Bel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bel Bundle
Bel Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive pressures shaping its market. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for any strategic decision.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bel’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of milk suppliers for Bel can be significant, especially if a large portion of dairy farmers are organized into cooperatives. These cooperatives can act as a unified front, negotiating better prices and terms for their members. For instance, in 2024, European dairy cooperatives often represent a substantial share of milk production in their respective regions, giving them considerable leverage.
Bel's strategy to mitigate this power involves sourcing milk from diverse geographical locations and a broad base of individual farmers, thereby reducing reliance on any single supplier group. However, if Bel requires specialized or particularly high-quality milk for specific products, its dependence on suppliers who can consistently meet those stringent standards increases their bargaining power.
Bel faces significant switching costs when changing milk suppliers, especially for those providing specialized milk or large volumes. These costs include the complexities of renegotiating contracts and potential disruptions to their production schedules. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a business to switch to a new energy supplier in Europe could range from €500 to €2,000, illustrating the tangible financial impact of such transitions, which would similarly apply to milk sourcing.
Bel's position as a significant buyer of dairy products means it holds some sway over its suppliers. However, the extent of this power varies. For many dairy farmers, their revenue stream is diversified, supplying to multiple processors or cooperatives, which limits their dependence on any single buyer like Bel. This reduces the bargaining power of individual farmers against Bel.
Conversely, for suppliers of specialized ingredients or packaging, Bel's business can represent a substantial portion of their revenue. In such cases, these smaller, specialized suppliers may have less leverage due to their reliance on Bel. For instance, if a unique cheese rind producer primarily serves Bel, their ability to negotiate terms is diminished.
In 2024, the global dairy market saw fluctuating prices, with raw milk costs impacting supplier margins. For example, in the US, average milk prices per hundredweight can swing significantly based on feed costs and demand. This volatility means that while Bel is a large customer, the supplier's own cost structure and market alternatives play a crucial role in determining their bargaining power.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
For conventional dairy cheese, the availability of substitute inputs is quite limited, particularly for high-quality milk. This means suppliers of this essential raw material hold significant leverage.
While Bel, a major cheese producer, might explore sourcing milk from various geographical locations or different farming practices, the core input remains dairy milk. This inherent characteristic restricts Bel's flexibility to easily substitute away from its existing dairy suppliers for its primary product lines, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of these suppliers.
- Limited Direct Substitutes: For dairy-based cheese, milk is the fundamental and largely irreplaceable input.
- Supplier Leverage: The lack of readily available substitutes for high-quality milk empowers dairy farmers and cooperatives.
- Regional Sourcing Constraints: While geographic diversification is possible, it doesn't eliminate the reliance on milk itself.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Dairy farmers or cooperatives might consider investing in their own cheese processing plants. This would allow them to move into cheese production themselves, essentially becoming competitors to existing cheese manufacturers. For instance, a large dairy cooperative in Wisconsin, which processes millions of pounds of milk annually, could potentially reallocate capital towards its own branded cheese lines.
However, the financial hurdles are substantial. Establishing a large-scale cheese processing facility requires significant capital investment, often in the tens of millions of dollars, for equipment, land, and regulatory compliance. Furthermore, developing the necessary marketing expertise and building robust distribution networks to compete with established brands presents a considerable challenge.
- Capital Investment: Building a modern cheese processing plant can cost upwards of $50 million, as seen in recent expansions by major dairy processors.
- Marketing Expertise: Successfully launching and growing a consumer-facing cheese brand requires substantial investment in advertising, branding, and market research, areas where farmers may lack direct experience.
- Distribution Networks: Securing shelf space in major grocery chains and establishing efficient logistics for product delivery are complex and costly endeavors.
The bargaining power of milk suppliers for Bel is influenced by the limited availability of direct substitutes for high-quality milk, a critical input for cheese production. This scarcity grants significant leverage to dairy farmers and cooperatives, especially when they can collectively influence supply or pricing. While Bel aims to diversify sourcing, the fundamental reliance on milk itself restricts its ability to easily switch suppliers for core products, thereby enhancing supplier power.
| Factor | Impact on Bel | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Substitutes for Milk | Increases supplier leverage; restricts Bel's flexibility. | Milk remains the primary input for most cheeses, with few viable alternatives. |
| Supplier Concentration (Cooperatives) | Enhances collective bargaining power for farmers. | European dairy cooperatives often control a significant share of regional milk production. |
| Switching Costs | Makes changing suppliers costly and disruptive for Bel. | Estimated €500-€2,000 for businesses to switch utility suppliers, indicative of transition expenses. |
| Supplier Diversification of Customers | Reduces individual farmer dependence on Bel, limiting Bel's buyer power. | Many farmers supply multiple processors, lessening reliance on any single buyer. |
What is included in the product
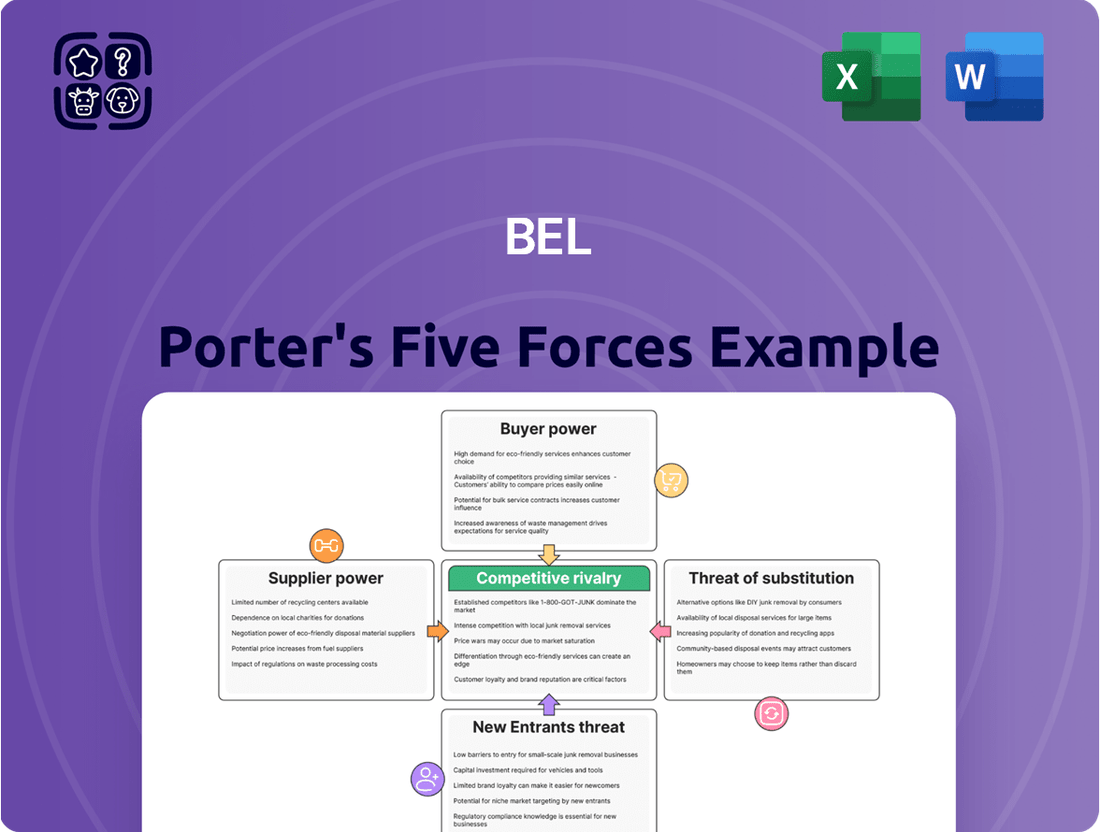
The Porter's Five Forces Analysis framework systematically examines the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry by evaluating threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and prioritize competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
The increasing consolidation among retailers, with a few major supermarket chains and discounters dominating the global market, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. These large entities, acting as key customers for companies like Bel, can dictate terms more effectively.
This concentration of buying power allows these retailers to exert considerable influence over pricing, demand for shelf space, and the terms of promotional activities. For instance, in 2024, the top five global grocery retailers accounted for a substantial portion of the overall market share, giving them considerable leverage in negotiations with suppliers.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Bel, particularly with staple food items like cheese. In 2024, the global cheese market, valued at approximately $130 billion, is characterized by intense competition. This means that even with strong brands, Bel faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing, as consumers can readily switch to more affordable options if prices increase notably.
For end consumers, the ease of switching between snacking cheese brands is a significant factor. This minimal cost and effort empower them to easily explore alternatives, including private labels, if Bel's products don't align with their perceived value. For instance, in 2024, the private label segment of the cheese market continued to gain share, reflecting consumer sensitivity to price and value.
Availability of Information for Customers
Customers today have an unprecedented amount of information at their fingertips, significantly boosting their bargaining power. Online platforms, review sites, and price comparison tools allow consumers and retailers to easily research product ingredients, compare pricing across different vendors, and understand the competitive landscape. This transparency means customers can make much more informed purchasing decisions, often leading them to seek out the best value or specific product attributes.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers actively used online resources before making a purchase. Studies indicate that over 80% of shoppers conduct online research, even for in-store purchases. This readily available data empowers them to negotiate better prices or switch to competitors if their demands aren't met.
This increased access to information translates directly into greater customer leverage. They can easily identify alternatives and understand the true cost and value of a product or service. This forces businesses to be more competitive on price, quality, and service to retain their customer base.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers leverage online reviews, price comparisons, and detailed product specifications to make informed choices.
- Price Transparency: Websites and apps allow for immediate comparison of prices from multiple retailers, driving down margins for businesses.
- Access to Alternatives: The digital marketplace makes it easy for customers to discover and evaluate competing products and services.
- Empowered Negotiation: With knowledge of market rates and competitor offerings, customers are better positioned to negotiate terms and prices.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge for companies like Bel, particularly in the dairy sector. Large retail chains, in their pursuit of higher margins and greater control over their product offerings, increasingly develop and promote their own private label brands. This strategy directly impacts branded manufacturers by creating a competitive alternative, often at a lower price point.
For instance, major supermarket chains commonly introduce private label cheese products that compete head-to-head with established brands. This capability allows retailers to shift consumer preference and sales volume away from external suppliers towards their own offerings. Such a move grants them considerable bargaining power, as they can reduce orders from incumbent brands like Bel, thereby pressuring those brands on pricing and terms.
In 2024, the private label share of the grocery market continued to grow, with some categories seeing private label penetration exceeding 20%. This trend highlights the tangible impact of backward integration. Retailers leveraging this strategy can dictate terms more effectively, as they possess the means to produce similar goods internally, diminishing their reliance on external suppliers and strengthening their position in negotiations.
- Private Label Growth: Private label market share in many Western countries reached or surpassed 25% in key grocery categories by early 2024, indicating a strong trend of retailers integrating backward.
- Retailer Leverage: The ability of large retailers to launch their own brands, such as cheese, directly challenges branded manufacturers by offering lower-priced alternatives.
- Impact on Suppliers: This backward integration allows retailers to reduce orders from established brands, increasing their bargaining power and potentially impacting supplier profitability.
- Competitive Landscape: The increasing prevalence of private label products intensifies competition, forcing branded companies to innovate and differentiate to maintain market share.
Customers hold significant power when they are concentrated, price-sensitive, or have easy access to alternatives. For Bel, this means that large retailers, who represent a substantial portion of sales, can negotiate favorable terms due to their buying volume. In 2024, the increasing consolidation in the grocery sector meant that a few dominant players held considerable sway over pricing and product placement.
Consumer price sensitivity is a key lever. With the global cheese market valued at around $130 billion in 2024, and facing intense competition, Bel must remain competitive. If prices rise too steeply, consumers can easily switch to more affordable options, including private labels, which continued to gain market share throughout 2024.
The ease with which consumers can switch between brands, especially for everyday items, further amplifies their bargaining power. This accessibility to information and alternatives, readily available through online platforms in 2024, empowers customers to demand better value. Consequently, businesses must focus on competitive pricing and product quality to retain their customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Bel | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Retailer Consolidation | Increased leverage for large buyers | Top global grocery retailers held significant market share. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on pricing for staple products | Global cheese market valued at ~$130 billion, with strong competition. |
| Ease of Switching | Consumers readily explore alternatives | Private label cheese market share continued to grow. |
| Information Access | Customers make more informed purchasing decisions | Over 80% of shoppers researched online before purchasing in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
Bel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a deep dive into the competitive landscape of your chosen industry, equipping you with actionable insights. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global cheese market is intensely competitive, populated by major multinational corporations like Lactalis and Savencia, alongside robust regional players and a vast number of local dairies. This diverse competitive landscape means Bel Porter faces rivals with varying scales and strategies across different cheese segments.
Bel Porter's competitive environment spans multiple product categories, including fresh cheese, processed cheese, and snacking cheese. Each of these segments presents its own unique set of competitors, from large-scale manufacturers to niche artisanal producers, intensifying the rivalry.
For instance, in 2024, the global cheese market was valued at approximately $140 billion, with significant growth projected. Bel Porter must navigate this expansive and dynamic market, where established giants and agile local businesses vie for market share, impacting pricing power and innovation.
The global dairy market is projected for moderate growth, but specific segments where Bel Porter excels, such as snacking and portioned cheese, are anticipated to expand at a faster pace. For instance, the global cheese market was valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 4% through 2030.
While this growth offers some relief from intense competition, it also acts as a magnet for new entrants and spurs existing competitors to ramp up their expansion efforts. This dynamic means that even in growing markets, competitive pressures can remain significant as companies vie for market share.
Bel Porter's competitive rivalry is significantly softened by its strong product differentiation and the resulting brand loyalty. The company boasts a portfolio of globally recognized brands such as Laughing Cow, Kiri, and Babybel, each with a substantial history of consumer trust and preference. This deep-rooted recognition allows Bel to command premium pricing, effectively insulating it from intense price wars that often plague less differentiated markets.
High Fixed Costs in Production
The dairy processing industry demands significant capital for its plants and machinery, resulting in high fixed costs for companies like Bel. To spread these expenses and achieve profitability, businesses often aim for large-scale production.
This drive for high volumes can fuel aggressive pricing and intense competition as companies fight to secure and maintain market share, a dynamic particularly relevant in the competitive landscape of 2024.
- High Capital Investment: Dairy processing facilities require substantial upfront investment in specialized equipment and infrastructure.
- Economies of Scale Imperative: Companies must operate at high volumes to make these fixed costs manageable.
- Pricing Pressure: The need to maintain volume can lead to price wars, intensifying rivalry among established players.
Exit Barriers
High capital investments in processing facilities and specialized equipment, often running into millions of dollars, create substantial exit barriers in the dairy sector. For instance, a modern dairy processing plant can cost upwards of $50 million to build and equip.
Furthermore, maintaining established supply chain relationships with farmers is crucial and difficult to sever, adding another layer of complexity to exiting the market. These entrenched relationships mean that even struggling dairy companies may continue operating rather than face the costs and complexities of divesting assets and dissolving contracts.
- High Capital Investment: Dairy processing plants require significant upfront capital, often exceeding $50 million for a single facility.
- Specialized Equipment: The need for specialized machinery for pasteurization, homogenization, and packaging locks in capital and expertise.
- Supply Chain Entrenchment: Long-term contracts and established relationships with dairy farmers make it difficult and costly to exit supply chains.
- Persistence of Underperformers: These barriers encourage less efficient or unprofitable firms to remain in the market, thereby intensifying competitive rivalry.
The competitive rivalry within the global cheese market is robust, fueled by a mix of large multinational corporations and numerous regional and local players. This diverse field means Bel Porter faces competition across various cheese segments, from fresh to processed and snacking varieties.
The market's value, estimated at around $140 billion in 2024, continues to attract both established giants and agile newcomers, intensifying the fight for market share and impacting pricing strategies.
Bel Porter benefits from strong brand loyalty with names like Laughing Cow and Babybel, allowing for premium pricing and a buffer against price wars. However, the industry's high capital investment, with new plants costing upwards of $50 million, creates significant exit barriers, encouraging even underperforming firms to remain, thus sustaining competitive pressure.
| Factor | Impact on Bel Porter | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size & Growth | Intense competition due to market attractiveness | Global cheese market valued at ~$140 billion in 2024 |
| Competitor Landscape | Diverse rivals from global to local | Lactalis, Savencia, numerous regional dairies |
| Brand Loyalty | Mitigates price competition | Strong recognition for Laughing Cow, Kiri, Babybel |
| Capital Investment | High exit barriers, sustained rivalry | New plants can cost >$50 million |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing consumer interest in plant-based diets presents a significant threat of substitutes for Bel's traditional cheese products. The market has seen a surge in dairy-free cheese alternatives crafted from ingredients like nuts, soy, and other plant-based sources.
These alternatives are directly competing with Bel's core offerings, and their continuous improvement in taste and texture makes them increasingly appealing to consumers seeking to reduce dairy consumption. For instance, the global plant-based cheese market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong and expanding substitute market.
Bel's snacking cheese products, like The Laughing Cow, face significant competition from a vast range of alternative convenient snack options. These include items such as fresh fruit, nuts, yogurt cups, crackers, and various savory snacks. This broad competitive landscape means consumers have many readily available choices when looking for a quick bite.
In 2024, the global healthy snacks market was valued at approximately $130 billion, highlighting the substantial demand for convenient and health-conscious food choices. A shift in consumer dietary preferences, perhaps towards plant-based options or low-sugar alternatives, could easily divert demand away from traditional dairy-based cheese snacks, impacting Bel's market share.
The price-performance trade-off of substitutes presents a significant challenge for Bel. While some plant-based alternatives, like certain vegan cheese shreds, might have historically commanded higher prices or offered a less-than-ideal texture, their value proposition is rapidly improving. For instance, reports from 2024 indicate that the average price premium for plant-based dairy alternatives has narrowed considerably compared to previous years, with many now offering comparable or even superior taste and texture profiles, directly impacting consumer choice.
Furthermore, other snack categories, such as traditional dairy snacks or even fruit-based options, frequently provide a more attractive price point and inherent convenience. This competitive pricing pressure forces Bel to continually re-evaluate its own pricing strategies and the perceived value of its products, especially as consumers become more discerning about cost versus quality in their everyday purchases.
Changing Consumer Health Perceptions
Changing consumer health perceptions represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional dairy. As awareness grows around issues like saturated fats, cholesterol, and lactose intolerance, consumers are actively seeking alternatives. This shift is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental change in dietary priorities.
For instance, the global plant-based milk market is projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027, indicating a substantial move away from dairy. This accelerated adoption of substitutes is driven by a desire for perceived healthier or more digestible options. By 2024, the demand for lactose-free products has also seen consistent year-over-year growth, further demonstrating this evolving consumer preference.
This evolving health perception can accelerate the adoption of substitutes in several ways:
- Increased demand for plant-based alternatives: Consumers are increasingly opting for almond, soy, oat, and coconut milk due to perceived health benefits and dietary restrictions.
- Growth in lactose-free dairy products: Traditional dairy producers are responding by offering lactose-free versions, but the underlying preference for avoiding lactose can still lead consumers to non-dairy substitutes.
- Focus on functional ingredients: Consumers are looking for products with added benefits, such as probiotics or omega-3s, which are often more readily available in alternative product categories.
- Dietary trends and lifestyle choices: Veganism and flexitarianism are growing lifestyle choices that directly impact dairy consumption, pushing consumers towards plant-based substitutes.
Innovation in Substitute Products
The threat of substitutes for traditional dairy cheese is escalating, driven by relentless innovation in the food industry. Ongoing research and development, particularly in the burgeoning plant-based sector, are continuously introducing new and improved alternatives. For instance, by 2024, the global plant-based cheese market was projected to reach significant growth, with analysts anticipating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8-10% in the coming years.
Advances in food science are key to this evolution. These scientific breakthroughs are enabling the creation of substitutes that more closely mimic the taste, texture, and melting properties of dairy cheese. This technological progress directly increases their competitive threat, making them more appealing to a wider consumer base.
The impact of these innovations can be observed in consumer adoption trends. By early 2025, reports indicated a notable increase in the market share of plant-based cheese alternatives, with some regions seeing double-digit percentage growth in sales. This suggests that substitutes are becoming increasingly viable and attractive options for consumers seeking alternatives to dairy.
Key areas of innovation include:
- Ingredient advancements: Utilizing novel proteins and fats to replicate dairy cheese characteristics.
- Fermentation technology: Employing precision fermentation to produce dairy-identical proteins without animals.
- Flavor and texture profiling: Developing sophisticated methods to achieve authentic cheese-like sensory experiences.
- Nutritional enhancement: Fortifying plant-based options with essential nutrients often found in dairy.
The threat of substitutes for Bel's cheese products is substantial, driven by evolving consumer preferences and advancements in food technology. Plant-based alternatives, in particular, are rapidly improving in taste and texture, directly challenging traditional dairy cheese. By 2024, the global plant-based cheese market was projected for significant growth, with analysts anticipating an 8-10% CAGR in the coming years.
This innovation extends to other snack categories as well, with a vast array of convenient and healthier options available. The global healthy snacks market, valued at approximately $130 billion in 2024, underscores the competitive landscape. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing health, leading them to explore alternatives to dairy-based products.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Value (Approx.) | Projected Growth Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Cheese | $3.0 Billion | Improved taste, texture, and wider availability |
| Healthy Snacks (General) | $130 Billion | Consumer focus on health and convenience |
| Plant-Based Milk Market | $60 Billion by 2027 | Health perceptions and dietary restrictions |
Entrants Threaten
The cheese market presents a significant hurdle for newcomers due to the immense capital required. Establishing a robust cheese production and distribution network necessitates substantial investment in advanced processing facilities, specialized equipment, and a reliable cold chain infrastructure. For instance, setting up a modern dairy processing plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, not to mention the ongoing expenses for marketing and brand building.
Bel Porter's existing players, including Bel itself, benefit immensely from economies of scale. This advantage is evident in their ability to source milk, manufacture products, and distribute them at a lower per-unit cost. For instance, in 2024, major dairy producers often secured milk contracts at rates significantly below what a new entrant could negotiate, simply due to the sheer volume they commit to.
Newcomers entering the market face a steep uphill battle to replicate these cost efficiencies. Without the established volume that allows for bulk purchasing discounts and optimized logistics, new entrants would find it challenging to compete on price. This initial cost disadvantage makes it difficult to gain market share against incumbents who have honed their operations over years, achieving a cost structure that is hard to match early on.
Bel's portfolio, featuring beloved brands like The Laughing Cow and Babybel, has cultivated strong consumer recognition and loyalty over many years. This deep-rooted brand equity makes it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold.
New entrants struggle to replicate Bel's established brand appeal and differentiate their offerings in a saturated marketplace. For instance, in 2024, the global cheese market, a key sector for Bel, was valued at an estimated $140 billion, highlighting the intense competition and the significant investment required to build brand awareness in such a large arena.
Access to Distribution Channels
Securing prime shelf space in major grocery chains and establishing efficient distribution networks presents a significant hurdle for new food and beverage companies. The cost and complexity of achieving widespread market access can be prohibitive. For instance, in 2024, the average slotting fee for a new product in a large supermarket chain could range from $25,000 to $100,000 or more, depending on the retailer and product category.
Established players like Bel, with decades of operation, have cultivated deep-seated, often exclusive, relationships with retailers. These long-standing partnerships grant incumbents preferential treatment, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to secure comparable distribution agreements and gain the necessary visibility to compete effectively.
- High Slotting Fees: New entrants often face substantial upfront costs for shelf placement.
- Incumbent Relationships: Existing brands benefit from established trust and favorable terms with retailers.
- Distribution Network Costs: Building a comprehensive and reliable distribution system is a major capital investment.
- Limited Retailer Capacity: Retailers have finite shelf space, prioritizing proven performers over unproven products.
Regulatory and Food Safety Hurdles
The dairy industry presents significant barriers to entry due to rigorous food safety regulations, quality control mandates, and detailed labeling obligations. New companies must meticulously adhere to these complex legal structures, requiring substantial investment in compliance measures. This regulatory landscape directly increases the cost and complexity associated with establishing a presence in the market.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continued to enforce strict standards under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), impacting dairy processing facilities. Compliance often involves extensive testing, traceability systems, and facility upgrades. These requirements can easily add millions of dollars to initial setup costs for new dairy businesses.
- Stringent Food Safety Standards: Dairy products are highly perishable and susceptible to contamination, necessitating adherence to rigorous safety protocols.
- Quality Assurance Requirements: Maintaining consistent product quality is crucial for consumer trust and brand reputation, demanding robust quality management systems.
- Complex Labeling Regulations: Accurate ingredient lists, nutritional information, and origin claims are legally mandated, adding to operational complexity.
- High Compliance Costs: Investing in certified equipment, specialized personnel, and ongoing safety audits represents a significant financial commitment for new entrants.
New entrants face substantial capital requirements for production, distribution, and marketing, making it difficult to compete with established players. Bel's existing scale and brand recognition, built over years, create a significant advantage, as evidenced by the $140 billion global cheese market in 2024 where brand building is costly. Furthermore, stringent regulations and high slotting fees, potentially $25,000-$100,000 per product in 2024, add further layers of difficulty for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing production, cold chain, and distribution | Tens of millions for a modern dairy plant |
| Brand Equity | Consumer recognition and loyalty | Significant investment needed to build awareness in a $140B market |
| Distribution Access | Securing shelf space and logistics | $25,000 - $100,000+ in slotting fees per product |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to food safety and labeling laws | Millions in upgrades and compliance systems (e.g., FSMA) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and publicly available company filings. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive intensity and market dynamics.
