GFT Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GFT Technologies Bundle
GFT Technologies operates in a dynamic IT services sector, where understanding the competitive landscape is crucial. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intense rivalry among existing competitors and the significant threat posed by emerging technologies. Furthermore, the power of buyers and the availability of substitutes heavily influence pricing and service offerings.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore GFT Technologies’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
GFT Technologies' reliance on highly skilled IT professionals, especially those with expertise in financial services, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, gives significant leverage to its talent suppliers. The intense global competition for these specialized skills means that the availability and cost of such talent can directly impact GFT's operational efficiency and project delivery schedules.
With a workforce exceeding 12,000 professionals and over 10,000 engineers trained on their GenAI product Wynxx, GFT is a major employer in the IT services sector. This scale, however, also highlights their dependence on a robust supply of skilled individuals, making the 'war for talent' a critical factor in their cost structure and strategic execution.
GFT Technologies' reliance on specialized software and platform providers, such as SAP for its extensive ERP solutions or advanced AI development frameworks, highlights a significant area of supplier bargaining power. When GFT requires unique or industry-standard tools where alternatives are scarce, or where switching to a different vendor would incur substantial costs and disruptions, these suppliers gain considerable leverage.
GFT's strategic moves, including acquisitions like Megawork to bolster its SAP implementation capabilities and partnerships with innovators such as Neura Robotics for physical AI integration, underscore the critical nature of these supplier relationships. These actions demonstrate GFT's commitment to securing access to essential, often proprietary, technologies that are fundamental to delivering its custom IT solutions.
GFT Technologies' reliance on major cloud infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform is significant. These hyperscalers hold considerable bargaining power due to their market dominance and the high switching costs associated with migrating cloud services. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $700 billion, with these three providers holding a substantial majority share, demonstrating their entrenched positions.
Data and Analytics Tool Vendors
GFT Technologies' focus on Enterprise AI and data solutions makes it dependent on vendors supplying advanced analytics tools, AI platforms, and specialized data. The unique capabilities or proprietary nature of these tools can grant suppliers significant leverage, influencing GFT's costs and its capacity for innovation. The growing integration of AI and machine learning within the financial services sector, a key market for GFT, further amplifies the demand for these essential vendor offerings. For instance, the global AI market in financial services was projected to reach over $25 billion by 2024, highlighting the critical reliance on these technology providers.
The bargaining power of these data and analytics tool vendors can be assessed through several factors:
- Vendor Concentration: A market dominated by a few key players in advanced AI platforms or specialized datasets grants those vendors higher bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with integrating new data analytics tools or migrating away from existing AI development platforms can strengthen vendor leverage.
- Availability of Substitutes: The existence of readily available, comparable tools or datasets can reduce vendor power.
- Importance of the Tool: If a vendor's tool is critical to GFT's core AI offerings and cannot be easily replicated, their bargaining power increases.
Consulting and Subcontracting Partners
GFT Technologies might leverage external consulting firms or individual contractors for large or highly specialized projects, expanding its service offerings and geographical presence. The bargaining power of these consulting and subcontracting partners is influenced by their specialized knowledge, industry reputation, and the overall demand for their unique skills. For instance, the global IT consulting market was valued at approximately $370 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong demand for specialized expertise which can empower niche suppliers.
The ability of these partners to command higher fees or dictate terms is directly tied to their unique value proposition and GFT's reliance on them for critical project components. If GFT requires very specific, hard-to-find skills, these suppliers will have greater leverage. This dynamic is particularly relevant as the demand for specialized IT services continues to rise, with projections suggesting the IT consulting sector will see continued robust growth in the coming years, potentially increasing the bargaining power of highly sought-after niche providers.
- Specialized Expertise: Partners with unique or in-demand skills hold more sway.
- Project Criticality: GFT's dependence on a partner for essential project phases increases their leverage.
- Market Demand: A tight market for specific consulting services empowers suppliers.
- Reputation and Track Record: Proven success and strong client references enhance a partner's bargaining position.
GFT Technologies faces significant supplier bargaining power from cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These dominant players, controlling a vast majority of the over $700 billion global cloud market in 2024, benefit from high switching costs for GFT. This reliance means GFT's operational costs and strategic flexibility are heavily influenced by these hyperscalers' pricing and service terms.
The company's dependence on vendors for advanced AI platforms and specialized data also grants these suppliers considerable leverage. As the AI in financial services market, projected to exceed $25 billion by 2024, grows, the unique capabilities of these tools amplify vendor power. Factors like vendor concentration and high integration costs further strengthen their position, impacting GFT's innovation capacity and expenses.
GFT's reliance on specialized IT talent, particularly in areas like financial services, cloud, and AI, empowers its human capital suppliers. The intense global competition for these skills, especially with over 12,000 professionals in its workforce, means talent availability and cost directly affect GFT's project timelines and operational efficiency.
External consulting firms and niche subcontractors also wield bargaining power, especially when providing specialized or hard-to-find expertise. The robust growth in the approximately $370 billion global IT consulting market (as of 2023) means highly sought-after providers can dictate terms, particularly for critical project components where GFT has limited alternatives.
What is included in the product
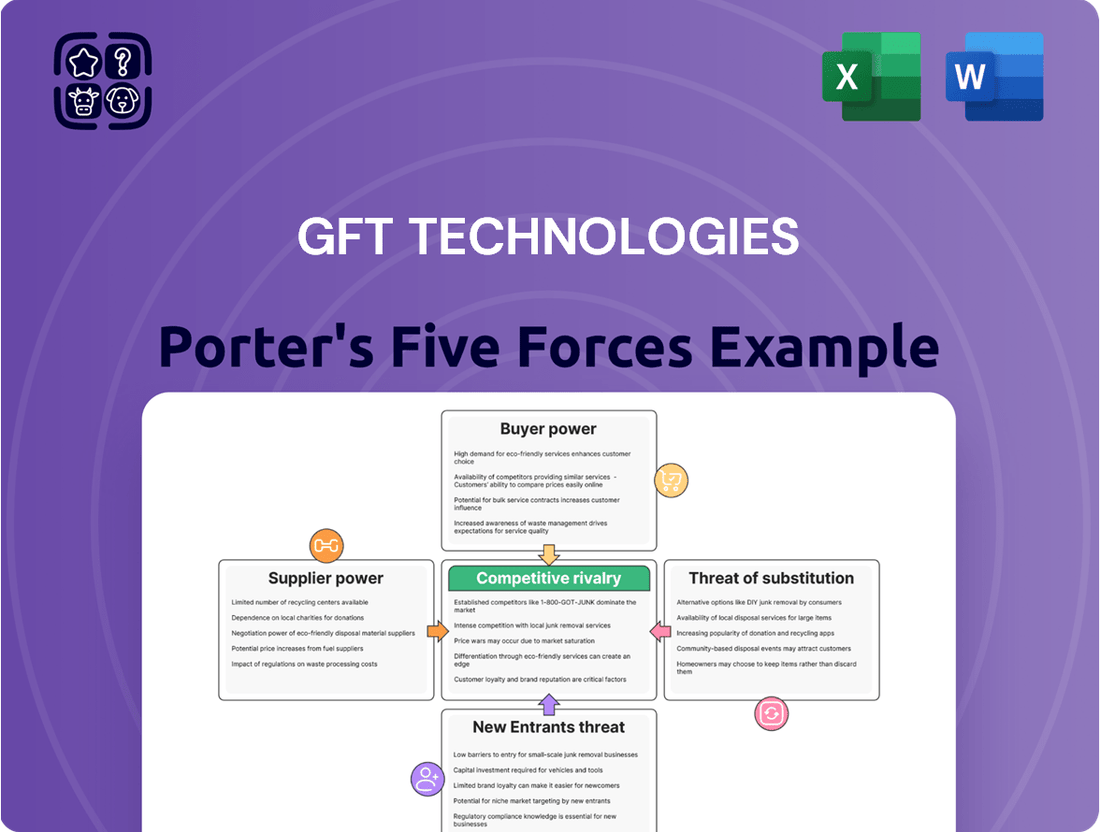
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting GFT Technologies, assessing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
GFT Technologies' Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a dynamic framework to proactively identify and mitigate competitive threats, offering actionable insights for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
GFT Technologies' core clientele consists of major financial institutions, including prominent banks and insurance companies. These clients typically manage substantial IT budgets and have intricate operational needs, giving them significant leverage.
The sheer size of the projects undertaken and the potential for enduring partnerships mean these large customers can effectively negotiate favorable pricing, contract terms, and service level agreements. This bargaining power is a key factor in GFT's operational strategy.
For instance, GFT's involvement in significant core banking system overhauls, such as the project with Bancolombia, demonstrates the substantial influence these large financial institutions wield in shaping project scope and commercial arrangements.
GFT Technologies benefits from high switching costs for its clients. Once GFT's custom IT solutions are deeply integrated and core platforms are modernized, clients face significant expense and operational disruption if they decide to switch providers. This integration complexity, often involving proprietary systems and extensive data migration, effectively locks in customers, diminishing their immediate bargaining power on existing service agreements.
The digital transformation journey in the banking sector, a key market for GFT, is inherently complex and ongoing. This continuous evolution means that changing IT partners is not a simple task but a costly undertaking involving substantial financial investment and potential operational downtime, further solidifying customer relationships with GFT.
Financial institutions are laser-focused on their return on investment (ROI) and overall cost efficiency, especially when it comes to digital transformation initiatives. This means they're scrutinizing every dollar spent and demanding tangible benefits. For GFT, this translates into customers pushing for solutions that not only deliver advanced capabilities but also do so at a competitive price point, directly impacting GFT's pricing power.
In 2024, the banking sector continued to prioritize digital investments aimed squarely at reducing operating expenses and boosting profitability. For instance, many banks are actively seeking to automate processes to cut down on manual labor costs, a trend that directly benefits technology providers like GFT who can demonstrate significant cost savings. This intense pressure for demonstrable financial gains empowers customers to negotiate harder on pricing and demand stringent performance guarantees.
Availability of Alternative IT Service Providers
The IT services market for financial institutions is intensely competitive. This means clients have many options, from large global IT firms to specialized fintech companies and niche consultancies, all vying to provide similar services. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these customers.
For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, with a substantial portion serving the financial sector. The sheer number of vendors means clients can easily switch or negotiate better terms if GFT Technologies cannot demonstrate a clear, unique value proposition.
GFT Technologies' ability to command pricing power and retain customers hinges on its capacity to offer differentiated services. Unless GFT can provide truly unique or superior solutions, such as its AI-centric capabilities that set it apart, customers will leverage the readily available alternatives to their advantage.
- High Market Competition: The IT services landscape for financial institutions features numerous global, specialized, and niche providers.
- Customer Choice Amplified: The widespread availability of alternative IT service providers directly increases customer bargaining power.
- Differentiation is Key: GFT Technologies must offer unique or superior solutions, like its AI focus, to counter this customer leverage.
- Market Value Context: The global IT services market's significant size in 2024 underscores the competitive pressures and customer options.
Customer Sophistication and In-house Capabilities
GFT Technologies' clients, particularly those in the financial sector, often boast advanced internal IT departments. This sophistication means they can thoroughly assess GFT's offerings and even opt for in-house development, which naturally boosts their bargaining power.
This trend is widespread; for instance, a 2024 survey indicated that nearly 60% of British business leaders recognize the critical need for IT modernization to maintain their competitive edge. Such internal capabilities empower these clients to negotiate more effectively with external providers like GFT.
- Client IT Sophistication: Many large financial institutions have well-developed internal IT teams.
- In-house Development: Clients can choose to build solutions themselves, reducing reliance on external vendors.
- Negotiation Leverage: Enhanced internal capabilities increase clients' power to negotiate terms and pricing with GFT.
- Market Trend Awareness: Clients' deep understanding of technology and market trends allows for critical evaluation of service providers.
GFT Technologies' major clients, primarily large financial institutions, possess substantial IT budgets and complex needs, granting them significant leverage. Their ability to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms is amplified by the competitive IT services market, where numerous providers vie for business. In 2024, the global IT services market, valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, highlighted the extensive choices available to these clients.
| Factor | Impact on GFT | Evidence/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Client Size & Budget | High bargaining power due to large project values and IT spending. | Major banks and insurance companies manage significant IT budgets. |
| Market Competition | Customers have many alternatives, increasing negotiation leverage. | Global IT services market valued at ~$1.3 trillion in 2024. |
| Client IT Sophistication | Internal IT capabilities enable clients to assess and negotiate effectively. | ~60% of British business leaders prioritize IT modernization (2024 survey). |
| Switching Costs | High integration costs for clients can reduce immediate bargaining power on existing contracts. | Deep integration of custom IT solutions creates customer lock-in. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
GFT Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for GFT Technologies, providing an in-depth examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You're looking at the actual document, ready for download and application to inform your strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
GFT Technologies operates within a fiercely competitive landscape, contending with global IT service behemoths such as Accenture, Capgemini, IBM, and Infosys. These industry titans leverage substantial financial backing, expansive international reach, and comprehensive service offerings to vie for significant digital transformation and artificial intelligence initiatives, particularly within the financial services industry.
In 2024, the IT services market continues to be shaped by strategic maneuvers like mergers, acquisitions, and the development of distinct service specializations. For instance, Capgemini’s acquisition of RXP Services in Australia in late 2023, and IBM’s ongoing divestitures and strategic partnerships, highlight the dynamic nature of competition and the pursuit of market share through consolidation and focused growth.
GFT Technologies also contends with nimble fintech startups and specialized consulting firms. These players often target specific, high-growth areas like blockchain solutions or advanced AI applications, offering innovative and focused services that can disrupt GFT's market share in particular segments. For instance, the global fintech market was projected to reach $3.1 trillion by 2022, highlighting the significant competition from these agile entities.
GFT Technologies is sharpening its competitive edge by fully embracing an AI-centric strategy, a move that clearly differentiates it in the market. This strategic pivot is anchored by the development of proprietary AI products, such as Wynxx.
Wynxx is designed to significantly enhance software development productivity, reportedly achieving up to a 90% improvement. This focus on AI-driven efficiency is GFT's key to carving out a competitive advantage and capturing market share in the lucrative, high-value-added services segment.
Pricing Pressure and Margin Erosion
The IT services industry, especially for standardized solutions, is fiercely competitive, driving down prices and squeezing profit margins for companies like GFT Technologies. This intense rivalry forces GFT to constantly re-evaluate its pricing strategies to remain competitive.
GFT's revised 2025 guidance illustrates this challenge, anticipating a decline in adjusted EBIT. This adjustment stems directly from ongoing market pressures and necessary internal structural changes aimed at addressing these competitive realities.
Factors exacerbating this margin erosion include underutilized on-site personnel and a strategic pivot towards more cost-effective offshore service delivery in specific regions. These operational shifts are responses to the prevailing pricing pressures.
- Intense Competition: The IT services sector faces significant rivalry, particularly for less specialized services.
- Pricing Pressure: This competition directly translates into downward pressure on pricing for IT solutions.
- Margin Erosion: Companies like GFT experience compressed profit margins as a result of this pricing pressure.
- Operational Adjustments: GFT is adapting by optimizing on-site teams and increasing offshore service utilization to mitigate these effects.
Dynamic Market Conditions and Regional Shifts
Competitive rivalry for GFT Technologies is significantly shaped by shifting global market dynamics. While the company sees robust expansion, particularly in North America and the Asia-Pacific region, it contends with intensified competition and revenue pressures in other areas, such as the United Kingdom.
These regional disparities underscore the need for GFT to maintain agile competitive strategies and closely track evolving market landscapes. For instance, GFT's revenue growth in the Americas and APAC contrasts with challenges in its UK operations, highlighting the uneven competitive environment.
- Regional Growth vs. Decline: GFT reports strong performance in the USA, Canada, Latin America, and APAC, indicating areas of lower competitive intensity or higher demand.
- UK Market Challenges: Conversely, the UK market presents a more competitive scenario, leading to revenue declines and requiring strategic adjustments.
- Adaptability is Key: The company's success hinges on its ability to adapt its competitive approach and continuously monitor regional market conditions to counter rival pressures.
The competitive rivalry for GFT Technologies is intense, especially in standardized IT services where price wars can erode margins. GFT faces competition from large, established players like Accenture and Capgemini, as well as agile fintech startups. This dynamic forces GFT to focus on specialized, high-value AI-driven solutions, like its Wynxx product, to differentiate itself and maintain profitability.
In 2024, the IT services market continues to be shaped by mergers and acquisitions, with companies like Capgemini acquiring RXP Services to bolster their market position. GFT’s own revised 2025 guidance, anticipating a decline in adjusted EBIT, reflects the ongoing market pressures and the need for operational adjustments, such as increasing offshore service delivery, to combat margin erosion.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on GFT |
|---|---|---|
| Global IT Service Behemoths (e.g., Accenture, Capgemini, IBM) | Financial backing, global reach, comprehensive offerings | Significant pressure on large-scale digital transformation and AI projects |
| Fintech Startups & Specialized Firms | Agility, focus on niche high-growth areas (e.g., blockchain, advanced AI) | Disruption in specific segments, potential loss of market share in specialized services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A significant threat of substitution for GFT Technologies' services arises from large financial institutions opting to develop and manage their IT solutions internally. Many major banks and investment firms possess substantial IT departments with the expertise and resources to undertake complex digital transformation projects. For instance, in 2023, the global IT spending by financial services firms was projected to reach over $300 billion, indicating the significant investment many institutions are making in their internal capabilities.
Clients may lean towards in-house development to maintain tighter control over their core systems, sensitive data, and strategic IT roadmaps. This preference is particularly strong when these institutions have cultivated sufficient internal expertise and have the capacity to manage intricate projects independently. The ability to tailor solutions precisely to their unique business needs and regulatory environments can be a compelling factor in choosing internal development over external providers like GFT.
The rise of standardized software and SaaS solutions presents a significant threat to GFT Technologies. For many business functions, clients can now choose from readily available commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software or cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms instead of investing in custom-developed applications. This trend is driven by the increasing sophistication and comprehensive feature sets of these standardized products, which can effectively reduce the perceived need for GFT's bespoke development services.
For example, cloud-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become highly advanced, offering centralized financial management, supply chain, and human resources capabilities. In 2024, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $320 billion, demonstrating the widespread adoption and perceived value of these off-the-shelf solutions. This broad availability and competitive pricing can make it harder for GFT to justify the cost and time associated with custom software development for clients seeking more generic functionalities.
The rise of automation platforms and low-code/no-code tools presents a significant threat of substitution for GFT Technologies. These platforms enable clients to develop and integrate applications internally, lessening their dependence on external IT service providers like GFT for custom coding and development.
For instance, the global low-code development platform market was valued at approximately $11.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong trend towards self-service application development. This empowers internal teams to accelerate their digital transformation initiatives, particularly in sectors like banking where automation and AI are crucial, potentially reducing the demand for GFT's traditional development services.
Pure Management Consulting Services
Pure management consulting firms present a significant threat by offering specialized strategic advice and technology roadmapping. Clients might opt for these niche providers for high-level guidance, subsequently handling implementation internally or partnering with alternative technology vendors, bypassing GFT's integrated service model.
The consulting landscape thrives on specialized expertise, meaning clients often seek out firms with deep knowledge in specific areas, potentially diverting business from broader service providers like GFT. For instance, in 2024, the global management consulting market was valued at approximately $300 billion, with a notable portion driven by specialized practices.
- Specialized Expertise: Clients prioritize niche consulting firms for targeted solutions.
- Alternative Implementation: Clients may implement strategies independently or with other vendors.
- Strategic Roadmapping: Pure-play consultants excel in defining future technology paths.
- Market Dynamics: The consulting industry's fragmentation allows for specialized players to capture market share.
Emerging Technologies for Self-Service IT
Advancements in artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies pose a potential threat by enabling financial institutions to manage their IT more autonomously. This could reduce reliance on external service providers for complex digital transformation projects. For instance, by 2024, the global AI market is projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating significant investment in these capabilities.
However, GFT Technologies is proactively addressing this substitution threat by integrating AI into its own service offerings. Their Wynxx platform, for example, is designed to enhance client self-sufficiency and productivity. This strategic move allows GFT to evolve alongside technological shifts, turning a potential threat into an opportunity by empowering their clients.
- AI Market Growth: The global AI market is anticipated to exceed $200 billion by 2024, signaling a strong trend towards automation and self-service capabilities within various industries, including finance.
- GFT's Wynxx Platform: GFT's investment in AI-powered solutions like Wynxx directly counters the threat of substitutes by offering clients tools that increase their operational independence.
- Evolving Service Models: The integration of AI into GFT's services reflects a broader industry shift where IT service providers are becoming enablers of client autonomy rather than sole providers of expertise.
The threat of substitutes for GFT Technologies is significant, as clients can opt for in-house IT development, standardized software, SaaS solutions, low-code/no-code platforms, or specialized consulting firms. These alternatives often promise greater control, cost-effectiveness for simpler needs, or niche expertise. The increasing maturity of these substitute offerings, coupled with substantial market investments in areas like AI and cloud services, necessitates GFT's continuous adaptation to remain competitive.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Market Context (2023-2024 Estimates) | Impact on GFT |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Control, data security, tailored solutions | Financial services IT spending > $300 billion (2023) | Reduces demand for external development services |
| Standardized Software/SaaS | Off-the-shelf functionality, rapid deployment | Global SaaS market > $320 billion (2024) | Challenges custom development pricing and necessity |
| Low-Code/No-Code | Internal agility, faster application building | Low-code market ~$11.2 billion (2023) | Empowers clients to build solutions independently |
| Specialized Consulting | Niche expertise, strategic roadmapping | Global management consulting market ~$300 billion (2024) | Can bypass GFT's integrated service model |
| AI & Emerging Tech | Automation, enhanced autonomy | Global AI market > $200 billion (2024) | Potential to reduce reliance on external providers |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the financial services IT sector, where GFT Technologies operates, requires significant upfront capital. This includes investing in cutting-edge technology, attracting skilled professionals, and ongoing research and development. For instance, the global financial services consulting market was projected to reach $150 billion in 2025, indicating the scale of investment needed.
Beyond financial resources, new competitors must also acquire specialized knowledge. This means understanding complex financial regulations, intricate core banking systems, and the latest technological advancements such as artificial intelligence. This deep industry-specific expertise acts as a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants.
Established client relationships and trust represent a significant barrier for new entrants. GFT Technologies, like many established players, benefits from long-standing partnerships with major financial institutions. These institutions are inherently risk-averse and prioritize proven reliability, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. For instance, in 2024, the financial services sector continued to emphasize vendor stability, with many large banks renewing contracts with established IT service providers rather than exploring unproven alternatives.
The financial services sector, including companies like GFT Technologies, faces significant regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to refine regulations like MiFID II and GDPR, demanding substantial compliance investments from all players. New entrants must dedicate considerable resources to legal counsel and robust compliance systems to navigate these intricate rules, especially concerning data privacy and security, which are paramount in financial transactions.
Talent Acquisition and Retention Challenges
New entrants in the IT services sector, particularly those targeting financial institutions like GFT Technologies, face significant hurdles in acquiring and retaining top-tier talent. The demand for specialized skills in areas such as financial technology, cloud infrastructure, and artificial intelligence is exceptionally high, creating a fierce 'war for talent'. This intense competition drives up recruitment costs and makes it challenging for newcomers to assemble the necessary expertise to compete effectively.
The difficulty in securing a skilled workforce directly impacts a new entrant's ability to scale and deliver complex projects. For instance, a report in late 2023 indicated that the global IT talent shortage was projected to reach 85 million workers by 2030, exacerbating these recruitment challenges. This scarcity means that new companies must invest heavily in competitive compensation packages and attractive work environments to lure experienced professionals away from established players.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: IT professionals with expertise in AI, cloud computing, and fintech are in short supply globally.
- Increased Recruitment Costs: The competitive landscape for talent significantly inflates the cost of hiring for new entrants.
- Impact on Scaling: A lack of readily available skilled personnel hinders the ability of new companies to grow and take on larger projects.
- Barrier to Digitization: For banks, a deficiency in internal IT skills can slow down or prevent crucial digital transformation initiatives, a market new entrants aim to serve.
Proprietary Technology and Innovation
GFT Technologies' significant and ongoing investment in proprietary artificial intelligence products, exemplified by its Wynxx platform, establishes a robust competitive advantage. This focus on advanced digital transformation solutions acts as a considerable barrier for potential new entrants.
To effectively challenge GFT, new companies would need to replicate or surpass GFT's technological capabilities, a feat demanding substantial research and development expenditure and considerable lead time. GFT's deliberate AI-centric strategy is designed to differentiate it within the market.
- Proprietary AI Development: GFT's commitment to developing unique AI solutions like Wynxx creates a technological moat.
- High Entry Barriers: New entrants face significant hurdles in matching GFT's innovation and R&D investment.
- Competitive Differentiation: GFT's AI focus aims to provide a distinct market position against rivals.
The threat of new entrants for GFT Technologies is moderated by several factors. Significant capital investment is required to enter the financial IT services sector, encompassing technology, talent, and R&D, with the global financial services consulting market projected to reach $150 billion by 2025. Newcomers also need specialized knowledge of financial regulations and complex systems, a substantial hurdle.
Established trust and long-standing client relationships with financial institutions present another barrier; in 2024, many banks continued to renew contracts with proven IT providers. Furthermore, navigating stringent regulations, such as the EU's MiFID II and GDPR, demands considerable investment in compliance systems and legal expertise, with ongoing refinements in 2024 requiring continuous adaptation.
The intense competition for skilled IT professionals, particularly in AI and fintech, drives up recruitment costs for new entrants. The global IT talent shortage, projected to reach 85 million by 2030, exacerbates this challenge, making it difficult for newcomers to build the necessary expertise to compete effectively against established firms like GFT Technologies.
GFT's investment in proprietary AI solutions, such as its Wynxx platform, creates a technological moat, requiring substantial R&D expenditure and lead time for new entrants to match. This AI-centric strategy aims to differentiate GFT and poses a significant barrier to entry for companies seeking to replicate its advanced digital transformation capabilities.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in technology, talent, and R&D. | Significant financial hurdle. | Global financial services consulting market projected at $150 billion by 2025. |
| Specialized Knowledge | Understanding complex financial regulations and systems. | Requires deep industry-specific expertise. | Navigating intricate core banking systems and AI advancements. |
| Customer Loyalty & Switching Costs | Established trust and long-standing partnerships. | Difficult for newcomers to gain traction. | Banks prioritizing vendor stability in 2024 contract renewals. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance with financial sector regulations (e.g., GDPR, MiFID II). | Demands substantial investment in legal and compliance systems. | Ongoing regulatory refinements in the EU in 2024. |
| Talent Acquisition | Competition for AI, cloud, and fintech specialists. | Increases recruitment costs and hinders scaling. | Global IT talent shortage projected at 85 million by 2030. |
| Proprietary Technology | Investment in unique AI solutions (e.g., Wynxx). | Requires significant R&D to replicate. | GFT's AI-centric differentiation strategy. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for GFT Technologies is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data from financial reports, industry-specific market research, and public company disclosures. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets and analyst reports to capture current market dynamics.
