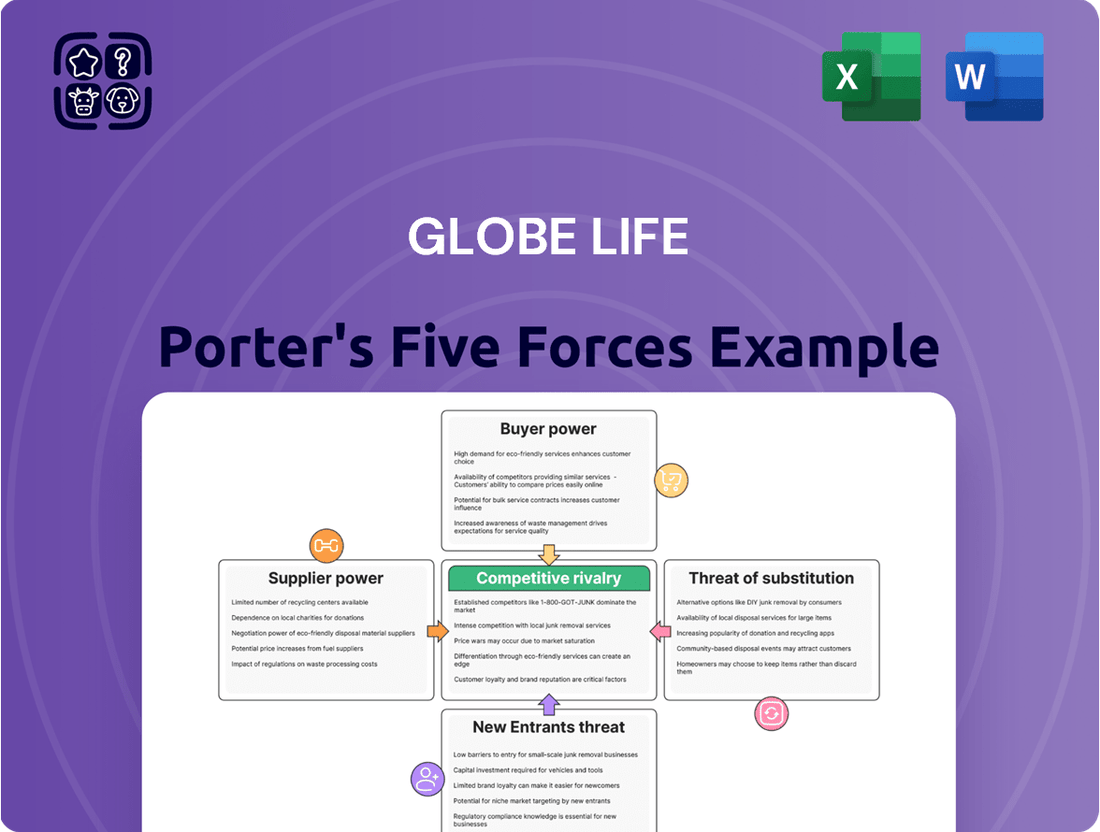
Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Globe Life Bundle
Globe Life operates in a dynamic insurance landscape, with Porter's Five Forces offering a crucial lens into its competitive environment. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry is paramount for strategic success. This brief overview highlights key pressures, but the full analysis dives much deeper.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Globe Life’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The scarcity of specialized reinsurance capacity significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power for Globe Life. When specific, niche, or high-risk coverages are difficult to find in the reinsurance market, Globe Life faces fewer options. This limited availability allows the few reinsurers who *can* provide such specialized coverage to command higher prices and more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the market for certain catastrophic event reinsurances tightened considerably, leading to an average price increase of 20-30% for affected insurers, directly impacting their cost of risk transfer.
Globe Life's dependence on specialized actuarial data and analytics providers significantly influences its bargaining power. The insurance industry relies heavily on accurate risk assessment and pricing, which are driven by sophisticated models and vast datasets. If the number of providers offering these critical services is limited, or if their technology is proprietary and difficult to replicate, these suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms. For example, in 2024, the global insurance analytics market was valued at approximately $9.8 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial investment in these services, but also highlighting potential supplier leverage if competition remains constrained.
Globe Life's reliance on specialized third-party technology and IT infrastructure significantly shapes the bargaining power of its suppliers. Core insurance software, essential for policy administration and claims, often comes from a limited number of vendors. For instance, in 2024, the global IT infrastructure market, which includes cloud services and cybersecurity, continued to see consolidation, giving larger players more leverage. Companies offering integrated platforms or highly specialized cybersecurity solutions can command higher prices due to the critical nature of these services for Globe Life's operations.
Availability and Cost of Qualified Insurance Agents
Globe Life's reliance on a network of both independent and captive insurance agents highlights a critical aspect of supplier power. The availability and cost of qualified agents, especially those adept at serving middle and lower-middle-income markets, directly influence Globe Life's distribution efficiency and market penetration.
A scarcity of highly productive agents or escalating commission demands can significantly bolster the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continued to face challenges in agent recruitment and retention, particularly for roles requiring specialized skills in customer engagement and product explanation to diverse income segments.
- Agent Availability: A tight labor market for skilled insurance agents can limit Globe Life's expansion and increase recruitment costs.
- Commission Structures: Increased competition for talented agents may force Globe Life to offer more attractive commission rates, impacting profitability.
- Productivity Levels: The ability of agents to effectively sell Globe Life's products is a key factor; lower average productivity among a supplier pool can necessitate higher agent numbers or increased training investment.
- Market Specialization: Agents with proven success in Globe Life's target demographics represent a valuable, and potentially scarce, resource.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Service Providers
The insurance industry, including companies like Globe Life, operates within a heavily regulated landscape, necessitating continuous engagement with legal and compliance service providers. These specialized firms, focusing on areas like insurance law and regulatory affairs, hold a unique and often limited pool of expertise crucial for navigating intricate state and federal regulations. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. insurance market saw ongoing adjustments to regulations concerning data privacy and cybersecurity, directly impacting the demand for specialized legal counsel.
This specialized knowledge and the critical nature of compliance give these providers significant bargaining power. They can influence Globe Life's operational costs through their fees and impact strategic decisions by advising on regulatory adherence. The scarcity of truly expert legal and compliance professionals in this niche field means Globe Life, like its peers, must often accept terms dictated by these service providers, particularly when facing complex legal challenges or significant regulatory shifts.
- Specialized Expertise: Law firms and consultants with deep knowledge of insurance regulations are essential for compliance.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating state and federal laws in the insurance sector requires highly specific legal advice.
- Limited Supply: The scarcity of these specialized professionals enhances their bargaining position.
- Cost Impact: Their fees and the necessity of their services can significantly affect Globe Life's operating expenses.
Globe Life's reliance on reinsurers for risk transfer significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. The availability and cost of reinsurance capacity, especially for specialized or catastrophic coverages, can dictate terms. In 2024, the reinsurance market experienced price hikes, with some catastrophe reinsurance renewals seeing increases of 20-30%, underscoring the leverage reinsurers hold when capacity is constrained.
Providers of specialized actuarial data and analytics also wield considerable power due to the critical nature of their services. The global insurance analytics market, valued at approximately $9.8 billion in 2024, highlights the demand, but a limited number of high-quality providers can lead to higher costs for Globe Life. This dependence on niche expertise strengthens supplier negotiation leverage.
Furthermore, Globe Life's distribution through agents, particularly those targeting specific demographics, can create supplier leverage. Challenges in agent recruitment and retention in 2024 meant that skilled agents could command higher commissions, impacting Globe Life's cost of sales and market reach.
| Factor | Impact on Globe Life | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Reinsurance Capacity | Increased bargaining power for reinsurers when capacity is scarce. | Catastrophe reinsurance price increases of 20-30% in 2024. |
| Specialized Analytics Providers | Higher costs and potentially dictated terms due to reliance on niche expertise. | Global insurance analytics market valued at ~$9.8 billion in 2024. |
| Insurance Agents | Potential for higher commission demands due to recruitment/retention challenges. | Continued challenges in agent acquisition and retention observed in 2024. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Globe Life's position in the insurance industry.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry rivals and their impact.
Customers Bargaining Power
Globe Life's core customer base, primarily middle and lower-middle-income Americans, exhibits significant price sensitivity when it comes to insurance policies. This means customers actively compare offerings to find the most cost-effective plans, directly impacting Globe Life's pricing strategies and potentially squeezing profit margins. For instance, data from 2024 indicates that a substantial portion of households in these income brackets prioritize affordability when selecting financial services, making price a primary decision driver.
The life and supplemental health insurance sector is teeming with options, presenting customers with a vast marketplace. This saturation means individuals and families have ample opportunity to shop around, comparing policies and prices from a multitude of companies, from well-known national brands to specialized local insurers.
This abundance of choice significantly bolsters the bargaining power of customers. They can readily switch providers if they find better rates, more comprehensive coverage, or superior customer service elsewhere, compelling Globe Life to remain competitive and constantly refine its value proposition.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. life insurance industry saw a robust competitive landscape, with over 700 life insurance companies operating nationwide. This competitive density means consumers have a wide spectrum of options at their fingertips, directly influencing pricing and product innovation.
Low switching costs for policyholders significantly boost customer bargaining power. For many standard life and supplemental health insurance policies, moving to a new provider is straightforward, often requiring little more than completing new application forms and perhaps a medical exam. There are rarely substantial financial penalties for early termination of these types of policies, making it easy for customers to shop around.
This ease of switching allows customers to readily compare offerings and move to competitors who provide better rates or enhanced services. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer surveyed reported spending less than two hours researching and completing the paperwork to switch insurance providers, highlighting the minimal effort involved. This dynamic means Globe Life, and similar insurers, must remain competitive on price and service to retain their customer base.
Access to Comparative Pricing Information Online
The widespread availability of online comparison tools has dramatically shifted the power dynamics in the insurance sector, including for companies like Globe Life. Consumers can now effortlessly sift through numerous policy options, scrutinizing features and premiums from various providers in mere moments. This ease of access to comparative pricing information directly amplifies the bargaining power of customers, as they are better equipped to identify and demand the most advantageous terms available in the market.
This increased transparency means customers are less reliant on individual insurers for information and more empowered to make informed choices based on a broad market view. For instance, a significant portion of consumers actively use comparison websites to research insurance products. In 2024, studies indicated that over 60% of individuals purchasing insurance in developed markets utilized online comparison tools as a primary research method, directly impacting their negotiation leverage with providers.
- Increased Transparency: Online platforms provide a clear view of pricing and policy details across multiple insurers.
- Empowered Consumers: Customers can easily compare offers, leading to greater demand for competitive pricing.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: The internet levels the playing field, giving consumers access to data previously held by insurers.
- Price Sensitivity: The ability to compare prices makes customers more sensitive to price differentials, pushing insurers to offer better value.
Influence of Independent Agents on Customer Choices
Globe Life's reliance on independent agents, who also represent other insurance providers, significantly impacts customer bargaining power. These agents, acting as intermediaries, often prioritize their clients' best interests, recommending policies that offer superior value or lower premiums, even if from a competitor. This can lead customers to leverage competing offers, increasing their ability to negotiate better terms with Globe Life.
The influence of independent agents means customers can easily access and compare a wider range of insurance products. For instance, in 2024, the independent agent channel continued to be a substantial part of the U.S. insurance distribution landscape, with many consumers actively seeking advice from these agents to navigate complex policy options. This broad market access empowers customers by providing them with ample choices and the knowledge to demand more favorable terms.
- Customer Empowerment: Independent agents act as client advocates, guiding choices towards the best fit, thereby increasing customer leverage.
- Market Access: Customers can easily compare Globe Life's offerings with those of numerous other carriers through these agents.
- Competitive Pressure: Agents can direct business to competitors, creating pressure on Globe Life to offer competitive pricing and benefits.
- Information Asymmetry Reduction: Agents equip customers with knowledge, diminishing the information advantage insurers might otherwise hold.
Globe Life faces significant customer bargaining power due to the sheer volume of insurance providers and the ease with which consumers can switch. In 2024, the U.S. insurance market featured over 700 life insurance companies, offering consumers a vast array of choices. This abundance, coupled with low switching costs—often taking less than two hours for a customer to switch providers in 2024 according to surveys—empowers customers to demand competitive pricing and better terms. The widespread use of online comparison tools, utilized by over 60% of insurance purchasers in developed markets in 2024, further amplifies this power by increasing price transparency and reducing information asymmetry.
| Factor | Impact on Globe Life | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High bargaining power | Over 700 life insurance companies in the U.S. |
| Switching Costs | High bargaining power | Average < 2 hours to switch providers |
| Online Comparison Tools | High bargaining power | > 60% of consumers use comparison tools |
| Independent Agents | Moderate bargaining power | Significant distribution channel, advocates for customer value |
Preview Before You Purchase
Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a deep dive into the competitive landscape of the life insurance industry. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This comprehensive document is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights to inform strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Globe Life operates in the life and supplemental health insurance sectors, which are quite fragmented. This means there are many companies, big and small, all trying to win over the same customers. Think of national giants, smaller companies that focus on specific needs, and even local businesses – they all compete directly. This intense rivalry is particularly strong when targeting middle and lower-middle-income individuals, a key demographic for Globe Life.
Globe Life operates in a market where price is a major driver for its typically price-sensitive customer base, especially for standardized life and supplemental health insurance products. This inherent price sensitivity fuels intense competition, with rivals frequently employing aggressive pricing tactics to capture market share.
This constant price pressure can significantly impact profitability, forcing companies like Globe Life to prioritize stringent cost management to maintain healthy margins. In 2023, the life insurance industry saw a continued focus on competitive pricing, with direct-to-consumer models and simplified underwriting aiming to reduce overhead and offer more attractive rates.
Globe Life's basic life and supplemental health insurance products often face limited differentiation, making them appear as commodities to many consumers. This means that competing effectively often hinges more on factors like price, the strength of the brand name, and how efficiently the company reaches its customers, rather than unique product features.
In 2024, the insurance industry continues to see this trend, where the fundamental value proposition of many insurance policies is quite similar across providers. For Globe Life, this necessitates a strong focus on operational efficiency and brand trust to stand out in a crowded market where price sensitivity can be a significant driver of consumer choice.
Aggressive Marketing and Distribution Strategies by Rivals
Competitors in the insurance sector are known for their vigorous marketing and distribution efforts. This includes significant spending on advertising across various media, targeted digital campaigns, and the cultivation of extensive agent networks to reach a broad customer base. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. life insurance industry saw substantial advertising expenditures aimed at capturing market share.
Globe Life, to remain competitive, must consistently allocate resources to its own marketing and distribution channels. This ongoing investment is crucial for maintaining brand awareness and effectively reaching prospective policyholders, thereby intensifying the overall competitive rivalry in the market.
- Aggressive Advertising: Competitors often run broad advertising campaigns, utilizing television, radio, and online platforms to build brand recognition.
- Digital Engagement: Many rivals heavily invest in digital marketing, including social media advertising, search engine optimization (SEO), and pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns to attract online leads.
- Agent Networks: A significant number of insurance companies rely on large, well-trained agent forces, offering incentives and support to drive sales and customer acquisition.
- Distribution Channel Investment: The industry sees continuous investment in diverse distribution channels, from direct-to-consumer models to partnerships with financial institutions, all contributing to the competitive landscape.
Regulatory Environment Influencing Competitive Dynamics
The insurance sector operates under a dense web of regulations, with each state in the U.S. imposing its own unique solvency standards and operational rules. This patchwork of requirements can significantly influence how companies, including Globe Life, compete against one another. For instance, varying capital requirements can create barriers for new entrants, thereby reducing competitive intensity, but also dictate operational flexibility for established players.
These regulatory frameworks shape the very nature of competition. Insurers must navigate differing rules on product development, marketing, and claims processing, which can lead to competitive advantages or disadvantages. For 2024, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) continues to harmonize certain standards, but significant state-level variations persist, impacting factors like pricing strategies and the speed of new product launches.
- State-Specific Regulations: Varying solvency margins and reserve requirements across states create a complex compliance landscape for insurers like Globe Life.
- Barriers to Entry: Stringent licensing and capital requirements, driven by regulation, can limit new competitors from entering the market, thus influencing rivalry.
- Product Innovation Constraints: Regulatory approval processes for new insurance products can slow down innovation, forcing competitors to focus on refining existing offerings or operational efficiency.
- Impact on Pricing and Claims: Differing regulations on pricing structures and claims handling procedures can lead to variations in customer experience and competitive positioning.
The competitive rivalry within Globe Life's operating sectors is fierce due to market fragmentation and a price-sensitive customer base. Many companies, from national players to niche providers, vie for the same middle and lower-middle-income consumers, often competing on price for standardized life and supplemental health insurance products.
This intense competition, driven by similar product offerings and a focus on cost management, necessitates robust marketing and distribution strategies from companies like Globe Life. In 2023, substantial advertising expenditures were noted across the U.S. life insurance industry as firms sought to capture market share through various channels, including digital engagement and extensive agent networks.
Navigating a complex, state-specific regulatory environment further shapes this rivalry, influencing product innovation, pricing, and operational flexibility. For instance, varying capital requirements can act as a barrier to entry, indirectly affecting the intensity of competition among established insurers in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Rivalry | 2023/2024 Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | High number of competitors | Continues to be a fragmented market |
| Price Sensitivity | Intensifies price-based competition | Key driver for consumer choice |
| Product Differentiation | Limited; focus on price and brand | Commoditization of basic products |
| Marketing & Distribution | High investment in advertising and agents | Significant ad spend and digital focus |
| Regulatory Environment | State-specific rules create complexity | Persistent state-level variations impacting operations |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Individuals can choose to build personal savings or emergency funds as a substitute for life or supplemental health insurance. For instance, by mid-2024, the average savings account interest rate hovered around 4.35%, potentially offering a modest return for those self-insuring. This approach can be seen as more flexible, allowing direct access to funds without policy limitations.
Investing in financial instruments like mutual funds or bonds presents another substitute. By the end of 2023, the S&P 500 saw a significant increase, and bond yields remained competitive, offering potential for higher returns than insurance premiums for some. This self-insurance strategy, backed by accumulated wealth, might appeal to those seeking greater control and perceived higher growth.
Government social safety nets like Social Security survivor benefits, Medicare, and Medicaid can act as substitutes for some private insurance. These programs provide a baseline of support, potentially diminishing the demand for certain types of supplemental private coverage, especially among lower-income individuals.
For instance, Medicare provides health insurance for those 65 and older, and Medicaid offers coverage for low-income individuals and families. These public services can reduce the reliance on private health insurance, thereby posing a threat to insurers like Globe Life that offer similar supplemental health products.
While Globe Life's products are designed to complement, not replace, these government programs, the existence of robust public safety nets can still influence consumer purchasing decisions. In 2024, the U.S. Social Security Administration disbursed over $1.3 trillion in benefits, demonstrating the significant role government programs play in providing financial security.
Employer-sponsored group insurance plans present a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Globe Life. Many Americans rely on their employers for life and health insurance, reducing their demand for individual policies. In 2024, it's estimated that over 150 million Americans receive health insurance through their employers, a substantial portion of the population that might otherwise be customers for private insurers.
When these employer plans are comprehensive and cost-effective, they directly compete with the offerings of independent insurance providers. This can limit the market share and growth potential for companies that don't directly benefit from employer-based enrollment. The convenience and often lower out-of-pocket costs associated with employer plans make them a powerful substitute.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Other Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance products. These tax-advantaged accounts allow individuals to set aside money for qualified medical expenses, effectively acting as a self-funded alternative for certain healthcare needs. For those enrolled in high-deductible health plans, HSAs, in particular, can reduce reliance on supplemental insurance by empowering individuals to manage their healthcare savings directly.
The appeal of HSAs and FSAs is bolstered by their tax benefits and the growing trend towards consumer-driven healthcare. As of early 2024, HSA contribution limits for individuals were $4,150 and $8,300 for families, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for those aged 55 and over. These accounts offer a triple tax advantage: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
- Growing Adoption: HSA enrollment has seen substantial growth, with over 37 million Americans enrolled in an HSA by January 2024, according to HSA market research.
- Tax Advantages: The triple tax benefit of HSAs makes them an attractive financial tool for managing healthcare costs, potentially reducing out-of-pocket expenses significantly.
- Flexibility: Unlike FSAs, HSA funds roll over year after year and can be invested, offering long-term savings and investment potential beyond immediate healthcare needs.
- Substitute for Supplemental Needs: For individuals with high-deductible plans, HSAs can cover routine medical costs and deductibles, diminishing the need for some supplemental insurance policies.
Alternative Risk Management Strategies
The threat of substitutes for Globe Life's core insurance products isn't solely from other insurance companies. Informal support systems, like family assistance or community aid, can act as alternatives, particularly for individuals facing unexpected medical expenses or in the event of a death. These informal networks, while not a direct financial product, can reduce the perceived need for formal insurance coverage for certain demographics.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of the population, especially in lower-income brackets, may rely more heavily on these informal safety nets. While difficult to quantify precisely, the reliance on family support during financial hardship is a recurring theme in sociological studies. This can lessen the demand for life or health insurance among those who believe their immediate needs will be met through personal connections, effectively substituting for a formal insurance policy.
- Informal Support Networks: Family, friends, and community organizations can provide financial assistance during emergencies.
- Reduced Insurance Propensity: Individuals with strong social ties or high risk aversion may see less need for insurance.
- Alternative Solutions: Savings accounts, emergency funds, or even borrowing from family can substitute for immediate insurance payouts.
The threat of substitutes for Globe Life's offerings is multifaceted, extending beyond traditional insurance. Individuals can opt for self-insurance through personal savings or investments, capitalizing on market growth, such as the S&P 500's performance in late 2023. Government programs like Medicare and Medicaid also serve as substitutes, particularly for health coverage, with Medicare serving millions aged 65+ in 2024. Employer-sponsored plans are a significant substitute, covering over 150 million Americans with health insurance in 2024, often providing comprehensive and cost-effective benefits. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) offer tax-advantaged alternatives for healthcare expenses, with HSA enrollment exceeding 37 million by early 2024. Informal support systems, like family aid, can also reduce the perceived need for formal insurance.
Entrants Threaten
The insurance industry, particularly for companies like Globe Life, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Establishing an insurer requires significant upfront investment to manage underwriting risks, build robust reserves, and ensure solvency, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, in 2024, state-specific statutory capital and surplus requirements can easily exceed $10 million for basic operations, escalating dramatically for larger or more specialized lines of business.
Beyond initial capital, regulatory hurdles are substantial and multifaceted. New entrants must navigate a complex web of state-by-state licensing and compliance regulations, each with its own set of rules and oversight bodies. This patchwork of regulations adds considerable cost and time to market entry, demanding specialized legal and compliance expertise. The sheer administrative burden of adhering to diverse insurance codes across multiple jurisdictions acts as a strong deterrent for potential competitors looking to challenge established players like Globe Life.
In the financial services industry, especially insurance, a strong brand and customer trust are incredibly important. New companies entering this market find it difficult to gain the credibility needed to attract customers. They must overcome the significant hurdle of competing with established companies like Globe Life, which has built a solid reputation over many years.
Globe Life, for instance, has a long history of serving customers, which translates into a deep reservoir of trust. In 2023, Globe Life reported total revenue of $11.1 billion, demonstrating its substantial market presence. This established brand recognition makes it challenging for new entrants to persuade consumers to switch their business.
Globe Life's formidable distribution strength, utilizing direct response, a vast independent agent network, and captive agencies, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. Building comparable networks requires immense capital, years of dedicated effort, and fostering deep relationships across diverse channels. For instance, in 2024, Globe Life continued to expand its agent force, a testament to its ongoing investment in this critical area.
Newcomers would face substantial challenges in rapidly replicating Globe Life's established and efficient distribution infrastructure. This difficulty in quickly accessing a broad customer base through multiple avenues severely limits their ability to compete effectively in the market.
Requirement for Sophisticated Actuarial and Underwriting Expertise
The life and health insurance sectors demand sophisticated actuarial and underwriting expertise. Developing accurate pricing models, assessing risk, and managing claims effectively are intricate processes. New entrants face a substantial hurdle in acquiring this specialized knowledge, particularly given the limited availability of experienced professionals and the complex nature of risk assessment.
This expertise is crucial for profitability. For instance, in 2024, the average tenure for a certified actuary in the US insurance industry often exceeds 10 years, highlighting the investment required to build such a talent pool.
- Specialized Knowledge: Actuaries and underwriters need deep understanding of statistics, finance, and risk management.
- Talent Scarcity: There's a global shortage of qualified actuaries, making it difficult for new companies to staff effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex insurance regulations requires specialized legal and actuarial understanding.
- Data Analytics Skills: Advanced data analytics and modeling capabilities are essential for competitive pricing and risk assessment.
Economies of Scale Enjoyed by Incumbent Insurers
Established insurers, including Globe Life, leverage significant economies of scale. This advantage is particularly pronounced in administrative functions, technology investments, and broad-reaching marketing campaigns. For example, a large insurer can spread its fixed costs over a much larger policy base, reducing the per-policy cost.
New entrants face an immediate cost disadvantage. Without the established infrastructure and customer volume, they cannot achieve the same per-unit efficiencies. This makes it challenging to compete on price against incumbents who benefit from lower operating costs, impacting their ability to gain market share profitably.
- Administrative Efficiency: Large insurers reduce overhead per policy by centralizing functions.
- Technology Investment: Incumbents can afford more advanced, cost-saving technology.
- Marketing Reach: Established brands benefit from wider recognition and lower cost per acquisition.
- Pricing Pressure: New entrants struggle to match the lower price points offered by scaled competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the life and health insurance market, particularly for a company like Globe Life, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape that act as significant barriers to entry.
New companies must contend with high upfront investments for licensing, reserves, and operational infrastructure, often exceeding millions of dollars. For instance, in 2024, state-specific capital requirements alone can easily surpass $10 million, making market entry financially demanding.
Furthermore, the complex, state-by-state regulatory compliance adds considerable cost and time, requiring specialized legal and actuarial expertise. This intricate web of rules discourages smaller, less-resourced entities from attempting to compete with established players like Globe Life.
The established brand loyalty and trust enjoyed by incumbents like Globe Life, which reported $11.1 billion in revenue in 2023, are also difficult for newcomers to overcome. Building comparable distribution networks and actuarial talent pools, which often require over a decade of experience as seen with actuaries, further solidifies the advantage of existing firms.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront investment needed for solvency and reserves. | High; deters undercapitalized entrants. | State minimum capital often >$10 million. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex, state-specific licensing and compliance. | High; increases cost and time to market. | Navigating varied insurance codes across jurisdictions. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established reputation built over time. | High; difficult for new brands to attract customers. | Globe Life's 2023 revenue of $11.1 billion reflects market presence. |
| Distribution Networks | Extensive agent and direct response channels. | High; costly and time-consuming to replicate. | Globe Life's ongoing agent force expansion. |
| Specialized Expertise | Actuarial, underwriting, and risk management skills. | High; talent scarcity and long training periods. | Average actuary tenure often exceeds 10 years. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Globe Life is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and financial news outlets to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.
