leading to tighter profit margins for all involved.
For instance, in markets with a higher banking density, Hancock Whitney might face intensified competition, potentially impacting its net interest margin. The company's strategic move to expand into new, growing markets, such as Dallas, Texas, is a direct response to this localized competitive pressure. This expansion, slated for 2025, is designed to diversify its market presence and reduce reliance on areas with concentrated banking activity.
- Localized Competition: Hancock Whitney's Gulf Coast focus means rivalry intensity varies by local market.
- Margin Pressure: High banking density in certain areas leads to fierce competition for deposits and loans, squeezing profit margins.
- Strategic Expansion: Plans for 2025 include entering high-growth markets like Dallas, Texas, to counter localized competitive intensity.
Hancock Whitney faces intense rivalry from a diverse set of competitors, ranging from large national banks with extensive resources to agile fintech firms and community banks deeply entrenched in local markets. This multifaceted competition necessitates continuous innovation in product offerings, service quality, and digital capabilities to maintain market share and profitability.
The pressure is particularly acute in areas of high banking density, where competition for deposits and loans can significantly impact profit margins. For example, in 2024, many regional banks reported increased competition on deposit pricing, with average savings account rates rising to attract and retain customer funds.
Hancock Whitney's strategic expansion into markets like Dallas by 2025 is a direct response to mitigate the impact of localized competitive intensity and diversify its revenue streams. This move aims to capture growth in less saturated markets, thereby reducing its vulnerability to intense rivalry in its core Gulf Coast region.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Factors | Hancock Whitney's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Regional/Community Banks | Local relationships, personalized service | Emphasize community engagement, tailored solutions |
| National/Global Banks | Economies of scale, broad product suite, technology | Invest in digital transformation, enhance service offerings |
| Fintech Companies | Digital-first experience, innovation, competitive pricing | Accelerate digital platform development, improve mobile banking |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Credit unions present a significant threat of substitution for Hancock Whitney. These member-owned cooperatives offer a comparable suite of financial products and services, including checking and savings accounts, mortgages, and personal loans. Their non-profit structure often allows them to provide more competitive rates and lower fees, appealing to cost-conscious consumers.
In 2024, the credit union movement continued its robust growth, with total assets reaching over $2.4 trillion by the end of the first quarter, according to the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA). This expansion signifies their increasing appeal as an alternative to traditional banks, especially for individuals and small businesses prioritizing community focus and member benefits over large corporate banking structures.
Online lending platforms and peer-to-peer services present a formidable threat to traditional banks like Hancock Whitney. For personal, small business, and mortgage loans, these digital alternatives often provide a faster, more user-friendly experience. For instance, by mid-2024, fintech lenders continued to capture market share, with some platforms reporting application approval times measured in minutes rather than days, directly challenging the established pace of bank lending.
Customers looking for wealth management have many choices beyond Hancock Whitney's offerings. Independent investment firms and brokerage houses present direct competition, providing specialized services. The rise of robo-advisors, which leverage technology for low-cost investment management, further intensifies this threat, attracting a growing segment of investors seeking automated, affordable solutions.
Alternative Payment Systems
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking payment systems is intensifying. Digital wallets and mobile payment apps like Apple Pay and Google Pay are becoming increasingly popular, offering users a streamlined and often faster way to conduct transactions. For instance, Zelle, a peer-to-peer payment network owned by a consortium of major U.S. banks, facilitated over $700 billion in payments in 2023, demonstrating a significant shift in transaction behavior.
These alternative payment methods can bypass traditional bank infrastructure, reducing customer reliance on bank accounts for everyday purchases and money transfers. Venmo, another popular peer-to-peer payment service, saw its payment volume reach $246 billion in 2023. This growing adoption means customers may see less need for traditional debit or credit cards linked directly to their bank accounts.
Furthermore, the emergence and evolving acceptance of cryptocurrencies, while still nascent for widespread daily use, represent a potential long-term substitute for conventional payment rails. This diversification of payment options puts pressure on traditional banks to innovate and adapt their own payment services to remain competitive and retain customer engagement.
- Digital Wallets and Mobile Payment Apps: Increasing adoption offers convenience and speed, potentially reducing reliance on traditional bank accounts.
- Zelle's Growth: Facilitated over $700 billion in payments in 2023, highlighting a substantial shift in transaction patterns.
- Venmo's Payment Volume: Reached $246 billion in 2023, showcasing the growing popularity of peer-to-peer payment services.
- Cryptocurrency Potential: Represents a future, albeit currently limited, substitute for conventional payment methods.
Direct-to-Consumer Financial Products
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services is growing significantly. Many non-bank companies are now offering specialized financial products directly to consumers, effectively cutting out the middleman. This means you can get a mortgage from a direct lender or insurance from a provider that isn't a bank, for example.
This trend is particularly evident in areas like lending and insurance. For instance, the direct-to-consumer mortgage market has seen substantial growth, with companies leveraging technology to streamline the application and approval process. By 2024, fintech lenders are projected to capture an even larger share of the mortgage market, offering competitive rates and faster closing times compared to some traditional banks.
- Direct Mortgage Lenders: Companies like Rocket Mortgage and Better.com bypass traditional bank branches, offering online-first mortgage origination.
- Insurtech Providers: Digital-native insurance companies such as Lemonade offer streamlined policy management and claims processing.
- Embedded Finance: Financial services, like buy-now-pay-later options from Affirm or Klarna, are integrated directly into e-commerce checkout experiences.
- Robo-advisors: Platforms like Betterment and Wealthfront provide automated investment management, substituting for traditional financial advisors.
The threat of substitutes for Hancock Whitney is multifaceted, encompassing credit unions, online lending platforms, wealth management alternatives, and evolving payment systems. These alternatives often offer competitive rates, lower fees, greater convenience, or specialized services that directly challenge traditional banking models.
By mid-2024, credit unions continued their expansion, holding over $2.4 trillion in assets, indicating their growing appeal. Fintech lenders are also capturing market share, with some approving loans in minutes. Robo-advisors are attracting investors with low-cost, automated solutions, while digital payment apps like Zelle and Venmo processed hundreds of billions in transactions in 2023, reducing reliance on traditional bank accounts.
| Substitute Category | Key Players/Examples | 2023-2024 Data/Trends | Impact on Hancock Whitney |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Unions | Navy Federal Credit Union, Pentagon Federal Credit Union | Over $2.4 trillion in total assets (Q1 2024) | Offer competitive rates and lower fees, attracting cost-conscious customers. |
| Online Lending Platforms | Rocket Mortgage, LendingClub, Prosper | Fintech lenders projected to increase mortgage market share; rapid loan approval times. | Disintermediate traditional loan origination, offering faster and potentially cheaper alternatives. |
| Wealth Management Alternatives | Charles Schwab, Vanguard, Betterment | Robo-advisors gaining traction for automated, low-cost investment management. | Attract investors seeking efficient and affordable wealth management services. |
| Payment Systems | Zelle, Venmo, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay | Zelle: $700+ billion in payments (2023); Venmo: $246 billion payment volume (2023). | Reduce customer reliance on traditional banking for everyday transactions. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into the banking sector, particularly from fintech startups and neobanks, remains a significant concern for established institutions like Hancock Whitney. These digital-native companies often operate with lower overheads and a greater capacity for rapid innovation, allowing them to disrupt traditional banking models.
In 2024, the fintech landscape continued to flourish, with venture capital funding for fintech companies remaining robust, indicating a sustained appetite for new digital financial solutions. For instance, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion by 2024, demonstrating the immense growth potential and the scale of competition these new entrants represent.
These agile players frequently target underserved customer segments or offer specialized services, such as streamlined payment processing or digital lending, often at more competitive pricing. Their ability to quickly adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements poses a direct challenge to the market share of incumbent banks.
Tech giants like Apple, Google, and Amazon are increasingly encroaching on financial services, leveraging their massive user bases and data analytics. For instance, Apple Card, launched in 2019, has quickly amassed millions of users, demonstrating the potential for tech firms to capture significant market share in areas like credit and payments. Their ability to integrate financial offerings seamlessly into existing ecosystems presents a formidable challenge to traditional financial institutions.
The banking sector, while traditionally protected by stringent regulations, licensing, and substantial capital requirements, is seeing shifts that could alter entry barriers. For instance, open banking frameworks, increasingly adopted globally, aim to democratize financial data access, potentially easing some of the hurdles for innovative fintech firms. However, the dynamic regulatory environment in 2025 continues to present both challenges and opportunities for new players looking to enter the market.
Low Switching Costs in Certain Segments
For certain basic banking services, customers face low switching costs. The increasing prevalence of digital account opening and effortless fund transfers means consumers can move their business with minimal friction. This ease of transition allows new players, particularly those with strong digital platforms or competitive interest rates, to attract customers swiftly.
This is especially true for younger, digitally-savvy customers. For instance, in 2024, the digital banking sector continued its rapid expansion, with many neobanks and fintech companies reporting significant user growth. These entities often leverage lower overheads to offer more attractive terms, directly challenging traditional institutions where switching might involve more complex processes.
- Low Switching Costs: Facilitates easier customer acquisition for new entrants in basic banking services.
- Digital Onboarding: Streamlined digital processes reduce friction for customers changing banks.
- Fintech Competition: Digital-native banks can quickly gain market share by offering competitive rates and user experiences.
- Demographic Shift: Younger, tech-oriented customers are more likely to switch for digital convenience and better offers.
Access to Capital and Talent
The threat of new entrants into the banking sector, particularly for institutions like Hancock Whitney, is influenced by evolving access to capital and talent. While traditional banking demands substantial capital, many fintech startups have successfully secured significant funding from venture capital, with global fintech funding reaching approximately $20 billion in the first half of 2024, indicating a strong appetite for innovation in the sector.
Furthermore, the proliferation of cloud-based infrastructure and API-driven financial services has demonstrably lowered the initial technology investment barrier. This allows new players to build and scale operations more efficiently than in the past. For instance, companies leveraging cloud platforms can reduce their infrastructure costs by an estimated 30-40% compared to on-premise solutions.
However, a persistent challenge for all participants, including established banks and new entrants alike, is the intense competition for top talent. Specialized roles in areas like cybersecurity, data science, and AI are in high demand, with average salaries for AI engineers in the financial sector potentially exceeding $150,000 annually in 2024, creating a significant hurdle for any new entity aiming to build a competitive technological edge.
- Fintech Funding: Global fintech funding saw around $20 billion in H1 2024.
- Cloud Cost Savings: Cloud adoption can reduce infrastructure costs by 30-40%.
- Talent Demand: High demand for AI engineers with average salaries over $150,000 in finance.
The threat of new entrants for Hancock Whitney is moderate but growing, driven by lower barriers to entry in certain banking segments and the rise of agile fintech competitors. While significant capital and regulatory hurdles remain for full-service banking, specialized financial services are more accessible.
In 2024, the fintech sector continued to attract substantial investment, with global fintech funding reaching approximately $20 billion in the first half of the year. This influx of capital allows new players to develop innovative digital platforms and customer acquisition strategies, directly challenging incumbent institutions by offering streamlined services and competitive pricing, particularly to younger demographics.
The ease with which customers can switch providers for basic banking services, facilitated by digital onboarding and seamless fund transfers, further empowers new entrants. This low switching cost, combined with the increasing digital savviness of consumers, means that fintechs and neobanks can rapidly gain market share by focusing on user experience and attractive offers.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to Hancock Whitney |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Funding (H1 2024) | ~$20 billion | Indicates strong capital availability for new competitors. |
| Cloud Infrastructure Savings | 30-40% reduction in costs | Lowers operational overhead for digital-first entrants. |
| AI Engineer Salaries (Finance, 2024) | >$150,000 annually | Highlights the high cost of acquiring essential tech talent, a challenge for both new and established players. |
| Global Fintech Market Projection (2024) | >$1.1 trillion | Illustrates the significant market size and growth potential for new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hancock Whitney is built upon a foundation of verified data, including their annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
