Fong's Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fong's Bundle
Understanding Fong's competitive landscape is crucial, and a Porter's Five Forces analysis provides the framework. It reveals how industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes all shape Fong's market. This initial look offers a glimpse into these critical forces.
However, this brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fong's competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fong's Industries, a leader in advanced textile machinery, faces significant supplier bargaining power from providers of specialized components. These include precision motors, sophisticated control systems, and novel, sustainable materials crucial for their high-tech equipment. The power of these suppliers is amplified when their offerings are proprietary or when alternative sourcing options are scarce, particularly for advanced sustainable technologies that are in high demand. For instance, a 2024 market report indicated that the global market for advanced textile components, including specialized motors, saw price increases of up to 8% due to supply chain constraints and high demand for innovation. This dependency directly impacts Fong's cost structure, potentially eroding profit margins.
The bargaining power of suppliers for raw materials like metals, plastics, and electronic components significantly impacts machinery manufacturers such as Fong's. The availability of these materials and how much their prices fluctuate, particularly for commodities like steel, directly affects production costs. For instance, global steel prices saw considerable volatility in 2024, with benchmarks like hot-rolled coil experiencing significant swings due to supply chain disruptions and demand shifts.
Furthermore, the concentration of the supply market for critical components can empower suppliers. If only a few companies produce specialized electronic parts or high-grade alloys essential for Fong's machinery, those suppliers gain leverage. This leverage can translate into higher prices or less favorable payment terms, squeezing profit margins for the machinery manufacturer.
The volume of Fong's purchases also plays a role; larger orders might grant them more negotiation power, while smaller, specialized material needs could strengthen supplier positions. For example, in early 2024, the demand for advanced semiconductors used in industrial machinery remained high, giving semiconductor suppliers substantial pricing power.
Suppliers of highly skilled labor, such as specialized engineers for R&D in textile technology or skilled technicians for manufacturing complex machinery, can exert significant bargaining power over Fong's. The scarcity of such talent, particularly in niche areas like sustainable textile processing or advanced automation, can drive up labor costs. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a textile research engineer in advanced economies saw a notable increase due to high demand and limited supply, impacting companies like Fong's that rely on innovation.
Software and Digital Solution Providers
The increasing reliance on specialized software and digital solutions for modern textile machinery, particularly with the integration of IoT, AI, and automation, can significantly bolster the bargaining power of software providers. If these providers offer proprietary platforms essential for smart factory operations or advanced predictive maintenance, Fong's may face limited alternatives, leading to higher costs or unfavorable terms. For instance, the global market for industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions, which underpins many of these digital advancements, was projected to reach over $115 billion in 2024, indicating the significant value and often unique nature of these offerings.
These specialized software providers can exert substantial influence due to the critical nature of their intellectual property and the expertise required to develop and maintain such sophisticated systems. Fong's may find it difficult and costly to switch providers if the software is deeply embedded in its manufacturing processes or if the provider holds patents on key functionalities. The cost of custom software development or adapting generic solutions can be prohibitive, further strengthening the supplier's position.
- Specialized Software Dependency: Fong's reliance on unique software for smart factory integration and predictive maintenance grants providers significant leverage.
- High Switching Costs: The expense and complexity of migrating deeply integrated software systems make it challenging for Fong's to change suppliers.
- Intellectual Property and Expertise: Proprietary algorithms and specialized knowledge held by software providers create a barrier to entry for competitors and enhance their bargaining power.
- Market Value of Digital Solutions: The substantial global market for IIoT and related digital solutions underscores the inherent value and often limited substitutability of these services.
Compliance and Certification Services
Fong's commitment to sustainability means they rely on specialized compliance and certification services, such as those for OEKO-TEX or Global Recycled Standard (GRS). The market for these accreditations is often concentrated, with a limited number of recognized bodies. This scarcity, coupled with the essential nature of these certifications for market access and brand reputation, grants these service providers significant bargaining power.
For instance, the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) has a stringent approval process for its certifying bodies, limiting the available options. Similarly, achieving certifications like Bluesign, which focuses on sustainable textile production, requires engaging with a select group of accredited auditors. The critical role these certifications play in meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly products amplifies the suppliers' leverage.
- Limited Accredited Bodies: The number of organizations qualified to issue key environmental certifications for textiles is often small.
- Criticality of Certifications: Compliance with standards like OEKO-TEX or GRS is vital for Fong's to access certain markets and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Supplier Dependence: Fong's reliance on these specialized services, which are not easily substituted, strengthens the bargaining power of the certification providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key factor for Fong's Industries, influencing their cost structure and profitability. When suppliers offer unique or critical inputs, and alternatives are scarce, their leverage increases significantly.
This is particularly true for specialized components like precision motors and advanced sustainable materials, where proprietary technology or limited production capacity can drive up prices. For example, in 2024, the market for advanced textile components experienced price increases of up to 8% due to supply chain issues and high demand for innovation.
The concentration within the supply market for essential parts, such as specialized electronic components or high-grade alloys, further empowers suppliers. A limited number of manufacturers for these critical inputs can dictate terms, impacting Fong's margins.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also influenced by the volume of purchases; larger orders may give Fong's more negotiation clout, but specialized, lower-volume needs can shift power to the supplier. For instance, the high demand for semiconductors in industrial machinery in early 2024 gave semiconductor suppliers considerable pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on Fong's | 2024 Data/Context |
| Specialized Component Scarcity | Increased costs, reduced margins | Price increases up to 8% for advanced textile components |
| Supply Market Concentration | Higher prices, less favorable terms | Limited number of suppliers for critical alloys and electronics |
| Proprietary Technology | Dependency, limited alternatives | High demand for unique sustainable materials |
| Skilled Labor Demand | Increased labor costs | Notable salary increases for textile research engineers |
What is included in the product
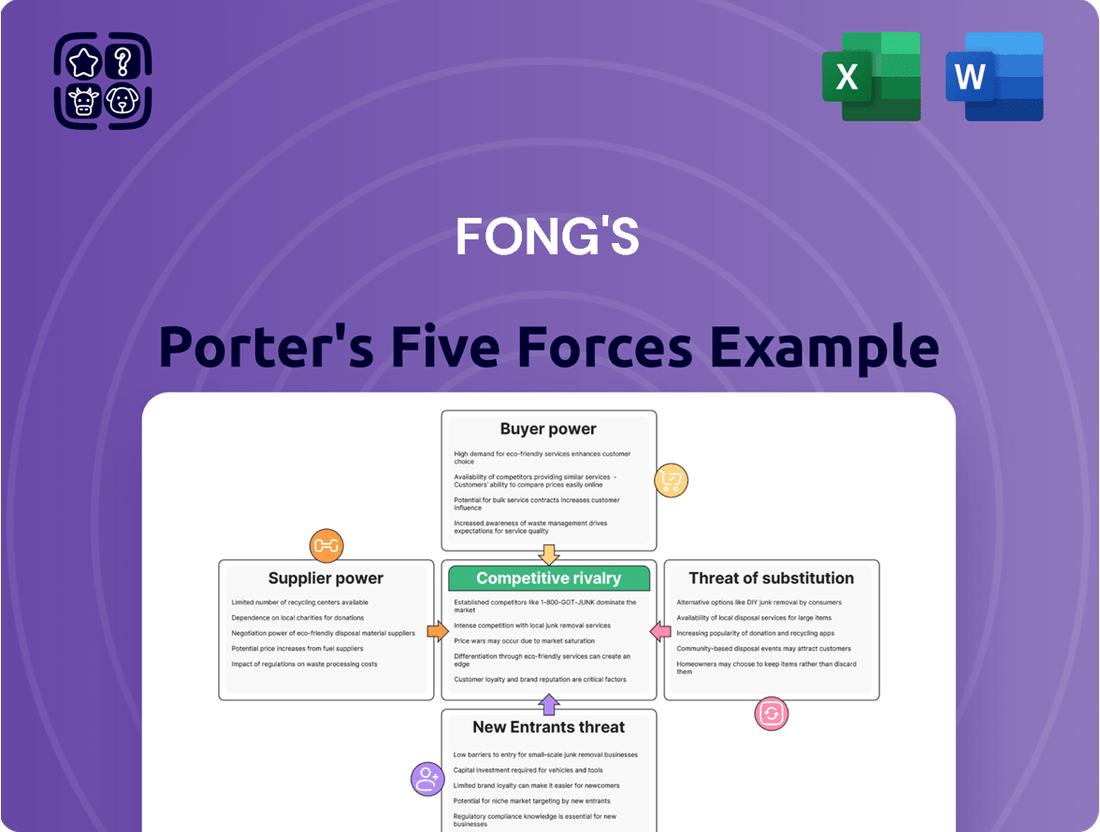
Fong's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the availability of substitutes.
Fong's Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a visual, one-page overview, alleviating the pain of sifting through lengthy reports to grasp competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fong's key customers are major textile manufacturers operating on a global scale. These clients often commit substantial capital to acquiring advanced machinery, which inherently grants them leverage. Their considerable purchase volumes mean they can exert significant pressure on Fong's pricing and terms. For instance, a single large order can represent a substantial portion of Fong's revenue, making these customers highly influential. If Fong's pricing is not competitive, or if their machinery lacks the latest features and robust after-sales support, these powerful customers have a genuine incentive and the capability to shift their business to alternative suppliers.
Customers in the global textile industry are increasingly prioritizing sustainable and efficient machinery. This shift is driven by evolving consumer preferences and mounting regulatory pressures, leading buyers to seek out solutions that minimize water usage, reduce energy consumption, and cut down on waste. Fong's capacity to deliver on these specific requirements directly impacts its market standing.
For instance, the demand for waterless dyeing technologies, a key area of efficiency, is on the rise. Reports from 2024 indicate a growing market share for companies offering such innovations. If Fong can demonstrably lead in providing these eco-friendly and cost-saving machines, it can mitigate customer power. However, if multiple competitors offer comparable sustainable solutions, the bargaining power of customers to negotiate better terms or switch suppliers will naturally increase.
The bargaining power of customers in the textile machinery sector, specifically for a company like Fong's, is significantly influenced by customization requirements. Textile manufacturers often seek bespoke machinery to align with unique production needs, fabric types, and intricate process flows. This demand for tailored solutions can actually limit customer bargaining power if Fong's possesses a distinct capability to deliver these specialized outputs.
When customers have highly specific and niche requirements, their options for alternative suppliers may be limited. For instance, if Fong's is one of a select few manufacturers able to engineer machinery for highly specialized dyeing processes or unique fabric finishing techniques, these customers have less leverage to negotiate on price or terms. This is because switching costs are high when a competitor cannot replicate the precise functionality required.
After-Sales Service and Support
The intricate nature of textile dyeing and finishing machinery means that dependable after-sales service, maintenance, and technical support are crucial for customers. Fong's ability to consistently deliver high-quality service directly impacts customer loyalty and their propensity to switch suppliers. For example, in 2024, a survey of industrial equipment buyers indicated that 70% consider after-sales support a primary factor in their purchasing decisions, even over initial price.
By excelling in providing reliable and responsive service, Fong's can significantly diminish the bargaining power of its customers. When customers know they can count on prompt repairs and expert technical assistance, they are less likely to pressure for lower prices or more favorable terms. This commitment to support builds trust, a vital asset in a competitive market where machine downtime can be incredibly costly.
- Reliable Service Reduces Customer Leverage: Strong after-sales support minimizes the need for customers to seek alternative solutions or negotiate aggressively on price.
- Technical Expertise is Key: Given the complexity of textile machinery, customers value partners who can offer in-depth technical knowledge and troubleshooting.
- Downtime Costs Drive Demand for Support: For many textile manufacturers, machine downtime directly translates to lost production and revenue, making efficient service paramount.
- Customer Loyalty Through Support: Companies that prioritize excellent after-sales service often foster greater customer retention, thereby reducing the bargaining power of individual clients.
Geographical Concentration of Customers
Fong's customers are heavily concentrated in Asia-Pacific, a key region for textile manufacturing. This geographical concentration, while providing significant market scale, also amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, by mid-2024, countries like Vietnam and Bangladesh were major textile exporters, creating dense customer bases for machinery suppliers.
Within these hubs, numerous textile manufacturers operate, leading to a competitive landscape for Fong's. This heightened competition among machinery providers in concentrated regions allows customers to more easily compare offerings and negotiate prices. For example, in 2024, reports indicated a slight oversupply of certain textile machinery in Southeast Asia, which would typically empower buyers.
- Geographical Focus: Fong's primary customer base is in Asia-Pacific textile manufacturing centers.
- Market Density: High concentration of textile firms in these regions increases customer leverage.
- Competitive Pressure: Increased competition among suppliers in concentrated areas empowers Fong's customers to negotiate better terms.
- 2024 Market Conditions: Reports in 2024 suggested a competitive environment for textile machinery in key Asian markets, benefiting buyers.
Fong's major customers, large global textile manufacturers, hold significant bargaining power due to their substantial capital investment in advanced machinery and large order volumes. This leverage allows them to heavily influence Fong's pricing and terms. If Fong's offerings are not competitive or lack essential features and support, these clients can readily switch to rivals.
The increasing demand for sustainable and efficient textile machinery, driven by consumer preferences and regulations, further empowers customers. For instance, the market for waterless dyeing technologies saw notable growth in 2024. Fong's ability to meet these specific demands, like providing eco-friendly solutions, directly impacts its standing and can mitigate customer pressure, especially if competitors offer similar innovations.
Customers' bargaining power is also shaped by their need for customization. Textile manufacturers often require bespoke machinery tailored to unique production needs and fabric types. When Fong's can deliver these specialized solutions, especially for niche processes where alternatives are scarce, it limits the bargaining power of those customers due to high switching costs. Dependable after-sales service is also critical; a 2024 survey found 70% of industrial equipment buyers prioritize it over initial price, enhancing customer loyalty and reducing negotiation leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Fong's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size & Volume | High leverage due to large orders | Key for major textile conglomerates |
| Switching Costs | Lower if Fong's offers unique customization | High for specialized machinery needs |
| After-Sales Support | Reduces power through loyalty and reliability | 70% of buyers consider it primary |
| Sustainability Demand | Customers gain leverage if Fong's lags | Growing market for eco-friendly machinery |
| Geographic Concentration (Asia-Pacific) | Amplifies power due to dense, competitive markets | Vietnam & Bangladesh major textile hubs in 2024 |
Preview Before You Purchase
Fong's Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Fong's that you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a deep understanding of the competitive landscape influencing Fong's operations. The analysis meticulously details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This document is your complete, ready-to-use resource for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global textile machinery market is quite crowded, featuring major players such as Rieter, Saurer, Toyota Industries, and Jingwei Textile Machinery, with Fong's also being a significant participant. This mix of large, established companies and smaller, specialized firms means there's a good deal of competition. For instance, Rieter reported a revenue of CHF 1.7 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of some of these competitors.
This diversity means that different companies excel in various segments of textile machinery, from spinning to weaving and finishing. For Fong's, this translates into a competitive environment where innovation and efficiency are key differentiators. The presence of numerous global and regional players, each with their own strengths, intensifies the rivalry for market share.
Competitive rivalry in the textile machinery sector is significantly fueled by technological innovation. Companies are in a perpetual race to develop advanced machinery that boosts efficiency, introduces higher levels of automation, and promotes sustainability in production processes. This relentless pursuit of innovation means that staying ahead requires substantial investment in research and development.
Fong's competitive edge is directly tied to its innovation in dyeing and finishing machinery. The company's efforts are focused on developing features that address key industry needs, such as minimizing water and energy consumption, which is crucial for sustainability. Furthermore, enhancing fabric quality through advanced machinery is a primary differentiator in a market where performance and output quality are paramount.
For instance, the global textile machinery market was valued at approximately $23.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow. Companies investing heavily in R&D, like Fong, aim to capture market share by offering solutions that address both operational cost savings and improved product output, directly impacting their competitive standing.
Pricing and cost efficiency are crucial battlegrounds for textile manufacturers. While Fong might focus on unique designs, competitors can undercut them by leveraging economies of scale or cheaper labor. For instance, in 2024, many Asian textile exporters maintained a competitive edge through significantly lower production costs compared to Western counterparts.
This pressure intensifies when customers prioritize value over brand. A competitor that can deliver similar quality at a lower price point, perhaps through optimized supply chains or advanced manufacturing techniques, directly challenges Fong's market share. In the first half of 2024, the global textile industry saw an average price reduction of 3-5% in certain mass-market segments due to intense competition.
Global Market Share and Regional Dominance
The global textile market is highly fragmented, meaning there are many companies vying for a piece of the pie, rather than a few dominant giants. This fragmentation means Fong's faces intense competition from a diverse range of players, each with their own strengths and market focus. For instance, while Fong's might aim for global reach, it directly contends with companies that have deeply entrenched positions in specific geographical areas.
Asia-Pacific stands out as a particularly competitive region, being a powerhouse for textile manufacturing. Fong's must therefore contend with strong regional players in this area, many of whom benefit from established supply chains and lower production costs. This regional dominance translates into significant market share for local competitors, making it challenging for global players like Fong's to gain significant traction without a tailored strategy.
- Market Fragmentation: The textile industry is characterized by a large number of competitors, leading to intense rivalry.
- Regional Dominance: Companies with strong footholds in key manufacturing regions, especially Asia-Pacific, pose a significant competitive threat.
- Global vs. Regional Competition: Fong's must compete for global market share against players who excel within specific, often high-volume, regional markets.
- Key Competitor Landscape: Major players in 2024 include Inditex, H&M Group, and PVH Corp., alongside numerous strong regional manufacturers in Asia.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions
Competitive rivalry in the textile machinery sector is heating up as demand for sustainability surges. Companies are aggressively innovating to provide the most eco-friendly and energy-efficient equipment, creating a dynamic market landscape.
Fong's commitment to sustainability positions it favorably, but this advantage is challenged as key rivals are also channeling significant investments into developing and adopting green technologies. For instance, by 2024, many major players in the textile machinery industry reported substantial increases in R&D spending specifically allocated to eco-friendly solutions, with some allocating over 20% of their R&D budgets to this area.
- Intensified Competition: The market sees companies competing fiercely on the eco-credentials of their machinery.
- Investment in Green Tech: Rivals are matching or exceeding Fong's investment in sustainable technologies.
- Innovation Race: Companies are in a race to develop and market the most energy-efficient and environmentally sound textile machinery.
- Market Share Battle: This competition directly impacts market share as customers increasingly prioritize sustainable options.
The textile machinery market is highly competitive, with numerous global and regional players. Fong's faces intense rivalry from established giants like Rieter, which reported CHF 1.7 billion in revenue in 2023, and agile regional manufacturers, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. This fragmentation means competition is fierce across various machinery segments, from spinning to finishing.
Innovation is a key battleground, with companies heavily investing in R&D to offer more efficient, automated, and sustainable solutions. Fong's focus on eco-friendly dyeing and finishing machinery is a strategic differentiator, but rivals are also prioritizing green technologies, with some allocating over 20% of their 2024 R&D budgets to sustainable innovations.
Pricing and cost-efficiency are also critical, especially in mass-market segments where a 3-5% price reduction was observed in early 2024 due to intense competition. Companies leveraging economies of scale or lower production costs, prevalent among Asian manufacturers, directly challenge Fong's market share by offering value-driven alternatives.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Focus Area | Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rieter | CHF 1.7 billion | Spinning Machinery | Scale and Innovation |
| Saurer | Not publicly disclosed | Spinning & Twisting Machinery | Technological Advancement |
| Toyota Industries | Not specific to textile machinery | Broad Industrial Machinery | Diversified Strength |
| Jingwei Textile Machinery | Not publicly disclosed | Various Textile Machinery | Regional Strength (China) |
| Fong's | Not publicly disclosed | Dyeing & Finishing Machinery | Sustainability & Efficiency |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes in textile processing primarily stems from alternative methods that bypass or reduce reliance on specialized machinery like that used by Fong's. Innovations such as digital printing and waterless dyeing technologies are key examples, offering ways to achieve desired textile effects without the traditional, capital-intensive dyeing and finishing processes.
While these newer methods often necessitate their own specialized equipment, they fundamentally change the nature of the value chain. For instance, digital printing can bypass traditional dyeing entirely for certain applications, directly applying colorants to fabric with high precision. This directly challenges the market share of companies focused on conventional dyeing machinery.
The global digital textile printing market was valued at approximately $2.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a tangible shift towards these substitute technologies. This growth suggests that a portion of the market previously reliant on traditional machinery may migrate to digital solutions, impacting demand for Fong's core offerings.
Furthermore, advancements in eco-friendly finishing techniques, including those that reduce water and chemical usage, can also act as substitutes. If these methods become more cost-effective and widely adopted, they might lessen the demand for machinery designed for more resource-intensive traditional finishing processes.
A significant threat to Fong's business arises from the textile industry's evolving material landscape. A substantial shift towards materials requiring less intensive dyeing or finishing processes, such as pre-colored synthetic fibers or naturally colored organic cottons, could directly reduce the demand for Fong's traditional dyeing and finishing machinery. For instance, the global market for sustainable textiles, which often prioritize less chemically intensive production methods, was projected to reach $10.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow significantly.
Furthermore, the emergence of entirely new fabric innovations, like smart textiles with integrated functionalities, presents another substitution threat. These advanced materials may bypass traditional manufacturing steps where Fong's machinery is critical, potentially siphoning off market share. The smart textiles market, valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023, is anticipated to experience robust growth, indicating a potential diversion of resources and innovation away from conventional textile production methods.
The outsourcing of dyeing and finishing presents a significant threat of substitutes for textile manufacturers. Companies can choose to contract these services to specialized third-party providers instead of maintaining in-house operations. This decision is often fueled by the potential for cost savings and access to cutting-edge technologies that might be too capital-intensive to acquire independently. For instance, many smaller textile firms in emerging markets in 2024 are leveraging specialized finishing houses to achieve premium fabric qualities previously only accessible to larger players.
Development of Dyes with Integrated Finishing Properties
The development of dyes with integrated finishing properties presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional textile processing. If new dye technologies emerge that can simultaneously impart desired finishes like wrinkle resistance or water repellency, this could reduce the reliance on separate, costly finishing machinery. This innovation could lower capital expenditure and operational complexity for textile manufacturers, making it an attractive alternative to existing methods.
Furthermore, the growing interest in sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives fuels the search for novel dyeing and finishing solutions. Bio-based or natural dyes are gaining traction, although challenges related to consistency and scalability still need to be fully addressed. For instance, research in 2024 highlighted advancements in microbial fermentation for producing textile dyes, potentially offering a more sustainable pathway.
- Technological Advancement: New dye formulations integrating finishing properties reduce the need for separate finishing equipment.
- Cost Reduction: Manufacturers can potentially lower capital and operational expenses by adopting these integrated technologies.
- Sustainability Drive: Increased demand for eco-friendly processes encourages the development of alternatives like bio-based dyes.
- Market Impact: Successful integration of finishing properties into dyes could disrupt traditional dyeing and finishing markets, shifting competitive dynamics.
Advancements in Pre-Treated Fabrics
The rise of pre-treated and pre-colored fabrics presents a significant threat of substitution for Fong's machinery. These innovative materials reduce or eliminate the need for traditional dyeing and finishing processes, directly impacting demand for Fong's core offerings. This trend signifies a potential shift of value-adding activities further up the textile supply chain, away from the machinery manufacturers.
This advancement means customers might bypass the need for Fong's equipment altogether. For instance, in 2024, the global textile finishing chemicals market, which includes pre-treatment agents, was projected to reach over $25 billion, indicating substantial investment and innovation in this area. This growing market for ready-to-use fabrics could directly erode Fong's market share.
- Reduced Demand: Pre-treated fabrics lessen the necessity for Fong's dyeing and finishing machinery.
- Upstream Shift: Processing is moving earlier in the supply chain, potentially bypassing Fong's role.
- Market Growth: The expanding market for advanced textile treatments offers viable alternatives.
- Competitive Pressure: Fabric suppliers offering these integrated solutions gain a competitive edge.
The threat of substitutes for Fong's machinery is significant, driven by technological advancements and evolving industry practices. Innovations like digital printing and waterless dyeing directly challenge traditional methods, potentially reducing the need for conventional dyeing and finishing equipment.
The global digital textile printing market, valued at approximately $2.2 billion in 2023, is a prime example of this substitution trend, with projected growth indicating a shift away from older technologies. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of pre-colored or pre-treated fabrics bypasses traditional dyeing steps altogether, impacting demand for Fong's machinery.
The growing sustainable textile market, projected to reach $10.1 billion in 2023, also favors less chemically intensive processes, potentially decreasing reliance on Fong's equipment. These substitutes offer cost savings and environmental benefits, making them increasingly attractive to manufacturers.
| Substitute Technology | 2023 Market Value (approx.) | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Textile Printing | $2.2 billion | Bypasses traditional dyeing |
| Sustainable Textiles | $10.1 billion (projected) | Favors less intensive processing |
| Pre-colored/Pre-treated Fabrics | Growing Market | Eliminates need for dyeing/finishing machinery |
Entrants Threaten
The textile dyeing and finishing machinery sector demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to stay competitive, alongside building or acquiring advanced manufacturing facilities and specialized equipment. For example, the global textile machinery market was valued at approximately $45 billion in 2023, with a substantial portion attributed to the dyeing and finishing segment, indicating the scale of investment required.
The need for skilled labor and extensive testing further elevates these initial costs, creating a formidable barrier. This high capital requirement effectively deters many potential new entrants who may lack the financial resources to compete effectively from the outset, thus protecting existing players.
The threat of new entrants in the textile industry, particularly concerning Fong's, is significantly influenced by the need for substantial technological expertise and robust R&D capabilities. For any newcomer to effectively challenge Fong's, which is deeply invested in innovation, they would require considerable skill in advanced textile engineering, sophisticated automation, and cutting-edge sustainable processing techniques.
Acquiring or developing these competencies represents a high barrier. For instance, the global textile machinery market, a key enabler of technological advancement, was valued at approximately USD 35.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating the significant investment required for state-of-the-art equipment and the associated technical knowledge.
Fong's established brand reputation and deep-rooted customer relationships present a significant barrier to new entrants in the textile machinery market. With decades of experience, Fong's has cultivated trust and loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, Fong's continued to leverage its strong brand equity, securing key contracts with major textile manufacturers globally, a testament to its enduring appeal.
Intellectual Property and Patents
The threat of new entrants in the semiconductor industry, particularly concerning intellectual property and patents, is significantly shaped by the established players' robust patent portfolios. Existing manufacturers often hold a vast number of patents covering critical aspects of their specialized machinery, manufacturing processes, and chip designs. This extensive IP acts as a substantial barrier. For instance, in 2024, leading semiconductor companies continued to invest heavily in R&D, with companies like TSMC and Intel filing thousands of new patents annually, reinforcing their technological dominance.
New companies looking to enter this space face the daunting task of either developing entirely new, proprietary technologies from scratch or acquiring licenses for existing patented technologies. Both paths are exceptionally costly and time-consuming. Developing novel processes can take years and require billions in investment, while licensing fees can be prohibitive, impacting a new entrant's cost competitiveness from the outset. The sheer volume of patents held by incumbents means navigating the IP landscape to avoid infringement is a complex and expensive undertaking.
- Existing manufacturers possess extensive patent portfolios covering advanced manufacturing equipment and proprietary processes.
- New entrants must either invest heavily in developing their own unique technologies or pay substantial licensing fees.
- The cost and time required to develop or license IP are significant deterrents to market entry.
- Patent infringement lawsuits can severely cripple or bankrupt a new company.
Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability Standards
The textile industry faces escalating environmental regulations and sustainability standards worldwide. New companies entering this market must navigate complex compliance requirements from day one, significantly increasing initial costs and operational complexity.
For instance, by 2024, many regions have implemented stricter wastewater discharge limits and chemical usage restrictions. Companies like those in the European Union are facing enhanced Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes for textiles, demanding significant investment in circular economy practices and take-back programs. These mandates create a substantial barrier to entry, especially for smaller, less capitalized ventures, as they require advanced technology and robust management systems to meet compliance.
- Increased Capital Investment: New entrants need to invest heavily in eco-friendly machinery and processes to meet standards.
- Operational Complexity: Managing compliance with evolving regulations adds significant administrative and operational burdens.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Ensuring sustainable sourcing and ethical labor practices throughout the supply chain is now a non-negotiable requirement.
- Market Access Barriers: Non-compliance can lead to penalties and restricted access to key markets, particularly in developed economies.
The threat of new entrants for textile dyeing and finishing machinery manufacturers like Fong's is generally moderate to low. High capital requirements for advanced machinery and R&D, coupled with established brand loyalty and extensive patent portfolios, create significant hurdles.
Furthermore, navigating stringent environmental regulations and sustainability standards demands substantial upfront investment and expertise, acting as a further deterrent for potential new players entering the market.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data) |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in machinery, R&D, and facilities. | Deters undercapitalized entrants. | Global textile machinery market valued at ~$35.8 billion in 2023, with significant portion for dyeing/finishing. |
| Technological Expertise | Need for advanced engineering, automation, and sustainable processing knowledge. | Requires significant skill acquisition or hiring. | Fong's investment in innovative, eco-friendly solutions highlights this need. |
| Brand Reputation & Relationships | Established trust and loyalty with existing customers. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market share. | Fong's secured key global contracts in 2024 due to its brand equity. |
| Intellectual Property (IP) | Extensive patent portfolios of incumbents. | Risk of infringement, high licensing costs, or need for novel development. | Major semiconductor firms filed thousands of patents in 2024, indicating intense IP protection. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting evolving environmental and sustainability standards. | Increases initial costs and operational complexity. | EU's EPR schemes for textiles by 2024 necessitate investment in circular economy practices. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from publicly available company filings, industry-specific market research reports, and reputable financial news outlets. This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
