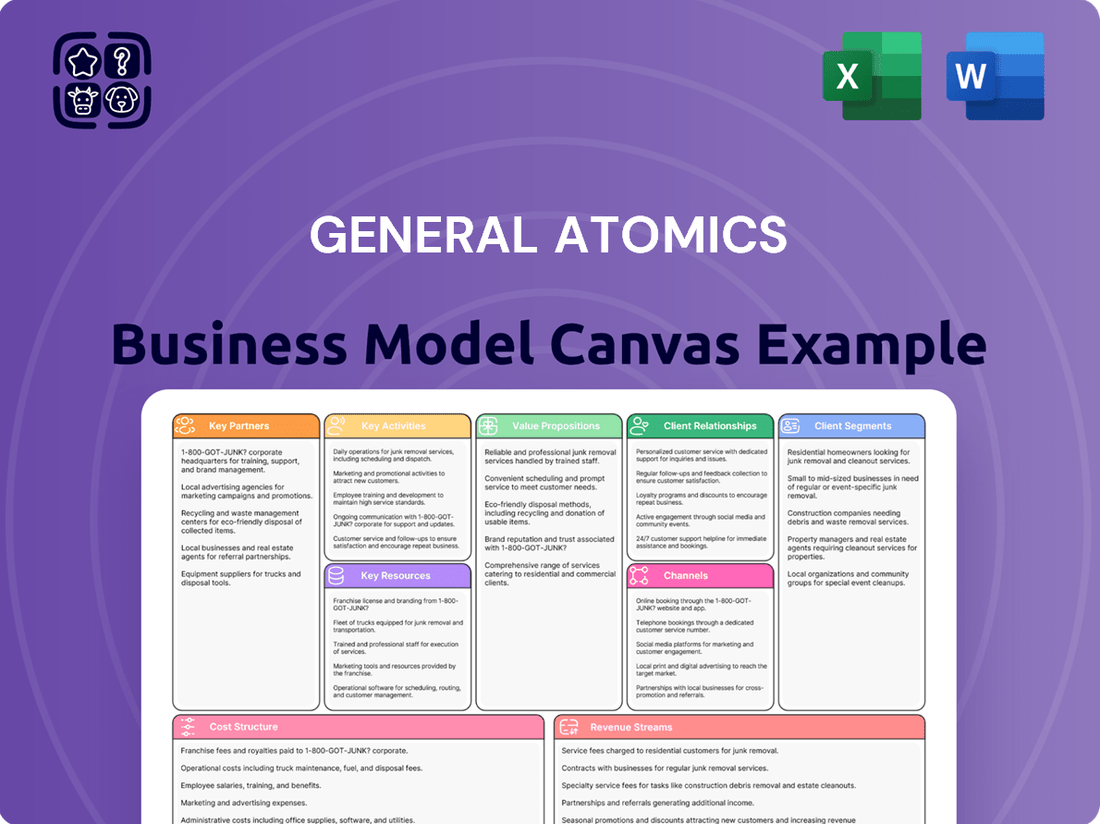
General Atomics Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
General Atomics Bundle
Unlock the strategic blueprint behind General Atomics's success with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. This detailed analysis reveals how they innovate and deliver advanced technological solutions, from key partners to revenue streams. It's an essential tool for anyone looking to understand their competitive edge.
Dive deeper into General Atomics’s real-world strategy with the complete Business Model Canvas. From value propositions to cost structure, this downloadable file offers a clear, professionally written snapshot of what makes this company thrive—and where its opportunities lie.
Partnerships
General Atomics’ key government agency partnerships are foundational, especially with the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and the Department of Energy (DoE). These collaborations are vital for the company’s revenue streams, as evidenced by the significant defense spending. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, the DoD alone awarded billions in contracts for advanced systems, many of which General Atomics is a prime contractor for, underscoring the critical nature of these relationships for R&D funding and market access.
General Atomics actively collaborates with leading academic and research institutions, such as the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). These partnerships are crucial for advancing research in fields like controlled nuclear fusion, a key area for GA's energy division. For instance, GA’s involvement with the DIII-D National Fusion Facility, a DOE national user facility operated by GA, directly benefits from and contributes to university research programs.
General Atomics relies on a robust network of technology suppliers and component manufacturers for everything from advanced sensor systems to specialized materials for its energy projects. These partnerships are crucial for maintaining the high standards of quality and innovation required in their diverse product lines. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to secure contracts with leading aerospace component providers, ensuring access to cutting-edge avionics and structural materials for their unmanned aerial systems.
The company's strategic sourcing ensures the reliable availability of critical inputs, which is vital for complex projects like the development of fusion energy technologies. By collaborating with manufacturers specializing in high-tolerance machining and advanced metallurgy, General Atomics can meet the stringent specifications needed for these groundbreaking endeavors. This focus on supply chain resilience was evident in 2024 as they navigated global supply chain challenges, prioritizing suppliers with proven track records of dependability.
International Defense Organizations and Allied Nations
General Atomics actively cultivates strategic alliances with international defense organizations and allied nations to broaden its market presence beyond the United States. These partnerships are crucial for the export, collaborative development, and ongoing support of its advanced military platforms, especially its unmanned aerial systems (UAS).
These collaborations often encompass intricate technology transfer agreements, joint operational training initiatives, and the establishment of localized support infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, General Atomics continued to engage with numerous NATO members and other key allies, facilitating the integration of its Predator and Reaper series UAS into their respective defense architectures. This global outreach is vital for fostering interoperability and advancing shared security objectives, as evidenced by the increasing number of nations adopting these capabilities for surveillance and strike missions.
- International Sales Growth: General Atomics' UAS have seen significant adoption by allied nations, contributing to substantial international revenue streams. For example, by mid-2024, sales to several European and Asian allies for advanced ISR and strike capabilities were on track to exceed previous years' figures.
- Co-development Projects: Collaborative development programs with select allied nations are underway to tailor UAS capabilities to specific operational requirements, enhancing platform versatility and market appeal.
- Technology Transfer & Training: Agreements facilitate the transfer of critical technologies and provide comprehensive training packages, ensuring effective operation and maintenance of General Atomics systems by partner forces.
- Global Interoperability: These partnerships are instrumental in achieving seamless interoperability between allied forces, a key objective for multinational operations and collective defense strategies, particularly in evolving geopolitical landscapes.
Joint Venture and Strategic Alliance Partners
General Atomics frequently forms joint ventures and strategic alliances to tackle large defense projects and enter new geographical or technological markets. These collaborations are crucial for pooling resources and sharing the substantial financial risks involved in complex, multi-billion dollar defense contracts. For instance, in 2024, the company was part of consortia bidding on major aerial drone programs, where sharing development costs and leveraging specialized expertise from partners was essential for competitive positioning.
These alliances allow General Atomics to leverage complementary capabilities, which is vital when developing highly integrated systems that require expertise across various domains. By partnering with other defense contractors or advanced technology firms, they can offer more comprehensive solutions to government clients. This approach not only enhances their bid competitiveness but also accelerates the development and deployment timelines for cutting-edge defense technologies.
The strategic advantage of these partnerships lies in their ability to reduce the individual investment burden for each participating company. This is particularly important in the defense sector, where research and development costs can be astronomical. For example, in 2023, General Atomics entered into a strategic alliance with a European aerospace firm to co-develop next-generation surveillance aircraft, significantly lowering the upfront capital expenditure for both entities.
- Resource Pooling: General Atomics leverages partners’ financial, technological, and human resources for large-scale defense projects.
- Risk Sharing: Joint ventures distribute the financial and operational risks associated with complex program bids and new market entries.
- Capability Enhancement: Partnerships allow access to specialized expertise and technologies that complement General Atomics’ core competencies.
- Market Access: Alliances facilitate entry into new international markets or segments by combining local knowledge and established networks.
General Atomics' key partnerships are vital for its success, particularly with U.S. government agencies like the Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Energy (DoE), which are major revenue sources. These collaborations are crucial for research and development funding, as seen in the billions in DoD contracts awarded in fiscal year 2023. The company also partners with leading universities for advancements in areas like fusion energy, benefiting from and contributing to university research programs.
Furthermore, General Atomics relies on a strong network of technology suppliers and manufacturers to maintain product quality, securing contracts with aerospace component providers in 2024 for advanced materials. Strategic sourcing ensures reliable access to critical inputs for complex projects, with a focus on supply chain resilience evident in 2024. The company also forms joint ventures and alliances to share the significant financial risks of large defense contracts, as demonstrated by consortia bids on major aerial drone programs in 2024.
| Partnership Type | Key Collaborators | Strategic Importance | 2023-2024 Impact |
| Government Agencies | U.S. DoD, U.S. DoE | Revenue, R&D Funding, Market Access | Billions in DoD contracts (FY23); DOE fusion research support |
| Academic & Research | MIT, UCSD, DIII-D National Fusion Facility | Innovation, Advanced Research (Fusion) | Direct contribution to fusion science advancement |
| Technology Suppliers | Aerospace Component Providers | Quality, Innovation, Supply Chain Resilience | Secured contracts for advanced avionics and materials (2024) |
| Joint Ventures/Alliances | Defense Contractors, Aerospace Firms | Risk Sharing, Resource Pooling, Market Entry | Consortia bids on drone programs (2024); Co-development of surveillance aircraft (2023) |
| International Allies | NATO Members, Asian Allies | Global Market Presence, Co-development, Interoperability | Increased UAS adoption by allies (mid-2024); Technology transfer agreements |
What is included in the product
A comprehensive overview of General Atomics' business model, detailing its customer segments (defense, energy, research), value propositions (advanced technology, reliable solutions), and key partnerships.
This model showcases General Atomics' operational strengths in R&D and manufacturing, highlighting revenue streams from government contracts and product sales, all within the 9 classic Business Model Canvas blocks.
The General Atomics Business Model Canvas offers a structured approach to efficiently map and analyze complex defense and energy solutions, streamlining strategic planning and decision-making.
Activities
General Atomics' core strength lies in its relentless pursuit of research and development, driving innovation across critical sectors like advanced unmanned aerial systems, nuclear fusion, and electromagnetic launch technology. This dedication to scientific advancement and technological breakthroughs is central to their business model, enabling them to develop pioneering solutions for complex defense and energy needs.
The company consistently invests heavily in R&D, a crucial factor in maintaining its leadership position and delivering cutting-edge capabilities. For instance, their work on the MQ-9 Reaper drone, a product of sustained R&D, has significantly impacted modern warfare. While specific R&D spending figures for 2024 are not publicly detailed, General Atomics’ historical commitment suggests substantial allocations to fuel these advanced technological endeavors.
System integration and engineering are paramount for General Atomics, focusing on merging diverse technological components into sophisticated, functional systems like their advanced unmanned aerial vehicles and energy solutions. This involves intricate engineering to guarantee reliability and meet demanding performance benchmarks.
The company's expertise lies in its ability to synthesize various technologies, creating complete, operational platforms. For instance, the development of the MQ-9 Reaper drone showcases this, integrating advanced sensor suites, communication systems, and propulsion into a single, effective platform.
In 2024, General Atomics continued to invest heavily in R&D for these integrated systems, with a significant portion of its budget allocated to engineering and integration efforts, underscoring the critical nature of this activity to its product development and market competitiveness.
General Atomics engages in the specialized manufacturing and production of its cutting-edge systems. This often necessitates precision engineering, the use of advanced materials, and operating within highly controlled environments to ensure the highest quality.
Key products include sophisticated unmanned aircraft systems, critical components for fusion energy research reactors, and advanced electromagnetic railgun systems. These complex manufacturing endeavors are central to their operations.
The company's production processes are meticulously designed to adhere to the stringent quality and safety standards demanded by both the defense and energy sectors. For instance, in 2024, their commitment to advanced manufacturing was evident in the continued development and production of their Predator and Reaper series of UAVs, which are vital assets for global defense forces.
Testing, Certification, and Validation
General Atomics places immense importance on rigorous testing, certification, and validation for its advanced products, especially given their deployment in high-stakes defense and energy sectors. This ensures every system adheres to stringent operational requirements, safety protocols, and regulatory mandates.
Activities like extensive flight testing for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) or performance validation for advanced nuclear reactor components are crucial. These demonstrate the inherent reliability and build essential customer trust and acceptance.
- Defense Systems: Successful flight tests of the MQ-9 Reaper drone in 2023, demonstrating extended loiter times and payload delivery accuracy, underscore GA's commitment to validation.
- Energy Sector: Validation of advanced materials for fusion reactors, like the recent successful testing of novel alloys under extreme conditions, is a testament to their rigorous approach.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all systems meet FAA or NRC standards, for instance, is a non-negotiable aspect of their validation processes, often involving thousands of hours of simulated and real-world testing.
Post-Sales Support and Maintenance
General Atomics prioritizes robust post-sales support and maintenance to ensure the ongoing success of its advanced systems. This commitment fosters enduring customer partnerships and guarantees the operational readiness of critical assets.
Key activities include offering expert technical assistance, ensuring timely availability of spare parts, and providing necessary system upgrades. Furthermore, comprehensive training programs are delivered to operators and maintenance crews, enhancing system longevity and performance.
- Technical Assistance: Providing 24/7 technical support and troubleshooting for complex systems.
- Spare Parts Management: Maintaining an efficient supply chain for critical components to minimize downtime.
- System Upgrades: Offering and implementing upgrades to enhance performance and incorporate new technologies.
- Training Services: Delivering specialized training for customer personnel on operation and maintenance procedures.
General Atomics' key activities revolve around pioneering research and development, intricate system integration and engineering, specialized manufacturing, rigorous testing and validation, and comprehensive post-sales support. These pillars collectively enable the company to deliver advanced solutions in defense and energy sectors, maintaining its competitive edge through continuous innovation and unwavering commitment to quality and performance.
What You See Is What You Get
Business Model Canvas
The General Atomics Business Model Canvas you are previewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This is not a sample or a mockup, but a direct representation of the comprehensive analysis that will be yours. You'll gain full access to this professionally structured and detailed canvas, ready for immediate use.
Resources
General Atomics' intellectual property, encompassing patents and proprietary designs for technologies like the Predator drone and advanced nuclear reactors, is a cornerstone of its business model. This extensive IP portfolio, a result of substantial R&D investments, shields their innovations and solidifies their market leadership in critical sectors.
The company’s commitment to innovation is reflected in its significant R&D spending, which directly fuels the creation and expansion of this valuable intellectual property. For instance, in 2023, General Atomics reported billions in revenue, a portion of which is continually reinvested into developing next-generation technologies protected by this IP.
General Atomics' core strength lies in its highly specialized engineering and scientific talent. This human capital is the engine behind their innovation in fields like aerospace, nuclear physics, electromagnetics, and advanced software development. Without these experts, the conception, design, and execution of their complex systems would be impossible.
The company's success is directly tied to its ability to attract and retain individuals with deep expertise. For instance, in 2024, the demand for aerospace engineers alone remained exceptionally high, with projections indicating a continued need for skilled professionals in advanced manufacturing and defense technologies.
General Atomics boasts advanced manufacturing and testing facilities, including specialized plants and research labs. These sites are crucial for producing complex defense and energy systems, featuring large assembly lines for drones and dedicated environments for nuclear research. This physical infrastructure underpins their unique production capabilities.
Long-Term Government Contracts and Funding
General Atomics heavily relies on substantial, long-term contracts with U.S. government entities, primarily the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Department of Energy (DoE). These agreements are a cornerstone of their financial stability, providing predictable revenue streams that fuel innovation and production.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, General Atomics Aeronautical Systems secured a significant contract modification valued at $1.7 billion for the Advanced Medium Altitude Reconnaissance System (AMARS) program. This type of sustained government funding is crucial for supporting their extensive research and development efforts and ensuring the continuous production of advanced defense systems.
- Government Contracts: Predictable revenue from long-term agreements with U.S. DoD and DoE.
- R&D Support: Funding for ongoing research and development in defense and energy sectors.
- Production Funding: Secures capital for manufacturing critical defense and energy assets.
- Financial Stability: Government relationships provide a reliable financial foundation and project pipeline.
Strategic Relationships and Industry Reputation
General Atomics' strong industry reputation, built on a legacy of innovation and reliability in defense and energy, is a core intangible asset. This reputation translates into trust with major clients, particularly government agencies. For instance, their long-standing work with the U.S. Department of Defense on advanced drone technology, like the MQ-9 Reaper, underscores this reliability.
These strategic relationships are vital for securing future contracts and driving research and development. General Atomics actively cultivates ties with government stakeholders, industry peers, and academic institutions. This collaborative approach allows them to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
- Innovation and Reliability: Decades of successful project execution in complex sectors.
- Customer Trust: Strong partnerships with government and industry leaders.
- Technological Leadership: A reputation for cutting-edge solutions in defense and energy.
- Future Opportunities: Cultivating relationships for continued growth and development.
General Atomics' key resources include its extensive intellectual property, particularly patents for advanced technologies like the Predator drone and nuclear reactors. This IP portfolio, bolstered by significant R&D investments, protects their innovations and market position.
The company also relies heavily on its highly skilled workforce, comprising specialized engineers and scientists crucial for developing complex aerospace, nuclear, and software systems. Attracting and retaining this talent is paramount for their continued innovation.
Furthermore, General Atomics possesses advanced manufacturing and testing facilities, essential for producing sophisticated defense and energy systems. These specialized sites enable the company to undertake unique production capabilities.
Finally, robust government contracts, primarily with the U.S. Department of Defense and Department of Energy, provide a stable financial foundation and predictable revenue streams. These long-term agreements are critical for funding ongoing R&D and production.
| Key Resource | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Intellectual Property | Patents for drones, nuclear reactors, and other advanced technologies. | Market leadership, competitive advantage, barrier to entry. |
| Human Capital | Specialized engineers and scientists in aerospace, nuclear, and software. | Innovation engine, design and execution of complex systems. |
| Physical Infrastructure | Advanced manufacturing and testing facilities, research labs. | Unique production capabilities, development of cutting-edge systems. |
| Government Contracts | Long-term agreements with DoD and DoE. | Financial stability, predictable revenue, funding for R&D and production. |
Value Propositions
General Atomics delivers exceptional value by pioneering advanced defense and security solutions. Their unmanned aerial systems, like the Predator and Reaper, provide vital intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike capabilities, significantly boosting national security and enabling precise operations with reduced risk to personnel.
These cutting-edge systems are instrumental in modern conflict and surveillance, with General Atomics consistently investing in research and development to maintain their technological edge. For instance, in 2023, the company reported substantial revenue growth, underscoring the market's demand for their sophisticated offerings.
General Atomics drives progress in nuclear energy by leading innovation in both fusion and advanced fission technologies. This commitment provides customers with access to cutting-edge, potentially limitless, and cleaner energy solutions. Their work directly addresses the growing global need for sustainable power.
The company's pioneering efforts in fusion, like the DIII-D National Fusion Facility, contribute to the scientific understanding needed for future commercial fusion power. In fission, their development of advanced reactor designs aims for enhanced safety and efficiency, offering robust energy security. This dual focus positions them as a critical enabler of the future energy landscape.
General Atomics excels in developing advanced electromagnetic systems, such as railguns and aircraft launch and recovery systems for naval applications. These systems are designed to significantly enhance military capabilities.
The value proposition centers on delivering revolutionary improvements in combat effectiveness and energy efficiency for naval forces. For example, electromagnetic aircraft launch systems (EMALS) offer a more efficient and powerful alternative to traditional steam catapults.
These innovations provide a distinct strategic advantage in naval and ground combat scenarios by offering enhanced operational flexibility and power. The U.S. Navy's adoption of EMALS on its Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers underscores the practical application and value of these advanced systems.
Comprehensive Engineering and Integration Expertise
General Atomics' comprehensive engineering and integration expertise offers significant value by enabling the seamless incorporation of intricate systems. This capability allows them to deliver highly customized solutions that precisely match specific operational needs.
Clients benefit from General Atomics' end-to-end proficiency in designing, developing, and integrating a wide array of technologies into unified, high-performing units. This ensures both exceptional performance and unwavering reliability for critical applications.
This holistic approach simplifies the often-complex procurement process for customers, as General Atomics manages the entire lifecycle of system development and integration.
- Deep Engineering Bench: Access to a vast pool of specialized engineering talent across multiple disciplines.
- System Integration Mastery: Proven ability to combine diverse technologies into cohesive, functional systems.
- Tailored Solutions: Development of bespoke solutions addressing unique and demanding client requirements.
- End-to-End Capability: Management of the entire process from initial design to final integration and deployment.
Reliability and Proven Performance in Critical Environments
General Atomics' value proposition centers on unwavering reliability and a history of proven performance, especially critical in demanding military and energy sectors. Their systems are engineered for extreme conditions, ensuring functionality when stakes are highest.
The company's extensive operational track record, built over decades, provides customers with a high degree of confidence in system dependability. This deep well of experience translates into robust, effective solutions that meet stringent operational requirements.
For instance, General Atomics' unmanned aerial systems (UAS), like the Predator and Reaper, have accumulated millions of flight hours in diverse and challenging environments, demonstrating consistent performance. This operational history is a key differentiator, fostering trust and establishing them as a go-to provider for critical applications.
- Proven Reliability: Systems designed and tested for extreme operational conditions.
- Extensive Track Record: Millions of flight hours and decades of successful deployment.
- Customer Trust: Demonstrated effectiveness assures clients of dependable performance in high-stakes scenarios.
General Atomics provides advanced defense and energy solutions, offering unparalleled capabilities in unmanned systems, nuclear energy, and electromagnetic applications. Their expertise ensures enhanced national security, cleaner energy, and superior military performance.
The company’s commitment to innovation is evident in its cutting-edge development of technologies like the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS), which significantly improves naval aviation efficiency and capability. This focus on revolutionary advancements drives their value proposition.
General Atomics' value is amplified by its deep engineering talent and end-to-end system integration capabilities, allowing for the creation of highly customized and reliable solutions. This holistic approach simplifies complex projects for clients.
Their proven track record of reliability, demonstrated through millions of flight hours for their unmanned systems, instills confidence and assures clients of dependable performance in critical applications.
| Value Proposition Area | Key Offering | Benefit to Customer |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Defense Solutions | Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) | Enhanced intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike capabilities, boosting national security and reducing personnel risk. |
| Energy Innovation | Fusion and Advanced Fission Technologies | Access to cutting-edge, cleaner, and potentially limitless energy solutions, addressing global sustainable power needs. |
| Electromagnetic Systems | EMALS, Railguns | Revolutionary improvements in naval combat effectiveness and energy efficiency, offering strategic advantages. |
| Engineering & Integration Expertise | Customized System Development | Seamless incorporation of complex technologies into high-performing, reliable, and tailored solutions. |
| Proven Reliability | Extensive Operational Track Record | High degree of confidence in system dependability due to decades of successful deployment and millions of flight hours. |
Customer Relationships
General Atomics cultivates enduring strategic partnerships with key clients, notably government defense and energy sectors. These collaborations transcend mere sales, encompassing joint innovation, ongoing technical assistance, and aligned long-term objectives, fostering a symbiotic relationship built on reliability and shared vision.
General Atomics places a strong emphasis on dedicated program management and account teams for its major contracts. These specialized teams act as the primary liaison, ensuring seamless communication and proactive problem resolution for clients. This structure is vital given the intricate nature of their defense and energy solutions, fostering trust and efficient project delivery.
General Atomics actively engages in collaborative research and development with its clients, a key aspect of its customer relationships. This involves working hand-in-hand to pinpoint exact requirements and refine product designs. For instance, in developing advanced unmanned aerial systems, GA often partners with defense agencies, incorporating their operational feedback directly into the design cycle, ensuring the final product meets stringent military specifications and evolving battlefield needs.
High-Touch Technical Support and Training
General Atomics understands that their advanced technologies, often used in critical defense and energy applications, require more than just a product sale. They offer robust, high-touch technical support and comprehensive training programs. This ensures clients can effectively operate, maintain, and troubleshoot complex systems, leading to maximum uptime and operational readiness. This dedication fosters strong customer loyalty.
- Specialized Training Programs: General Atomics develops tailored training curricula for its clients, ensuring personnel are proficient in operating and maintaining sophisticated platforms like the MQ-9 Reaper.
- 24/7 Technical Assistance: To address immediate issues, especially for systems deployed in remote or time-sensitive operations, round-the-clock technical support is available.
- Field Service Representatives: For complex deployments and ongoing maintenance, General Atomics dispatches experienced field service representatives to provide on-site expertise and support.
- Performance Metrics: In 2024, General Atomics reported an average system availability rate exceeding 95% for its key defense platforms, directly attributable to its proactive support and maintenance initiatives.
Secure and Confidential Engagement
Given the highly sensitive nature of defense and energy technologies, General Atomics prioritizes secure and confidential customer engagements. This commitment is reinforced through stringent information security measures, including classified communication channels and controlled facility access, ensuring the utmost discretion.
Trust and confidentiality are the cornerstones of General Atomics' customer relationships. The company employs robust protocols to safeguard classified information and strategic plans, reflecting the critical importance of discretion in its operational domain.
- Information Security: Implementation of advanced cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols.
- Classified Communications: Utilization of secure and encrypted channels for all sensitive exchanges.
- Facility Access Control: Strict protocols for physical access to facilities handling classified projects.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements: Comprehensive legal frameworks to ensure confidentiality of proprietary information.
General Atomics fosters deep, long-term relationships through collaborative R&D and dedicated support. This approach ensures their advanced defense and energy solutions meet evolving client needs, as demonstrated by a 2024 system availability rate exceeding 95% for key defense platforms.
Their customer relationship strategy centers on proactive engagement via specialized program management teams and round-the-clock technical assistance. This high-touch model is crucial for the complex systems they deliver, building reliability and trust.
The company prioritizes secure and confidential interactions, implementing stringent information security and classified communication protocols. This commitment to discretion is paramount given the sensitive nature of their work in defense and energy sectors.
| Customer Relationship Aspect | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Collaboration & Co-Development | Joint innovation and R&D with clients. | Incorporating defense agency feedback into MQ-9 Reaper design. |
| Technical Support & Training | High-touch support and comprehensive training. | 24/7 technical assistance and specialized training programs. |
| Program Management | Dedicated teams for liaison and problem resolution. | Specialized account teams for major defense contracts. |
| Confidentiality & Security | Strict protocols for sensitive information. | Advanced cybersecurity measures and classified communication channels. |
| Performance Metric | System availability for defense platforms. | Exceeded 95% average system availability. |
Channels
General Atomics' primary sales channel is direct engagement with government agencies, notably the U.S. Department of Defense and Department of Energy. This involves responding to formal Requests for Proposals (RFPs) and securing long-term procurement agreements.
This direct sales approach allows General Atomics to tailor its advanced technological solutions precisely to government needs. It also facilitates crucial direct feedback, enabling continuous improvement and alignment with evolving defense and energy requirements.
General Atomics heavily relies on established government contracting vehicles, including Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contracts and GSA Schedules. These frameworks are crucial for simplifying and accelerating the acquisition of their advanced defense and energy solutions by government agencies.
These contracting vehicles significantly reduce the administrative burden and time associated with traditional procurement. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, the U.S. government awarded over $700 billion in prime contract obligations, with a substantial portion flowing through IDIQ and GSA Schedule contracts, highlighting their importance in government spending.
By utilizing these pre-negotiated agreements, General Atomics can more efficiently deliver its products and services, such as unmanned aerial systems and advanced energy technologies, to meet critical national security and infrastructure needs.
General Atomics leverages key international defense exhibitions and trade shows as vital channels to connect with global clientele. These events are crucial for demonstrating advanced defense and energy technologies to potential foreign military and government buyers.
Participation in shows like the Paris Air Show or Eurosatory allows General Atomics to directly engage with international partners, fostering relationships and exploring new market opportunities. In 2024, the global defense market is projected to reach over $2.2 trillion, highlighting the significant potential for growth through such international engagements.
Strategic Partnerships and Prime Contractor Relationships
General Atomics frequently operates as a key subcontractor, integrating its advanced technologies into larger defense systems developed by prime contractors. This collaborative approach allows them to participate in significant government initiatives, leveraging their expertise in areas like unmanned aerial systems and advanced electronics. For instance, in 2024, their contributions to major defense platforms underscore the value of these prime contractor relationships in securing substantial program work.
These strategic alliances are crucial for General Atomics, providing access to a broader spectrum of procurement opportunities and enabling them to showcase their specialized capabilities within extensive, multi-faceted projects. By partnering with established prime contractors, they can effectively navigate complex government acquisition processes and expand their market penetration.
- Subcontractor Role: General Atomics leverages its specialized technologies by integrating them into systems managed by prime defense contractors, thereby accessing larger government programs.
- Access to Projects: These partnerships allow General Atomics to participate in projects that might be too extensive or complex to pursue as a sole prime contractor.
- Expanded Reach: Strategic alliances with prime contractors broaden General Atomics' market reach and provide access to a wider array of government procurement opportunities.
- Technology Integration: The company's ability to integrate its advanced technologies, such as those in unmanned systems, makes it a valuable partner for major defense initiatives.
Direct Proposals and Unsolicited Innovation Pitches
General Atomics doesn't just wait for formal requests. They proactively develop and submit unsolicited proposals, showcasing innovative solutions for evolving defense and energy needs. This forward-thinking strategy allows them to anticipate challenges and offer novel approaches.
The company also directly pitches new capabilities and solutions to potential customers, often addressing specific, identified needs. This direct engagement can lead to crucial research grants or pilot programs, validating their technological advancements.
- Proactive Innovation: General Atomics submits unsolicited proposals, demonstrating a commitment to developing solutions for future defense and energy challenges.
- Direct Customer Engagement: The company actively pitches new capabilities and solutions directly to customers, addressing identified needs.
- Securing Early Funding: This approach frequently results in research grants and pilot programs, providing early-stage financial backing and market validation.
- Shaping Future Requirements: By presenting novel solutions, General Atomics influences the development of future customer requirements and technological roadmaps.
General Atomics utilizes its role as a key subcontractor to integrate advanced technologies into larger defense systems. This strategic position allows them to participate in significant government initiatives, leveraging expertise in areas like unmanned aerial systems. In 2024, their contributions to major defense platforms underscore the value of these prime contractor relationships in securing substantial program work.
These alliances are crucial for General Atomics, providing access to broader procurement opportunities and showcasing specialized capabilities within extensive projects. By partnering with established prime contractors, they effectively navigate complex government acquisition processes and expand market penetration.
The company also proactively develops and submits unsolicited proposals, showcasing innovative solutions for evolving defense and energy needs. This forward-thinking strategy allows them to anticipate challenges and offer novel approaches, often leading to crucial research grants or pilot programs to validate their technological advancements.
| Channel | Description | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Government Engagement | Responding to RFPs and securing long-term procurement agreements with agencies like the DoD. | Essential for tailored solutions and direct feedback. |
| Government Contracting Vehicles | Utilizing IDIQ contracts and GSA Schedules for simplified acquisition. | Facilitates efficient delivery of advanced defense and energy solutions. |
| International Exhibitions | Connecting with global clientele at defense trade shows to demonstrate technologies. | The global defense market in 2024 is projected to exceed $2.2 trillion, indicating significant growth potential. |
| Subcontractor Role | Integrating technologies into larger systems developed by prime contractors. | Provides access to major government programs and expands market reach. |
| Unsolicited Proposals & Direct Pitches | Proactively offering innovative solutions and pitching new capabilities to customers. | Secures research grants and pilot programs, validating advancements and shaping future requirements. |
Customer Segments
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) stands as General Atomics' most significant customer, representing a critical pillar of their business. This segment includes all branches of the U.S. military, such as the Air Force, Navy, Army, and Marine Corps, all of whom rely on advanced defense solutions.
General Atomics supplies the DoD with a range of sophisticated technologies, including unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and electromagnetic launch systems, vital for national security and global military operations. In 2023, the DoD's budget for research, development, testing, and evaluation (RDT&E) alone was approximately $143 billion, highlighting the immense scale of potential procurement for companies like General Atomics.
The demands and strategic priorities of the DoD heavily influence General Atomics' research and development initiatives and production schedules. For instance, the ongoing modernization of military platforms and the increasing emphasis on drone technology directly shape the company's innovation pipeline and manufacturing focus.
General Atomics supplies advanced defense solutions, including sophisticated reconnaissance drones and surveillance systems, to allied nations worldwide. These international partners are focused on bolstering their national security, integrating into multinational coalition efforts, and upgrading their military assets with reliable, cutting-edge technology.
Transactions with these military entities frequently occur through government-managed Foreign Military Sales (FMS) programs. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. approved over $80 billion in FMS, highlighting the significant scale of these international defense procurements, with platforms like General Atomics' MQ-9 Reaper being key components in many such agreements.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) is a key customer for General Atomics, particularly for its advanced nuclear technologies like fusion energy research and next-generation fission reactors. In 2024, the DoE continued to invest heavily in clean energy, with a significant portion allocated to nuclear energy innovation, aiming to bolster energy security and achieve ambitious carbon reduction targets.
Commercial energy utilities also represent an important segment, showing growing interest in sustainable and reliable power sources. They are increasingly exploring advanced nuclear solutions to meet rising energy demands while adhering to environmental regulations. General Atomics' innovations in fusion and advanced fission directly address these utility needs for cleaner, more secure energy generation.
Research Institutions and National Laboratories
Academic institutions and national laboratories represent a crucial customer segment for General Atomics, particularly for its advanced research and development services. These entities, often supported by substantial government funding, seek out General Atomics' expertise in areas like nuclear physics and cutting-edge materials science. For instance, in 2023, federal funding for research and development in the United States reached an estimated $160 billion, a significant portion of which flows to institutions engaging in high-impact scientific exploration.
These collaborations are vital for foundational research, allowing universities and labs to tap into General Atomics' specialized equipment and unique scientific knowledge. This symbiotic relationship facilitates advancements in scientific understanding and drives technological breakthroughs. Such partnerships are not merely about current projects; they frequently serve as a pipeline for future product development and innovation for General Atomics.
Key aspects of this customer segment include:
- Collaboration on Foundational Research: Engaging in projects that push the boundaries of scientific knowledge.
- Leveraging Specialized Equipment: Accessing unique facilities and instrumentation not readily available elsewhere.
- Seeking Advanced Expertise: Benefiting from General Atomics' deep knowledge base in specialized scientific fields.
- Driving Future Product Development: Partnerships often lay the groundwork for new technologies and commercial applications.
Aerospace and Defense Prime Contractors
Aerospace and Defense Prime Contractors are a crucial customer segment for General Atomics. These large companies, such as Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman, often integrate General Atomics' specialized subsystems and components into their own complex platforms. For instance, a prime contractor might procure advanced sensor packages or communication modules developed by General Atomics to enhance the capabilities of a fighter jet or a surveillance aircraft.
This business-to-business relationship is fundamental to the defense supply chain, where General Atomics acts as a key supplier of critical technologies. These primes purchase specific, often proprietary, technologies to bolster their competitive edge and fulfill government contracts. In 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense continued to award significant contracts to these prime contractors, many of which would necessitate specialized components from companies like General Atomics.
- Integration of Specialized Technologies: Prime contractors purchase advanced subsystems like sensors, communication systems, and propulsion components.
- B2B Defense Supply Chain: This segment represents a vital business-to-business relationship within the broader defense industry.
- Enhancing Platform Capabilities: General Atomics' offerings help prime contractors improve the performance and features of their larger defense systems.
- Strategic Partnerships and Competition: While sometimes partners, primes also compete, driving demand for differentiated technology from suppliers.
General Atomics serves a diverse set of customers, primarily focusing on government entities and large industrial partners. The U.S. Department of Defense is its largest client, procuring advanced unmanned aerial systems and other defense technologies. Allied nations also represent a significant market through Foreign Military Sales programs.
Beyond defense, the company supplies the U.S. Department of Energy and commercial energy utilities with advanced nuclear technologies, including fusion and fission reactor solutions. Academic institutions and national laboratories are key partners for research and development, leveraging General Atomics' specialized expertise and equipment.
Furthermore, major aerospace and defense prime contractors integrate General Atomics' components and subsystems into their own complex platforms, forming a critical business-to-business relationship within the defense supply chain.
| Customer Segment | Key Offerings | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Department of Defense | Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS), Electromagnetic Launch Systems | DoD RDT&E budget ~ $143 billion (2023) |
| Allied Nations | Reconnaissance Drones, Surveillance Systems | U.S. approved over $80 billion in FMS (2023) |
| U.S. Department of Energy | Fusion Energy Research, Advanced Fission Reactors | Continued heavy investment in clean energy innovation (2024) |
| Commercial Energy Utilities | Sustainable Power Sources, Advanced Nuclear Solutions | Increasing demand for cleaner, secure energy generation |
| Academic Institutions & National Labs | Advanced R&D Services, Scientific Expertise | Federal R&D funding ~ $160 billion (2023) |
| Aerospace & Defense Prime Contractors | Specialized Subsystems (Sensors, Communication Modules) | Significant DoD contracts awarded to primes (2024) |
Cost Structure
General Atomics' cost structure is heavily influenced by significant investments in research and development, particularly in areas like nuclear fusion and advanced unmanned aerial systems. These expenditures cover the substantial salaries of highly skilled scientists and engineers, the acquisition and maintenance of specialized laboratory equipment, and the iterative processes of prototyping and rigorous testing. For instance, the company's commitment to fusion energy research, a field known for its long development cycles and high capital requirements, directly contributes to this cost base, reflecting a strategy focused on long-term technological advancement.
General Atomics faces significant expenses in securing and keeping its highly specialized workforce. This includes top-tier engineers, physicists, and aerospace specialists, whose niche skills command competitive compensation packages. For instance, in 2024, the demand for aerospace engineers remained exceptionally high, with average salaries often exceeding $120,000 annually, a key component of General Atomics' operational costs.
General Atomics invests heavily in state-of-the-art manufacturing and testing infrastructure. This includes specialized machinery and secure testing ranges, crucial for producing complex defense and energy systems.
These capital-intensive facilities require ongoing maintenance and upgrades to remain at the forefront of technology. The company's commitment to innovation means substantial fixed asset investment is a constant.
Compliance, Regulatory, and Security Costs
General Atomics operates in defense and nuclear energy, sectors demanding significant investment in compliance, regulatory adherence, and robust security measures. These costs are fundamental to maintaining operational licenses and eligibility for contracts.
These expenses encompass a broad range, including:
- Adherence to stringent government regulations: This involves navigating complex legal frameworks and reporting requirements specific to defense contracting and nuclear operations.
- Security clearances and cybersecurity: Obtaining and maintaining security clearances for personnel and implementing advanced cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and intellectual property are critical. For instance, the US Department of Defense alone spent over $11.5 billion on cybersecurity in fiscal year 2023.
- Environmental safety protocols: Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and implementing safety protocols, particularly in nuclear operations, represents a substantial ongoing cost.
These ongoing expenditures are not merely operational overhead; they are essential investments that safeguard the company's reputation, ensure contract viability, and protect its technological advancements.
Supply Chain and Material Procurement Costs
General Atomics faces substantial costs in procuring specialized materials, components, and subsystems from a global network. This includes sourcing critical inputs like rare earth elements, advanced composite materials, and high-performance electronics essential for their sophisticated systems. The complexity and global nature of this procurement directly impact the cost of goods sold, making supply chain management a significant expense.
- Global Sourcing: Reliance on international suppliers for specialized materials contributes to procurement costs through logistics, tariffs, and currency fluctuations.
- Advanced Materials: The high cost of advanced composites and rare earth elements, often subject to volatile market prices, represents a major expenditure.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Investments in ensuring a secure and reliable supply chain, including supplier qualification and inventory management, add to overall costs.
General Atomics' cost structure is dominated by high R&D spending, particularly in fusion energy and UAS, alongside significant personnel costs for specialized talent. These are compounded by investments in advanced manufacturing infrastructure and stringent regulatory compliance, including cybersecurity and safety protocols. Procurement of specialized global components also represents a substantial expenditure, impacting overall operational expenses.
| Cost Category | Key Drivers | 2024 Relevance/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Research & Development | Fusion energy, UAS, advanced materials | High demand for specialized R&D personnel, with average salaries for R&D engineers often exceeding $130,000 in 2024. |
| Personnel Costs | Highly skilled scientists, engineers, technicians | Competitive compensation for niche skills; aerospace engineer salaries averaged over $120,000 in 2024. |
| Infrastructure & Facilities | Specialized manufacturing, testing ranges, labs | Ongoing investment in advanced machinery and secure testing sites is crucial for complex systems. |
| Regulatory & Compliance | Defense contracting, nuclear energy, security | Significant costs for security clearances, cybersecurity (US defense cybersecurity spending exceeded $11.5 billion in FY2023), and environmental safety. |
| Procurement | Specialized materials, components, global sourcing | Costs influenced by advanced materials like rare earth elements and supply chain resilience investments. |
Revenue Streams
General Atomics’ primary revenue source stems from extensive, multi-year contracts with the U.S. Department of Defense and other governmental bodies. These agreements cover the development, manufacturing, and upkeep of sophisticated defense technologies, including unmanned aerial vehicles and advanced electromagnetic systems.
These long-term procurements, often spanning several years, coupled with continuous support and maintenance services, ensure a consistent and significant income stream for the company. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, the U.S. Department of Defense allocated substantial funding towards advanced drone programs, a key area for General Atomics.
General Atomics generates substantial revenue from selling its advanced Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS), notably the Predator and Reaper series. This includes the sale of essential components like ground control stations, sophisticated sensor payloads, and secure data link systems. These sales are primarily directed towards military clients, both domestically and internationally, reflecting the growing global demand for advanced aerial surveillance and combat capabilities.
Beyond the hardware, General Atomics also derives significant income from a comprehensive suite of services supporting its UAS platforms. This encompasses crucial pilot training programs, ongoing maintenance and logistics support, and vital system upgrades. These services ensure the continued operational effectiveness and longevity of their drone fleets, creating a recurring revenue stream and fostering long-term customer relationships.
The market for military UAS is experiencing robust growth. For instance, the global military drone market was valued at approximately $12.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach around $21.5 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of about 10.7%. This expansion underscores the significant revenue potential for companies like General Atomics that are at the forefront of this technology.
General Atomics generates substantial revenue from research and development grants and contracts awarded by key government entities. These include significant funding from agencies like the Department of Energy, NASA, and DARPA, supporting their cutting-edge work.
These grants fuel innovation in critical sectors such as nuclear fusion research, the development of advanced materials, and novel energy storage solutions. This R&D investment is crucial for developing technologies that can lead to future, larger-scale production contracts.
Energy Project Development and Engineering Services
General Atomics generates revenue through its extensive involvement in energy project development and engineering services. This includes pioneering work in advanced fission reactor designs and significant contributions to fusion energy research, with an eye toward future commercial applications. The company also offers specialized engineering, consulting, and project management expertise for intricate energy infrastructure projects.
This segment of their business model signifies a strategic diversification into the commercial energy market. For instance, their subsidiary, General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems (GA-EMS), is actively involved in developing advanced nuclear technologies. While specific revenue figures for this segment are not always publicly itemized, the substantial investment and ongoing projects in areas like the Demonstration Power Upgrades for the DIII-D National Fusion Facility highlight the scale of their engagement.
- Advanced Fission Reactor Development: Revenue from designing and potentially licensing next-generation fission reactor concepts.
- Fusion Energy Research & Development: Income from government contracts and partnerships focused on advancing fusion power technology, such as work on tokamaks and other confinement concepts.
- Specialized Engineering & Consulting: Fees for providing expert engineering, design, and project management services for complex energy infrastructure, including nuclear and renewable energy systems.
- Project Management & Turnkey Solutions: Revenue from managing and delivering complete energy project solutions, from initial concept to operational phases.
Intellectual Property Licensing and Technology Transfer
General Atomics monetizes its vast intellectual property by licensing its advanced technologies and specialized components to other organizations, including government agencies and commercial enterprises. This revenue stream is crucial, allowing GA to leverage its significant research and development investments beyond direct product sales, creating value through partnerships and technology transfer agreements.
These agreements enable licensees to utilize or manufacture specific General Atomics innovations under defined terms and conditions. This approach effectively extends the reach and impact of GA's technological advancements across various sectors.
- Intellectual Property Licensing: General Atomics licenses its patents and proprietary technologies, often for specialized applications and components, generating ongoing revenue.
- Technology Transfer: Agreements facilitate the transfer of GA's innovations to partners, allowing them to utilize or produce specific technologies under agreed-upon terms.
- Leveraging R&D: This revenue stream maximizes the return on GA's substantial R&D investments by creating value beyond its core product offerings.
- Market Reach: Licensing expands the application and adoption of GA's technologies across different industries and government programs.
General Atomics also generates revenue from its advanced energy research, particularly in nuclear fusion and fission. This includes government grants and contracts for developing next-generation reactor designs and fusion power technologies. For example, the company's ongoing work on fusion energy research, supported by agencies like the Department of Energy, represents a significant, albeit long-term, revenue driver.
The company's energy segment also includes specialized engineering and consulting services for complex energy infrastructure projects. This diversification into the commercial energy sector, while not always publicly detailed, underscores their strategic aim to leverage technological advancements for broader market applications.
General Atomics' intellectual property licensing and technology transfer agreements provide another revenue stream. By allowing other organizations to utilize its patented innovations, the company capitalizes on its substantial R&D investments, extending the reach of its technologies across various sectors and government programs.
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The General Atomics Business Model Canvas is constructed using a blend of internal operational data, market intelligence reports, and competitive landscape analyses. This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive and accurate representation of the company's strategic framework.
