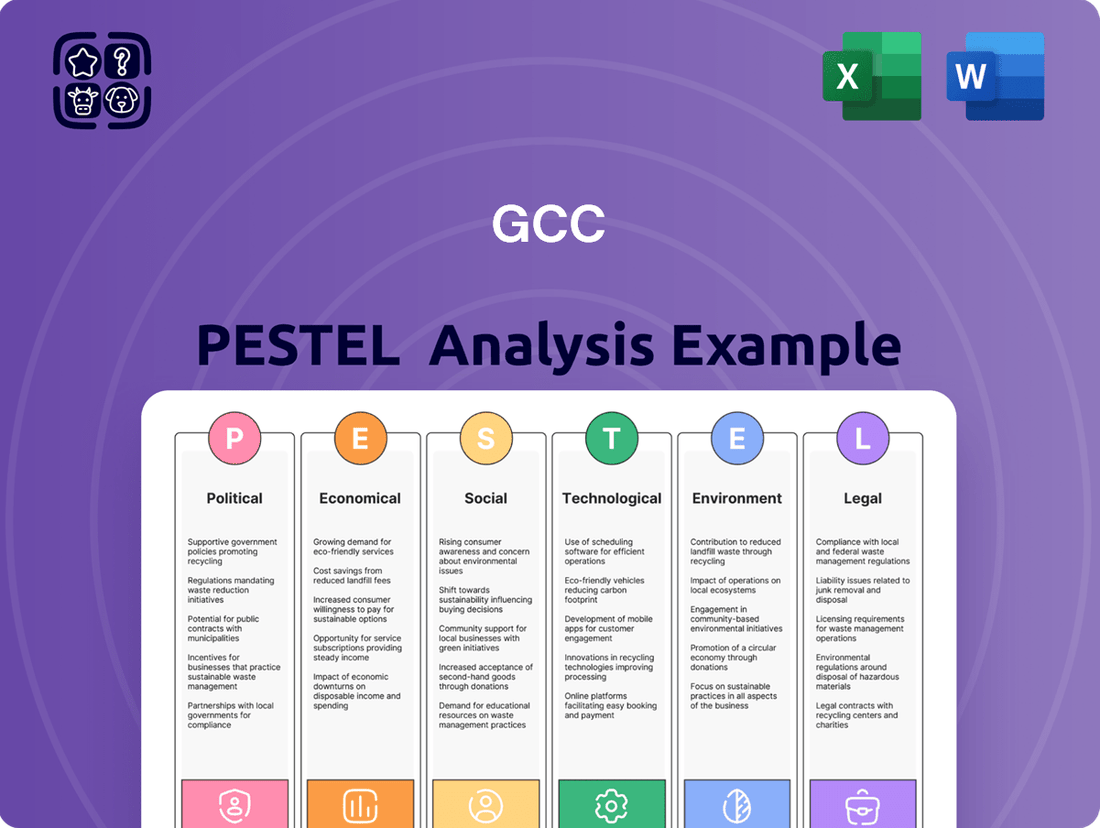
GCC PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GCC Bundle
Unlock the critical external factors shaping the GCC market with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political stability, economic shifts, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and socio-cultural trends are impacting businesses in the region. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to navigate this dynamic landscape and secure your competitive advantage.
Political factors
Government investment in infrastructure projects, like roads and utilities, significantly influences demand for GCC's products. For instance, the US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, enacted in 2021, allocates $1.2 trillion over five years to upgrade roads, bridges, public transit, and water systems, creating substantial opportunities for construction material suppliers. This sustained government commitment to infrastructure development across North America directly boosts demand in the construction materials sector.
Trade policies significantly shape the operational landscape for GCC. Agreements like the USMCA, while not directly involving GCC, exemplify how such pacts impact cross-border flows of goods and capital, which can indirectly influence GCC's supply chains and market access. For instance, if a major trading partner of a GCC nation enacts new tariffs, it could increase the cost of imported raw materials essential for GCC's manufacturing processes.
Changes in import/export regulations or tariffs directly affect GCC's cost structure and market competitiveness. For example, a 5% increase in import duties on key components could add millions to GCC's annual operating expenses, necessitating price adjustments or a search for alternative suppliers. Conversely, favorable trade agreements can reduce these costs, boosting profitability and market share.
GCC's ability to operate seamlessly across diverse regions is heavily reliant on stable and predictable trade relations. In 2024, global trade volumes are projected to see moderate growth, but geopolitical tensions and protectionist measures remain a concern. Maintaining strong diplomatic ties and adapting to evolving trade frameworks are therefore critical for GCC's sustained growth and operational efficiency.
Regulatory stability in the GCC construction sector is paramount for sustained growth. For instance, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 has introduced significant regulatory reforms, aiming to streamline processes and attract foreign investment, which is a positive indicator for predictability. However, the pace of these changes can sometimes create a learning curve for businesses.
Frequent shifts in zoning laws or permitting procedures, as observed in some emerging markets, can lead to project delays and inflated compliance costs. In 2024, construction firms operating in the GCC are closely monitoring regulatory frameworks, particularly concerning environmental standards and labor laws, seeking consistency to facilitate accurate financial forecasting and risk management.
A predictable regulatory landscape, where changes are well-communicated and implemented gradually, fosters confidence among developers, contractors, and suppliers like GCC. This stability encourages long-term investment and commitment, as companies can better plan resource allocation and manage potential risks associated with compliance, ultimately contributing to a healthier project pipeline.
Political Stability in Operating Regions
Political stability within the United States, Mexico, and Canada significantly shapes the business landscape for construction. Geopolitical tensions, shifts in government leadership, or internal unrest can create significant disruptions. For instance, in 2024, ongoing political discourse around trade agreements and infrastructure spending in the US created uncertainty for cross-border construction projects.
These instabilities can ripple through supply chains, affecting the availability and cost of materials. They also impact consumer and investor confidence, potentially leading to reduced demand for new construction and a slowdown in economic activity. For example, the 2024 US presidential election cycle, with its various policy proposals, directly influenced investor sentiment towards large-scale infrastructure projects.
- US Political Stability: Continued focus on infrastructure investment, with potential impacts from election outcomes on project funding.
- Mexico Political Environment: Government policies on foreign investment and resource management can influence project viability.
- Canada's Political Climate: Environmental regulations and interprovincial trade policies directly affect construction timelines and costs.
Government Procurement Policies
Government agencies represent a substantial customer base for construction materials within the GCC. For instance, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 includes massive infrastructure projects like NEOM, requiring extensive material procurement. Policies favoring local content, such as those mandating a certain percentage of materials sourced domestically, directly impact suppliers' competitiveness and market access.
These procurement strategies can significantly shape market dynamics. For example, the UAE's emphasis on sustainable building materials in government tenders encourages the adoption of eco-friendly products. Understanding the nuances of bidding processes, including pre-qualification requirements and tender evaluation criteria, is crucial for GCC companies aiming to secure these valuable public sector contracts.
- GCC governments are major buyers of construction materials for large-scale public works, with projects like Saudi Arabia's NEOM driving significant demand.
- Procurement policies often include preferences for local suppliers and mandates for sustainable materials, influencing market entry and product development.
- Adapting to specific bidding processes and tender requirements is essential for GCC firms to capitalize on public sector sales opportunities.
Political stability and government spending are key drivers for the GCC construction materials market. In 2024, significant government investment in mega-projects across Saudi Arabia (e.g., NEOM) and the UAE continues to fuel demand. Trade policies and regulatory frameworks, including those favoring local content and sustainability, directly impact operational costs and market access for companies like GCC.
| Factor | 2024/2025 Outlook | Impact on GCC |
| Government Infrastructure Spending | Continued strong investment, particularly in Saudi Arabia and UAE. | Directly increases demand for construction materials. |
| Trade Agreements & Tariffs | Potential for increased protectionism globally, but regional agreements remain stable. | Affects raw material costs and export competitiveness. |
| Regulatory Stability | Focus on streamlining processes and attracting foreign investment in key GCC nations. | Enhances predictability for long-term planning and investment. |
| Local Content Policies | Increasingly prevalent, encouraging domestic sourcing. | Requires adaptation in supply chain management and sourcing strategies. |
What is included in the product
This GCC PESTLE Analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors impacting the region.
It offers strategic insights for businesses to navigate the dynamic GCC landscape and identify actionable opportunities and potential challenges.
Provides a clear, actionable framework that simplifies complex external factors, enabling businesses to proactively address potential challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Economic factors
Interest rate fluctuations significantly affect the GCC housing market. For instance, in early 2024, many GCC central banks maintained or slightly adjusted their benchmark rates, often mirroring US Federal Reserve decisions. This directly impacts mortgage affordability for individuals and the cost of capital for developers.
When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive. This can dampen demand for new homes and slow down the pace of construction projects across the region, from Dubai to Riyadh. Conversely, lower interest rates typically stimulate the market, encouraging more investment in real estate and boosting demand for construction materials like cement and aggregates.
The overall health of the GCC housing sector is a crucial economic indicator. In 2023, several GCC countries saw robust real estate activity, partly supported by favorable financing conditions, although the impact of global monetary policy tightening remained a consideration for 2024.
The economic vitality of the United States, Mexico, and Canada, as reflected in their Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, directly influences construction demand. In 2024, the U.S. economy is projected to grow around 2.5%, while Mexico's GDP is expected to expand by approximately 2.2% and Canada's by about 1.8%.
Strong GDP expansion in these key operating regions typically fuels greater investment in infrastructure, commercial developments, and residential building, thereby boosting the need for construction materials. For instance, a healthy economic outlook often translates to more government spending on public works and increased private sector confidence for new projects.
Conversely, economic downturns or recessions in these North American markets tend to dampen construction spending significantly. A slowdown in GDP growth can lead to reduced consumer spending, tighter credit conditions, and a general hesitancy to commit to large-scale construction projects, impacting material suppliers.
Inflationary pressures in the GCC region directly impact GCC's profitability by driving up the cost of essential inputs like limestone and energy. For instance, global energy prices, a key component of raw material and transportation costs, saw significant volatility throughout 2023 and into early 2024, with oil prices fluctuating.
While GCC can absorb some of these rising costs through price adjustments, persistent high inflation, potentially exceeding 5% in some GCC economies as projected for parts of 2024, can squeeze profit margins. This makes construction projects less affordable, potentially dampening demand for GCC's products and services.
Therefore, effective management of input costs, including securing favorable supplier contracts for raw materials and optimizing logistics, alongside strategic pricing adjustments, are crucial for GCC to maintain profitability amidst these economic headwinds.
Construction Industry Growth Forecasts
The construction industry in the GCC is poised for significant expansion. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5% for the period of 2024-2028, driven by substantial government investments in infrastructure and mega-projects. This growth translates directly into increased demand for construction materials and services, offering a positive outlook for businesses operating within or supplying to this sector.
Specifically, the residential and commercial segments are expected to see robust activity. The UAE, for instance, anticipates a 7% growth in its construction sector for 2024, fueled by ongoing urban development and major event preparations. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 continues to be a major catalyst, with giga-projects like NEOM driving massive infrastructure and real estate development, creating substantial opportunities.
Key growth drivers and their impact include:
- Infrastructure Development: Continued investment in transportation networks, utilities, and renewable energy projects will bolster demand. For example, Qatar's focus on post-World Cup infrastructure upgrades is expected to sustain construction momentum.
- Residential and Commercial Real Estate: Population growth and urbanization are fueling demand for new housing and commercial spaces across the region, particularly in hubs like Dubai and Riyadh.
- Tourism and Hospitality Expansion: Major tourism initiatives in countries like Saudi Arabia and Oman are leading to significant hotel and resort construction, creating further market opportunities.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Exchange rate fluctuations pose a significant challenge for companies operating across the GCC, particularly when dealing with currencies like the US Dollar (USD), Mexican Peso (MXN), and Canadian Dollar (CAD). For instance, if a company has significant revenue streams in Mexico, a strengthening USD against the MXN can reduce the repatriated USD value of those earnings, impacting overall profitability. This volatility directly affects the cost of imported goods and the competitiveness of exports.
The impact of these currency movements can be substantial. As of early 2024, the USD has shown resilience against many global currencies. For example, the USD to MXN exchange rate has seen fluctuations, with the USD often trading in a range that can make Mexican operations less lucrative when converting profits back to dollars. Similarly, the USD to CAD rate can affect the cost of goods sourced from Canada or the profitability of Canadian sales when translated into USD.
- Revenue Impact: A stronger USD can decrease the USD equivalent of revenues earned in MXN or CAD. For example, if a company earns $100 million MXN, and the rate moves from 17 MXN/USD to 18 MXN/USD, the USD revenue drops from approximately $5.88 million to $5.56 million.
- Cost Management: Conversely, a stronger USD can make imports from Mexico or Canada cheaper in USD terms, but it increases the cost of goods sourced from the US for Mexican or Canadian operations.
- Profitability Squeeze: Unfavorable currency movements can erode profit margins, especially if costs are denominated in a strengthening currency while revenues are in a weakening one.
- Strategic Hedging: Managing foreign exchange risk through hedging strategies, such as forward contracts or options, is crucial for maintaining financial stability and predictable earnings.
Economic factors significantly shape the GCC's business environment. Interest rate adjustments, often mirroring global trends like those of the US Federal Reserve, directly influence borrowing costs for real estate projects and consumer affordability. In 2024, many GCC central banks maintained stable rates, a factor that supported continued, albeit cautious, growth in the housing market.
Inflationary pressures remain a key concern, with some GCC economies experiencing inflation rates potentially exceeding 5% in parts of 2024, impacting raw material and energy costs. Despite these pressures, the GCC construction sector is projected for robust growth, with an estimated CAGR of 5.5% between 2024 and 2028, driven by substantial infrastructure investments and mega-projects like NEOM in Saudi Arabia.
Economic performance in North America, specifically GDP growth in the US (projected ~2.5% in 2024), Mexico (~2.2%), and Canada (~1.8%), indirectly affects GCC economies by influencing global demand for construction materials and services. Exchange rate volatility, particularly between the USD and currencies like the Mexican Peso and Canadian Dollar, presents challenges, impacting revenue conversion and cost management for companies with cross-border operations.
Full Version Awaits
GCC PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact GCC PESTLE Analysis document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive analysis covers all critical factors impacting the Gulf Cooperation Council region, providing valuable insights for strategic planning. You can be confident that the detailed information and professional structure you see will be yours to download instantly.
Sociological factors
The GCC region is experiencing significant population growth, projected to reach over 70 million by 2030, with a substantial portion concentrating in urban hubs like Dubai and Riyadh. This demographic surge directly fuels demand for construction materials, as evidenced by the ongoing mega-projects across the region, such as Saudi Arabia's NEOM and UAE's various urban expansion plans.
Urbanization is a key driver, with cities becoming magnets for employment and opportunity, leading to increased construction of residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. For GCC, this means a sustained need for its core products, requiring strategic planning for production capacity and efficient logistics to serve these expanding urban centers effectively.
Societal expectations in the GCC are shifting towards environmental responsibility, influencing the construction sector significantly. There's a clear upward trend in demand for construction practices and materials that minimize ecological impact, a sentiment echoed by consumers, businesses, and governmental bodies alike.
This growing preference is evidenced by the increasing adoption of green building certifications. For example, the number of LEED-certified projects in the GCC has seen steady growth, with the UAE and Saudi Arabia leading the charge, demonstrating a tangible commitment to sustainability. This indicates a market readiness for and expectation of environmentally conscious building solutions.
To remain competitive, construction material suppliers in the GCC must innovate. Offering product lines that cater to this demand, such as low-carbon cement alternatives or building materials incorporating recycled content, is becoming essential. Companies that proactively embrace these sustainable options are better positioned to capture market share and meet the evolving needs of a more environmentally aware clientele.
The availability of skilled labor significantly influences the operational efficiency and project timelines within the GCC's construction and manufacturing sectors. For instance, a shortage of qualified truck drivers, plant operators, and construction workers can directly translate into higher labor costs and project delays. In 2024, reports indicated specific skill shortages in areas like specialized welding and project management within the region's booming infrastructure projects.
Addressing this skills gap is paramount for the GCC's sustained operational capacity. Initiatives focusing on vocational training programs and the adoption of advanced technologies are seen as crucial strategies to bridge this divide. The region is actively investing in upskilling its workforce, with several countries launching national training initiatives in 2025 aimed at boosting the competency of local talent in key industrial areas.
Public Perception of Construction Industry
Public perception of the construction industry in the GCC is crucial for its ongoing development and social license to operate. Concerns about environmental impact, particularly in relation to large-scale projects and resource consumption, can lead to increased regulatory oversight and public opposition. For instance, in 2024, several GCC nations intensified environmental impact assessments for new developments, reflecting growing public and governmental pressure for sustainable practices.
Safety records are another significant factor. A history of accidents, even if isolated, can tarnish the industry's reputation and make it harder to attract skilled labor. While specific GCC-wide safety statistics for 2024 are still emerging, individual country initiatives in 2023 and early 2024 saw a focus on implementing stricter safety training and enforcement, aiming to improve public confidence.
Furthermore, the industry's engagement with local communities influences its acceptance. Projects that demonstrate clear benefits, such as job creation or improved infrastructure, and involve transparent communication tend to foster more positive public sentiment. In 2024, many major construction firms in the region highlighted their corporate social responsibility programs, including local hiring and community development initiatives, as key to maintaining a favorable public image.
- Environmental Awareness: Growing public concern over the carbon footprint and resource intensity of construction projects in the GCC is driving demand for greener building practices and materials.
- Safety Standards: A strong emphasis on worker safety and transparent reporting of incidents is vital for building public trust and attracting a qualified workforce. In 2023, Saudi Arabia's construction sector reported a 15% decrease in major safety violations compared to the previous year, reflecting improved oversight.
- Community Relations: Proactive community engagement, including local employment opportunities and minimizing disruption during construction, significantly impacts public perception and support for development projects.
- Talent Acquisition: A positive public image, particularly regarding safety and sustainability, is essential for attracting and retaining talent in a competitive labor market.
Demographic Shifts Impacting Housing Demand
Demographic shifts are significantly reshaping housing demand across the GCC. Beyond general population increases, the aging demographic is driving demand for specialized housing, such as assisted living facilities and smaller, low-maintenance homes. This contrasts with the needs of younger generations, like millennials, who are increasingly entering the homeownership market, often favoring urban, multi-family dwellings. In 2024, for instance, countries like the UAE saw a continued rise in expatriate populations, a key driver of rental and purchase demand, particularly for apartments.
Changing household sizes also play a crucial role. As families become smaller or more individuals opt for single living, the demand for larger, single-family homes may decrease in certain segments, while the need for studios and one-bedroom apartments grows. This evolution directly impacts the types of building materials and construction methods favored by developers. For example, a trend towards smaller, more efficient living spaces could boost demand for modular construction components and sustainable materials.
- Aging Population: GCC countries are experiencing an increase in their elderly population, creating a demand for age-appropriate housing solutions and healthcare-integrated residences.
- Millennial Homeownership: Younger demographics are showing a growing interest in property ownership, often prioritizing modern amenities and convenient urban locations, influencing the development of mid-rise and high-rise residential projects.
- Household Size: A general trend towards smaller household sizes in many GCC nations is shifting demand towards smaller unit types like studios and one-bedroom apartments.
- Expatriate Influence: The significant expatriate population in many GCC states continues to be a primary driver of housing demand, particularly in major urban centers, influencing rental yields and property values.
Societal expectations in the GCC are increasingly focused on sustainability and ethical practices, influencing consumer choices and regulatory frameworks. This shift is evident in the growing demand for eco-friendly construction materials and a greater emphasis on corporate social responsibility from businesses. For instance, in 2024, green building certifications like LEED saw a notable increase in adoption across the region, with the UAE and Saudi Arabia leading this trend.
The availability and perception of skilled labor are critical. Shortages in specialized construction roles, such as project managers and skilled tradespeople, can lead to project delays and increased costs, impacting the construction material supply chain. In response, many GCC nations are investing in vocational training programs, with national initiatives in 2025 aiming to upskill the local workforce.
Public sentiment towards the construction industry is also a key factor, with concerns about environmental impact and worker safety influencing project approvals and company reputations. In 2024, intensified environmental impact assessments for new developments reflect this growing public and governmental pressure for more sustainable construction methods.
Technological factors
Automation is reshaping production and logistics across the GCC. Cement plants, quarries, and concrete facilities are increasingly adopting automated systems to boost efficiency and cut labor expenses. For instance, by 2024, many GCC construction projects are expected to see a significant reduction in manual labor needs due to advanced robotics and AI integration, aiming for up to a 20% decrease in operational costs.
In logistics, the GCC is investing heavily in autonomous vehicles for material transport. This move is designed to create more streamlined supply chains and reduce distribution costs. By 2025, it's projected that autonomous trucking could lower transportation expenses by as much as 15% in key GCC trade routes, directly impacting the region's competitive edge in delivery speed and cost-effectiveness.
Innovations like self-healing concrete and advanced composites are reshaping construction, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traditional materials in the GCC. For instance, the global advanced composites market is projected to reach $77.1 billion by 2026, indicating a significant shift towards lighter, stronger building solutions.
GCC companies must invest in research and development to explore these new materials and modular construction techniques. This strategic move could lead to diversified product portfolios or adaptations of existing offerings, ensuring continued relevance in a rapidly evolving industry.
The GCC region is actively embracing the digitalization of its supply chains and operations. For instance, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 includes significant investments in smart logistics and advanced technologies, aiming to boost efficiency across various sectors. By implementing IoT sensors and big data analytics, businesses can achieve real-time inventory tracking and predictive maintenance, as seen in the growing adoption of such solutions by major logistics players in the UAE.
Innovations in Sustainable Cement Production
The cement industry, a cornerstone of construction, faces significant pressure to decarbonize. Innovations in sustainable cement production are therefore paramount, with the GCC region actively exploring these advancements. For instance, the global cement industry accounts for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions, underscoring the urgency for change.
Key technological drivers include carbon capture and utilization (CCU), the adoption of alternative fuels, and the development of low-carbon cement formulations. These technologies are not only vital for environmental stewardship but also for compliance with increasingly stringent global regulations.
The GCC's commitment to these innovations is evident. For example, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 includes ambitious sustainability goals, encouraging investments in green technologies within heavy industries like cement. By embracing these advancements, the GCC can bolster its environmental credentials and solidify its competitive edge in the global market.
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU): Technologies aimed at capturing CO2 emissions from cement plants for reuse or storage.
- Alternative Fuels: Shifting from traditional fossil fuels to biomass, waste-derived fuels, or hydrogen to power kilns.
- Low-Carbon Cement Formulations: Developing cements with reduced clinker content or using supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) like fly ash and slag.
- GCC Investment Trends: Significant capital allocation towards R&D and pilot projects for sustainable cement technologies, aligning with national sustainability agendas.
Data Analytics for Operational Efficiency
Leveraging data analytics is revolutionizing operational efficiency across the GCC. By processing extensive data from production, sales, and logistics, companies gain critical insights to streamline processes, pinpoint inefficiencies, and refine demand forecasts. This analytical approach enables more strategic decision-making, leading to better resource management and cost savings.
For instance, in 2024, Saudi Aramco reported significant operational improvements attributed to advanced analytics in its upstream operations, contributing to a more stable and efficient oil production process. Similarly, Dubai's logistics sector is increasingly adopting AI-driven analytics to optimize shipping routes and warehouse management, aiming to reduce transit times and operational costs. The adoption of these technologies is projected to boost productivity by an estimated 15-20% in key industrial sectors by 2025.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Data analytics helps in precisely allocating resources based on real-time demand and performance metrics, reducing waste and improving utilization.
- Bottleneck Identification: Advanced algorithms can quickly identify constraints in production lines or supply chains, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Enhanced Demand Forecasting: Predictive analytics improves the accuracy of demand forecasts, minimizing overstocking and stockouts, thereby boosting customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing processes and resource use, data analytics directly contributes to lower operational expenditures.
Technological advancements are significantly boosting efficiency in GCC industries, particularly in manufacturing and logistics. Automation and AI are reducing manual labor needs; for example, by 2024, many GCC construction projects anticipate up to a 20% decrease in operational costs due to robotics. Autonomous vehicles are also streamlining supply chains, with projections indicating up to a 15% reduction in transportation expenses on key trade routes by 2025.
Innovations like self-healing concrete are transforming construction, with the global advanced composites market expected to reach $77.1 billion by 2026, signaling a move towards advanced building materials. The GCC's embrace of digitalization, including IoT and big data analytics, is enhancing supply chain visibility and predictive maintenance, as seen in the UAE's logistics sector.
The cement industry is prioritizing decarbonization through technologies like carbon capture and utilization (CCU), alternative fuels, and low-carbon cement formulations, crucial given the industry's 8% global CO2 emissions contribution. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030, for instance, actively supports green technology investments in heavy industries.
Data analytics is a key enabler of operational improvements across the GCC. Saudi Aramco reported significant gains in upstream operations from advanced analytics in 2024, while Dubai's logistics sector uses AI to optimize routes and warehousing. These technologies are projected to boost productivity by 15-20% in key industrial sectors by 2025.
| Technology Area | GCC Adoption Trend (2024-2025) | Projected Impact | Key Initiatives/Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automation & Robotics | Increasing adoption in manufacturing and construction | Up to 20% reduction in operational costs by 2024 | GCC construction projects integrating advanced robotics; Cement plants adopting automated systems |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Growing investment in logistics and material transport | Up to 15% reduction in transportation costs by 2025 | Autonomous trucking on key GCC trade routes |
| Advanced Materials | Emerging adoption in construction | Market growth to $77.1 billion by 2026 (global) | Self-healing concrete, advanced composites |
| Digitalization (IoT, Big Data) | Widespread implementation in supply chains | Enhanced visibility, predictive maintenance, optimized operations | Saudi Vision 2030 smart logistics; UAE logistics sector AI adoption |
| Decarbonization Technologies (CCU, Alt Fuels) | Active exploration and investment in cement industry | Reduced CO2 emissions, regulatory compliance | Low-carbon cement formulations, alternative fuels in kilns |
| Data Analytics | Significant integration across industries | 15-20% productivity boost by 2025 in key sectors | Saudi Aramco upstream operations; Dubai logistics route optimization |
Legal factors
Building codes and construction standards across the US, Mexico, and Canada are critical for ensuring the quality and safety of building materials. GCC must navigate these diverse and often changing regulations to maintain compliance.
For instance, updated codes in 2024 and projected for 2025 are increasingly emphasizing energy efficiency and seismic resilience. This means GCC's product specifications may need to adapt to meet new performance requirements, potentially impacting market demand for existing offerings and driving innovation in sustainable materials.
GCC nations are increasingly enforcing stringent environmental regulations. For instance, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 includes ambitious targets for emissions reduction, aiming to cut carbon intensity by 50% by 2035. Compliance with these evolving standards for air, water, and waste management is crucial for manufacturers to avoid substantial penalties and maintain operational continuity.
Failure to adhere to environmental permits and emission limits can lead to significant financial repercussions. In 2024, several industrial facilities across the UAE faced fines totaling millions of dollars for non-compliance with wastewater discharge regulations. This underscores the need for ongoing investment in advanced environmental control technologies and robust monitoring systems.
Compliance with labor laws, including minimum wage, working hours, and collective bargaining rights, is crucial for businesses operating in the GCC. For instance, Saudi Arabia’s Labor Law mandates a standard workweek of 48 hours and outlines provisions for overtime pay, while the UAE's Ministry of Human Resources and Emiratisation enforces similar regulations. Adherence to these standards helps avoid penalties and fosters a stable workforce.
Worker safety regulations are particularly critical in industries like quarrying and manufacturing. In 2024, the GCC region has seen increased focus on occupational health and safety, with countries like Qatar implementing stricter guidelines following international benchmarks. Ensuring a safe working environment, compliant with standards similar to OSHA, is not just a legal requirement but also vital for preventing accidents, mitigating legal liabilities, and boosting employee morale and operational efficiency.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Antitrust and competition laws are a significant consideration for GCC's cement and construction materials sector. These regulations aim to foster a fair playing field by preventing monopolistic behavior and ensuring competitive pricing. For instance, the UAE's Competition Law (Federal Decree-Law No. 4 of 2012, as amended) and similar legislation across the GCC countries, like Saudi Arabia's Competition Law, actively monitor market concentration and potential anti-competitive agreements. Companies must navigate these rules carefully, especially concerning mergers and acquisitions, to avoid substantial penalties and legal disputes.
Regulatory bodies in the GCC, such as the UAE's Competition Regulation and Saudi Arabia's General Authority for Competition, are increasingly vigilant. They scrutinize pricing strategies and market dominance to protect consumers and smaller businesses. In 2023, several competition authorities across the region issued warnings and initiated investigations into potential price-fixing or cartel activities within various industries, underscoring the importance of strict adherence. Failure to comply can result in significant fines, potentially impacting a company's financial performance and market reputation.
- Regulatory Oversight: GCC competition authorities actively monitor market share and pricing to prevent monopolies in the construction materials sector.
- Merger Control: Acquisitions and mergers within the cement industry require careful review and approval to ensure they do not stifle competition.
- Compliance Importance: Adherence to antitrust laws is crucial to avoid hefty fines, legal challenges, and reputational damage.
- Market Fairness: These laws are designed to promote fair market practices, benefiting both consumers and smaller market participants.
Permitting and Zoning Requirements
GCC's operations are significantly shaped by permitting and zoning regulations across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states. Obtaining and maintaining necessary permits for quarrying, plant operations, and expansion projects is a complex and often lengthy legal process. For instance, in Saudi Arabia, environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are mandatory for new industrial projects, with the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture overseeing approvals, a process that can take 12-18 months or longer depending on project scope and complexity as of early 2024.
Zoning laws are equally critical, dictating where industrial activities, including quarrying and manufacturing plants, can legally take place. These regulations vary by emirate in the UAE and by province in Saudi Arabia, often requiring specific land-use designations. Failure to comply can result in significant fines or operational shutdowns. For example, Dubai's Development Department enforces strict zoning for industrial zones, with penalties for non-compliance potentially reaching AED 100,000 (approximately $27,200 USD) for violations related to land use as of late 2023.
Navigating these requirements and securing timely approvals are critical for GCC's ability to operate and grow its production capacity in its various locations. The ability to secure new quarrying licenses, for example, directly impacts raw material availability. In Qatar, the Ministry of Municipality and Environment manages land use and permits, with recent reforms in 2023 aiming to streamline the process for strategic industrial developments, though timelines remain a key consideration for project planning.
- Permit Complexity: Securing quarrying, operational, and expansion permits involves navigating distinct legal frameworks in each GCC country, often requiring detailed environmental and safety compliance.
- Zoning Impact: Land-use regulations dictate operational sites, influencing logistics and expansion potential; non-compliance can lead to substantial financial penalties.
- Timeliness is Key: The duration of the approval process, which can extend over a year in some cases, directly impacts GCC's strategic planning for capacity growth and new project timelines.
- Regulatory Evolution: GCC countries are periodically updating their permitting and zoning laws to attract investment and streamline processes, requiring continuous monitoring by GCC.
Legal frameworks governing intellectual property rights are increasingly important for GCC's innovation in materials science and manufacturing processes. Protecting proprietary technologies, patents, and trademarks is essential to maintain a competitive edge. For instance, Saudi Arabia's robust intellectual property laws, aligned with international standards, aim to safeguard innovation, encouraging R&D investment.
Contract law is fundamental to GCC's business operations, covering agreements with suppliers, customers, and partners. Ensuring contracts are legally sound and enforceable prevents disputes and financial losses. For example, the UAE's Commercial Code provides a clear framework for contractual obligations, with recent amendments in 2023 focusing on digital contracts and e-signatures, reflecting the evolving business landscape.
GCC must also comply with international trade laws and customs regulations, especially for imported raw materials and exported finished goods. Understanding tariffs, import duties, and trade agreements is vital for cost management and market access. For example, the GCC unified customs tariff, implemented across member states, standardizes import duties on many goods, simplifying cross-border transactions.
Data privacy regulations are gaining prominence across the GCC, impacting how companies collect, store, and process customer and employee information. Compliance with laws like Saudi Arabia's Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL) and the UAE's Federal Decree-Law No. 45 of 2021 on Personal Data Protection is crucial to avoid penalties. These laws mandate secure data handling and consent requirements, influencing digital operations and customer relations.
Environmental factors
GCC, like many in the cement sector, faces mounting pressure to slash carbon emissions. The industry is a significant CO2 contributor, prompting governments, investors, and the public to demand ambitious reduction goals. For instance, the global cement industry accounts for roughly 7% of all anthropogenic CO2 emissions, a stark figure driving this environmental focus.
To meet these evolving environmental standards and stakeholder expectations, GCC must invest in cleaner technologies, explore alternative fuels, and innovate low-carbon cement products. This strategic shift is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and social license to operate in a world increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
The GCC's reliance on raw materials like limestone and gypsum for its booming construction sector, particularly in cement and concrete production, presents significant resource depletion concerns. For instance, Saudi Arabia alone consumed an estimated 60 million tons of cement in 2023, driving substantial quarrying activity. This extraction process inherently leads to land disturbance, habitat disruption, and dust pollution, impacting local ecosystems and air quality.
To address these environmental challenges, the GCC nations are increasingly emphasizing sustainable quarry management. This includes implementing stricter regulations for land reclamation, promoting biodiversity restoration in quarried areas, and investing in dust suppression technologies. Furthermore, there's a growing push towards incorporating recycled aggregates into construction materials, a trend supported by initiatives like the UAE's Al Dhafra Recycling Facility, which processes construction and demolition waste.
Climate change presents significant environmental challenges for the GCC region, with extreme weather events like intense heatwaves and potential for increased flooding impacting infrastructure. These events could disrupt supply chains for construction materials and affect the operational efficiency of existing infrastructure. For instance, the UAE experienced record-breaking rainfall in April 2024, causing widespread disruption and highlighting the vulnerability of existing infrastructure to extreme weather.
The demand for climate-resilient infrastructure is expected to grow, potentially boosting the market for advanced construction materials like high-performance concrete. This shift could create opportunities for businesses offering specialized, durable building solutions. Globally, the market for green building materials is projected to reach over $400 billion by 2027, indicating a strong trend towards sustainable construction practices in response to climate concerns.
Waste Management and Recycling in Construction
Growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations across the GCC are compelling the construction sector to adopt more robust waste management practices and boost the recycling of construction and demolition (C&D) debris. This shift is driven by a desire to reduce landfill burden and conserve natural resources.
The region has a significant opportunity to integrate recycled aggregates into concrete production and explore innovative methods for reusing cementitious materials. This aligns with circular economy principles, fostering sustainability and potentially opening up new avenues for revenue generation within the construction industry.
For instance, Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 emphasizes sustainability, with targets to reduce waste generation. In 2023, the UAE's construction sector was estimated to generate millions of tons of C&D waste annually, highlighting the scale of the challenge and the potential impact of improved recycling initiatives.
- Increased Regulation: GCC countries are implementing stricter environmental laws mandating waste segregation and recycling on construction sites.
- Circular Economy Focus: The push for reusing C&D waste, such as crushed concrete for aggregate, is gaining momentum, mirroring global trends.
- Economic Opportunities: Developing local markets for recycled construction materials can reduce reliance on virgin resources and create new business models.
- Technological Adoption: Investments in advanced sorting and processing technologies are crucial for efficient C&D waste recycling.
Demand for Green Building Materials
The increasing global emphasis on sustainability is driving a significant surge in demand for green building materials across the GCC. This trend is fueled by a growing awareness of environmental impact and a desire for healthier living and working spaces. Governments in the region are also playing a role, with many introducing regulations and incentives that favor eco-friendly construction.
This shift presents both a challenge and a substantial opportunity for GCC manufacturers. They are increasingly pressured to innovate, developing and offering building materials that boast lower embodied carbon footprints, incorporate recycled content, or are produced using less energy. For instance, the UAE's commitment to net-zero by 2050 and Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 initiatives, which heavily feature sustainable development, are creating a fertile ground for these materials.
Key areas of growth include:
- Recycled Content: Increased use of recycled steel, concrete aggregates, and plastics in construction.
- Low Embodied Carbon Materials: Greater adoption of materials like sustainable timber, low-carbon concrete alternatives, and bio-based insulation.
- Energy-Efficient Products: Demand for advanced insulation, high-performance glazing, and cool roofing materials is on the rise.
The market for green building materials in the GCC is projected to see robust growth, with some estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 15% in the coming years, reflecting the region's commitment to a more sustainable built environment.
Environmental regulations are tightening across the GCC, pushing industries like cement towards lower carbon footprints and sustainable practices. The region's construction boom, while driving economic growth, also exacerbates concerns about resource depletion and waste generation. Extreme weather events linked to climate change are also a growing threat, necessitating climate-resilient infrastructure and materials.
The GCC is actively promoting circular economy principles, with a focus on recycling construction and demolition waste. This includes incorporating recycled aggregates into concrete and reusing cementitious materials. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 and the UAE's net-zero by 2050 commitment are key drivers for adopting sustainable construction methods.
The demand for green building materials is surging, with a projected compound annual growth rate exceeding 15% in the GCC. This includes materials with recycled content, low embodied carbon, and enhanced energy efficiency, reflecting a regional shift towards sustainability.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our GCC PESTLE analysis is meticulously constructed using data from official government bodies across the region, international financial institutions, and reputable market research firms. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of political stability, economic growth, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks impacting the Gulf Cooperation Council.
