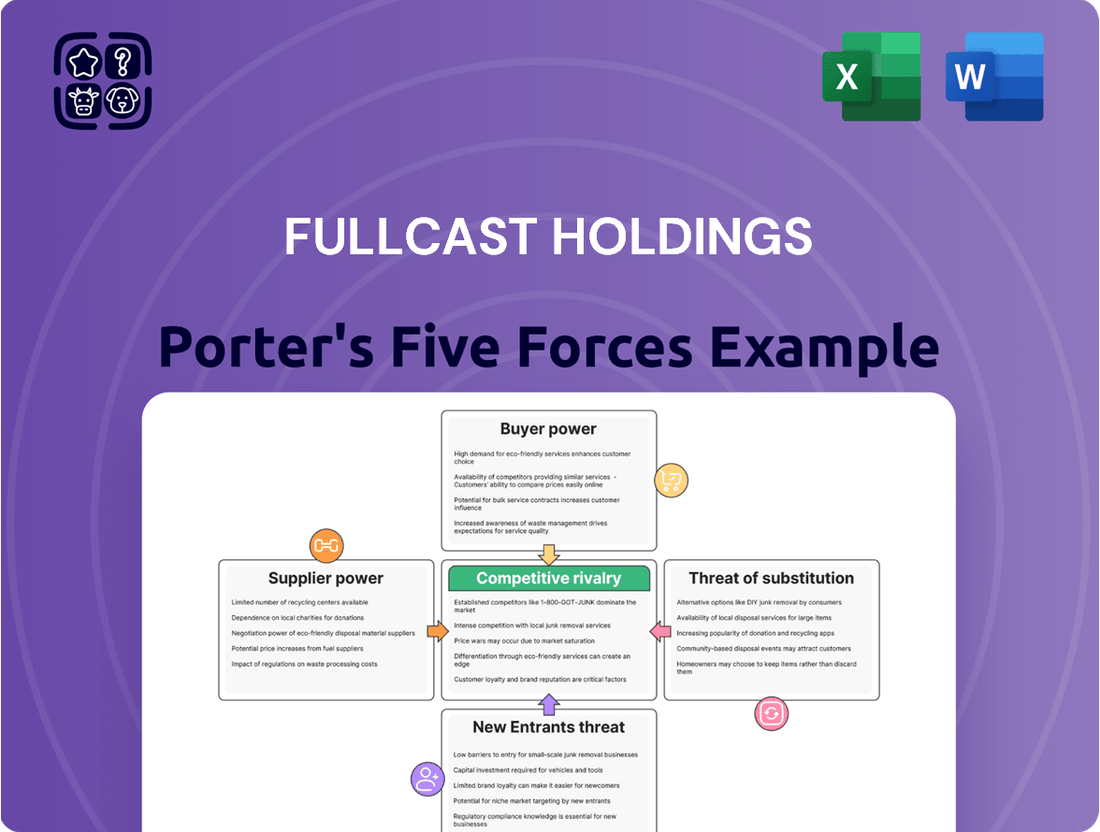
Fullcast Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fullcast Holdings Bundle
Fullcast Holdings operates in an industry shaped by moderate buyer power and the significant threat of substitutes, demanding a nuanced understanding of its competitive landscape. The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors and the bargaining power of suppliers also play crucial roles in defining its market position. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fullcast Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Japan's demographic shifts are dramatically amplifying the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly in the labor market. A persistent and deepening labor shortage, fueled by a shrinking and aging population, means job seekers are in high demand. This scarcity of talent inherently strengthens their negotiating position with companies.
In 2024, Japan's unemployment rate remained remarkably low, hovering around 2.6% for much of the year. This tight labor market forces businesses to compete fiercely for workers, often leading to higher wages and improved benefits to attract and retain talent. The demographic trend, with fewer young people entering the workforce and a growing elderly population, is a long-term structural issue that will continue to empower labor as a key supplier.
Rising wage expectations are significantly impacting the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly human talent, for companies like Fullcast Holdings. In 2024, the persistent tight labor market has fueled demands for higher salaries and improved benefits. For instance, reports indicate that average hourly earnings in the US saw a 4.1% increase year-over-year in early 2024, signaling a clear upward trend in compensation.
This trend is not isolated; recent high-profile wage negotiations across various sectors have resulted in substantial pay hikes, setting new benchmarks for what employees expect. Companies that are slow to adapt and offer competitive compensation packages face the very real risk of losing their most valuable employees to competitors, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of the remaining and incoming workforce.
The increasing demand for flexibility and work-life balance significantly enhances the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly in the staffing industry where Fullcast Holdings operates. Job seekers are actively seeking remote options and better work-life integration, giving them more leverage in a candidate-driven market.
This trend pressures staffing firms to offer more appealing terms to both temporary and permanent placements. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of employees would consider a job change for greater flexibility, a clear signal to companies like Fullcast Holdings to adapt their offerings.
Furthermore, governmental initiatives, such as recent legislation in several regions aimed at supporting flexible working for parents, further solidify this shift. This legislative backing amplifies the bargaining power of employees, compelling staffing agencies to prioritize and offer flexible arrangements to attract and retain talent.
Specialized Skills Scarcity
The demand for specialized skills, particularly in areas like IT, digital transformation, and green-driven occupations, is exceptionally high, and there's a noticeable scarcity of candidates possessing these proficiencies. This imbalance makes individuals with in-demand skills incredibly valuable, significantly boosting their bargaining power over both staffing agencies and direct employers. Fullcast Holdings, like many companies, must therefore engage in fierce competition to secure this critical talent.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected that employment in computer and information technology occupations would grow 15% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations. This rapid growth, coupled with a limited supply of qualified professionals, directly translates to increased supplier power for these skilled individuals.
- High Demand for Niche Expertise: Sectors like AI development, cybersecurity, and cloud computing consistently report talent shortages.
- Wage Inflation for Specialists: Companies are often forced to offer higher salaries and more attractive benefits to attract and retain individuals with these scarce, specialized skill sets.
- Impact on Fullcast Holdings: This scarcity directly influences the cost of labor and the ability to staff critical projects, potentially impacting project timelines and overall operational efficiency.
Increased Mobility of Talent
The increased mobility of talent significantly bolsters the bargaining power of employees, particularly younger generations who actively seek career growth and superior opportunities. This greater fluidity in the job market grants individuals more leverage, reducing their dependence on any single employer or staffing firm.
This trend means workers are better positioned to negotiate terms and compensation, as evidenced by the continued high quit rates seen in many sectors throughout 2024. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that millions of Americans voluntarily left their jobs each month in early 2024, underscoring this willingness to move for better prospects.
- Employee Leverage: Younger workers prioritize skill development and advancement, making them less hesitant to switch jobs.
- Market Fluidity: A dynamic labor market with abundant opportunities strengthens individual negotiation power.
- Reduced Dependency: Workers are less tied to specific companies, increasing their options and bargaining strength.
- 2024 Trends: High quit rates in 2024 reflect a workforce actively pursuing better career paths and compensation.
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly labor, is significantly elevated due to Japan's demographic challenges, leading to a persistent talent shortage. This scarcity empowers job seekers, compelling companies to offer more competitive compensation and benefits to attract and retain staff.
In 2024, Japan's low unemployment rate, around 2.6%, intensified competition for workers, driving up wages and benefits. This structural demographic shift, with fewer young workers and an aging population, will continue to strengthen labor's negotiating position.
The increasing demand for specialized skills, especially in tech and green sectors, further amplifies supplier power. Individuals with in-demand proficiencies are highly valued, leading to wage inflation and increased negotiation leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Suppliers | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics (Japan) | Increased Labor Scarcity | Low unemployment (~2.6%) |
| Wage Expectations | Higher Compensation Demands | US average hourly earnings up 4.1% YoY (early 2024) |
| Flexibility Demand | Employee Leverage | 70%+ employees would change jobs for flexibility (2024 survey) |
| Specialized Skills | Talent Shortages, Wage Inflation | IT occupations projected to grow 15% (2022-2032) |
| Talent Mobility | Increased Worker Leverage | Millions voluntarily quit jobs monthly (early 2024) |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Fullcast Holdings' industry, examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the availability of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Japanese businesses are experiencing significant labor shortages, a trend that intensified in 2024. This scarcity drives a high demand for staffing and outsourcing services, as companies struggle to fill essential roles. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of Japanese SMEs faced difficulties in recruitment, directly increasing their reliance on external staffing providers.
This consistent and growing need for workforce solutions inherently weakens the bargaining power of individual customers. When demand outstrips supply, businesses seeking talent are less able to dictate terms, making them more amenable to the pricing and service structures offered by staffing firms like Fullcast Holdings. The urgency to secure personnel in a competitive market means customers have less leverage to push for lower prices or more favorable contract conditions.
Customers, particularly those in sectors experiencing high demand, are increasingly prioritizing cost optimization and operational efficiency. This trend directly influences their bargaining power by making them more receptive to solutions that promise reduced labor costs and streamlined processes.
The growing interest in business process outsourcing (BPO) and temporary staffing exemplifies this customer behavior. For instance, the global BPO market was valued at approximately $232 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong customer drive towards efficiency and cost reduction.
By leveraging BPO and temporary staffing, clients can effectively manage their workforce, scale operations as needed, and ultimately lower their overall expenditure without sacrificing productivity, thereby enhancing their negotiating position.
The Japanese HR and BPO market is quite crowded, featuring many domestic and international companies offering their services. This abundance of choice means customers can easily shop around, comparing different providers based on their service offerings, cost, and the specific skills they bring to the table. For instance, in 2024, the HR outsourcing market in Japan was estimated to be worth billions of dollars, with numerous vendors vying for market share.
Digital Transformation and In-house Solutions
Larger clients, especially those with substantial IT budgets, are increasingly developing their own digital transformation projects. This can include building proprietary AI-powered recruitment platforms or enhancing existing internal HR systems. For example, in 2024, many enterprise-level companies reported increased investment in in-house technology to streamline their hiring processes, aiming to reduce their dependency on external staffing providers.
This growing capability to create or significantly improve in-house solutions directly translates into greater bargaining power for these customers. They can leverage their internal technological advancements to negotiate more favorable terms with staffing agencies like Fullcast Holdings, potentially seeking lower fees or more customized service packages.
- Customer Investment in In-house Tech: Many large enterprises are allocating significant capital to develop bespoke digital recruitment tools and internal HR management systems.
- Reduced Reliance on External Staffing: The development of these internal capabilities allows clients to manage more of their talent acquisition needs internally.
- Negotiating Leverage: Enhanced in-house solutions empower customers to negotiate from a stronger position with staffing firms, influencing pricing and service agreements.
Industry-Specific Labor Shortages
Industry-specific labor shortages can significantly diminish customer bargaining power, particularly in sectors where Fullcast Holdings operates. In 2024, the U.S. manufacturing sector, for instance, faced persistent labor gaps, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics reporting over 800,000 unfilled manufacturing jobs for much of the year. This scarcity means businesses in these fields, like logistics and services, are often desperate for talent.
When demand for labor outstrips supply, customers become more reliant on staffing providers like Fullcast. Their urgent need to fill critical roles can lead them to accept less favorable terms, such as higher placement fees or less flexible contract conditions, simply to secure the necessary workforce. This dependency reduces their ability to negotiate aggressively.
- Reduced Negotiation Leverage: Businesses facing critical staffing needs in sectors like logistics and manufacturing have less room to push back on pricing or terms from staffing agencies.
- Increased Dependence on Staffing Solutions: Acute labor shortages, as seen in the U.S. manufacturing sector with over 800,000 vacancies in 2024, make companies more reliant on external talent acquisition.
- Acceptance of Less Favorable Terms: The urgency to fill essential roles can lead customers to agree to terms they might otherwise contest, thereby weakening their bargaining position.
- Focus on Talent Acquisition Over Cost: In a tight labor market, the priority shifts from minimizing costs to acquiring talent, giving staffing firms more pricing power.
The bargaining power of customers for Fullcast Holdings is generally moderate to low, primarily due to persistent labor shortages in key markets. When businesses struggle to find qualified personnel, their ability to negotiate favorable terms with staffing agencies diminishes, as the urgency to fill roles takes precedence over cost savings.
For example, in 2024, many Japanese small and medium-sized enterprises reported significant recruitment challenges, with over 60% finding it difficult to hire staff. This situation directly increases their reliance on external staffing solutions, weakening their negotiating position with firms like Fullcast.
While the crowded nature of the HR and BPO market offers some choice, the fundamental imbalance created by labor scarcity limits the extent to which customers can exert significant pressure on pricing or contract terms.
However, larger clients investing heavily in in-house recruitment technology can develop greater bargaining power. These companies, by enhancing their internal capabilities, can reduce their dependency on external providers and negotiate more effectively for customized services or reduced fees.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Shortages | Decreases power | Over 60% of Japanese SMEs faced recruitment difficulties. |
| In-house Tech Investment | Increases power | Enterprise-level companies increased investment in internal HR tech. |
| Market Competition | Slightly increases power | Crowded HR/BPO market with numerous vendors. |
| Customer Focus on Efficiency | Neutral to slightly decreases power | Global BPO market growth indicates drive for cost reduction. |
What You See Is What You Get
Fullcast Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, professionally written Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Fullcast Holdings that you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within its industry. You're looking at the actual document, so you can be confident that the detailed insights into buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry are precisely what you'll get. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll gain instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning and decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese human resources and BPO market is a vibrant and expanding sector, drawing in a multitude of companies. This growth, while promising, results in a highly fragmented competitive landscape where many firms are actively seeking to capture market share. Fullcast Holdings navigates this environment by providing a range of services, including temporary staffing, permanent placement, and business process outsourcing.
Fullcast Holdings operates in a highly competitive environment, facing pressure from both domestic HR firms and significant global competitors. These international players, such as Accenture, IBM, and NTT Data, possess vast resources and offer a broad range of services, often including HR solutions as part of larger business process outsourcing (BPO) packages. This broad reach means Fullcast must constantly adapt.
The presence of these large BPO providers, alongside numerous specialized staffing agencies, intensifies the competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the global HR outsourcing market was projected to reach over $35 billion, indicating a substantial arena where Fullcast must carve out its niche. This intense competition demands continuous innovation and a clear strategy for differentiation to maintain market share and attract clients.
The recruitment industry is seeing a significant surge in AI and machine learning adoption, fundamentally reshaping competitive dynamics. Companies are actively investing in these advanced technologies to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and refine the accuracy of candidate matching, a key differentiator in talent acquisition.
Fullcast Holdings, to remain competitive, must embrace these technological advancements. For instance, in 2024, the global HR tech market was valued at over $35 billion, with AI-driven solutions representing a substantial and rapidly growing segment, underscoring the critical need for adaptation.
Differentiation Through Specialized Services
Competitive rivalry in the staffing and workforce solutions sector, particularly for companies like Fullcast Holdings, is often driven by the ability to offer highly specialized services. This specialization can target specific industries, such as logistics, manufacturing, or various service sectors where Fullcast has a presence, or address unique workforce challenges like skill shortages in niche areas.
Firms actively differentiate themselves by showcasing deep expertise within these chosen niches, emphasizing the quality and suitability of their talent pool, and highlighting the speed and efficiency of their placement processes. Comprehensive outsourcing solutions, which go beyond simple staffing to manage entire workforce functions, also serve as a key differentiator.
- Industry Specialization: Fullcast focuses on industries like manufacturing, logistics, and technology, allowing for tailored talent solutions.
- Talent Quality: Emphasis is placed on vetting and matching candidates with specific industry skill requirements, a key differentiator in a competitive market.
- Service Speed: Rapid fulfillment of staffing needs, especially for critical roles, is a significant competitive advantage.
- Outsourcing Solutions: Offering end-to-end workforce management services provides a deeper value proposition than traditional staffing.
Talent Acquisition and Retention Strategies
Competitive rivalry is fierce in Japan's HR sector, with firms vying not only for business but also for the very talent they place. This intense competition drives companies to offer compelling compensation, flexible work arrangements, and robust career growth paths to secure and keep skilled professionals.
The demand for specialized HR expertise, particularly in areas like digital transformation and compliance, further intensifies this rivalry. Companies are investing heavily in employer branding and creating positive work environments to stand out.
- Talent Scarcity: Japan's demographic shifts and a highly skilled workforce create a challenging environment for talent acquisition.
- Compensation Wars: Leading HR firms are reportedly offering salary increases of 5-10% for in-demand specialists in 2024 to attract top performers.
- Retention Focus: Beyond salary, benefits like remote work options, upskilling programs, and clear promotion tracks are crucial retention tools.
- Innovation in Recruitment: Companies are leveraging AI-powered sourcing and candidate experience platforms to gain a competitive edge in securing talent.
The competitive rivalry within Japan's HR and BPO market is intense, with numerous domestic and global players vying for market share. Fullcast Holdings faces significant pressure from large international BPO providers and specialized staffing agencies, necessitating continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain its position. The market's fragmentation, driven by high demand and a multitude of service providers, amplifies this rivalry.
Companies are differentiating through industry specialization, focusing on sectors like manufacturing and logistics to offer tailored talent solutions. The quality of talent, speed of placement, and the offering of comprehensive outsourcing solutions beyond basic staffing are key competitive advantages in this dynamic environment. For instance, in 2024, the global HR outsourcing market was projected to exceed $35 billion, highlighting the scale of competition.
The adoption of AI and machine learning in recruitment is fundamentally reshaping competitive dynamics, with companies investing heavily in these technologies for efficiency and improved candidate matching. The global HR tech market, valued at over $35 billion in 2024, with AI solutions forming a rapidly growing segment, underscores the critical need for Fullcast to embrace technological advancements to stay competitive.
Talent scarcity in Japan, exacerbated by demographic shifts, intensifies competition, leading to compensation adjustments. In 2024, leading HR firms reportedly offered 5-10% salary increases for in-demand specialists to attract top performers. Beyond compensation, firms are focusing on retention through flexible work, upskilling, and clear career paths, while also leveraging AI for recruitment to gain an edge.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Companies increasingly leverage advanced HR technology and internal expertise to manage recruitment directly, reducing reliance on external staffing firms. In 2024, the global HR tech market was valued at approximately $37.1 billion, indicating a strong trend towards in-house solutions.
The feasibility of direct hiring is further boosted by the availability of sophisticated applicant tracking systems (ATS) and AI-powered recruitment tools, allowing businesses to streamline candidate sourcing and onboarding internally.
This internal capability acts as a significant substitute for external staffing agencies, particularly for filling permanent roles where long-term employee integration and company culture fit are paramount.
The increasing integration of automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence across various industries poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional labor. As clients adopt these technologies, the demand for human workers, particularly for routine and repetitive functions, is likely to decline. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that AI adoption in customer service could reduce the need for human agents by up to 30% in certain sectors.
This shift directly impacts workforce management providers like Fullcast Holdings by potentially reducing the overall volume of temporary or outsourced staff required. While new opportunities may arise for specialized technical roles, the core business model reliant on supplying a broad base of human talent could face pressure. Companies are increasingly looking for efficiency gains, and automation offers a compelling alternative to traditional staffing solutions.
The burgeoning gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for Fullcast Holdings. As more individuals opt for freelance and contract work, companies gain direct access to talent for project-based needs, bypassing traditional staffing agencies. This trend offers businesses greater flexibility and the potential for cost savings, directly challenging the value proposition of Fullcast's services.
By 2024, the freelance workforce in the US alone was estimated to comprise over 60 million individuals, a figure that has steadily climbed. This vast pool of independent talent means companies can source specialized skills on demand, reducing their reliance on intermediaries like Fullcast for temporary or project-specific staffing solutions.
Internal Workforce Restructuring and Upskilling
Companies facing labor shortages might invest in upskilling their current employees instead of hiring external staff. This internal talent development can lessen reliance on outsourcing firms for specific functions, effectively acting as a substitute for external workforce solutions.
For instance, in 2024, many businesses are prioritizing internal training programs to bridge skill gaps. A significant portion of companies reported an increase in their learning and development budgets, aiming to equip their workforce with new capabilities. This strategic shift reduces the perceived need for external staffing agencies or specialized contractors, thereby increasing the threat of substitutes.
- Internal Training Investment: Many organizations are boosting their L&D budgets to reskill existing employees.
- Reduced Outsourcing Dependence: Companies are less likely to outsource roles that can be filled by upskilled internal staff.
- Talent Retention Strategy: Upskilling initiatives can also improve employee retention, further diminishing the need for external hires.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: A more adaptable internal workforce can respond to evolving market demands without external dependencies.
Flexible Work Models and Policy Changes
The increasing adoption of flexible work models, driven by government initiatives and evolving workplace norms, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional staffing solutions. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of the workforce continued to embrace remote or hybrid arrangements, reducing the reliance on external agencies for roles that can be performed from home.
These shifts allow companies to manage fluctuating demands internally through existing staff who may work adjusted hours or take on different responsibilities, thereby mitigating the need for temporary hires. Data from early 2024 indicated that many businesses found success in retaining talent and managing operational needs through these internal flexibilities, effectively substituting the need for external workforce augmentation.
- Government Support for Flexible Work: Policies encouraging teleworking and adjusted hours reduce the demand for external staffing to cover workforce gaps.
- Internal Workforce Optimization: Companies are increasingly able to manage fluctuating workloads by reallocating tasks among their existing flexible workforce.
- Reduced Reliance on Temporary Staff: The ability to retain employees through flexible arrangements directly substitutes the need for temporary or contract workers.
- Evolving Workplace Norms: Societal acceptance and preference for flexible work arrangements make it easier for companies to adapt without external staffing support.
The rise of direct sourcing platforms and advanced HR technology allows companies to bypass traditional staffing agencies. In 2024, the global HR tech market reached approximately $37.1 billion, reflecting a significant shift towards in-house recruitment solutions powered by applicant tracking systems and AI.
The gig economy, with millions of independent contractors available, offers businesses flexible talent acquisition for project-based needs, directly substituting the services of staffing firms. This trend, evidenced by over 60 million US freelancers in 2024, provides cost-effective and agile access to specialized skills.
Furthermore, companies are increasingly investing in internal upskilling and reskilling programs, with many boosting their learning and development budgets in 2024. This focus on internal talent development reduces the need for external hires, acting as a potent substitute for traditional staffing solutions.
Flexible work models, supported by government initiatives and evolving norms, enable companies to manage fluctuating demands internally. By reallocating tasks among existing staff or adjusting hours, businesses can mitigate the need for temporary external hires, a trend observed to be successful in 2024.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Value/Size | Impact on Staffing Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| HR Technology & In-house Recruitment | Global HR Tech Market: ~$37.1 billion | Reduces reliance on external recruiters for permanent roles. |
| Gig Economy/Freelancers | US Freelance Workforce: >60 million | Provides direct access to specialized skills for project-based needs. |
| Internal Upskilling & Reskilling | Increased L&D Budgets (general trend) | Diminishes the need for external talent acquisition for skill gaps. |
| Flexible Work Models | Widespread adoption (general trend) | Enables internal workforce optimization, reducing demand for temporary staff. |
Entrants Threaten
The difficulty in building a comprehensive talent network, encompassing both a wide pool of job seekers and a strong base of employer clients across various industries, presents a substantial hurdle for newcomers. Fullcast Holdings, by virtue of its established presence, leverages existing relationships and a demonstrated history of successfully matching talent with opportunities, creating a significant advantage.
Navigating Japan's intricate regulatory landscape, especially concerning labor laws, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants into the market. Recent adjustments in 2024, for instance, have further refined rules for freelancers and employment conditions, demanding meticulous adherence.
These stringent compliance requirements, encompassing everything from contract stipulations to working hours, translate into substantial upfront costs and extended timelines for new businesses. For example, understanding and implementing the nuances of the recently revised Labor Contract Act can require specialized legal counsel, adding to operational expenses.
The continuous evolution of these laws means ongoing investment in legal and HR expertise is essential, creating a substantial barrier to entry. Failure to comply can result in penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions, making it a critical factor for any potential competitor.
The HR technology landscape demands considerable capital. New entrants must invest heavily in sophisticated digital platforms, advanced AI tools, and robust data analytics to even approach the capabilities of established competitors. For instance, companies developing comprehensive HR management systems often see initial development costs easily exceeding tens of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for smaller players.
Brand Recognition and Trust
In the human resources sector, brand recognition and trust are paramount. Fullcast Holdings, as an established player, has cultivated significant credibility over years of operation. This established reputation makes it difficult for new entrants to quickly win over clients and job seekers who often prioritize reliability and proven track records.
Gaining market acceptance requires substantial investment in marketing and building relationships, hurdles that new companies must overcome. For instance, in 2024, recruitment firms often highlight their long-standing client lists and positive testimonials as key differentiators.
- Established Brand Equity: Fullcast Holdings benefits from years of building trust and a recognizable brand in the HR space.
- Client and Candidate Loyalty: Existing relationships create a barrier, as clients and candidates are often hesitant to switch to unproven entities.
- High Initial Investment: New entrants need significant capital to build comparable brand awareness and trust, a challenge in a competitive market.
Intense Competition for Skilled Talent
New entrants aiming to establish a presence in Japan would immediately contend with established companies for a finite supply of skilled professionals. This competition extends to attracting and retaining not only recruiters and internal staff but also the very job seekers the new entity seeks to engage.
The Japanese labor market, particularly for specialized roles, presents a significant hurdle. For instance, in 2024, Japan's unemployment rate remained low, hovering around 2.6% for much of the year, indicating a tight labor market where skilled talent is at a premium.
- Talent Scarcity: Limited availability of experienced recruiters and specialized personnel in Japan.
- Retention Challenges: Existing firms have established employer brands and compensation packages, making it difficult for new entrants to poach talent.
- Recruitment Costs: Higher marketing and compensation expenses would be necessary to attract qualified candidates in a competitive environment.
- Job Seeker Competition: New entrants must offer compelling value propositions to draw in desirable candidates already engaged with established players.
The threat of new entrants for Fullcast Holdings is moderate. While the HR technology and services sector requires significant capital investment for sophisticated platforms and AI tools, as seen with development costs for comprehensive HR systems often exceeding tens of millions of dollars, established players like Fullcast benefit from strong brand equity and client loyalty. Newcomers face considerable challenges in replicating the trust and credibility built over years, necessitating substantial marketing expenditure to gain market acceptance, a hurdle exemplified by recruitment firms in 2024 highlighting long-standing client lists and testimonials.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Fullcast Holdings Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements (HR Tech) | High (e.g., millions for advanced platforms) | Established infrastructure, lower marginal cost for new services |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Low initially, requires significant investment | High due to years of operation and proven track record |
| Regulatory Compliance (Japan) | Demands meticulous adherence, increasing upfront costs | Existing expertise and established compliance processes |
| Talent Acquisition & Retention | Challenging in a tight market (e.g., Japan's ~2.6% unemployment in 2024) | Strong employer brand and existing talent network |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fullcast Holdings is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their official SEC filings, investor relations materials, and proprietary market research from industry-leading firms. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate assessment of competitive intensity and strategic positioning.
