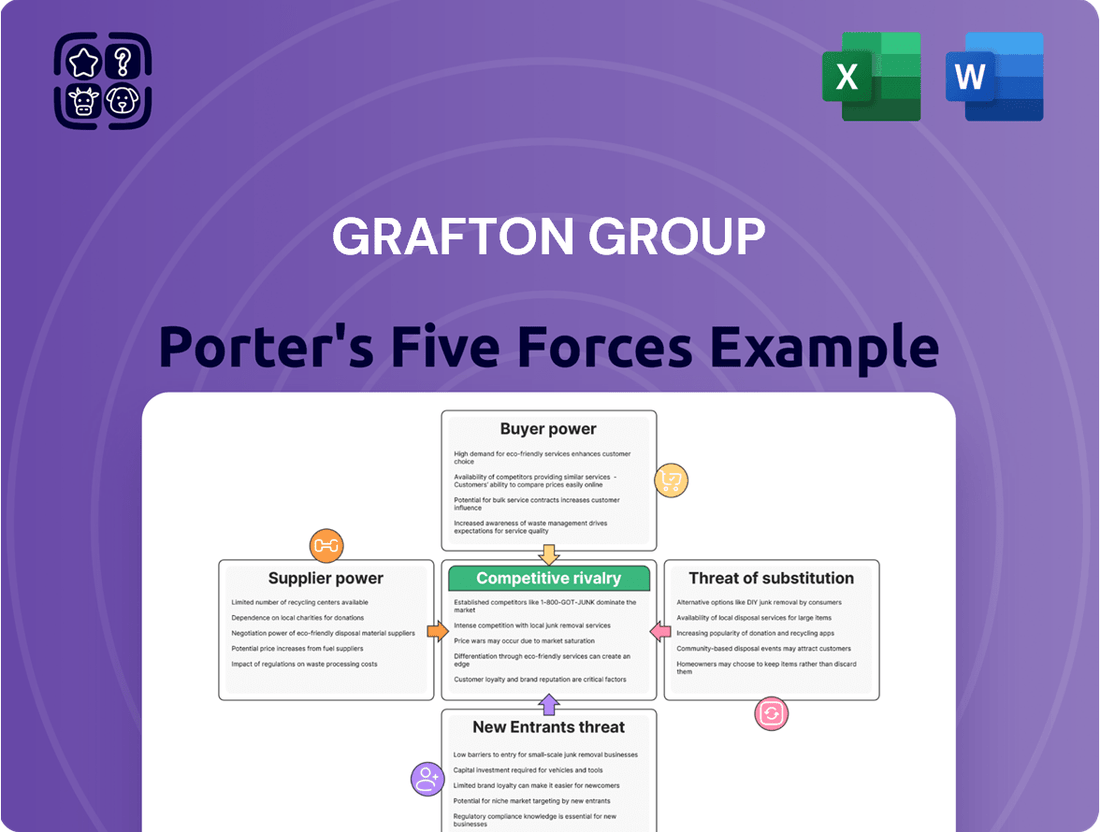
Grafton Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grafton Group Bundle
Grafton Group navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and significant rivalry among existing players in the building materials sector. The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by capital requirements, but the influence of suppliers can vary depending on product specialization.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Grafton Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration within the building materials sector for Grafton Group is generally low due to the industry's diverse nature, encompassing both large-scale commodity producers and specialized niche manufacturers. Grafton's extensive international operations across the UK, Ireland, Netherlands, and Finland likely mean they source from a wide array of suppliers, diluting the power of any single entity.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers can escalate significantly for specialized or proprietary building materials where only a few manufacturers exist. For instance, if Grafton Group requires a specific, patented insulation material or a unique architectural component, the limited availability of such products could grant those concentrated suppliers greater leverage in pricing and terms.
Switching costs for Grafton Group when changing suppliers are not uniform across its product range. For common building materials, the effort to switch suppliers is typically minimal, mainly involving administrative updates and minor adjustments to how they order. This low barrier means suppliers of these generic items have less power.
However, for specialized or bespoke building products, Grafton's switching costs can escalate. These higher costs stem from the need to re-evaluate and potentially re-engineer integrated supply chain systems, including logistics and quality assurance protocols. Compatibility issues with existing infrastructure or product lines can further complicate and increase the expense of changing suppliers for these specialized items.
The uniqueness of supplier offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power. When suppliers provide highly differentiated products or proprietary technologies, they gain more leverage over buyers. In the building materials sector, while many items are standardized, certain specialized brands or innovative, sustainable materials can offer distinct advantages, thereby increasing the power of those specific suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into distribution or retail for a company like Grafton Group is generally low, but it’s not entirely absent. For many suppliers, especially those focused on manufacturing, moving into distribution or retail would require a substantial investment in logistics, warehousing, and direct customer engagement. This is often a significant departure from their core manufacturing expertise.
However, some larger manufacturers could potentially establish direct sales channels for specific product lines. This would allow them to bypass intermediaries like Grafton, particularly for high-volume or specialized products. For instance, a major building materials manufacturer might develop its own online portal or regional distribution centers to reach end-users directly, potentially impacting Grafton's market share in those segments.
- Low Likelihood of Full Forward Integration: Most suppliers lack the capital and operational infrastructure to replicate Grafton's extensive retail and distribution network.
- Potential for Direct Sales Channels: Larger, well-capitalized manufacturers may establish direct-to-consumer or direct-to-business sales routes for select product categories.
- Impact on Specific Product Lines: Direct sales by suppliers could erode Grafton's margins on the specific products they choose to sell directly.
Importance of Grafton Group to Suppliers
Grafton Group's extensive market presence, with a vast network of branches spanning the UK, Ireland, and the Netherlands, positions it as a crucial customer for numerous suppliers in the building materials and DIY sectors. This significant purchasing volume inherently grants Grafton considerable leverage.
For many suppliers, especially smaller and medium-sized enterprises, securing and retaining Grafton's business is vital. The potential loss of such a substantial client could severely impact their revenue streams and market stability. In 2024, for instance, Grafton Group reported revenue of approximately £3.5 billion, highlighting the scale of its operations and its importance to its supply chain partners.
- Significant Customer: Grafton's substantial annual revenue underscores its importance as a major buyer for its suppliers.
- Market Reach: Operations across multiple countries amplify Grafton's demand and, consequently, its influence over suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: Many suppliers rely heavily on Grafton, giving the company considerable bargaining power.
- Impact of Lost Business: Losing Grafton as a customer would represent a significant financial setback for many of its suppliers.
Grafton Group's substantial purchasing power, demonstrated by its reported revenue of approximately £3.5 billion in 2024, significantly reduces supplier bargaining power. This scale means many suppliers are highly dependent on Grafton, making them less able to dictate terms or prices.
While Grafton's overall supplier concentration is low, suppliers of specialized or proprietary materials can exert more influence. However, the company's ability to switch to alternative, albeit perhaps less ideal, suppliers for common items limits the leverage of those providing standardized building materials.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward is minimal for most, though larger manufacturers might explore direct sales for specific product lines, potentially impacting Grafton's margins on those particular items.
| Factor | Assessment for Grafton Group | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Generally low, with diverse sources for common materials. Higher for specialized items. | Low for commodity suppliers, moderate for specialized suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard products, high for bespoke or integrated systems. | Low for commodity suppliers, moderate for specialized suppliers. |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Low for most building materials, high for patented or innovative products. | Low for commodity suppliers, high for specialized suppliers. |
| Supplier Dependence on Grafton | High for many, especially SMEs, due to Grafton's £3.5bn (2024) revenue. | Low overall, as Grafton's volume reduces individual supplier leverage. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low for most, but potential for direct sales from larger manufacturers on specific lines. | Low, but could impact specific product categories. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Grafton Group meticulously dissects the competitive intensity within its operating sectors, evaluating the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the overall rivalry among existing firms.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for Grafton Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
Grafton Group's customer base is broad, encompassing trade professionals, large construction companies, house builders, DIY enthusiasts, and individual homeowners. This wide distribution of customers, particularly the numerous DIY homeowners, significantly reduces the bargaining power of any single customer.
However, the situation shifts for large trade customers. Major construction firms, for instance, can exert considerable influence due to the sheer volume of their purchases. For example, in 2023, Grafton's UK & Ireland Merchanting division reported revenue of £2.25 billion, with a substantial portion likely coming from these larger trade accounts.
Switching costs for Grafton Group's customers are a key factor in their bargaining power. For trade customers, the effort to switch to another supplier might seem minimal, involving little more than updating account details or credit lines. However, Grafton's established relationships, dependable product supply, and consistent delivery performance cultivate loyalty, making these implicit switching costs more substantial.
For DIY customers, convenience and a strong sense of brand familiarity are paramount. These elements can significantly deter them from exploring alternative suppliers, even if minor price differences exist. In 2024, Grafton Group continued to emphasize its customer service and product availability, aiming to solidify these advantages.
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Grafton Group's bargaining power. During economic downturns, both professional tradespeople and DIY enthusiasts become more attuned to pricing, actively seeking the best value. This heightened sensitivity is especially pronounced for standard building materials where numerous suppliers offer comparable products.
In 2024, with persistent inflation impacting household budgets and construction project costs, Grafton's customers are demonstrating increased price consciousness. For instance, the UK construction output saw a 1.7% decrease in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the previous quarter, indicating a slowdown that often correlates with greater price scrutiny from buyers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by Grafton Group's customers, meaning customers producing their own building materials or distribution networks, is largely minimal across its diverse customer base. While some larger construction firms might undertake limited in-house fabrication of certain components, the economics rarely support a full-scale move into manufacturing or distributing a broad range of building materials. For the significant DIY customer segment, the concept of backward integration is practically non-existent due to the scale and complexity involved.
This low threat is a key factor in Grafton's stable market position. For instance, in 2024, the UK construction sector, a primary market for Grafton, saw a substantial 7.8% increase in output, indicating robust demand but also highlighting the specialized nature of material production that deters most contractors from backward integration. The capital investment and expertise required to manufacture everything from timber to cement or to establish nationwide distribution channels are prohibitive for most of Grafton's clientele.
- Low Likelihood of Backward Integration: Most of Grafton's customers, including large construction companies and individual DIY consumers, face significant barriers to backward integration.
- Cost-Effectiveness Barrier: For construction firms, the cost and complexity of producing a wide array of building materials or managing extensive distribution networks outweigh the potential benefits.
- DIY Customer Incapacity: DIY customers lack the resources and scale to engage in any meaningful backward integration.
- Industry Specialization: The building materials sector requires specialized manufacturing processes and logistics, making it impractical for most end-users to replicate.
Customer Information Availability
The digital age has dramatically shifted the landscape of customer information availability. With online platforms, customers can easily access comparative pricing, detailed product specifications, and reviews from various distributors. This transparency empowers them, allowing for informed comparisons and potentially stronger negotiation positions when seeking better deals. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent over 30 hours researching purchases online, highlighting the impact of readily available information.
Grafton Group, recognizing this trend, has implemented strategies to cater to increasingly informed customers. Their diversified customer base, encompassing both trade professionals and DIY consumers, requires tailored approaches. By leveraging an omnichannel strategy, Grafton aims to provide seamless access to information and consistent service across all touchpoints, thereby mitigating some of the intensified bargaining power stemming from enhanced customer knowledge.
- Increased Transparency: Digital platforms provide customers with easy access to pricing, product details, and reviews.
- Enhanced Negotiation Power: Customers can compare offerings from multiple sources, leading to potential price negotiations.
- Grafton's Response: The company utilizes a diversified customer base and omnichannel approach to meet evolving customer expectations.
Grafton Group's customer bargaining power is moderate, influenced by customer segmentation and switching costs. While individual DIY customers have low power due to fragmented demand, large trade customers can leverage their purchasing volume. In 2023, Grafton's UK & Ireland Merchanting division generated £2.25 billion in revenue, indicating the significance of these larger accounts.
Switching costs are relatively low for trade customers, but Grafton's established relationships and service reliability create implicit switching barriers. For DIY customers, brand familiarity and convenience are key deterrents to switching. The company's 2024 focus on customer service aims to reinforce these advantages.
Price sensitivity is a significant factor, especially during economic slowdowns like the Q1 2024 UK construction output decrease of 1.7%. This heightened price consciousness empowers customers to seek better value, particularly for standardized materials. Digital transparency further amplifies this, with customers spending over 30 hours researching purchases online in 2024, enabling easier price comparisons.
What You See Is What You Get
Grafton Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the Grafton Group's Porter's Five Forces Analysis. You will gain immediate access to this comprehensive report, which thoroughly examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, ensuring you receive precisely what you need for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The building materials distribution and DIY retail sectors where Grafton Group operates, including the UK, Ireland, Netherlands, Finland, and Spain, present a dynamic competitive environment. This landscape features a blend of large, established international corporations and a multitude of smaller, localized businesses, creating a fragmented yet competitive market.
Grafton Group's strong regional and national market positions underscore the intensity of this rivalry. In 2023, for instance, Grafton Group reported revenue of £3.3 billion, demonstrating its substantial presence amidst these varied competitors. The presence of numerous significant players actively competing for market share means that maintaining and growing these positions requires continuous strategic effort and adaptation.
The industry growth rate is a major driver of competitive rivalry. When an industry is expanding rapidly, there's often enough demand for all players, leading to less intense competition. However, in slower-growing or contracting markets, companies are forced to fight harder for market share, which can escalate rivalry.
For Grafton Group, the construction and home improvement sectors in its key markets present a mixed picture for 2024. While Ireland's construction outlook is generally positive, the UK and Finland have faced headwinds. These challenging conditions, characterized by subdued demand in 2024, naturally intensify competition as businesses vie for a limited pool of available projects and customer spending.
In the building materials sector, product differentiation can be tricky because many items are seen as similar. Grafton Group stands out by having a vast network of branches and stores, serving a wide range of customers, and offering specialized brands. This strategy helps them avoid constant price wars.
Grafton Group's focus on service, ensuring products are readily available, and creating a positive customer experience are also crucial ways they differentiate themselves. For instance, in 2023, Grafton reported a revenue of £3.2 billion, demonstrating the scale of their operations and their ability to serve a broad market, which supports their differentiation efforts.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for Grafton Group within the building materials distribution sector are considerable. These include substantial investments in physical infrastructure like warehouses and delivery fleets, along with long-standing supplier agreements and the need for a specialized, trained workforce. These factors make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market.
The presence of high exit barriers means that even when profitability dips, firms may continue to operate, potentially exacerbating competitive pressures. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense rivalry as companies fight to maintain market share rather than exiting.
For instance, in 2024, the building materials sector continued to see significant capital tied up in logistics and inventory. Companies like Grafton Group, which operate extensive networks, face substantial write-downs and operational disruption if they were to attempt a rapid exit. This financial commitment effectively locks them into the industry, influencing strategic decisions and competitive behavior.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Warehousing, distribution centers, and specialized transport fleets represent major capital outlays.
- Established Supply Chain Linkages: Long-term contracts and relationships with manufacturers and suppliers create inertia.
- Specialized Workforce and Know-how: The industry requires skilled personnel in areas like logistics, sales, and product knowledge, which are not easily transferable.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty: Years of service build trust, making it difficult for new entrants or exiting firms to divest customer bases easily.
Diversity of Competitors
The competitive landscape for Grafton Group is notably diverse, featuring a mix of national chains, regional specialists, and independent merchants. This variety in competitor origins and strategies, including price leadership, niche market focus, and service excellence, intensifies the rivalry. For instance, in the UK, national DIY retailers like B&Q and Homebase, alongside specialized trade suppliers, present significant competition, each vying for market share through distinct value propositions.
This broad spectrum of competitors means Grafton Group must constantly adapt its strategies. In 2024, the UK construction and home improvement market saw continued consolidation and strategic realignments among various players. Independent merchants, while smaller in scale, often offer specialized product ranges and personalized customer service, directly challenging Grafton's broader market approach.
- Diverse Competitors: Grafton Group faces competition from national DIY chains, regional specialists, and local independent merchants, each with unique strategies.
- Strategic Variety: Competitors employ diverse approaches such as price competition, niche market specialization, and superior customer service, making the market dynamic.
- Market Complexity: The varied origins and objectives of competitors create a complex and challenging environment for Grafton Group.
- Example Scenario: In the UK, national retailers and specialized trade suppliers offer distinct value propositions that directly compete with Grafton's offerings.
Competitive rivalry within Grafton Group's operating sectors is intense due to the presence of numerous players, ranging from large international firms to smaller local businesses. This fragmentation means companies must constantly innovate and adapt to capture market share, especially in markets experiencing slower growth in 2024, such as the UK and Finland.
Grafton Group differentiates itself through its extensive branch network, product availability, and customer service, aiming to avoid pure price competition. In 2023, its revenue of £3.3 billion highlights its significant market presence, which is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge against diverse rivals employing various strategies.
| Competitor Type | Key Strategies | Impact on Grafton |
|---|---|---|
| National DIY Chains | Price leadership, broad product range | Pressure on pricing and market share |
| Regional Specialists | Niche focus, tailored service | Challenge for specific customer segments |
| Independent Merchants | Personalized service, local knowledge | Competition for smaller projects and loyal customers |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitute products for traditional building materials remains a significant factor for Grafton Group. New materials and composites, alongside sustainable and recycled options, are continuously entering the market, offering alternatives that can impact demand for conventional offerings. For instance, the market has seen a notable rise in wood-alternative products such as composite decking and interior composite wall cladding.
The price-performance trade-off for substitutes is a significant threat to Grafton Group. While established materials are familiar, newer alternatives offering superior durability or energy efficiency could attract customers despite a higher upfront cost, especially if their total cost of ownership is lower. For instance, the increasing emphasis on sustainability and reduced lifecycle costs is making advanced composite materials or recycled content products more appealing, even if their initial price point is higher than traditional timber or concrete.
Switching costs for buyers considering alternative building materials for Grafton Group can be substantial. These include expenses related to redesigning plans, implementing new installation techniques, and retraining construction workers. For instance, a shift from traditional timber framing to a new composite material might necessitate updated building codes compliance and specialized tools, adding to the initial outlay.
However, these barriers can be overcome if substitute materials offer compelling benefits. Significant cost savings, such as a 15% reduction in material expenses or a 20% decrease in labor time due to easier installation, can quickly offset initial switching costs. Furthermore, substitutes that provide enhanced durability, improved energy efficiency, or meet stricter environmental regulations may prove more attractive in the long run, making the transition worthwhile for developers and contractors.
Buyer Propensity to Substitute
Buyer propensity to substitute for Grafton Group's products is rising, driven by growing environmental awareness and a push for sustainable building solutions. As homeowners and construction firms increasingly prioritize energy efficiency, they become more receptive to alternative materials that offer these benefits.
Technological advancements are also playing a key role, making substitute products more viable and cost-effective. Government incentives for green building further encourage the adoption of these alternatives, directly impacting demand for traditional materials.
For instance, the global green building materials market was valued at approximately USD 273.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This trend suggests a tangible shift in buyer preference away from conventional options.
Key factors influencing buyer propensity to substitute include:
- Environmental Concerns: Increasing awareness of climate change and resource depletion makes sustainable options more attractive.
- Technological Innovation: Development of new, high-performance building materials that offer comparable or superior benefits to traditional ones.
- Government Regulations and Incentives: Policies promoting energy efficiency and the use of eco-friendly materials can accelerate substitution.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory shifts, like more stringent building codes or requirements for sustainable construction, can rapidly drive the use of substitute materials. For instance, in the UK, the Building Regulations 2022 introduced enhanced energy efficiency standards, potentially favoring materials with lower embodied carbon.
Government incentives, such as subsidies for home energy upgrades, further boost the appeal of alternative products. In 2024, many European countries continued to offer grants for retrofitting buildings with more efficient insulation and heating systems, directly impacting the demand for traditional building supplies. This creates a dynamic environment for Grafton Group, necessitating flexibility in its product portfolio to align with evolving compliance and market preferences.
- Stricter Building Codes: Mandates for improved energy efficiency and fire safety can favor alternative materials over traditional ones.
- Government Subsidies: Financial incentives for sustainable building practices and renovations directly increase the attractiveness of substitute products.
- Market Adaptation: Grafton Group must monitor and respond to these regulatory pressures by potentially diversifying its offerings or investing in new material technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Grafton Group is moderate but growing, influenced by innovation and sustainability trends. While traditional materials are established, newer alternatives offer advantages in performance and environmental impact. For instance, composite decking and recycled content building materials are gaining traction, presenting viable alternatives to wood and concrete respectively.
The price-performance ratio of substitutes is a key driver. Although some advanced materials may have higher initial costs, their long-term benefits like enhanced durability or energy efficiency can make them more appealing. For example, a 10% increase in upfront cost for a highly energy-efficient insulation material might be offset by projected savings of 15% on energy bills over its lifespan.
Switching costs for customers considering substitutes can be significant, involving redesign, new installation methods, and worker retraining. However, if substitutes offer substantial cost savings, such as a 20% reduction in installation labor, these barriers become less prohibitive.
| Substitute Material Example | Potential Benefit | Estimated Switching Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Composite Decking | Lower maintenance, higher durability | Moderate (new tools, installation training) |
| Recycled Content Insulation | Environmental appeal, potential energy savings | Low to Moderate (installation similar to traditional) |
| Advanced Composite Cladding | Weather resistance, aesthetic variety | High (design changes, specialized installation) |
Entrants Threaten
The building materials distribution sector demands substantial capital for essential assets like warehouses, inventory management systems, and robust logistics networks. Grafton Group's established presence, with operations spanning the UK, Ireland, and the Netherlands, underscores the high financial commitment needed to build and maintain such an extensive infrastructure, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Established players like Grafton Group leverage significant economies of scale in procurement, manufacturing, and distribution. For instance, Grafton Group's extensive store network across the UK and Ireland allows for bulk purchasing, driving down unit costs for building materials and home improvement products. This scale advantage makes it challenging for new entrants to achieve comparable cost efficiencies, particularly in competitive segments like timber and plumbing supplies.
Grafton Group benefits from its extensive and established distribution network, comprising numerous branches and retail outlets that directly serve both trade professionals and do-it-yourself consumers. This physical presence is a significant barrier to entry for newcomers.
New entrants would struggle to replicate Grafton's reach, needing to invest heavily in acquiring or developing comparable distribution infrastructure. Securing prime retail locations and forging robust supply chain partnerships with manufacturers would also present considerable hurdles, demanding substantial capital and time.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
Grafton Group benefits significantly from strong brand loyalty across its key brands, such as Selco Builders Warehouse in the UK and Chadwicks and Woodie's in Ireland. These established names have cultivated deep relationships with trade professionals over many years, creating a powerful barrier to entry for newcomers.
The implicit switching costs for customers are substantial. For instance, a builder relying on Selco for consistent product availability and knowledgeable staff might find it inefficient to switch to an unknown competitor, even if prices are slightly lower. This customer stickiness is a critical factor in deterring new entrants.
- Established Brand Recognition: Grafton's brands are household names within the trade, built over decades.
- Customer Relationships: Long-standing ties with trade customers create loyalty and reduce the incentive to switch.
- Implicit Switching Costs: The effort and potential disruption involved in changing suppliers act as a deterrent.
- Market Penetration: Grafton's widespread presence, with over 700 branches as of early 2024, further entrenches its customer base.
Regulatory Hurdles and Government Policy
The building materials sector faces significant regulatory challenges. New entrants must comply with stringent building codes, environmental standards, and health and safety regulations, which can be costly and time-consuming to navigate. For instance, in 2024, the UK government continued to emphasize stricter fire safety regulations for construction materials following the Grenfell Tower inquiry, adding a layer of complexity for any new player entering the market.
Government policies also play a crucial role in shaping market attractiveness and the threat of new entrants. Initiatives like those seen in 2024, such as increased investment in affordable housing projects or national infrastructure development, can signal opportunities but also attract established players with existing supply chains and regulatory expertise. Conversely, shifts in policy, such as changes to planning permissions or material sourcing mandates, can create barriers.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial upfront costs to meet building codes and environmental standards, potentially deterring smaller companies.
- Evolving Standards: Changes in regulations, such as those related to sustainability or material performance, require continuous investment in research and development for new entrants.
- Government Incentives and Mandates: Policies promoting specific materials or construction methods can either lower barriers for aligned entrants or create advantages for incumbents with established compliance.
The threat of new entrants for Grafton Group is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established economies of scale. Significant investment is needed for infrastructure like warehouses and logistics, a barrier Grafton's extensive network already overcomes. Newcomers also struggle to match Grafton's procurement power, which drives down costs for building materials.
Brand loyalty and customer switching costs further solidify Grafton's position, making it difficult for new players to gain traction. While regulatory hurdles exist, they impact all market participants. Grafton's market penetration, with over 700 branches by early 2024, reinforces its competitive advantage against potential new entrants.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Grafton's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (Warehousing, Logistics) | Established Infrastructure |
| Economies of Scale | Difficult to Achieve | Bulk Purchasing Power |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Significant Barrier | Strong Customer Relationships |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly and Time-Consuming | Existing Expertise |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Grafton Group is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld. We also leverage financial databases and regulatory filings to capture competitor strategies and market dynamics.
