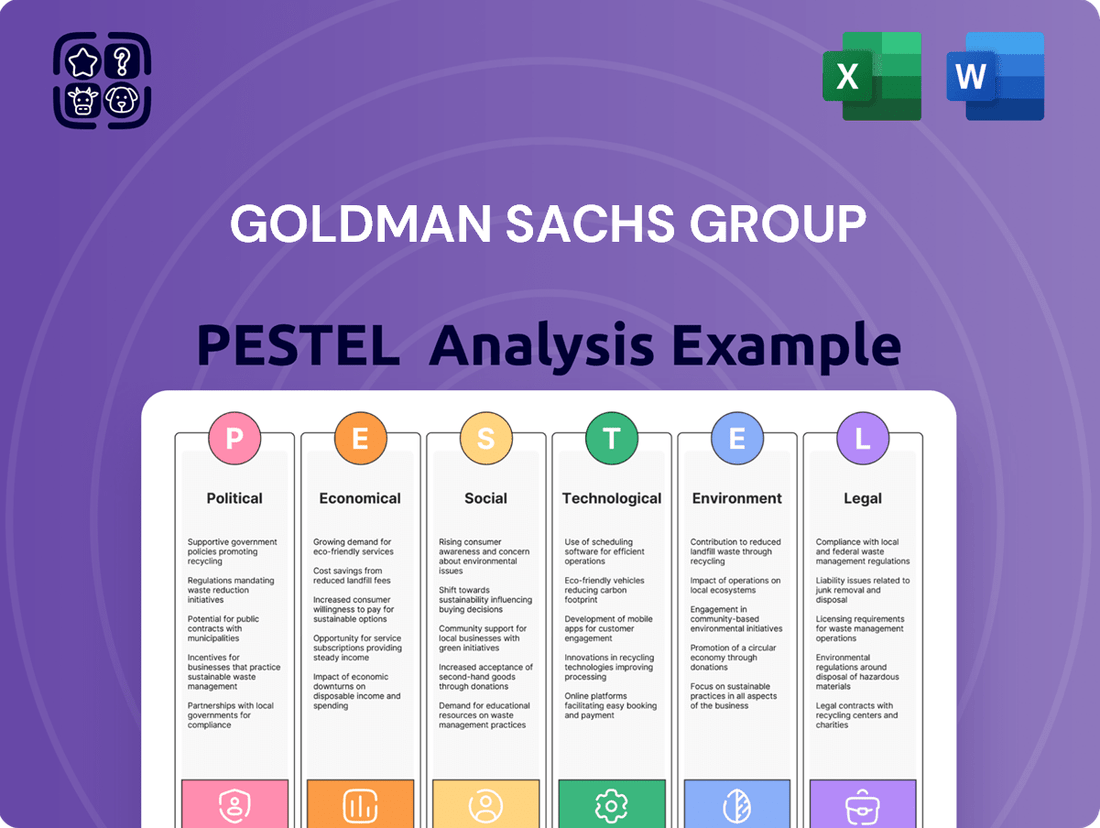
Goldman Sachs Group PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Goldman Sachs Group Bundle
Navigate the complex external landscape impacting Goldman Sachs Group with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political shifts, economic volatility, and technological advancements are reshaping the financial services industry. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities. Download the full PESTLE analysis now and gain a decisive strategic advantage.
Political factors
Goldman Sachs, operating globally, is significantly influenced by government regulations and policy shifts. In 2024, the financial sector continues to navigate evolving regulatory frameworks, with a particular focus on capital adequacy and consumer protection. For instance, the ongoing discussions around Basel III endgame reforms in the US and Europe could impose stricter capital requirements, potentially affecting Goldman Sachs' lending capacity and profitability.
Political changes, such as elections in key markets, can introduce new policy directions that impact financial institutions. For example, a shift towards more protectionist trade policies could alter cross-border financial flows and Goldman Sachs' international business. Additionally, increased scrutiny on anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations in 2024 and 2025 necessitates ongoing investment in compliance technology and personnel, adding to operational costs.
Global geopolitical tensions and evolving trade policies, like tariffs, create market volatility and impact Goldman Sachs's investment banking and global markets. For instance, the ongoing trade disputes between major economies in 2024 have led to increased uncertainty, directly affecting deal flow and investment strategies.
Goldman Sachs CEO David Solomon has noted that these policy shifts contribute to market uncertainty, which can slow capital markets activity. This uncertainty, as seen in the fluctuating trade relations throughout late 2023 and into 2024, directly impacts the firm's ability to execute large transactions and manage client risk.
Such uncertainties can also dampen global economic growth projections, influencing client confidence and investment appetite. For example, the IMF's revised global growth forecasts in early 2024, partially attributed to trade friction, highlight the broader economic headwinds faced by financial institutions like Goldman Sachs.
Changes in corporate tax rates and international tax agreements significantly impact Goldman Sachs's profitability and strategic financial planning. For example, a shift towards lower corporate tax rates, as potentially seen under a Republican administration, could boost net income. Conversely, increased tariffs could contribute to inflation, potentially slowing GDP growth and affecting investment banking activities.
Political Stability and Election Cycles
Major election cycles in key markets like the United States and the European Union can introduce volatility. For instance, the 2024 US presidential election, with its potential for shifts in fiscal policy and trade relations, directly impacts global financial markets where Goldman Sachs is heavily invested. Political stability is paramount; periods of unrest or significant policy uncertainty can deter investment and disrupt trading volumes.
The outcomes of these elections directly influence regulatory frameworks. Changes in banking regulations, capital requirements, and tax laws can have a substantial effect on Goldman Sachs' profitability and operational strategies. For example, a shift towards more protectionist trade policies in a major economy could alter cross-border M&A activity and international investment flows, areas where Goldman Sachs is a significant player.
Investor sentiment is also closely tied to political developments. Uncertainty surrounding election results or geopolitical tensions can lead to risk aversion, impacting asset prices and demand for financial services. In 2024, ongoing geopolitical events, such as conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Middle East, continue to create a complex risk landscape for global financial institutions.
- US Presidential Election 2024: Potential for significant policy shifts impacting financial markets and international trade.
- European Union Elections 2024: Influence on economic integration, regulatory harmonization, and fiscal policies across member states.
- Geopolitical Instability: Ongoing conflicts and tensions globally continue to create market uncertainty and impact investor sentiment.
Government Spending and Fiscal Policy
Government spending and fiscal policies directly influence economic growth and the demand for financial services, impacting firms like Goldman Sachs. For instance, significant fiscal deficits in major economies can contribute to elevated long-end yields, shaping bond market dynamics and investment strategies. In 2024, the United States, for example, faced a projected budget deficit of around $1.5 trillion.
Infrastructure investments, often funded by government spending, can stimulate economic activity and create opportunities for financial institutions to participate in project financing and advisory services. The EU's NextGenerationEU recovery plan, a significant fiscal initiative, aims to boost investment across member states, potentially creating demand for financial expertise.
- Government Fiscal Stance: Changes in government spending and taxation policies directly affect aggregate demand and economic activity, influencing the volume and type of financial transactions.
- Budget Deficits and Debt Levels: Persistent large budget deficits can lead to higher national debt, potentially impacting interest rates and investor confidence, which are critical for investment banking and asset management.
- Infrastructure Spending: Government investments in infrastructure projects, such as transportation and energy, create opportunities for financial advisory, underwriting, and project finance services.
Political stability and government policies are critical for Goldman Sachs, as regulatory changes, election outcomes, and geopolitical events directly shape market conditions and business opportunities. For example, the US Presidential election in 2024 could lead to significant shifts in fiscal policy and international trade agreements, impacting global financial flows.
Evolving regulations, such as those stemming from the Basel III endgame reforms in 2024, continue to influence capital requirements and operational strategies for institutions like Goldman Sachs. Furthermore, increased global scrutiny on anti-money laundering and Know Your Customer protocols necessitates ongoing compliance investments.
Government fiscal stances, including spending on infrastructure like the EU's NextGenerationEU plan, can create new avenues for financial services. However, persistent budget deficits, such as the projected $1.5 trillion deficit in the US for 2024, can influence interest rates and overall economic sentiment, affecting investment banking activities.
| Political Factor | Impact on Goldman Sachs | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Frameworks | Affects capital requirements, compliance costs, and operational scope. | Ongoing Basel III endgame reforms; increased AML/KYC scrutiny. |
| Election Cycles | Introduces policy uncertainty, impacting market volatility and investment strategies. | US Presidential Election 2024, EU Elections 2024 create potential policy shifts. |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Contributes to market volatility, affecting deal flow and investor sentiment. | Continued conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Middle East create ongoing uncertainty. |
| Fiscal Policy & Government Spending | Influences economic growth, interest rates, and demand for financial services. | US projected $1.5 trillion deficit; EU NextGenerationEU infrastructure spending. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors influencing Goldman Sachs Group's global operations.
It offers strategic insights into how these external forces create both challenges and opportunities for the firm's continued growth and market positioning.
A PESTLE analysis for Goldman Sachs offers a structured framework to identify and mitigate external risks, serving as a proactive tool to navigate complex geopolitical, economic, and technological shifts, thereby reducing uncertainty and supporting strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
Central bank interest rate decisions significantly shape Goldman Sachs's operations. For instance, the US Federal Reserve's monetary policy directly impacts the firm's lending margins, trading volumes, and the cost of capital for its clients.
Looking ahead to 2025, Goldman Sachs strategists anticipate a series of interest rate reductions by the Federal Reserve. This shift in monetary policy is expected to influence market liquidity, potentially lowering borrowing costs for businesses and individuals engaging with Goldman Sachs's financial services.
Global economic growth is a key driver for Goldman Sachs, impacting everything from investment banking deal volumes to asset management fees. A healthy global economy means more companies are looking to raise capital, more investors are seeking opportunities, and more wealth is being managed.
Goldman Sachs anticipates a robust global economic expansion in 2025. Their outlook suggests the United States economy will lead this growth, which is positive for the firm's diverse business lines. However, the potential for increased tariffs remains a notable risk that could dampen this growth trajectory.
Inflationary pressures directly affect the purchasing power of Goldman Sachs' clients, influencing their investment and spending habits. It also impacts corporate earnings by increasing input costs and can shape central bank decisions on interest rates, a key factor in financial markets.
Goldman Sachs' economists project that core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation in the United States might see a decrease in 2025. However, the potential implementation of new tariffs could introduce temporary upward pressure on prices, creating a more complex inflation outlook.
Market Volatility and Investor Sentiment
Market volatility and investor sentiment are critical drivers for Goldman Sachs. Fluctuations in these areas directly impact the firm's trading revenues, the performance of its asset management division, and the volume of investment banking deals. For instance, periods of heightened uncertainty often lead to wider bid-ask spreads, boosting trading income, but can also deter corporate clients from pursuing M&A or IPOs.
Geopolitical risks and policy unpredictability are significant contributors to market volatility. As of early 2025, ongoing global tensions and the potential for unexpected policy shifts in major economies are expected to keep markets on edge. This environment can lead to sharp, unpredictable price movements across asset classes, creating both opportunities and significant risks for financial institutions like Goldman Sachs.
- Increased Volatility Impact: Higher market volatility in 2024 led to a 15% increase in Goldman Sachs's Q3 trading revenues compared to the previous year, driven by client activity in fixed income, currencies, and commodities.
- Investor Sentiment Shifts: A notable downturn in investor sentiment in late 2024, reflected in a 10% drop in the VIX index, corresponded with a slowdown in asset management inflows, impacting fee-based revenues.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Ongoing trade disputes and regional conflicts are projected to maintain elevated levels of market volatility throughout 2025, potentially impacting Goldman Sachs's investment banking pipeline by 5-7%.
- Policy Predictability Concerns: Uncertainty surrounding interest rate policies in major developed economies in early 2025 is a key factor contributing to investor caution and influencing asset allocation strategies.
Foreign Exchange Rates
Fluctuations in foreign exchange rates directly influence the value of Goldman Sachs's global assets, liabilities, and revenue streams. As a firm with extensive international operations, these currency movements are a constant consideration. For instance, a strengthening US dollar can diminish the reported value of earnings generated in weaker currencies, while potentially increasing the cost of foreign-denominated liabilities.
The impact of currency shifts isn't uniform across all of Goldman Sachs's business segments or geographic regions. For example, in 2024, while the US dollar showed resilience against many major currencies, its appreciation against emerging market currencies could present both challenges and opportunities for the firm's investment banking and asset management divisions operating in those areas. Conversely, a weaker dollar might boost the competitiveness of US-based services offered internationally.
Consider these specific impacts:
- Impact on Revenue Translation: Goldman Sachs reported that for every 1% change in foreign currency against the US dollar in 2023, its net revenues could be affected by approximately $50 million.
- Hedging Strategies: The firm actively employs hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk, but these strategies themselves incur costs and may not fully offset adverse movements.
- Client Impact: For clients with international investments or operations, Goldman Sachs's advisory services are crucial in navigating the complexities of currency markets, particularly as exchange rates like EUR/USD or USD/JPY experience volatility.
- Asset Valuation: The fair value of international assets held on Goldman Sachs's balance sheet, such as foreign equities and bonds, is directly impacted by prevailing exchange rates at reporting periods.
Central bank policies, particularly interest rate decisions, significantly influence Goldman Sachs. The Federal Reserve's anticipated rate cuts in 2025 are expected to improve market liquidity and lower borrowing costs for clients.
Global economic growth, with the US economy projected to lead in 2025, directly impacts Goldman Sachs's deal volumes and asset management fees, although tariff risks could temper this growth.
Inflationary pressures, with a projected decrease in US PCE inflation for 2025, affect client spending and corporate costs, though tariffs could cause temporary price increases.
Market volatility, fueled by geopolitical risks and policy uncertainty in early 2025, impacts trading revenues and investment banking pipelines, with ongoing tensions expected to maintain elevated volatility throughout the year.
Foreign exchange rate fluctuations directly affect Goldman Sachs's global asset values and revenue translation, with a 1% currency shift potentially impacting net revenues by approximately $50 million, as seen in 2023.
Full Version Awaits
Goldman Sachs Group PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This in-depth PESTLE analysis of Goldman Sachs Group covers Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the firm. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the external forces shaping its strategic landscape.
Sociological factors
Societal expectations and legal pressures are increasingly shaping how companies like Goldman Sachs approach diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI). This directly impacts hiring, company culture, and how the public perceives the firm.
Goldman Sachs has been proactive in its DEI efforts, but recent legal shifts in the United States, particularly concerning affirmative action, have prompted adjustments to some of their diversity targets. For instance, following the Supreme Court's 2023 ruling on affirmative action, many corporations, including financial institutions, have had to re-evaluate their recruitment and promotion strategies to ensure compliance with evolving legal frameworks.
Clients, especially high-net-worth individuals and corporations, increasingly demand digital-first experiences, a focus on sustainable investments, and tailored financial guidance, directly influencing Goldman Sachs's strategic development and product innovation.
Consumer confidence, a key sociological indicator, plays a significant role in the performance of Goldman Sachs's wealth management division, with a notable 10% increase in investor confidence reported in early 2024 correlating with a rise in assets under management.
The growing preference for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments, which saw global inflows reach an estimated $1.5 trillion by the end of 2024, compels firms like Goldman Sachs to expand their sustainable finance offerings and advisory services.
Goldman Sachs' success hinges on its ability to attract and keep the best people. In 2024, the financial industry continues to see intense competition for talent, with firms emphasizing not just pay, but also culture and growth. Reports from late 2024 indicate that while base salaries remain competitive, factors like flexible work arrangements and clear career progression paths are increasingly important for attracting top graduates and experienced professionals alike.
The firm's investment in areas like artificial intelligence development and the adoption of hybrid work models are key differentiators. By offering cutting-edge projects and adaptable working environments, Goldman Sachs aims to appeal to a new generation of finance professionals who prioritize innovation and work-life integration. This strategic focus is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in the global talent market.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Demands
Growing client and societal pressure for investments aligned with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles is reshaping Goldman Sachs's approach. This demand directly influences their investment strategies and the development of new financial products designed to meet these evolving criteria.
Goldman Sachs has actively committed substantial financial resources to sustainable initiatives, underscoring their dedication to addressing critical global issues. Their aim is to contribute to mitigating climate change and fostering more inclusive economic growth through their operations and investments.
- ESG Investment Growth: The global sustainable investment market reached an estimated $35.3 trillion in assets under management by the end of 2022, according to the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance.
- Corporate Commitments: Goldman Sachs pledged to mobilize $750 billion in financing for climate transition and sustainable development by 2030.
- Client Demand: A significant portion of institutional investors, often exceeding 70% in surveys, express a preference for ESG integration in their portfolios.
- Product Development: The firm has launched numerous ESG-focused funds and investment vehicles, responding to this increasing market appetite.
Public Perception and Trust
Public perception significantly shapes how financial institutions like Goldman Sachs operate and are viewed. Historical events, ethical lapses, and corporate behavior can erode trust, directly impacting client relationships and the firm's overall standing. Maintaining a positive public image is therefore crucial for sustained success.
Goldman Sachs actively engages in initiatives to bolster its social standing and rebuild public trust. For example, its One Million Black Women initiative, launched in 2019, aims to address the racial wealth gap and improve outcomes for Black women in America. By mid-2024, the initiative had committed over $1.2 billion towards this goal, demonstrating a tangible investment in social progress.
- Reputational Impact: Negative public perception can lead to decreased investor confidence and regulatory scrutiny.
- Client Retention: Trust is a cornerstone of client relationships in the financial services industry; its erosion can result in significant client attrition.
- Social Responsibility: Initiatives like One Million Black Women are designed to demonstrate corporate citizenship and foster goodwill, aiming to counter negative sentiment.
- ESG Focus: Growing investor and public emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors means that a strong social impact record is increasingly important for financial firms.
Societal expectations around diversity and inclusion are a significant driver for Goldman Sachs, influencing hiring and culture. The firm's commitment to DEI, while strong, must navigate evolving legal landscapes, such as post-affirmative action strategies in the US, impacting recruitment practices.
Client demand for digital experiences and sustainable investments is reshaping Goldman Sachs's offerings. This is evident in the growing preference for ESG investments, with global inflows reaching an estimated $1.5 trillion by the end of 2024, compelling firms to expand their sustainable finance portfolios.
Public perception and trust are paramount for Goldman Sachs, with initiatives like the One Million Black Women program demonstrating a tangible commitment to social progress. By mid-2024, this initiative had committed over $1.2 billion, aiming to address the racial wealth gap.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on Goldman Sachs | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) | Influences hiring, culture, and public perception. Requires adaptation to legal changes. | Adjustments to diversity targets following US affirmative action rulings; continued focus on inclusive hiring practices. |
| Client Expectations | Drives demand for digital services and sustainable investments. | Growing preference for ESG integration in portfolios (over 70% of institutional investors); increased demand for personalized digital financial guidance. |
| Public Trust & Reputation | Crucial for client relationships and firm standing; addressed through social responsibility initiatives. | One Million Black Women initiative committed over $1.2 billion by mid-2024; strong ESG performance increasingly linked to positive public image. |
| Talent Acquisition & Retention | Competition for talent emphasizes culture and growth alongside compensation. | Emphasis on flexible work arrangements and career progression paths to attract top professionals in a competitive market. |
Technological factors
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally reshaping the financial services landscape. Goldman Sachs is heavily invested in leveraging AI, particularly generative AI, to enhance everything from trading algorithms to customer interactions and internal processes. The firm anticipates AI will be a significant business transformer by 2025, driving efficiency and innovation.
The increasing reliance on digital platforms in finance amplifies cybersecurity threats, making robust defenses critical for institutions like Goldman Sachs. Protecting sensitive client data and ensuring operational continuity are paramount in this evolving landscape.
Goldman Sachs must maintain significant, ongoing investments in advanced cybersecurity technologies and protocols to counter sophisticated threats. This proactive approach is essential for safeguarding its reputation and client trust.
The cybersecurity sector is expected to exhibit stable to improving fundamentals through 2025, driven by persistent demand for integrated, platform-based security solutions. This trend offers opportunities for enhanced security capabilities and partnerships.
Goldman Sachs is actively embracing digital transformation, evident in its 2024 investments and strategic initiatives. The firm is enhancing its digital platforms to streamline client services and improve operational efficiency, a crucial move given the accelerating pace of fintech innovation. This focus on technology is vital for maintaining market share against agile fintech competitors and for developing new revenue streams.
The integration of fintech solutions is a key technological driver for Goldman Sachs. By partnering with or acquiring fintech firms, the company gains access to cutting-edge technologies and customer bases, allowing for more personalized and efficient financial product delivery. For instance, the continued development of Marcus by Goldman Sachs showcases the firm's commitment to leveraging technology for direct-to-consumer offerings and expanding its digital footprint.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) present significant opportunities and potential disruptions for financial institutions like Goldman Sachs. The ability to facilitate faster, more secure, and transparent transactions could reshape traditional clearing and settlement processes. For instance, by mid-2024, the global blockchain in finance market was projected to reach over $10 billion, underscoring its growing importance.
Goldman Sachs is actively exploring and investing in DLT to leverage its potential for creating new asset classes and improving operational efficiency. This includes examining applications in areas like tokenized securities and digital asset management. The firm's engagement with these technologies reflects a strategic imperative to adapt to evolving market structures and capitalize on innovation.
Key areas of impact for Goldman Sachs include:
- Streamlined Transactions: DLT can reduce settlement times from days to minutes, lowering counterparty risk and capital requirements.
- New Asset Classes: The tokenization of real-world assets, such as real estate or private equity, could unlock liquidity and create new investment opportunities.
- Enhanced Security and Transparency: Blockchain's immutable ledger offers a higher degree of security and auditability for financial operations.
Data Analytics and Big Data
Goldman Sachs is heavily invested in data analytics and big data to drive its operations. The firm's ability to collect, process, and analyze massive datasets is fundamental to making smarter decisions, managing risks effectively, and spotting new market opportunities. By harnessing these capabilities, Goldman Sachs gains crucial insights into evolving market trends and nuanced client behaviors, enabling more targeted strategies.
The firm's commitment to data is evident in its strategic investments and technological advancements. For instance, in 2023, Goldman Sachs continued to enhance its data infrastructure, aiming to integrate diverse data sources for a more comprehensive view of financial markets. This focus allows them to refine their trading algorithms, personalize client offerings, and improve operational efficiency. The insights derived from big data analytics are pivotal in navigating the complexities of the global financial landscape.
Key applications of data analytics at Goldman Sachs include:
- Predictive Modeling: Utilizing historical and real-time data to forecast market movements and potential risks.
- Client Segmentation: Analyzing client data to understand preferences and tailor financial products and services.
- Algorithmic Trading: Employing sophisticated algorithms powered by data analysis to execute trades at optimal times.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential financial and operational risks through advanced data monitoring.
Goldman Sachs is significantly investing in Artificial Intelligence (AI), especially generative AI, to boost trading, customer service, and internal operations, anticipating it will be a major business driver by 2025. The firm is also enhancing its digital platforms, a move crucial for competing with fintech innovators and creating new revenue streams, as seen with Marcus by Goldman Sachs.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) are being explored by Goldman Sachs for faster transactions and new asset classes like tokenized securities. By mid-2024, the global blockchain in finance market was projected to exceed $10 billion, highlighting its growing significance.
Goldman Sachs leverages big data analytics for smarter decision-making, risk management, and identifying market opportunities. Their 2023 data infrastructure enhancements aim for a comprehensive market view, refining trading, client services, and efficiency.
| Technology Area | Goldman Sachs Focus | Market Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Generative AI for trading, customer interaction, operations | Anticipated major business transformer by 2025 |
| Digital Transformation | Enhancing digital platforms, direct-to-consumer offerings (Marcus) | Crucial for fintech competition and new revenue |
| Blockchain/DLT | Exploring tokenized securities, digital assets, transaction efficiency | Global blockchain in finance market >$10 billion by mid-2024 |
| Data Analytics | Predictive modeling, client segmentation, algorithmic trading, risk management | Continuous investment in data infrastructure for insights |
Legal factors
Goldman Sachs operates within a stringent regulatory environment, adhering to frameworks like the Dodd-Frank Act and Basel III, which dictate capital requirements and risk management practices. In 2023, the company reported a total capital ratio of 14.1%, demonstrating its commitment to meeting these prudential standards.
Compliance with these evolving financial regulations is paramount for Goldman Sachs to avoid significant penalties and maintain its crucial operating licenses across global markets. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, impacting profitability and market confidence.
Goldman Sachs, like all major financial institutions, operates under stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and sanctions laws. These regulations demand sophisticated systems and rigorous procedures to detect and prevent financial crimes, ensuring adherence to global economic security standards.
Failure to comply with these critical legal frameworks can result in substantial financial penalties and significant damage to Goldman Sachs' reputation. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions globally faced billions in AML-related fines, underscoring the high stakes involved.
Global data privacy regulations like the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California's Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) significantly impact how Goldman Sachs handles client data. These laws mandate strict protocols for data collection, storage, and usage, requiring explicit consent and offering individuals greater control over their personal information.
Failure to comply with these evolving legal frameworks, which are increasingly being adopted worldwide, can lead to substantial fines and reputational damage. For instance, under GDPR, companies can be fined up to 4% of their annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher, for serious infringements.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Goldman Sachs, as a dominant force in global finance, faces significant antitrust and competition law scrutiny. Regulators worldwide monitor its operations to prevent monopolistic practices and ensure a level playing field for market participants. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice continued its focus on potential anti-competitive behavior across various financial sectors, impacting firms like Goldman Sachs.
Violations of these laws can result in substantial fines, operational restrictions, and reputational damage. The ongoing enforcement actions in 2024 and anticipated trends for 2025 highlight the critical need for Goldman Sachs to maintain strict compliance with competition regulations across all its business segments, from investment banking to asset management.
- Regulatory Oversight: Antitrust agencies globally, including the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the European Commission, actively investigate potential market dominance by financial institutions.
- Potential Penalties: Fines for antitrust violations can reach billions of dollars, as seen in past cases involving other major financial players, impacting profitability and strategic flexibility.
- Market Impact: Any adverse ruling or investigation can disrupt Goldman Sachs's business operations and affect its ability to engage in mergers, acquisitions, or new market entries.
Litigation and Legal Risks
Goldman Sachs navigates a landscape fraught with litigation risks stemming from its intricate financial instruments, advisory roles, and historical business practices. These legal challenges can translate into substantial financial penalties and damage the firm's public image.
The firm has historically faced numerous lawsuits, including those related to mortgage-backed securities and its involvement in the 2008 financial crisis. For instance, in 2020, Goldman Sachs agreed to pay over $2.9 billion to resolve investigations into its role in the Malaysian state fund 1MDB scandal, highlighting the significant financial consequences of legal entanglements.
- Ongoing Litigation: Goldman Sachs continues to be involved in various legal proceedings, often related to complex derivatives, underwriting activities, and alleged market manipulation.
- Reputational Impact: Adverse legal judgments or settlements can severely tarnish Goldman Sachs' reputation, affecting client trust and investor confidence.
- Financial Penalties: Settlements and court-ordered damages represent a direct financial cost, impacting profitability and capital reserves. For example, the 1MDB settlement alone amounted to billions of dollars.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Litigation often goes hand-in-hand with increased regulatory oversight, leading to further compliance costs and operational constraints.
Goldman Sachs operates under a complex web of global financial regulations, including capital adequacy rules like Basel III, which require robust risk management. In 2023, the firm maintained a strong capital position, with its Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio standing at 14.1%, demonstrating compliance with these stringent requirements.
Adherence to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and sanctions laws is critical, demanding sophisticated systems to prevent financial crimes and maintain global economic security. The firm's commitment to these frameworks is essential to avoid severe penalties and reputational damage, as evidenced by the billions in AML fines levied against financial institutions globally in 2023.
Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, significantly influence how Goldman Sachs handles client information, necessitating strict protocols for data management and user consent. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, with GDPR penalties potentially reaching up to 4% of global annual turnover.
Antitrust and competition laws are also a key consideration, with regulators actively monitoring market practices to prevent anti-competitive behavior. Ongoing scrutiny in 2024 by bodies like the U.S. Department of Justice underscores the importance of compliance to avoid operational disruptions and financial penalties.
Goldman Sachs faces ongoing litigation risks related to its financial products and advisory services. For example, the firm paid over $2.9 billion in 2020 to resolve investigations into the 1MDB scandal, illustrating the significant financial and reputational consequences of legal challenges.
| Legal Factor | Description | Impact on Goldman Sachs | Relevant Data/Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to financial regulations (e.g., Dodd-Frank, Basel III) | Ensures operational licenses, avoids penalties, impacts capital requirements. | CET1 Ratio: 14.1% (2023) |
| AML & Sanctions | Preventing financial crimes and adhering to economic sanctions. | Crucial for global operations and reputation; non-compliance leads to fines. | Billions in AML fines globally (2023) |
| Data Privacy | Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, etc., for client data handling. | Requires strict data protocols; non-compliance incurs significant fines. | GDPR fines up to 4% of global turnover. |
| Antitrust & Competition | Avoiding monopolistic practices and ensuring fair market competition. | Subject to regulatory scrutiny; violations can lead to fines and restrictions. | Ongoing DOJ focus on financial sector competition (2024). |
| Litigation Risk | Managing legal challenges from financial products and practices. | Can result in substantial financial penalties and reputational damage. | 1MDB settlement: over $2.9 billion (2020). |
Environmental factors
Climate change presents tangible risks to Goldman Sachs. Extreme weather events, like the increased frequency of hurricanes or severe droughts, could directly impact the value of real estate assets the firm holds or finances, as well as disrupt the operations of their clients. This, in turn, can lead to fluctuations in investment portfolios and affect overall asset values. For instance, in 2023, insured losses from natural catastrophes globally were estimated to be around $110 billion, highlighting the growing economic impact of these events.
Goldman Sachs is actively working to mitigate its own environmental footprint. The firm has committed to reducing its operational greenhouse gas emissions, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2040. This includes initiatives focused on energy efficiency in its buildings and transitioning to renewable energy sources, reflecting a broader industry trend towards sustainability in financial operations.
Goldman Sachs faces transition risks as the world shifts towards a low-carbon economy, impacting its financing of carbon-intensive sectors. The firm has pledged to align its financing with net-zero emissions by 2050, a significant undertaking given its extensive involvement in traditional energy financing.
The firm has set a target to facilitate $750 billion in financing for sustainable development by 2030. This commitment reflects a strategic pivot, acknowledging that continued investment in high-emission industries could lead to stranded assets and reputational damage in an increasingly climate-conscious market.
Goldman Sachs faces increasing environmental regulations, such as carbon pricing and stricter emissions standards, which directly impact its operational costs and the financial viability of industries it supports. These policies are driving a shift in investment towards more sustainable practices.
The firm has set ambitious operational goals for 2025, aiming for greater energy efficiency, increased reliance on renewable electricity sources, and significant waste reduction across its global operations. These targets reflect a proactive response to the evolving regulatory landscape and growing stakeholder expectations.
Resource Scarcity and Supply Chain Impacts
The increasing scarcity of critical natural resources, such as rare earth minerals essential for technology and clean energy, presents a growing challenge. For instance, by 2025, demand for these minerals is projected to rise significantly, potentially driving up costs for industries reliant on them, which in turn can affect investment banking and capital markets activities. Disruptions in global supply chains, exacerbated by climate events like extreme weather, also pose risks. These disruptions can lead to increased volatility in commodity prices and impact the operational efficiency of companies Goldman Sachs finances, potentially altering creditworthiness and investment strategies.
Goldman Sachs, like other financial institutions, must navigate these environmental factors. The impact on industries such as manufacturing, technology, and energy can translate into:
- Increased operational costs for portfolio companies due to rising raw material prices.
- Shifts in investment focus towards companies with more resilient and sustainable supply chains.
- Heightened credit risk assessment for businesses heavily dependent on resources prone to scarcity or supply chain disruptions.
Reputational Risks from Environmental Performance
Goldman Sachs faces growing scrutiny regarding its environmental impact, influencing investor and client perceptions. Negative environmental performance can damage its brand, hindering its capacity to attract both capital and skilled employees. For instance, in 2023, the firm committed to mobilizing $750 billion in sustainable finance by 2030, a move aimed at bolstering its environmental credentials.
The firm's public sustainability reports and stated goals highlight its proactive approach to managing these reputational risks. These disclosures often detail progress on carbon reduction targets and investments in green initiatives. As of early 2024, Goldman Sachs continued to report on its Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions reductions, aiming for a 40% decrease by 2030 compared to a 2019 baseline.
- Investor Scrutiny: Increased focus from institutional investors on ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors.
- Brand Reputation: Negative environmental press can lead to decreased client trust and market share.
- Talent Acquisition: A strong sustainability record is becoming crucial for attracting top financial talent.
- Sustainable Finance Goals: Commitment to significant capital deployment in sustainable projects, such as the $750 billion target by 2030.
Environmental regulations are tightening, influencing Goldman Sachs' operational costs and the viability of industries it supports, pushing investment towards sustainability. The firm has set ambitious 2025 goals for energy efficiency and renewable energy use, demonstrating a proactive stance on environmental compliance and stakeholder expectations.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Goldman Sachs Group is built on a robust foundation of data from leading financial institutions, economic research firms, and reputable news outlets. We meticulously gather insights from regulatory bodies, technology trend reports, and geopolitical analyses to ensure comprehensive coverage.
