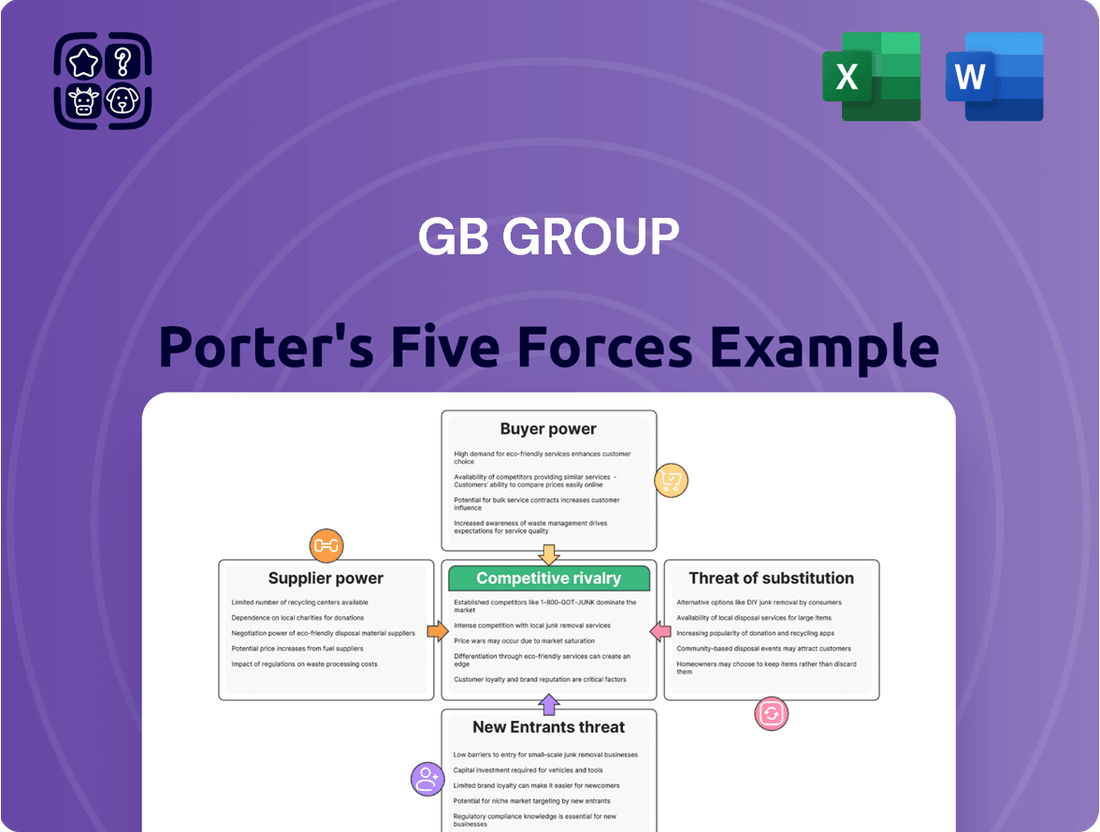
GB Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GB Group Bundle
GB Group faces intense competition, with significant threats from new entrants and the constant pressure of substitute products. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping GB Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
GB Group's reliance on external data providers for identity and location information is substantial, as this data forms the bedrock of their verification and fraud prevention services. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be considerable, especially when they offer unique, proprietary, or hard-to-replicate datasets crucial for GB Group's specialized offerings.
For instance, in 2024, the market for specialized identity verification data saw consolidation, with a few key providers holding significant market share. This concentration can amplify their leverage, allowing them to command higher prices or impose stricter terms on GB Group if alternative data sources are limited or less comprehensive.
However, GB Group is actively working to diversify its data sourcing and leverage advanced analytics to combine information from multiple, more readily available sources. This strategy aims to reduce dependence on any single supplier and mitigate their bargaining power, particularly as the broader data landscape continues to evolve with increased accessibility and interoperability.
GB Group's reliance on specialized software and hardware providers for advanced functionalities, such as sophisticated fraud detection algorithms or biometric verification, can significantly influence supplier bargaining power. If these vendors possess highly differentiated or patented technologies, they hold a stronger position to negotiate terms, potentially impacting GB Group's cost structure and its ability to adapt its technological offerings.
In the specialized realm of identity data intelligence, the availability of talent in AI, machine learning, cybersecurity, and data science is paramount. A scarcity of these highly skilled professionals significantly bolsters their bargaining power.
This talent shortage directly translates into increased labor costs for companies like GB Group. For instance, the average salary for a data scientist in the UK saw a notable increase in 2024, reflecting the high demand for these specialized skills.
Such elevated costs can strain a company's profitability and hinder its ability to invest in crucial areas like innovation and service enhancement, impacting overall competitiveness.
Cloud Infrastructure Providers
GB Group, as a technology company, heavily relies on cloud infrastructure providers for its operations. Major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market, giving them considerable bargaining power. This concentration means GB Group may face limited alternatives if it becomes deeply integrated with a single provider, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or service agreements.
While GB Group can mitigate this by using multiple cloud providers, the cost and complexity of managing a multi-cloud strategy can be substantial. The sheer scale and market dominance of these providers mean they can dictate terms, especially for specialized services or large-scale deployments. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, with the top three providers holding a significant majority share, underscoring their market leverage.
- Market Concentration: The cloud infrastructure market is highly concentrated, with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud accounting for roughly 65% of the global market share as of early 2024.
- Switching Costs: Migrating data and applications between cloud providers can be technically complex and expensive, increasing GB Group's dependence on its current provider.
- Service Differentiation: While core services are commoditized, specialized offerings or unique integrations can lock customers in, further strengthening supplier power.
Regulatory Data Sources
GB Group's reliance on official or governmental data sources for identity verification and compliance presents a significant factor in supplier bargaining power. Access to these crucial datasets, such as national identity registers and public records, is often a prerequisite for GB Group's core services.
The concentration of control over these vital data sources by a limited number of entities, or the imposition of stringent access requirements, can amplify their bargaining leverage. For instance, if a government agency tightly controls access to its citizen data, it can dictate terms, potentially increasing operational costs for GB Group or limiting the scope of its data acquisition capabilities.
In 2024, the increasing global emphasis on data privacy and regulatory compliance, such as GDPR and similar frameworks, further solidifies the power of entities controlling official data. These regulations can create barriers to entry and necessitate specific licensing or partnership agreements, giving data providers considerable sway over companies like GB Group.
- Data Source Control: Governments or specific agencies often hold exclusive rights to essential data, granting them significant leverage.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with data protection laws can necessitate costly agreements with data providers, increasing their power.
- Limited Alternatives: If few alternative sources exist for critical data, suppliers face less competition and can exert greater influence on pricing and terms.
GB Group's dependence on specialized data and technology suppliers is a key driver of supplier bargaining power. When these suppliers offer unique, proprietary, or hard-to-replicate datasets and technologies, their leverage increases significantly.
The market for identity verification data, for example, saw consolidation in 2024, with a few dominant players commanding higher prices. Similarly, the scarcity of AI and machine learning talent in 2024 drove up labor costs for companies like GB Group, as the average salary for data scientists in the UK saw a notable increase.
GB Group mitigates this by diversifying data sources and investing in internal analytics capabilities, aiming to reduce reliance on any single supplier and lessen their bargaining power.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on GB Group | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Providers (Identity, Location) | Data uniqueness, proprietary nature, market concentration | Higher costs, potential service limitations | Market consolidation for specialized identity data |
| Technology/Software Providers | Differentiated/patented technology, switching costs | Increased operational costs, slower adaptation | High demand for specialized AI/ML talent |
| Cloud Infrastructure Providers | Market dominance, switching costs, service differentiation | Potential for less favorable pricing, integration lock-in | Top 3 providers held ~65% global market share (early 2024) |
| Government/Official Data Sources | Exclusive control of data, regulatory compliance demands | Increased operational costs, limited data acquisition scope | Growing emphasis on data privacy regulations |
What is included in the product
This analysis of GB Group's competitive landscape reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of industry pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
GB Group's large enterprise clients, particularly in sectors like financial services and government, possess considerable bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes. These clients often negotiate for tailored solutions and aggressive pricing, impacting GB Group's margins.
For instance, in 2024, major financial institutions, a key market for GB Group, continued to consolidate their vendor relationships, seeking economies of scale and demanding more favorable contract terms. This trend amplifies the leverage these large entities hold.
While switching costs can be a deterrent, the potential for significant cost savings or superior functionality from alternative providers means these large enterprises can still exert considerable influence over GB Group's service offerings and pricing structures.
Industry consolidation among GB Group's customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. As fewer, larger entities emerge, their collective purchasing volume grants them leverage to demand lower prices or more favorable contract terms. For instance, if a major sector GB Group serves, like retail, sees significant mergers in 2024, the resulting larger chains could negotiate harder, potentially squeezing GB Group's margins.
Switching costs for customers are a key factor in the bargaining power of buyers. For GB Group, implementing identity verification and fraud prevention solutions can be complex, involving integration and data migration. However, if these processes become simpler, customers gain more leverage.
While high switching costs can limit customer power, the trend towards standardized APIs and modular solutions is making it easier for businesses to change providers. This potential reduction in switching costs could increase customer bargaining power in the future, impacting GB Group's pricing and service agreements.
Price Sensitivity and Budget Constraints
Customers, particularly in crowded markets, often watch their spending closely and have strict budgets. This can drive tough negotiations and a lean towards cheaper options. For GB Group, clearly showing the return on investment and the unique value they offer is key to softening this customer influence.
For instance, in the software sector, a significant portion of IT budgets is allocated to essential services, leaving less room for premium solutions unless a compelling business case is made. In 2024, many businesses are scrutinizing operational expenditures, making price a paramount factor in purchasing decisions.
- Price Sensitivity: Many customers prioritize cost savings, especially when alternative solutions are readily available.
- Budget Constraints: Limited budgets force customers to seek the most cost-effective options, impacting vendor choice.
- ROI Demonstration: GB Group must clearly articulate the financial benefits and return on investment to justify its pricing.
- Value Proposition: Highlighting unique features and benefits that address specific customer needs is crucial to counter price-based decision-making.
Customer Knowledge and Solution Alternatives
Customers are increasingly informed about identity verification and fraud prevention technologies. This heightened awareness extends to understanding a wider array of alternative solutions, from building capabilities internally to engaging with competing vendors.
The growing availability of these alternatives significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For GB Group, this means a constant need to innovate and clearly distinguish its product and service portfolio to maintain a competitive edge.
In 2024, the identity verification market saw significant investment, with companies like Onfido raising substantial funding, indicating a competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount. This trend directly impacts GB Group's ability to negotiate terms and pricing.
- Customer Awareness: Buyers are more educated on the nuances of identity verification and fraud prevention.
- Alternative Solutions: The market offers more options, including in-house development and numerous competing vendors.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Greater knowledge and more alternatives empower customers in negotiations.
- GB Group's Imperative: Continuous innovation and clear differentiation are crucial for GB Group to retain and attract clients.
GB Group's customers, particularly large enterprise clients, wield significant bargaining power. This is driven by their substantial purchasing volumes, increasing price sensitivity, and a growing awareness of alternative solutions. These factors compel GB Group to focus on demonstrating clear ROI and differentiating its offerings to maintain favorable terms and pricing, especially in a competitive 2024 market.
| Factor | Impact on GB Group | 2024 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Purchasing Volume | High volume clients can negotiate better pricing and tailored solutions. | Major financial institutions seeking vendor consolidation in 2024. |
| Price Sensitivity & Budget Constraints | Customers prioritize cost-effectiveness, pressuring margins. | Businesses scrutinizing operational expenditures in 2024. |
| Availability of Alternatives | More options increase customer leverage and require GB Group to innovate. | Increased investment in identity verification startups in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Lower switching costs empower customers to change providers more easily. | Trend towards standardized APIs simplifying integration. |
Same Document Delivered
GB Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete GB Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You'll gain instant access to this professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis, empowering your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The identity verification and fraud prevention sector is booming, drawing in everyone from tech titans to nimble startups. This influx of competitors means intense rivalry as companies battle for customers and market dominance. For instance, the global identity verification market is expected to see a substantial increase in checks, growing from 75 billion in 2024 to 86 billion by 2025, highlighting a very active and crowded competitive arena.
The competition in identity verification is fierce because it's so crucial for stopping fraud and meeting legal requirements. Companies in this space know that if their systems fail, their clients can suffer huge financial losses and damage to their reputation, which makes the reliability and effectiveness of these solutions incredibly important.
This intense focus on performance naturally drives up the stakes for everyone involved. The fraud detection and prevention market is a prime example, projected to hit USD 58.69 billion by 2025, highlighting the significant financial rewards and the resulting competitive pressures in this vital industry.
Competitive rivalry in the identity verification sector is intensely fueled by rapid technological innovation, especially in artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advancements are vital for creating more precise identity checks and robust fraud prevention. For example, GB Group, a key player, invests heavily in R&D to enhance its AI capabilities, aiming to offer market-leading accuracy and speed.
Companies must continually differentiate themselves by offering superior performance and user experience. The integration of AI-powered biometrics and sophisticated liveness detection is becoming a standard expectation, as it's essential for staying ahead of increasingly complex fraud methods, such as the proliferation of deepfakes. This arms race for technological superiority means that companies like GB Group must consistently update their offerings to maintain a competitive edge.
Global and Regional Players
GB Group contends with a dual threat: large global technology firms offering broad solutions and niche regional competitors with localized expertise. This dynamic requires GB Group to maintain a strong international presence while remaining agile enough to cater to specific regional needs and regulatory environments.
The competitive intensity is amplified by the presence of established global players who leverage economies of scale and extensive R&D budgets. For instance, in the identity verification space, companies like Experian and TransUnion, with significant global footprints, present a formidable competitive force.
- Global Giants: Large, diversified technology companies often have substantial resources for innovation and market expansion, posing a broad competitive threat.
- Regional Specialists: Smaller, focused companies can excel in specific geographic markets by offering highly tailored solutions and leveraging deep local knowledge.
- Market Saturation: In certain segments, the market is becoming increasingly saturated, leading to price pressures and a greater need for differentiation.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid evolution in areas like AI and machine learning means competitors constantly introduce new capabilities, demanding continuous investment in R&D from GB Group.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Partnerships
The competitive landscape for GB Group is significantly influenced by mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships. Companies are actively consolidating their market positions, broadening their service portfolios, and acquiring new technologies or customer bases through these activities. This trend is evident as businesses aim to enhance their competitive edge and adapt to evolving market demands.
For instance, in 2024, LexisNexis Risk Solutions completed its acquisition of IDVerse, a move designed to bolster its risk and fraud solutions. This acquisition exemplifies the ongoing consolidation and strategic maneuvering within the industry, as major players seek to integrate complementary capabilities and expand their market reach.
These strategic combinations can lead to:
- Increased Market Concentration: Fewer, larger players can dominate specific segments.
- Enhanced Service Offerings: Acquired companies often bring specialized technologies or customer access.
- Synergistic Efficiencies: Mergers can lead to cost savings and operational improvements.
- Heightened Barriers to Entry: Larger, integrated entities can make it harder for new competitors to emerge.
Competitive rivalry within the identity verification sector is exceptionally high, driven by a crowded market and the critical nature of fraud prevention. Companies like GB Group face pressure from both global tech giants and specialized regional players, necessitating continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain market share.
The battle for customers is fierce, with performance and reliability being paramount due to the significant financial and reputational risks associated with identity fraud. This intense competition is further fueled by ongoing consolidation, as seen in 2024 with acquisitions like LexisNexis Risk Solutions' purchase of IDVerse, aimed at strengthening capabilities and expanding market reach.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on GB Group |
| Global Giants (e.g., Experian, TransUnion) | Extensive resources, broad solutions, economies of scale | Significant competitive pressure, requires strong global presence and R&D investment |
| Regional Specialists | Localized expertise, tailored solutions | Requires agility and ability to adapt to specific regional needs and regulations |
| Emerging Tech Firms | Rapid innovation (AI, biometrics), focus on niche solutions | Drives need for continuous technological advancement and differentiation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Manual identity verification, while less efficient and scalable, can still act as a substitute, particularly for smaller businesses or low-risk situations. For instance, some local businesses might still rely on physical ID checks for certain transactions. However, the increasing prevalence of digital transactions and advanced fraud techniques makes these manual methods increasingly impractical and expensive for most businesses operating in GB Group's core markets.
Large enterprises with substantial IT budgets and technical expertise are increasingly developing proprietary identity verification and fraud prevention solutions. This trend represents a significant threat of substitutes for specialized providers, as these internal systems can offer tailored functionality and potentially lower long-term operational costs. For instance, major financial institutions or tech giants might invest millions in custom-built platforms, bypassing the need for third-party vendors.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and decentralized identity (DID) solutions present a potential substitute threat to traditional identity verification methods. These systems, still in their early stages, emphasize user control and privacy, offering an alternative to centralized identity management. For instance, the global decentralized identity market was valued at approximately USD 135.5 million in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a shift in how identity can be managed and verified.
Enhanced Traditional Security Measures
Organizations might lean on robust traditional security measures, like multi-factor authentication (MFA) or advanced encryption, as their main fraud prevention strategies. This can lessen the perceived need for more comprehensive identity verification solutions.
However, these enhanced traditional measures often act as complements to, rather than direct substitutes for, the actual process of verifying an individual's identity. For instance, while MFA verifies access, it doesn't inherently confirm the user's identity in the same way a dedicated verification service does.
- MFA Adoption: In 2024, a significant majority of organizations, estimated to be over 90%, have implemented some form of MFA, reflecting its widespread adoption as a baseline security practice.
- Encryption Standards: Advanced encryption, such as AES-256, is a standard for protecting data in transit and at rest, bolstering overall security but not replacing identity proofing.
- Complementary Nature: These security layers are most effective when integrated with identity verification, creating a defense-in-depth strategy rather than relying on a single point of security.
Less Sophisticated, Cheaper Solutions
For businesses operating with tighter financial constraints or facing less rigorous compliance mandates, simpler, more affordable identity verification or fraud detection tools can emerge as viable substitutes. These alternatives, while potentially lacking the advanced capabilities and comprehensive feature sets found in GB Group's solutions, might still meet the fundamental requirements of certain market segments.
For instance, some smaller e-commerce platforms or businesses in nascent markets might opt for basic data validation checks or manual review processes instead of investing in sophisticated, automated systems. This is particularly relevant in sectors where the risk of sophisticated fraud is perceived as lower or where the cost of compliance is a primary barrier to entry.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cheaper solutions appeal to businesses with limited capital, allowing them to address basic verification needs without significant upfront investment.
- Simplicity of Use: Less sophisticated tools often require less technical expertise to implement and manage, making them accessible to a broader range of businesses.
- Regulatory Nuance: In industries with less stringent regulatory oversight, the need for advanced, multi-layered verification may be diminished, opening the door for simpler alternatives.
- Market Accessibility: The availability of these less complex solutions can lower the barrier to entry for new businesses, allowing them to operate with more basic identity and fraud management protocols.
The threat of substitutes for GB Group's services comes from various sources, including less sophisticated manual processes, in-house developed solutions by large enterprises, and emerging technologies like blockchain. While these alternatives may not offer the same depth of functionality or security, they can be attractive due to cost or specific use cases. For example, simpler data validation checks can serve as a substitute for businesses with lower risk profiles or tighter budgets.
The market for identity verification is dynamic, with evolving threats and solutions. For instance, while advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are crucial security layers, they often complement rather than directly substitute core identity verification processes. In 2024, over 90% of organizations utilize MFA, highlighting its widespread adoption as a foundational security measure.
| Substitute Type | Description | Key Considerations | Market Trend Example (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Verification | Physical ID checks, basic data validation | Less efficient, scalable, and secure for complex fraud | Still used by some small businesses, but declining |
| In-house Solutions | Proprietary platforms developed by large enterprises | Tailored functionality, potential long-term cost savings | Major financial institutions invest millions in custom platforms |
| Emerging Technologies | Blockchain, Decentralized Identity (DID) | User control, privacy focus, early stage | Global DID market valued ~USD 135.5 million in 2023 |
| Enhanced Traditional Security | MFA, Advanced Encryption | Complementary, not direct substitutes for identity proofing | >90% of organizations use MFA in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The identity data intelligence market presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to exceptionally high capital investment requirements. Companies looking to compete with established players like GB Group need significant funds for advanced technology development, securing comprehensive data sources, and building robust IT infrastructure. For instance, the global data analytics market was projected to reach $332.9 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of investment needed to even participate in this sector.
The financial services sector, where GB Group operates, is a prime example of high regulatory barriers. Strict Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and data privacy regulations like GDPR are not just guidelines but operational necessities. For instance, in 2023, fines for AML non-compliance alone reached billions globally, underscoring the cost of missteps.
New companies entering this space must invest heavily in legal and compliance infrastructure. Navigating the patchwork of international regulations, which can differ significantly even between neighboring countries, demands specialized expertise that established players have already developed. This complexity acts as a significant deterrent, making it difficult and expensive for potential new entrants to establish a foothold and operate legally.
The threat of new entrants into the identity verification and fraud prevention market, particularly for companies like GB Group, is significantly shaped by the need for advanced technological expertise, especially in AI and machine learning. Developing cutting-edge solutions to combat sophisticated fraud, such as deepfakes, requires substantial investment in specialized talent and the creation of proprietary algorithms. For instance, the global fraud detection and prevention market was valued at approximately $36.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $120.7 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth and the potential for new players to emerge if they can master these complex technologies.
Brand Reputation and Trust
In the identity verification and fraud prevention space, a company's brand reputation and the trust it has cultivated are incredibly powerful deterrents to new entrants. Established firms like GB Group have spent years building this credibility, which is crucial when dealing with large enterprise clients, particularly in highly regulated sectors such as financial services and government.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in convincing these demanding clients to switch from trusted, proven providers. This is especially true when the stakes involve sensitive data and compliance requirements. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions continue to prioritize robust security and reliability, often favoring vendors with a long track record of successful implementations and minimal breaches.
- Reputation as a Barrier: GB Group's established brand name and history of dependable service make it challenging for new companies to gain market traction.
- Client Trust in Sensitive Sectors: Enterprises in finance and government demand high levels of trust, which new entrants struggle to demonstrate quickly.
- Risk Aversion: Large organizations are often risk-averse, preferring to stick with known entities that have a proven ability to prevent fraud and verify identities effectively.
Network Effects and Customer Lock-in
Existing providers within the software and IT services sector, like GB Group, often leverage powerful network effects. This means the more users and data a platform accumulates, the more valuable it becomes for everyone involved. For instance, in identity verification, a larger database of verified identities enhances accuracy and efficiency for all users, making it harder for a new player to compete on data quality from day one.
Furthermore, significant customer lock-in presents a substantial barrier to entry. Once businesses integrate GB Group's solutions into their core operations, such as customer onboarding or data management, the costs and complexities associated with switching to a new provider can be prohibitive. These switching costs can include data migration, retraining staff, and reconfiguring existing systems, effectively deterring potential new entrants from challenging established market positions.
- Network Effects: GB Group's platforms gain value as more users and data are added, improving accuracy and utility.
- Customer Lock-in: High switching costs due to integration with existing business systems deter customers from moving to new providers.
- Data Value: The increasing volume and quality of data held by established players create a competitive advantage that new entrants struggle to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants for GB Group is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements for technology and data acquisition. High regulatory hurdles, particularly in financial services, demand extensive investment in compliance and legal expertise. Furthermore, established brand reputation and customer trust, especially with large enterprises, create a formidable barrier that newcomers find difficult to overcome quickly.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for advanced technology and data sources. | Deters new players lacking significant funding. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict KYC, AML, and data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR). | Increases operational costs and complexity for new entrants. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Years of building credibility with enterprise clients. | Makes it hard for new companies to win over risk-averse customers. |
| Technological Expertise | Need for advanced AI/ML skills to combat sophisticated fraud. | Requires substantial investment in specialized talent and R&D. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data, including financial statements, industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and Forrester, and publicly available company filings. This ensures a robust understanding of competitive intensity, supplier and buyer leverage, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
