Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Geo-Jade Petroleum Bundle
Geo-Jade Petroleum faces significant pressures from powerful suppliers and intense rivalry within the oil and gas sector, impacting its profitability and market share. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Geo-Jade Petroleum’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized oil and gas exploration and production equipment, like advanced seismic imaging and horizontal drilling technology, wield considerable bargaining power. Geo-Jade Petroleum's operational efficiency and asset development hinge on these critical inputs, making partnerships with leading technology providers essential. The substantial capital investment required for these technologies naturally restricts the pool of qualified suppliers, amplifying their influence.
The oilfield services (OFS) sector has experienced a significant rebound, driven by innovation and efficiency improvements that have boosted financial results. For instance, many OFS companies reported strong revenue growth in 2023, with some seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year, reflecting increased demand from exploration and production (E&P) companies.
While consolidation among E&P firms can sometimes shift power dynamics, the ongoing demand for advanced, technology-driven solutions keeps specialized OFS providers in a strong position. Companies offering cutting-edge drilling technology or specialized completion services can command better terms due to their unique capabilities, which are essential for optimizing production and reducing costs in complex environments.
Geo-Jade Petroleum, like its peers in the E&P industry, relies heavily on OFS companies for critical operations such as drilling new wells, completing existing ones, and ongoing maintenance. The performance and cost-effectiveness of these services directly impact Geo-Jade's operational efficiency and profitability, giving well-established and technologically advanced OFS providers a notable bargaining advantage.
A noticeable shortage of highly skilled professionals, such as geoscientists and seasoned operational personnel, significantly bolsters the bargaining power of the labor force within the petroleum sector. This scarcity directly translates into upward pressure on wages and can introduce unwelcome project delays, particularly when dealing with intricate international ventures.
The persistent optimism surrounding long-term industry growth ensures that the demand for top-tier talent will remain robust. For instance, in 2024, the global oil and gas industry faced a projected deficit of approximately 15% in specialized engineering roles, a factor that directly impacts labor costs and project timelines.
Geopolitical and Regulatory Influence
Suppliers in regions like Central Asia and Iraq, where Geo-Jade Petroleum has substantial operations, are subject to local government policies and regulations. These can affect everything from pricing to the availability of essential resources, directly impacting Geo-Jade's supply chain stability.
For instance, in 2024, Iraq's Ministry of Oil continued to implement policies aimed at increasing domestic refining capacity, potentially influencing the terms for suppliers of crude oil and refined products. Similarly, regulations in Central Asian countries can dictate local content requirements, giving suppliers with strong local ties increased bargaining power.
- Geopolitical Stability: Fluctuations in regional stability, such as those experienced in parts of the Middle East, can disrupt supply lines and increase the cost of doing business, thereby strengthening supplier leverage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to evolving environmental and operational regulations in countries like Iraq and Uzbekistan can necessitate specialized services or materials, empowering suppliers who meet these specific demands.
- State-Owned Enterprises: The presence of state-owned entities as suppliers or intermediaries in resource-rich regions can introduce additional layers of negotiation and policy-driven pricing, impacting Geo-Jade's procurement costs.
Infrastructure Providers
Infrastructure providers, like pipeline operators, can wield significant bargaining power over Geo-Jade Petroleum. This power stems from the critical role their assets play in transporting oil, especially in regions where alternative export routes are scarce. For instance, Geo-Jade's reliance on the CPC pipeline for its Kazakhstan exports means that any disruptions or unfavorable terms from the pipeline operator directly impact its ability to get its product to market.
In 2024, the global energy infrastructure landscape continued to present challenges. Bottlenecks in transportation networks, including pipelines, can significantly constrain production expansion and elevate the overall cost of oil delivery. This situation directly affects companies like Geo-Jade, as it can lead to higher operational expenses and potentially reduced profit margins if infrastructure access becomes more expensive or less reliable.
- Limited Alternative Routes: The scarcity of alternative transportation infrastructure in key operational regions grants significant leverage to existing providers.
- Production Constraints: Infrastructure bottlenecks can directly limit Geo-Jade's ability to scale production and reach its target markets efficiently.
- Cost of Market Access: The cost associated with utilizing essential infrastructure, such as pipelines, directly impacts Geo-Jade's overall cost structure and profitability.
- Strategic Dependence: Geo-Jade's reliance on specific infrastructure, like the CPC pipeline, underscores the critical nature of these supplier relationships.
Suppliers of specialized oil and gas equipment and services hold significant sway due to the critical nature of their offerings and the high barriers to entry for competitors. Geo-Jade Petroleum's reliance on advanced drilling technology and skilled labor means that providers of these essential inputs can command favorable terms. This is further amplified by a notable shortage of highly skilled professionals in the sector, as evidenced by a projected 15% deficit in specialized engineering roles globally in 2024.
Infrastructure providers, particularly pipeline operators in regions with limited alternative export routes, also possess substantial bargaining power. Geo-Jade's dependence on specific pipelines, such as the CPC for its Kazakhstan operations, means that any unfavorable terms or disruptions from these infrastructure suppliers directly impact market access and profitability. Global energy infrastructure bottlenecks in 2024 continued to constrain production and elevate delivery costs, reinforcing the leverage of these essential service providers.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Geo-Jade Petroleum | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology Providers | High R&D costs, proprietary technology, limited competition | Higher equipment/service costs, potential delays if key tech unavailable | Global oil & gas sector saw strong revenue growth for OFS companies in 2023; continued demand for innovation in 2024. |
| Skilled Labor Providers | Scarcity of specialized expertise (geoscientists, engineers) | Increased labor costs, project delays due to talent shortages | Projected 15% deficit in specialized engineering roles globally in 2024. |
| Infrastructure Operators (Pipelines) | Limited alternative routes, critical for market access | Higher transportation costs, potential production constraints, reduced profit margins | Infrastructure bottlenecks remained a challenge globally in 2024, impacting delivery costs and reliability. |
What is included in the product
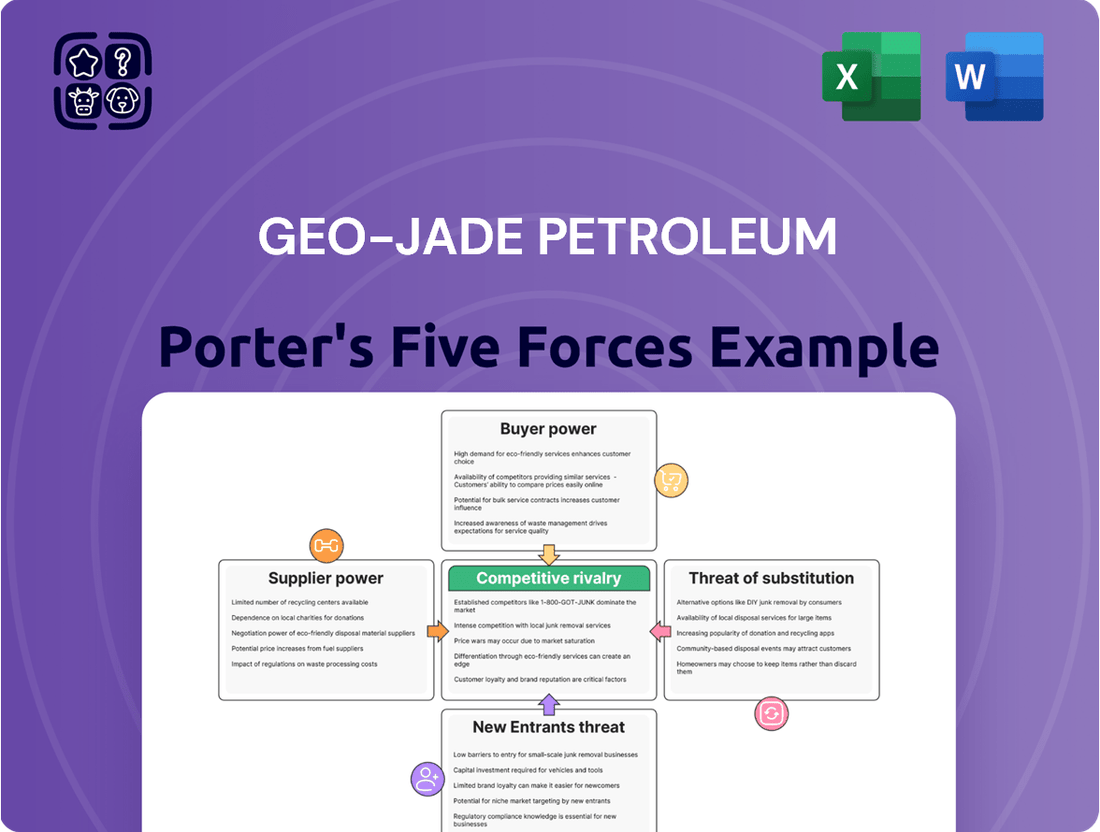
Geo-Jade Petroleum's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the competitive intensity within the oil and gas sector, assessing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces chart, clarifying strategic threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for Geo-Jade Petroleum is significantly influenced by global commodity prices, particularly crude oil and natural gas. As an exploration and production (E&P) company, Geo-Jade has minimal sway over these prices, which are primarily dictated by worldwide supply and demand. This lack of control empowers buyers, as price volatility directly affects Geo-Jade's revenue and profitability. For instance, while crude oil prices remained relatively stable through much of 2024, averaging around $80 per barrel, ongoing geopolitical tensions and OPEC+ production decisions continue to create market uncertainty, amplifying customer leverage.
In Central Asia and China, Geo-Jade Petroleum's major customers are typically large state-owned enterprises and significant refiners. These entities command considerable purchasing power due to their sheer size and their critical role in national economies. For instance, in 2024, China's state-owned oil companies like Sinopec and PetroChina processed millions of barrels of crude oil daily, giving them immense leverage in negotiations.
The substantial scale of these buyers allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Geo-Jade's revenue streams and profit margins. Their ability to switch suppliers or even influence domestic production policies means they can exert significant pressure on oil producers, making the bargaining power of customers a key factor in the industry.
Demand from emerging economies, especially in Asia, is a significant driver of global oil consumption. Projections indicate continued growth in these regions, which can strengthen Geo-Jade Petroleum's market position by ensuring a steady customer base. For instance, China's crude oil imports reached a record high in 2023, signaling robust demand.
This rising demand in Geo-Jade's core markets, like China and India, offers a degree of leverage against customer power. A consistent and growing market naturally reduces the ability of individual customers to dictate terms. However, this is not without risk; any economic downturn or policy change in these critical areas could rapidly alter the demand landscape.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers
Geo-Jade Petroleum's customers, particularly those in the oil and gas sector, often have a wide array of alternative suppliers available globally. This means they can readily switch to a different producer if Geo-Jade's pricing or contract terms are not competitive. For instance, in 2024, the global oil market saw significant production from major players alongside emerging producers, offering buyers numerous options.
The sheer volume of oil and gas available from diverse international sources directly impacts Geo-Jade's ability to dictate prices. Customers can leverage this widespread availability to negotiate more favorable terms, as they are not reliant on a single supplier. This dynamic inherently reduces the pricing power of individual companies like Geo-Jade.
Consider the following factors contributing to customer bargaining power:
- Global Supply Options: Customers can source oil and gas from numerous countries and companies, not just Geo-Jade.
- Price Sensitivity: Oil and gas are largely commoditized, making price a primary decision factor for buyers.
- Switching Costs: While some switching costs exist, the availability of standardized contracts and logistics often makes it feasible for customers to change suppliers.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in global oil prices in 2024, influenced by geopolitical events and production levels, further empower buyers to seek the best available deals.
Customer Downstream Integration
Large customers in the oil and gas sector, particularly those operating refineries or extensive distribution networks, can significantly leverage their downstream integration. This control over the value chain allows them to absorb price volatility more easily and exert considerable pressure on upstream suppliers like Geo-Jade. For instance, major oil companies with integrated refining capacity often dictate terms to independent producers, seeking favorable pricing and supply agreements.
Geo-Jade Petroleum’s strategic moves, such as its involvement in building refineries and petrochemical plants in Iraq, demonstrate a potential for vertical integration. However, the company's primary upstream exploration and production (E&P) output remains largely dependent on external buyers. This means that while Geo-Jade might gain some control over processing, its core revenue stream from crude oil sales is still subject to the bargaining power of its customers.
- Downstream Integration Impact: Customers owning refineries can process crude oil themselves, reducing their need to purchase from independent producers and giving them leverage in price negotiations.
- Value Chain Control: Integration allows customers to manage costs and risks across refining and distribution, making them less susceptible to upstream supply fluctuations.
- Geo-Jade's Position: While Geo-Jade is exploring downstream assets, its upstream production faces direct customer bargaining power, particularly from integrated refiners.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, global refining margins have seen fluctuations, influencing the appetite of integrated players to negotiate aggressively with upstream suppliers for feedstock.
The bargaining power of Geo-Jade Petroleum's customers is substantial, primarily due to the commoditized nature of oil and gas and the wide availability of alternative suppliers globally. In 2024, with crude oil prices fluctuating around $80 per barrel, buyers could easily switch producers to secure better terms, as numerous countries and companies offered competitive supply options. Large state-owned enterprises in China, such as Sinopec and PetroChina, process millions of barrels daily, giving them immense leverage in negotiations.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Geo-Jade | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Global Supply Options | High leverage for customers | Numerous global producers available |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers prioritize cost | Oil is a commodity, price is key |
| Switching Costs | Low for many customers | Standardized contracts facilitate changes |
| Customer Scale (e.g., China's SOEs) | Significant negotiation power | Sinopec/PetroChina process millions of barrels daily |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for the company. You're looking at the actual document, which will be instantly accessible upon purchase, providing you with a complete and ready-to-use strategic assessment. This includes an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry, all professionally formatted for immediate application.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Geo-Jade Petroleum faces intense competition from National Oil Companies (NOCs) in Central Asia and China. These state-backed giants, like CNPC in China, benefit from privileged access to resources and significant government backing, making them powerful rivals. For instance, CNPC's 2023 revenue was over $850 billion, dwarfing independent players.
The competition for petroleum reserves and acquisitions is fierce, directly impacting Geo-Jade Petroleum's growth strategy. Companies in the exploration and production (E&P) sector are constantly vying for promising exploration rights and valuable producing assets. This intense rivalry means that securing new opportunities, such as those pursued by Geo-Jade, requires significant capital and strategic foresight.
Geo-Jade's approach of expanding its reserves through strategic investments places it in direct competition with numerous other E&P companies. These rivals are also actively seeking to acquire new exploration licenses and purchase existing petroleum assets to bolster their own reserve bases. The global market for oil and gas assets is highly dynamic, with many players constantly evaluating and bidding on opportunities.
The competitive landscape is further highlighted by significant industry transactions. For instance, the pursuit of projects like the South Basra Integrated Project in Iraq demonstrates the high stakes involved in acquiring and developing new petroleum resources. Companies must be prepared to offer competitive terms and demonstrate technical and financial capabilities to win these valuable opportunities.
The global oil and gas market is characterized by intense competitive rivalry, driven by its nature as a commodity market. Prices fluctuate significantly due to geopolitical events, OPEC+ decisions, and global economic trends, forcing companies like Geo-Jade to constantly adjust strategies to secure profitability and market position.
In 2024, the Brent crude oil price has seen considerable volatility, trading in a range that reflects ongoing supply concerns and demand uncertainties. For instance, average prices in the first half of 2024 hovered around $80-$85 per barrel, influenced by factors such as the conflict in Eastern Europe and production cuts by major oil-producing nations. This price environment directly affects Geo-Jade's revenue streams and operational margins.
Cost Structures and Operational Efficiency
Companies that can produce oil and gas at a lower cost and operate more efficiently naturally hold a stronger position, particularly when energy prices fluctuate. This is crucial for maintaining profitability and market share.
Geo-Jade Petroleum's focus on streamlining operations and controlling expenditures is key to its ability to compete effectively. Rivals might possess different cost structures or benefit from larger economies of scale, making efficient management a vital differentiator for Geo-Jade.
- Cost Advantage: Companies with lower production costs, often achieved through efficient operations and technological adoption, are better positioned to weather price downturns and capture market share.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes and optimizing resource utilization directly impacts a company's cost base and profitability, enhancing its competitive edge.
- Technological Investment: Investing in advanced technologies can significantly boost operational efficiency, leading to cost reductions and improved output. For example, advancements in drilling and extraction techniques can lower per-barrel costs.
- Competitive Landscape: Geo-Jade's operational efficiency is measured against competitors who may have inherent cost advantages due to their scale or access to cheaper resources.
Technological Advancements in E&P
The competitive landscape in exploration and production (E&P) is significantly shaped by the relentless pace of technological innovation. Companies are locked in a race to adopt and master advanced techniques like enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and sophisticated digital solutions. Those that effectively integrate these advancements can achieve higher recovery rates and lower operational costs, thereby gaining a crucial edge over rivals. For instance, investments in digital oilfield technologies, which can optimize production and reduce downtime, are becoming a key differentiator. This ongoing technological arms race necessitates substantial and continuous investment, demanding strategic planning to stay ahead of the curve.
Key technological drivers impacting rivalry include:
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): Techniques such as chemical flooding and CO2 injection are crucial for maximizing output from mature fields, with global EOR market projected to reach $42.5 billion by 2027.
- Digitalization and Automation: The adoption of AI, IoT, and advanced analytics in E&P operations is improving efficiency and safety, with the oil and gas digital transformation market expected to grow to $115.5 billion by 2026.
- Advanced Seismic Imaging: Innovations in seismic data acquisition and processing allow for more precise identification of hydrocarbon reserves, reducing exploration risk and cost.
- Drilling and Completion Technologies: Improvements in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing continue to unlock previously uneconomical reserves, intensifying competition for resource access.
Geo-Jade Petroleum operates in a highly competitive environment, facing pressure from both large national oil companies and other independent exploration and production firms. This rivalry is amplified by the commodity nature of oil and gas, where price volatility, as seen with Brent crude averaging around $80-$85 per barrel in early 2024, directly impacts profitability and strategic maneuvering.
Companies with lower production costs, achieved through operational efficiency and technological adoption, gain a significant advantage. For instance, advancements in drilling technologies can unlock reserves more cost-effectively, intensifying the competition for resource access and market share.
The drive for technological innovation, such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and digitalization, creates an ongoing arms race. Companies investing in these areas, like the projected $42.5 billion EOR market by 2027, aim to boost recovery rates and reduce operational costs, thereby outmaneuvering rivals.
| Competitor Type | Key Advantage | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| National Oil Companies (NOCs) | Government backing, privileged resource access | CNPC's substantial revenue ($850B+ in 2023) allows aggressive investment |
| Independent E&P Companies | Agility, technological adoption | Focus on operational efficiency to counter price fluctuations (e.g., Brent crude $80-$85/bbl H1 2024) |
| Technology Providers | Innovation in EOR, digitalization | EOR market growth to $42.5B by 2027; digital transformation market to $115.5B by 2026 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rapid expansion of renewable energy, especially solar and wind, presents a significant long-term challenge to fossil fuel demand. By the end of 2023, global renewable capacity additions reached a record 510 gigawatts (GW), a 50% increase from 2022, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This growth, while not yet fully offsetting rising energy needs, clearly indicates a future where hydrocarbons will face increased competition.
While renewables are currently more impactful in the power generation sector, their increasing integration into transportation and industrial processes will further erode the market for Geo-Jade's products. The IEA's 2024 report highlights that renewables are projected to account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion in the coming years, a trend Geo-Jade must closely track.
The accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional petroleum products. In 2024, China, a major global consumer of refined fuels, continued its strong push towards EV integration. While overall liquid fuel demand in China was still projected for growth in 2025, the long-term trajectory of EV penetration directly challenges the demand for gasoline, a key product for companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum.
Ongoing advancements in energy efficiency present a significant threat to oil and gas demand. For instance, by 2024, the International Energy Agency (IEA) projected that energy efficiency measures could save the equivalent of nearly 10 million barrels of oil per day globally. This means industries and households can achieve the same or better results with less energy consumption.
Technological progress, coupled with supportive government policies, is a key driver of these efficiency gains. This trend allows for greater economic output with reduced energy input, effectively acting as an alternative to the need for increased hydrocarbon extraction and supply.
Natural Gas as a Transition Fuel
Natural gas serves as a significant substitute for oil, particularly in power generation and industrial applications, positioning itself as a cleaner-burning 'transition fuel' away from coal. This substitution dynamic can influence demand within the broader hydrocarbon sector, potentially favoring natural gas in specific market segments. For instance, in 2024, the global natural gas market continued to see robust demand, with prices fluctuating based on geopolitical events and supply dynamics, impacting the economic viability of gas versus oil in various energy mixes.
The threat of substitution is amplified as technological advancements and environmental regulations increasingly favor lower-emission energy sources. While Geo-Jade Petroleum produces both oil and gas, the shift towards natural gas in certain sectors can directly impact its oil segment's market share.
- Natural Gas as a Cleaner Alternative: Natural gas emits significantly less carbon dioxide and other pollutants compared to coal and, in many applications, oil, making it an attractive option for meeting environmental targets.
- Substitution in Power Generation: Natural gas-fired power plants can be brought online and ramped down more quickly than coal plants, offering flexibility and reliability, which can displace oil in this sector.
- Industrial Applications: Industries requiring heat or steam can often utilize natural gas as an efficient and cost-effective substitute for oil-based fuels.
- Market Dynamics in 2024: Global natural gas prices in 2024 reflected a complex interplay of supply security concerns and the ongoing energy transition, influencing its competitiveness against oil in various end-use markets.
Government Policies and Environmental Regulations
Government policies and environmental regulations are increasingly pushing the oil and gas industry towards cleaner alternatives, thereby strengthening the threat of substitutes. For instance, many nations are implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, like carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, which directly increase the operational costs for fossil fuel producers. In 2024, the average carbon price across countries with such policies is projected to continue its upward trend, making renewable energy sources comparatively more cost-effective.
Stricter emissions standards for vehicles and industrial processes also compel a shift away from traditional fuels. As these regulations tighten, the demand for oil and gas naturally declines, while the market share for electric vehicles and other low-emission technologies expands. This regulatory push, coupled with government incentives for renewable energy deployment, significantly enhances the attractiveness and viability of substitute energy sources.
- Increased Production Costs: Carbon pricing and stricter emissions standards directly raise the cost of extracting and processing fossil fuels.
- Enhanced Substitute Attractiveness: Government incentives for renewables and electric vehicles make cleaner alternatives more economically competitive.
- Shifting Market Demand: Regulatory pressure encourages consumers and industries to adopt low-carbon solutions, reducing reliance on oil and gas.
- Long-Term Industry Threat: The evolving regulatory landscape poses a significant, persistent threat to the traditional business models within the oil and gas sector.
The threat of substitutes for Geo-Jade Petroleum is substantial and growing, driven by advancements in renewable energy and energy efficiency. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) directly impacts demand for gasoline, a core product for oil companies. Furthermore, natural gas presents a cleaner alternative, particularly in power generation and industrial uses, positioning itself as a transition fuel that can displace oil. Government policies and environmental regulations are actively promoting these substitutes, making them more economically competitive and further intensifying the pressure on traditional fossil fuel markets.
| Substitute | Impact on Oil Demand | 2024 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind) | Reduces demand for fossil fuels in power generation. | Global renewable capacity additions reached a record 510 GW in 2023, a 50% increase from 2022 (IEA). Renewables expected to account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion. |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Decreases demand for gasoline and diesel. | China's EV integration continued strongly in 2024, impacting long-term gasoline demand. |
| Energy Efficiency | Lowers overall energy consumption, reducing the need for all energy sources. | IEA projected energy efficiency measures could save nearly 10 million barrels of oil per day globally by 2024. |
| Natural Gas | Substitutes oil in power generation and industrial applications. | Robust global natural gas demand in 2024, with prices influenced by supply and energy transition dynamics. |
Entrants Threaten
The oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) industry demands colossal upfront investments. Companies need to fund extensive geological surveys, the costly process of drilling wells, and the development of essential infrastructure like pipelines and processing facilities. This immense capital requirement is a significant hurdle, effectively discouraging many potential new players from entering the market.
For instance, Geo-Jade Petroleum's commitment to significant strategic investments, such as the planned $848 million allocation for its South Basra project, underscores the substantial financial outlays characteristic of this sector. Such large-scale financial commitments create a formidable barrier to entry, protecting established companies from new competition.
Success in oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) hinges on sophisticated proprietary technologies and deep technical expertise. New companies entering this arena must make substantial investments in acquiring or developing these advanced capabilities, alongside recruiting seasoned professionals, creating a considerable barrier.
Geo-Jade Petroleum, for instance, leverages its established operational knowledge and existing technological infrastructure, giving it an advantage over potential newcomers. The high capital expenditure required for cutting-edge exploration and drilling equipment, often running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars for a single project, further deters new entrants.
Access to proven oil and gas reserves is a significant barrier for new entrants in the petroleum industry. Acquiring exploration and production licenses is a complex, lengthy, and often competitive process involving governmental approvals, bidding rounds, or strategic alliances. Established companies frequently possess long-term rights to the most promising geological areas, making it challenging for newcomers to secure commercially viable assets.
For instance, Geo-Jade Petroleum's recent acquisition of exploration rights in Iraq highlights the intense competition and the need for strategic positioning to gain access to prospective acreage. The global oil and gas industry saw significant investment in exploration and production licenses in 2024, with countries like Brazil and Guyana attracting substantial interest, further intensifying the competition for new entrants.
Governmental and Environmental Regulations
The oil and gas sector faces significant hurdles for newcomers due to extensive government oversight. Environmental protection, safety protocols, and obtaining necessary permits are all areas demanding strict adherence. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce regulations like the Clean Air Act, impacting operational standards for all players.
Meeting these rigorous and often changing regulatory demands necessitates considerable financial investment and specialized knowledge. This creates a substantial barrier, making it difficult for new entities to enter the market and compete effectively. Geopolitical factors and direct government intervention also heavily influence market entry and operational freedom for companies in this industry.
- Stringent Environmental Standards: Compliance with regulations like those governing emissions and wastewater discharge requires significant capital expenditure for new entrants.
- Safety and Operational Licensing: Obtaining and maintaining licenses for exploration, production, and transportation involves rigorous safety audits and approvals.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Changes in climate policy and energy transition initiatives can introduce new compliance costs and operational challenges.
- Governmental Influence on Market Access: National oil companies and government policies can dictate terms for market participation and resource access.
Brand Reputation and Established Relationships
While less pronounced than in consumer-facing industries, an established reputation for reliable production and strong relationships with national oil companies or state entities can be a significant barrier. New entrants lack this track record and established network, which is crucial for securing large-scale projects. For instance, in 2024, major national oil companies continued to favor partners with proven operational histories and existing geopolitical ties, making it harder for newcomers to gain traction.
These established relationships are vital for navigating complex operational environments, particularly in regions like Central Asia and Iraq. Companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum, with years of experience and embedded partnerships, benefit from smoother regulatory processes and access to prime exploration blocks. A new entrant would struggle to replicate this level of trust and access in the short to medium term.
- Reputation as a Barrier: Established players benefit from a proven track record of reliable production and operational success.
- Relationship Advantage: Strong, long-standing ties with national oil companies and state entities provide preferential access and smoother operations.
- New Entrant Challenges: Lacking this history and network, new companies face significant hurdles in securing major projects and navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
- Geopolitical Significance: In regions like Central Asia and Iraq, these relationships are not just commercial but also geopolitical, further solidifying the advantage of incumbents.
The threat of new entrants for Geo-Jade Petroleum is generally low due to the industry's high capital requirements and the need for specialized technology. Significant upfront investments in exploration, drilling, and infrastructure, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, act as a substantial deterrent. Furthermore, established companies benefit from proprietary technologies and deep technical expertise, which are difficult and costly for newcomers to acquire.
Access to proven reserves and navigating complex governmental regulations present further barriers. Securing exploration rights is a competitive and lengthy process, with established players often holding long-term access to prime acreage. For instance, in 2024, significant investment in exploration licenses globally intensified competition for new entrants. Stringent environmental and safety regulations also demand considerable financial and knowledge investment, creating a high entry barrier.
Established reputations and strong relationships with national oil companies are also critical advantages for incumbents like Geo-Jade Petroleum. These relationships facilitate smoother operations and access to projects, which new entrants struggle to replicate. In 2024, national oil companies continued to favor partners with proven track records, underscoring the difficulty for newcomers to gain market traction.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for exploration, drilling, and infrastructure. | Significant deterrent due to massive financial outlay. | Planned investments in projects often exceed $800 million. |
| Technology & Expertise | Need for proprietary technologies and deep technical knowledge. | Costly to acquire or develop, creating a steep learning curve. | High expenditure on advanced exploration and drilling equipment. |
| Access to Reserves | Complex process of acquiring exploration and production licenses. | Established players often hold rights to the most promising areas. | Intense competition for licenses in regions like Brazil and Guyana. |
| Governmental Regulations | Strict environmental, safety, and operational compliance. | Requires substantial investment and specialized knowledge. | Continued enforcement of environmental protection regulations. |
| Reputation & Relationships | Proven track record and established ties with state entities. | Facilitates smoother operations and preferential access. | National oil companies favoring partners with existing geopolitical ties. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and expert industry commentary to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
