GSK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GSK Bundle
GSK navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the influence of suppliers and the availability of substitutes is crucial for any competitor in this sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore GSK’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
GSK's reliance on highly specialized raw materials and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) significantly influences supplier power. For instance, the development and production of complex biological therapies often require unique compounds with very few, if any, qualified manufacturers.
The limited number of approved suppliers for these critical components, particularly for patented or cutting-edge biological ingredients, grants them considerable leverage. This scarcity directly translates into suppliers having more power to dictate pricing and contract terms.
Switching costs for GSK are substantial when it comes to these specialized materials. Stringent regulatory approvals and rigorous quality assurance processes mean that changing suppliers is not a simple or quick undertaking, further solidifying supplier bargaining power.
Suppliers of proprietary manufacturing equipment and advanced technologies crucial for producing complex pharmaceuticals, like those GSK develops, wield significant influence. These specialized, often patented, machines and processes are not readily available from multiple sources, creating a dependency for GSK.
This reliance can translate into higher acquisition costs and less flexible terms for GSK when procuring or servicing these essential assets. For instance, the specialized bioreactors or sterile filling lines required for biologics production can have limited suppliers, giving them leverage.
GSK relies on Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for clinical trials and Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) for specialized drug production. The availability of highly qualified and compliant CROs/CMOs for specific or niche services can be limited.
This scarcity of specialized providers gives them significant bargaining power. They can often command higher fees, especially when GSK requires unique expertise or when industry-wide demand for these services is elevated.
For example, in 2024, the global CRO market was valued at over $50 billion, with growth driven by the increasing complexity of drug development and outsourcing trends. A concentrated segment within this market, serving highly specialized needs, would possess even greater leverage.
Skilled Labor and R&D Talent
The biopharmaceutical sector, including companies like GSK, is intensely dependent on a workforce possessing specialized scientific, research, and manufacturing expertise. This reliance on human capital means that the bargaining power of skilled labor and R&D talent is substantial.
A scarcity of professionals with niche skills, especially in rapidly advancing areas such as gene editing or personalized medicine, directly impacts GSK by escalating recruitment expenses and lengthening hiring timelines. These specialized individuals, acting as critical suppliers of intellectual and operational capability, consequently wield significant influence over compensation packages and employment terms.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Fields like oncology, immunology, and neuroscience consistently see high demand for researchers and scientists, driving up compensation.
- Impact on R&D Costs: In 2023, the global biopharmaceutical R&D spending reached an estimated $200 billion, with talent acquisition being a significant component.
- Talent Retention Challenges: Companies face pressure to offer competitive salaries and benefits to retain top talent, as competitors actively recruit skilled professionals.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Suppliers to the pharmaceutical sector face rigorous regulatory hurdles, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and approvals from bodies like the FDA and EMA. These compliance demands necessitate substantial capital outlay for suppliers, effectively raising the barrier to entry for new players and increasing the cost for pharmaceutical companies like GSK to switch suppliers. This situation naturally bolsters the leverage of established, compliant suppliers, enabling them to exert more influence on pricing and contract terms.
The financial commitment to maintaining regulatory adherence means that suppliers of critical raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) often operate with higher overheads. For instance, maintaining GMP certification can involve millions of dollars in facility upgrades and ongoing quality control processes. This financial burden translates into higher prices for their products, as these costs are factored into their pricing models.
- High Compliance Costs: Suppliers must invest heavily in quality assurance, validation, and documentation to meet pharmaceutical industry standards.
- Barriers to Entry: The significant upfront investment required to achieve and maintain regulatory compliance deters potential new suppliers from entering the market.
- Increased Switching Costs: Pharmaceutical companies face substantial costs and risks associated with vetting and onboarding new suppliers, making it expensive to switch from existing, compliant partners.
- Pricing Power: Compliant suppliers can command higher prices due to the limited pool of qualified competitors and the essential nature of their products for drug manufacturing.
The bargaining power of suppliers for GSK is significant, primarily driven by the specialized nature of raw materials and the limited number of qualified manufacturers. This scarcity, coupled with high switching costs due to stringent regulatory requirements, grants suppliers considerable leverage in pricing and contract negotiations.
Suppliers of proprietary manufacturing equipment and crucial technical expertise also hold substantial influence. Furthermore, the demand for highly skilled labor in specialized fields like gene editing, alongside the high compliance costs for raw material suppliers, further amplifies their bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on GSK | Supporting Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Raw Materials/APIs | High supplier leverage due to limited qualified producers. | Global API market projected to reach $279.2 billion by 2027. (Source: Grand View Research) |
| Proprietary Equipment | Dependency on niche equipment suppliers, leading to higher costs. | The biopharmaceutical equipment market is growing, with specialized bioreactors being a key segment. |
| Skilled Labor/R&D Talent | Increased recruitment costs and hiring timelines due to talent scarcity. | Global biopharmaceutical R&D spending reached ~$200 billion in 2023. (Source: Statista) |
| Regulatory Compliance Costs | Higher supplier overheads and increased switching costs for GSK. | GMP compliance can require millions in facility upgrades, impacting supplier pricing. |
What is included in the product
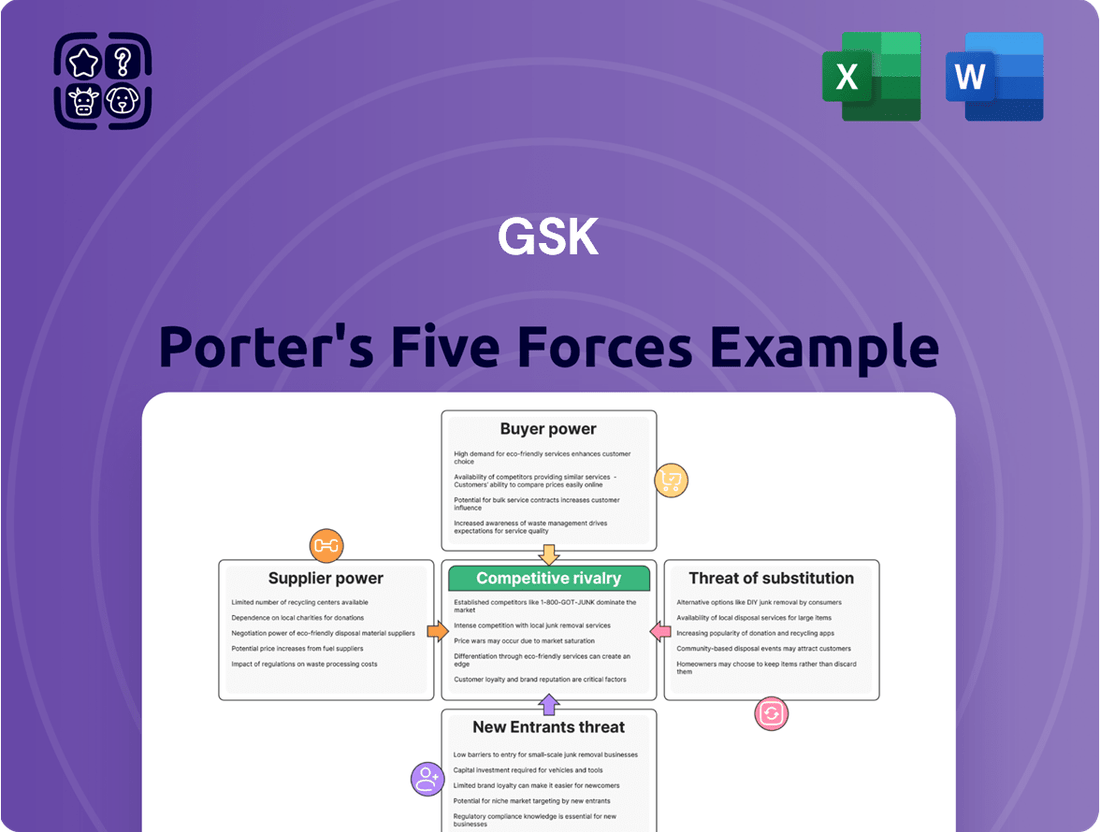
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting GSK, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the pharmaceutical industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, actionable breakdown of GSK's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large healthcare systems and Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) wield considerable bargaining power over pharmaceutical companies like GSK. These entities aggregate demand from numerous hospitals and clinics, creating substantial purchasing volumes. In 2024, the consolidation trend within healthcare continued, with major systems like HCA Healthcare and Ascension managing vast patient populations, translating to significant influence in drug procurement negotiations.
This concentrated buying power enables these organizations to demand lower prices and more favorable contract terms from GSK. For instance, GPOs often negotiate rebates and discounts based on the total volume purchased across their member institutions. The ability to switch suppliers or develop alternative treatment protocols if pricing demands aren't met further amplifies their leverage, putting direct downward pressure on the prices GSK can command for its medicines.
Governmental bodies, particularly ministries of health and public health agencies, represent significant customers for pharmaceutical companies like GSK. They frequently act as bulk purchasers for national immunization programs and emergency medical supplies. For instance, in 2024, governments globally continued to be major buyers of vaccines, with many countries allocating substantial budgets towards public health initiatives.
The bargaining power of these governmental entities is considerable due to their sheer volume of purchases and the public mandate to ensure affordable access to medicines. This often translates into rigorous tender processes and price negotiations, compelling suppliers to offer competitive pricing. In 2024, many developing nations leveraged this power to secure essential medicines at reduced costs, impacting the revenue streams of multinational pharmaceutical firms.
Public health programs are often driven by cost-effectiveness and the need to serve large populations, which amplifies the negotiation leverage of these customer segments. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in markets where government procurement accounts for a substantial portion of a company's sales. GSK, like its peers, has had to adapt its pricing strategies to accommodate these demands, especially in 2024 as global health budgets faced scrutiny.
Insurance companies and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) hold significant sway over pharmaceutical markets. They manage drug formularies, dictating which medications patients have access to and at what cost, directly affecting GSK's market penetration. In 2024, the top PBMs like CVS Caremark, Optum Rx, and Express Scripts managed benefits for tens of millions of Americans, giving them substantial leverage in negotiating drug prices.
This power is amplified through their ability to negotiate substantial rebates and discounts with drug manufacturers for preferred placement on formularies. These negotiations can significantly impact GSK's revenue and profitability, compelling the company to engage in competitive pricing strategies to ensure its products are accessible to patients. For instance, PBMs' influence on list prices and net prices, after rebates, is a critical factor in market access for new and existing GSK therapies.
Availability of Generic and Biosimilar Alternatives
The availability of generic and biosimilar alternatives significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. As patents on GSK's blockbuster drugs expire, lower-cost copies flood the market. This direct price competition incentivizes customers, including healthcare providers and patients, to switch away from GSK's branded products to more affordable options. For instance, GSK has identified approximately $4.2 billion in revenue potentially exposed to generic competition as key patents lapse.
This dynamic directly erodes GSK's pricing leverage for off-patent medications. Customers can readily access chemically identical generics or highly similar biosimilars, forcing GSK to either drastically reduce prices or risk losing substantial market share. The ease of switching and the clear cost savings empower purchasers, making them less reliant on GSK's original formulations.
- Generic and Biosimilar Entry: The expiry of patents allows for the introduction of cheaper alternatives, directly impacting GSK's revenue streams.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers, particularly in cost-conscious healthcare systems, will gravitate towards significantly lower-priced options.
- Market Share Erosion: GSK faces the risk of losing significant market share for its established drugs once generic or biosimilar competition emerges.
- Revenue at Risk: An estimated $4.2 billion in GSK's revenue is potentially vulnerable due to upcoming generic competition.
Patient Advocacy and Public Pressure on Drug Pricing
While individual patients usually don't have much say in drug prices, groups advocating for patients and public opinion can really put pressure on pharmaceutical companies like GSK. This pressure often leads to calls for lower prices and better access to medications.
Public scrutiny, frequently highlighted by the media and discussed in political circles, can indirectly push governments and insurance providers to negotiate for reduced drug costs. For instance, in 2024, several patient advocacy groups actively campaigned against high prescription drug costs, leading to increased legislative attention on drug pricing transparency.
- Patient Advocacy Influence: Groups like the Patient Access Network (PAN) Foundation reported assisting over 100,000 patients in 2023 with out-of-pocket costs, demonstrating their reach and impact.
- Public Opinion Impact: A 2024 KFF survey found that 89% of Americans believe prescription drug prices are too high, indicating strong public sentiment that policymakers often consider.
- Media Amplification: News outlets frequently publish stories detailing the financial burdens faced by patients, further galvanizing public and political pressure on drug manufacturers.
- Government and Insurer Action: This collective pressure can influence policy decisions, such as Medicare's ability to negotiate drug prices, which began impacting a select number of high-cost drugs in 2026, following legislative groundwork laid in prior years.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant force impacting GSK. Large entities like Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) and major healthcare systems possess considerable leverage due to aggregated purchasing volumes. In 2024, the ongoing consolidation in healthcare meant these groups, such as HCA Healthcare, managed vast patient bases, giving them considerable sway in drug price negotiations.
This concentrated buying power allows them to demand lower prices and more favorable terms, often through volume-based rebates. Their ability to seek alternative suppliers or treatment protocols if their price demands aren't met directly pressures GSK to offer competitive pricing, especially for high-volume medications.
Governmental bodies, acting as bulk purchasers for public health programs and national initiatives, also exert substantial bargaining power. In 2024, governments worldwide continued to be major buyers of vaccines and essential medicines, leveraging their purchasing volume to secure competitive pricing through rigorous tender processes.
The immense purchasing power of governments, driven by the need to serve large populations affordably, directly influences pharmaceutical pricing strategies. This is particularly true in markets where government procurement forms a significant portion of a company's sales, compelling firms like GSK to adapt their pricing to meet these demands.
The influence of insurance companies and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) is substantial, as they control drug formularies and negotiate rebates for preferred placement. In 2024, leading PBMs like CVS Caremark and Optum Rx managed benefits for millions, giving them significant leverage in dictating drug access and cost, impacting GSK's market penetration and revenue.
The rise of generic and biosimilar alternatives significantly empowers customers by offering lower-cost options once GSK's patents expire. This direct price competition incentivizes switching from branded products, potentially eroding GSK's market share and pricing power for established drugs. GSK has noted approximately $4.2 billion in revenue is potentially exposed to generic competition as key patents lapse.
Public opinion and patient advocacy groups also exert indirect pressure on GSK by campaigning for lower drug prices and increased access. Media coverage amplifying patient financial burdens can galvanize public and political action, influencing policy decisions related to drug pricing and negotiation. For instance, a 2024 KFF survey indicated that 89% of Americans found prescription drug prices too high, signaling strong public sentiment that policymakers often consider.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on GSK | Key 2024 Trend/Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPOs & Large Healthcare Systems | Aggregated demand, volume purchasing | Demand for lower prices, rebates | Continued consolidation in healthcare systems |
| Governmental Bodies | Bulk purchasing for public health | Price negotiations, tender processes | Major buyers of vaccines and essential medicines |
| Insurance Companies & PBMs | Formulary control, rebate negotiation | Impact on market access, net pricing | Top PBMs manage tens of millions of beneficiaries |
| Generic & Biosimilar Buyers | Lower-cost alternatives post-patent expiry | Market share erosion, price reduction pressure | $4.2 billion GSK revenue at risk from generic competition |
| Patient Advocacy Groups & Public Opinion | Public pressure for affordability | Indirect influence on pricing policy | 89% of Americans believe drug prices are too high (2024 KFF survey) |
What You See Is What You Get
GSK Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for GSK meticulously details the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis immediately upon purchase, offering actionable insights into GSK's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
GSK contends with formidable global pharmaceutical rivals like Pfizer, Merck & Co., and AstraZeneca, all boasting significant R&D investments and broad product offerings. These established players compete intensely for market dominance across numerous therapeutic categories.
The sheer scale of these competitors, each with comparable R&D prowess and expansive global distribution channels, intensifies the rivalry. This parity in capabilities fuels aggressive competition for market share, particularly in high-growth areas.
For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market, valued at over $1.5 trillion, sees these giants vie for position through innovation and strategic acquisitions. GSK's competitive standing is directly influenced by the R&D pipelines and market penetration of these peers.
The pharmaceutical sector thrives on a relentless pursuit of groundbreaking treatments, creating intense competitive rivalry. Companies like GSK are locked in an innovation race, pouring substantial resources into research and development to discover novel drugs and vaccines.
GSK's commitment is evident in its substantial R&D expenditure; for instance, in 2023, the company reported £6.7 billion in R&D investment, underscoring the industry's high cost of innovation. This significant outlay reflects the strategic imperative to stay ahead, particularly in fast-evolving fields such as precision medicine and immuno-oncology.
Maintaining a competitive edge hinges on a company's ability to consistently bring differentiated, patent-protected products to market. The pressure to innovate is perpetual, as existing treatments face patent expirations and new therapeutic challenges emerge, demanding continuous pipeline development to ensure long-term viability and revenue growth.
The pharmaceutical industry, including GSK, faces intense competitive rivalry driven by patent expirations. When blockbuster drugs lose their patent protection, known as the 'patent cliff,' generic and biosimilar manufacturers can enter the market, drastically reducing prices and eroding the original innovator's revenue. For instance, in 2024, several key medications are expected to see their exclusivity expire, intensifying this pressure.
This constant cycle necessitates continuous innovation for GSK. The company must actively invest in research and development to bring new, high-margin products to market, effectively replacing the revenue lost from aging drugs. This proactive approach is crucial for sustaining growth and profitability in a landscape where established revenue streams are consistently challenged by lower-cost alternatives.
Companies like GSK are compelled to aggressively defend their existing market share against these new entrants. Strategies include lifecycle management for existing products, further clinical studies to extend indications, and robust marketing efforts. Simultaneously, the pressure from patent cliffs pushes these firms to explore new therapeutic areas and emerging markets to secure future growth opportunities.
Therapeutic Area Overlap and Pipeline Duplication
The biopharmaceutical industry, including GSK, sees intense rivalry stemming from significant therapeutic area overlap. Companies like GSK are heavily invested in high-growth areas such as oncology, immunology, and infectious diseases. This shared focus means multiple firms are often pursuing the same drug targets and competing for the same patient populations.
GSK's robust pipeline, featuring 71 specialty medicines and vaccines in clinical development as of early 2025, underscores this competitive landscape. This extensive pipeline directly contributes to the rivalry as GSK aims to bring novel treatments to market in these crowded fields.
- Therapeutic Area Focus: Major biopharma players, including GSK, concentrate on oncology, immunology, and infectious diseases, leading to direct competition.
- Pipeline Duplication: Multiple companies are developing drugs for the same diseases and targeting similar biological pathways.
- GSK's Pipeline Strength: As of early 2025, GSK has 71 specialty medicines and vaccines in clinical development, highlighting its active role in competitive therapeutic areas.
Marketing, Distribution, and Market Access Strategies
Beyond groundbreaking research and development, the pharmaceutical industry, including GSK, faces intense rivalry in marketing, sales, and securing crucial market access. Companies actively compete to influence physician prescribing patterns, gain preferred placement on pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) formularies, and establish efficient distribution networks. This battle for market share requires sophisticated strategies to reach both healthcare providers and patients effectively.
GSK's success hinges on its capacity to differentiate its offerings, particularly in high-growth areas like specialty medicines and vaccines. For instance, the strong commercial performance of its shingles vaccine Shingrix and its RSV vaccine Arexvy demonstrates the importance of robust marketing and market access efforts. These products not only require clinical validation but also effective communication of their value proposition to key stakeholders.
- Physician Prescribing Habits: Pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in sales representatives and medical education to inform and persuade physicians about the benefits of their products.
- PBM Formulary Inclusion: Gaining a favorable position on PBM formularies is critical for patient access and cost-effectiveness, often involving complex negotiations and rebates.
- Distribution Channels: Ensuring efficient and reliable distribution of medicines, especially temperature-sensitive vaccines, to pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics is a key competitive differentiator.
- Marketing of Specialty Medicines and Vaccines: GSK's ability to highlight the unique benefits of products like Shingrix (which saw sales of approximately £3.4 billion in 2023) and Arexvy (launched in 2023) through targeted marketing campaigns is paramount to capturing market share.
Competitive rivalry within the pharmaceutical sector, where GSK operates, is exceptionally intense. This stems from the presence of numerous well-established global players, each with substantial research and development budgets and extensive product portfolios. The race to innovate and secure market share in lucrative therapeutic areas like oncology and immunology is fierce, with companies frequently pursuing similar drug targets.
GSK faces direct competition from giants like Pfizer, Merck & Co., and AstraZeneca. These firms possess comparable R&D capabilities and global reach, intensifying the battle for market dominance. The pharmaceutical market, exceeding $1.5 trillion in 2024, is characterized by a constant drive for new treatments, making pipeline strength and market access critical differentiators.
The expiration of patents, known as patent cliffs, further fuels competition. When blockbuster drugs lose exclusivity, generic and biosimilar manufacturers enter the market, driving down prices and impacting innovator revenues. For instance, in 2024, several key medications are slated for patent expiry, increasing pressure on companies like GSK to continuously replenish their product pipelines. GSK's significant R&D investment, totaling £6.7 billion in 2023, highlights the necessity of innovation to counter these challenges and maintain revenue streams.
| Competitor | Key Therapeutic Areas | 2023 R&D Spend (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Pfizer | Oncology, Vaccines, Internal Medicine | $11.7 billion |
| Merck & Co. | Oncology, Vaccines, Hospital Acute Care | $13.1 billion |
| AstraZeneca | Oncology, Cardiovascular, Respiratory & Immunology | $9.8 billion |
| GSK | Immunology, Infectious Diseases, Respiratory | £6.7 billion ($8.4 billion) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct and significant threat of substitution for GSK's products comes from generic medications once a drug's patent expires. These generics contain the same active ingredients but are offered at substantially lower prices, which inevitably leads to a rapid and significant erosion of market share for the original branded products. GSK, like other pharmaceutical giants, faces this challenge across a broad segment of its general medicine portfolio.
For instance, in 2023, the global generic drugs market was valued at approximately $450 billion, demonstrating the sheer scale of this competitive force. As patents for blockbuster drugs expire, the availability of cheaper generic alternatives intensifies price competition. This pressure forces companies like GSK to either heavily invest in new product development or focus on differentiated offerings to maintain profitability in the face of generic entry.
The rise of biosimilars presents a significant threat to GSK's biologic drug portfolio. These products, while not exact copies, are designed to be highly similar in terms of safety, effectiveness, and purity to GSK's branded biologics. This similarity, coupled with typically lower price points, directly challenges the market share and pricing power of GSK's innovative biologic treatments.
The global biosimilar market is on a strong growth trajectory, with projections indicating it could reach $35.7 billion by 2025. This expansion means more biosimilar options will become available, increasing competitive pressure on GSK's established biologic drugs. For instance, the market for adalimumab biosimilars, a key therapy area for many biopharma companies, has seen significant activity and price erosion following patent expiries.
Patients increasingly explore alternative and complementary therapies like herbal remedies, acupuncture, and dietary changes as substitutes for traditional pharmaceuticals. This trend presents a significant threat to conventional drug manufacturers.
The global alternative medicine market was valued at approximately $78.4 billion in 2024, highlighting a substantial and growing demand for non-pharmaceutical health solutions. This market size suggests a real potential for diverting patient spending away from GSK's core product lines.
While not always backed by the same rigorous clinical validation as pharmaceuticals, the growing acceptance and accessibility of these alternatives can erode demand for conventional treatments. This shift in patient preference requires pharmaceutical companies to consider how they might integrate or compete with these emerging modalities.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventative Measures
Lifestyle changes and preventative measures present a significant threat of substitution for pharmaceutical companies like GSK. For many conditions, such as type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease, adopting healthier diets and increasing physical activity can significantly reduce or even eliminate the need for medication. For instance, public health initiatives promoting balanced nutrition and regular exercise can directly compete with treatments for these chronic ailments.
These non-pharmacological approaches can diminish the demand for GSK's product portfolio. Consider the growing awareness around wellness; in 2024, global spending on health and wellness products and services reached an estimated $5.6 trillion, indicating a strong consumer shift towards preventative health. This trend directly impacts the market share for certain GSK offerings.
- Reduced Demand: Increased adoption of healthy lifestyles can lower the incidence of preventable diseases, thereby decreasing the overall market for relevant pharmaceutical treatments.
- Public Health Impact: Successful public health campaigns focused on hygiene and preventative care, like widespread vaccination drives or improved sanitation, can directly substitute for treatments of infectious diseases.
- Consumer Preference Shift: A growing consumer preference for natural remedies and holistic wellness approaches can also divert spending away from traditional pharmaceutical products.
- Economic Efficiency: For consumers, preventative measures are often more cost-effective in the long run than managing chronic conditions with medication, further incentivizing substitution.
Technological Advancements in Diagnostics and Prevention
Technological advancements present a significant threat of substitution for GSK. Innovations in diagnostics, such as AI-driven early disease detection and personalized risk assessments, are enabling earlier interventions and preventative strategies. This reduces the long-term need for traditional pharmaceutical treatments for chronic conditions.
For instance, the rise of advanced medical devices and wearable technology allows for continuous health monitoring and proactive management of conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular disease. These innovations can substitute for the ongoing use of prescription medications.
Furthermore, breakthroughs in areas like gene therapy and cell-based treatments are offering curative solutions. These emerging therapies could directly replace chronic drug regimens for certain diseases, fundamentally altering the treatment landscape and impacting the demand for GSK's existing product portfolio.
- Diagnostic Technology Advancement: Improved early detection methods reduce reliance on long-term treatments.
- Preventative Strategies: Personalized risk assessments and lifestyle interventions substitute for reactive pharmaceutical care.
- Curative Therapies: Gene therapies and advanced medical devices offer alternatives to chronic drug management.
- Market Shift: The focus is moving from managing symptoms to preventing or curing diseases entirely.
The threat of substitutes for GSK is multifaceted, encompassing everything from generic and biosimilar drugs to alternative therapies and lifestyle changes. The sheer size of the global generic drug market, valued around $450 billion in 2023, underscores the immediate impact of patent expirations on GSK's revenue streams. Similarly, the projected growth of the biosimilar market to $35.7 billion by 2025 highlights a significant challenge to GSK's biologic portfolio.
Furthermore, the growing acceptance of alternative medicine, with a global market size of approximately $78.4 billion in 2024, and a massive $5.6 trillion spent globally on health and wellness in the same year, indicates a substantial shift in consumer preference away from traditional pharmaceuticals. These trends are amplified by technological advancements in diagnostics and curative therapies, which increasingly offer preventative or complete solutions rather than ongoing symptom management.
| Substitute Type | Market Size / Growth Indicator | Impact on GSK |
| Generic Drugs | Global Market: ~$450 billion (2023) | Erodes market share and pricing power of branded drugs. |
| Biosimilars | Global Market: Projected $35.7 billion by 2025 | Challenges GSK's biologic drug portfolio with lower-priced alternatives. |
| Alternative & Complementary Medicine | Global Market: ~$78.4 billion (2024) | Diverts patient spending and preference from conventional pharmaceuticals. |
| Lifestyle & Preventative Health | Global Health & Wellness Spending: ~$5.6 trillion (2024) | Reduces demand for treatments by addressing root causes and preventing illness. |
| Advanced Diagnostics & Curative Therapies | Rapid Technological Advancement | Offers alternatives to chronic drug regimens, potentially displacing existing treatments. |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical industry, including companies like GSK, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to the extremely high costs associated with research and development. Developing a single new drug can cost upwards of $2.5 billion, a substantial financial hurdle that discourages many potential competitors from entering the market.
These immense R&D expenditures create a formidable barrier to entry, as new companies require substantial capital and a long-term commitment to navigate the complex and lengthy drug discovery and approval processes. This high investment requirement effectively limits the number of new players that can realistically challenge established firms.
For context, GSK itself demonstrated its commitment to innovation by investing £6.4 billion in research and development during 2024. This significant outlay underscores the capital-intensive nature of staying competitive in the pharmaceutical sector and highlights the challenge new entrants face in matching such investment levels.
Stringent regulatory approval processes represent a significant barrier to entry in the pharmaceutical sector. Companies like GSK must navigate complex pathways involving extensive clinical trials and rigorous evaluations by authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
These lengthy and costly approval procedures, often taking years and millions of dollars, demand specialized scientific and legal expertise. For instance, a new drug's journey from discovery to market approval can easily exceed a decade. This complexity deters many potential new entrants who may lack the resources or experience to manage such demanding regulatory landscapes.
Furthermore, evolving regulatory standards and requirements introduce additional layers of challenge. A shift in FDA guidelines, for example, can necessitate costly redesigns of clinical trial protocols, further increasing the time and investment required for market access and solidifying the advantage of established players like GSK.
Strong patent protection significantly deters new entrants in the pharmaceutical industry, a sector where GSK operates. Companies like GSK possess extensive patent portfolios covering their innovative drugs, creating substantial legal and financial hurdles for new players looking to introduce similar therapies. This intellectual property is a critical barrier, as developing novel treatments without infringing on existing patents requires immense R&D investment and time, effectively limiting the threat of new competition.
Need for Extensive Distribution and Sales Networks
The pharmaceutical industry, particularly for companies like GSK, presents a significant barrier to new entrants due to the sheer necessity of establishing extensive distribution and sales networks. Building a global supply chain capable of reaching diverse markets, coupled with a robust sales and marketing force to effectively promote and distribute pharmaceutical products, is an immensely costly, time-consuming, and complex undertaking.
Newcomers would find it incredibly challenging to replicate the deeply entrenched and sophisticated networks that established players, such as GSK, have cultivated over years. For instance, in 2024, GSK's operational footprint spanned approximately 75 countries, supported by a formidable infrastructure including 37 manufacturing sites.
This global reach and intricate logistical framework are not easily replicated, creating a substantial hurdle for any new entity aiming to compete effectively.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront capital is required to build manufacturing facilities, establish supply chains, and fund sales and marketing operations globally.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating diverse regulatory landscapes in each country for product distribution and sales adds layers of complexity and cost.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Established companies benefit from years of building brand recognition and trust with healthcare providers and patients, which is difficult for new entrants to achieve quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Existing players leverage economies of scale in procurement, manufacturing, and distribution, allowing them to offer products at competitive prices, a challenge for smaller new entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Physician Prescribing Habits
Physicians often develop strong brand loyalty and established prescribing habits, favoring drugs from established companies like GSK due to perceived reliability and consistent performance. This ingrained trust, built over years of experience and demonstrated efficacy, creates a significant hurdle for new entrants. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of physicians cited physician-established relationships and trust in a company's track record as key factors in their prescribing decisions, rather than solely focusing on new product launches.
Developing this level of physician confidence is a long-term endeavor. New entrants face the challenge of not only demonstrating the clinical superiority of their products but also of overcoming decades of established prescribing patterns. This loyalty is not easily swayed; it is cemented through consistent product quality, robust clinical data, and extensive medical education efforts, all of which require substantial investment and time. In 2023, pharmaceutical companies spent an estimated $30 billion on physician engagement and education in the US alone, highlighting the significant resources needed to influence prescribing habits.
- Physician Trust: Decades of consistent product performance and safety data build deep trust.
- Established Habits: Doctors are creatures of habit, often sticking with what they know works.
- Market Entry Barrier: It takes time and significant investment to displace these ingrained habits.
- Data Preference: Physicians prioritize well-documented efficacy and safety profiles.
The threat of new entrants for GSK is moderate. While the pharmaceutical industry demands immense capital for R&D, estimated at over $2.5 billion per drug, and faces rigorous regulatory hurdles, established players like GSK have significant advantages. GSK’s 2024 R&D investment of £6.4 billion and its global distribution network across 75 countries in 2024, supported by 37 manufacturing sites, create substantial barriers.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | GSK's Position (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R&D Costs | Developing new drugs is extremely expensive, often exceeding $2.5 billion per drug. | High capital requirement, deterring many potential entrants. | £6.4 billion invested in R&D. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex, lengthy approval processes by agencies like the FDA and EMA. | Requires specialized expertise, significant time, and investment. | Navigates global regulatory frameworks for market access. |
| Distribution Networks | Establishing global supply chains and sales forces is costly and complex. | Difficult to replicate established players' reach. | Operates in ~75 countries with 37 manufacturing sites. |
| Physician Loyalty | Doctors often prefer established brands due to trust and consistent performance. | Challenging to displace ingrained prescribing habits. | Benefits from long-standing physician relationships. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our GSK Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including GSK's official annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with insights from reputable pharmaceutical industry reports, market research databases, and competitor analysis to provide a comprehensive view.
